Simple Summary
Patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) might present with different clinical behaviors, even when classified at the same stage. This perspective highlights the recent findings on prognostic biomarkers that can aid in improving the staging of HNSCC. This was conducted with an aim of subsequently improving prognostic stratification and, hence, treatment planning.
Abstract
Tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging system is the cornerstone for treatment planning of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Many prognostic biomarkers have been introduced as modifiers to further improve the TNM classification of HNSCC. Here, we provide an overview on the use of the recent prognostic biomarkers, with a focus on histopathologic parameters, in improving the risk stratification of HNSCC and their application in the next generation of HNSCC staging systems.
1. Introduction
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a common and heterogenous malignancy in regard to etiology, pattern of progression and survival [1]. Risk factors of HNSCC include tobacco and/or alcohol consumption. Additionally, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is an important risk factor, specifically for the oropharyngeal subgroup The incidence of HNSCC has increased in many countries according to recent reports [2,3]. Furthermore, a large number of HNSCC cases are usually diagnosed at an advanced stage and will thus have poor survival [1]. Therefore, the mortality rate of some head and neck cancer subsites still remains high [3]. Various non- or mini-invasive methods are currently under investigation to aid in early diagnosis [4]. For example, blood or exhaled breath sampling and analysis may prove as promising potential novel tools during cancer screening [4,5]. In moving towards establishing a complete understanding of HNSCC, it is necessary to consider a multidisciplinary process traditionally involving a collaboration of head and neck surgeons, radiologists, and pathologists. This will aid in the proper management of HNSCC. Thus, clinical decision making should be based on the conclusion of clinical, radiological, and pathological evaluations of the tumor and the patient status.
The next step after diagnosis of HNSCC is to design treatment planning. Notably, cases sharing the same tumor–node–metastasis (TNM) stage usually receive the same treatment, although they may present with dramatically different clinical behavior [6]. Of note, recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses have highlighted many promising biomarkers that have the potential to prove useful in HNSCC prognostication. However, none of them are included in daily practice due to differences among the evaluation methods and staining protocols, or otherwise a lack of validation [7,8,9,10]. There were major changes in the techniques used to stage HNSCC in the latest release of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (i.e., 8th edition of the AJCC-TNM classification) manual [11,12]. Furthermore, many recent studies have proposed further refinement of the HNSCC classification based on the clinical significance of the recently emerged prognostic biomarkers.
2. Emerging Prognostic Biomarkers of HNSCC
The field of biomarker cancer research has introduced numerous candidates (Table 1) that have been proven to be associated with the prognosis of HNSCC using different techniques [13]. Among these, immunohistochemistry is an essential technique in the diagnostics and prognostication of HNSCC due to its facilitation of qualitative information. For example, immunohistochemical expression of programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) has shown a significant value in predicting response to treatment [14,15], with recent studies comparing the methods of assessment including Tumor Proportion Score (TPS) and Combined Positive Score (CPS) for scoring of PD-L1 [16]. Other techniques, such as genomic approaches including microarrays and quantitative PCR, provide technical usefulness. However, their role in the prognostication has remained limited due to the lack of validation studies from large homogenous cohorts into tumor location and tumor stage. Of note, circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) has been analyzed in HNSCC, showing a clinical significance in diagnosis and risk assessment of HNSCC. These findings require further validation [17,18]. In addition, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA) have been studied in HNSCC, with accumulating evidence suggesting they have a powerful prognostic value [19].

Table 1.
Summary of prognostic classifiers/markers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
During the last decade, and with the use of the above-mentioned methods/techniques, several molecules have been studied for their significance in initiation and/or progression of HNSCC [13]. However, few molecular biomarkers are assessed in tumor tissue specimens during routine pathology reporting on some subsites of HNSCC. In oropharyngeal subsite, as an example, p16 (INK4A) immunohistochemistry is a widely used and generally accepted surrogate tool to identify HPV association and therefore, to classify oropharyngeal SCC as either associated with the viral infection (i.e. HPV positive that usually has better prognosis) or not associated (i.e. HPV negative having poor survival) [33]. Although using polymerase chain reactions or in situ hybridization can result in a more accurate result in such a HPV status-based classification [36], it has now been widely accepted that p16 immunohistochemistry, if interpreted in the appropriate anatomic (orppahyngeal location and moprhological (HPV-typical or compatile mrophology) context using standardized assessment (usually block-type expression in >80% tumor cells), correlates highly with the presence of oncogenically active HPV infection. Indeed, p16 status is the basis of the current TNM classification system.
