Impact of Progressive Site-Directed Therapy in Oligometastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer on Subsequent Treatment Response
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
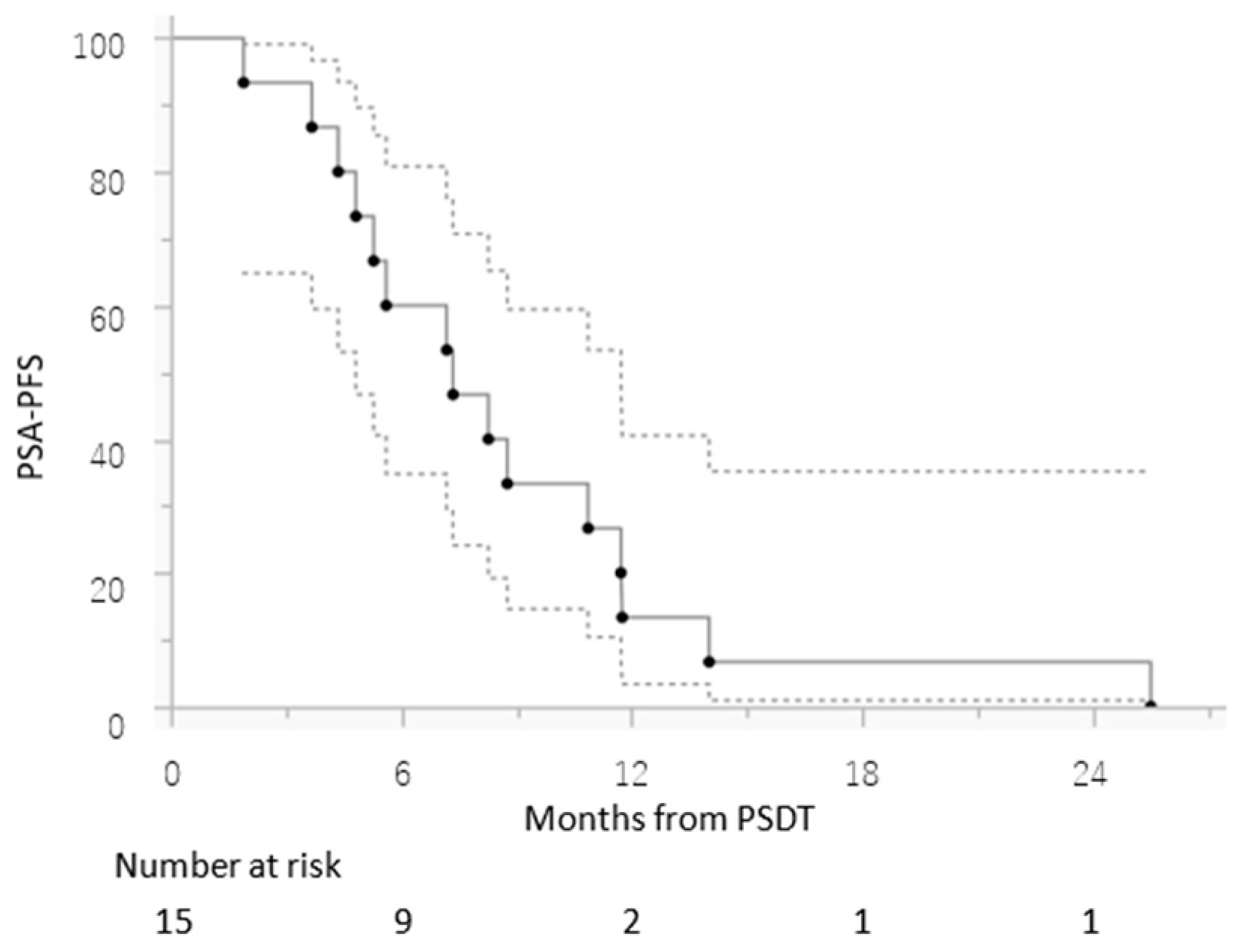
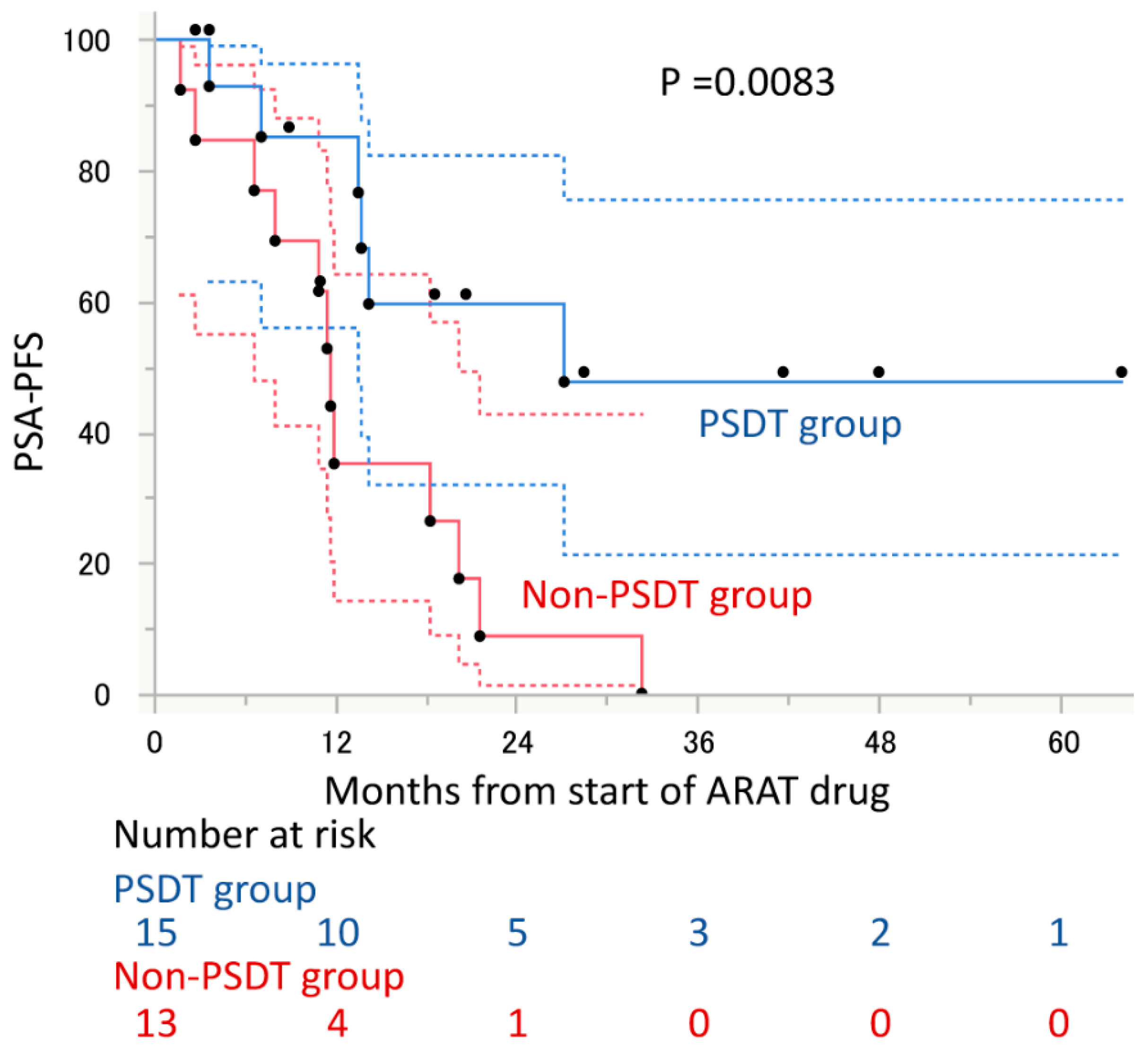
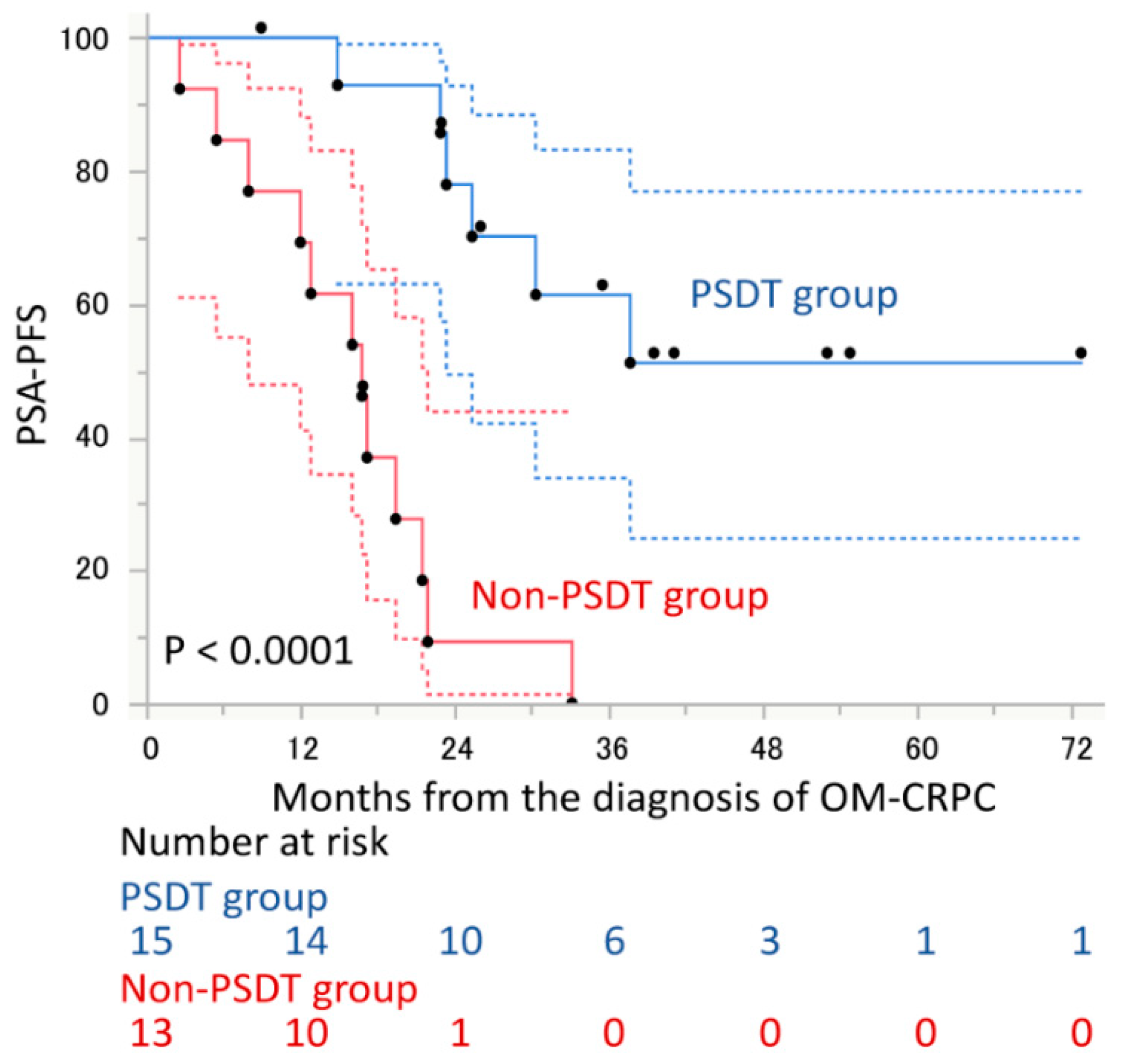
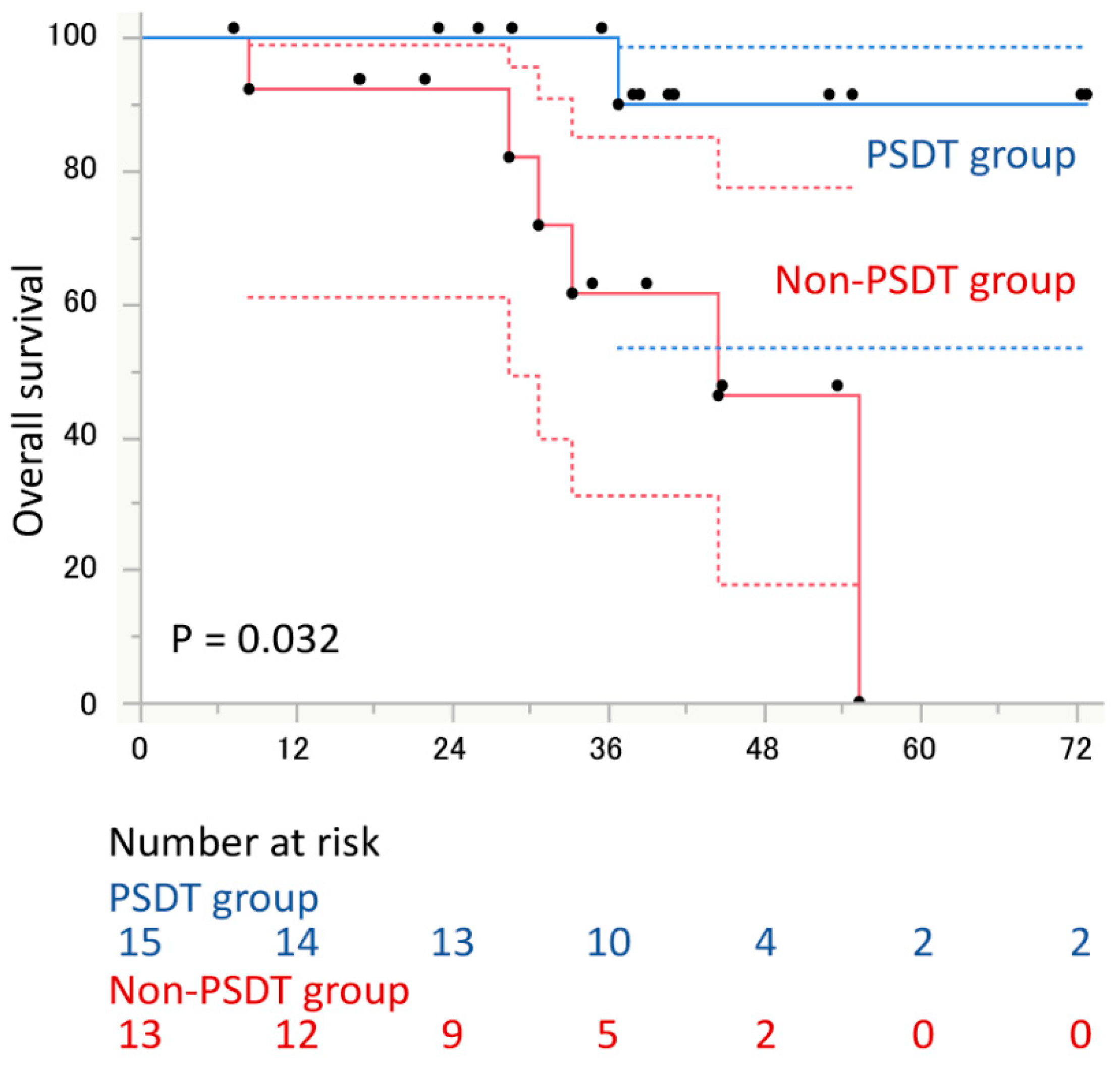
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guckenberger, M.; Lievens, Y.; Bouma, A.B.; Collette, L.; Dekker, A.; de Souza, N.M.; Dingemans, A.-M.C.; Fournier, B.; Hurkmans, C.; Lecouvet, F.E.; et al. Characterisation and classification of oligometastatic disease: A European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer consensus recommendation. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e18–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellman, S.; Weichselbaum, R.R. Oligometastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, M.T.; Biswas, T.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Lo, S.S. Oligometastases: History of a hypothesis. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 5923–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichselbaum, R.R.; Hellman, S. Oligometastases revisited. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Eito, A.; García-Cabezas, S. Oligometastatic disease, the curative challenge in radiation oncology. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 6, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ost, P.; Reynders, D.; Decaestecker, K.; Fonteyne, V.; Lumen, N.; De Bruycker, A.; Lambert, B.; Delrue, L.; Bultijnck, R.; Claeys, T.; et al. Surveillance or Metastasis-Directed Therapy for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer Recurrence: A Prospective, Randomized, Multicenter Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, R.; Shi, W.Y.; Deek, M.; Radwan, N.; Lim, S.J.