UCHL5 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Bladder Cancer Cells by Activating c-Myc via AKT/mTOR Signaling
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. BCa Cohort Collection and Preprocessing
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Antibodies and Reagents
2.4. Lentivirus-Mediated Stable Low Expression Cells
2.5. Lentivirus-Mediated Stable Overexpression
2.6. Cell Proliferation Assays
2.7. Colony Formation Assays
2.8. Wound-Healing Assay
2.9. Transwell Assay
2.10. Real-Time PCR
2.11. Western Blotting Analysis
2.12. Xenograft Assays
2.13. Immunohistochemical (IHC)
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
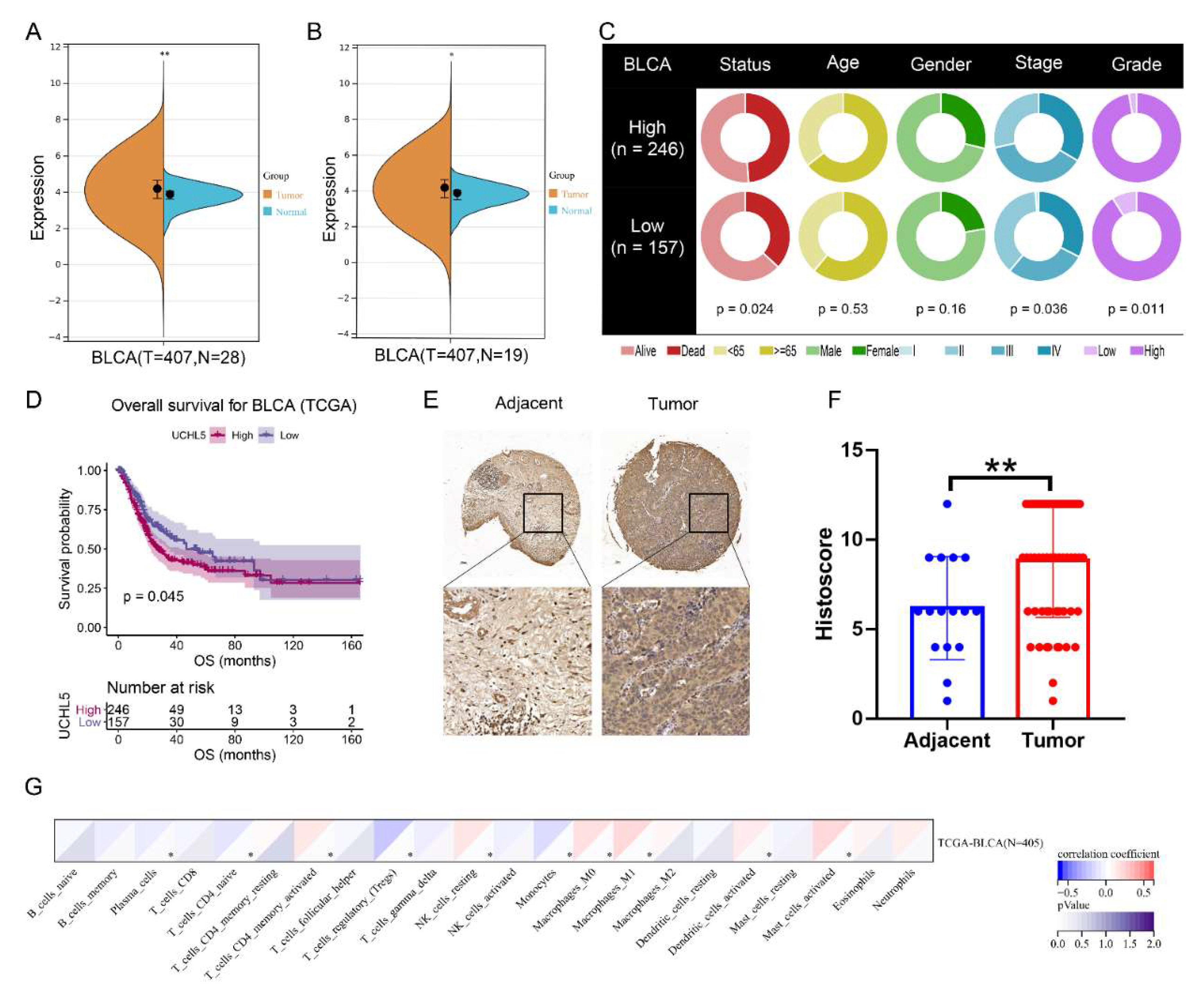
3.1. The Expression of UCHL5 in Bladder Cancer and Its Role in Survival and Clinical Applications
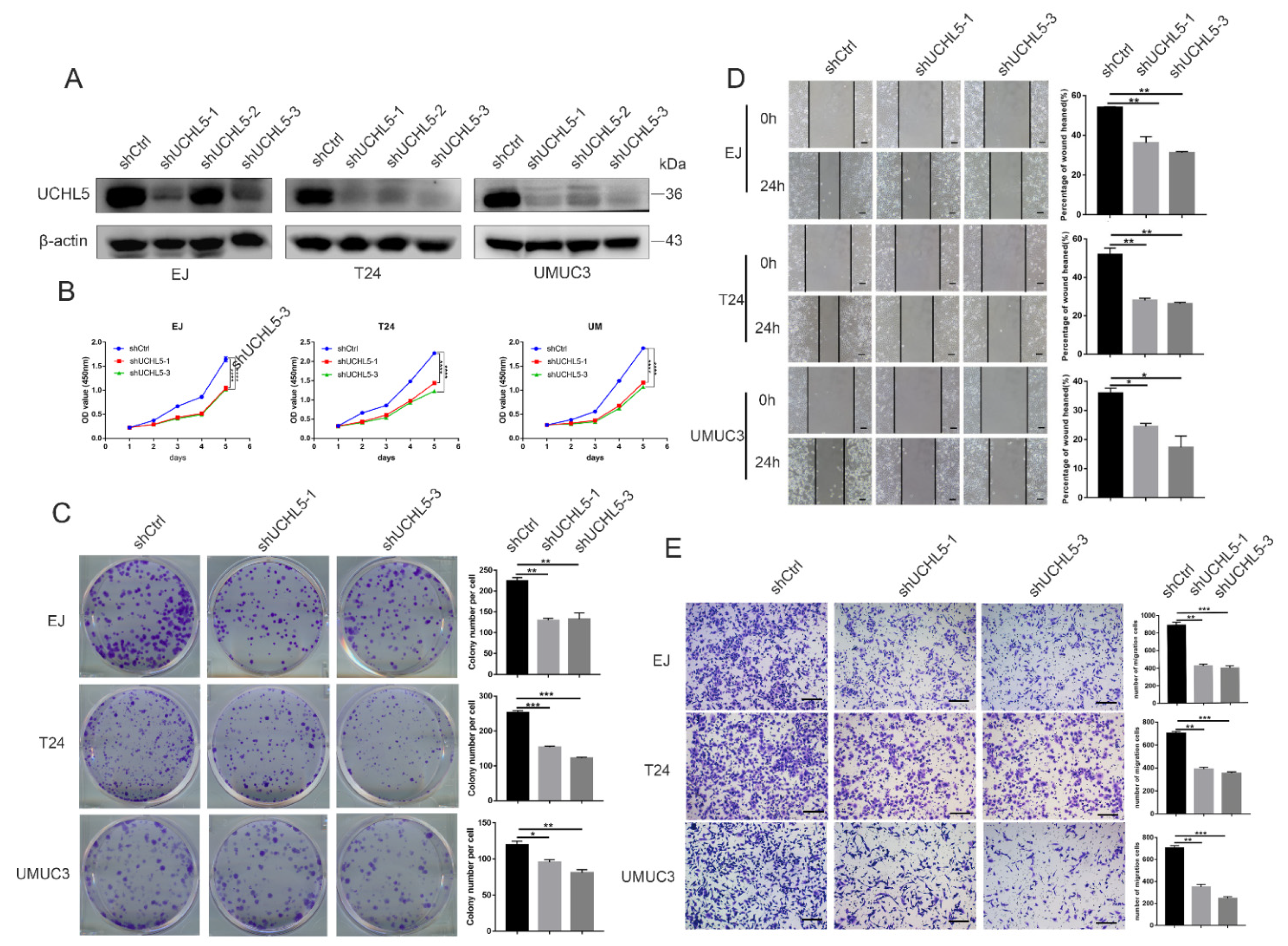
3.2. Knocking Down UCHL5 Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Migration
3.3. UCHL5 Overexpression Increases Cell Proliferation and Migration in Bladder Cancer
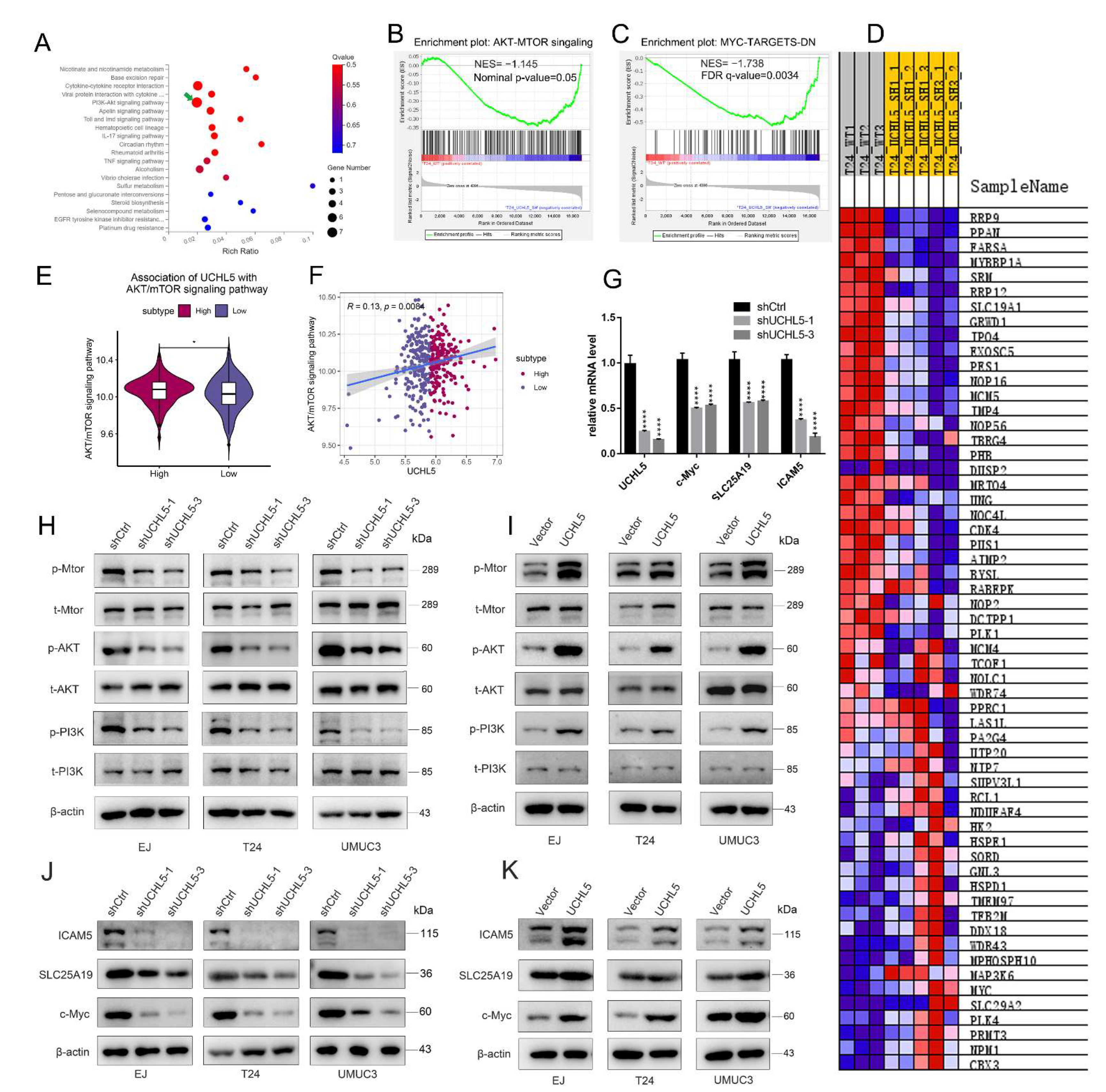
3.4. UCHL5 Silencing Results in Inactivation of AKT/mTOR Signal Pathway and Repressing the Downstream Expression of c-Myc, SLC25A19, and ICAM5
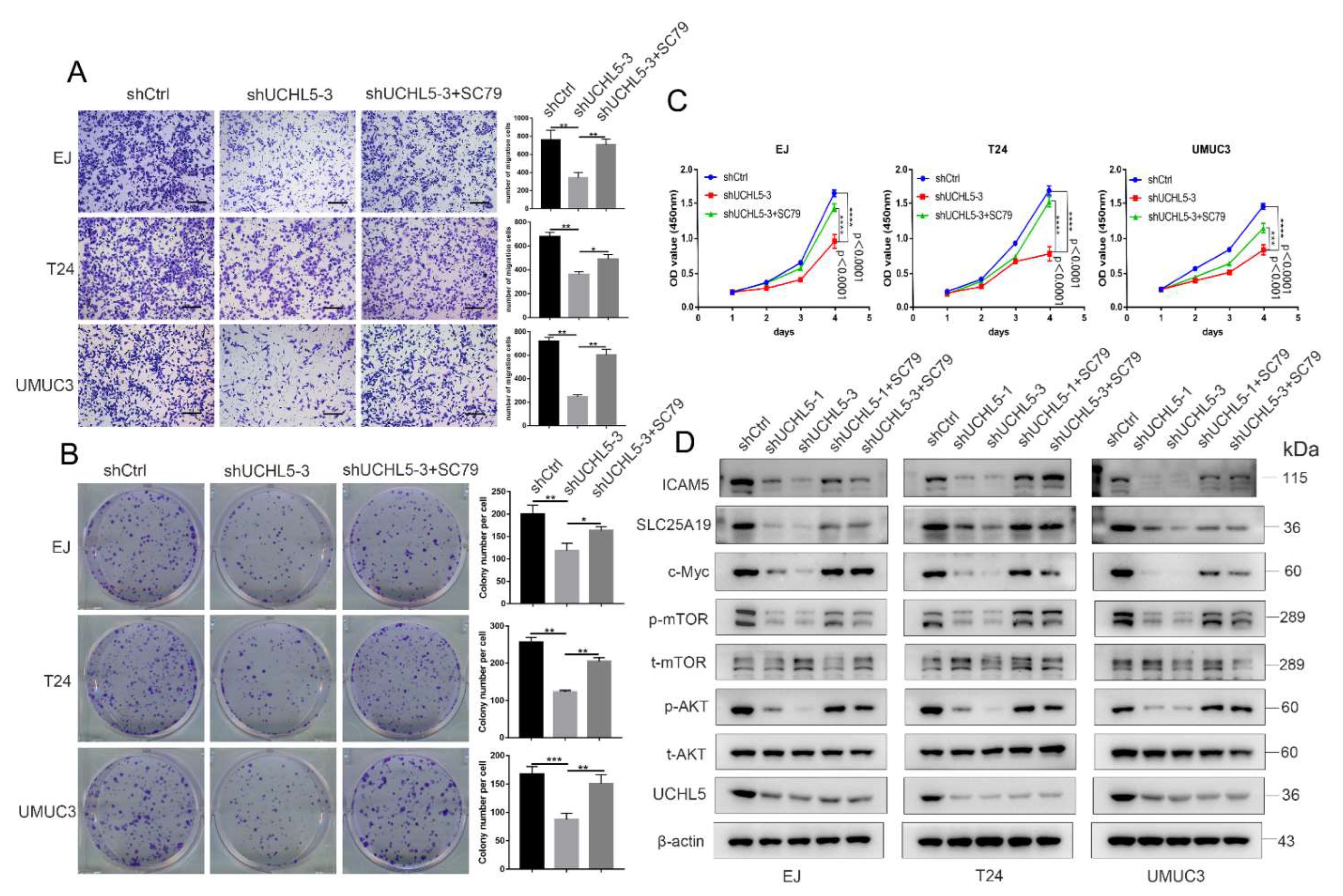
3.5. SC79 Reverses the Effect of UCHL5 Downregulation in Bladder Cancer Cells
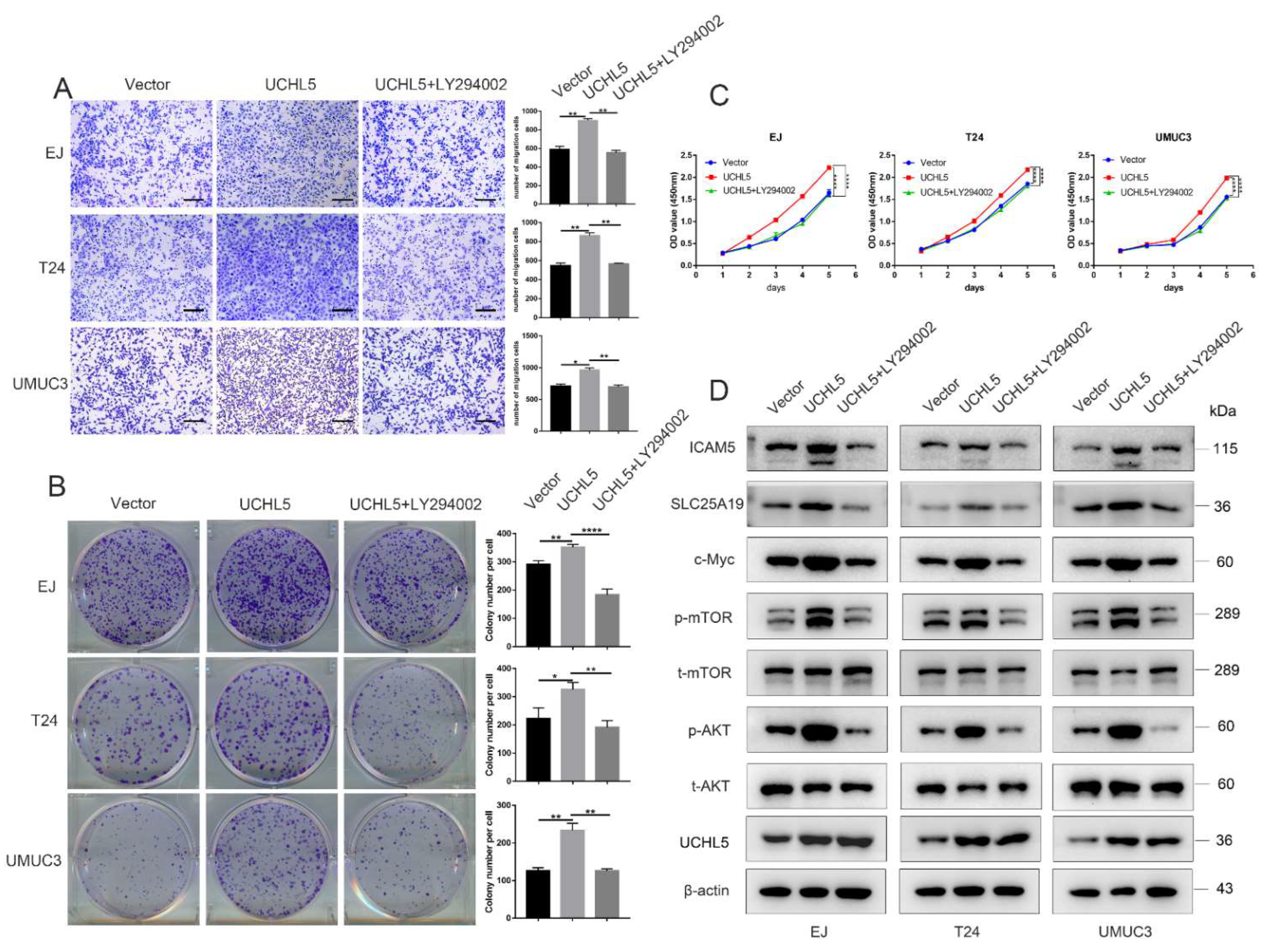
3.6. LY294002 Recovers the Effects of UCHL5 Upregulation in Bladder Cancer Cells
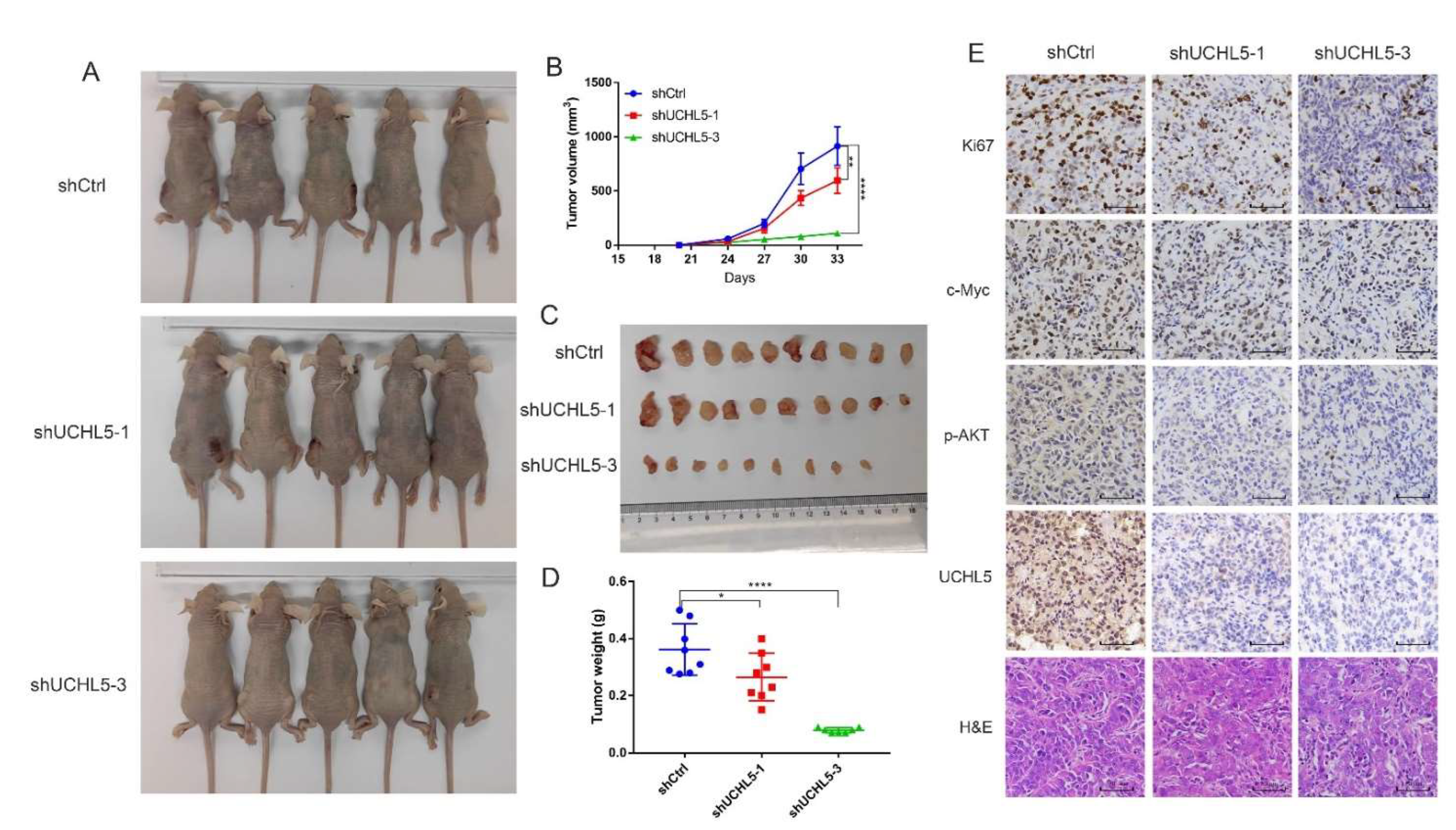