Focusing on body fluids, namely blood and saliva, recent research on HNSCC has highlighted the prognostic significance of many molecular-based biomarkers [37,38,39]. The assessment of such parameters has the advantages of being non-invasive and easily assessed preoperatively. Blood biomarkers, including neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), have been widely studied in HNSCC. Evidence from recent meta-analysis indicated that NLR is an important prognostic factor in HNSCC, while PLR was not of similar significance in survival prediction [40,41]. Similarly, salivary biomarkers have been studied in HNSCC, with a greater focus on oral SCC [37]. However, molecular biomarkers from body fluids are not yet considered in daily practice. The challenges in biomarker development, such as false negativity, false positivity and small size of cohorts, were widely noticed in studies of HNSCC [13]. In addition, the cost of the molecular biomarkers is a challenge. Therefore, the main focus in daily practice remains on histopathologic-based prognostic markers.
3. Histologic Markers Proposed Recently to Improve Risk Stratification of HNSCC
Conventional tumor histomorphology and anatomic characteristics of the tumor are the cornerstones of risk stratification methods in the analysis of many tumors, including HNSCC [23]. Daily practice in pathology reporting considers depth of invasion, perineural invasion, tumour grade, status of surgical margins, lymphovascular invasion, and local extension to adjacent structures (e.g., muscular and bone invasion). Some of these parameters have a clinical relevance in all subsites of HNSCC, e.g., perineural invasion [24] and lymphovascular invasion [25,26]; while some parameters are clinically more important for specific subsites, such as depth of invasion in oral SCC [27,28].
Furthermore, recent research has underlined many markers that can be assessed using HE-stained sections. Here, we will underline those that have been reported as modifiers to further develop and refine the classification of HNSCC, both for TNM staging and histologic grading. These include tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), tumor–stroma ratio and tumor budding (Figure 1) since they have been widely studied in HNSCC [10,29,30] and proposed for incorporation into the staging and/or grading systems. For example, the TNM-Immune system has been recently introduced as a superior prognostic classifier compared with the traditional TNM staging system [42]. The fact that immune cells are key components in the tumor microenvironment has led to large research efforts to identify immune biomarkers. Specifically, TILs have been among the widely studied immune cells, and their prognostic significance has been repeatedly reported in HNSCC [29,43,44,45]. Interestingly, our recent study proposed a modification for the TNM staging by incorporating the immune response (as assessed by the score of TILs in HE-stained sections), i.e., “TNM-Immune system”, and which showed a promising value in improving risk stratification of early oral tongue SCC [46]. In addition, a recent study by Bjerkli and colleagues [31] combined lymphocytic infiltrate and tumor differentiation in a “histo-score” that showed a prognostic value superior to the traditional tumor differentiation grade in assessments of oral tongue SCC. Similarly, the combination of infiltrating lymphocytes with type of histology has shown a promising prognostic value in a recent study of nasopharyngeal cancer [44].
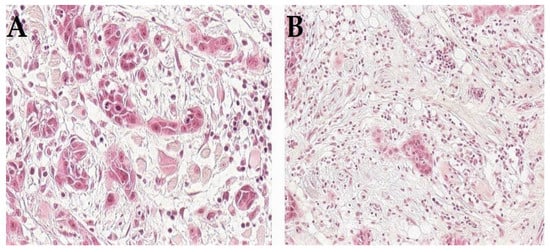
Figure 1.
Histologic appearance of HNSCC with adverse prognostic features such as tumor budding (A) or high amount of stroma (B).
