Regression of Human Breast Carcinoma in Nude Mice after Adsflt Gene Therapy Is Mediated by Tumor Vascular Endothelial Cell Apoptosis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
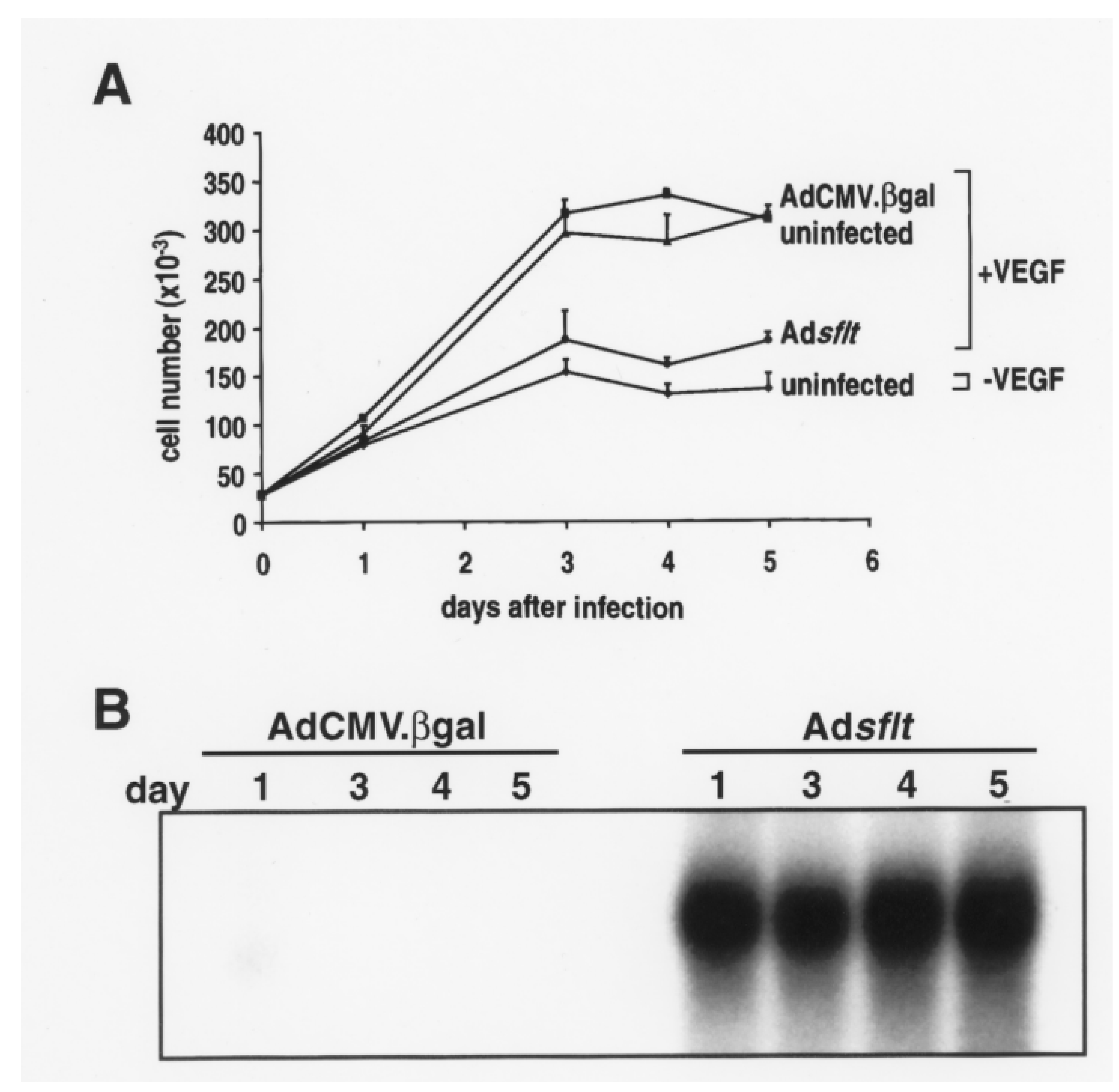
2.1. sFLT-1 Overexpression Inhibits VEGF-Induced Endothelial Cell Proliferation In Vitro
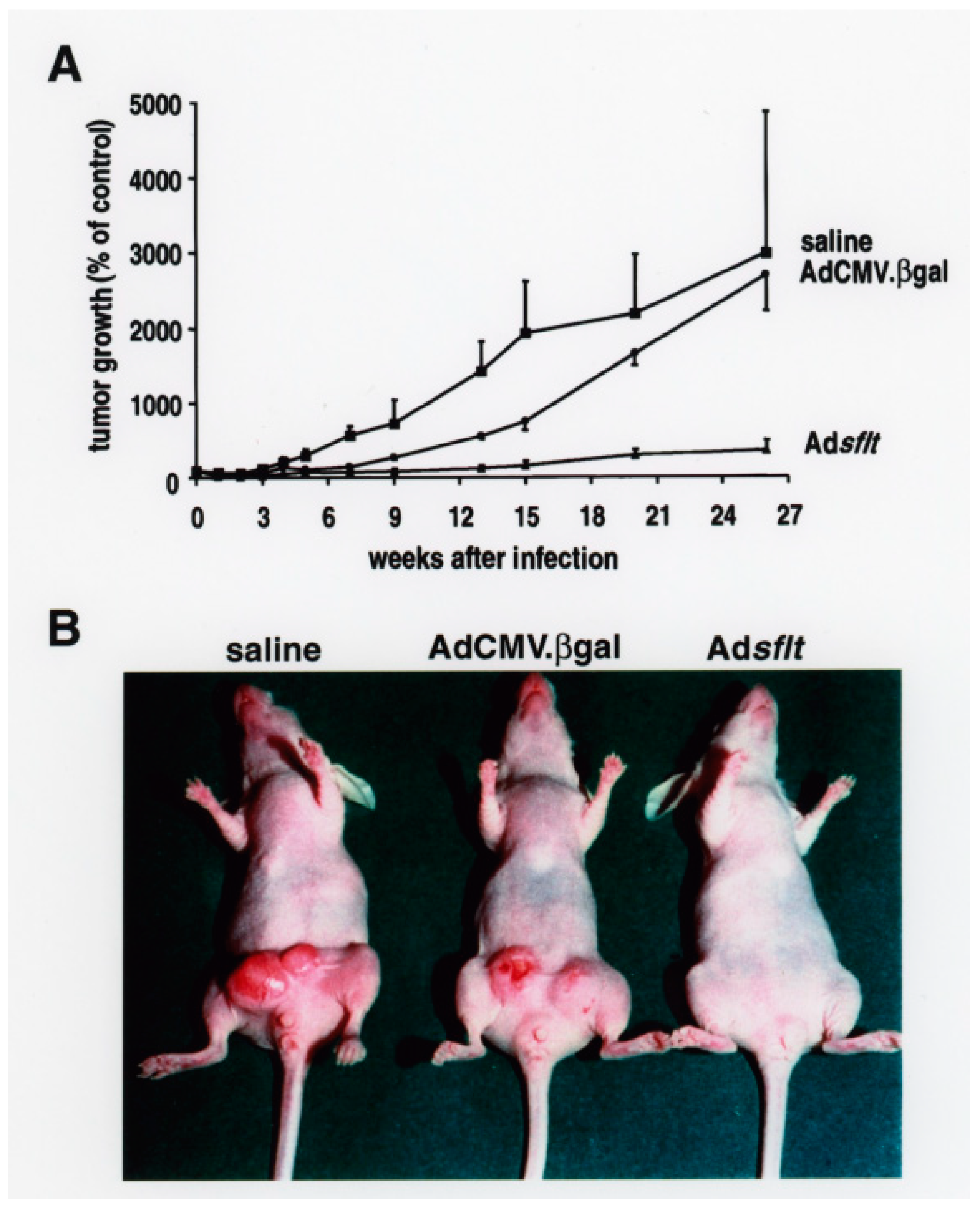
2.2. Adsflt Inhibits Tumor Growth In Vivo and Induces Long-Term Tumor Regression
2.3. Expression of sFLT-1 in Adsflt-Treated Tumors
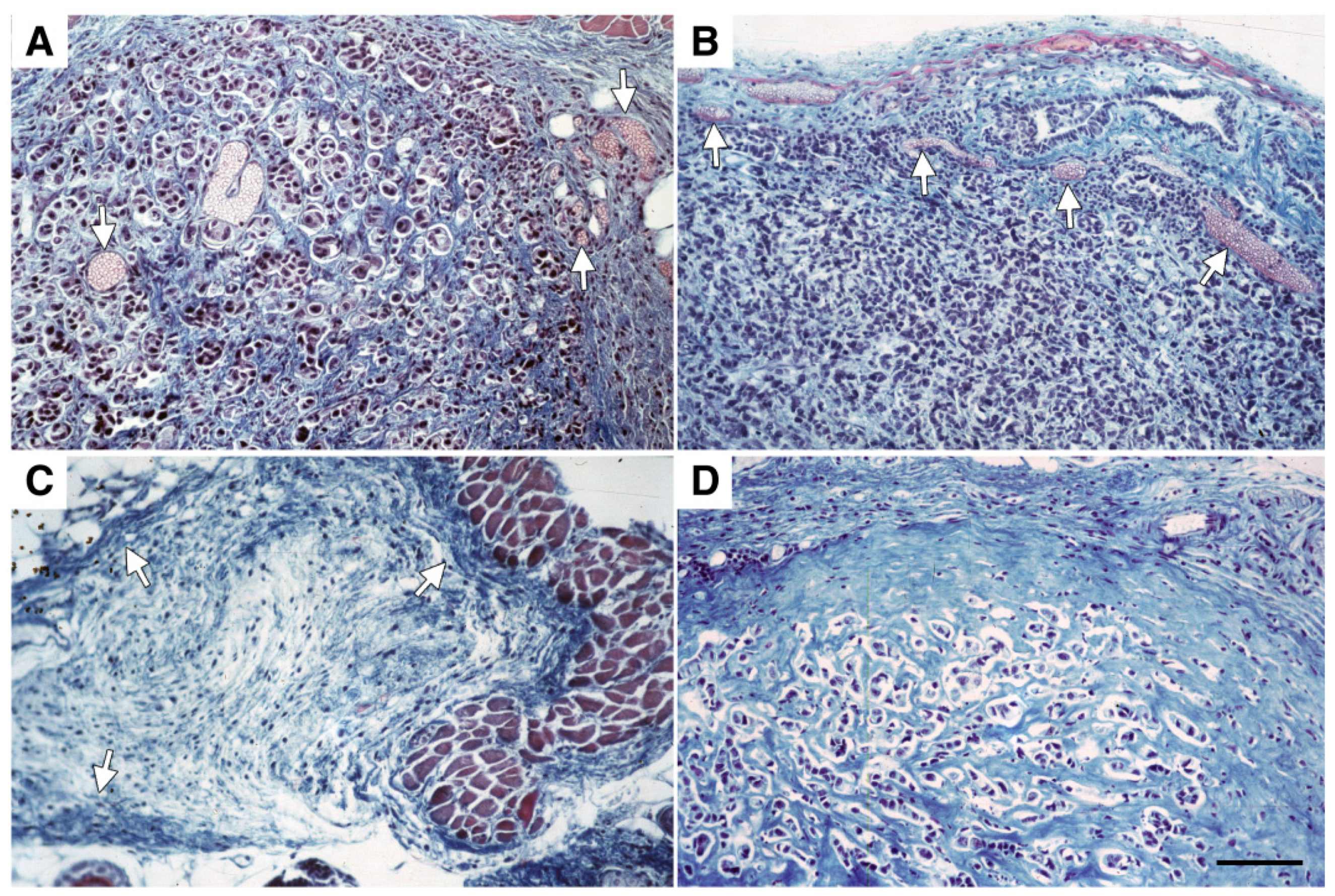
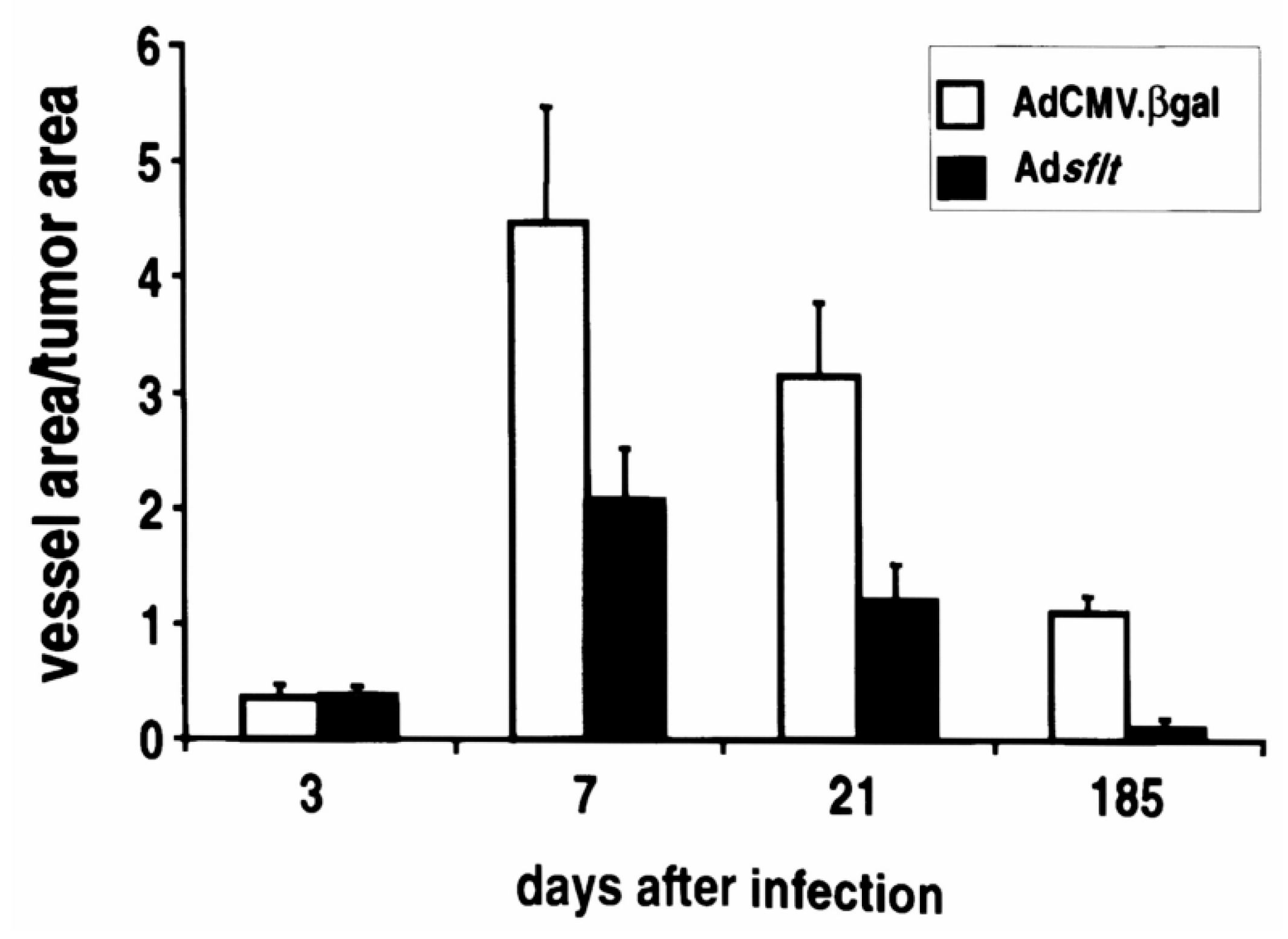
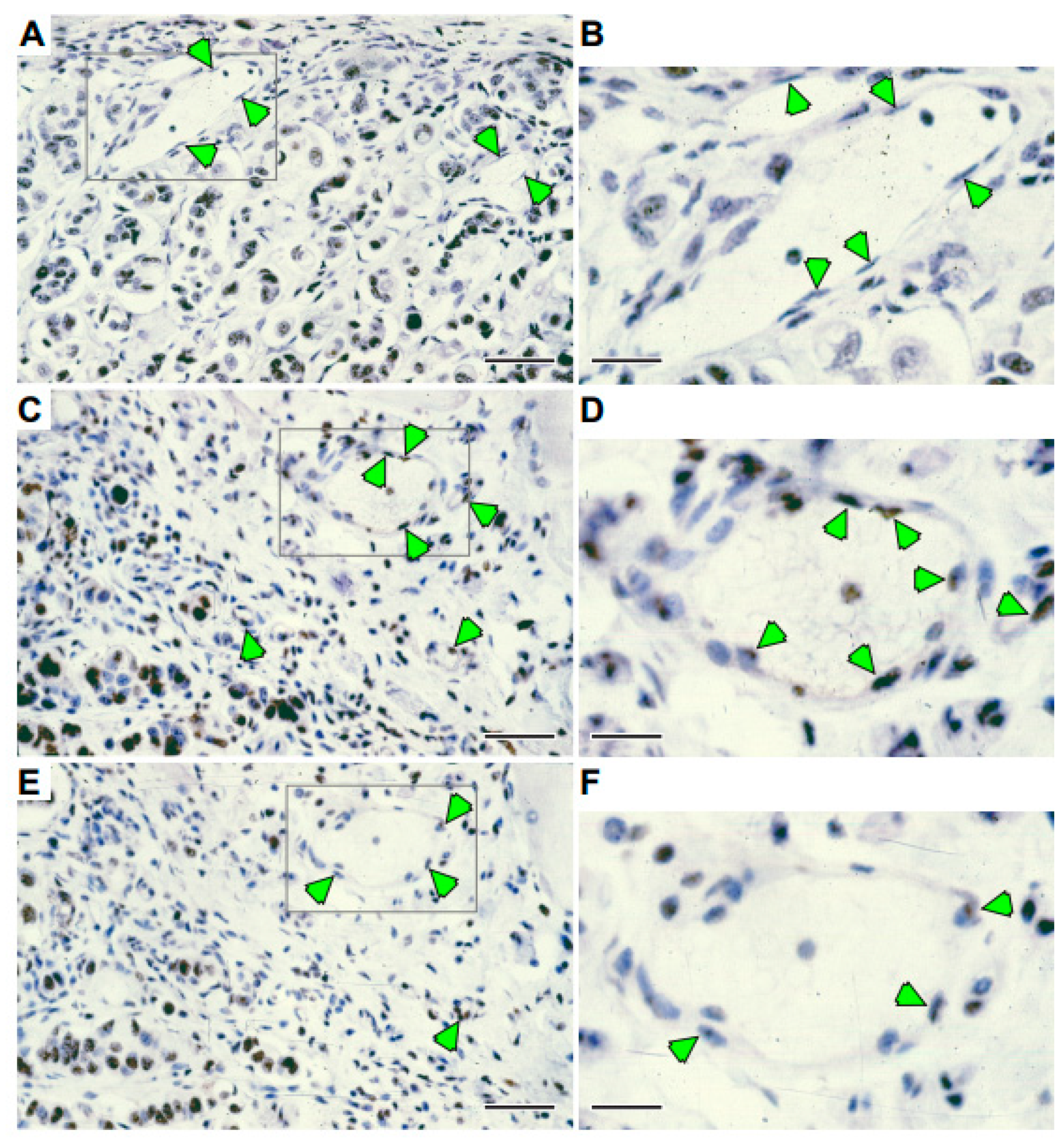
2.4. Adsflt Induces Vascular Regression In Vivo and Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis
2.5. A Single Injection of Adsflt Induces Endothelial Cell Apoptosis
2.6. Serum Levels of sFLT-1
2.7. Regional Overexpression of sFLT-1 Does Not Inhibit Neovascularization during Wound Repair
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Adenoviral Vectors
4.3. Proliferation Assay
4.4. Animal Studies
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Northern Blot Analysis
4.7. Quantification of Tumor and Blood Vessel Areas
4.8. sFLT-1-Specific ELISA
4.9. Statistical Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ad | adenovirus |
| CMV | cytomegalovirus |
| sFLT-1 | soluble FLT-1 |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Folkman, J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.L.; Zhang, H.; Moghaddam, A.; Fox, S.; Scott, P.; Pattison, A.; Gatter, K.; Stratford, I.; Bicknell, R. Breast cancer angiogenesis—New approaches to therapy via antiangiogenesis, hypoxic activated drugs, and vascular targeting. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1996, 38, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senger, D.R.; Van de Water, L.; Brown, L.F.; Nagy, J.A.; Yeo, K.T.; Yeo, T.K.; Berse, B.; Jackman, R.W.; Dvorak, A.M.; Dvorak, H.F. Vascular permeability factor (VPF, VEGF) in tumor biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1993, 12, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, M. Role of VEGF-flt receptor system in normal and tumor angiogenesis. Adv. Cancer Res. 1995, 67, 281–316. [Google Scholar]