3.7. Knocking Down UCHL5 Inhibits Bladder Cancer Growth In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babjuk, M.; Burger, M.; Zigeuner, R.; Shariat, S.F.; van Rhijn, B.W.G.; Compérat, E.; Sylvester, R.J.; Kaasinen, E.; Böhle, A.; Palou Redorta, J.; et al. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: Update 2013. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.; Xiao, J.-F.; Agarwal, N.; Duex, J.E.; Theodorescu, D. Advances in bladder cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, A.; Hoskin, P.J. Predictive Biomarkers for Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: The Search for the Holy Grail Continues. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdik, C. Unlocking bladder cancer. Nature 2017, 551, S34–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquale, V.; Ducci, G.; Campioni, G.; Ventrici, A.; Assalini, C.; Busti, S.; Vanoni, M.; Vago, R.; Sacco, E. Profiling and Targeting of Energy and Redox Metabolism in Grade 2 Bladder Cancer Cells with Different Invasiveness Properties. Cells 2020, 9, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, J.C.; Schroers-Martin, J.; Lazzareschi, D.V.; Shi, W.Y.; Chen, S.B.; Esfahani, M.S.; Trivedi, D.; Chabon, J.J.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Stehr, H.; et al. Detection and Surveillance of Bladder Cancer Using Urine Tumor DNA. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfred Witjes, J.; Lebret, T.; Compérat, E.M.; Cowan, N.C.; De Santis, M.; Bruins, H.M.; Hernández, V.; Espinós, E.L.; Dunn, J.; Rouanne, M.; et al. Updated 2016 EAU Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevissen, T.E.T.; Komander, D. Mechanisms of Deubiquitinase Specificity and Regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 159–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, V.V.; Kapoor, A.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, T.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Bressan, R.A.; Zhu, J.-K. Control of DNA methylation and heterochromatic silencing by histone H2B deubiquitination. Nature 2007, 447, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Buus, R.; Clague, M.J.; Urbé, S. Regulation of ErbB2 receptor status by the proteasomal DUB POH1. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Turcu, F.E.; Ventii, K.H.; Wilkinson, K.D. Regulation and cellular roles of ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinating enzymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 363–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolén, U.; Kobzeva, V.; Gasparjan, N.; Ovaa, H.; Winberg, G.; Kisseljov, F.; Masucci, M.G. Activity profiling of deubiquitinating enzymes in cervical carcinoma biopsies and cell lines. Mol. Carcinog 2006, 45, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, D.; Xi, J.; Ji, Z.; Liu, T.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, L.; Wang, Q.; Shen, X. Expression and clinical significance of UCH37 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 2310–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.