The significance of stromal microenvironment has been recently underlined in HNSCC [10,47]. Thus, assessing prognostic markers related to the tumor–stroma can provide prognostic information of important clinical relevance. Of note, the tumor–stroma ratio has been recently reported to provide reliable prognostic value in different subsites of HNSCC, according to our recent systematic review [10]. In tongue SCC, a recent study by Mascitti et al. [32] proposed adding tumor–stroma ratio to the 8th edition of the AJCC-TNM classification to improve survival prediction. Remarkably, a Tumor–Stroma Node Metastasis (TSNM) (TSNM) staging system has also been recently proposed for gastric cancer [48], breast cancer [49] and esophageal cancer [50] and has demonstrated better ability in risk stratification compared with the traditional TNM staging system. Indeed, this proposal still needs to be further studied, as the addition of tumor–stroma ratio to TNM classification of HNSCC is still a preliminary proposal from a single study.
Tumor budding has been defined as single cancer cell/s or small cluster/s of less than five cancer cells, and it has become increasingly reported as a promising prognostic marker in solid tumors [51]. Tumor budding represents tumor cell dissociation at the invasion front and has shown an association with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition [52,53,54]. It is well-documented that tumor budding has significant clinical relevance in HNSCC [30] and other solid cancers as well, including in particular colorectal cancer where it has been very extensively studied [51]. Of note, the significance of tumor budding in HNSCC has been confirmed in a recent meta-analysis [55]. Many recent studies have incorporated tumor budding as a part of the grading system in studies of oral tongue SCC [56] oral SCC [57], laryngeal SCC and hypopharyngeal SCC [58].
It is important to take into consideration that tumor heterogeneity might represent a challenge in regard to representativity of the tumor sample when assessing these emerging prognostic biomarkers in preoperative biopsies. This is a common limitation for most of histopathological markers. However, recent studies have shown a good concordance in small biopsies and resection samples for some of these histopathologic parameters (e.g., TILs in oropharyngeal SCC [59] and tumor budding in oral SCC [60]) in cases with good-quality representative biopsies. This issue, however, still needs more comparative studies to be conducted in large cohorts.
Regarding histopathological grading, the current WHO classification has adopted a dichotomous approach to oropharyngeal SCC, with conventional (tobacco-associated, HPV-negative) tumors to be graded as usual while HPV-positive (p16-positive) tumors should not be graded. Inclusion of mixed etiology tumors in historical series with HPV-positive tumors (usually assigned Grade 3, but showing better outcome) and lower-grade (G1/G2) conventional tumors that are by definition virtually HPV-negative, is likely responsible for a great amount of the contradictory grading-related survival data. The proposal of two different sets of TNM categories for p16-positive (HPV-related) and p16-negative (HPV-negative) oropharyngeal SCC represents a first step in adopting an individualized staging risk stratification system for HNSCC.
4. Discussion
Cancer management in general is a medical field with many multidisciplinary aspects. The current comprehensive evaluation of HNSCC patients for decision making regarding management includes several patient-related factors. These include, but are not limited to, demographics [20], performance status [61], nutritional status [21], and comorbidities [22]. Diagnosis needs to be regarded as a summary of many factors and not just the ‘histo-patho-molecular’ diagnosis. The aforementioned factors will provide more comprehensive and individualized diagnostic and prognostic information. Clinical decision making in head and neck oncology aims to offer the best options for personalized management of the patient. Up-to-date TNM staging remains a major determinant for prognosis of HNSCC and therefore, it is widely considered during treatment planning. Aiming towards a more personalized cancer staging, the 8th edition of the AJCC-TNM classification staging manual introduced major changes in the staging system of some anatomical subsites of HNSCC. The most significant modifications from the previous 7th edition were the separate staging algorithm for high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV)-associated cancer of the oropharynx; the addition of extra-nodal extension to the lymph node category (N) in all but the viral-related cancers; and the inclusion of depth of invasion in the evaluation of the tumor category (T) of oral cancers. During preoperative staging and treatment planning, however, it can be sometimes challenging to exactly evaluate these modifiers that are included in the 8th edition of the AJCC-TNM classification. Therefore, it is of research interest and clinical importance to take into account the strategies that can aid in the best preoperative assessment of these modifiers. Similarly, it is important to identify the optimal cutoff for the number of metastatic lymph nodes. This can be considered to refine the N-staging, as has been reported in recent studies that proposed new classifications mostly redefining the optimal cutoff in the number of metastatic nodes in HPV-negative HNSCC [62,63]. Such refinement can aid in overcoming the limitations of the current N-staging. Further, it is necessary to consider the prognostic significance of nodal yield that has also been highlighted in studies of HNSCC [64].
