Association between Antibiotic Exposure and Systemic Immune Parameters in Cancer Patients Receiving Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Data Collection
2.2. Biospecimen Collection and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Cohort
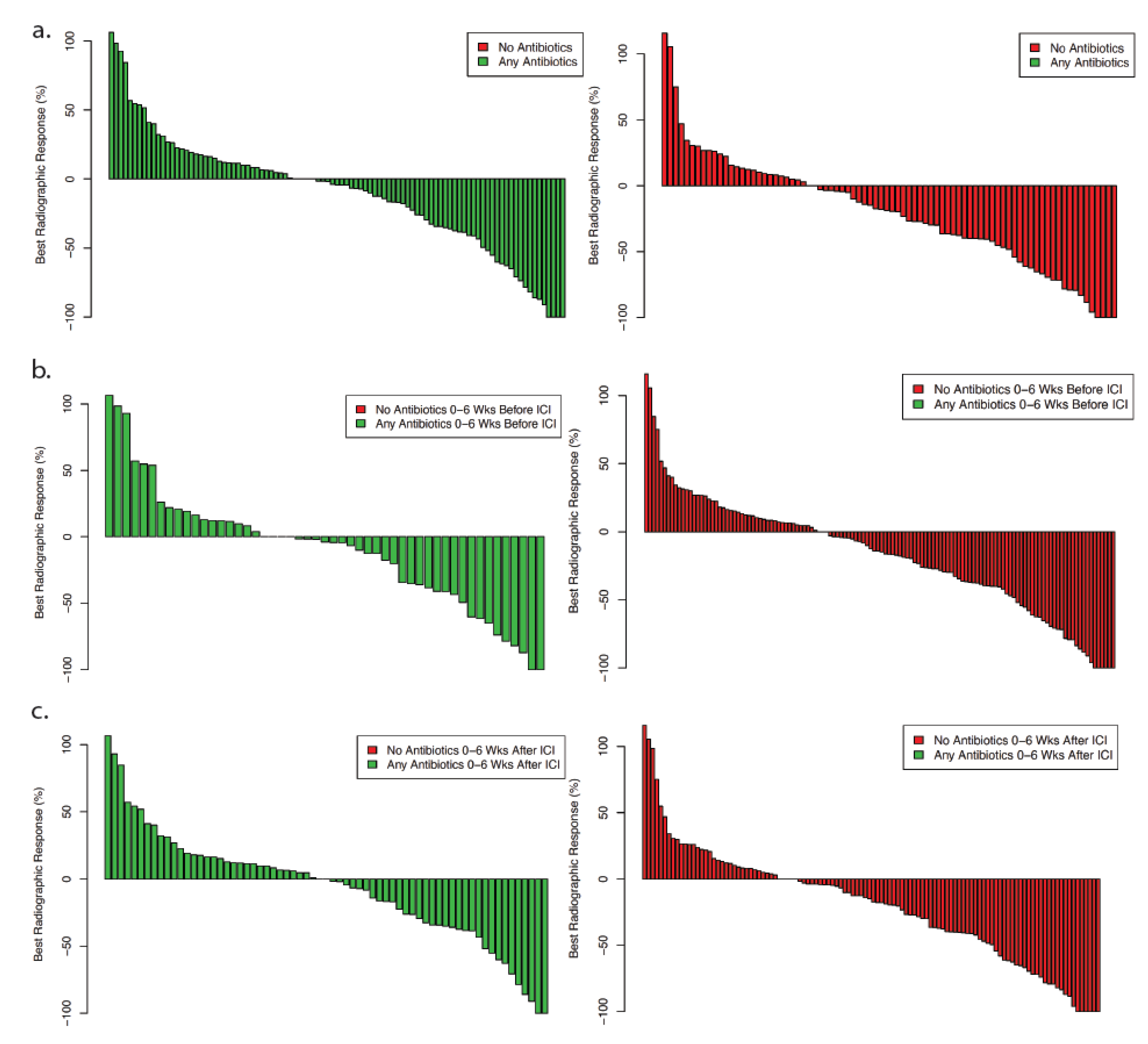
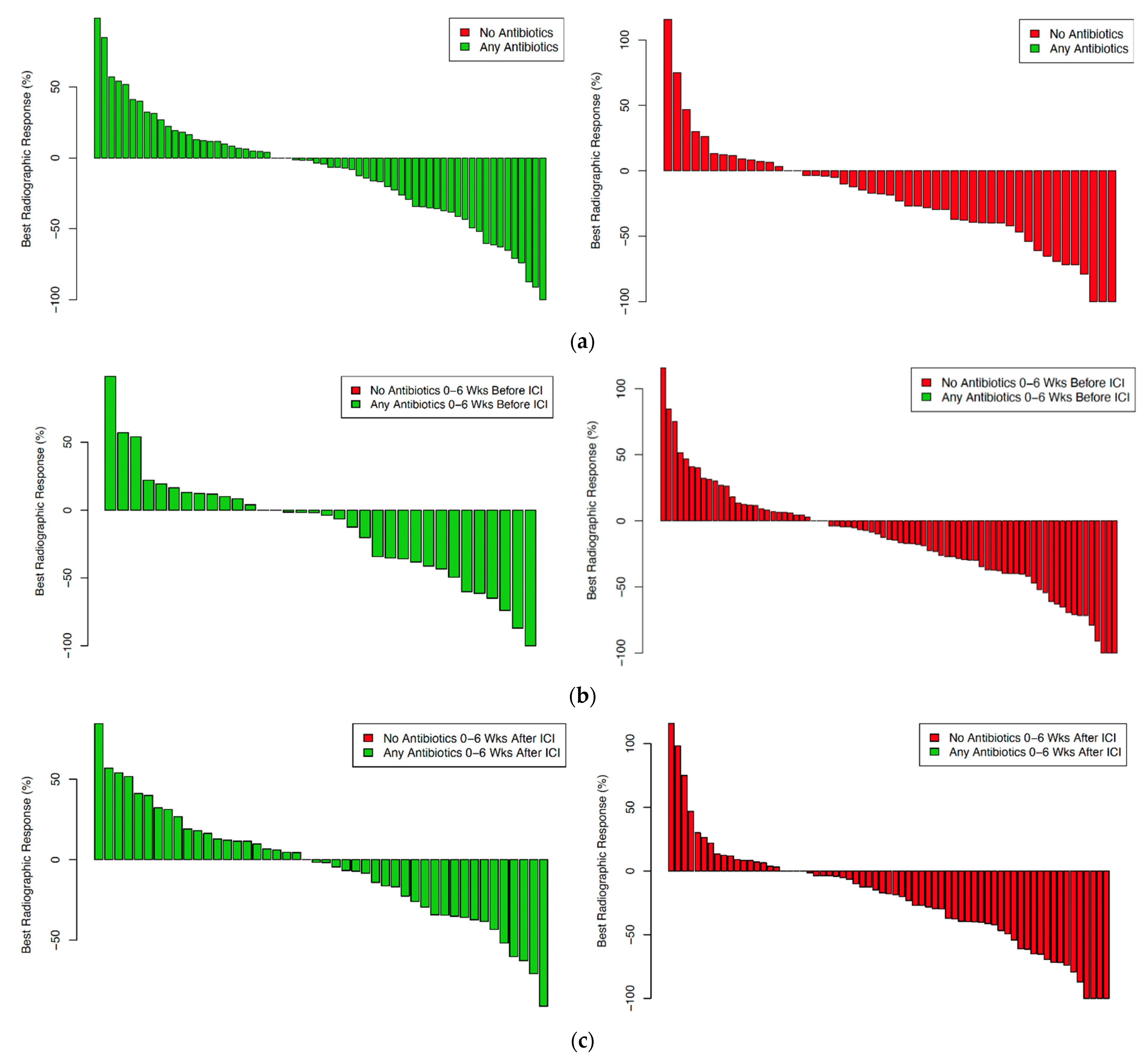
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
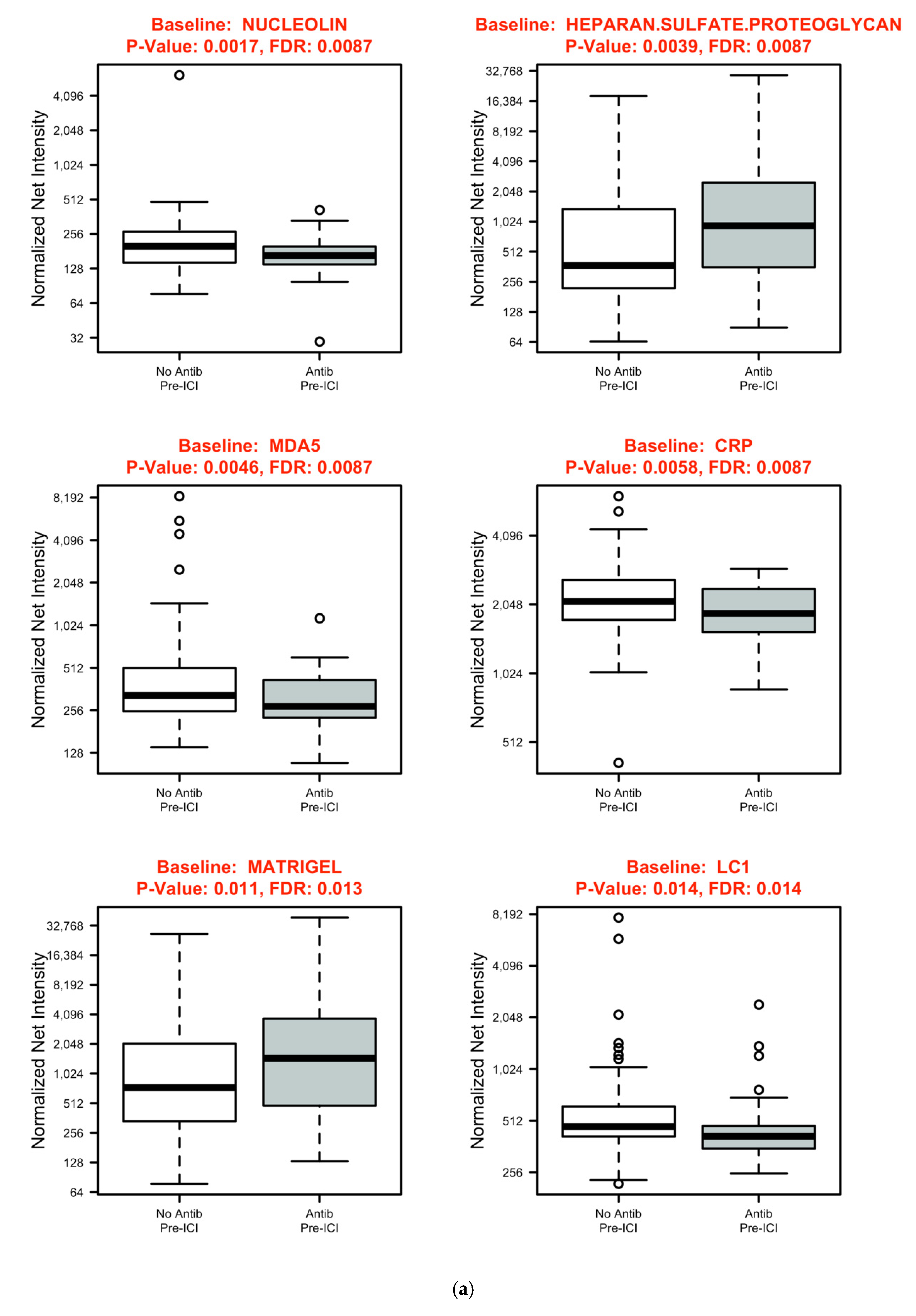
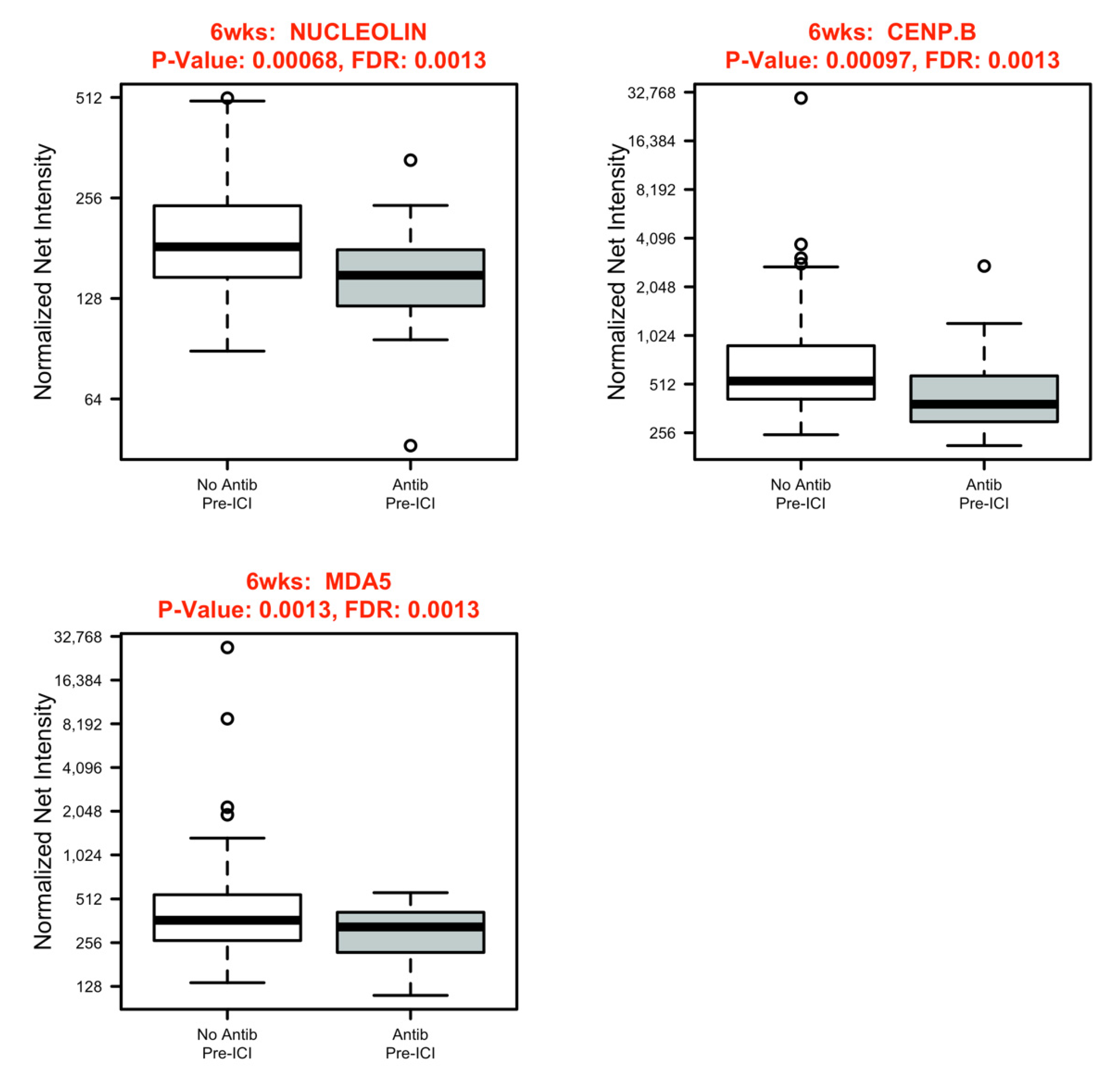
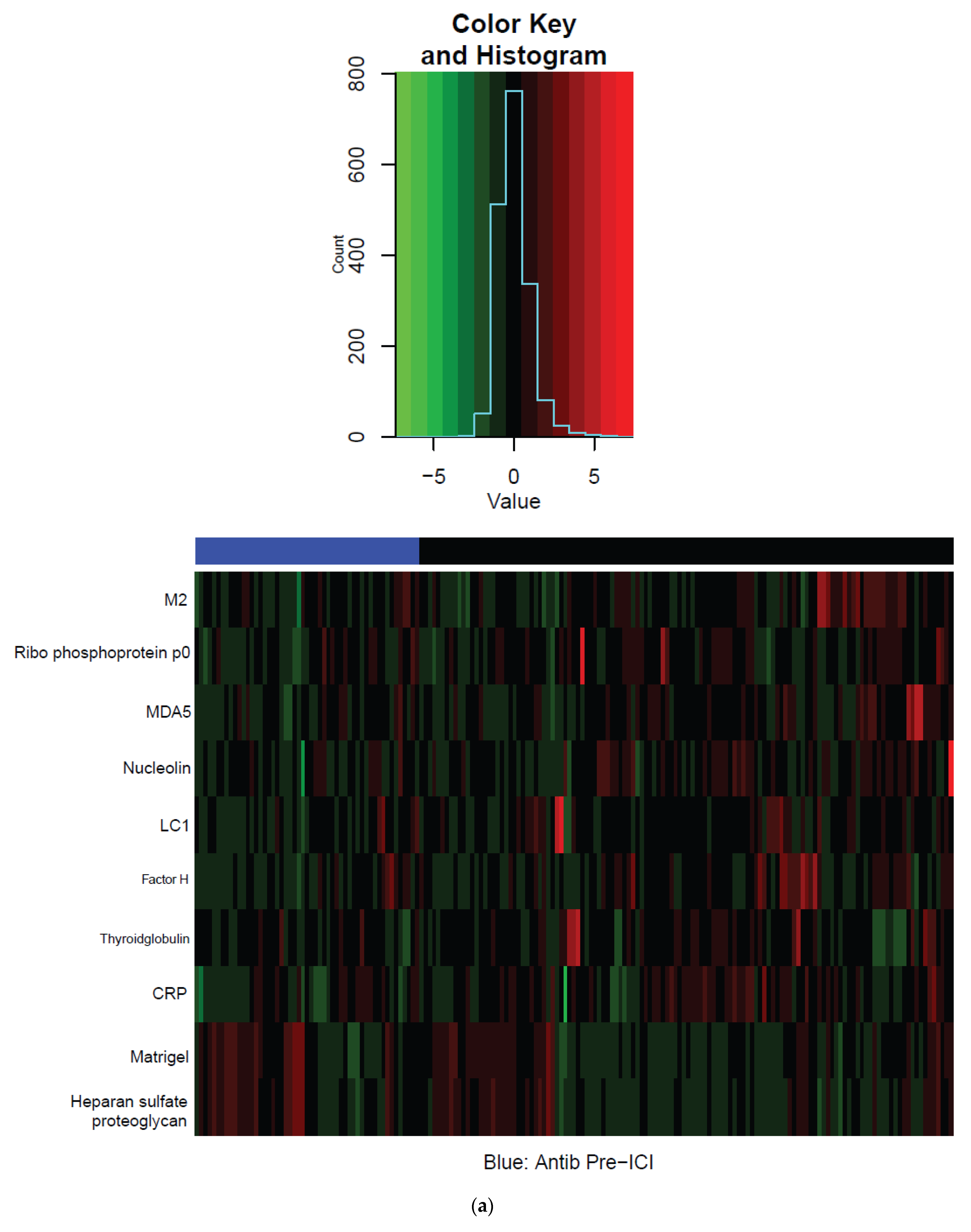
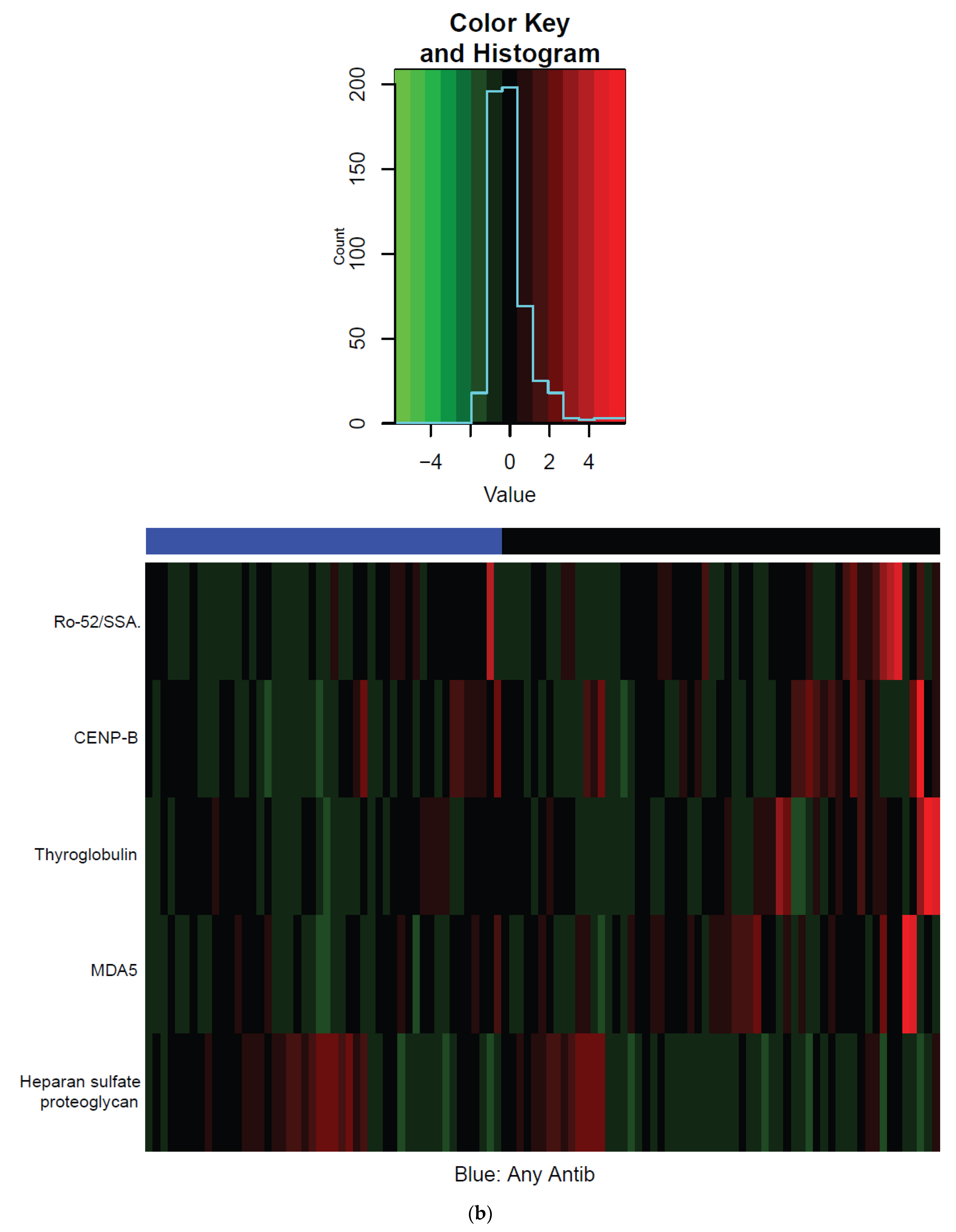
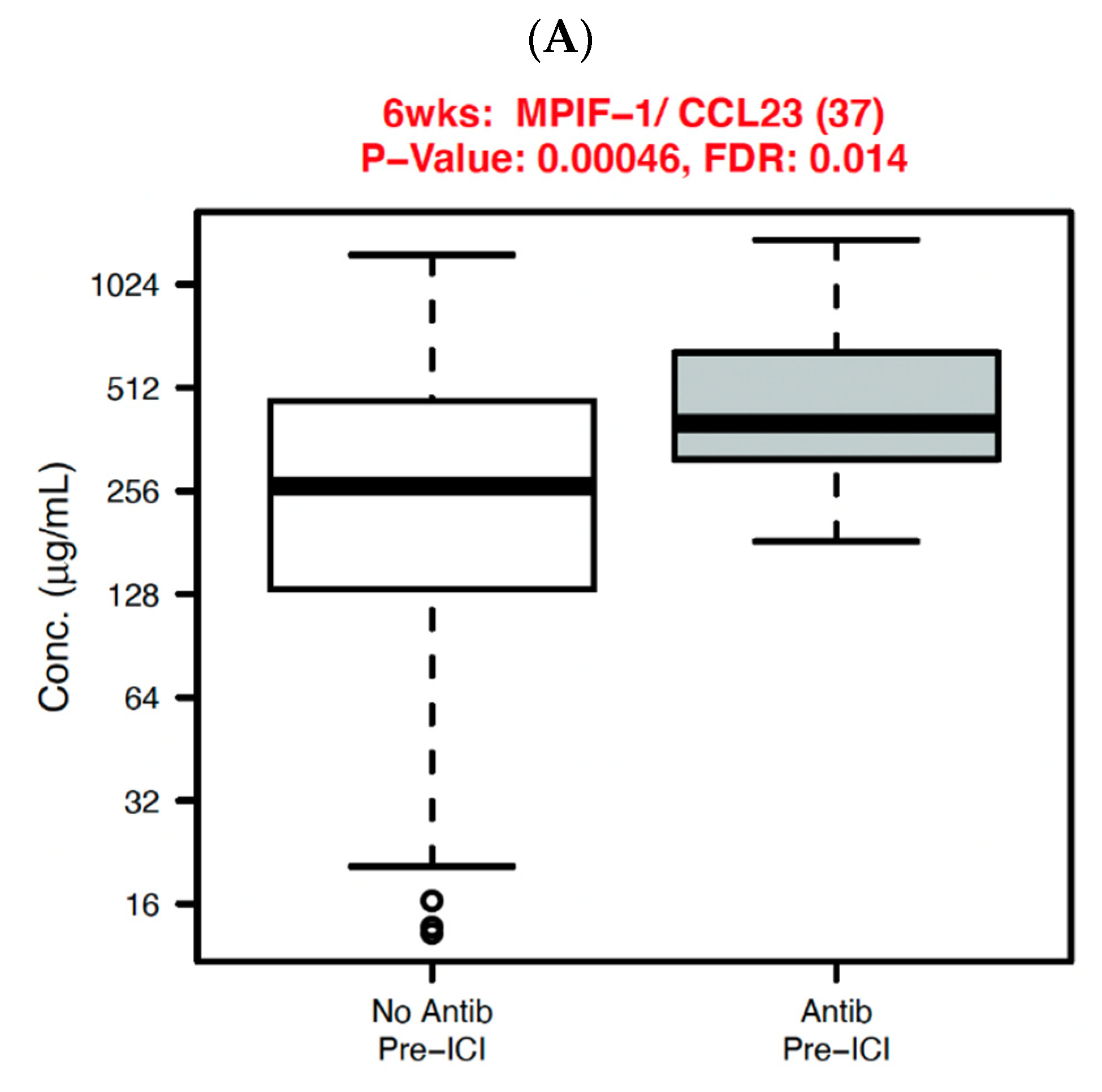
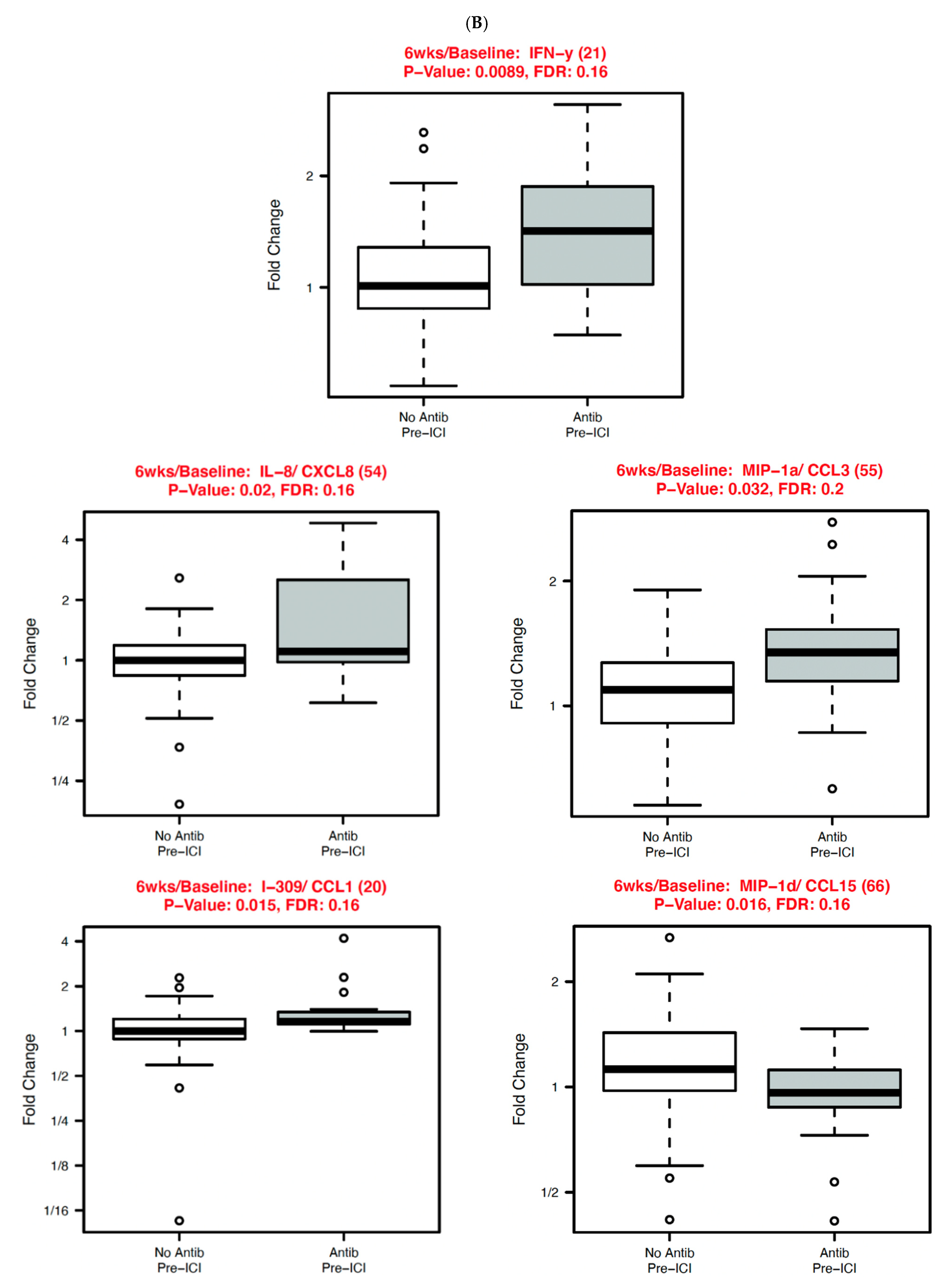
3.3. Systemic Immune Parameters
3.4. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Subset Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Topalian, S.L.; Taube, J.M.; Anders, R.A.; Pardoll, D.M. Mechanism-driven biomarkers to guide immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overman, M.J.; Lonardi, S.; Wong, K.Y.M.; Lenz, H.-J.; Gelsomino, F.; Aglietta, M.; Morse, M.A.; Van Cutsem, E.; McDermott, R.; Hill, A.; et al. Durable Clinical Benefit With Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in DNA Mismatch Repair-Deficient/Microsatellite Instability-High Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarchoan, M.; Johnson, B.A., 3rd; Lutz, E.R.; Laheru, D.A.; Jaffee, E.M. Targeting neoantigens to augment antitumour immunity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, N.A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Snyder, A.; Kvistborg, P.; Makarov, V.; Havel, J.J.; Lee, W.; Yuan, J.; Wong, P.; Ho, T.S.; et al. Cancer immunology. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science 2015, 348, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yarchoan, M.; Hopkins, A.; Jaffee, E.M. Tumor Mutational Burden and Response Rate to PD-1 Inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2500–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holch, J.W.; Held, S.; Stintzing, S.; von Weikersthal, L.F.; Decker, T.; Kiani, A.; Kaiser, F.; Heintges, T.; Kahl, C.; Kullmann, F.; et al. Relation of cetuximab-induced skin toxicity and early tumor shrinkage in metastatic colorectal cancer patients: Results of the randomized phase 3 trial FIRE-3 (AIO KRK0306). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weide, B.; Martens, A.; Hassel, J.C.; Berking, C.; Postow, M.A.; Bisschop, K.; Simeone, E.; Mangana, J.; Schilling, B.