Beneficial Effect of Combining Radiotherapy and Transarterial Chemoembolization on Patient Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinomas and Macrovascular Invasion Treated with Sorafenib
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
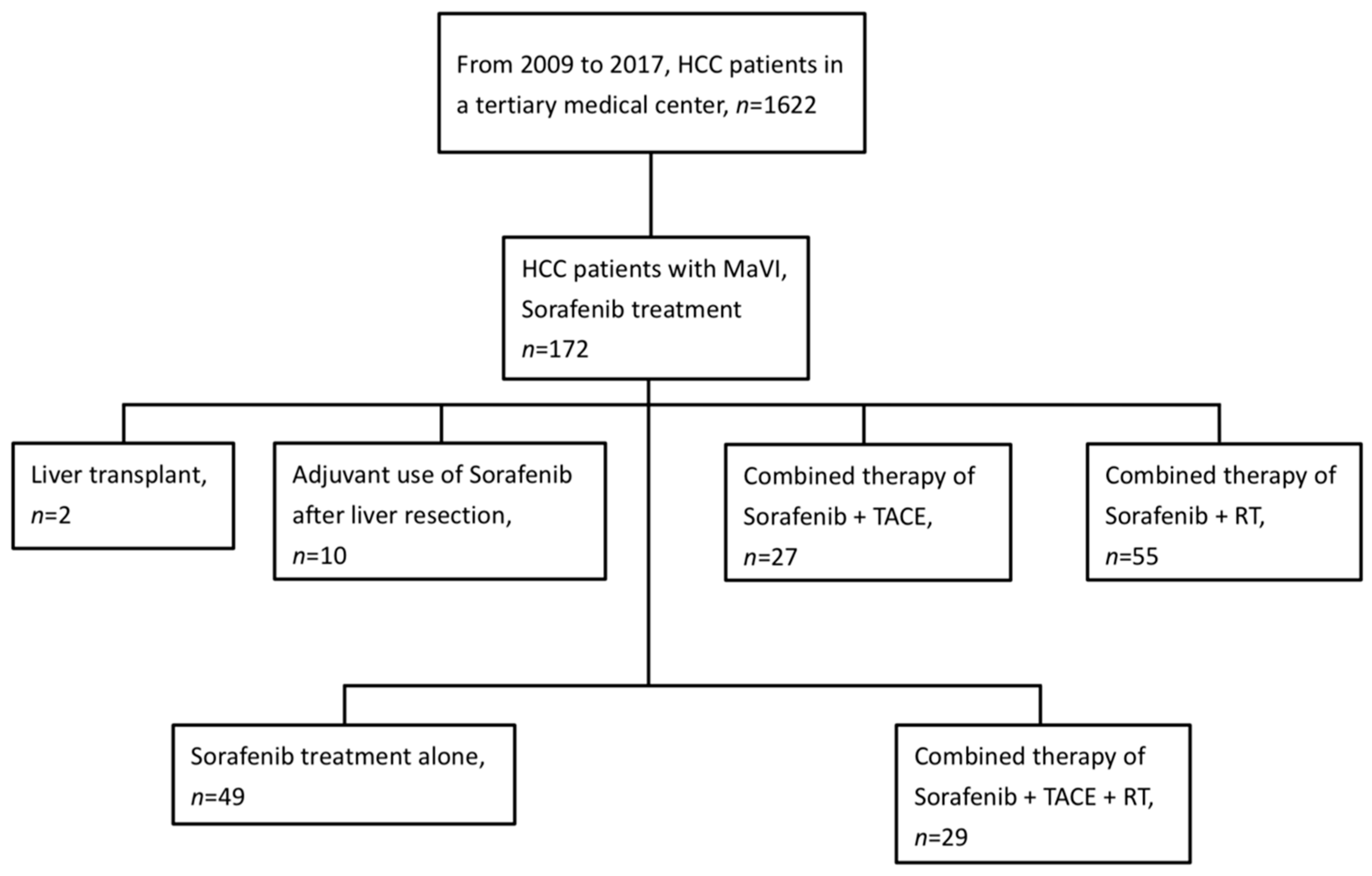
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Sorafenib
2.3. TACE Procedure
2.4. Radiotherapy
2.5. Follow-Up and Toxicity Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Survival
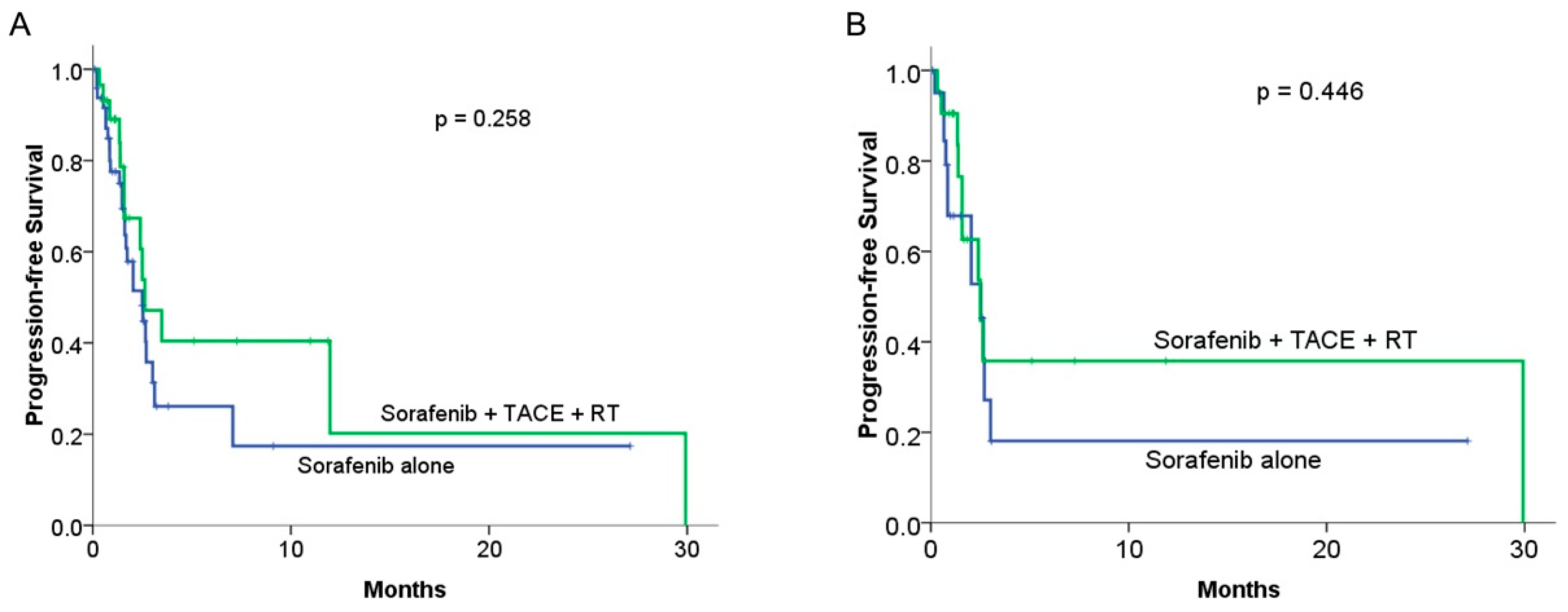
3.3. Progression-Free Survival
3.4. Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, D.R.; Stenmark, M.H.; Tao, Y.; Pollom, E.L.; Caoili, E.M.; Lawrence, T.S.; Schipper, M.J.; Feng, M. Outcomes after stereotactic body radiotherapy or radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, Y.-H.; Li, W.-F.; Kee, K.-M.; Wang, C.-C.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Wang, J.-H.; Lu, S.-N.; Hung, C.-H. The characteristics of patients with macrovascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: When East meets West. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2021, 407, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, T.; Tani, J.; Deguchi, A.; Nakahara, M.; Oura, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Fujita, K.; Mimura, S.; Sakamoto, T.; Morishita, A. Efficacy of combined modality therapy with sorafenib following hepatic arterial injection chemotherapy and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with major vascular invasion. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 11, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.M.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, J.H.; An, J.H.; Lee, H.C.; Lim, Y.-S. Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization plus external beam radiotherapy vs sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma with macroscopic vascular invasion: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Dong, D.; Gao, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, W. Safety and efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization plus radiotherapy combined with sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma showing macrovascular invasion. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bustamante, J.; Castells, A.; Vilana, R.; Ayuso, M.D.C.; Sala, M.; Brú, C.; Rodés, J.; Bruix, J. Natural history of untreated nonsurgical hepatocellular carcinoma: Rationale for the design and evaluation of therapeutic trials. Hepatology 1999, 29, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, M.; Makuuchi, M. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma accompanied by portal vein tumor thrombus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.