Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Accumulation of Natural Killer Cells with Enhanced Lymphotoxin-β Expression during Glioblastoma Progression
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Processing and Analysis
2.2. Visualization of the Data
3. Results
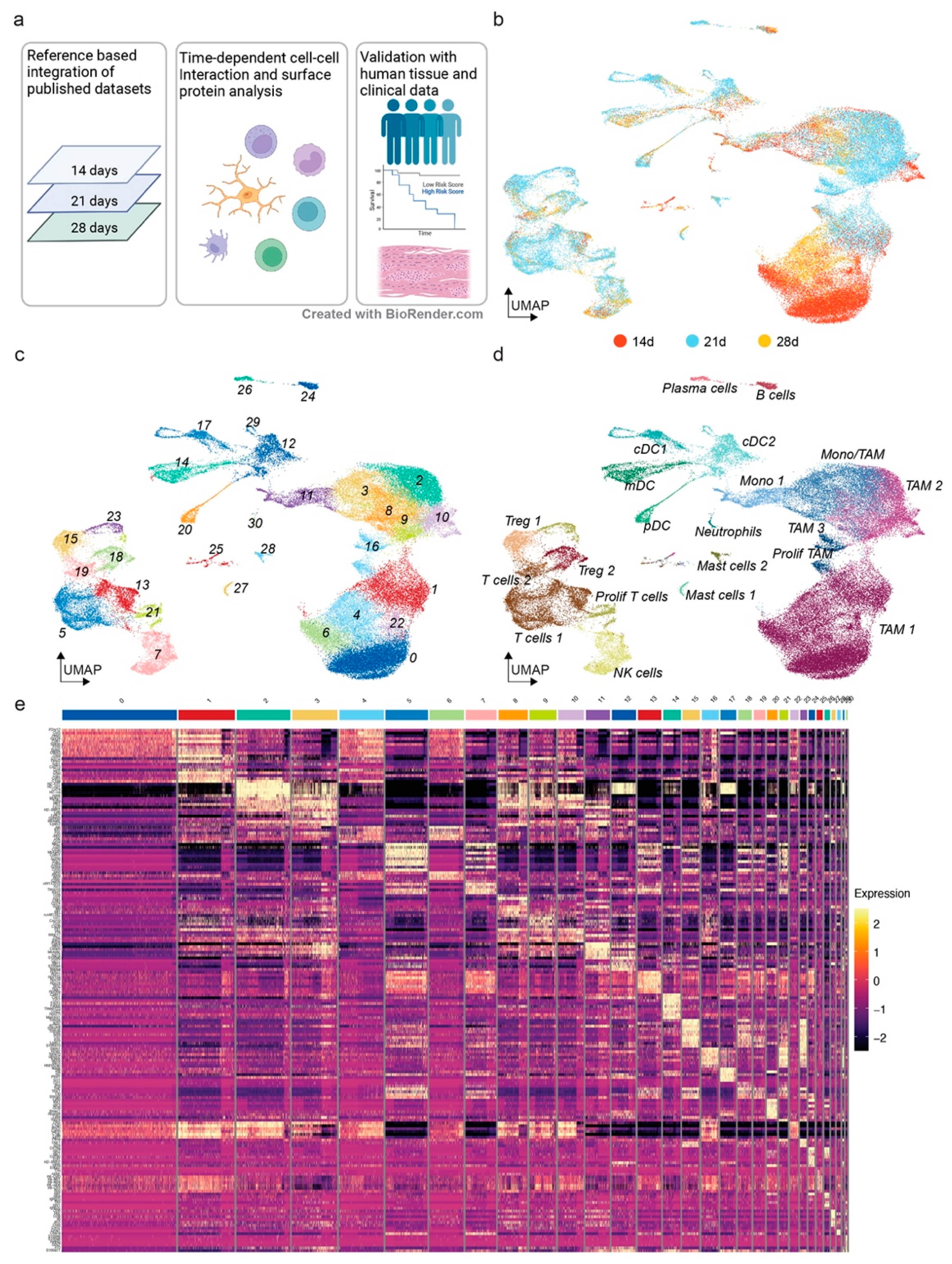
3.1. The Mouse Glioma Model GL261 Shows a Diverse Immune Cell Compartment with Changes throughout Tumor Progression
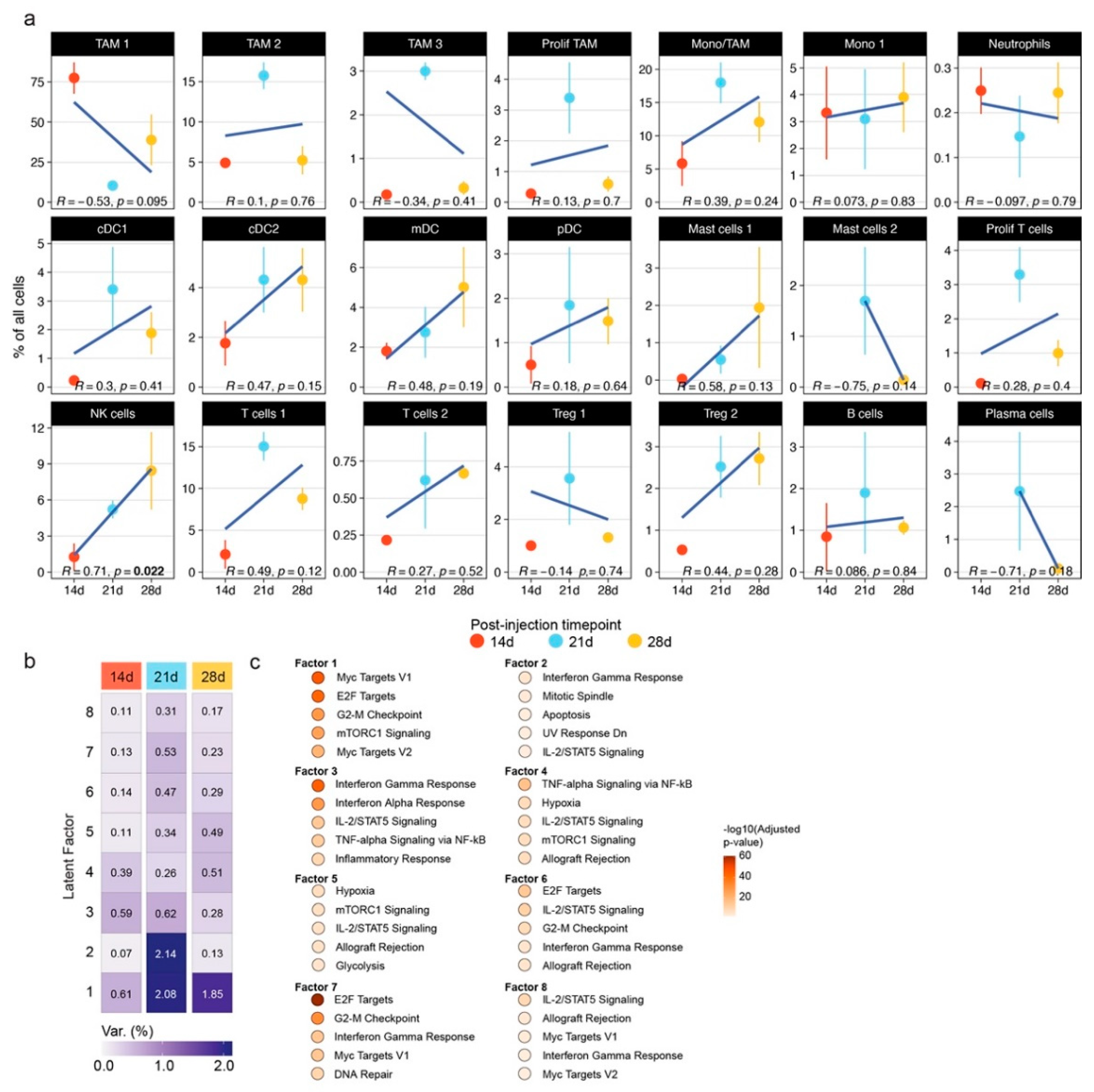
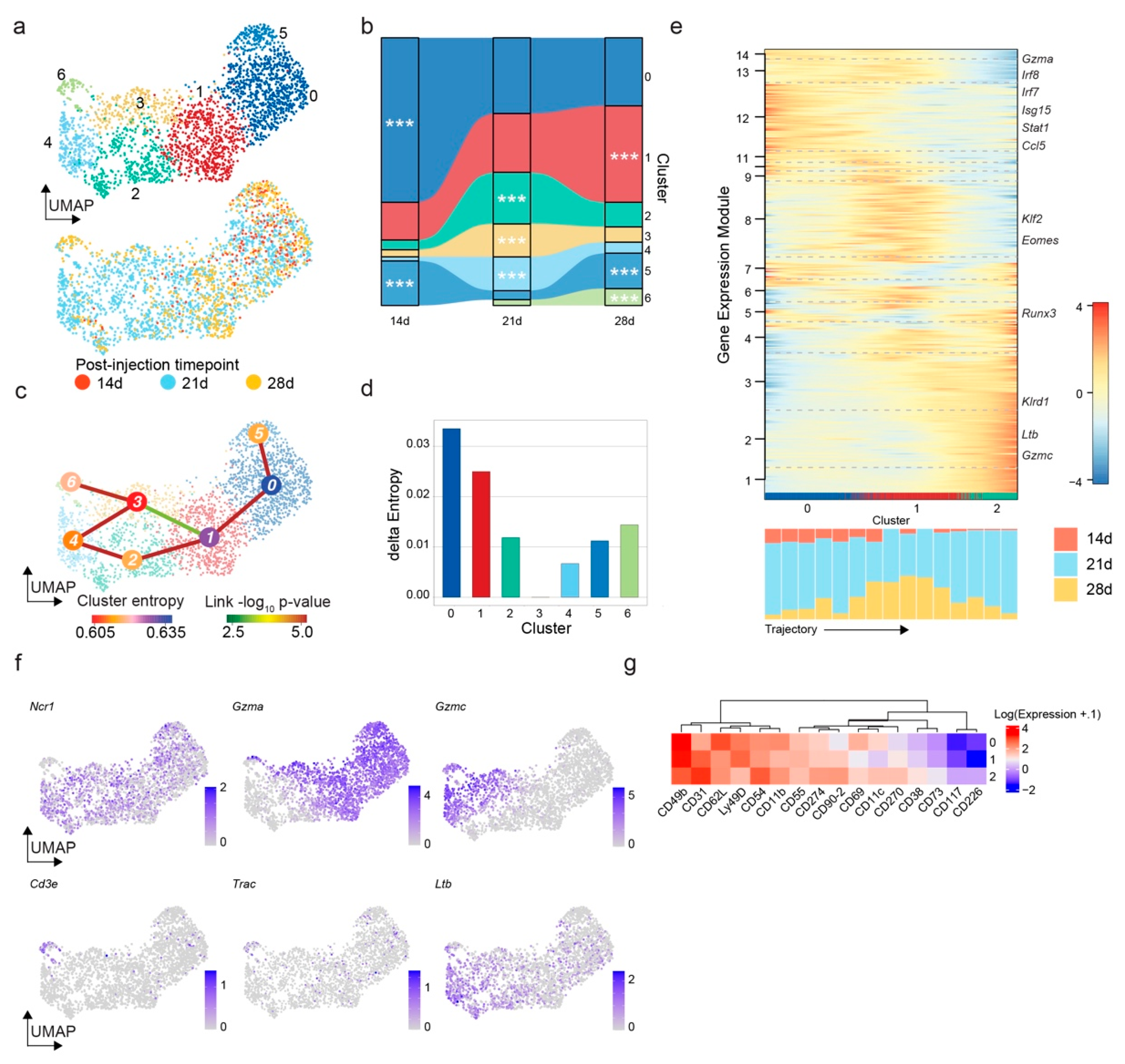
3.2. The Mouse Glioma Model GL261 Shows a Time-Dependent Accumulation of NK Cells with Downregulation of Activation Markers and Enhanced Lymphotoxin-β Expression
3.3. Myeloid Cells Are the Main Putative Ligands for Lymphotoxin-β
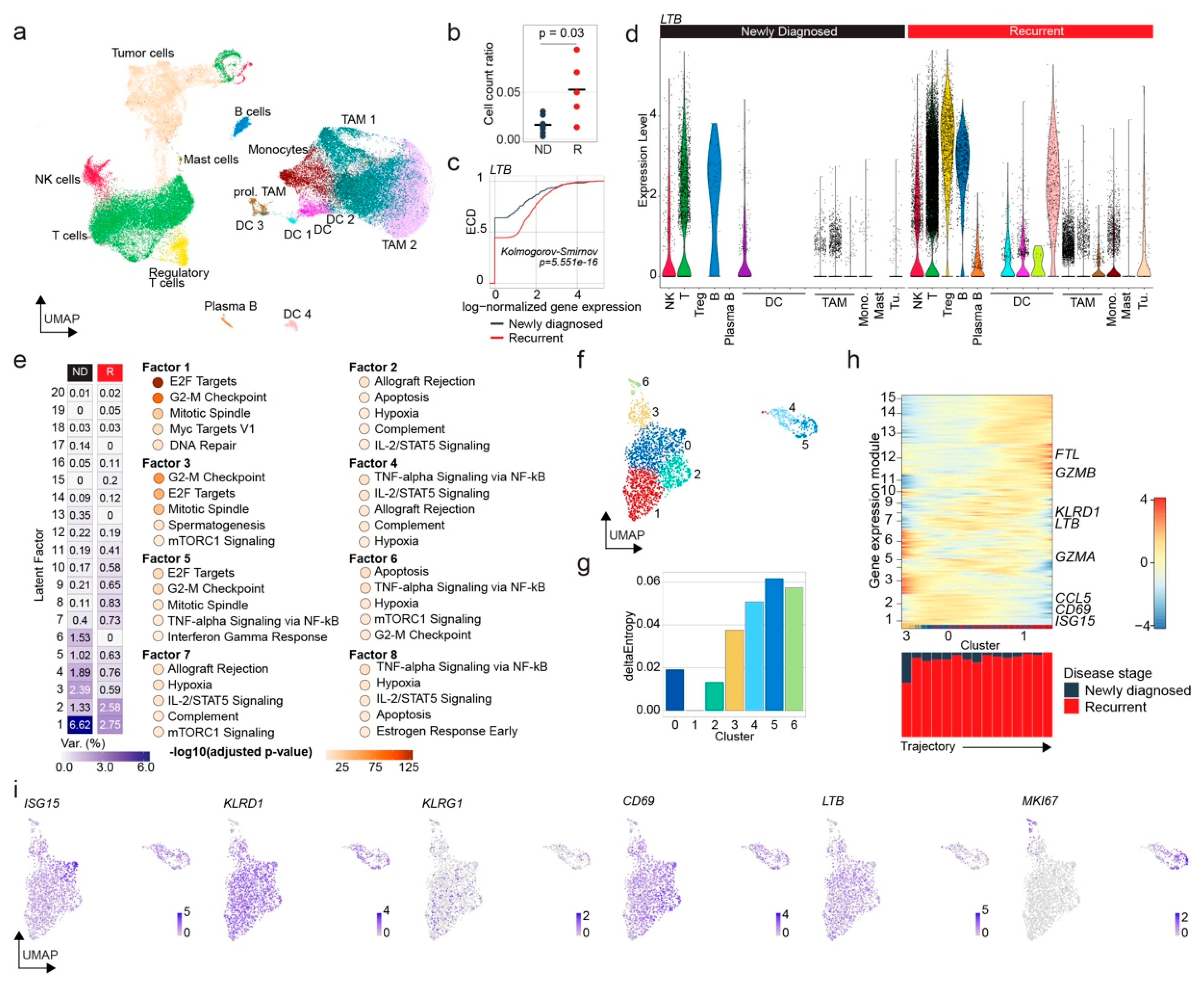
3.4. Human Glioblastoma Progression Is Associated with Dysfunctional NK Cell Accumulation and Enhanced Lymphotoxin-β Expression
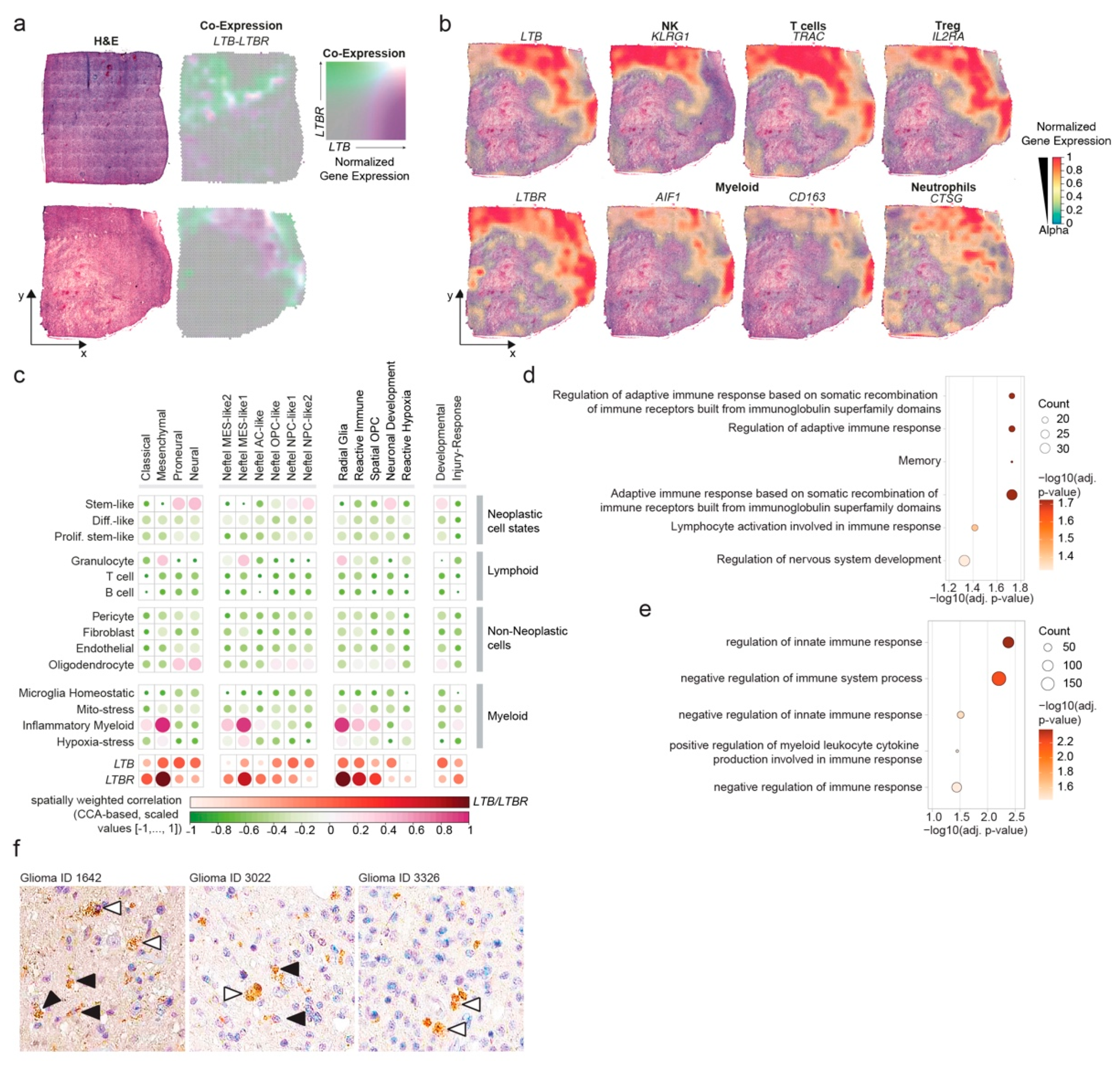
3.5. LTB–LTBR Crosstalk Is Associated with MES-like Regions of Glioblastomas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neftel, C.; Laffy, J.; Filbin, M.G.; Hara, T.; Shore, M.E.; Rahme, G.J.; Richman, A.R.; Silverbush, D.; Shaw, M.L.; Hebert, C.M.; et al. An Integrative Model of Cellular States, Plasticity, and Genetics for Glioblastoma. Cell 2019, 178, 835–849.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couturier, C.P.; Ayyadhury, S.; Le, P.U.; Nadaf, J.; Monlong, J.; Riva, G.; Allache, R.; Baig, S.; Yan, X.; Bourgey, M.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals that glioblastoma recapitulates a normal neurodevelopmental hierarchy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, B.; Hu, X.; Kim, H.; Squatrito, M.; Scarpace, L.; Decarvalho, A.C.; Lyu, S.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; et al. Tumor Evolution of Glioma-Intrinsic Gene Expression Subtypes Associates with Immunological Changes in the Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 42–56.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofano, L.; Migliozzi, S.; Oh, Y.T.; D’Angelo, F.; Najac, R.D.; Ko, A.; Frangaj, B.; Caruso, F.P.; Yu, K.; Yuan, J.; et al. Pathway-based classification of glioblastoma uncovers a mitochondrial subtype with therapeutic vulnerabilities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 2, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramani, V.; Yang, Y.; Schubert, M.C.; Reyhan, E.; Tetzlaff, S.K.; Wißmann, N.; Botz, M.; Soyka, S.J.; Beretta, C.A.; Pramatarov, R.L.; et al. Glioblastoma hijacks neuronal mechanisms for brain invasion. Cell 2022, 185, 2899–2917.