Difference in Efficacy and Safety of Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy Containing 4-1BB and CD28 Co-Stimulatory Domains for B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Modeling Analysis of Overall and Progression-Free Survival
2.5. Meta-Analysis for the Secondary and Safety Outcomes
2.6. Correlation between ORR, MRD-Negative CR, PFS, and OS
2.7. Software and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.2. Model Establishment and Evaluation
3.3. Typical Overall and Progression-Free Survival Simulation
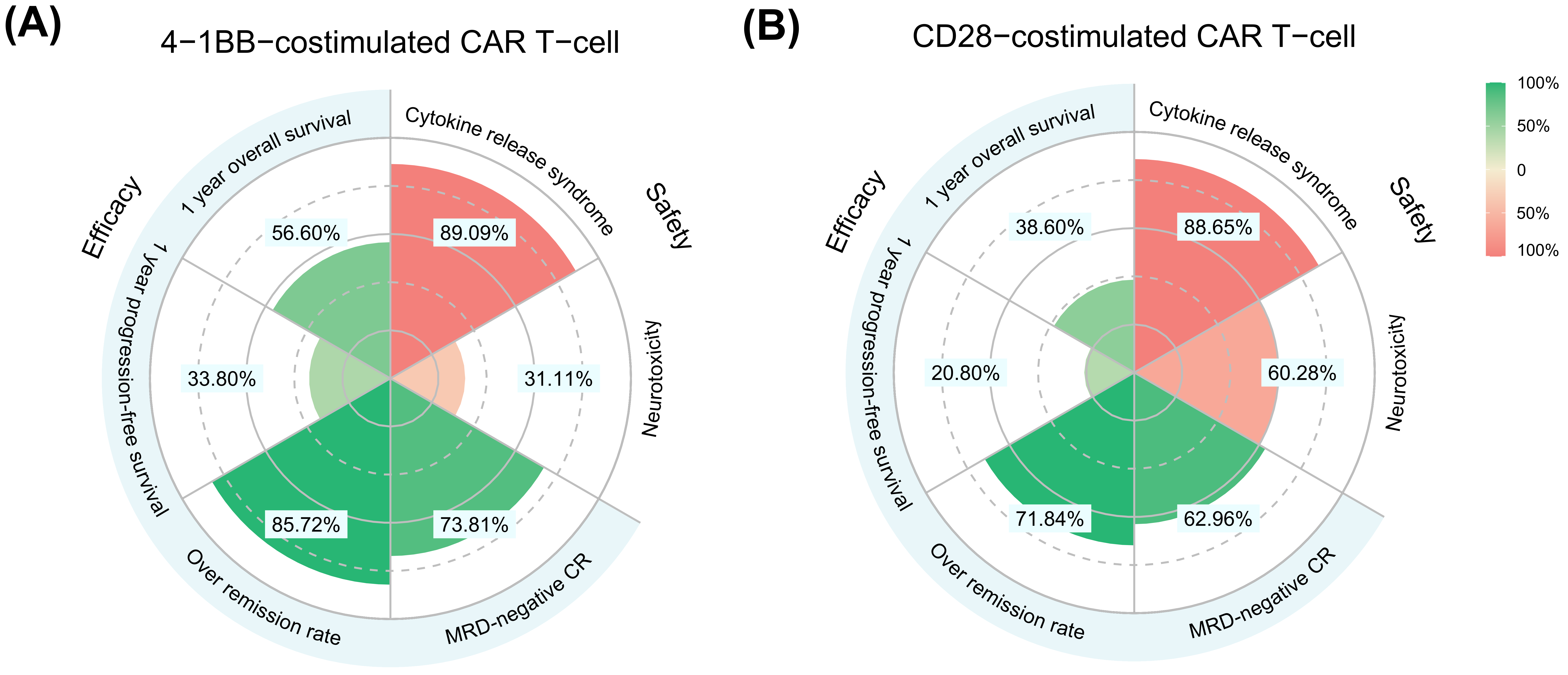
3.4. Meta-Analysis for Secondary and Safety Outcomes
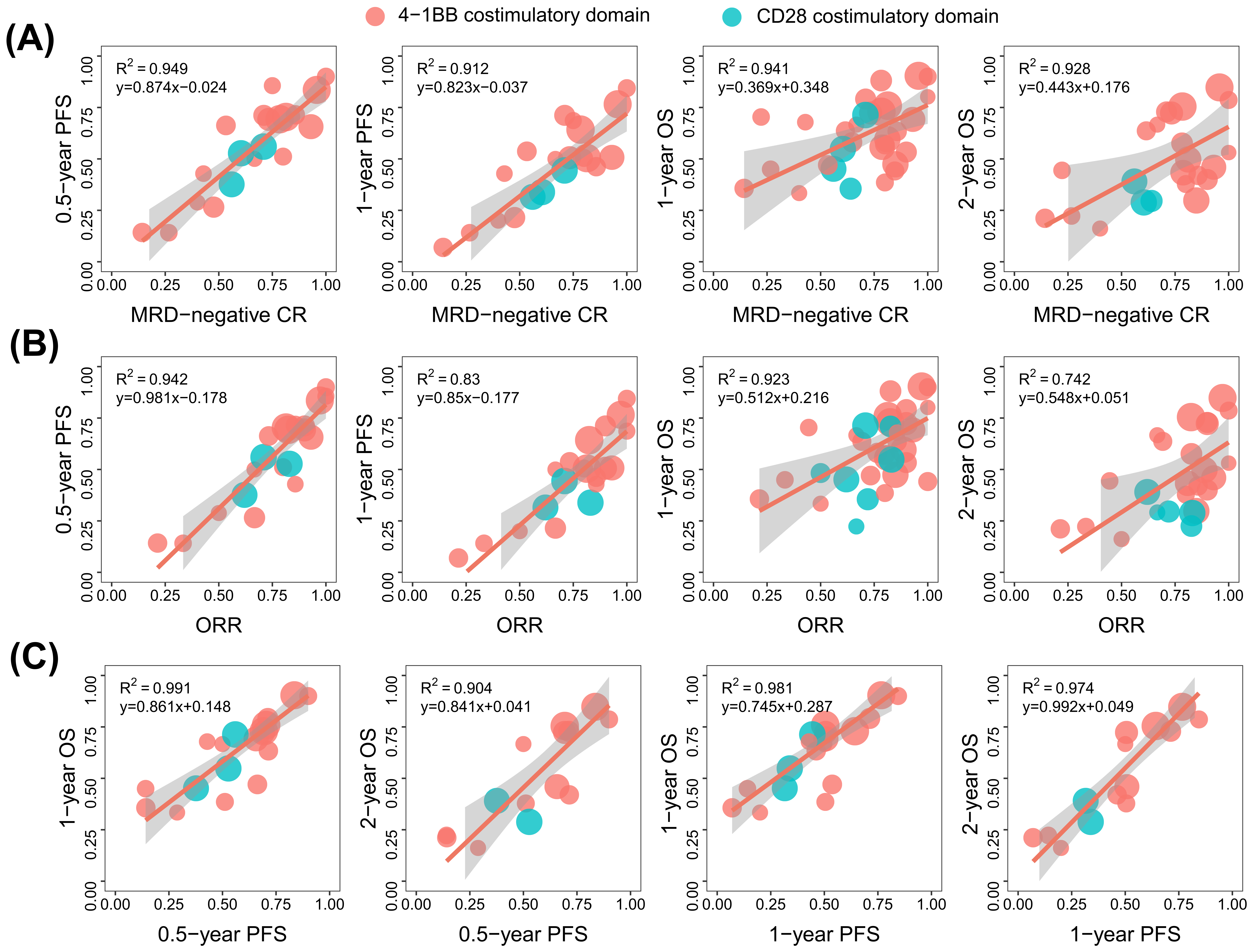
3.5. Correlation between ORR, MRD-Negative CR, PFS, and OS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Safarzadeh Kozani, P.; Safarzadeh Kozani, P.; O’Connor, R.S. In Like a Lamb; Out Like a Lion: Marching CAR T Cells Toward Enhanced Efficacy in B-ALL. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Kantarjian, H.; Jabbour, E.J. Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 1645–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulte, D.; Redaniel, M.T.; Jansen, L.; Brenner, H.; Jeffreys, M. Recent trends in survival of adult patients with acute leukemia: Overall improvements, but persistent and partly increasing disparity in survival of patients from minority groups. Haematologica 2013, 98, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sive, J.I.; Buck, G.; Fielding, A.; Lazarus, H.M.; Litzow, M.R.; Luger, S.; Marks, D.I.; McMillan, A.; Moorman, A.V.; Richards, S.M.; et al. Outcomes in older adults with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL): Results from the international MRC UKALL XII/ECOG2993 trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 157, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, S.J.; Rowe, J.M. The myth of the second remission of acute leukemia in the adult. Blood 2013, 121, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Charwudzi, A.; Li, Q.; Zhu, W.; Tao, Q.; Xiong, S.; Zhai, Z. Anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy bridge to HSCT decreases the relapse rate and improves the long-term survival of R/R B-ALL patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maude, S.L.; Frey, N.; Shaw, P.A.; Aplenc, R.; Barrett, D.M.; Bunin, N.J.; Chew, A.; Gonzalez, V.E.; Zheng, Z.; Lacey, S.F.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells for sustained remissions in leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Rivière, I.; Gonen, M.; Wang, X.; Sénéchal, B.; Curran, K.J.; Sauter, C.; Wang, Y.; Santomasso, B.; Mead, E.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of CD19 CAR Therapy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Lee, D.W.; Yates, B.; Yuan, C.M.; Shalabi, H.; Martin, S.; Wolters, P.L.; Steinberg, S.M.; Baker, E.H.; Delbrook, C.P.; et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of CD19-CAR T-Cell Therapy in Children and Young Adults With B-ALL. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.C.; Maus, M.V. Recent advances and discoveries in the mechanisms and functions of CAR T cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Flies, D.B. Molecular mechanisms of T cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, R.H. T cell anergy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 305–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappell, K.M.; Kochenderfer, J.N. A comparison of chimeric antigen receptors containing CD28 versus 4-1BB costimulatory domains. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostou, T.; Riaz, I.B.; Hashmi, S.K.; Murad, M.H.; Kenderian, S.S. Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in acute lymphocytic leukaemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e816–e826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Fu, G.; Li, Y.; Pei, L.; Xiong, Z.; Qin, D.; Zhang, R.; Tian, X.; et al. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with the second generation of CD19 CAR-T containing either CD28 or 4-1BB. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 181, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandema, J.W.; Gibbs, M.; Boyd, R.A.; Wada, D.R.; Pfister, M. Model-based meta-analysis for comparative efficacy and safety: Application in drug development and beyond. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 90, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mould, D.R. Model-based meta-analysis: An important tool for making quantitative decisions during drug development. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, M.J.; Robinson, A.; Booth, C.M.; O’Donnell, J.; Palmer, M.; Eisenhauer, E.; Brundage, M. The Value of Progression-Free Survival as a Treatment End Point Among Patients With Advanced Cancer: A Systematic Review and Qualitative Assessment of the Literature. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1779–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Gao, T.T.; Liu, S.L.; Xi, M.; Liu, M.Z.; Wang, J.Y.; Qi, S.N.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L. Progression-free survival at 3 years is a reliable surrogate for 5-year overall survival for patients suffering from locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 3751–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; He, X.; Zhang, L.L.; Wu, G.; Qu, B.L.; Qian, L.T.; Hou, X.R.; Zhang, F.Q.; et al. Progression-free survival at 24 months and subsequent survival of patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: A China Lymphoma Collaborative Group (CLCG) study. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1671–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Q.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Influence of patient characteristics on chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Wang, G.; Cheng, H.; Wei, C.; Qi, K.; Sang, W.; Zhenyu, L.; Shi, M.; Li, H.; Qiao, J.; et al. Potent anti-leukemia activities of humanized CD19-targeted Chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells in patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curran, K.J.; Margossian, S.P.; Kernan, N.A.; Silverman, L.B.; Williams, D.A.; Shukla, N.; Kobos, R.; Forlenza, C.J.; Steinherz, P.; Prockop, S.; et al. Toxicity and response after CD19-specific CAR T-cell therapy in pediatric/young adult relapsed/refractory B-ALL. Blood 2019, 134, 