-F.; De Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Forner, A. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Kang, Y.-K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.-J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Luo, R.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Yang, T.-S. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Guan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.-J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Yang, T.-S.; Tak, W.Y.; Pan, H.; Yu, S. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma according to baseline status: Subset analyses of the phase III Sorafenib Asia–Pacific trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1452–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.-H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.-W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-L.; Chan, S.-K.; Lee, S.-F.; Choi, H.C.-W. First-line atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma: A cost-effectiveness analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wu, B. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sorafenib as first-line treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A cost-effectiveness analysis. Cancer Commun. 2020, 40, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Kaneko, R.; Yano, Y.; Kamada, K.; Ikehara, T.; Nagai, H.; Sato, Y.; Igarashi, Y. The prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib in combination with TACE. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-A.; Shim, J.H.; Yoon, S.M.; Jung, J.; Kim, J.H.; Ryu, M.-H.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Kang, Y.-K.; Lee, D.; Kim, K.M. Comparison of chemoembolization with and without radiation therapy and sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: A propensity score analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 320–329.e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Paik, Y.H.; Park, H.C.; Yu, J.I.; Sohn, W.; Gwak, G.Y.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, K.C.; Paik, S.W. The feasibility of combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, Y.; Kimura, T.; Aikata, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Fukuhara, T.; Masaki, K.; Nakahara, T.; Naeshiro, N.; Ono, A.; Miyaki, D. Stereotactic body radiation therapy combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for small hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.-L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.-C.; Chang, W.-C.; Lo, C.-H.; Yang, J.-F.; Lee, M.-S.; Dai, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-S.; Fan, C.-Y.; Huang, W.