- Barleon, B.; Siemeister, G.; Martiny-Baron, G.; Weindel, K.; Herzog, C.; Marmé, D. Vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulates its receptor fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (FLT-1) and a soluble variant of FLT-1 in human vascular endothelial cells. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 5421–5425. [Google Scholar]
- Millauer, B.; Wizigmann-Voos, S.; Schnurch, H.; Martinez, R.; Moller, N.P.; Risau, W.; Ullrich, A. High affinity VEGF binding and developmental expression suggest Flk-1 as a major regulator of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Cell 1993, 72, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terman, B.I.; Dougher-Vermazen, M.; Carrion, M.E.; Dimitrov, D.; Armellino, D.C.; Gospodarowicz, D.; Bohlen, P. Identification of the KDR tyrosine kinase as a receptor for vascular endothelial cell growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 187, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, C.; Escobedo, J.A.; Ueno, H.; Houck, K.; Ferrara, N.; Williams, L.T. The fms-like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Science 1992, 255, 989–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yamane, A.; Ikeda, T.; Tojo, A.; Matsushime, H.; Sato, M. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a novel human receptor-type tyrosine kinase gene (flt) closely related to the fms family. Oncogene 1990, 4, 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, G.H.; Rossant, J.; Gertsenstein, M.; Breitman, M.L. Role of the Flt-1 receptor tyrosine kinase in regulating the assembly of vascular endothelium. Nature 1995, 376, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, F.; Rossant, J.; Yamaguchi, T.P.; Gertsenstein, M.; Wu, X.F.; Breitman, M.L.; Schuh, A.C. Failure of blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1-deficient mice. Nature 1995, 376, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dameron, K.M.; Volpert, O.V.; Tainsky, M.A.; Bouck, N. Control of angiogenesis in fibroblasts by p53 regulation of thrombospondin-1. Science 1994, 265, 1582–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Manome, Y.; Wen, P.; Kufe, D.W.; Fine, H.A. Viral vector-mediated transduction of a modified platelet factor 4 cDNA inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, M.S.; Holmgren, L.; Shing, Y.; Chen, C.; Rosenthal, R.A.; Moses, M.; Lane, W.S.; Cao, Y.; Sage, E.H.; Folkman, J. Angiostatin: A novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell 1994, 79, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, M.S.; Boehm, T.; Shing, Y.; Fukai, N.; Vasios, G.; Lane, W.S.; Flynn, E.; Birkhead, J.R.; Olsen, B.R.; Folkman, J. Endostatin: An endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 1997, 88, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, M.A.; Langer, R.J. A metalloproteinase inhibitor as an inhibitor of neovascularization. Cell. Biochem. 1991, 47, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, J.M.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. The role of matrix metalloproteases and their inhibitors in tumour invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Eur. Respir. J. 1994, 7, 2062–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Folkman, J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 1996, 86, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, R.J.; Loughnan, M.S.; Flynn, E.; Folkman, J. Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4082–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingber, D.; Fujita, T.; Kishimoto, S.; Sudo, K.; Kanamaru, T.; Brem, H.; Folkman, J. Synthetic analogues of fumagillin that inhibit angiogenesis and suppress tumour growth. Nature 1990, 348, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Li, B.; Winer, J.; Armanini, M.; Gillett, N.; Phillips, H.S.; Ferrara, N. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 1993, 362, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, T.; Lindley, C. Bevacizumab: An angiogenesis inhibitor for the treatment of solid malignancies. Clin. Ther. 2006, 28, 1779–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siemeister, G.; Schirner, M.; Reusch, P.; Barleon, B.; Marmè, D.; Martiny-Baron, G. An antagonistic vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) variant inhibits VEGF-stimulated receptor autophosphorylation and proliferation of human endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4625–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millauer, B.; Shawver, L.K.; Plate, K.H.; Risau, W.; Ullrich, A. Glioblastoma