Microglia-Based Gene Expression Signature Highly Associated with Prognosis in Low-Grade Glioma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Utilized in this Study
2.2. Curation of Immune-Related Genes (IRGs)
2.3. Immune Cell Inference
2.4. Generation of Microglia Signatures
2.5. Lasso Cox Regression
2.6. Survival Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analyses
2.8. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. Immune-Related Genes (IRGs) Are Negatively Associated with Prognosis in Glioma
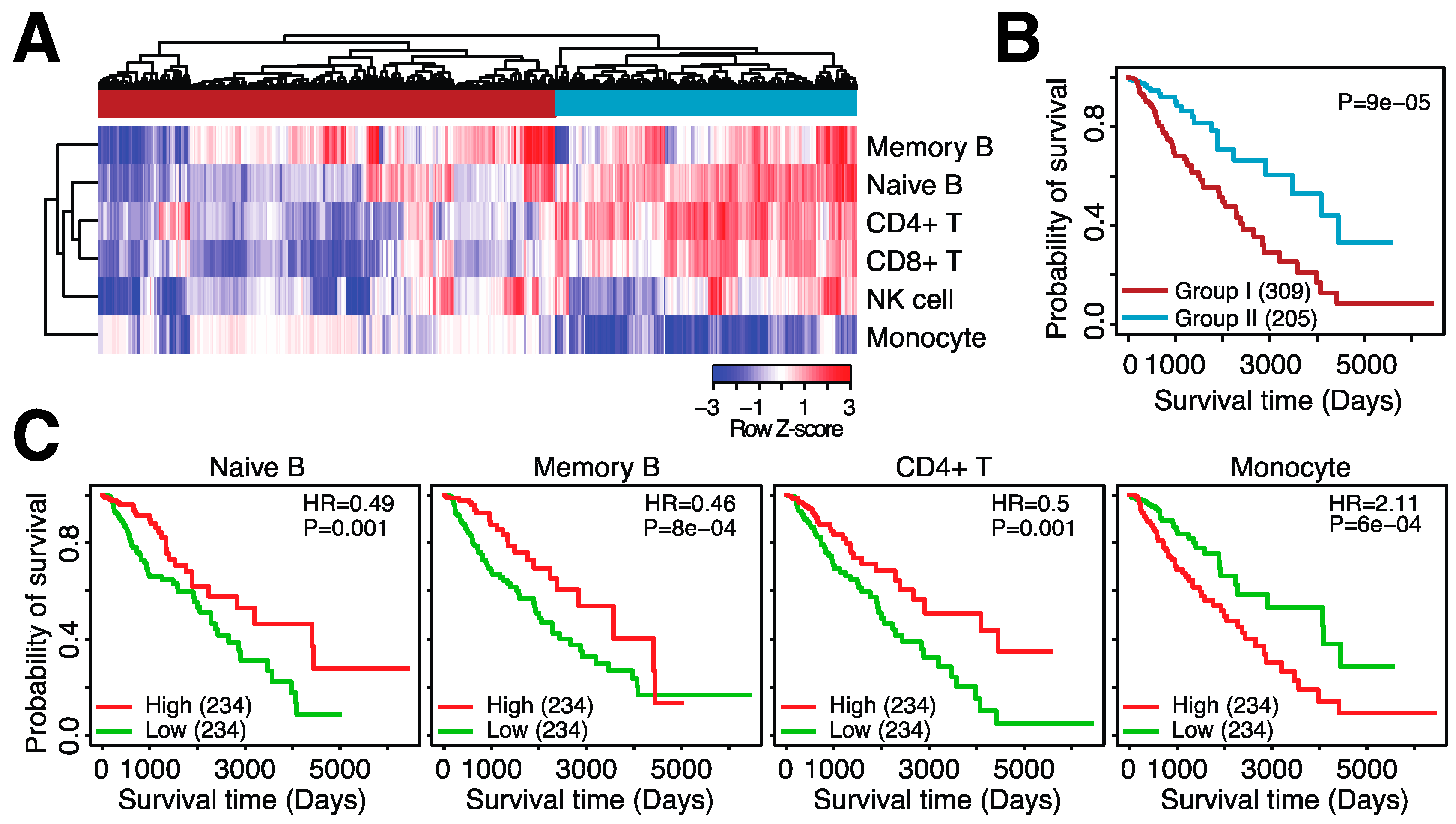
3.2. Microglia Abundance Is Negatively Associated with Prognosis in Glioma
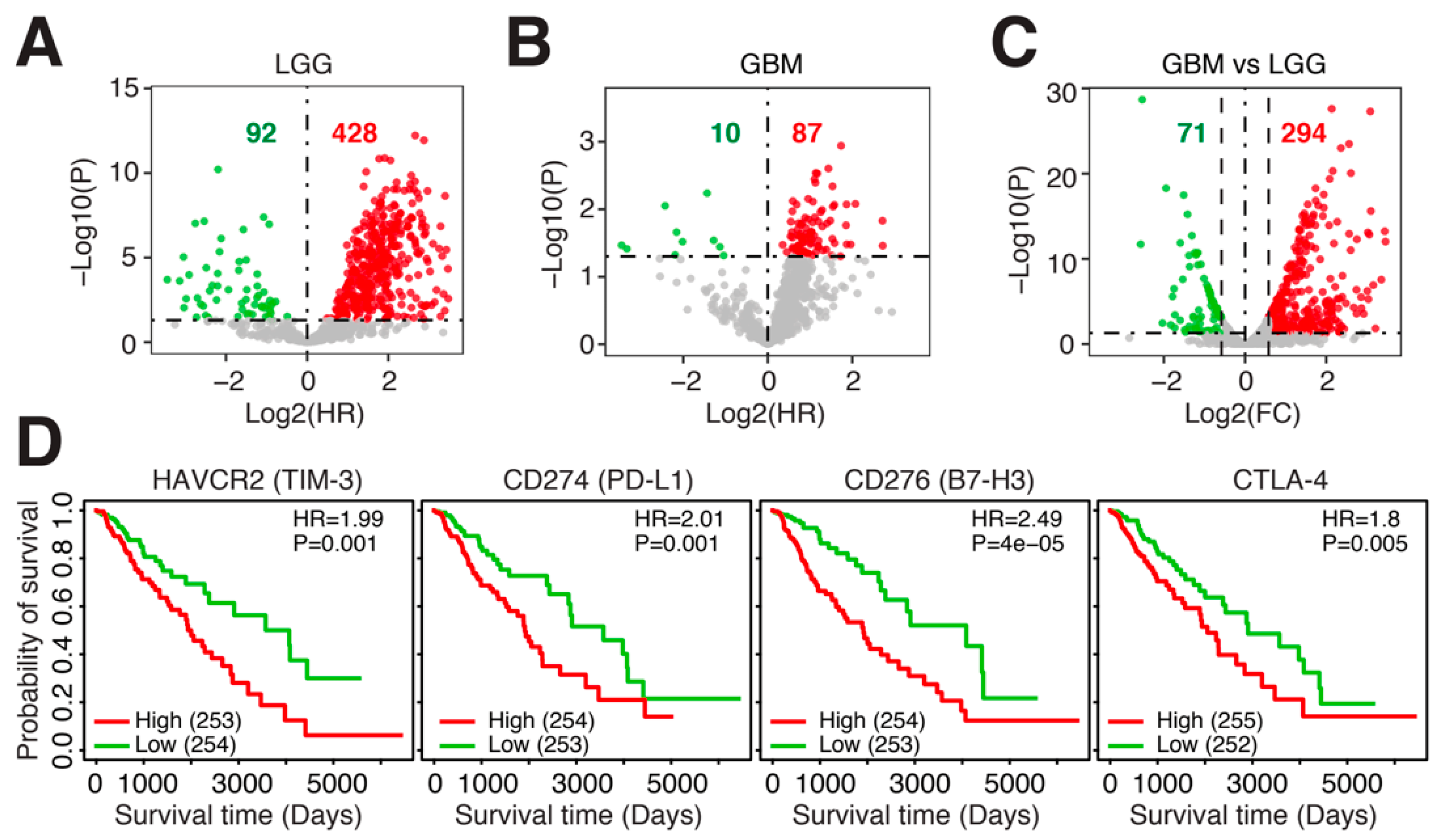
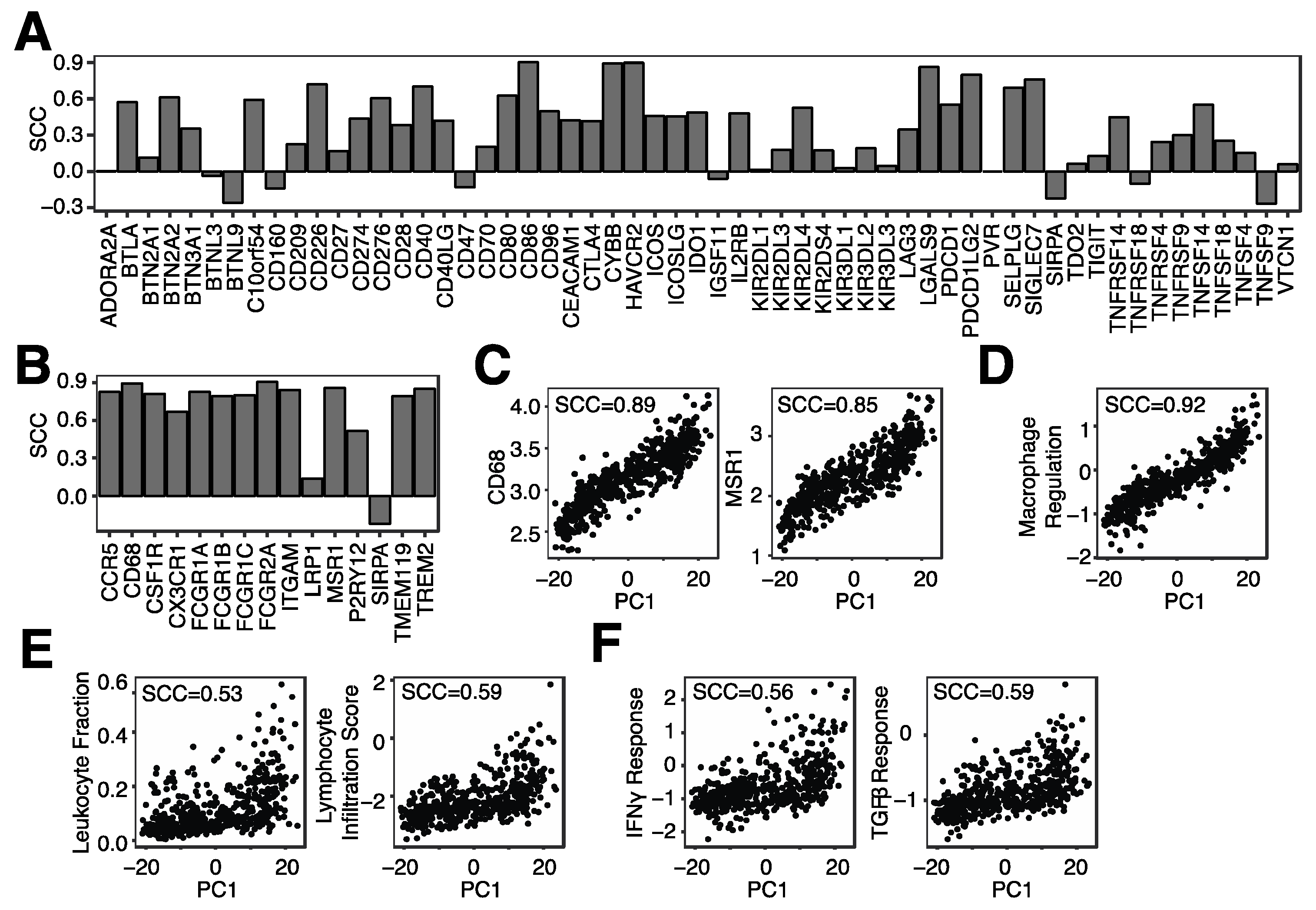
3.3. Microglia Infiltration Is Associated with the mRNA Expression of Immune Checkpoint Genes and Immune Regulatory Pathways