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; et al. Baseline Biomarkers for Outcome of Melanoma Patients Treated with Pembrolizumab. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5487–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krieg, C.; Nowicka, M.; Guglietta, S.; Schindler, S.; Hartmann, F.J.; Weber, L.M.; Dummer, R.; Robinson, M.D.; Levesque, M.P.; Becher, B. High-dimensional single-cell analysis predicts response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, K.C.; Liu, L.F.; Gupta, V.; Madireddi, S.; Keerthivasan, S.; Li, C.; Rishipathak, D.; Williams, P.; Kadel, E.E., 3rd; Koeppen, H.; et al. High systemic and tumor-associated IL-8 correlates with reduced clinical benefit of PD-L1 blockade. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moel, E.C.; Rozeman, E.A.; Kapiteijn, E.H.; Verdegaal, E.M.E.; Grummels, A.; Bakker, J.A.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Haanen, J.B.; Toes, R.E.M.; van der Woude, D. Autoantibody Development under Treatment with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalper, K.A.; Carleton, M.; Zhou, M.; Chen, T.; Feng, Y.; Huang, S.P.; Walsh, A.M.; Baxi, V.; Pandya, D.; Baradet, T.; et al. Elevated serum interleukin-8 is associated with enhanced intratumor neutrophils and reduced clinical benefit of immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowell, D.; Krishna, C.; Pierini, F.; Makarov, V.; Rizvi, N.A.; Kuo, F.; Morris, L.G.T.; Riaz, N.; Lenz, T.L.; Chan, T.A. Evolutionary divergence of HLA class I genotype impacts efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbour, K.C.; Mezquita, L.; Long, N.; Rizvi, H.; Auclin, E.; Ni, A.; Martinez-Bernal, G.; Ferrara, R.; Lai, W.V.; Hendriks, L.E.L.; et al. Impact of Baseline Steroids on Efficacy of Programmed Cell Death-1 and Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Blockade in Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2872–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciuti, B.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Adeni, A.; Sholl, L.M.; Nishino, M.; Awad, M.M. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Outcomes for Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Receiving Baseline Corticosteroids for Palliative Versus Nonpalliative Indications. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, W.J.; Longo, D.L. The Surprisingly Positive Association Between Obesity and Cancer Immunotherapy Efficacy. JAMA 2019, 321, 1247–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Aguilar, E.G.; Luna, J.I.; Dunai, C.; Khuat, L.T.; Le, C.T.; Mirsoian, A.; Minnar, C.M.; Stoffel, K.M.; Sturgill, I.R.; et al. Paradoxical effects of obesity on T cell function during tumor progression and PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsoian, A.; Bouchlaka, M.N.; Sckisel, G.D.; Chen, M.; Pai, C.C.; Maverakis, E.; Spencer, R.G.; Fishbein, K.W.; Siddiqui, S.; Monjazeb, A.M.; et al. Adiposity induces lethal cytokine storm after systemic administration of stimulatory immunotherapy regimens in aged mice. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 2373–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, G.S.; Waikar, S.S.; Johnson, A.E.W.; Buchbinder, E.I.; Haq, R.; Hodi, F.S.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Ott, P.A. Complex inter-relationship of body mass index, gender and serum creatinine on survival: Exploring the obesity paradox in melanoma patients treated with checkpoint inhibition. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, M.; von Itzstein, M.S.; Sheffield, T.; Khan, S.; Fattah, F.; Park, J.Y.; Popat, V.; Saltarski, J.M.; Gloria-McCutchen, Y.; Hsiehchen, D.; et al. Association between body mass index, dosing strategy, and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocariz-Diez, M.; Cruellas, M.; Gascon, M.; Lastra, R.; Martinez-Lostao, L.; Ramirez-Labrada, A.; Pano, J.R.; Sesma, A.; Torres, I.; Yubero, A.; et al. Microbiota and Lung Cancer. Opportunities and Challenges for Improving Immunotherapy Efficacy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 568939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkrief, A.; El Raichani, L.; Richard, C.; Messaoudene, M.; Belkaid, W.; Malo, J.; Belanger, K.; Miller, W.; Jamal, R.; Letarte, N.; et al. Antibiotics are associated with decreased progression-free survival of advanced melanoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1568812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinato, D.J.; Howlett, S.; Ottaviani, D.; Urus, H.; Patel, A.; Mineo, T.; Brock, C.; Power, D.; Hatcher, O.; Falconer, A.; et al. Association of Prior Antibiotic Treatment With Survival and Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Patients With Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1774–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Spencer, C.N.; Nezi, L.; Reuben, A.; Andrews, M.C.; Karpinets, T.V.; Prieto, P.A.; Vicente, D.; Hoffman, K.; Wei, S.C.; et al. Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science 2018, 359, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matson, V.; Fessler, J.; Bao, R.; Chongsuwat, T.; Zha, Y.; Alegre, M.L.; Luke, J.J.; Gajewski, T.F. The commensal microbiome is associated with anti-PD-1 efficacy in metastatic melanoma patients. Science 2018, 359, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derosa, L.; Hellmann, M.D.; Spaziano, M.; Halpenny, D.; Fidelle, M.; Rizvi, H.; Long, N.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Arbour, K.C.; Chaft, J.E.; et al. Negative association of antibiotics on clinical activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced renal cell and non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zheng, P.; Gao, L.; Li, H.; Tao, P.; Wang, D.; Ding, F.; Shi, Q.; Chen, H. Effects of Antibiotic Use on Outcomes in Cancer Patients Treated Using Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Immunother. 2021, 44, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortellini, A.; Di Maio, M.; Nigro, O.; Leonetti, A.; Cortinovis, D.L.; Aerts, J.G.; Guaitoli, G.; Barbieri, F.; Giusti, R.; Ferrara, M.G.; et al. Differential influence of antibiotic therapy and other medications on oncological outcomes of patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with first-line pembrolizumab versus cytotoxic chemotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.A.; Shaw, H.M.; Bataille, V.; Nathan, P.; Spector, T.D. Role of the gut microbiome for cancer patients receiving immunotherapy: Dietary and treatment implications. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 138, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.; Buerger, M.; Stallmach, A.; Bruns, T. Effects of Antibiotics on Gut Microbiota. Dig. Dis. 2016, 34, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruch, E.N.; Youngster, I.; Ben-Betzalel, G.; Ortenberg, R.; Lahat, A.; Katz, L.; Adler, K.; Dick-Necula, D.; Raskin, S.; Bloch, N.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplant promotes response in immunotherapy-refractory melanoma patients. Science 2021, 371, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davar, D.; Dzutsev, A.K.; McCulloch, J.A.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Chauvin, J.M.; Morrison, R.M.; Deblasio, R.N.; Menna, C.; Ding, Q.; Pagliano, O.