growth inhibited in vivo by a dominant-negative Flk-1 mutant. Nature 1994, 367, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, L.P.; Pierce, E.A.; Foley, E.D.; Takagi, H.; Chen, H.; Riddle, L.; Ferrara, N.; King, G.L.; Smith, L.E. Suppression of retinal neovascularization in vivo by inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) using soluble VEGF-receptor chimeric proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10457–10461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Sankar, S.; Shan, S.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Polverini, P.J.; Quinn, T.Q.; Peters, K.G. Inhibition of tumor growth by targeting tumor endothelium using a soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor. Cell Growth Differ. 1998, 9, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sallinen, H.; Anttila, M.; Narvainen, J.; Koponen, J.; Hamalainen, K.; Kholova, I.; Heikura, T.; Toivanen, P.; Kosma, V.M.; Heinonen, S.; et al. Antiangiogenic gene therapy with soluble VEGFR-1, -2, and -3 reduces the growth of solid human ovarian carcinoma in mice. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.L.; Hecht, D.; Song, W.; Kovesdi, I.; Hackett, N.R.; Yayon, A.; Crystal, R.G. Regional suppression of tumor growth by in vivo transfer of a cDNA encoding a secreted form of the extracellular domain of the flt-1 vascular endothelial growth factor receptor. Hum. Gene Ther. 1998, 9, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, R.L.; Thomas, K.A. Inhibition of vascular endothelial cell growth factor activity by an endogenously encoded soluble receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10705–10709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazan-Peregrino, M.; Sainson, R.C.; Carlisle, R.C.; Thoma, C.; Waters, R.A.; Arvanitis, C.; Harris, A.L.; Hernandez-Alcoceba, R.; Seymour, L.W. Combining virotherapy and angiotherapy for the treatment of breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, V.; Duffour, M.T.; Mathieu, M.C.; Fernandez, N.; Cordier, L.; Abina, M.A.; Kremer, E.; Perricaudet, M.; Haddada, H.J. Strategies for cancer gene therapy using adenoviral vectors. Mol. Med. 1996, 74, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, H.L.; Crystal, R.G. Gene therapy