Analysis of Lenvatinib’s Efficacy against Intermediate-Stage Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Definition of TACE-Refractory and -Unsuitable
2.3. Lenvatinib Treatment Regimens
2.4. Assessment of Response to Lenvatinib
2.5. Lenvatinib-TACE Sequential Therapy
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Participating Patients
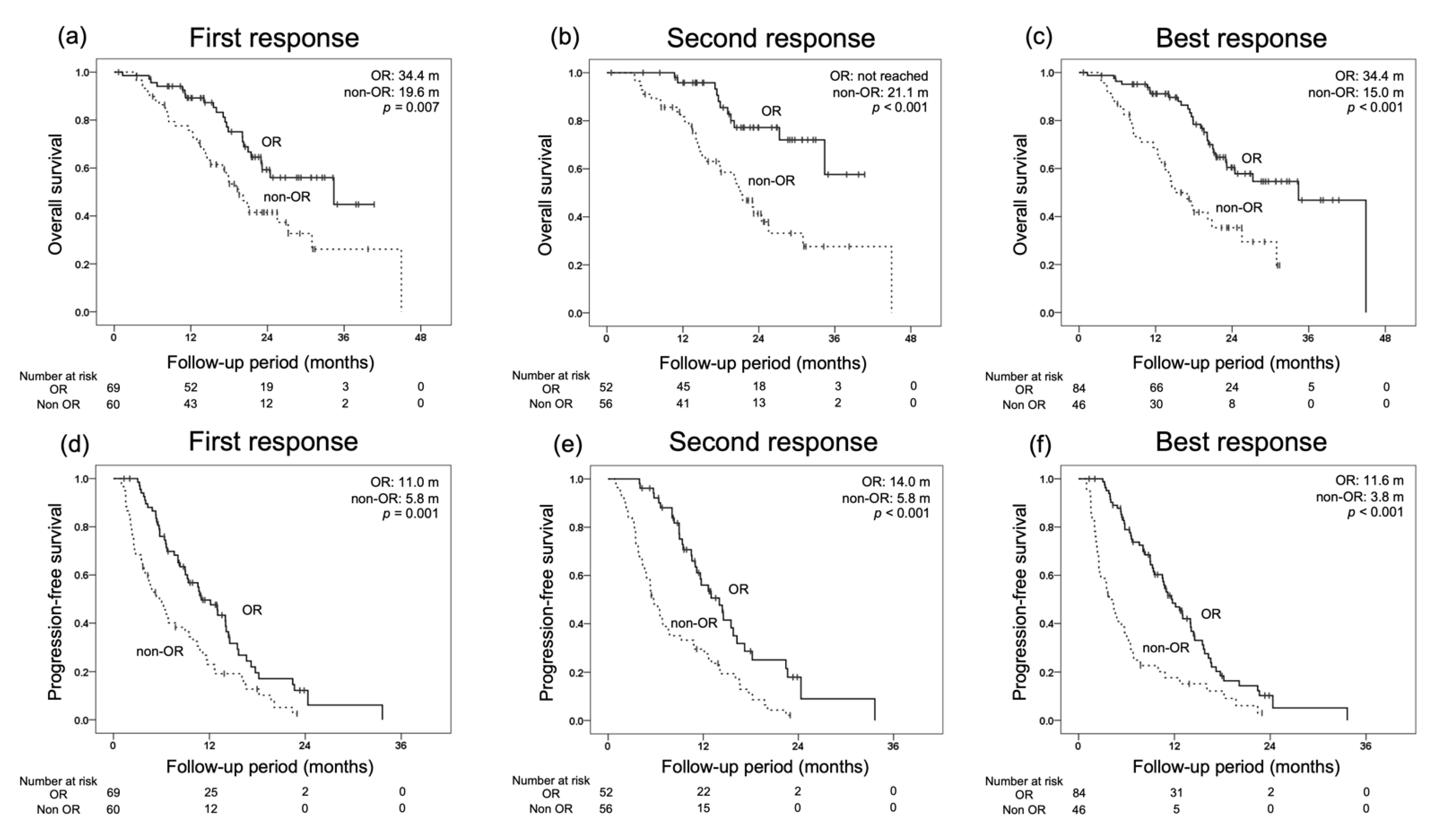
3.2. Treatment Response and Survival
3.3. OS for Each Initial Radiological Response and Prognostic Factors for OS
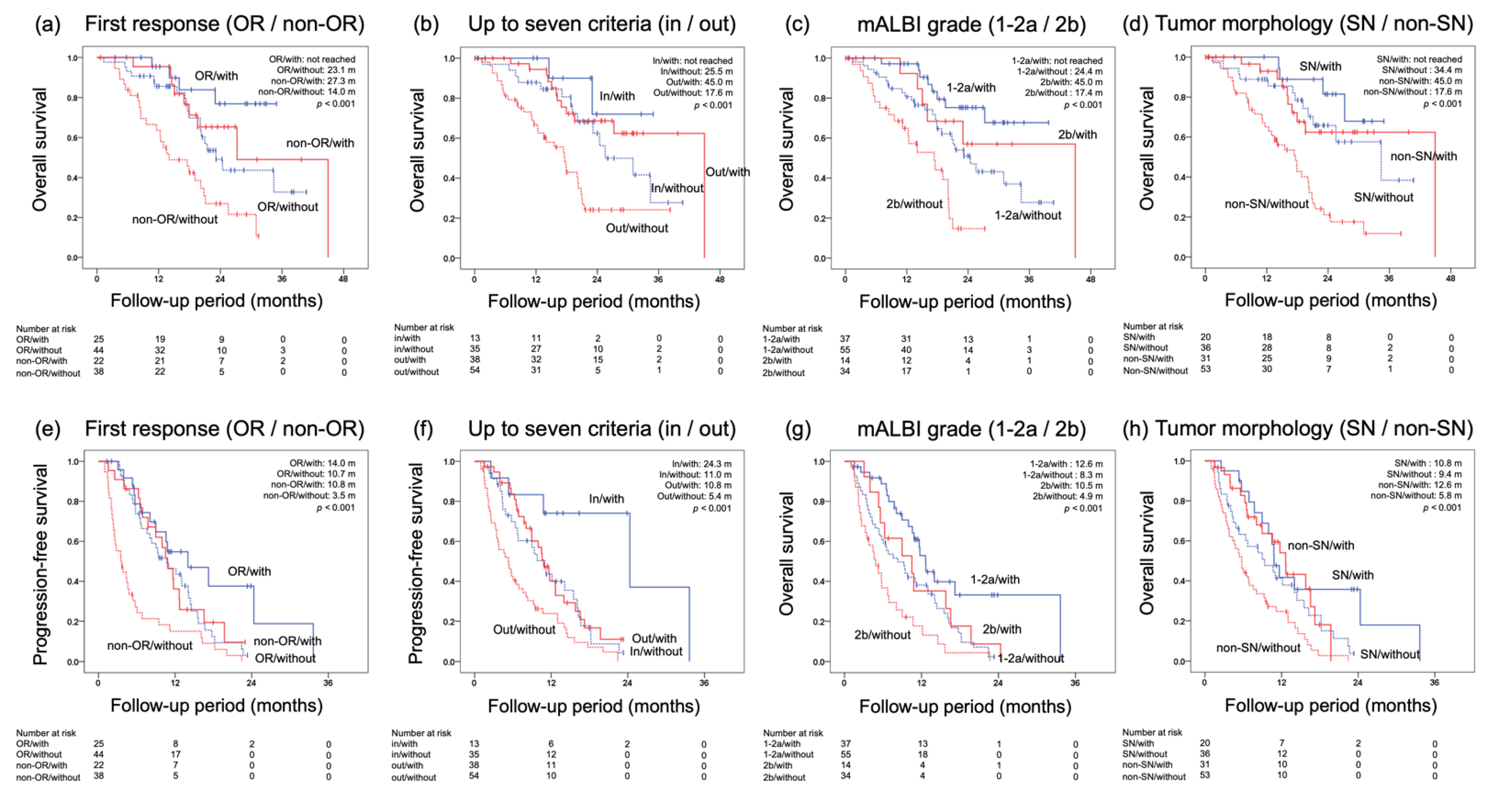
3.4. Prognostic Factors for OS and PFS
3.5. Lenvatinib in Combination with TACE
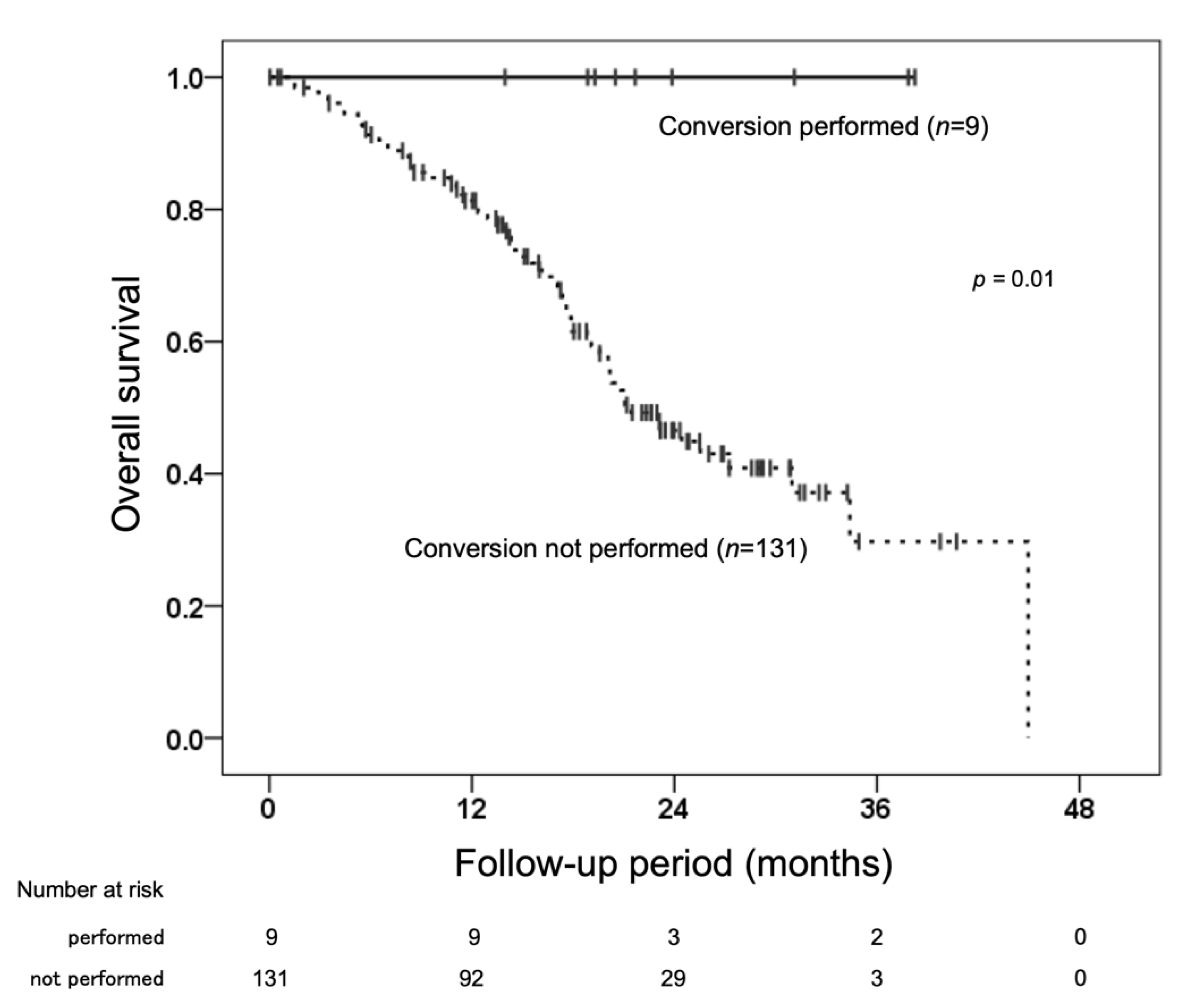
3.6. Conversion Therapy after Initiation of Lenvatinib
3.7. Subsequent Therapy after Lenvatinib
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Galle, P.R.; Llovet, J.M.; Kudo, M. Ramucirumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in REACH-2: The true value of alpha-fetoprotein. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.W.; et al. Cabozantinib in patients with advanced and progressing hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Qin, S. Atezolizumab and bevacizumab for hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanism, pharmacokinetics and future treatment strategies. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 2243–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Tateishi, R.; Yamashita, T.; Ikeda, M.; Furuse, J.; Ikeda, K.; Kokudo, N.; Izumi, N.; Matsui, O. Current status of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment in Japan: Case study and discussion-voting system. Clin. Drug Investig. 2012, 32 (Suppl. S2), 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Matsui, O.; Izumi, N.; Iijima, H.; Kadoya, M.; Imai, Y.; Okusaka, T.; Miyayama, S.; Tsuchiya, K.; Ueshima, K.; et al. JSH consensus-based clinical practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2014 update by the Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan. Liver Cancer 2014, 3, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Han, K.-H.; Ye, S.-L.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, S.-M.; Wang, C.