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplant overcomes resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in melanoma patients. Science 2021, 371, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinsley, N.; Zhou, C.; Tan, G.; Rack, S.; Lorigan, P.; Blackhall, F.; Krebs, M.; Carter, L.; Thistlethwaite, F.; Graham, D.; et al. Cumulative Antibiotic Use Significantly Decreases Efficacy of Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Oncologist 2020, 25, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huemer, F.; Rinnerthaler, G.; Westphal, T.; Hackl, H.; Hutarew, G.; Gampenrieder, S.P.; Weiss, L.; Greil, R. Impact of antibiotic treatment on immune-checkpoint blockade efficacy in advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16512–16520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, B.E.; Routy, B.; Nagrial, A.; Chin, V.T. The effect of antibiotics on clinical outcomes in immune-checkpoint blockade: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Khan, S.A.; Luo, X.; Fattah, F.J.; Saltarski, J.; Gloria-McCutchen, Y.; Lu, R.; Xie, Y.; Li, Q.; Wakeland, E.; et al. Immune dysregulation in cancer patients developing immune-related adverse events. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, W.E.; Li, C.; Rabinovic, A. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics 2007, 8, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Itzstein, M.S.; Khan, S.; Popat, V.; Lu, R.; Khan, S.A.; Fattah, F.J.; Park, J.Y.; Bermas, B.L.; Karp, D.R.; Ahmed, M.; et al. Statin Intolerance, Anti-HMGCR Antibodies, and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Myositis: A "Two-Hit" Autoimmune Toxicity or Clinical Predisposition? Oncologist 2020, 25, e1242–e1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; von Itzstein, M.S.; Lu, R.; Bermas, B.L.; Karp, D.R.; Khan, S.A.; Fattah, F.J.; Park, J.Y.; Saltarski, J.M.; Gloria-McCutchen, Y.; et al. Late-Onset Immunotherapy Toxicity and Delayed Autoantibody Changes: Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Raynaud’s-Like Phenomenon. Oncologist 2020, 25, e753–e757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.Z.; Zhou, J.; Wandstrat, A.E.; Carr-Johnson, F.; Branch, V.; Karp, D.R.; Mohan, C.; Wakeland, E.K.; Olsen, N.J. Protein array autoantibody profiles for insights into systemic lupus erythematosus and incomplete lupus syndromes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 147, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandstrat, A.E.; Carr-Johnson, F.; Branch, V.; Gray, H.; Fairhurst, A.M.; Reimold, A.; Karp, D.; Wakeland, E.K.; Olsen, N.J. Autoantibody profiling to identify individuals at risk for systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Autoimmun. 