strategies for tumor antiangiogenesis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998, 90, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyder, S.M.; Murthy, L.; Stancel, G.M. Progestin regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McLeskey, S.W.; Tobias, C.A.; Vezza, P.R.; Filie, A.C.; Kern, F.G.; Hanfelt, J. Tumor growth of FGF or VEGF transfected MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells correlates with density of specific microvessels independent of the transfected angiogenic factor. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 1993–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.F.; Yeo, K.T.; Berse, B.; Yeo, T.K.; Senger, D.R.; Dvorak, H.F.; van de Water, L.J. Expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) by epidermal keratinocytes during wound healing. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.; Hubner, G.; Breier, G.; Longaker, M.T.; Greenhalgh, D.G.; Werner, S.J. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cultured keratinocytes. Implications for normal and impaired wound healing. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 12607–12613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, R.L.; Wang, G.; Thomas, K.A. Identification of a natural soluble form of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, FLT-1, and its heterodimerization with KDR. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 226, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauber, N.; Rohan, R.M.; Flynn, E.; D’Amato, R.J. Critical components of the female reproductive pathway are suppressed by the angiogenesis inhibitor AGM-1470. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.; Cortes, M.; de Felipe, P.; Martin, V.; Diez-Guerra, J.; Talavera, A.; Perez-Higueras, A. Long-term rat survival after malignant brain tumor regression by retroviral gene therapy. Gene Ther. 1995, 2, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Maron, A.; Gustin, T.; Le Roux, A.; Mottet, I.; Dedieu, J.F.; Brion, J.P.; Demeure, R.; Perricaudet, M.; Octave, J.N. Gene therapy of rat C6 glioma using adenovirus-mediated transfer of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene: Long-term follow-up by magnetic resonance imaging. Gene Ther. 