In the daily practice of pathology, histologic risk stratification/classification of HNSCC is routinely determined using HE staining and mainly considers the degree of differentiation. HNSCC can be categorized for the majority of subsites into two groups: keratinizing SCC (usually showing squamous differentiation) and non-keratinizing SCC (usually showing limited maturation) [65]. Conventional HNSCCs are further histopathologically classified as well-, moderately and poorly differentiated tumors. Although this classification is classically reported by pathology reports, it has a limited value in the treatment planning of certain HNSCCs. For instance, in oral SCC, the aforementioned three groups do not associate well with the clinical outcome [65]. Therefore, recent studies have attempted to revise this system by, for example, incorporating tumor budding [56,58,66] or lymphocytic infiltrate [31,44] as part of histologic classification of HNSCC. Such recent modifications have showed superior prognostic value compared with the conventional WHO grading scheme and therefore remain necessary for consideration in further validation studies. In addition to histologic conventional histologic grading, there are other histopathologic parameters (e.g., pattern of invasive front, perineural invasion and lymphovascular invasion) that are widely evaluated in HNSCC using HE staining and can aid in understanding the behavior of each individual HNSCC case.
While the 8th edition of AJCC-TNM classification has incorporated the above-mentioned modifiers, there are other emerging prognostic biomarkers that have shown clinical significance in HNSCC and can be routinely evaluated and considered during the classification in daily diagnostics. Among these, immune-related biomarkers have been underlined in recent research and can be utilized for another kind of an important stratification in many cancers including HNSCC as either immune-hot (highly infiltrated) or immune-cold (non-infiltrated) tumors based on quantification of specific molecules such as CD3 and CD8 [34,67]. Of note, such findings on the prognostic significance of immune biomarkers have been approved in recent meta-analyses [35,68,69,70]. Further, accumulating evidence from recent studies indicates that HNSCC immune-hot tumors with a high infiltration of immune cells have an improved survival rate compared with immune-cold tumors, as simply assessed on HE-stained sections [29]. Furthermore, “hot” solid tumors with prominent CD8 infiltrate were reported to have a good response to immunotherapy [71]. Better understanding of immune microenvironment and immune classifier/s of HNSCC is of a high clinical significance, as it can identify suitable patients to benefit from immunotherapy [72]. Immune score has been introduced as a novel classification in colorectal cancer [73], and emerging evidence is indicating that such a score is of a significant value in HNSCC [70]. However, the accumulated evidence about novel IHC-based biomarkers in HNSCC still requires further validation to be included in daily practice.
There are a number of “Major Challenges” that need to be taken into account when considering the biomarkers of HNSCC. This includes, for example, the heterogenity of HNSCC tumors in regard to tumor location (subsites such as oral cavity, oropharynx, larynx, etc.) and risk factors (smoking/alcohol use vs. virus-related). Such heterogenity influences survival prediction and risk stratification, as one biomarker can be reliable for one subsite but not for the other subsite/s. Indeed, there are somehow universal prognostic markers that have been successfully predictive in more than one subsite [29,30]. Therefore, conducting a sub-analysis of each subsite separately is mandatory. The second challenge is defining the cutoff points in regard to dividing the cases into risk groups. For example, using a cutoff point of 20% has been widely used when considering TILs for risk stratification for HNSCC, but a cutoff point of 5% has been specifically suggested for nasopharyngeal cancer [29]. Thus, reporting the results of different cutoff points in each study can aid in recognizing the most suitable threshold for risk stratification. The third challenge is the small number of included cases, specifically in single-institution studies. Such small cohorts might be one of the reasons for conflicting findings on the studied biomarker/s and have caused difficulty in reaching a definitive conclusion on the significance of the prognostic biomarkers [7]. Overcoming these challenges in future studies is warranted to clarify if the introduced markers are suitable for all subsites of the head and neck region and to find the optimal cutoff point for every marker. Large multicenter cohorts are preferred for such studies.