-K.; Ikeda, M.; Chan, S.L.; Choo, S.P.; et al. A Changing Paradigm for the Treatment of Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Asia-Pacific Primary Liver Cancer Expert Consensus Statements. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japanese Society of Hepatology. Clinical Practice Manual for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, 4th ed.; IGAKU-SHOIN Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2020; pp. 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, A.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Kudo, M.; Raoul, J.-L.; Lee, H.C.; Decaens, T.; Heo, J.; Lin, S.-M.; Shan, H.; Yang, Y.; Bayh, I.; et al. Outcomes of patients (pts) with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treated with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE): Global OPTIMIS final analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Tsuji, K.; Takaguchi, K.; Itobayashi, E.; Kariyama, K.; Ochi, H.; Tajiri, K.; Hirooka, M.; Shimada, N.; et al. Validation of modified ALBI grade for more detailed assessing hepatic function of hepatocellular carcinoma—Multicenter analysis. Liver Cancer 2019, 8, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Llovet, J.M.; Miceli, R.; Bhoori, S.; Schiavo, M.; Mariani, L.; Camerini, T.; Roayaie, S.; Schwartz, M.E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Predicting survival after liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria: A retrospective, exploratory analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, L.H.; Seymour, L.; Litière, S.; Ford, R.; Gwyther, S.; Mandrekar, S.; Shankar, L.; Bogaerts, J.; Chen, A.; Dancey, J.; et al. RECIST 1.1-Standardisation and disease-specific adaptations: Perspectives from the RECIST Working Group. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 62, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Kawaoka, T.; Amioka, K.; Naruto, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Kikukawa, C.; Kosaka, Y.; Uchikawa, S.; Morio, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of lenvatinib-transcatheter arterial chemoembolization sequential therapy for patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 2021, 99, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arizumi, T.; Ueshima, K.; Chishina, H.; Kono, M.; Takita, M.; Kitai, S.; Inoue, T.; Yada, N.; Hagiwara, S.; Minami, Y.; et