1996, 3, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Pirollo, K.F.; Hao, Z.; Rait, A.; Jang, Y.J.; Fee, W.E., Jr.; Ryan, P.; Chiang, Y.; Chang, E.H. p53 mediated sensitization of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck to radiotherapy. Oncogene 1997, 14, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Song, H.; Yu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z. Ad-p53 enhances the sensitivity of triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-468 cells to the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, T.; Folkman, J.; Browder, T.; O’Reilly, M.S. Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature 1997, 390, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, C.K.; Kendall, R.L.; Cabrera, G.; Soroceanu, L.; Heike, Y.; Gillespie, G.Y.; Siegal, G.P.; Mao, X.; Bett, A.J.; Huckle, W.R.; et al. Paracrine expression of a native soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibits tumor growth, metastasis, and mortality rate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8795–8800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alon, T.; Hemo, I.; Itin, A.; Pe’er, J.; Stone, J.; Keshet, E. Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melder, R.J.; Koenig, G.C.; Witwer, B.P.; Safabakhsh, N.; Munn, L.L.; Jain, R.K. During angiogenesis, vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor regulate natural killer cell adhesion to tumor endothelium. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Ferreira, V.; Breier, G.; Pollefeyt, S.; Kieckens, L.; Gertsenstein, M.; Fahrig, M.; Vandenhoeck, A.; Harpal, K.; Eberhardt, C.; et al. Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature 1996, 380, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Carver-Moore, K.; Chen, H.; Dowd, M.; Lu, L.; O’Shea, K.S.; Powell-Braxton, L.; Hillan, K.J.; Moore, M.W. Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature 1996, 380, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K.; Safabakhsh, N.; Sckell, A.