5. Conclusions
From the anatomical, morphological and biological aspects pointed out above, it can be concluded that many histological, immunohistochemical, immunological, and molecular markers have been proposed for incorporation into the staging and grading systems of various HNSCC subsites. They might thus be further eligible to be considered in the next generation of the clinical and histological classifications. The improvement in the performance of 8th edition of the AJCC-TNM classification, together with the potentially forthcoming markers that can be implemented in routine pathology, is an important step towards a more personalized management of HNSCC. Namely, tumor budding, TSR and TILs have been simple to assessed and have high clinical relevance, and thus are important to considered in HNSCC pathology reporting. Taking into consideration such cancer-related and stromal-related prognostic biomarkers, at the same time, can aid in more accurate prediction. The current TNM staging system can be further modified/revised according to recent reports as discussed above. Future research is warranted to validate the proposed modifications in large multi-institutional studies.
Author Contributions
Writing—review and editing the manuscript: A.A.M., A.A. (Abbas Agaimy) and A.A. (Alhadi Almangush). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Helsinki University Hospital Research Fund (TYH2021220). Open access funding provided by University of Helsinki.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, K.K.; Gronhoj, C.; Jensen, D.H.; Karnov, K.K.S.; Agander, T.K.; Specht, L.; von Buchwald, C. Increasing incidence and survival of head and neck cancers in Denmark: A nation-wide study from 1980 to 2014. Acta Oncol. 2018, 57, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makitie, A.A.; Almangush, A.; Youssef, O.; Metsala, M.; Silen, S.; Nixon, I.J.; Haigentz, M., Jr.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Saba, N.F.; Vander Poorten, V.; et al. Exhaled breath analysis in the diagnosis of head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2020, 42, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuhkuri, A.; Saraswat, M.; Makitie, A.; Mattila, P.; Silen, R.; Dickinson, A.; Carpen, T.; Tohmola, T.; Joenvaara, S.; Renkonen, S. Patients with early-stage oropharyngeal cancer can be identified with label-free serum proteomics. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budach, V.; Tinhofer, I. Novel prognostic clinical factors and biomarkers for outcome prediction in head and neck cancer: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e313–e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Heikkinen, I.; Makitie, A.A.; Coletta, R.D.; Laara, E.; Leivo, I.; Salo, T. Prognostic biomarkers for oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.A.; Forouzanfar, T.; Bloemena, E.; de Visscher, J.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Leemans, C.R.; Helder, M.N. A review of the most promising biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis prediction of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Salo, T.; Hagstrom, J.; Leivo, I. Tumour budding in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma—A systematic review. Histopathology 2014, 65, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Alabi, R.O.; Troiano, G.; Coletta, R.D.; Salo, T.; Pirinen, M.; Makitie, A.A.; Leivo, I. Clinical significance of tumor-stroma ratio in head and neck cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.; Greene, F.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lydiatt, W.M.; Patel, S.G.; O’Sullivan, B.; Brandwein, M.S.; Ridge, J.A.; Migliacci, J.C.; Loomis, A.M.; Shah, J.P. Head and Neck cancers-major changes in the American Joint Committee on cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.C.; Wang, H.M.; Wu, M.H.; Chang, K.P.; Chang, P.H.; Liao, C.T.; Liau, C.T. Review of emerging biomarkers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in the era of immunotherapy and targeted therapy. Head Neck 2019, 41 (Suppl. 1), 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandberg, D.P.; Algazi, A.P.; Jimeno, A.; Good, J.S.; Fayette, J.; Bouganim, N.; Ready, N.E.; Clement, P.M.; Even, C.; Jang, R.W.; et al. Durvalumab for recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Results from a single-arm, phase II study in patients with >/=25% tumour cell PD-L1 expression who have progressed on platinum-based chemotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 107, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelatto, M.C.; Midha, A.; Mistry, A.; Sabalos, C.; Schechter, N.; Li, X.; Jin, X.; Steele, K.E.; Robbins, P.B.; Blake-Haskins, J.A.; et al. Development of a programmed cell death ligand-1 immunohistochemical assay validated for analysis of non-small cell lung cancer and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Diagn. Pathol. 