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Rowe, S.P.; Ross, A.E.; Gorin, M.A.; Deville, C.; et al. Outcomes of Observation vs Stereotactic Ablative Radiation for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: The ORIOLE Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siva, S.; Bressel, M.; Murphy, D.G.; Shaw, M.; Chander, S.; Violet, J.; Tai, K.H.; Udovicich, C.; Lim, A.; Selbie, L.; et al. Stereotactic Abative Body Radiotherapy (SABR) for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: A Prospective Clinical Trial. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deek, M.P.; Van der Eecken, K.; Phillips, R.; Parikh, N.R.; Isaacsson Velho, P.; Lotan, T.L.; Kishan, A.U.; Maurer, T.; Boutros, P.C.; Hovens, C.; et al. The Mutational Landscape of Metastatic Castration-sensitive Prostate Cancer: The Spectrum Theory Revisited. Eur. Urol. 2021, 80, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deek, M.P.; Tran, P.T. Oligometastatic and Oligoprogression Disease and Local Therapies in Prostate Cancer. Cancer J. (Sudbury Mass) 2020, 26, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillessen, S.; Attard, G.; Beer, T.M.; Beltran, H.; Bjartell, A.; Bossi, A.; Briganti, A.; Bristow, R.; Chi, K.N.; Clarke, N.; et al. Management of Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer: Report of the Advanced Prostate Cancer Consensus Conference 2019. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 508–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francolini, G.; Loi, M.; Detti, B.; Desideri, I.; Mangoni, M.; Simontacchi, G.; Meattini, I.; Livi, L. Integrating stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) and systemic treatments in oligoprogressive prostate cancer: New evidence from the literature. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2021, 38, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deek, M.P.; Yu, C.; Phillips, R.; Song, D.Y.; Deville, C.; Greco, S.; De Weese, T.L.