2361–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Han, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Tolerance and efficacy of autologous or donor-derived T cells expressing CD19 chimeric antigen receptors in adult B-ALL with extramedullary leukemia. OncoImmunology 2015, 4, e1027469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, N.V.; Shaw, P.A.; Hexner, E.O.; Pequignot, E.; Gill, S.; Luger, S.M.; Mangan, J.K.; Loren, A.W.; Perl, A.E.; Maude, S.L.; et al. Optimizing Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Adults With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.A.; Finney, O.; Annesley, C.; Brakke, H.; Summers, C.; Leger, K.; Bleakley, M.; Brown, C.; Mgebroff, S.; Kelly-Spratt, K.S.; et al. Intent-to-treat leukemia remission by CD19 CAR T cells of defined formulation and dose in children and young adults. Blood 2017, 129, 3322–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, J.; Bezerra, E.D.; Hirayama, A.V.; Fiorenza, S.; Sheih, A.; Chou, C.K.; Kimble, E.L.; Pender, B.S.; Hawkins, R.M.; Vakil, A.; et al. Factors associated with outcomes after a second CD19-targeted CAR T-cell infusion for refractory B-cell malignancies. Blood 2021, 137, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorashian, S.; Kramer, A.M.; Onuoha, S.; Wright, G.; Bartram, J.; Richardson, R.; Albon, S.J.; Casanovas-Company, J.; Castro, F.; Popova, B.; et al. Enhanced CAR T cell expansion and prolonged persistence in pediatric patients with ALL treated with a low-affinity CD19 CAR. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Liu, F.; Zou, D.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Guo, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of CD19 CAR T constructed with a new anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor in relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, K.A.; Gauthier, J.; Hirayama, A.V.; Voutsinas, J.M.; Wu, Q.; Li, D.; Gooley, T.A.; Cherian, S.; Chen, X.; Pender, B.S.; et al. Factors associated with durable EFS in adult B-cell ALL patients achieving MRD-negative CR after CD19 CAR T-cell therapy. Blood 2019, 133, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, G.; Jia, J.; Li, S.; Fu, G.; Wang, M.; Qin, D.; Li, Y.; Pei, L.; Tian, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Sustained Therapeutic Efficacy of Humanized Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells in Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, H.; Adachi, S.; Umeda, K.; Kato, I.; Eldjerou, L.; Agostinho, A.C.; Natsume, K.; Tokushige, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Grupp, S.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tisagenlecleucel in Japanese pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2020, 111, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Shi, J.; Yu, J.; Pu, C.; Liang, Z.; Wei, G.; Cui, Q.; Sun, J.; et al. Potent Anti-leukemia Activities of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells against CD19 in Chinese Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3297–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Zhou, L.; Bao, X.; Han, Y.; Miao, M.; Li, C.; Fu, C.; et al. Donor-derived anti-CD19 CAR T cells compared with donor lymphocyte infusion for recurrent B-ALL after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, L.; Guo, T.; Wu, Y.; Ai, L.; Deng, J.; Dong, J.; Mei, H.; Hu, Y. Improving the safety of CAR-T cell therapy by controlling CRS-related coagulopathy. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 1721–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadauke, S.; Myers, R.M.; Li, Y.; Aplenc, R.; Baniewicz, D.; Barrett, D.M.; Barz Leahy, A.; Callahan, C.; Dolan, J.G.; Fitzgerald, J.C.; et al. Risk-Adapted Preemptive Tocilizumab to Prevent Severe Cytokine Release Syndrome After CTL019 for Pediatric B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Prospective Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Liu, M.; Lyu, C.; Lu, W.; Cui, R.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Mou, N.; Deng, Q.; Yang, D. Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease After Humanized Anti-CD19-CAR T Therapy in Relapsed B-ALL Patients After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 573822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Ho, J.Y.; Du, H.; Xuan, F.; Wu, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ba, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Evidence of long-lasting anti-CD19 activity of engrafted CD19 chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in a phase I study targeting pediatrics with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Rives, S.; Boyer, M.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Stefanski, H.E.; Myers, G.D.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.M.; Li, Y.; Barz Leahy, A.; Barrett, D.M.; Teachey, D.T.; Callahan, C.; Fasano, C.C.; Rheingold, S.R.; DiNofia, A.; Wray, L.; et al. Humanized CD19-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cells in CAR-Naive and CAR-Exposed Children and Young Adults With Relapsed or Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3044–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, B.D.; Bishop, M.R.; Oluwole, O.O.; Logan, A.C.; Baer, M.R.; Donnellan, W.B.; O’Dwyer, K.M.; Holmes, H.; Arellano, M.L.; Ghobadi, A.; et al. KTE-X19 anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in adult relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia: ZUMA-3 phase 1 results. Blood 2021, 138, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, B.D.; Ghobadi, A.; Oluwole, O.O.; Logan, A.C.; Boissel, N.; Cassaday, R.D.; Leguay, T.; Bishop, M.R.; Topp, M.S.; Tzachanis, D.; et al. KTE-X19 for relapsed or refractory adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Phase 2 results of the single-arm, open-label, multicentre ZUMA-3 study. Lancet 2021, 398, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Mou, N.; Yang, Z.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, J.; Liu, X.; Deng, Q. Efficacy and safety of humanized anti-CD19-CAR-T therapy following intensive lymphodepleting chemotherapy for refractory/relapsed B acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 191, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Feng, D.; Chang, A.E.; et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor-modified Donor Lymphocyte Infusion Improves the Survival of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients With Relapsed Diseases After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. J. Immunother. 