-Y. Comparison of stereotactic body radiation therapy and transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable medium-sized hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, R.; Sato, M.; Kawabata, M.; Nakatsuka, H.; Nakamura, K.; Takashima, S. Hepatic artery embolization in 120 patients with unresectable hepatoma. Radiology 1983, 148, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, J.J.; Xu, Y.Z.; Dong, J.H. Efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis: A meta-analysis. ANZ J. Surg. 2016, 86, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, T.-C.; Xie, X.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Yin, X.; Zhang, B.-H.; Ren, Z.-G. Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, G.E.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.Y.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Chung, J.W.; Yoon, J.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, Y.J. Transarterial chemoembolization can be safely performed in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma invading the main portal vein and may improve the overall survival. Radiology 2011, 258, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.I.; Kim, M.-S.; Bae, S.H.; Cho, C.K.; Yoo, H.J.; Seo, Y.S.; Kang, J.-K.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Han, C.J. High-dose stereotactic body radiotherapy correlates increased local control and overall survival in patients with inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.M.; Lim, Y.-S.; Park, M.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, B.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, H.C.; Chung, Y.-H.; Lee, Y.S. Stereotactic body radiation therapy as an alternative treatment for small hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.K.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, C.K.; Yang, K.M.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Bae, S.H.; Jung, D.H.; Kim, K.B.; Lee, D.H. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma as a local salvage treatment after incomplete transarterial chemoembolization. Cancer 2012, 118, 5424–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-Y.; Jen, Y.-M.; Lee, M.-S.; Chang, L.-P.; Chen, C.-M.; Ko, K.-H.; Lin, K.-T.; Lin, J.-C.; Chao, H.-L.; Lin, C.-S. Stereotactic body radiation therapy in recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapir, E.; Tao, Y.; Schipper, M.J.; Bazzi, L.; Novelli, P.M.; Devlin, P.; Owen, D.; Cuneo, K.C.; Lawrence, T.S.; Parikh, N.D. Stereotactic body radiation therapy as an alternative to transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, Q.-Q.; Guo, S.-P.; Feng, Z.-Z.; Deng, X.-W.; Huang, X.-Y.; Liu, M.-Z. Effectiveness of stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein and/or inferior vena cava tumor thrombosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shui, Y.; Yu, W.; Ren, X.; Guo, Y.; Xu, J.; Ma, T.