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, H.S.; Morishita, W.; Geraghty, A.C.; Silverbush, D.; Gillespie, S.M.; Arzt, M.; Tam, L.T.; Espenel, C.; Ponnuswami, A.; Ni, L.; et al. Electrical and synaptic integration of glioma into neural circuits. Nature 2019, 573, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramani, V.; Tanev, D.I.; Strahle, C.; Studier-Fischer, A.; Fankhauser, L.; Kessler, T.; Körber, C.; Kardorff, M.; Ratliff, M.; Xie, R.; et al. Glutamatergic synaptic input to glioma cells drives brain tumour progression. Nature 2019, 573, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, J.; Behringer, S.P.; Ravi, V.M.; Joseph, K.; Neidert, N.; Maier, J.P.; Doria-Medina, R.; Follo, M.; Delev, D.; Pfeifer, D.; et al. Astrogliosis Releases Pro-Oncogenic Chitinase 3-Like 1 Causing MAPK Signaling in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V.M.; Will, P.; Kueckelhaus, J.; Sun, N.; Joseph, K.; Salié, H.; Vollmer, L.; Kuliesiute, U.; von Ehr, J.; Benotmane, J.K.; et al. Spatially resolved multi-omics deciphers bidirectional tumor-host interdependence in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 639–655.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, H.S.; Kharbanda, S.; Chen, R.; Forrest, W.F.; Soriano, R.H.; Wu, T.D.; Misra, A.; Nigro, J.M.; Colman, H.; Soroceanu, L.; et al. Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis, delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in neurogenesis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, R.; Schüller, U.; Eckhardt, A.; Filipski, K.; Hartung, I.T.; Harter, P.N.; Divé, I.; Forster, M.-T.; Czabanka, M.; Jelgersma, C.; et al. DNA methylation subclasses predict the benefit from gross total tumor resection in IDH-wildtype glioblastoma patients. Neuro-Oncology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.C.; Anderson, K.J.; Courtois, E.T.; Gujar, A.D.; Barthel, F.P.; Varn, F.S.; Luo, D.; Seignon, M.; Yi, E.; Kim, H.; et al. Single-cell multimodal glioma analyses identify epigenetic regulators of cellular plasticity and environmental stress response. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1456–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. The Microenvironmental Landscape of Brain Tumors. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiland, D.H.; Ravi, V.M.; Behringer, S.P.; Frenking, J.H.; Wurm, J.; Joseph, K.; Garrelfs, N.W.C.; Strähle, J.; Heynckes, S.; Grauvogel, J.; et al. Tumor-associated reactive astrocytes aid the evolution of immunosuppressive environment in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangoso, E.; Southgate, B.; Bradley, L.; Rus, S.; Galvez-Cancino, F.; McGivern, N.; Güç, E.; Kapourani, C.-A.; Byron, A.; Ferguson, K.M.; et al. Glioblastomas acquire myeloid-affiliated transcriptional programs via epigenetic immunoediting to elicit immune evasion. Cell 2021, 184, 2454–2470.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, W.; Gordon, R.E.