al. Validation of the criteria of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization failure or refractoriness in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma proposed by the LCSGJ. Oncology 2014, 87 (Suppl. S1), 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arizumi, T.; Ueshima, K.; Minami, T.; Kono, M.; Chishina, H.; Takita, M.; Kitai, S.; Inoue, T.; Yada, N.; Hagiwara, S.; et al. Effectiveness of sorafenib in patients with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) refractory and intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2015, 4, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M. Systemic Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Latest Advances. Cancers 2018, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, S.; Ooka, Y.; Koroki, K.; Maruta, S.; Kanzaki, H.; Kanayama, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Kiyono, S.; Nakamura, M.; Kanogawa, N.; et al. Switching to systemic therapy after locoregional treatment failure: Definition and best timing. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M. A new treatment option for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma with high tumor burden: Initial lenvatinib therapy with subsequent selective TACE. Liver Cancer 2019, 8, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Shindoh, J.; Kobayashi, Y.; Okubo, S.; Tominaga, L.; Kajiwara, A.; Kasuya, K.; Iritani, S.; Fujiyama, S.; et al. Lenvatinib-transarterial chemoembolization sequential therapy as an effective treatment at progression during lenvatinib therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 756–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimose, S.; Iwamoto, H.; Tanaka, M.; Niizeki, T.; Shirono, T.; Noda, Y.; Kamachi, N.; Okamura, S.; Nakano, M.; Suga, H.; et al. Alternating lenvatinib and trans-arterial therapy prolongs overall survival in patients with inter-mediate stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matching study. Cancers 2021, 13, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K. Normalization of tumor vasculature: An emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 2005, 307, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.R.; Komuta, Y.; Iwata, C.; Oka, M.; Shirai, Y.; Morishita, Y.; Ouchi, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Miyazono, K. Comparison of the effects of the kinase inhibitors imatinib, sorafenib, and transforming growth factor- beta receptor inhibitor on extravasation of nanoparticles from neovasculature. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Ueshima, K.; Ikeda, M.; Torimura, T.; Tanabe, N.; Aikata, H.; Izumi, N.; Yamasaki, T.; Noriji, S.; Hino, K.; et al. Randomised, multicentre prospective trial of transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) plus sorafenib as compared with TACE alone in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: TACTICS trial. Gut 2019, 69, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueshima, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Saeki, I.; Morimoto, N.; Aikata, H.; Tanabe, N.; Inaba, Y.; Wada, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Tsuda, M.; et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization therapy in combination strategy with lenvatinib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (TACTICS-L) in Japan: Final analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22 January 2022. Abstract 417. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, K.; Kuroda, H.; Abe, T.; Sato, H.; Kooka, Y.; Oikawa, T.; Sato, A.; Nishiya, M.; Sugai, T.; Takikawa, Y. Two hepatectomy cases for initially unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma after achieving a radiological complete response to sequential therapy with lenvatinib and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Tada, T.; Hirooka, M.; Kariyama, K.; Tani, J.; Atsukawa, M.; Takaguchi, K.; Itobayashi, E.; Fukunishi, S.; et al. Early experience of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma BCLC-B stage patients classified as beyond up to seven criteria—Multicenter analysis. Hepatol. Res. 2022, 52, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Median (Range) or Patients, n |
|---|---|
| Age, range, y | 75 (46–90) |
| Sex (male/female), n | 123/17 |
| Weight (<60/≥60 kg), n | 58/82 |
| Performance status (0/1), n | 128/12 |
| Etiology (HBV/HCV/NBNC), n | 14/50/76 |
| Total bilirubin, range, mg/dL | 0.7 (0.3–2.4) |