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Markowski, M.; Paller, C.; et al. Radiation Therapy in the Definitive Management of Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: The Johns Hopkins Experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deek, M.P.; Taparra, K.; Phillips, R.; Velho, P.I.; Gao, R.W.; Deville, C.; Song, D.Y.; Greco, S.; Carducci, M.; Eisenberger, M.; et al. Metastasis-directed Therapy Prolongs Efficacy of Systemic Therapy and Improves Clinical Outcomes in Oligoprogressive Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohaus, F.; Zophel, K.; Lock, S.; Wirth, M.; Kotzerke, J.; Krause, M.; Baumann, M.; Troost, E.G.; Hölscher, T. Can Local Ablative Radiotherapy Revert Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer to an Earlier Stage of Disease? Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozaki, K.; Kawai, T.; Fujimura, T.; Matsui, H.; Teshima, T.; Oshina, T.; Takahashi, A.; Sato, Y.; Yamada, D.; Azuma, T.; et al. Carbon 11-choline positron emission tomography/computed tomography and palliative local therapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 51, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triggiani, L.; Mazzola, R.; Magrini, S.M.; Ingrosso, G.; Borghetti, P.; Trippa, F.; Lancia, A.; Detti, B.; Francolini, G.; Matrone, F.; et al. Metastasis-directed stereotactic radiotherapy for oligoprogressive castration-resistant prostate cancer: A multicenter study. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 2631–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Takahara, T.; Arita, Y.; Ishii, C.; Uchida, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Toda, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Kijima, T.; Yokoyama, M.; et al. Progressive Site-Directed Therapy for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Localization of the Progressive Site as a Prognostic Factor. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Takahara, T.; Arita, Y.; Toda, K.; Yamada, I.; Tanaka, H.; Yokoyama, M.; Matsuoka, Y.; Yoshimura, R.; Fujii, Y. Genuine- and induced-oligometastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Clinical features and clinical outcomes after progressive site-directed therapy. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 53, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghen, C.; Joniau, S.; Ost, P.; Poels, K.; Everaerts, W.; Decaestecker, K.; Haustermans, K.; Devos, G.; De Meerleer, G. Progression-directed Therapy for Oligoprogression in Castration-refractory Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, S.; Takahara, T.; Yokoyama, M.; Matsuoka, Y.; Yoshimura, R.; Fujii, Y. Can progressive site-directed therapy prolong the efficacy of subsequent androgen receptor axis-targeted drugs in oligometastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer? Int. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 241–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornford, P.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fanti, S.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Gillessen, S.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part II—2020 Update: Treatment of Relapsing and Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Waseda, Y.; Takahara, T.; Ishii, C.; Ueda, R.; Kwee, T.C.; Miyahira, K.; Ishii, R.; Okuda, S.; et al. Diagnostic value of computed high b-value whole-body diffusion-weighted imaging for primary prostate cancer. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 137, 109581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwee, T.C.; Takahara, T.; Ochiai, R.; Nievelstein, R.A.; Luijten, P.R. Diffusion-weighted whole-body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): Features and potential applications in oncology. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 1937–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahara, T.; Imai, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Yasuda, S.; Nasu, S.; Van Cauteren, M. Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): Technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display. Radiat. Med. 2004, 22, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.D.; Stetz, J.; Pajak, T.F. Toxicity criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1995, 31, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizokami, A.; Namiki, M. Reconsideration of progression to CRPC during androgen deprivation therapy. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 145, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makino, T.; Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A. Undesirable Status of Prostate Cancer Cells after Intensive Inhibition of AR Signaling: Post-AR Era of CRPC Treatment. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Hoang, C.D.; Kesarwala, A.H.; Schrump, D.S.; Guha, U.; Rajan, A. Role of Local Ablative Therapy in Patients with Oligometastatic and Oligoprogressive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Yaremko, B.P.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for the Comprehensive Treatment of Oligometastatic Cancers: Long-Term Results of the SABR-COMET Phase II Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2830–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PSDT † Group (n = 15) | Non-PSDT Group (n = 13) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year), median (range) | 76 (68–87) | 77 (69–87) | 0.87 |
| PSA * at the diagnosis of OM-CRPC ¶ (ng/ml), median (range) | 4.96 (0.22–32.0) | 4.33 (0.70–26.8) | 0.84 |
| PSA-DT ‡ at the diagnosis of OM-CRPC (month), median (range) | 3.1 (1.6–7.0) | 3.8 (0.9–18.1) | 0.12 |
| No. of received treatment lines, median (range) before WB-DWI | 2 (1–4) | 2 (1–4) | 0.98 |
| Received treatment lines before the diagnosis of OM-CRPC | |||
| Surgical orchiectomy/Leuprorelin/Goserelin/Degarelix | 15 (100%) | 13 (100%) | |
| Bicalutamide | 12 (80.0%) | 11 (84.6%) | |
| Estramustine phosphate | 1 (6.7%) | 4 (30.8%) | |
| Flutamide | 1 (6.7%) | 3 (23.1%) | |
| Docetaxel | 1 (6.7%) | 1 (7.7%) | |
| History of local treatment | 11 (73.3%) | 4 (30.8%) | 0.030 |