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, Z.J.; Qi, X.; et al. Pro-inflammatory and proliferative microglia drive progression of glioblastoma. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Chanoch-Myers, R.; Mathewson, N.D.; Myskiw, C.; Atta, L.; Bussema, L.; Eichhorn, S.W.; Greenwald, A.C.; Kinker, G.S.; Rodman, C.; et al. Interactions between cancer cells and immune cells drive transitions to mesenchymal-like states in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 779–792.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V.M.; Neidert, N.; Will, P.; Joseph, K.; Maier, J.P.; Kückelhaus, J.; Vollmer, L.; Goeldner, J.M.; Behringer, S.P.; Scherer, F.; et al. T-cell dysfunction in the glioblastoma microenvironment is mediated by myeloid cells releasing interleukin-10. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, A.R.P.; Scheyltjens, I.; Lodi, F.; Messiaen, J.; Antoranz, A.; Duerinck, J.; Kancheva, D.; Martens, L.; De Vlaminck, K.; Van Hove, H.; et al. Single-cell profiling of myeloid cells in glioblastoma across species and disease stage reveals macrophage competition and specialization. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.; Sankowski, R.; Bunse, L.; Kilian, M.; Green, E.; Guevara, C.R.; Pusch, S.; Poschet, G.; Sanghvi, K.; Hahn, M.; et al. Tryptophan metabolism drives dynamic immunosuppressive myeloid states in IDH-mutant gliomas. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmanis, S.; Sloan, S.A.; Croote, D.; Mignardi, M.; Chernikova, S.; Samghababi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Neff, N.; Kowarsky, M.; Caneda, C.; et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis of Infiltrating Neoplastic Cells at the Migrating Front of Human Glioblastoma. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankowski, R.; Böttcher, C.; Masuda, T.; Geirsdottir, L.; Sagar; Sindram, E.; Seredenina, T.; Muhs, A.; Scheiwe, C.; Shah, M.J.; et al. Mapping microglia states in the human brain through the integration of high-dimensional techniques. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 2098–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, M.; Hahn, M.; Michel, J.; Sankowski, R.; Kilian, M.; Kehl, N.; Günter, M.; Bunse, T.; Pusch, S.; von Deimling, A.; et al. Dysfunctional Dendritic Cells Limit Antigen-Specific T Cell Response in Glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2022, noac138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woroniecka, K.I.; Rhodin, K.E.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Keith, K.A.; Fecci, P.E. T-cell Dysfunction in Glioblastoma: Applying a New Framework. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3792–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathewson, N.D.; Ashenberg, O.; Tirosh, I.; Gritsch, S.; Perez, E.M.; Marx, S.; Jerby-Arnon, L.; Chanoch-Myers, R.; Hara, T.; Richman, A.R.; et al. Inhibitory CD161 receptor identified in glioma-infiltrating T cells by single-cell analysis. Cell 2021, 184, 1281–1298.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.C.; Beilke, J.N.; Lanier, L.L. Adaptive immune features of natural killer cells. Nature 2009, 457, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, T.J.; Biederstädt, A.; Rezvani, K. Natural killer cells in antitumour adoptive cell immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 557–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, C.A.; Austgen, K.; Haberthur, K.; Hofmann, C.; Moyes, K.W.; Avanesyan, L.; Fong, L.; Campbell, M.J.; Cooper, S.; Oakes, S.A.; et al. Immune evasion mediated by tumor-derived lactate dehydrogenase induction of NKG2D ligands on myeloid cells in glioblastoma patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12823–12828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaim, H.; Shanley, M.; Basar, R.; Daher, M.; Gumin, J.; Zamler, D.B.; Uprety, N.; Wang, F.; Huang, Y.; Gabrusiewicz, K.; et al. Targeting the αv integrin/TGF-β axis improves natural killer cell function against glioblastoma stem cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; He, K.; Gao, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, F.; An, L.; et al. Circular EZH2-encoded EZH2-92aa mediates immune evasion in glioblastoma via inhibition of surface NKG2D ligands. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochocka, N.; Segit, P.; Walentynowicz, K.A.; Wojnicki, K.; Cyranowski, S.; Swatler, J.; Mieczkowski, J.; Kaminska, B. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals functional heterogeneity of glioma-associated brain macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borelli, A.; Irla, M. Lymphotoxin: From the physiology to the regeneration of the thymic function. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2305–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; Pegg, L.E.; Fütterer, A.; Pfeffer, K.; Fu, Y.-X. Signal Via Lymphotoxin-βR on Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Is Required for an Early Checkpoint of NK Cell Development. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 1684–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Namineni, S.; Reisinger, F.; Zöller, J.; Yuan, D.; Heikenwälder, M. Lymphotoxin, NF-ĸB, and Cancer: The Dark Side of Cytokines. Dig. Dis. 2012, 30, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Shi, L.; Ying, R.S.; Wu, X.Y.; Li, G.Y.; Moorman, J.P.; Yao, Z.Q. KLRG1 Negatively Regulates Natural Killer Cell Functions through the Akt Pathway in Individuals with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11626–11636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Durovic, B.; Lanna, A.; Covre, L.P.; Mills, R.S.; Henson, S.M.; Akbar, A.N. Killer Cell Lectin-like Receptor G1 Inhibits NK Cell Function through Activation of Adenosine 5′-Monophosphate–Activated Protein Kinase. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judge, S.; Murphy, W.J.; Canter, R.J. Characterizing the Dysfunctional NK Cell: Assessing the Clinical Relevance of Exhaustion, Anergy, and Senescence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M., 3rd; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Lee, M.J.; Wilk, A.J.; Darby, C.; Zager, M.; et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573–3587.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsunsky, I.; Millard, N.; Fan, J.; Slowikowski, K.; Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Baglaenko, Y.; Brenner, M.; Loh, P.-R.; Raychaudhuri, S. Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argelaguet, R.; Arnol, D.; Bredikhin, D.; Deloro, Y.; Velten, B.; Marioni, J.C.; Stegle, O. MOFA+: A statistical framework for comprehensive integration of multi-modal single-cell data. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’Ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, D.; Muraro, M.J.; Boisset, J.-C.; Wiebrands, K.; Lyubimova, A.; Dharmadhikari, G.; Born, M.V.D.; van Es, J.; Jansen, E.; Clevers, H.; et al. De Novo Prediction of Stem Cell Identity using Single-Cell Transcriptome Data. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.S.; Sagar; Grün, D. FateID infers cell fate bias in multipotent progenitors from single-cell RNA-seq data. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibar, S.; González-Blas, C.B.; Moerman, T.; Huynh-Thu, V.A.; Imrichova, H.; Hulselmans, G.; Rambow, F.; Marine, J.-C.; Geurts, P.; Aerts, J.; et al. SCENIC: Single-cell regulatory network inference and clustering. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z. Complex heatmap visualization. iMeta 2022, 1, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.A.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires-Afonso, Y.; Muller, A.; Grzyb, K.; Oudin, A.; Yabo, A.Y.; Sousa, C.; Scafidi, A.; Poli, A.; Cosma, A.; Halder, R.; et al. Elucidating tumour-associated microglia/macrophage diversity along glioblastoma progression and under ACOD1 deficiency. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 3167–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankowski, R.; Monaco, G.; Prinz, M. Evaluating microglial phenotypes using single-cell technologies. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 45, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anavy, L.; Levin, M.; Khair, S.; Nakanishi, N.; Fernandez-Valverde, S.L.; Degnan, B.; Yanai, I. BLIND ordering of large-scale transcriptomic developmental timecourses. Development 2014, 141, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, W.; Shimizu, K.; Kojo, S.; Okeke, A.; Kohwi-Shigematsu, T.; Fujii, S.