| Albumin, range, g/dL | 3.8 (2.7–4.8) |
| Prothrombin activity, range, % | 90 (59–129) |
| Child–Pugh score (5/6/7), n | 89/42/9 |
| mALBI grade (1/2a/2b), n | 58/34/48 |
| Size of main tumor, range, mm | 26.0 (8.0–130.0) |
| Number of tumors (2–3/4–6//≥7), n | 39/45/56 |
| Relative tumor volume (<50/≥50%), n | 131/9 |
| Tumor morphology (SN type/non-SN type), n | 56/84 |
| Serum AFP value, range, ng/mL | 16.1 (0.9–84001.6) |
| Serum DCP value, range, mAU/mL | 175.5 (13.0–93112.0) |
| Up to seven criteria (in/out), n | 48/92 |
| History of systemic treatment (with/without), n | 22/118 |
| Number of previous TACE procedure beforelenvatinib (0/1-2//≥3), n | 37/40/63 |
| TACE-refractory or unsuitable(refractory/unsuitable/refractory plus unsuitable/without), n | 10/49/74/7 |
| Lenvatinib followed by TACE (with/without), n | 51/89 |
| Observation period, range, months | 17.7 (1.0–45.0) |
| RECIST % (n) | mRECIST % (n) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best | 1st | 2nd | Best | 1st | 2nd | |
| CR | 5.0 (7) | 3.6 (5) | 2.1 (3) | 21.4 (30) | 11.4 (16) | 13.6 (19) |
| PR | 35.0 (49) | 22.1 (31) | 19.3 (27) | 38.6 (54) | 37.9 (53) | 23.6 (33) |
| SD | 39.3 (55) | 52.1 (73) | 36.4 (51) | 17.1 (24) | 25.7 (36) | 18.6 (26) |
| PD | 16.4 (23) | 17.9 (25) | 22.9 (32) | 15.7 (22) | 17.1 (24) | 21.4 (30) |
| NE | 4.3 (6) | 4.3 (6) | 19.3 (27) | 7.1 (10) | 7.9 (11) | 22.9 (32) |
| ORR | 40.0 (56) | 25.7 (36) | 21.4 (30) | 60.0 (84) | 49.3 (69) | 37.1 (52) |
| DCR | 79.3 (111) | 77.9 (109) | 57.9 (81) | 77.1 (108) | 75.0 (105) | 55.7 (78) |
| Factors for Overall Survival | Univariate p-Value | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Sex (male vs. female) | 0.580 | |||
| Etiology (NBNC vs. viral) | 0.066 | |||
| Performance status (0 vs. 1) | 0.040 | 1.652 | 0.713–3.831 | 0.242 |
| mALBI grade (1/2a vs. 2b) | 0.002 | 1.998 | 1.149–3.476 | 0.014 |
| Up to seven criteria (in vs. out) | 0.046 | 1.220 | 0.632-2.354 | 0.553 |
| Relative tumor volume (<50% vs. ≥50%) | 0.045 | 1.026 | 0.396–2.653 | 0.958 |
| Serum AFP value (<400 vs. ≥400), ng/mL | 0.025 | 1.751 | 0.933–3.286 | 0.081 |
| Tumor morphology (SN type vs. non-SN type) | <0.001 | 2.105 | 1.093-4.052 | 0.026 |
| History of systemic treatment (without vs. with) | 0.038 | 1.395 | 0.734–2.652 | 0.309 |
