Preclinical Validation of an Advanced Therapy Medicinal Product Based on Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Specific for Mutated Nucleophosmin (NPM1mut) for the Treatment of NPM1mut-Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Samples
2.2. Production of Cytotoxic T Cell Lines Specific for NPM1mut
2.3. Immunophenotyping
2.4. NPM1-Specific T-Cytotoxic Activity Assessed as 51Cr Release
2.5. Cytokine Secretion Assessment by Enzyme-Linked Immunospot (ELISPOT) Assay or Flow Cytometry
2.6. Clonogenic Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
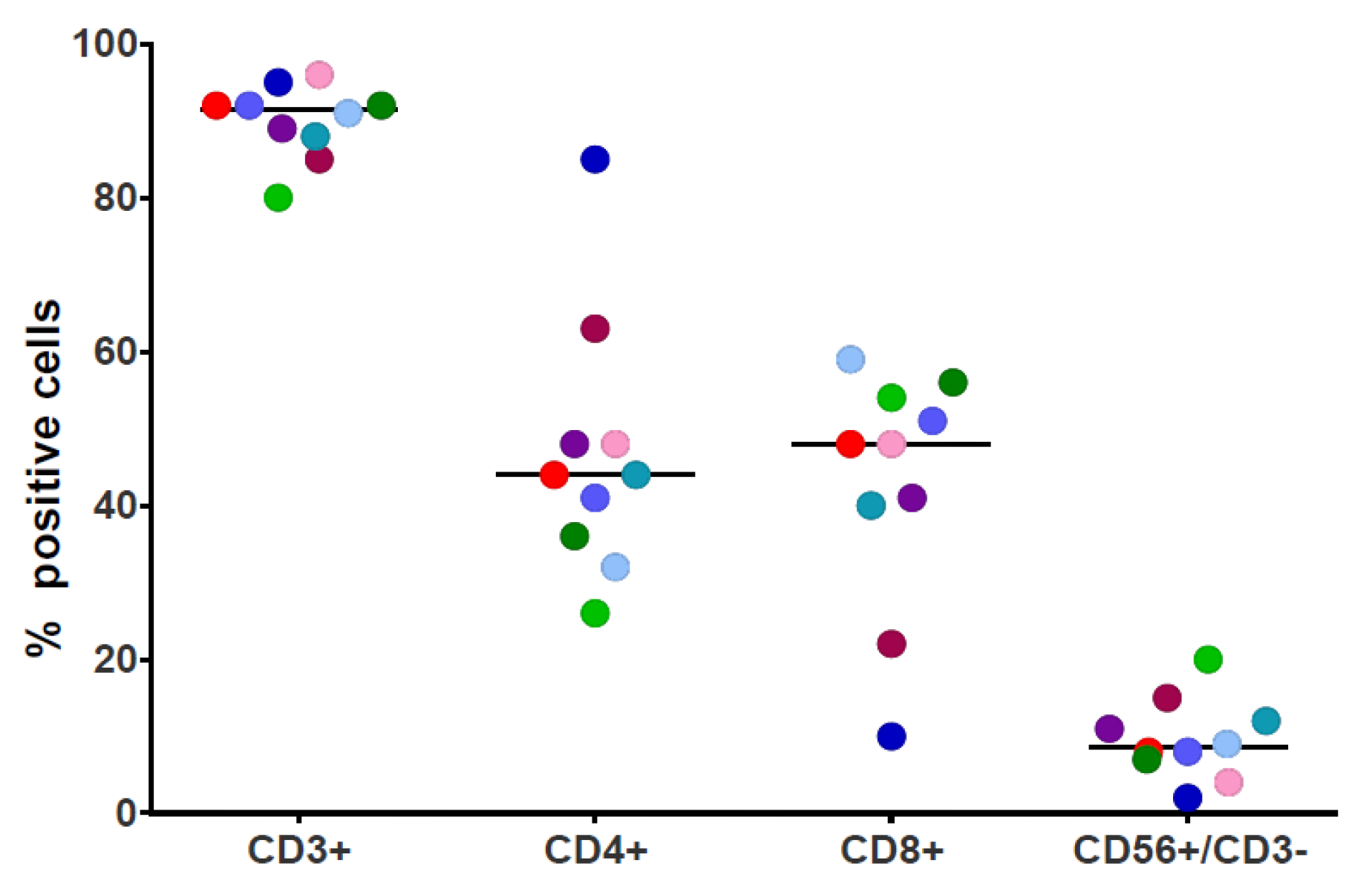
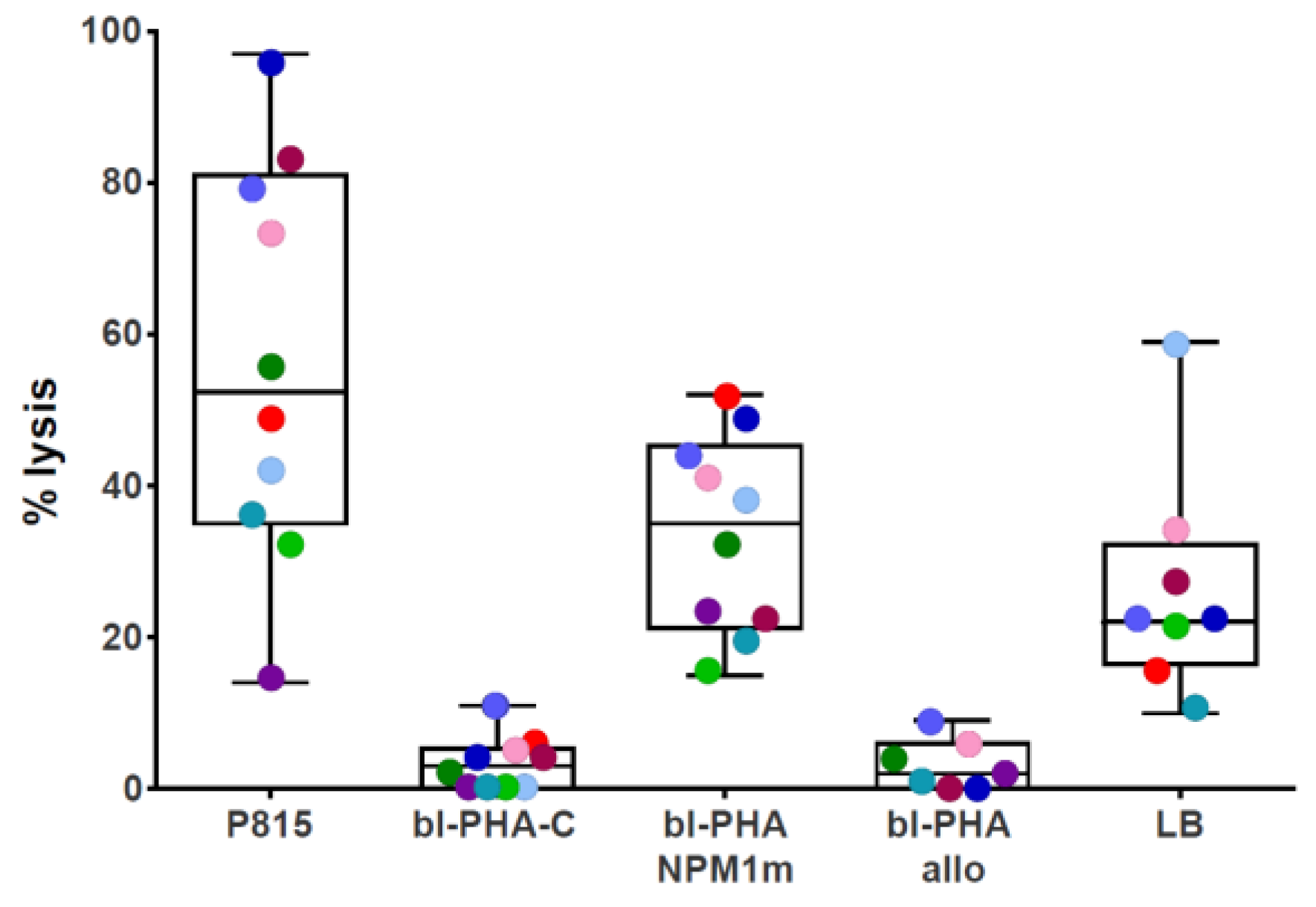
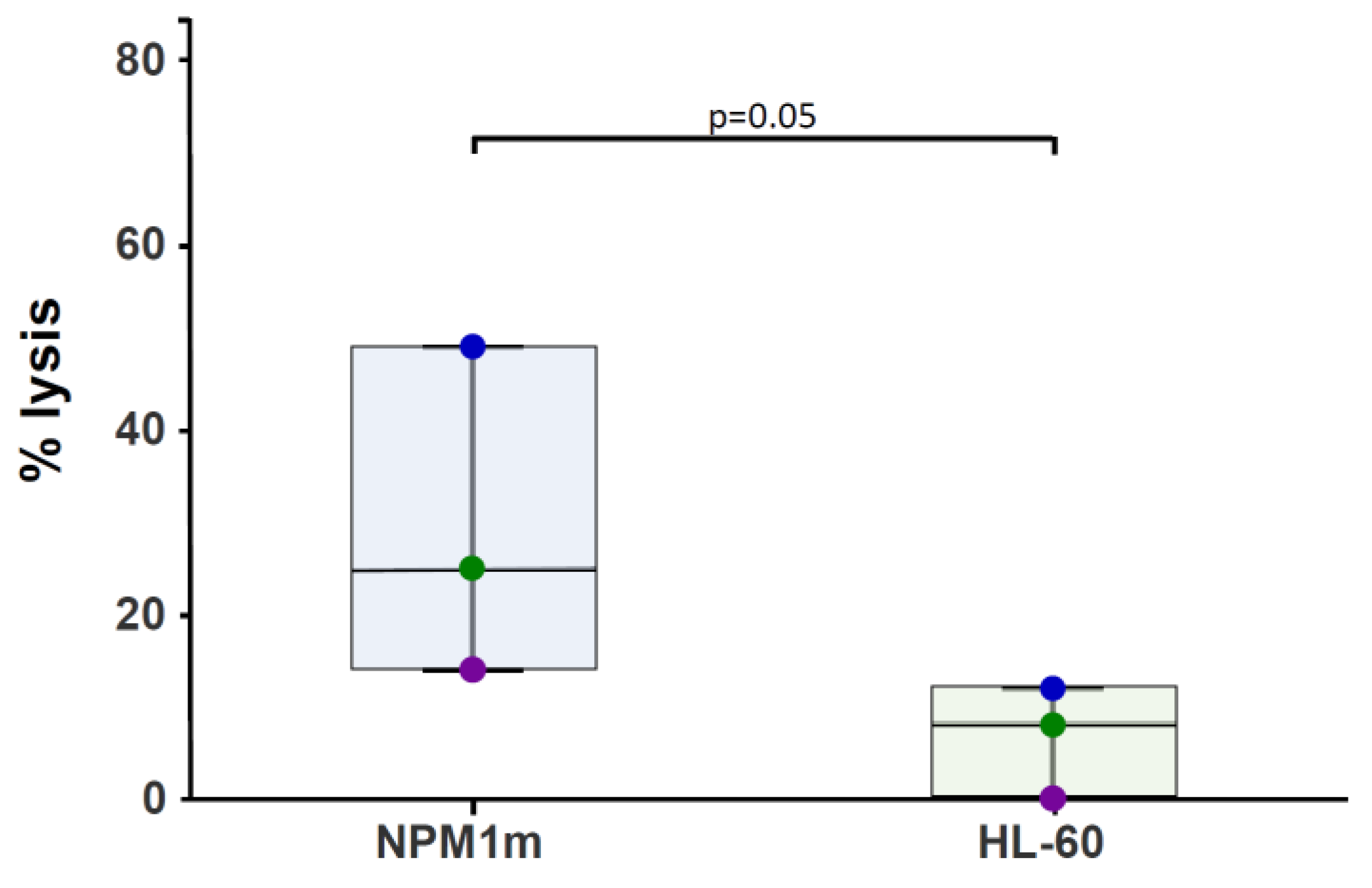
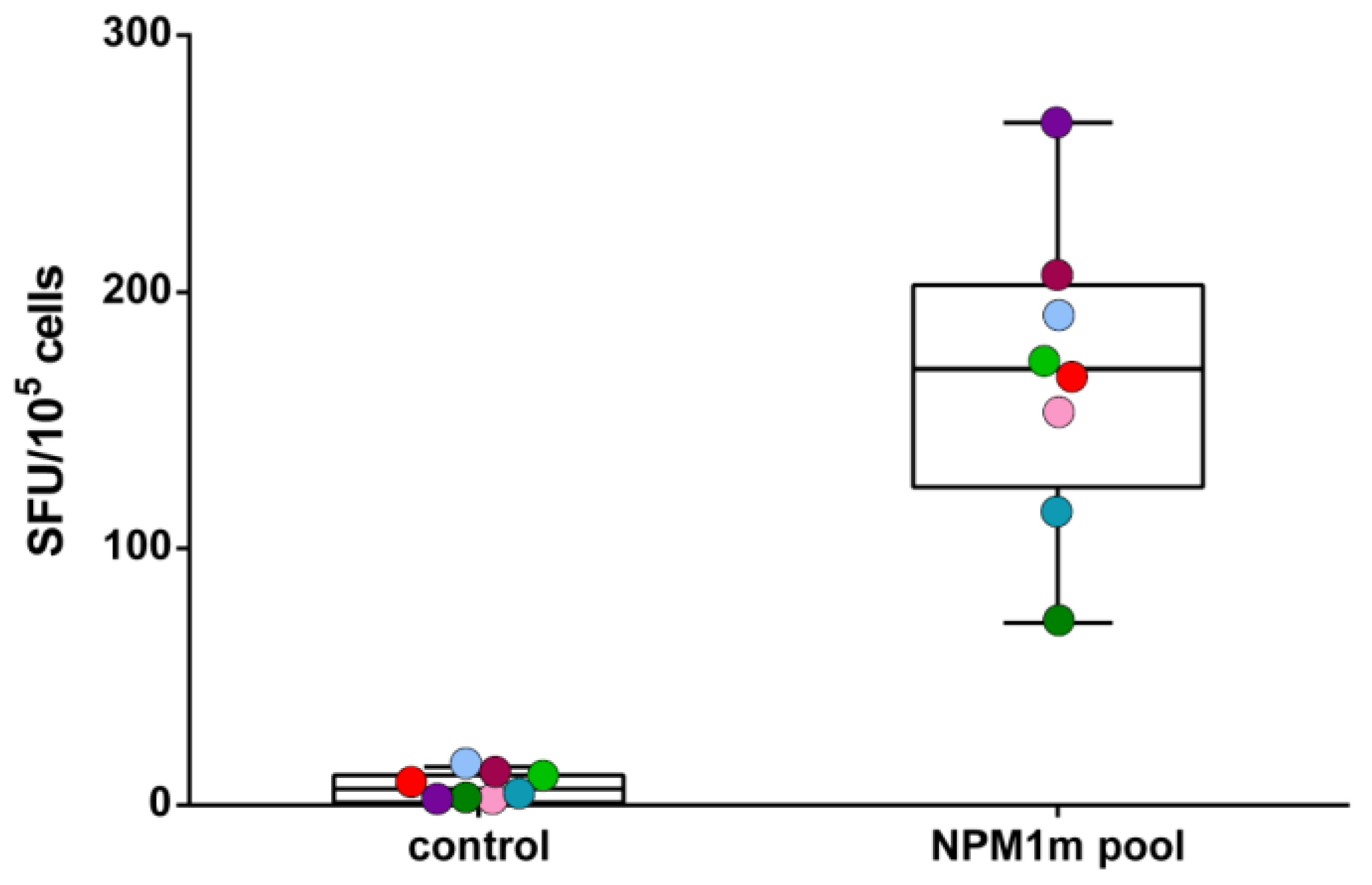
3.1. NPM1mut-CTLs Can Be Expanded from AML Patients and Healthy Donors by Stimulation with NPM1mut-Peptide Pools
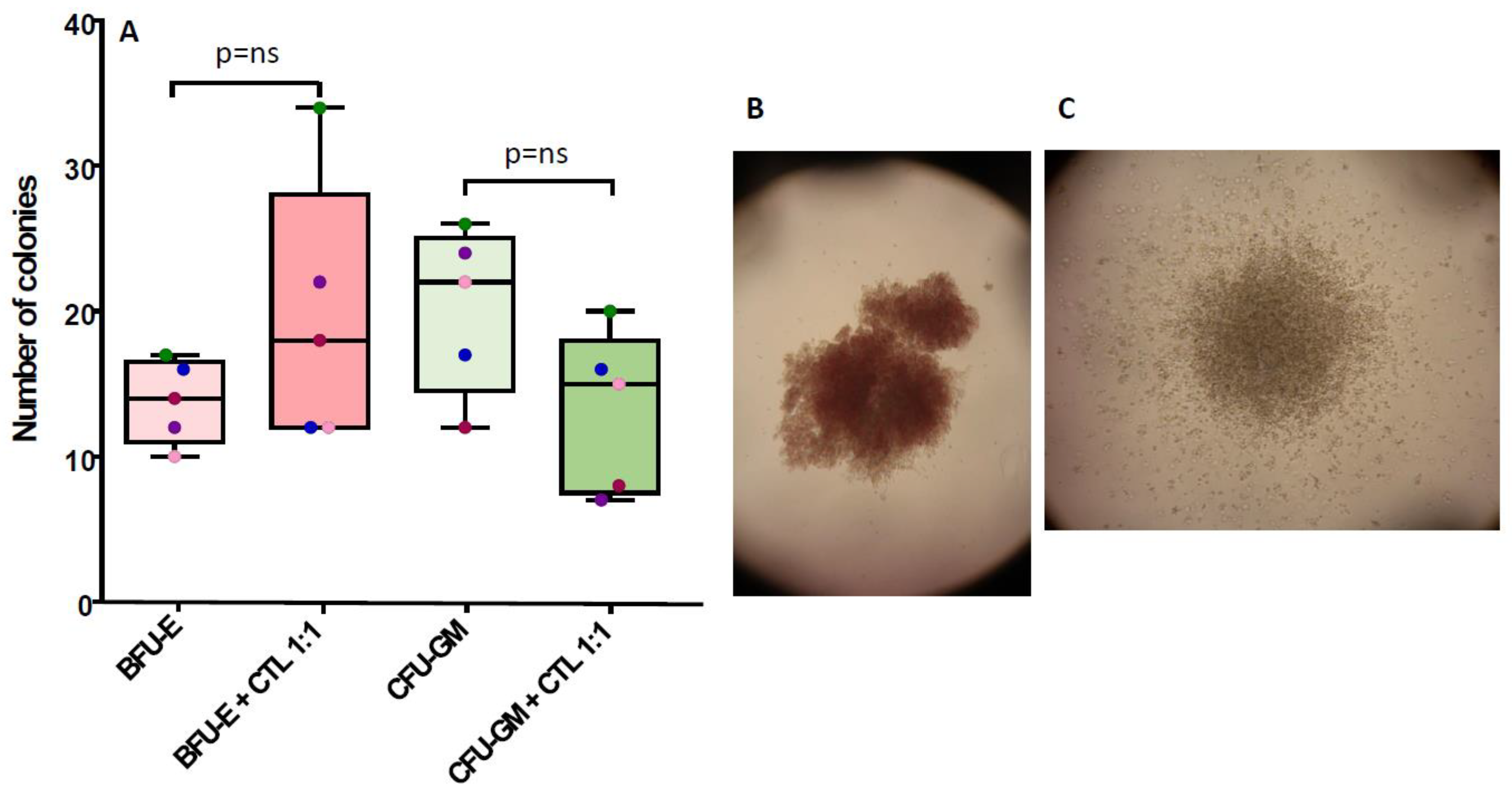
3.2. NPM1mut-CTLs Show Limited Inhibition of CFU-GM, but Not of BFU-E, When Cocultured with BM Progenitors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Döhner, H.; Wei, A.H.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Craddock, C.; DiNardo, C.D.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Godley, L.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of AML in Adults: 2022 Recommendations from an International Expert Panel on Behalf of the ELN. Blood 2022, 140, 1345–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimony, S.; Stahl, M.; Stone, R.M. Acute Myeloid Leukemia: 2023 Update on Diagnosis, Risk-stratification, and Management. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 502–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuser, M.; Freeman, S.D.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Buccisano, F.; Hourigan, C.S.; Ngai, L.L.; Tettero, J.M.; Bachas, C.; Baer, C.; Béné, M.-C.; et al. 2021 Update on MRD in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Consensus Document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood 2021, 138, 2753–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowiez, C.A.; DiNardo, C.D.; Loghavi, S. Molecularly Targeted Therapy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Current Treatment Landscape and Mechanisms of Response and Resistance. Cancers 2023, 15, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daver, N.; Alotaibi, A.S.; Bücklein, V.; Subklewe, M. T-Cell-Based Immunotherapy of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Current Concepts and Future Developments. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1843–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laetsch, T.W.; Maude, S.L.; Rives, S.; Hiramatsu, H.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Baruchel, A.; Boyer, M.; De Moerloose, B.; Qayed, M.; et al. Three-Year Update of Tisagenlecleucel in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the ELIANA Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 41, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Activity of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 1–2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koedam, J.; Wermke, M.; Ehninger, A.; Cartellieri, M.; Ehninger, G. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2022, 29, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, D.; Maccario, R.; Montini, E.; Tonelli, R.; Lisini, D.; Pagani, S.; Comoli, P.; Moretta, A.; Assirelli, E.; Basso, S.; et al. Generation and Ex Vivo Expansion of Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Directed toward Different Types of Leukemia or Myelodysplastic Cells Using Both HLA-Matched and Partially Matched Donors. Exp. Hematol. 2003, 31, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Lee, D.I.; Reijmers, R.M.; Honders, M.W.; Hagedoorn, R.S.; De Jong, R.C.M.; Kester, M.G.D.; Van Der Steen, D.M.; De Ru, A.H.; Kweekel, C.; Bijen, H.M.; et al. Mutated Nucleophosmin 1 as Immunotherapy Target in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, G.; Gerdemann, U.; Caruana, I.; Savoldo, B.; Hensel, N.F.; Rabin, K.R.; Shpall, E.J.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Leen, A.M.; Barrett, A.J.; et al. Generation of Multi-Leukemia Antigen-Specific T Cells to Enhance the Graft-versus-Leukemia Effect after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Brunetti, L.; Martelli, M.P. How I Diagnose and Treat NPM1-Mutated AML. Blood 2021, 137, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Martelli, M.P.; Bolli, N.; Sportoletti, P.; Liso, A.; Tiacci, E.; Haferlach, T. Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Mutated Nucleophosmin (NPM1): Is It a Distinct Entity? Blood 2011, 117, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Mecucci, C.; Tiacci, E.; Alcalay, M.; Rosati, R.; Pasqualucci, L.; La Starza, R.; Diverio, D.; Colombo, E.; Santucci, A.; et al. Cytoplasmic Nucleophosmin in Acute Myelogenous Leukemia with a Normal Karyotype. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, J.; Schneider, V.; Schmitt, M.; Götz, M.; Döhner, K.; Wiesneth, M.; Döhner, H.; Hofmann, S. Immune Responses against the Mutated Region of Cytoplasmatic NPM1 Might Contribute to the Favorable Clinical Outcome of AML Patients with NPM1 Mutations (NPM1mut). Blood 2013, 122, 1087–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghieri, F.; Riva, G.; Lagreca, I.; Barozzi, P.; Vallerini, D.; Morselli, M.; Paolini, A.; Bresciani, P.; Colaci, E.; Maccaferri, M.; et al. Characterization and Dynamics of Specific T Cells against Nucleophosmin-1 (NPM1)-Mutated Peptides in Patients with NPM1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, G.; Luppi, M.; Barozzi, P.; Quadrelli, C.; Basso, S.; Vallerini, D.; Zanetti, E.; Morselli, M.; Forghieri, F.; Maccaferri, M.; et al. Emergence of BCR-ABL–Specific Cytotoxic T Cells in the Bone Marrow of Patients with Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia during Long-Term Imatinib Mesylate Treatment. Blood 2010, 115, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H.; Cooke, K.R.; Grant, M.; Stanojevic, M.; Cruz, C.R.; Keller, M.; Fortiz, M.F.; Hoq, F.; Lang, H.; Barrett, A.J.; et al. Outcome of Donor-Derived TAA-T Cell Therapy in Patients with High-Risk or Relapsed Acute Leukemia Post Allogeneic BMT. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 2520–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janetzki, S.; Price, L.; Schroeder, H.; Britten, C.M.; Welters, M.J.P.; Hoos, A. Guidelines for the Automated Evaluation of Elispot Assays. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1098–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, M.; Rosti, V.; Ferrario, M.; Campanelli, R.; Ramajoli, I.; Rosso, R.; De Ferrari, G.M.; Ferlini, M.; Goffredo, L.; Bertoletti, A.; et al. Increased Circulating Hematopoietic and Endothelial Progenitor Cells in the Early Phase of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Blood 2005, 105, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, A.; Cerchione, C.; Daver, N.; DiNardo, C.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Konopleva, M.; Jabbour, E.; Ravandi, F.; Kadia, T.; de la Fuente Burguera, A.; et al. Immunotherapy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Where We Stand. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 656218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghieri, F.; Riva, G.; Lagreca, I.; Barozzi, P.; Bettelli, F.; Paolini, A.; Nasillo, V.; Lusenti, B.; Pioli, V.; Giusti, D.; et al. Neoantigen-Specific T-Cell Immune Responses: The Paradigm of NPM1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klossowski, S.; Miao, H.; Kempinska, K.; Wu, T.; Purohit, T.; Kim, E.; Linhares, B.M.; Chen, D.; Jih, G.; Perkey, E.; et al. Menin Inhibitor MI-3454 Induces Remission in MLL1-Rearranged and NPM1-Mutated Models of Leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 981–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzama, M.M.; Steiner, M.; Rausch, J.; Sasca, D.; Schönfeld, J.; Kunz, K.; Taubert, M.C.; McGeehan, G.M.; Chen, C.-W.; Mupo, A.; et al. Synergistic Targeting of FLT3 Mutations in AML via Combined Menin-MLL and FLT3 Inhibition. Blood 2020, 136, 2442–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gionfriddo, I.; Brunetti, L.; Mezzasoma, F.; Milano, F.; Cardinali, V.; Ranieri, R.; Venanzi, A.; Pierangeli, S.; Vetro, C.; Spinozzi, G.; et al. Dactinomycin Induces Complete Remission Associated with Nucleolar Stress Response in Relapsed/Refractory NPM1-Mutated AML. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2552–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, G.C.; Aldoss, I.; DiPersio, J.; Cuglievan, B.; Stone, R.; Arellano, M.; Thirman, M.J.; Patel, M.R.; Dickens, D.S.; Shenoy, S.; et al. The Menin Inhibitor Revumenib in KMT2A-Rearranged or NPM1-Mutant Leukaemia. Nature 2023, 615, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezvani, K.; Brenchley, J.M.; Price, D.A.; Kilical, Y.; Gostick, E.; Sewell, A.K.; Li, J.; Mielke, S.; Douek, D.C.; Barrett, A.J. T-Cell Responses Directed against Multiple HLA-A*0201-Restricted Epitopes Derived from Wilms’ Tumor 1 Protein in Patients with Leukemia and Healthy Donors: Identification, Quantification, and Characterization. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8799–8807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, D.; Maccario, R.; Locatelli, F.; Montini, E.; Pagani, S.; Bonetti, F.; Daudt, L.; Turin, I.; Lisini, D.; Garavaglia, C.; et al. Emergence of Antitumor Cytolytic T Cells Is Associated with Maintenance of Hematologic Remission in Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2006, 108, 3843–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, G.; Caruana, I.; Rouce, R.H.; Barrett, A.J.; Gerdemann, U.; Leen, A.M.; Rabin, K.R.; Bollard, C.M. Generation of Tumor Antigen-Specific T Cell Lines from Pediatric Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia—Implications for Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5079–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheibenbogen, C.; Letsch, A.; Thiel, E.; Schmittel, A.; Mailaender, V.; Baerwolf, S.; Nagorsen, D.; Keilholz, U. CD8 T-Cell Responses to Wilms Tumor Gene Product WT1 and Proteinase 3 in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2002, 100, 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, K.; Yong, A.S.M.; Mielke, S.; Savani, B.N.; Musse, L.; Superata, J.; Jafarpour, B.; Boss, C.; Barrett, A.J. Leukemia-Associated Antigen-Specific T-Cell Responses Following Combined PR1 and WT1 Peptide Vaccination in Patients with Myeloid Malignancies. Blood 2008, 111, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittger, S.; Kern, W.; Tschulik, C.; Weiss, T.; Dicker, F.; Falini, B.; Haferlach, C.; Haferlach, T. Minimal Residual Disease Levels Assessed by NPM1 Mutation–Specific RQ-PCR Provide Important Prognostic Information in AML. Blood 2009, 114, 2220–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Othus, M.; Walter, R.B.; Estey, E.H.; Wu, D.; Wood, B.L. Deep NPM1 Sequencing Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Improves Risk Assessment in Adults with NPM1-Mutated AML. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghieri, F.; Comoli, P.; Marasca, R.; Potenza, L.; Luppi, M. Minimal/Measurable Residual Disease Monitoring in NPM1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Clinical Viewpoint and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comoli, P.; Basso, S.; Riva, G.; Barozzi, P.; Guido, I.; Gurrado, A.; Quartuccio, G.; Rubert, L.; Lagreca, I.; Vallerini, D.; et al. BCR-ABL–Specific T-Cell Therapy in Ph+ ALL Patients on Tyrosine-Kinase Inhibitors. Blood 2017, 129, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornhäuser, M.; Thiede, C.; Platzbecker, U.; Kiani, A.; Oelschlaegel, U.; Babatz, J.; Lehmann, D.; Hölig, K.; Radke, J.; Tuve, S.; et al. Prophylactic Transfer of BCR-ABL–, PR1-, and WT1-Reactive Donor T Cells after T Cell–Depleted Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 7174–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, G.; Karbach, J.; Kuçi, S.; Kreyenberg, H.; Willasch, A.; Koscielniak, E.; Tonn, T.; Klingebiel, T.; Wels, W.S.; Jäger, E.; et al. WT1 Peptide-Specific T Cells Generated from Peripheral Blood of Healthy Donors: Possible Implications for Adoptive Immunotherapy