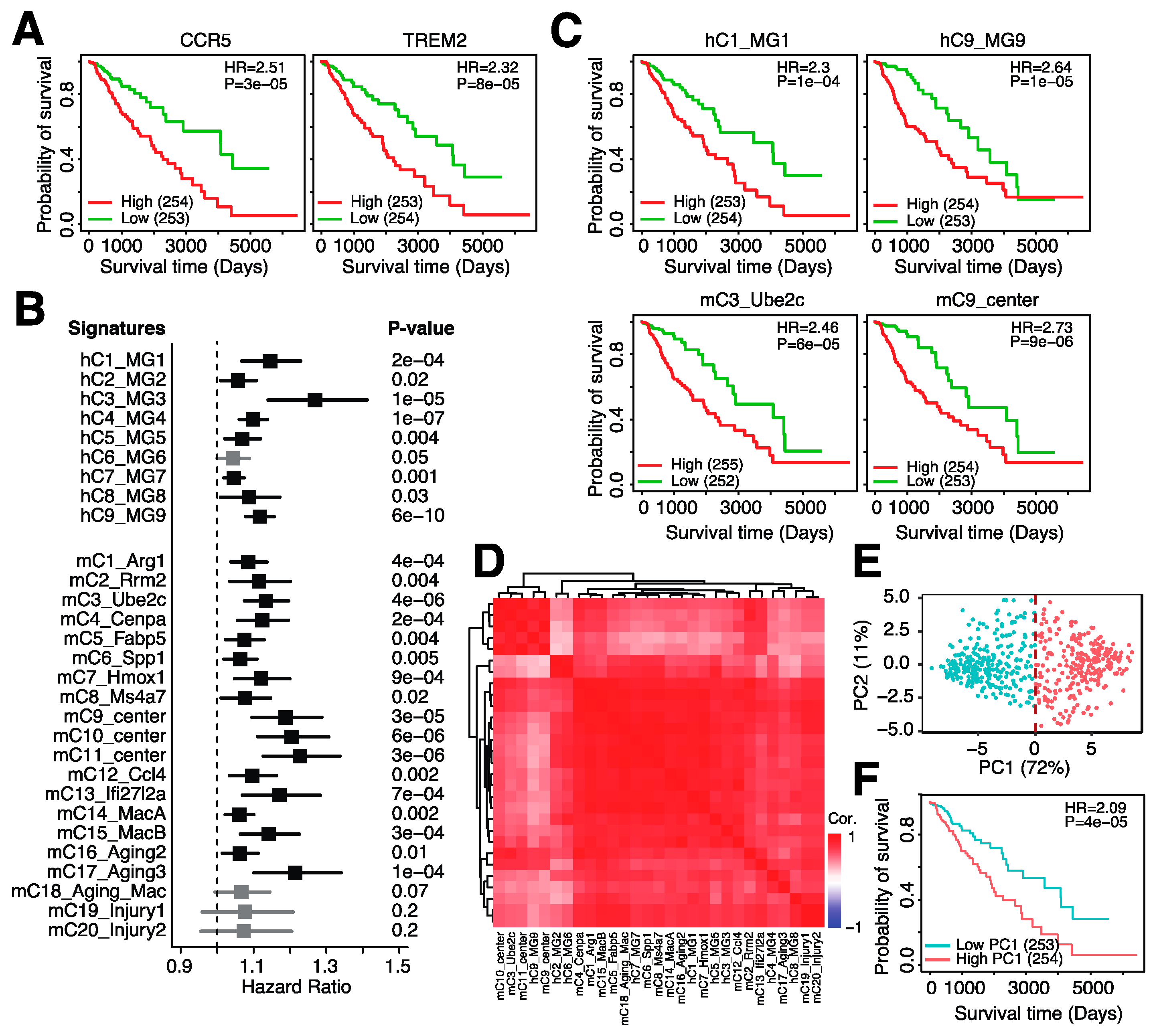
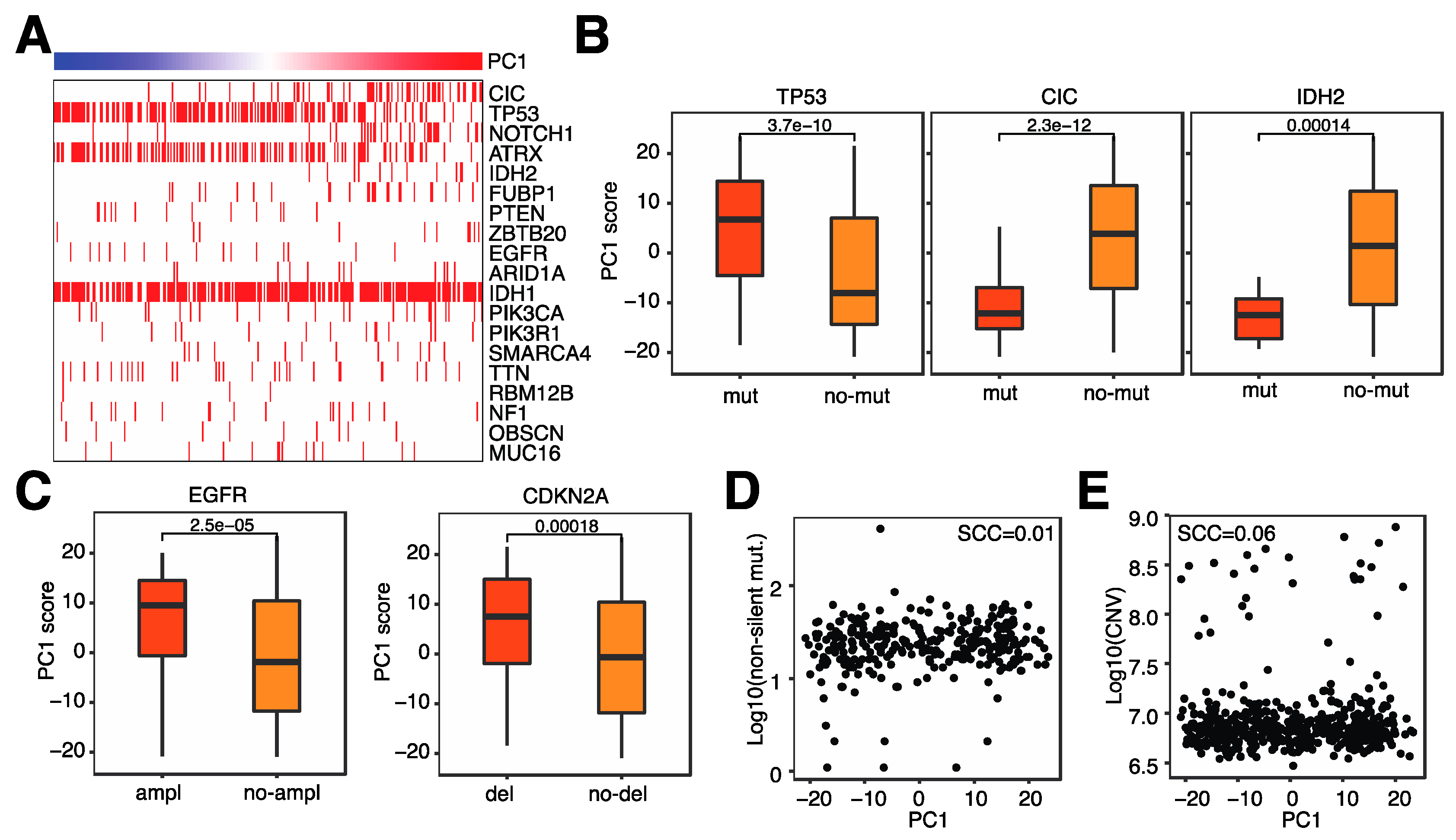
3.4. Microglia Infiltration Is Associated with Specific Genomic Alterations
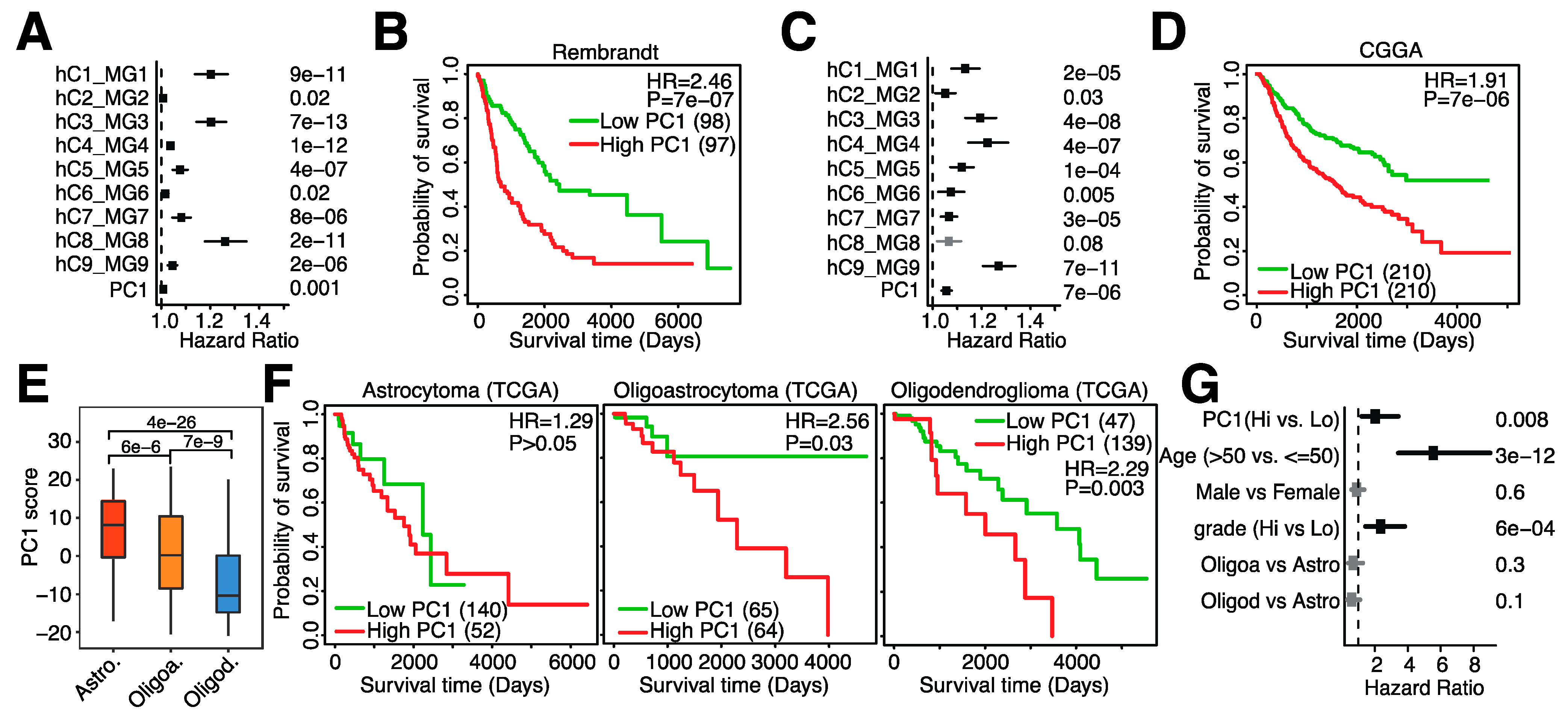
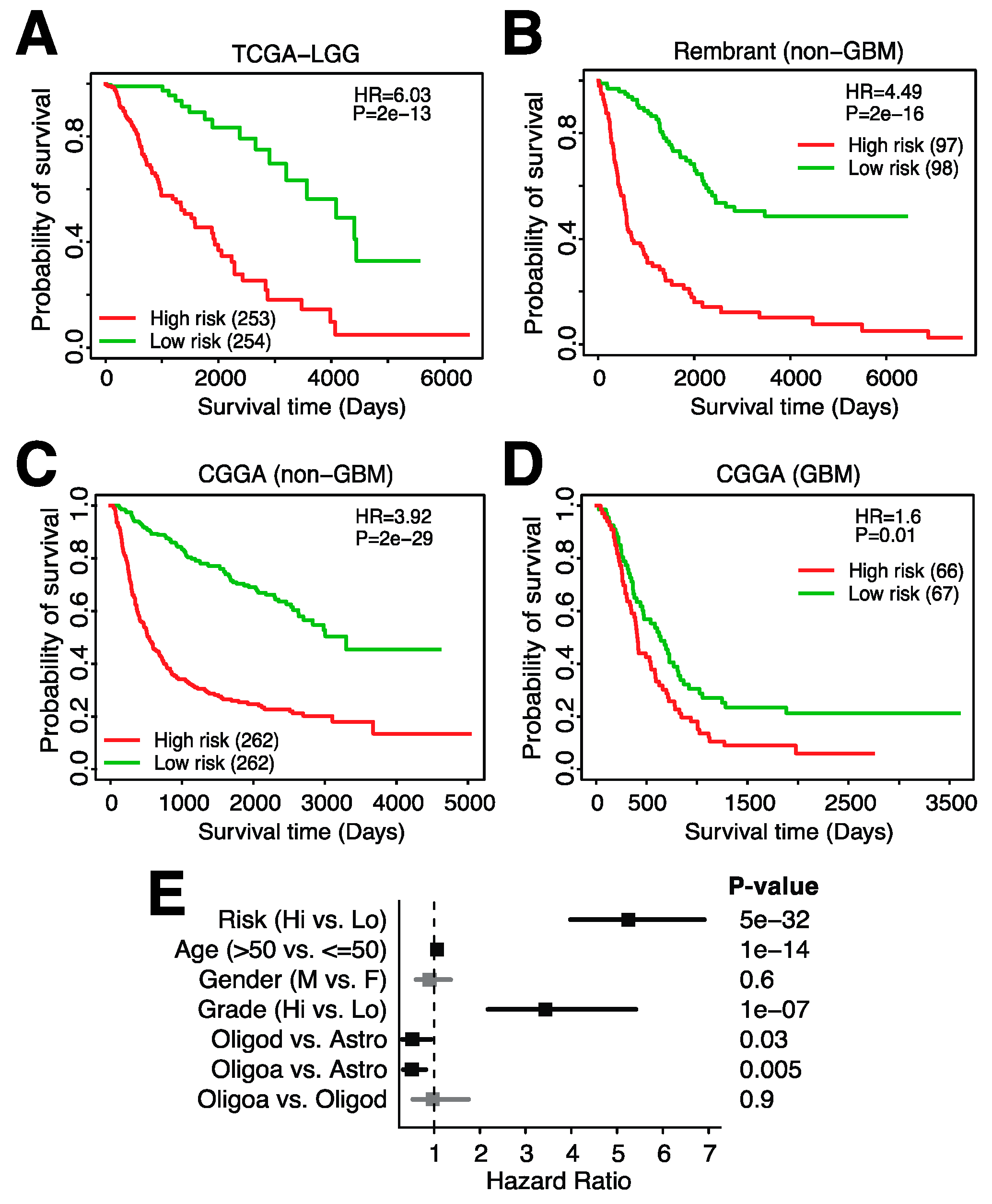
3.5. A 23-Gene Risk Score Is Highly Associated with Overall Survival in Glioma
