Conventional vs. Drug-Eluting Beads Transarterial Chemoembolization for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Propensity Score Weighted Comparison of Efficacy and Safety
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
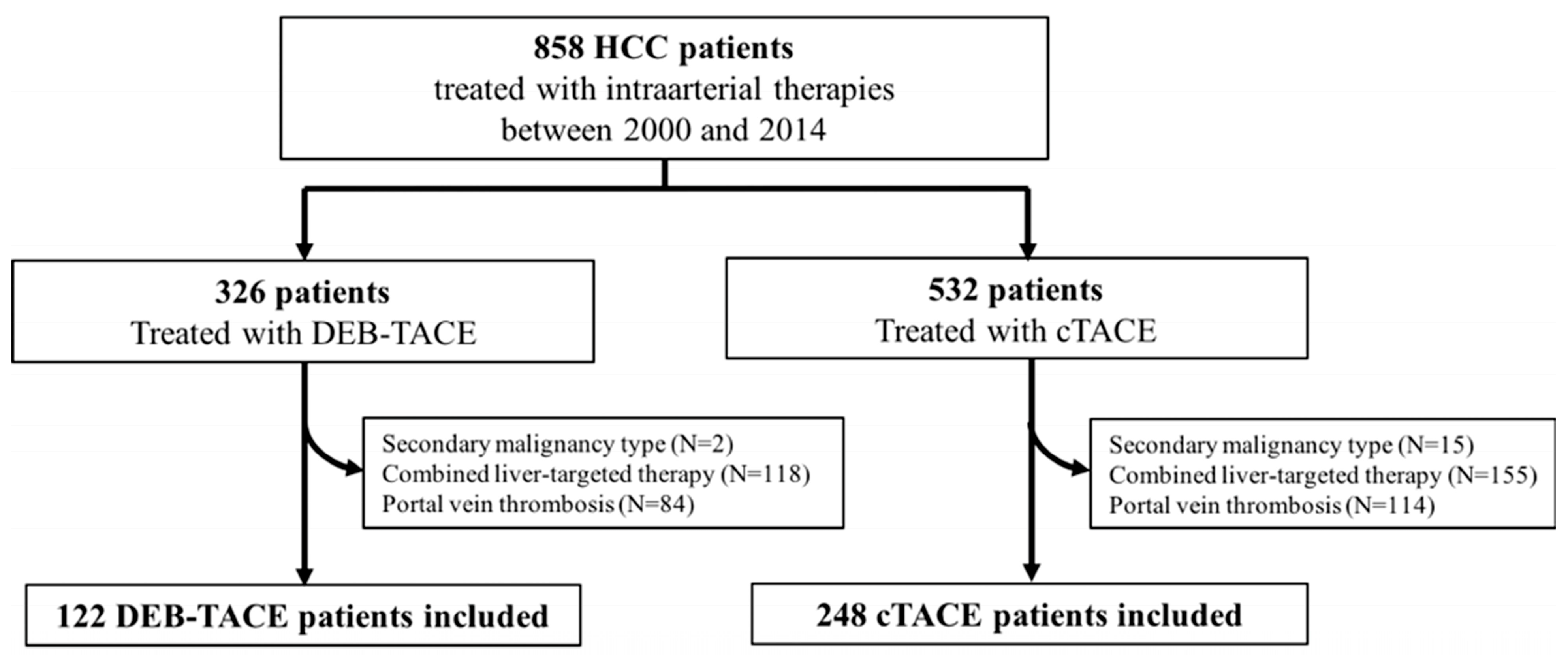
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Transarterial Chemoembolization Techniques
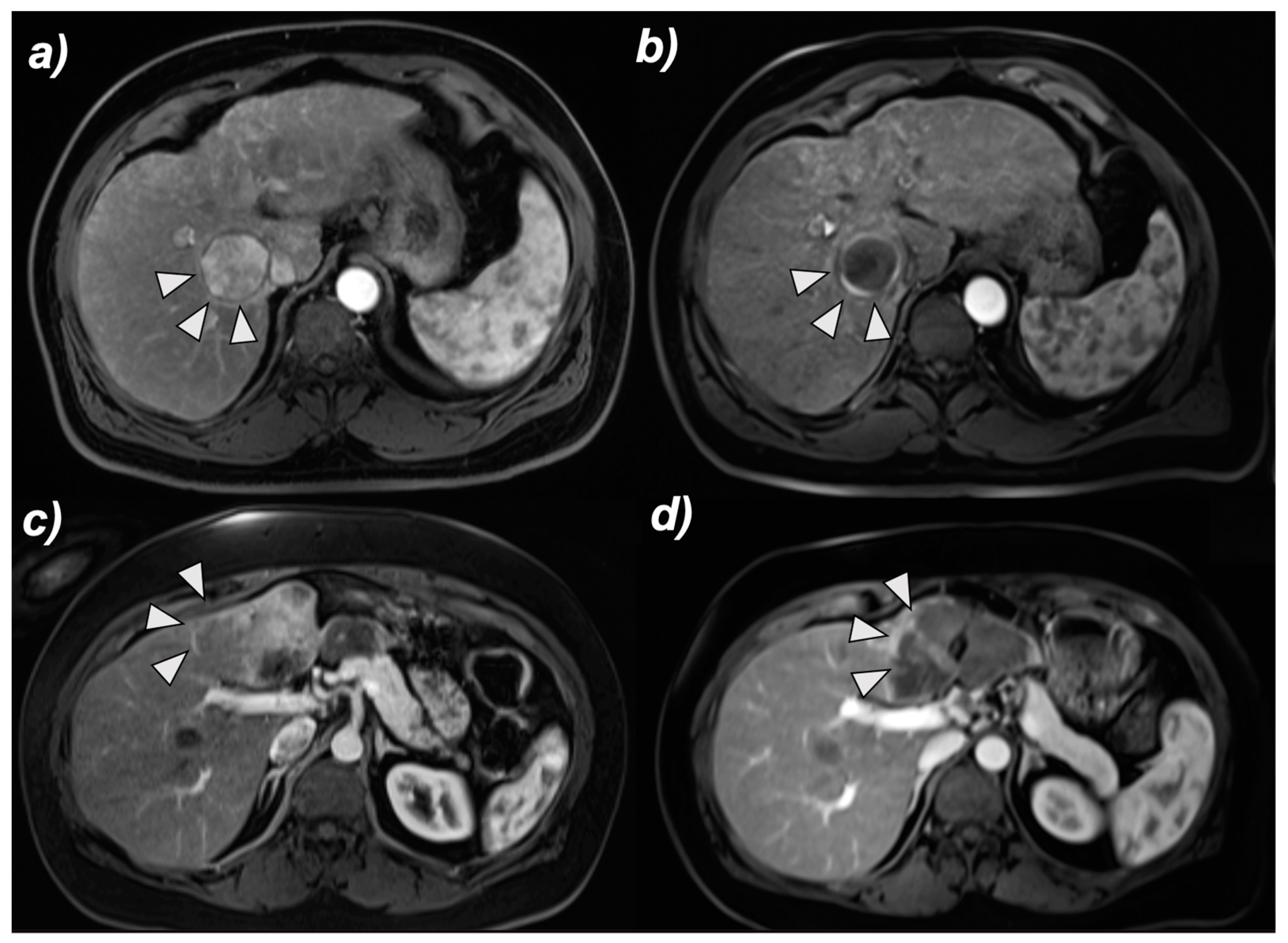
2.3. MRI and Image Analysis
2.4. Overall Survival
2.5. Adverse Events
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Predictors of the Overall Survival after TACE
3.1.1. Propensity Score Weighting
3.1.2. Multivariate Cox Proportional Hazards Regression
3.2. Survival Analysis
3.2.1. cTACE before vs. cTACE after the Introduction of DEB-TACE in 2006
3.2.2. cTACE vs. DEB-TACE after the Introduction of DEB-TACE in 2006
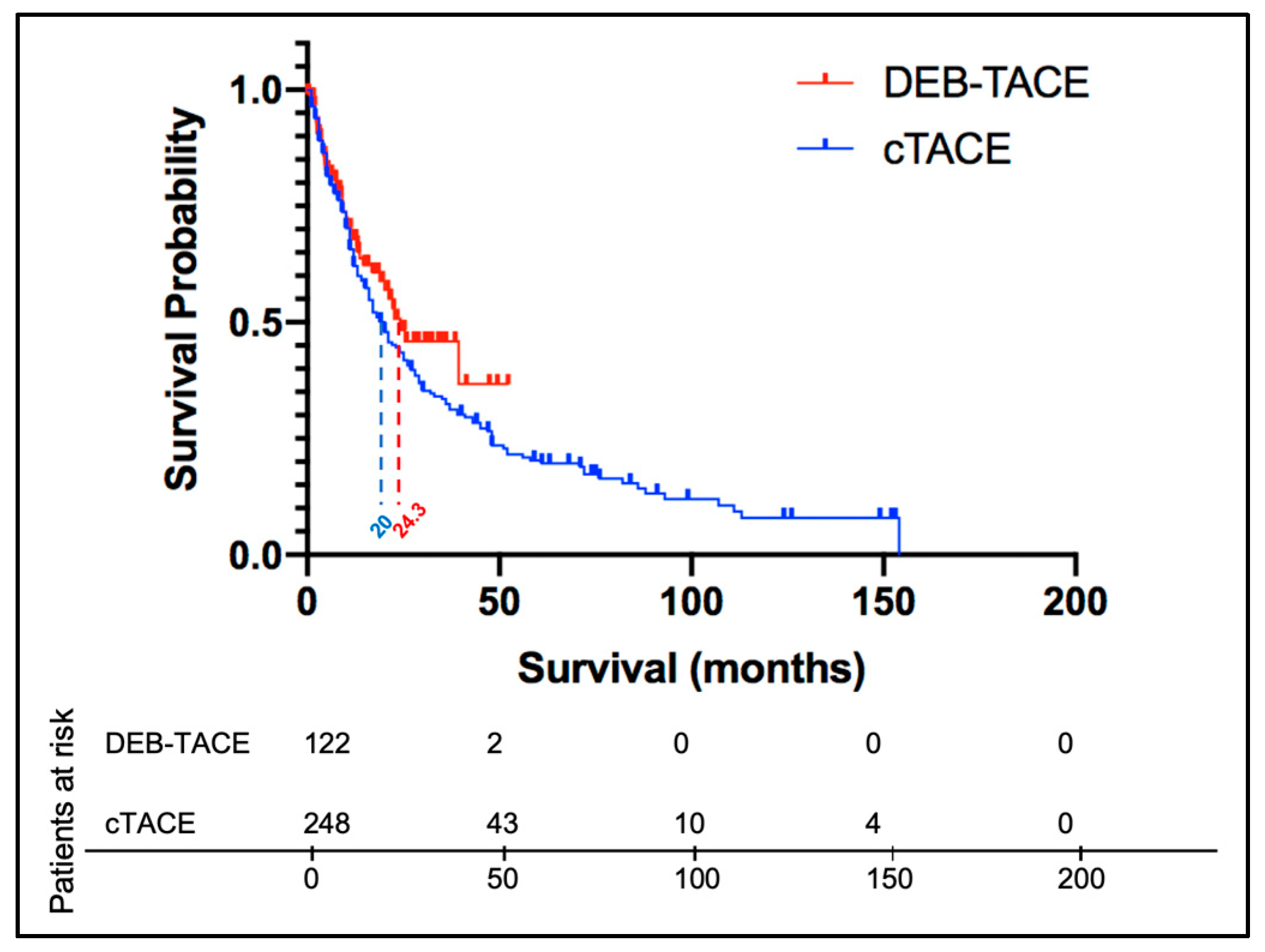
3.2.3. cTACE vs. DEB-TACE without Timeframe Restriction
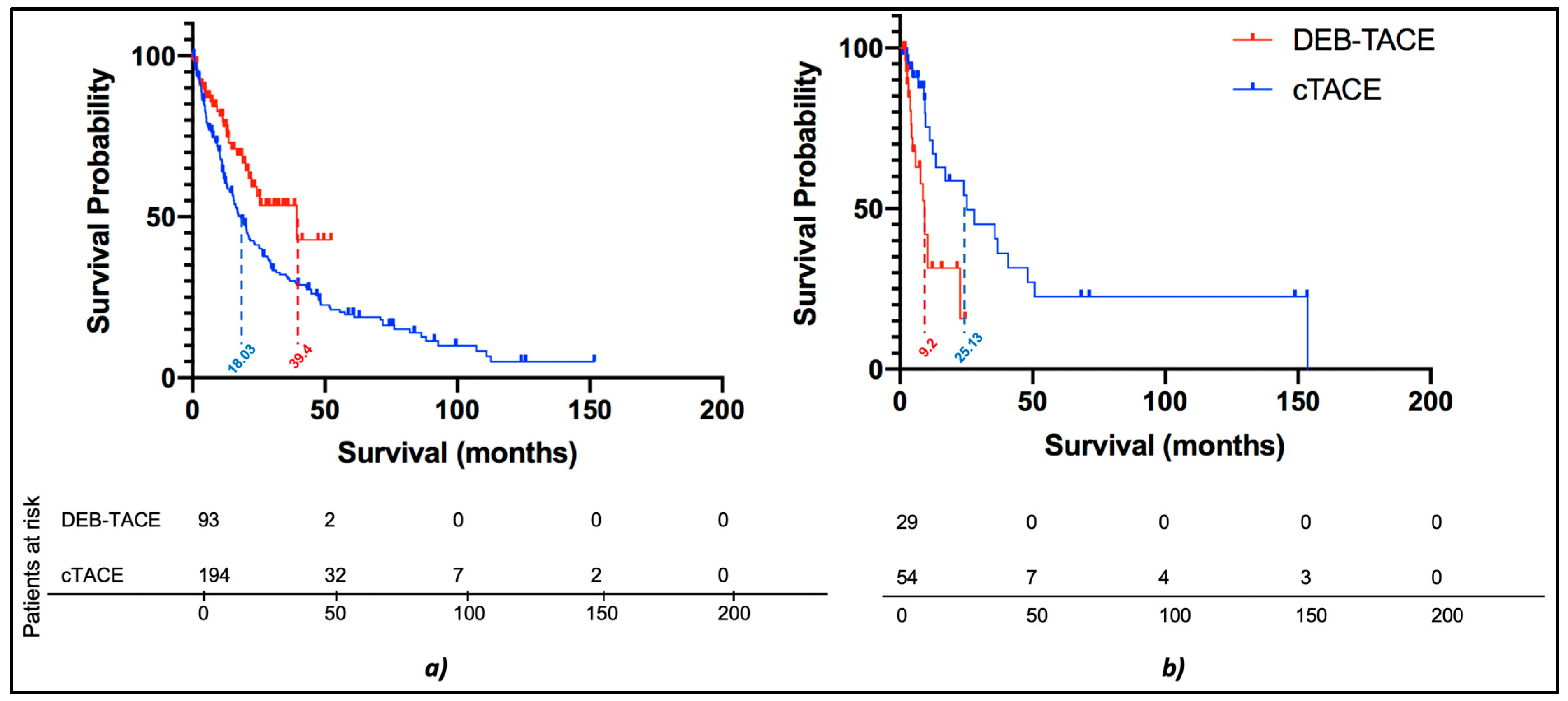
3.2.4. Subgroup Survival Analysis: cTACE vs. DEB-TACE without Timeframe Restriction
3.3. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalva, S.P.; Pectasides, M.; Liu, R.; Rachamreddy, N.; Surakanti, S.; Yeddula, K.; Ganguli, S.; Wicky, S.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Zhu, A.X. Safety and Effectiveness of Chemoembolization with Drug-Eluting Beads for Advanced-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 37, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Baere, T.; Arai, Y.; Lencioni, R.; Geschwind, J.-F.; Rilling, W.; Salem, R.; Matsui, O.; Soulen, M.C. Treatment of Liver Tumors with Lipiodol TACE: Technical Recommendations from Experts Opinion. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzulli, M.; Peta, G.; Vasuri, F.; Marasco, G.; Caretti, D.; Bartalena, L.; Spinelli, D.; Giampalma, E.; D’Errico, A.; Golfieri, R. Standardization of conventional chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 22, 100278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, M.; Real, M.I.; Burrel, M.; Forner, A.; Sala, M.; Brunet, M.; Ayuso, C.; Castells, L.; Montañá, X.; Llovet, J.M.; et al. Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with drug eluting beads: Efficacy and doxorubicin pharmacokinetics. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammer, J.; Malagari, K.; Vogl, T.; Pilleul, F.; Denys, A.; Watkinson, A.; Pitton, M.; Sergent, G.; Pfammatter, T.; Terraz, S.; et al. Prospective Randomized Study of Doxorubicin-Eluting-Bead Embolization in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results of the precision v Study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golfieri, R.; Giampalma, E.; Renzulli, M.; Cioni, R.; Bargellini, I.; Bartolozzi, C.; Breatta, A.D.; Gandini, G.; Nani, R.; Gasparini, D.; et al. Randomised controlled trial of doxorubicin-eluting beads vs conventional chemoembolisation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Malenstein, H.; Maleux, G.; Vandecaveye, V.; Heye, S.; Laleman, W.; Van Pelt, J.; Vaninbroukx, J.; Nevens, F.; Verslype, C. A Randomized Phase II Study of Drug-Eluting Beads versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Onkologie 2011, 34, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, R.; Bargellini, I.; Bertini, M.; Bozzi, E.; Romano, A.; Petruzzi, P.; Tumino, E.; Ginanni, B.; Federici, G.; Cioni, R.; et al. Conventional versus Doxorubicin-eluting Bead Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 22, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, L.J.; Chapiro, J.; Funai, E.; Bousabarah, K.; Schobert, I.T.; Isufi, E.; Geschwind, J.-F.H.; Stark, S.; He, P.; Rudek, M.A.; et al. Prospective study of Lipiodol distribution as an imaging marker for doxorubicin pharmacokinetics during conventional transarterial chemoembolization of liver malignancies. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 31, 3002–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, R.; Cheng, D.; Ma, Y. Doxorubicin-eluting beads versus conventional transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.-B.; Wang, X.-B.; Peng, Y.-C.; Zhu, S.-L.; Ma, L.; Xiang, B.-D.; Gong, W.-F.; Chen, J.; You, X.-M.; Jiang, J.-H.; et al. Systematic review comparing the safety and efficacy of conventional and drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, J.; Ritter, O.C.; Germer, C.-T.; Klein, I.; Kickuth, R.; Steger, U. Transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads versus conventional transarterial chemoembolization in locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatic Med. Évid. Res. 2016, 8, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Z.G.; Ye, S.L. Efficacy and safety of cTACEversusDEB-TACE in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. J. Dig. Dis. 2016, 17, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Di