after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferulli, F.; Tanzi, M.; Turin, I.; Montini, E.; Rosti, V.; Acquafredda, G.; Lisini, D.; Compagno, F.; Boghen, S.; Licari, A.; et al. Generation of Donor-Derived Wilms Tumor Antigen 1–Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes with Potent Anti-Leukemia Activity for Somatic Cell Therapy in Children given Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation: A Feasibility Pre-Clinical Study. Cytotherapy 2019, 21, 958–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulla, P.D.; Naik, S.; Vasileiou, S.; Tzannou, I.; Watanabe, A.; Kuvalekar, M.; Lulla, S.; Carrum, G.; Ramos, C.A.; Kamble, R.; et al. Clinical Effects of Administering Leukemia-Specific Donor T Cells to Patients with AML/MDS after Allogeneic Transplant. Blood 2021, 137, 2585–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, J.; Ono, Y.; Hofmann, S.; Schmitt, A.; Mehring, E.; Götz, M.; Guillaume, P.; Döhner, K.; Mytilineos, J.; Döhner, H.; et al. Mutated Regions of Nucleophosmin 1 Elicit Both CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Responses in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comoli, P.; Schilham, M.W.; Basso, S.; Van Vreeswijk, T.; Bernardo, M.E.; Maccario, R.; Van Tol, M.J.D.; Locatelli, F.; Veltrop-Duits, L.A. T-Cell Lines Specific for Peptides of Adenovirus Hexon Protein and Devoid of Alloreactivity Against Recipient Cells Can Be Obtained From HLA-Haploidentical Donors. J. Immunother. 2008, 31, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craddock, C.; Labopin, M.; Robin, M.; Finke, J.; Chevallier, P.; Yakoub-Agha, I.; Bourhis, J.H.; Sengelov, H.; Blaise, D.; Luft, T.; et al. Clinical Activity of Azacitidine in Patients Who Relapse after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberatore, C.; Stanghellini, M.T.L.; Lorentino, F.; Vago, L.; Carrabba, M.G.; Greco, R.; Marktel, S.; Assanelli, A.; Farina, F.; Corti, C.; et al. Azacitidine and Donor Lymphocytes Infusions in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome Relapsed after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation from Alternative Donors. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2022, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautenberg, C.; Bergmann, A.; Germing, U.; Fischermanns, C.; Pechtel, S.; Kaivers, J.; Jäger, P.; Schuler, E.; Haas, R.; Kobbe, G.; et al. Prediction of Response and Survival Following Treatment with Azacitidine for Relapse of Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Cancers 