2006, 27, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, W.; von Heydebreck, A.; Sultmann, H.; Poustka, A.; Vingron, M. Variance stabilization applied to microarray data calibration and to the quantification of differential expression. Bioinformatics 2002, 18 (Suppl. 1), S96–S104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippitz, B.E. Cytokine patterns in patients with cancer: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e218–e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, T.M.; Sandoval, D.R.; Spliid, C.B.; Pihl, J.; Perrett, H.R.; Painter, C.D.; Narayanan, A.; Majowicz, S.A.; Kwong, E.M.; McVicar, R.N.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Depends on Cellular Heparan Sulfate and ACE2. Cell 2020, 183, 1043–1057.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stikbakke, E.; Richardsen, E.; Knutsen, T.; Wilsgaard, T.; Giovannucci, E.L.; McTiernan, A.; Eggen, A.E.; Haugnes, H.S.; Thune, I. Inflammatory serum markers and risk and severity of prostate cancer: The PROCA-life study. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tayyari, F.; Marchant, D.; Moraes, T.J.; Duan, W.; Mastrangelo, P.; Hegele, R.G. Identification of nucleolin as a cellular receptor for human respiratory syncytial virus. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Kato, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Yoneyama, M.; Sato, S.; Matsushita, K.; Tsujimura, T.; Fujita, T.; Akira, S.; Takeuchi, O. LGP2 is a positive regulator of RIG-I- and MDA5-mediated antiviral responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junior, A.G.D.; Sampaio, N.G.; Rehwinkel, J. A Balancing Act: MDA5 in Antiviral Immunity and Autoinflammation. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, J.C.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Samedy, L.A.; Werner, J.; Owoyemi, K.; Danoff, S.K.; Christopher-Stine, L. Anti-melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5-associated dermatomyositis: Expanding the clinical spectrum. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, K.; Hoch, S.; Dima, C.; Varga, J.; Teodorescu, M. Circulating anticentromere CENP-A and CENP-B antibodies in patients with diffuse and limited systemic sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, V.P.; Kreider, B.L.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Leung, K.; Salcedo, T.; Nardelli, B.; Pippalla, V.; Gentz, S.; Thotakura, R.; et al. Molecular and functional characterization of two novel human C-C chemokines as inhibitors of two distinct classes of myeloid progenitors. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baggiolini, M.; Walz, A.; Kunkel, S.L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, R.I.; Castillo, M.D.; Litzinger, M.; Hamilton, D.H.; Palena, C. IL-8 signaling plays a critical role in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5296–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menten, P.; Wuyts, A.; Van Damme, J. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002, 13, 455–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernberg, C.; Lofmark, S.; Edlund, C.; Jansson, J.K. Long-term ecological impacts of antibiotic administration on the human intestinal microbiota. ISME J. 2007, 1, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohsen, S.; Dickinson, J.A.; Somayaji, R. Update on the adverse effects of antimicrobial therapies in community practice. Can. Fam. Physician 2020, 66, 651–659. [Google Scholar]
- Tamma, P.D.; Avdic, E.; Li, D.X.; Dzintars, K.; Cosgrove, S.E. Association of Adverse Events With Antibiotic Use in Hospitalized Patients. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shekhar, S.; Petersen, F.C. The Dark Side of Antibiotics: Adverse Effects on the Infant Immune Defense Against Infection. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 544460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.M.; Hicks, L.A.; Qaseem, A.; High Value Care Task Force of the American College of Physicians and for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Appropriate Antibiotic Use for Acute Respiratory Tract Infection in Adults: Advice for High-Value Care From the American College of Physicians and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 164, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burdet, C.; Nguyen, T.T.; Duval, X.; Ferreira, S.; Andremont, A.; Guedj, J.; Mentre, F.; Group, D.C.-S. Impact of Antibiotic Gut Exposure on the Temporal Changes in Microbiome Diversity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00820-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Characteristic | Total | Antibiotics | No Antibiotics | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (Range) or N (%) | Median (Range) or N (%) | Median (Range) or N (%) | ||
| Age (years) | 68 (29–2) | 67 (29–86) | 68 (35–92) | 0.27 |
| Gender | 0.8 | |||
| Female | 98 (39) | 54 (40) | 44 (38) | |
| Male | 153 (61) | 81 (60) | 72 (62) | |
| Race-ethnicity | 0.23 | |||