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J.; Li, Q.; Hu, Q. Stereotactic body radiotherapy based treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with extensive portal vein tumor thrombosis. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Takami, Y.; Matsushima, H.; Tateishi, M.; Ryu, T.; Yoshitomi, M.; Matsumura, T.; Saitsu, H. The safety and efficacy of combination therapy of sorafenib and radiotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brix, N.; Tiefenthaller, A.; Anders, H.; Belka, C.; Lauber, K. Abscopal, immunological effects of radiotherapy: Narrowing the gap between clinical and preclinical experiences. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 280, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Rodriguez, I.; Leaman, O.; López-Campos, F.; Montero, A.; Conde, A.J.; Aristu, J.; Lara, P.; Calvo, F.M.; Melero, I. Immune mechanisms mediating abscopal effects in radioimmunotherapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 196, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Vanpouille-Box, C.; Melero, I.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Immunological mechanisms responsible for radiation-induced abscopal effect. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, B.; Rubner, Y.; Wunderlich, R.; Weiss, E.-M.; G Pockley, A.; Fietkau, R.; S Gaipl, U. Induction of abscopal anti-tumor immunity and immunogenic tumor cell death by ionizing irradiation-implications for cancer therapies. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, W.-Y.; Chiou, Y.-Y.; Hung, H.-H.; Su, C.-W.; Chou, Y.-H.; Huo, T.-I.; Huang, Y.-H.; Wu, W.-C.; Lin, H.-C.; Lee, S.-D. Younger hepatocellular carcinoma patients have better prognosis after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation therapy. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.-H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, T.; Park, J.-W.; Finn, R.S.; Cheng, A.-L.; Mathurin, P.; Edeline, J.; Kudo, M.; Harding, J.J.; Merle, P.; Rosmorduc, O. Nivolumab versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 459): A randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sorafenib Alone | Sorafenib + TACE + RT | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | No. (%) | |||
| No. of patients | 49 (62.8) | 29 (37.2) | ||
| Sex | Male | 34 (69.4) | 23 (79.3) | 0.340 |
| Female | 15 (30.6) | 6 (20.7) | ||
| Age, years | Mean | 65 | 56 | 0.003 |
| Median | 64 | 56 | ||
| Min–Max | 37–91 | 33–79 | ||
| Viral hepatitis | No | 11 (22.4) | 1 (3.4) | 0.023 |
| HBV | 23 (46.9) | 22 (75.9) | ||
| HCV | 15 (30.6) | 6 (20.7) | ||
| ECOG | 0 | 6 (12.2) | 8 (27.6) | 0.055 |
| 1 | 23 (46.9) | 17 (58.6) | ||