| No. of progressive sites | 1 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 0.37 |
| Location of progressive sites | |||
| Prostate + bone | 2 (15.4%) | 3 (20.0%) | |
| Bone | 9 (69.2%) | 4 (26.7%) | |
| Prostate + lymph node | 1 (7.7%) | 2 (13.3%) | |
| Lymph node | 3 (23.1%) | 1 (6.7%) | |
| Bone + lymph node | 0 | 1 (6.7%) | |
| Lung | 0 | 1 (6.7%) | |
| Prostate + Liver + lymph node | 0 | 1 (6.7%) | |
| Received 1st ARAT § after the diagnosis of OM-CRPC | |||
| Enzalutamide | 8 (53.3%) | 9 (69.2%) | 0.32 |
| Abiraterone | 7 (46.7%) | 4 (30.8%) | |
| No. of received systemic treatment lines after the diagnosis of OM-CRPC, median (range) | 1 (1–4) | 3 (1–7) | 0.0085 |
| Received systemic treatment lines after the diagnosis of OM-CRPC | |||
| Enzalutamide | 10 (66.7%) | 11 (84.6%) | |
| Abiraterone | 8 (53.3%) | 8 (61.5%) | |
| Docetaxel | 2 (13.3%) | 9 (69.2%) | |
| Cabazitaxel | 3 (20.0%) | 4 (30.1%) | |
| Radiuim-223 | 2 (13.3%) | 3 (23.1%) | |
| Oraparib | 0 | 1 (7.7%) |
| Variable | N | Univariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Patients | HR †† (95% CI §) | p Value | |
| Age at the diagnosis of OM-CRPC # | 1.05 (0.97–1.05) | 0.24 | ||
| PSA * at the diagnosis of OM-CRPC | 1.03 (0.97–1.09) | 0.24 | ||
| PSA-DT ‡ at the diagnosis of OM-CRPC | 1.07 (0.93–1.20) | 0.27 | ||
| History of definitive therapy for prostate cancer | no vs. yes | 13/15 | 0.91 (0.36–2.41) | 0.51 |
| PSDT † | no vs. yes | 13/15 | 0.28 (0.10–0.74) | 0.010 |
| No. of received treatment lines before the diagnosis of OM-CRPC | 1.10 (0.63–1.76) | 0.76 | ||
| No. of progressive sites | 1.48 (0.75–2.72) | 0.23 | ||
| Type of ARAT † | Abiraterone vs. Enzalutamide | 1.16 (0.45–3.09) | 0.76 | |
| Variable | N | Univariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Patients | HR †† (95% CI §) | p Value | |
| Age at the diagnosis of OM-CRPC # | 1.05 (0.92–1.21) | 0.43 | ||
| PSA * at the diagnosis of OM-CRPC | 1.03 (0.94–1.11) | 0.46 | ||