Maso, M.; Muscatiello, N. Drug-eluting beads versus conventional chemoembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Yuan, P.; Chen, B.; Sun, J.; Shen, H.; Qian, Y. Evaluation of drug-eluting beads versus conventional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2017, 41, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Lee, B.C.; Kim, J.K.; Yim, N.Y.; Kim, H.O.; Cho, S.B.; Jeong, Y.Y. Conventional Versus Small Doxorubicin-eluting Bead Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Treating Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage 0/A Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhou, J.; Ling, G.; Zhu, D.; Long, Q. CalliSpheres drug-eluting beads versus lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A short-term efficacy and safety study. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baere, T.; Guiu, B.; Ronot, M.; Chevallier, P.; Sergent, G.; Tancredi, I.; Tselikas, L.; Burgio, M.D.; Raynaud, L.; Deschamps, F.; et al. Real Life Prospective Evaluation of New Drug-Eluting Platform for Chemoembolization of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: PARIS Registry. Cancers 2020, 12, 3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoul, J.-L.; Forner, A.; Bolondi, L.; Cheung, T.T.; Kloeckner, R.; de Baere, T. Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: How and when to use it based on clinical evidence. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 72, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodetski, B.; Chapiro, J.; Schernthaner, R.; Duran, R.; Lin, M.; Lee, H.; Lenis, D.; Stuart, E.A.; Nonyane, B.A.S.; Pekurovsky, V.; et al. Advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis: Conventional versus drug-eluting beads transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernyak, V.; Fowler, K.J.; Kamaya, A.; Kielar, A.Z.; Elsayes, K.M.; Bashir, M.R.; Kono, Y.; Do, R.K.; Mitchell, D.G.; Singal, A.G.; et al. Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) Version 2018: Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in At-Risk Patients. Radiology 2018, 289, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Bhoori, S.; Sposito, C.; Bongini, M.; Langer, M.; Miceli, R.; Mariani, L. Milan criteria in liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: An evidence-based analysis of 15 years of experience. Liver Transplant. 