-I.; Taniuchi, I. Runx-mediated regulation of CCL5 via antagonizing two enhancers influences immune cell function and anti-tumor immunity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhu, M.; Qiao, J.; Fu, Y.-X. Lymphotoxin signalling in tertiary lymphoid structures and immunotherapy. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torti, S.V.; Torti, F.M. Iron and cancer: More ore to be mined. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, D.; Bornmann, C.; Chappaz, S.; Schmutz, S.; Otten, L.A.; Ceredig, R.; Acha-Orbea, H.; Finke, D. Ectopic Lymphoid-Organ Development Occurs through Interleukin 7-Mediated Enhanced Survival of Lymphoid-Tissue-Inducer Cells. Immunity 2007, 26, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efremova, M.; Vento-Tormo, M.; Teichmann, S.A.; Vento-Tormo, R. CellPhoneDB: Inferring cell–cell communication from combined expression of multi-subunit ligand–receptor complexes. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1484–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, M.; Barthel, F.P.; Malta, T.M.; Sabedot, T.S.; Salama, S.R.; Murray, B.A.; Morozova, O.; Newton, Y.; Radenbaugh, A.; Pagnotta, S.M.; et al. Molecular Profiling Reveals Biologically Discrete Subsets and Pathways of Progression in Diffuse Glioma. Cell 2016, 164, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Meng, F.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, T. Comprehensive RNA-seq transcriptomic profiling in the malignant progression of gliomas. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaak, R.G.W.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Jill, P.; Alexe, G.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies Clinically Relevant Subtypes of Glioblastoma Characterized by Abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Unterkircher, T.; Kroon, P.; Oldrini, B.; Izzo, A.; Dramaretska, Y.; Ferrarese, R.; Kling, E.; Schnell, O.; Nelander, S.; et al. NF1 regulates mesenchymal glioblastoma plasticity and aggressiveness through the AP-1 transcription factor FOSL1. eLife 2021, 10, e64846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutmann, D.H.; Kettenmann, H. Microglia/Brain Macrophages as Central Drivers of Brain Tumor Pathobiology. Neuron 2019, 104, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eagles, E.M.; Nassiri, F.; Badhiwala, J.H.; Suppiah, S.; Almenawer, A.S.; Zadeh, G.; Aldape, K.D. Dendritic cell vaccines for high-grade gliomas. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 1299–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, S.J.; Desai, A.S.; Linette, G.P.; June, C.H.; O’Rourke, D.M. CAR T-cell therapy for glioblastoma: Recent clinical advances and future challenges. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, D.B.; Anandappa, A.J.; Sun, J.; Tirosh, I.; Mathewson, N.D.; Li, S.; Oliveira, G.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Felt, K.; Gjini, E.; et al. Neoantigen vaccine generates intratumoral T cell responses in phase Ib glioblastoma trial. Nature 2018, 565, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilf, N.; Kuttruff-Coqui, S.; Frenzel, K.; Bukur, V.; Stevanović, S.; Gouttefangeas, C.; Platten, M.; Tabatabai, G.; Dutoit, V.; Van Der Burg, S.H.; et al. Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Nature 2019, 565, 240–245, Erratum in Nature 2019, 566, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.A.; Brandes, A.A.; Omuro, A.; Mulholland, P.; Lim, M.; Wick, A.; Baehring, J.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Roth, P.; Bähr, O.; et al. Effect of Nivolumab vs Bevacizumab in Patients With Recurrent Glioblastoma: The CheckMate 143 Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocchi, K.B.; Miller, C.H.; Cush, S.; Bernard, S.A.; Dull, S.T.; Smith, M.; Gudeman, S.; Varia, M.A. Pilot Study of Local Autologous Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes for the Treatment of Recurrent Malignant Gliomas. J. Neuro-Oncol. 1999, 45, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castriconi, R.; Daga, A.; Dondero, A.; Zona, G.; Poliani, P.L.; Melotti, A.; Griffero, F.; Marubbi, D.; Spaziante, R.; Bellora, F.; et al. NK Cells Recognize and Kill Human Glioblastoma Cells with Stem Cell-Like Properties. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3530–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, T.; Puca, E.; Silginer, M.; Hemmerle, T.; Pazahr, S.; Bink, A.; Weller, M.; Neri, D.; Roth, P. Immunocytokines are a promising immunotherapeutic approach against glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, abb2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.C.; Zhang, C.; Harter, P.N.; Romanski, A.; Strassheimer, F.; Senft, C.; Tonn, T.; Steinbach, J.P.; Wels, W.S. CAR-Engineered NK Cells for the Treatment of Glioblastoma: Turning Innate Effectors Into Precision Tools for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Lu, T.; Li, Z.; Teng, K.-Y.; Mansour, A.G.; Yu, M.; Tian, L.; Xu, B.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; et al. An Oncolytic Virus Expressing IL15/IL15Rα Combined with Off-the-Shelf EGFR-CAR NK Cells Targets Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3635–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almand, B.; Clark, J.I.; Nikitina, E.; Van Beynen, J.; English, N.R.; Knight, S.C.; Carbone, D.P.