| 2 | 18 (36.7) | 3 (10.3) | ||
| 3 | 2 (4.1) | 1 (3.4) | ||
| Recurrent status | New diagnosis | 34 (69.4) | 3 (10.3) | <0.001 |
| Recurrence | 15 (30.6) | 26 (89.7) | ||
| No. of prior treatments | Median | 0 | 2 | <0.001 |
| Min–Max | 0–4 | 0–6 | ||
| Largest tumor size, cm | Mean | 9.83 | 9.57 | 0.868 |
| Median | 9.1 | 9.0 | ||
| Min–Max | 0–23 | 1–21 | ||
| AFP | Mean +/− SD | 10,360.3 (16,008.4) | 10,240.7 (14,721.0) | 0.974 |
| median | 665.0 | 3597.0 | ||
| IQR | 44.7–16,895.3 | 257.2–16,335.3 | ||
| Bilirubin | Mean +/− SD | 1.78 (2.21) | 1.88 (3.56) | 0.878 |
| median | 1.2 | 1.2 | ||
| IQR | 0.8–1.8 | 0.9–1.7 | ||
| Albumin | Mean +/− SD | 3.38 (0.54) | 3.34 (0.50) | 0.788 |
| median | 3.4 | 3.4 | ||
| IQR | 3.0–3.8 | 3.0–3.7 | ||
| INR | Mean +/− SD | 1.10 (0.19) | 1.08 (0.10) | 0.662 |
| median | 1.1 | 1.1 | ||
| IQR | 1.0–1.1 | 1.0–1.1 | ||
| AST | Mean +/− SD | 116.4 (125.0) | 186.8 (378.0) | 0.266 |
| median | 74.0 | 91.0 | ||
| IQR | 48.0–158.5 | 41.0–148.5 | ||
| ALT | Mean +/− SD | 83.0 (130.4) | 125.2 (274.1) | 0.361 |
| median | 42.0 | 53.0 | ||
| IQR | 22.5–83.5 | 30.5–101.0 | ||
| NLR | Mean +/− SD | 4. 70 (4.57) | 6.37 (3.80) | 0.102 |
| median | 3.6 | 4.8 | ||
| IQR | 2.5–4.9 | 3.1–9.7 | ||
| MaVI location | VP2 | 7 (14.3) | 2 (6.9) | 0.116 |
| VP3 | 21 (42.9) | 20 (69.0) | ||
| VP4 | 18 (36.7) | 7 (24.1) | ||
| IVC | 3 (6.1) | 0 (0) | ||
| N stage | 0 | 31 (63.3) | 24 (82.8) | 0.068 |
| 1 | 18 (36.7) | 5 (17.2) | ||
| M stage | 0 | 35 (71.4) | 27 (93.1) | 0.022 |
| 1 | 14 (28.6) | 2 (6.9) | ||
| CTP class | A | 29 (59.2) | 19 (62.1) | 0.801 |
| B | 20 (40.8) | 11 (37.9) | ||
| ALBI grade | 1 | 6 (12.2) | 2 (6.9) | 0.518 |
| 2 | 33 (67.3) | 24 (79.3) | ||
| 3 | 10 (20.4) | 4 (13.8) | ||
| OS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Univariable | Multivariable | ||
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age, years | ||||
| ≥60 vs. <60 | 1.22 (0.77–1.92) | 0.391 | ||
| Sex | ||||
| female vs. male | 0.83 (0.49–1.41) | 0.498 | ||
| Etiology | ||||
| HBV vs. no | 0.59 (0.30–1.14) | 0.116 | ||
| HCV vs. no | 1.10 (0.54–2.25) | 0.787 | ||
| ECOG | 0.005 | 1.11 (0.84–1.48) | 0.459 | |
| 0–1 vs. 2–3 | 0.48 (0.29–0.48) | |||
| Status | ||||
| recurrence vs. new diagnosis | 0.32 (0.20–0.53) | <0.001 | 0.52 (0.28–0.94) | 0.031 |
| Tumor size, cm | ||||
| ≥9 cm vs. <9 cm | 1.15 (0.72–1.82) | 0.563 | ||
| No of tumors | ||||
| single vs. multiple | 0.79 (0.47–1.32) | 0.370 | ||
| AFP | ||||
| ≥500 vs. <500 | 1.25 (0.78–2.00) | 0.348 | ||
| Bilirubin | ||||
| ≥1.2 vs. <1.2 | 0.98 (0.62–1.54) | 0.924 | ||
| Albumin | ||||
| ≥3.4 vs. <3.4 | 0.71 (0.45–1.12) | 0.141 | ||
| INR | ||||
| ≥1.1 vs. <1.1 | 1.08 (0.68–1.71) | 0.745 | ||
| AST | ||||
| ≥80 vs. <80 | 1.40 (0.88–2.22) | 0.151 | ||