-J.; Xu, K.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Shen, X.-Z.; Tu, R.-Q. High expression of UCH37 is significantly associated with poor prognosis in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 11427–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Niu, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Ye, X.; Lu, S.; Chen, Z. Effect of ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase 37 on apoptotic in A549 cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2011, 29, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutts, A.J.; Soond, S.M.; Powell, S.; Chantry, A. Early phase TGFβ receptor signalling dynamics stabilised by the deubiquitinase UCH37 promotes cell migratory responses. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Shen, X. Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolases: Involvement in cancer progression and clinical implications. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicks, S.J.; Haros, K.; Maillard, M.; Song, L.; Cohen, R.E.; Dijke, P.T.; Chantry, A. The deubiquitinating enzyme UCH37 interacts with Smads and regulates TGF-beta signalling. Oncogene 2005, 24, 8080–8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Song, Z.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, L. Ubiquitin C-Terminal Hydrolase L5 (UCHL5) Accelerates the Growth of Endometrial Cancer via Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Liao, Y.; Yan, Y.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, J.; Li, S.; Liu, T. BRCC3 Promotes Tumorigenesis of Bladder Cancer by Activating the NF-κB Signaling Pathway Through Targeting TRAF2. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 720349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Jiang, S. Immune Cell-Derived Exosomes in the Cancer-Immunity Cycle. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhao, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Gao, Z.; Jiang, K.; Ye, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Immune cell infiltration signatures identified molecular subtypes and underlying mechanisms in gastric cancer. NPJ Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichhart, T.; Hengstschläger, M.; Linke, M. Regulation of innate immune cell function by mTOR. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Jin, L.; Lai, H.; Wu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zhu, M.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. LncRNA DILA1 inhibits Cyclin D1 degradation and contributes to tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Fu, D.; Tang, W.; Cai, Y.; Ma, D.; Wang, H.; Xue, R.; Liu, T.; Huang, X.; Dong, L.; et al. Ubiquitin C-terminal Hydrolase 37, a novel predictor for hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence, promotes cell migration and invasion via interacting and deubiquitinating PRP19. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Kuang, J.; Liao, J.; Yuan, Q. LncRNA DRAIC inhibits proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells through interfering with NFRKB deubiquitination mediated by UCHL5. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanic, C.S.; Budhavarapu, V.; Graves, J.D.; Li, G.; Lin, W.-C. Regulation of E2 promoter binding factor 1 (E2F1) transcriptional activity through a deubiquitinating enzyme, UCH37. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26508–26522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, P.-M.; Dong, J.-R.; Chang, Y.-W.; Kuo, K.-L.; Lin, W.-C.; Liu, S.-H.; Huang, K.-H. The UCHL5 inhibitor b-AP15 overcomes cisplatin resistance via suppression of cancer stemness in urothelial carcinoma. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 26, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelengaris, S.; Khan, M.; Evan, G. c-MYC: More than just a matter of life and death. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korangath, P.; Teo, W.W.; Sadik, H.; Han, L.; Mori, N.; Huijts, C.M.; Wildes, F.; Bharti, S.; Zhang, Z.; Santa-Maria, C.A.; et al. Targeting Glutamine Metabolism in Breast Cancer with Aminooxyacetate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3263–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shachaf, C.M.; Kopelman, A.M.; Arvanitis, C.; Karlsson, A.; Beer, S.; Mandl, S.; Bachmann, M.H.; Borowsky, A.D.; Ruebner, B.; Cardiff, R.D.; et al. MYC inactivation uncovers pluripotent differentiation and tumour dormancy in hepatocellular cancer. Nature 2004, 431, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, E.; Bester, A.C.; Shifman, S.; Kerem, B. Transcriptional dynamics in colorectal carcinogenesis: New insights into the role of c-Myc and miR17 in benign to cancer transformation. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5532–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, C.M.; Gurel, B.; Sutcliffe, S.; Aryee, M.J.; Schultz, D.; Iwata, T.; Uemura, M.; Zeller, K.I.; Anele, U.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Alterations in nucleolar structure and gene expression programs in prostatic neoplasia are driven by the MYC oncogene. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 1824–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, R.; Meeson, A.; Lowes, S. Solute transporters and malignancy: Establishing the role of uptake transporters in breast cancer and breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Schatz, A.; Adeyemi, B.; Kozminski, D.; Welsh, J.; Tenniswood, M.; Wang, W.-L.W. Vitamin D and testosterone co-ordinately modulate intracellular zinc levels and energy metabolism in prostate cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol 2019, 189, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahmberg, C.G.; Ning, L.; Paetau, S. ICAM-5: A neuronal dendritic adhesion molecule involved in immune and neuronal functions. Adv. Neurobiol. 2014, 8, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- Maruya, S.I.; Myers, J.N.; Weber, R.S.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Lotan, R.; El-Naggar, A.K. ICAM-5 (telencephalin) gene expression in head and neck squamous carcinoma tumorigenesis and perineural invasion! Oral Oncol. 2005, 41, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Yan, X.; Bai, X.; Tang, F.; Si, P.; Bai, C.; Tuoheti, K.; Guo, L.; Yisha, Z.; Liu, T.; et al. UCHL5 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Bladder Cancer Cells by Activating c-Myc via AKT/mTOR Signaling. Cancers 2022, 14, 5538. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225538
Cao Y, Yan X, Bai X, Tang F, Si P, Bai C, Tuoheti K, Guo L, Yisha Z, Liu T, et al. UCHL5 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Bladder Cancer Cells by Activating c-Myc via AKT/mTOR Signaling. Cancers. 2022; 14(22):5538. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225538
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yuanfei, Xin Yan, Xiaojie Bai, Feng Tang, Penghui Si, Can Bai, Kuerban Tuoheti, Linfa Guo, Zuhaer Yisha, Tao Liu, and et al. 2022. "UCHL5 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Bladder Cancer Cells by Activating c-Myc via AKT/mTOR Signaling" Cancers 14, no. 22: 5538. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225538
APA StyleCao, Y., Yan, X., Bai, X., Tang, F., Si, P., Bai, C., Tuoheti, K., Guo, L., Yisha, Z., Liu, T., & Liu, T. (2022). UCHL5 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Bladder Cancer Cells by Activating c-Myc via AKT/mTOR Signaling. Cancers, 14(22), 5538. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225538