2019, 42, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yang, X.; Bao, X.; Kang, L.; Zhou, L.; Wu, X.; Tang, X.; Fu, Z.; Ma, X.; Sun, A.; et al. Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cells induce durable remission in relapsed Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL with T315I mutation. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dai, H.; Kang, L.; Qu, C.; Li, Z.; Yin, J.; Qiu, H.; Fu, C.; Han, Y.; Jin, Z.; et al. Donor origin CAR19 T cell infusion for B-ALL relapsed after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, R.; Graham, C.; Yallop, D.; Jozwik, A.; Mirci-Danicar, O.C.; Lucchini, G.; Pinner, D.; Jain, N.; Kantarjian, H.; Boissel, N.; et al. Genome-edited, donor-derived allogeneic anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cells in paediatric and adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Results of two phase 1 studies. Lancet 2020, 396, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, T.; Ding, L.; Song, L.; Miao, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Luo, C.; et al. Outcomes of Anti-CD19 CAR-T Treatment of Pediatric B-ALL with Bone Marrow and Extramedullary Relapse. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 54, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.M.; Taraseviciute, A.; Steinberg, S.M.; Lamble, A.J.; Sheppard, J.; Yates, B.; Kovach, A.E.; Wood, B.; Borowitz, M.J.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; et al. Blinatumomab Nonresponse and High-Disease Burden Are Associated With Inferior Outcomes After CD19-CAR for B-ALL. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Condomines, M.; van der Stegen, S.J.C.; Perna, F.; Kloss, C.C.; Gunset, G.; Plotkin, J.; Sadelain, M. Structural Design of Engineered Costimulation Determines Tumor Rejection Kinetics and Persistence of CAR T Cells. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malard, F.; Mohty, M. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 2020, 395, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, E.S.; Hunger, S.P. Optimal therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adolescents and young adults. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, C.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; Deol, A.; et al. Long-Term (≥4 Year and ≥5 Year) Overall Survival (OS) By 12- and 24-Month Event-Free Survival (EFS): An Updated Analysis of ZUMA-1, the Pivotal Study of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) in Patients (Pts) with Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma (LBCL). Blood 2021, 138, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.A.; Zhou, S.; Higley, H.; Mukundan, L.; Fu, S.; Reaman, G.H.; Wood, B.L.; Kelloff, G.J.; Jessup, J.M.; Radich, J.P. Association of Minimal Residual Disease With Clinical Outcome in Pediatric and Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, e170580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.; Jain, T.; Santomasso, B.D.; Mead, E.; Wudhikarn, K.; Silverberg, M.L.; Batlevi, Y.; Shouval, R.; Devlin, S.M.; Batlevi, C.; et al. Comparing CAR T-cell toxicity grading systems: Application of the ASTCT grading system and implications for management. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter (Co-Stimulatory Domain) | OS Model | PFS Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Final Model | Bootstrap (959/1000 *) | Final Model | Bootstrap (919/1000 *) | |||||