| TACE-refractory or unsuitable (with vs. without) | 0.244 | |||
| Factors for Progression-Free Survival | Univariate p-Value | Multivariate | ||
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Sex (male vs. female) | 0.235 | |||
| Etiology (NBNC vs. viral) | 0.992 | |||
| Performance status (0 vs. 1) | 0.063 | |||
| mALBI grade (1/2a vs. 2b) | 0.003 | 1.696 | 1.141–2.521 | 0.009 |
| Up to seven criteria (in vs. out) | 0.006 | 1.706 | 1.080–2.695 | 0.022 |
| Relative tumor volume (<50% vs. ≥50%) | 0.343 | |||
| Serum AFP value (<400 vs. ≥400), ng/mL | 0.933 | |||
| Tumor morphology (SN type vs. non-SN type) | 0.025 | 1.270 | 0.825–1.957 | 0.277 |
| History of systemic treatment (without vs. with) | 0.108 | |||
| TACE-refractory or unsuitable (with vs. without) | 0.050 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amioka, K.; Kawaoka, T.; Kinami, T.; Yamasaki, S.; Kosaka, M.; Johira, Y.; Yano, S.; Naruto, K.; Ando, Y.; Fujii, Y.; et al. Analysis of Lenvatinib’s Efficacy against Intermediate-Stage Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205066
Amioka K, Kawaoka T, Kinami T, Yamasaki S, Kosaka M, Johira Y, Yano S, Naruto K, Ando Y, Fujii Y, et al. Analysis of Lenvatinib’s Efficacy against Intermediate-Stage Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2022; 14(20):5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205066
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmioka, Kei, Tomokazu Kawaoka, Takahiro Kinami, Shintaro Yamasaki, Masanari Kosaka, Yusuke Johira, Shigeki Yano, Kensuke Naruto, Yuwa Ando, Yasutoshi Fujii, and et al. 2022. "Analysis of Lenvatinib’s Efficacy against Intermediate-Stage Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 14, no. 20: 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205066
APA StyleAmioka, K., Kawaoka, T., Kinami, T., Yamasaki, S., Kosaka, M., Johira, Y., Yano, S., Naruto, K., Ando, Y., Fujii, Y., Uchikawa, S., Ono, A., Yamauchi, M., Imamura, M., Kosaka, Y., Ohya, K., Mori, N., Takaki, S., Tsuji, K., ... Oka, S. (2022). Analysis of Lenvatinib’s Efficacy against Intermediate-Stage Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 14(20), 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205066