| PSA-DT ‡ at the diagnosis of OM-CRPC | 1.10 (0.86–1.31) | 0.37 | ||
| History of definitive therapy for prostate cancer | no vs. yes | 13/15 | 0.42 (0.08–1.93) | 0.26 |
| PSDT † | no vs. yes | 13/15 | 0.11 (0.01–0.67) | 0.014 |
| No. of received treatment lines before the diagnosis of OM-CRPC | 1.12 (0.47–2.46) | 0.79 | ||
| No. of progressive sites | 2.15 (0.69–6.46) | 0.16 | ||
| Type of ARAT † | Abiraterone vs. Enzalutamide | 0.73 (0.13–3.93) | 0.69 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshida, S.; Takahara, T.; Arita, Y.; Toda, K.; Kimura, K.; Tanaka, H.; Yokoyama, M.; Matsuoka, Y.; Yoshimura, R.; Fujii, Y. Impact of Progressive Site-Directed Therapy in Oligometastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer on Subsequent Treatment Response. Cancers 2022, 14, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030567
Yoshida S, Takahara T, Arita Y, Toda K, Kimura K, Tanaka H, Yokoyama M, Matsuoka Y, Yoshimura R, Fujii Y. Impact of Progressive Site-Directed Therapy in Oligometastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer on Subsequent Treatment Response. Cancers. 2022; 14(3):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030567
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshida, Soichiro, Taro Takahara, Yuki Arita, Kazuma Toda, Koichiro Kimura, Hajime Tanaka, Minato Yokoyama, Yoh Matsuoka, Ryoichi Yoshimura, and Yasuhisa Fujii. 2022. "Impact of Progressive Site-Directed Therapy in Oligometastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer on Subsequent Treatment Response" Cancers 14, no. 3: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030567
APA StyleYoshida, S., Takahara, T., Arita, Y., Toda, K., Kimura, K., Tanaka, H., Yokoyama, M., Matsuoka, Y., Yoshimura, R., & Fujii, Y. (2022). Impact of Progressive Site-Directed Therapy in Oligometastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer on Subsequent Treatment Response. Cancers, 14(3), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030567