| ALT | ||||
| ≥50 vs. <50 | 1.09 (0.68–1.73) | 0.719 | ||
| NLR | ||||
| ≥3.9 vs. <3.9 | 1.03 (0.65–1.62) | 0.917 | ||
| MaVI location | ||||
| Vp4 vs. others | 1.07 (0.91–1.26) | 0.405 | ||
| N stage | ||||
| 0 vs. 1 | 0.92 (0.71–1.19) | 0.517 | ||
| M stage | ||||
| 0 vs. 1 | 0.81 (0.61–1.08) | 0.152 | ||
| CTP class | ||||
| B vs. A | 1.53 (0.95–2.45) | 0.078 | 1.32 (0.79–2.20) | 0.295 |
| ALBI grade | ||||
| 3 vs. 1 and 2 | 1.58 (0.86–2.90) | 0.141 | ||
| Treatment | ||||
| Sorafenib + TACE + RT vs. sorafenib alone | 0.70 (0.59–0.82) | <0.001 | 0.80 (0.65–0.99) | 0.037 |
| Sorafenib Alone | Sorafenib + TACE + RT | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | No. (%) | |||
| No. of patients | 21 (100) | 21 (100) | ||
| Sex | Male | 14 (66.7) | 16 (76.2) | 0.495 |
| Female | 7 (33.3) | 5 (23.8) | ||
| Age, years | Mean | 63.7 | 55.2 | 0.032 |
| Median | 66 | 53 | ||
| Min–Max | 37–82 | 33–79 | ||
| Viral hepatitis | No | 5 (23.8) | 1 (4.8) | 0.101 |
| HBV | 8 (38.1) | 14 (66.7) | ||
| HCV | 8 (38.1) | 6 (28.6) | ||
| ECOG | 0 | 4 (19.0) | 3 (14.36) | 0.801 |
| 1 | 11 (52.4) | 14 (66.7) | ||
| 2 | 5 (23.8) | 3 (14.3) | ||
| 3 | 1 (4.8) | 1 (4.8) | ||
| Recurrent status | New diagnosis | 8 (38.1) | 3 (14.3) | 0.079 |
| Recurrence | 13 (61.9) | 18 (85.7) | ||
| No. of prior treatments | Median | 1 | 2 | 0.054 |
| Min–Max | 0–4 | 0–6 | ||
| Largest tumor size, cm | Mean | 10.1 | 9.05 | 0.516 |
| Median | 8.0 | 8.0 | ||
| Min–Max | 1–23 | 3–17 | ||
| AFP | Mean +/− SD | 12,282.5 (16,904.3) | 10,661.7 (15,148.2) | 0.745 |
| median | 2264 | 4530.0 | ||
| IQR | 40.3–26,711.8 | 178.5–16,485.3 | ||
| Bilirubin | Mean +/− SD | 2.38 (3.15) | 1.29 (0.56) | 0.125 |
| median | 1.4 | 1.2 | ||
| IQR | 0.8–2.2 | 0.9–1.9 | ||
| Albumin | Mean +/− SD | 3.38 (0.59) | 3.34 (0.54) | 0.808 |
| median | 3.4 | 3.3 | ||
| IQR | 3.0–3.9 | 3.0–3.8 | ||
| INR | Mean +/− SD | 1.10 (1.1) | 1.09 (0.11) | 0.779 |
| median | 1.1 | 1.1 | ||
| IQR | 1.0–1.2 | 1.0–1.1 | ||
| AST | Mean +/− SD | 104.8 (95.2) | 222.8 (441.2) | 0.238 |
| median | 74.0 | 57.0 | ||
| IQR | 48.0–103.5 | 38.5–202.5 | ||
| ALT | Mean +/− SD | 68.8 (63.7) | 143.1 (321.5) | 0.305 |
| median | 47.0 | 44.0 | ||
| IQR | 27.5–75.0 | 27.0–103.5 | ||
| NLR | Mean +/− SD | 3.83 (2.06) | 6.17 (3.63) | 0.014 |
| median | 3.6 | 4.8 | ||
| IQR | 2.6–4.9 | 3.1–9.6 | ||
| MaVI location | VP2 | 4 (19.0) | 2 (9.5) | 0.607 |
| VP3 | 12 (57.1) | 12 (57.1) | ||
| VP4 | 5 (23.9) | 7 (33.3) | ||
| IVC | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| N stage | 0 | 14 (66.7) | 16 (76.2) | 0.495 |
| 1 | 7 (33.3) | 5 (23.8) | ||
| M stage | 0 | 16 (76.2) | 197 (94.5) | 0.214 |
| 1 | 5 (23.8) | 2 (9.5) | ||
| CTP class | A | 11 (52.4) | 13 (61.9) | 0.533 |