| Non-Hispanic white | 193 (77) | 108 (80) | 85 (73) | |
| Other | 58 (23) | 27 (20) | 31 (27) | |
| Cancer type | 0.26 | |||
| NSCLC | 133 (53) | 73 (54) | 60 (52) | |
| Melanoma | 47 (19) | 29 (21) | 18 (16) | |
| Other | 71 (28) | 33 (24) | 38 (33) | |
| BMI | 0.61 | |||
| <25 | 103 (41) | 53 (39) | 50 (43) | |
| ≥25 | 147 (59) | 81 (60) | 66 (57) | |
| Receipt of anti-CTLA4 | 0.33 | |||
| No | 221 (88) | 116 (86) | 105 (91) | |
| Yes | 30 (12) | 19 (14) | 11 (9) | |
| ECOG Performance status | 0.11 | |||
| 0–1 | 185 (74) | 95 (70) | 90 (78) | |
| 2–4 | 28 (11) | 19 (14) | 9 (8) | |
| Missing | 38 (15) | 21 (16) | 17 (14) | |
| Cancer Stage | 0.29 | |||
| I/II | 13 (5) | 6 (4) | 7 (6) | |
| III | 50 (20) | 32 (24) | 18 (16) | |
| IV | 161 (64) | 84 (62) | 77 (66) | |
| Missing | 27 (11) | 13 (10) | 14 (12) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
von Itzstein, M.S.; Gonugunta, A.S.; Sheffield, T.; Homsi, J.; Dowell, J.E.; Koh, A.Y.; Raj, P.; Fattah, F.; Wang, Y.; Basava, V.S.; et al. Association between Antibiotic Exposure and Systemic Immune Parameters in Cancer Patients Receiving Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051327
von Itzstein MS, Gonugunta AS, Sheffield T, Homsi J, Dowell JE, Koh AY, Raj P, Fattah F, Wang Y, Basava VS, et al. Association between Antibiotic Exposure and Systemic Immune Parameters in Cancer Patients Receiving Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Cancers. 2022; 14(5):1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051327
Chicago/Turabian Stylevon Itzstein, Mitchell S., Amrit S. Gonugunta, Thomas Sheffield, Jade Homsi, Jonathan E. Dowell, Andrew Y. Koh, Prithvi Raj, Farjana Fattah, Yiqing Wang, Vijay S. Basava, and et al. 2022. "Association between Antibiotic Exposure and Systemic Immune Parameters in Cancer Patients Receiving Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy" Cancers 14, no. 5: 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051327
APA Stylevon Itzstein, M. S., Gonugunta, A. S., Sheffield, T., Homsi, J., Dowell, J. E., Koh, A. Y., Raj, P., Fattah, F., Wang, Y., Basava, V. S., Khan, S., Park, J. Y., Popat, V., Saltarski, J. M., Gloria-McCutchen, Y., Hsiehchen, D., Ostmeyer, J., Xie, Y., Li, Q.-Z., ... Gerber, D. E. (2022). Association between Antibiotic Exposure and Systemic Immune Parameters in Cancer Patients Receiving Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Cancers, 14(5), 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051327