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Increased Production of Immature Myeloid Cells in Cancer Patients: A Mechanism of Immunosuppression in Cancer. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupedo, T.; Crellin, N.K.; Papazian, N.; Rombouts, E.J.; Weijer, K.; Grogan, J.L.; Fibbe, W.E.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Spits, H. Human fetal lymphoid tissue–inducer cells are interleukin 17–producing precursors to RORC+ CD127+ natural killer–like cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 10, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratz, A.; Campos-Neto, A.; Hanson, M.S.; Ruddle, N.H. Chronic inflammation caused by lymphotoxin is lymphoid neogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1461–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnan, J.; Isakson, P.; Joel, M.; Cilio, C.; Langmoen, I.A.; Vik-Mo, E.O.; Badn, W. Recruited Brain Tumor-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Contribute to Brain Tumor Progression. Stem Cells 2013, 32, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, S.; Zhu, Q.; Saadatpour, A.; Fei, L.; Guo, G.; Yuan, G.-C. Revealing the Critical Regulators of Cell Identity in the Mouse Cell Atlas. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 1436–1445.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monaco, G.; Khavaran, A.; Gasull, A.D.; Cahueau, J.; Diebold, M.; Chhatbar, C.; Friedrich, M.; Heiland, D.H.; Sankowski, R. Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Accumulation of Natural Killer Cells with Enhanced Lymphotoxin-β Expression during Glioblastoma Progression. Cancers 2022, 14, 4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194915
Monaco G, Khavaran A, Gasull AD, Cahueau J, Diebold M, Chhatbar C, Friedrich M, Heiland DH, Sankowski R. Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Accumulation of Natural Killer Cells with Enhanced Lymphotoxin-β Expression during Glioblastoma Progression. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194915
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonaco, Gianni, Ashkan Khavaran, Adrià Dalmau Gasull, Jonathan Cahueau, Martin Diebold, Chintan Chhatbar, Mirco Friedrich, Dieter Henrik Heiland, and Roman Sankowski. 2022. "Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Accumulation of Natural Killer Cells with Enhanced Lymphotoxin-β Expression during Glioblastoma Progression" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194915
APA StyleMonaco, G., Khavaran, A., Gasull, A. D., Cahueau, J., Diebold, M., Chhatbar, C., Friedrich, M., Heiland, D. H., & Sankowski, R. (2022). Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Accumulation of Natural Killer Cells with Enhanced Lymphotoxin-β Expression during Glioblastoma Progression. Cancers, 14(19), 4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194915