2011, 17, S44–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojiro, M. Histopathology of liver cancers. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2005, 19, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, A.R.; Furlan, A.; Fetzer, D.; Sasatomi, E.; Borhani, A.A.; Heller, M.T.; Tublin, M.E. Infiltrative Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What Radiologists Need to Know. Radiographics 2015, 35, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanasekaran, R.; Kooby, D.A.; Staley, C.A.; Kauh, J.S.; Khanna, V.; Kim, H.S. Comparison of conventional transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and chemoembolization with doxorubicin drug eluting beads (DEB) for unresectable hepatocelluar carcinoma (HCC). J. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 101, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.J.; Chun, H.J.; Song, D.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Yoo, S.H.; Park, C.-H.; Bae, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Chang, U.I.; Yang, J.M.; et al. Comparative study between doxorubicin-eluting beads and conventional transarterial chemoembolization for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Park, D.I.; Cho, Y.K.; Sohn, C.I.; Jeon, W.K.; Kim, B.I.; Kim, M.-J. Radiologic response to transcatheter hepatic arterial chemoembolization and clinical outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Jung, K.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, S.U.; Park, J.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Han, K.-H.; Kim, G.M.; et al. Conventional versus drug-eluting beads chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: Emphasis on the impact of tumor size. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesselle, G.; Quirier-Leleu, C.; Velasco, S.; Charier, F.; Silvain, C.; Boucebci, S.; Ingrand, P.; Tasu, J.-P. Predictive factors for complete response of chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads (DEB-TACE) for hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, H.M.; Kim, E.-J.; Gwon, D.I.; Ko, G.-Y.; Yoon, H.-K.; Ko, H.K. Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Infiltrative Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Clinical Safety and Efficacy and Factors Influencing Patient Survival. Korean J. Radiol. 2014, 15, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.S.; Yoon, J.