2016, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emancipator, K.; Huang, L.; Aurora-Garg, D.; Bal, T.; Cohen, E.E.W.; Harrington, K.; Soulieres, D.; Le Tourneau, C.; Licitra, L.; Burtness, B.; et al. Comparing programmed death ligand 1 scores for predicting pembrolizumab efficacy in head and neck cancer. Mod. Pathol. Off. J. United States Can. Acad. Pathol. Inc. 2020, 34, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birknerova, N.; Mancikova, V.; Paul, E.D.; Matyasovsky, J.; Cekan, P.; Palicka, V.; Parova, H. Circulating Cell-Free DNA-Based Methylation Pattern in Saliva for Early Diagnosis of Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, S.S.; Silverman, D.A.; Young, K.; Dennis, S.K.; Birkeland, A.C. The Promise of Circulating Tumor DNA in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari Dilmaghani, N.; Khoshsirat, S.; Shanaki-Bavarsad, M.; Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A.; Bashash, D. The contributory role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in head and neck cancers: Possible biomarkers and therapeutic targets? Eur. J. Pharm. 2021, 900, 174053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, S.T.; Cass, L.M.; Challapalli, S.; Zahirsha, Z.; Simpson, M.; Ward, G.; Osazuwa-Peters, N. Demographic predictors of head and neck cancer survival differ in the elderly. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.W.; Tsai, Y.T.; Yang, H.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Chen, P.H.; Chou, H.H. Pretreatment prognostic nutritional index as a prognostic marker in head and neck cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, Y.; Takemoto, N.; Oya, R.; Ashida, N.; Kitamura, T.; Shimizu, K.; Takemura, K.; Michiba, T.; Hanamoto, A.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Development and validation of a new comorbidity index for patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in Japan. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Makitie, A.A.; Leivo, I. Back to basics: Hematoxylin and eosin staining is the principal tool for histopathological risk assessment of oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2021, 115, 105134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Y.; Yu, M. Perineural invasion as a prognostic factor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2019, 139, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, K.T.; Gal, T.J.; Ebelhar, A.J.; Valentino, J.; Brill, Y.M.; Dressler, E.V.; Aouad, R.K. Prognostic indicators and survival in salvage surgery for laryngeal cancer. Head Neck 2017, 39, 2021–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, J. Impact of lymphovascular invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2021, 131, 319–328.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldeira, P.C.; Soto, A.M.L.; de Aguiar, M.C.F.; Martins, C.C. Tumor depth of invasion and prognosis of early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolens, E.D.S.; Dourado, M.R.; Almangush, A.; Salo, T.A.; Gurgel Rocha, C.A.; da Silva, S.D.; Brennan, P.A.; Coletta, R.D. The Impact of Histopathological Features on the Prognosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 784924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Leivo, I.; Makitie, A.A. Overall assessment of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Time to take notice. Acta Otolaryngol. 2020, 140, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makitie, A.A.; Almangush, A.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Ferlito, A.; Leivo, I. Hallmarks of cancer: Tumor budding as a sign of invasion and metastasis in head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2019, 41, 3712–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerkli, I.H.; Hadler-Olsen, E.; Nginamau, E.S.; Laurvik, H.; Soland, T.M.; Costea, D.E.; Uhlin-Hansen, L.; Steigen, S.E. A combined histo-score based on tumor differentiation and lymphocytic infiltrate is a robust prognostic marker for mobile tongue cancer. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2020, 477, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascitti, M.; Zhurakivska, K.; Togni, L.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Almangush, A.; Balercia, P.; Balercia, A.; Rubini, C.; Lo Muzio, L.; Santarelli, A.; et al. Addition of the tumour-stroma ratio to the 8th edition American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system improves survival prediction for patients with oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2020, 77, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.M.; Song, L.J.; Shen, J.; Yue, H.; Han, Y.Q.; Yang, C.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Deng, J.W.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, G.H.; et al. Prognostic and predictive values of immune infiltrate in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 82, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ruiter, E.J.; Ooft, M.L.; Devriese, L.A.; Willems, S.M. The prognostic role of tumor infiltrating T-lymphocytes in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1356148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.S., Jr. Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma in 2020: Where Are We Now and Where Are We Going? Head Neck Pathol. 2020, 14, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, T.; Wong, D.T.W. Liquid Biopsy in Head and Neck Cancer: Promises and Challenges. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economopoulou, P.; Kotsantis, I.; Kyrodimos, E.; Lianidou, E.S.; Psyrri, A. Liquid biopsy: An emerging prognostic and predictive tool in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). Focus on Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs). Oral Oncol. 2017, 74, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, K.; Spruce, R.; Beggs, A.; Sharma, N.; Kong, A.; Martin, T.; Parmar, S.; Praveen, P.; Nankivell, P.; Mehanna, H. Circulating tumor DNA as a biomarker and liquid biopsy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2018, 40, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Dai, Y.; Hu, G. High pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of poor survival prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, T.; Bardash, Y.; Herman, S.W.; Costantino, P.D. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic indicator in head and neck cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2018, 40, 2546–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taube, J.M. Emerging immunologic biomarkers: Setting the (TNM-immune) stage. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2023–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkinen, I.; Bello, I.O.; Wahab, A.; Hagstrom, J.; Haglund, C.; Coletta, R.D.; Nieminen, P.; Makitie, A.A.; Salo, T.; Leivo, I.; et al. Assessment of Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes Predicts the Behavior of Early-stage Oral Tongue Cancer. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 1392–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almangush, A.; Ruuskanen, M.; Hagstrom, J.; Hirvikoski, P.; Tommola, S.; Kosma, V.M.; Nieminen, P.; Makitie, A.; Leivo, I. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes associate with outcome in nonendemic nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A multicenter study. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 81, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Jouhi, L.; Atula, T.; Haglund, C.; Makitie, A.A.; Hagstrom, J.; Leivo, I. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in oropharyngeal cancer: A validation study according to the criteria of the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almangush, A.; Bello, I.O.; Heikkinen, I.; Hagstrom, J.; Haglund, C.; Kowalski, L.P.; Coletta, R.D.; Makitie, A.A.; Salo, T.; Leivo, I. Improving Risk Stratification of Early Oral Tongue Cancer with TNM-Immune (TNM-I) Staging System. Cancers 2021, 13, 3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markwell, S.M.; Weed, S.A. Tumor and stromal-based contributions to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma invasion. Cancers 2015, 7, 382–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Liu, J.; Yang, G.; Li, Y. The tumor-stromal ratio as a strong prognosticator for advanced gastric cancer patients: Proposal of a new TSNM staging system. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yuan, J.P.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, L.W.; Xiong, B. Prognostic Significance of the Tumor-Stromal Ratio in Invasive Breast Cancer and a Proposal of a New Ts-TNM Staging System. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 9050631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Li, D.; Liu, B.; Rao, J.; Meng, H.; Lin, W.; Fan, T.; Hao, B.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; et al. The prognostic value of tumor-stromal ratio combined with TNM staging system in esophagus squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugli, A.; Zlobec, I.; Berger, M.D.; Kirsch, R.; Nagtegaal, I.D. Tumour budding in solid cancers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigore, A.D.; Jolly, M.K.; Jia, D.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Levine, H. Tumor Budding: The Name is EMT. Partial EMT. J Clin Med 2016, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smedt, L.; Palmans, S.; Andel, D.; Govaere, O.; Boeckx, B.; Smeets, D.; Galle, E.; Wouters, J.; Barras, D.; Suffiotti, M.; et al. Expression profiling of budding cells in colorectal cancer reveals an EMT-like phenotype and molecular subtype switching. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawlor, R.T.; Veronese, N.; Nottegar, A.; Malleo, G.; Smith, L.; Demurtas, J.; Cheng, L.; Wood, L.D.; Silvestris, N.; Salvia, R.; et al. Prognostic Role of High-Grade Tumor Budding in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with a Focus on Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. Cancers 2019, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, N.; Liu, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, C.; Hou, J. Impact of tumor budding in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Head Neck 2019, 41, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elseragy, A.; Salo, T.; Coletta, R.D.; Kowalski, L.P.; Haglund, C.; Nieminen, P.; Makitie, A.A.; Leivo, I.; Almangush, A. A Proposal to Revise the Histopathologic Grading System of Early Oral Tongue Cancer Incorporating Tumor Budding. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxberg, M.; Jesinghaus, M.; Dorfner, C.; Mogler, C.; Drecoll, E.; Warth, A.; Steiger, K.; Bollwein, C.; Meyer, P.; Wolff, K.D.; et al. Tumor budding activity and cell nest size determine patient outcome in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Proposal for an adjusted grading system. Histopathology 2017, 70, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxberg, M.; Kuhn, P.H.; Reiser, M.; Erb, A.; Steiger, K.; Pickhard, A.; Strassen, U.; Koob, I.; Kolk, A.; Warth, A.; et al. Tumor Budding and Cell Nest Size Are Highly Prognostic in Laryngeal and Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Further Evidence for a Unified Histopathologic Grading System for Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Upper Aerodigestive Tract. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brcic, I.; Gallob, M.; Schwantzer, G.; Zrnc, T.; Weiland, T.; Thurnher, D.; Wolf, A.; Brcic, L. Concordance of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, PD-L1 and p16 expression in small biopsies, resection and lymph node metastases of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2020, 106, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, I.O.; Wennerstrand, P.M.; Suleymanova, I.; Siponen, M.; Qannam, A.; Nieminen, P.; Leivo, I.; Almangush, A.; Salo, T. Biopsy quality is essential for preoperative prognostication in oral tongue cancer. APMIS 2020, 129, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalker, C.; Voutsinas, J.M.; Wu, Q.V.; Santana-Davila, R.; Hwang, V.; Baik, C.S.; Lee, S.; Barber, B.; Futran, N.D.; Houlton, J.J.; et al. Performance status (PS) as a predictor of poor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancer (RMHNSCC) patients. Cancer Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.S.; Kim, S.; Tighiouart, M.; Gudino, C.; Mita, A.; Scher, K.S.; Laury, A.; Prasad, R.; Shiao, S.L.; Van Eyk, J.E.; et al. Metastatic Lymph Node Burden and Survival in Oral Cavity Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3601–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.S.; Kim, S.; Tighiouart, M.; Gudino, C.; Mita, A.; Scher, K.S.; Laury, A.; Prasad, R.; Shiao, S.L.; Ali, N.; et al. Association of Quantitative Metastatic Lymph Node Burden With Survival in Hypopharyngeal and Laryngeal Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kort, W.W.B.; Maas, S.L.N.; Van Es, R.J.J.; Willems, S.M. Prognostic value of the nodal yield in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review. Head Neck 2019, 41, 2801–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.K.; Chan, J.K.C.; Grandis, J.R.; Takata, T.; Slootweg, P.J. WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours, 4th ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Boxberg, M.; Bollwein, C.; Johrens, K.; Kuhn, P.H.; Haller, B.; Steiger, K.; Wolff, K.D.; Kolk, A.; Jesinghaus, M.; Weichert, W. Novel prognostic histopathological grading system in oral squamous cell carcinoma based on tumour budding and cell nest size shows high interobserver and intraobserver concordance. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 72, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galon, J.; Bruni, D. Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination immunotherapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisheshar, S.K.; De Ruiter, E.J.; Devriese, L.A.; Willems, S.M. The prognostic role of NK cells and their ligands in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1747345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, J.P.; Sanchez-Canteli, M.; Lopez, F.; Wolf, G.T.; Hernandez-Prera, J.C.; Williams, M.D.; Willems, S.M.; Franchi, A.; Coca-Pelaz, A.; Ferlito, A. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in the Tumor Microenvironment of Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsetto, D.; Tomasoni, M.; Payne, K.; Polesel, J.; Deganello, A.; Bossi, P.; Tysome, J.R.; Masterson, L.; Tirelli, G.; Tofanelli, M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of CD4+ and CD8+ Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finck, A.; Gill, S.I.; June, C.H. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age and looks for maturity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Wang, Y.Q.; Lv, J.W.; Li, Y.Q.; Chua, M.L.K.; Le, Q.T.; Lee, N.; Colevas, A.D.; Seiwert, T.; Hayes, D.N.; et al. Identification and validation of novel microenvironment-based immune molecular subgroups of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Implications for immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Fridman, W.H.; Galon, J. The prognostic impact of anti-cancer immune response: A novel classification of cancer patients. Semin. Immunopathol. 2011, 33, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).