| B | 10 (47.6) | 8 (38.1) | ||
| ALBI grade | 1 | 2 (9.5) | 2 (9.5) | 0.282 |
| 2 | 13 (61.9) | 17 (81.0) | ||
| 3 | 6 (28.6) | 2 (9.5) | ||
| Sorafenib | Sorafenib, RT, and TACE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Patients (%) | No. of Patients (%) | |||||
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | |
| Leukopenia | 5/10.2 | 10/34.5 | 2/6.9 | |||
| Anemia | 29/59.2 | 22/75.9 | 2/6.9 | |||
| Thrombocytopenia | 16/32.7 | 3/6.1 | 9/31 | 6/20.7 | ||
| ALT | 12/24.5 | 6/12.2 | 8/27.6 | 7/24.1 | 2/6.9 | |
| Alk-P | 2/4.1 | 10/20.4 | 1/3.4 | |||
| Bilirubin | 11/22.4 | 2/4.1 | 1/2 | 8/27.6 | 6/20.7 | |
| r-GT | 4/8.2 | 11/22.4 | 1/3.4 | 1/3.47 | ||
| Nausea | 6/12.2 | 3/6.1 | 9/18.4 | 4/13.8 | ||
| Vomiting | 2/4.1 | 2/4.1 | 1/3.4 | |||
| Anorexia | 32/65.3 | 9/18.4 | 9/31 | |||
| Diarrhea | 6/12.2 | 1/2 | 5/17.2 | |||
| Hand–foot syndrome | 6/12.2 | 1/2 | 2/6.9 | 3/10.3 | ||
| Other skin reaction | 3/6.1 | 1/2 | 5/17.2 | 1/3.4 | 1/3.4 | |
| Fatigue | 38/77.6 | 20/69 | 1/3.4 | |||
| Hair loss | 1/2 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, M.-C.; Huang, W.-Y.; Fan, H.-L.; Chen, T.-W.; Chang, W.-C.; Lin, H.-H.; Shih, Y.-L.; Hsieh, T.-Y.; Huang, W.-C. Beneficial Effect of Combining Radiotherapy and Transarterial Chemoembolization on Patient Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinomas and Macrovascular Invasion Treated with Sorafenib. Cancers 2023, 15, 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102687
Lu M-C, Huang W-Y, Fan H-L, Chen T-W, Chang W-C, Lin H-H, Shih Y-L, Hsieh T-Y, Huang W-C. Beneficial Effect of Combining Radiotherapy and Transarterial Chemoembolization on Patient Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinomas and Macrovascular Invasion Treated with Sorafenib. Cancers. 2023; 15(10):2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102687
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Meng-Chuan, Wen-Yen Huang, Hsiu-Lung Fan, Teng-Wei Chen, Wei-Chou Chang, Hsuan-Hwai Lin, Yu-Lueng Shih, Tsai-Yuan Hsieh, and Wei-Chen Huang. 2023. "Beneficial Effect of Combining Radiotherapy and Transarterial Chemoembolization on Patient Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinomas and Macrovascular Invasion Treated with Sorafenib" Cancers 15, no. 10: 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102687
APA StyleLu, M.-C., Huang, W.-Y., Fan, H.-L., Chen, T.-W., Chang, W.-C., Lin, H.-H., Shih, Y.-L., Hsieh, T.-Y., & Huang, W.-C. (2023). Beneficial Effect of Combining Radiotherapy and Transarterial Chemoembolization on Patient Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinomas and Macrovascular Invasion Treated with Sorafenib. Cancers, 15(10), 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102687