-H.; Chung, J.W.; Cho, E.J.; Yu, S.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, C.Y. Survival of infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma patients with preserved hepatic function after treatment with transarterial chemoembolization. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloeckner, R.; Ruckes, C.; Kronfeld, K.; Wörns, M.A.; Weinmann, A.; Galle, P.R.; Lang, H.; Otto, G.; Eichhorn, W.; Schreckenberger, M.; et al. Selective internal radiotherapy (SIRT) versus transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for the treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma (CCC): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2014, 15, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, A.; Martinetti, L.; Crespi, S.; Maggioni, M.; Sangiovanni, A. Transarterial Chemoembolization with Epirubicin-eluting Beads versus Transarterial Embolization before Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namur, J.; Citron, S.J.; Sellers, M.T.; Dupuis, M.H.; Wassef, M.; Manfait, M.; Laurent, A. Embolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with drug-eluting beads: Doxorubicin tissue concentration and distribution in patient liver explants. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-C.; Hsu, H.-H.; Chiu, S.-H.; Huang, W.-Y.; Lo, C.-H.; Lin, H.-H.; Huang, P.-C.; Shih, Y.-L.; Wan, Y.-L. Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization with Drug-Eluting Beads for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Recommended Selection for Small-Caliber. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, G.; Cascella, T.; Facciorusso, A.; Nani, R.; Lanocita, R.; Morosi, C.; Vaiani, M.; Calareso, G.; Greco, F.G.; Ragnanese, A.; et al. Transarterial chemoembolization using 40 µm drug eluting beads for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Radiol. 2017, 9, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malagari, K.; Moschouris, H.; Kiakidis, T.; Harward, S.; Kelekis, A.; Vrakas, S.; Koundouras, D.; Filipiadis, D.; Glantzounis, G.; Emmanouil, E.; et al. Five-Years Outcome Analysis of 142 Consecutive Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Doxorubicin Eluting Microspheres 30–60 μm: Results from a Single-Centre Prospective Phase II Trial. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padia, S.A.; Shivaram, G.; Bastawrous, S.; Bhargava, P.; Vo, N.J.; Vaidya, S.; Valji, K.; Harris, W.P.; Hippe, D.S.; Kogut, M.J. Safety and Efficacy of Drug-eluting Bead Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Comparison of Small-versus Medium-size Particles. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.W.; Hong, H.P.; Kim, M.S.; Shin, B.S.; Kwon, H.-J.; Kim, B.I.; Sohn, W. Comparison of Clinical Efficacy and Safety between 70–150 µm and 100–300 µm Doxorubicin Drug-Eluting Bead Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Life 2022, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balli, H.; Aksungur, E.; Khalatai, B.; Aikimbaev, K. Super-Selective Transarterial Chemoembolization with Doxorubicin-Loaded Drug-Eluting Beads Sized Below and Above 100 Microns in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comparative Study. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2019, 103, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.R.; Xiang, H.; Chan, M.V.; Chan, C. Survival, tumour response and safety of 70-150 μm versus 100-300 μm doxorubicin drug-eluting beads in transarterial chemoembolisation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 63, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deipolyi, A.; Oklu, R.; Al-Ansari, S.; Zhu, A.X.; Goyal, L.; Ganguli, S. Safety and Efficacy of 70–150 μm and 100–300 μm Drug-Eluting Bead Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borde, T.; Gaupp, F.L.; Geschwind, J.-F.; Savic, L.J.; Miszczuk, M.; Rexha, I.; Adam, L.; Walsh, J.J.; Huber, S.; Duncan, J.S.; et al. Idarubicin-Loaded ONCOZENE Drug-Eluting Bead Chemoembolization in a Rabbit Liver Tumor Model: Investigating Safety, Therapeutic Efficacy, and Effects on Tumor Microenvironment. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1706–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | n | n | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment Demographics | DEB-TACE | cTACE | |
| 122 | 248 | ||
| Age | 0.577 | ||
| >65 | 49 (40.2%) | 108 (43.5%) | |
| ≤65 | 73 (59.8%) | 140 (56.5%) | |
| Gender | 0.285 | ||
| Male | 91 (74.6%) | 198 (79.8%) | |
| Female | 31 (25.4%) | 50 (20.2%) | |
| Staging System BCLC | 0.781 | ||
| A | 34 (27.9%) | 60 (24.2%) | |
| B | 28 (23%) | 62 (25.0%) | |
| C | 55 (45.1%) | 109 (44.0%) | |
| D | 7 (5.7%) | 17 (6.8%) | |
| ECOG PS | 0.869 | ||
| 0 | 69 (56.6%) | 129 (52.0%) | |
| 1 | 48 (39.3%) | 107 (43.1%) | |
| 2 | 4 (3.3%) | 10 (4.0%) | |