2020, 12, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazarbachi, A.; Bug, G.; Baron, F.; Brissot, E.; Ciceri, F.; Dalle, I.A.; Döhner, H.; Esteve, J.; Floisand, Y.; Giebel, S.; et al. Clinical Practice Recommendation on Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients with FLT3 -Internal Tandem Duplication: A Position Statement from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahas, M.R.; Stroopinsky, D.; Rosenblatt, J.; Cole, L.; Pyzer, A.R.; Anastasiadou, E.; Sergeeva, A.; Ephraim, A.; Washington, A.; Orr, S.; et al. Hypomethylating Agent Alters the Immune Microenvironment in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML) and Enhances the Immunogenicity of a Dendritic Cell/AML Vaccine. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Khan, D.H.; Hurren, R.; Xu, M.; Na, Y.; Kang, H.; Mirali, S.; Wang, X.; Gronda, M.; Jitkova, Y.; et al. Venetoclax Enhances T Cell–Mediated Antileukemic Activity by Increasing ROS Production. Blood 2021, 138, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loenen, M.M.; De Boer, R.; Amir, A.L.; Hagedoorn, R.S.; Volbeda, G.L.; Willemze, R.; Van Rood, J.J.; Falkenburg, J.H.F.; Heemskerk, M.H.M. Mixed T Cell Receptor Dimers Harbor Potentially Harmful Neoreactivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10972–10977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, G.L.; Gladney, W.L. Immune Escape Mechanisms as a Guide for Cancer Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitskaya, J.; Sharipo, A.; Leonchiks, A.; Ciechanover, A.; Masucci, M.G. Inhibition of Ubiquitin/Proteasome-Dependent Protein Degradation by the Gly-Ala Repeat Domain of the Epstein–Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12616–12621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disis, M.L.; Wallace, D.R.; Gooley, T.A.; Dang, Y.; Slota, M.; Lu, H.; Coveler, A.L.; Childs, J.S.; Higgins, D.M.; Fintak, P.A.; et al. Concurrent Trastuzumab and HER2/Neu -Specific Vaccination in Patients With Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4685–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkuri, T.; Sato, M.; Abe, H.; Tsuji, K.; Yamagishi, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Matsubara, N.; Kitamura, H.; Nishimura, T. Identification of a Novel NY-ESO-1 Promiscuous Helper Epitope Presented by Multiple MHC Class II Molecules Found Frequently in the Japanese Population. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeckova, S.; Alexova-Zurkova, K.; Hainz, P.; Krystofova, J.; Mackova, J.; Roubalova, K.; Stastna-Markova, M.; Vrana, M.; Vydra, J. Non-Mutated Nucleophosmin 1 Is Recognized by the CD8+ T Lymphocytes of an AML Patient after the Transplantation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells from an HLA-Haploidentical Donor. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2928–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Cicco, M.; Lagreca, I.; Basso, S.; Barozzi, P.; Muscianisi, S.; Bianco, A.; Riva, G.; Di Vincenzo, S.; Pulvirenti, C.; Sapuppo, D.; et al. Preclinical Validation of an Advanced Therapy Medicinal Product Based on Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Specific for Mutated Nucleophosmin (NPM1mut) for the Treatment of NPM1mut-Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2023, 15, 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102731
De Cicco M, Lagreca I, Basso S, Barozzi P, Muscianisi S, Bianco A, Riva G, Di Vincenzo S, Pulvirenti C, Sapuppo D, et al. Preclinical Validation of an Advanced Therapy Medicinal Product Based on Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Specific for Mutated Nucleophosmin (NPM1mut) for the Treatment of NPM1mut-Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers. 2023; 15(10):2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102731
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Cicco, Marica, Ivana Lagreca, Sabrina Basso, Patrizia Barozzi, Stella Muscianisi, Alba Bianco, Giovanni Riva, Sara Di Vincenzo, Chiara Pulvirenti, Davide Sapuppo, and et al. 2023. "Preclinical Validation of an Advanced Therapy Medicinal Product Based on Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Specific for Mutated Nucleophosmin (NPM1mut) for the Treatment of NPM1mut-Acute Myeloid Leukemia" Cancers 15, no. 10: 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102731
APA StyleDe Cicco, M., Lagreca, I., Basso, S., Barozzi, P., Muscianisi, S., Bianco, A., Riva, G., Di Vincenzo, S., Pulvirenti, C., Sapuppo, D., Siciliano, M., Rosti, V., Candoni, A., Zecca, M., Forghieri, F., Luppi, M., & Comoli, P. (2023). Preclinical Validation of an Advanced Therapy Medicinal Product Based on Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Specific for Mutated Nucleophosmin (NPM1mut) for the Treatment of NPM1mut-Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers, 15(10), 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102731