| Value (RSE%) | Shrinkage (%) | Median | 95% CI | Value (RSE%) | Shrinkage (%) | Median | 95% CI | |
| Survival parameters | ||||||||
| (4-1BB) | 1.52 (7.8) | 1.51 | 1.29–1.77 | 1.67 (8.9) | 1.67 | 1.40–2.00 | ||
| (CD28) | 1.42 (10.5) | 1.44 | 1.13–1.74 | 2.03 (24.4) | 2.17 | 1.12–5.00 | ||
| (4-1BB) | 2.83 (5.1) | 2.80 | 2.54–3.12 | 2.13 (12.5) | 2.16 | 1.63–2.79 | ||
| (CD28) | 2.23 (11.1) | 2.25 | 1.45–2.87 | 1.56 (20.9) | 1.59 | 0.90–4.00 | ||
| θMorphological relapse | 1.22 (43.4) | 1.30 | 0.44–2.61 | 1.78 (21.6) | 1.80 | 0.56–2.87 | ||
| Variability parameters | ||||||||
| η () | 0.329 (13.6) | 9.6 | 0.312 | 0.224–0.404 | 0.330 (14.4) | 10.7 | 0.301 | 0.162–0.423 |
| η () | 0.240 (13.7) | 3.0 | 0.240 | 0.170–0.327 | 0.459 (15.0) | 2.4 | 0.432 | 0.223–0.560 |
| ε | 0.623 (9.3) | 6.7 | 0.616 | 0.501–0.725 | 0.727 (10.0) | 6.9 | 0.729 | 0.574–0.858 |
| 4-1BB | CD28 | |
|---|---|---|
| Overall survival | ||
| Median OS, month | 15.0 (11.0–20.0) | 8.5 (5.0–14.0) |
| 1-year OS rate, % | 56.6 (47.1–67.6) | 38.6 (24.0–56.6) |
| 2-year OS rate, % | 34.8 (26.6–43.9) | 18.3 (8.7–31.6) |
| 5-year OS rate, % | 12.5 (7.9–18.3) | 4.2 (1.1–10.2) |
| Progression-free survival | ||
| Median PFS, month | 7.0 (4.0–11.5) | 3.0 (1.5–7.0) |
| 1-year PFS rate, % | 33.8 (20.7–49.6) | 20.8 (9.0–34.8) |
| 2-year PFS rate, % | 17.3 (8.8–29.0) | 10.5 (2.1–19.8) |
| 5-year PFS rate, % | 5.0 (1.7–10.9) | 3.4 (0.1–9.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Chen, J.; Cai, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, L. Difference in Efficacy and Safety of Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy Containing 4-1BB and CD28 Co-Stimulatory Domains for B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2023, 15, 2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102767
Wu L, Chen J, Cai R, Wang X, Liu Y, Zheng Q, Li L. Difference in Efficacy and Safety of Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy Containing 4-1BB and CD28 Co-Stimulatory Domains for B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers. 2023; 15(10):2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102767
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Lijuan, Junchao Chen, Ruifen Cai, Xinrui Wang, Yixiao Liu, Qingshan Zheng, and Lujin Li. 2023. "Difference in Efficacy and Safety of Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy Containing 4-1BB and CD28 Co-Stimulatory Domains for B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia" Cancers 15, no. 10: 2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102767
APA StyleWu, L., Chen, J., Cai, R., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Zheng, Q., & Li, L. (2023). Difference in Efficacy and Safety of Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy Containing 4-1BB and CD28 Co-Stimulatory Domains for B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers, 15(10), 2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102767