| 3 | 1 (0.8%) | 2 (0.9%) | |
| Child Pugh class | 0.557 | ||
| A5 | 49 (40.2%) | 86 (34.7%) | |
| A6 | 25 (20.5%) | 69 (27.8%) | |
| B7 | 17 (13.9%) | 35 (14.1%) | |
| B8 | 15 (12.3%) | 30 (12.1%) | |
| B9 | 10 (8.2%) | 13 (5.3%) | |
| C10 | 4 (3.3%) | 10 (4.0%) | |
| C11 | 1 (0.8%) | 3 (1.2%) | |
| C12 | 1 (0.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| C13 | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (0.8%) |
| Parameter | n | n | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | DEB-TACE | cTACE | |
| Demographics | 122 | 248 | |
| Size of the dominant lesion (Diameter) | 0.667 | ||
| >3 cm | 78 (63.9%) | 191 (77.0%) | |
| >5 cm | 52 (42.6%) | 115 (46.4%) | |
| Tumor multiplicity | 0.818 | ||
| unifocal | 42 (34.4%) | 90 (36.3%) | |
| multifocal | 80 (65.6%) | 158 (63.7%) | |
| Extrahepatic metastasis * | 0.114 | ||
| yes | 1 (0.8%) | 11 (4.4%) | |
| no | 121 (99.2%) | 237 (95.6%) | |
| Cirrhosis ** | 0.018 | ||
| present | 82 (67.2%) | 134 (54.0%) | |
| absent | 40 (32.8%) | 114 (46.0%) | |
| Tumor type | 0.895 | ||
| infiltrative | 29 (23.8%) | 54 (21.8%) | |
| nodular | 93 (76.2%) | 194 (78.2%) |
| Parameter | Univariate Analysis Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Multivariate Analysis Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 0.61 | |||
| DEB-TACE | 1.00 | |||
| cTACE | 1.09 (0.77–1.52) | |||
| Child Pugh Score | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| A | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| B-C | 2.20 (1.64–2.95) | 2.03 (1.47–2.80) | ||
| ECOG PS | <0.001 | 0.074 | ||
| 0 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| >0 | 2.03 (1.52–2.75) | 1.34 (0.97–1.84) | ||
| Cirrhosis | 0.66 | |||
| No | 1.00 | |||
| Yes | 0.93 (0.69–1.26) | |||
| Size of the dominant lesion | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| ≤3 cm | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| >3 cm | 2.29 (1.60–3.29) | 2.34 (1.60–3.43) | ||
| Number of lesions | 0.002 | 0.014 | ||
| Unifocal | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Multifocal | 1.67 (1.06–2.31) | 1.52 (1.09–2.12) | ||
| Extrahepatic metastases | <0.001 | 0.010 | ||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 1.98 (1.33–2.94) | 1.77 (1.14–2.74) | ||
| Infiltrative | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 2.23 (1.60–3.09) | 1.76 (1.22–2.53) |