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, P.; Benjamin, L.; Yuan, F.; Keshet, E. Endothelial cell death, angiogenesis, and microvascular function after castration in an androgen-dependent tumor: Role of vascular endothelial growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 10820–10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, L.E.; Keshet, E. Conditional switching of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in tumors: Induction of endothelial cell shedding and regression of hemangioblastoma-like vessels by VEGF withdrawal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8761–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, H.F.; Detmar, M.; Claffey, K.P.; Nagy, J.A.; van de Water, L.; Senger, D.R. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: An important mediator of angiogenesis in malignancy and inflammation. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1995, 107, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Chen, Y.; Dellian, M.; Safabakhsh, N.; Ferrara, N.; Jain, R.K. Time-dependent vascular regression and permeability changes in established human tumor xenografts induced by an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14765–14770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, M.A.; Siegfried, W.; Yoshimura, K.; Yoneyama, K.; Fukayama, M.; Stier, L.E.; Paakko, P.K.; Gilardi, P.; Stratford-Perricaudet, L.D.; Perricaudet, M.; et al. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of a recombinant alpha 1-antitrypsin gene to the lung epithelium in vivo. Science 1991, 252, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, M.A.; Yoshimura, K.; Trapnell, B.C.; Yoneyama, K.; Rosent Dalemans, W.; Fukayama, M.; Bargon, J.; Stier, L.E.; Stratford-Perricaudet, L.; Perricaudet, M.; et al. In vivo transfer of the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene to the airway epithelium. Cell 1992, 68, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Danel, C.; Crystal, R.G. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of human lipase complementary DNA to the gallbladder. Gastroenterology 1994, 106, 1638–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochmuller, H.; Jani, A.; Huard, J.; Prescott, S.; Simoneau, M.; Massie, B.; Karpati, G.; Acsadi, G. Emergence of early region 1-containing replication-competent adenovirus in stocks of replication-defective adenovirus recombinants (delta E1 + delta E3) during multiple passages in 293 cells. Hum. Gene Ther. 1994, 5, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barleon, B.; Totzke, F.; Herzog, C.; Blanke, S.; Kremmer, E.; Siemeister, G.; Marmé, D.; Martiny-Baron, G.J. Mapping of the sites for ligand binding and receptor dimerization at the extracellular domain of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor FLT-1. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 10382–10388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Days a | sFLT-1 (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| untreated | 0 | nd b |
| Adcontrol c | 3 | nd |
| Adsflt | 3 | 2.47 ± 0.82 |
| Adcontrol | 21 | nd |
| Adsflt | 21 | 5.86 ± 5.62 |
| Adcontrol | 185 | nd |
| Adsflt | 185 | 0.23 ± 0.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Felici, A.; Bottaro, D.P.; Mangoni, A.; Reusch, P.; Marmé, D.; Kovesdi, I.; De Silva, D.M.; Lee, Y.H.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Mühlhauser, J. Regression of Human Breast Carcinoma in Nude Mice after Adsflt Gene Therapy Is Mediated by Tumor Vascular Endothelial Cell Apoptosis. Cancers 2022, 14, 6175. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246175
Felici A, Bottaro DP, Mangoni A, Reusch P, Marmé D, Kovesdi I, De Silva DM, Lee YH, Capogrossi MC, Mühlhauser J. Regression of Human Breast Carcinoma in Nude Mice after Adsflt Gene Therapy Is Mediated by Tumor Vascular Endothelial Cell Apoptosis. Cancers. 2022; 14(24):6175. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246175
Chicago/Turabian StyleFelici, Angelina, Donald P. Bottaro, Antonella Mangoni, Petra Reusch, Dieter Marmé, Imre Kovesdi, Dinuka M. De Silva, Young H. Lee, Maurizio C. Capogrossi, and Judith Mühlhauser. 2022. "Regression of Human Breast Carcinoma in Nude Mice after Adsflt Gene Therapy Is Mediated by Tumor Vascular Endothelial Cell Apoptosis" Cancers 14, no. 24: 6175. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246175
APA StyleFelici, A., Bottaro, D. P., Mangoni, A., Reusch, P., Marmé, D., Kovesdi, I., De Silva, D. M., Lee, Y. H., Capogrossi, M. C., & Mühlhauser, J. (2022). Regression of Human Breast Carcinoma in Nude Mice after Adsflt Gene Therapy Is Mediated by Tumor Vascular Endothelial Cell Apoptosis. Cancers, 14(24), 6175. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246175