| n | n | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | DEB-TACE | cTACE | |
| Adverse event | n = 116 | n = 157 | |
| Abdominal pain/discomfort | 101 (87.1%) | 119 (75.8%) | 0.02 |
| Fatigue | 8 (6.9%) | 19 (12.1%) | 0.16 |
| Nausea/vomiting | 75 (64.7%) | 89 (56.7%) | 0.18 |
| Fever | 7 (6.0%) | 4 (2.5%) | 0.15 |
| Diarrhea | 4 (3.4%) | 3 (1.9%) | 0.44 |
| 30-day mortality | 4 (3.4%) | 10 (6.4%) | 0.27 |
| Biochemical toxicity | n = 115 | n = 125 | |
| Albumin | 1 (0.9%) | 1 (0.8%) | 0.93 |
| Bilirubin | 7 (6.1%) | 13 (10.4%) | 0.23 |
| ALP | 3 (2.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.07 |
| ALT | 4 (6.1%) | 11 (8.8%) | 0.43 |
| AST | 11 (12.2%) | 18 (14.4%) | 0.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Savic, L.J.; Chen, E.; Nezami, N.; Murali, N.; Hamm, C.A.; Wang, C.; Lin, M.; Schlachter, T.; Hong, K.; Georgiades, C.; et al. Conventional vs. Drug-Eluting Beads Transarterial Chemoembolization for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Propensity Score Weighted Comparison of Efficacy and Safety. Cancers 2022, 14, 5847. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235847
Savic LJ, Chen E, Nezami N, Murali N, Hamm CA, Wang C, Lin M, Schlachter T, Hong K, Georgiades C, et al. Conventional vs. Drug-Eluting Beads Transarterial Chemoembolization for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Propensity Score Weighted Comparison of Efficacy and Safety. Cancers. 2022; 14(23):5847. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235847
Chicago/Turabian StyleSavic, Lynn Jeanette, Evan Chen, Nariman Nezami, Nikitha Murali, Charlie Alexander Hamm, Clinton Wang, MingDe Lin, Todd Schlachter, Kelvin Hong, Christos Georgiades, and et al. 2022. "Conventional vs. Drug-Eluting Beads Transarterial Chemoembolization for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Propensity Score Weighted Comparison of Efficacy and Safety" Cancers 14, no. 23: 5847. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235847
APA StyleSavic, L. J., Chen, E., Nezami, N., Murali, N., Hamm, C. A., Wang, C., Lin, M., Schlachter, T., Hong, K., Georgiades, C., Chapiro, J., & Laage Gaupp, F. M. (2022). Conventional vs. Drug-Eluting Beads Transarterial Chemoembolization for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Propensity Score Weighted Comparison of Efficacy and Safety. Cancers, 14(23), 5847. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235847