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weller, M.; Wick, W.; Aldape, K. Glioma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabors, L.B.; Portnow, J.; Ahluwalia, M.; Baehring, J.; Brem, H.; Brem, S.; Butowski, N.; Campian, J.L.; Clark, S.W.; Fabiano, A.J.; et al. Central Nervous System Cancers, Version 3.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 1537–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varn, F.S.; Johnson, K.C.; Martinek, J.; Huse, J.T.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Wesseling, P.; Cooper, L.A.; Malta, T.M.; Wade, T.E.; Sabedot, T.S.; et al. Glioma progression is shaped by genetic evolution and microenvironment interactions. Cell 2022, 185, 2184–2199.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, B.M.; Akl, C.F.; Wheeler, M.A.; Chiocca, E.A.; Reardon, D.A.; Quintana, F.J. Glial and myeloid heterogeneity in the brain tumour microenvironment. Nat. Cancer 2021, 21, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, D.; Okada, H. T-Cell based therapies for overcoming neuroanatomical and immunosuppressive challenges within the glioma microenvironment. Neuro-Oncol. 2020, 147, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathewson, N.D.; Ashenberg, O.; Tirosh, I.; Gritsch, S.; Perez, E.M.; Marx, S.; Jerby-Arnon, L.; Chanoch-Myers, R.; Hara, T.; Richman, A.R.; et al. Inhibitory CD161 receptor identified in glioma-infiltrating T cells by single-cell analysis. Cell 2021, 184, 1281–1298.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, F.; Maas, R.R.; Bowman, R.L.; Kornete, M.; Soukup, K.; Nassiri, S.; Brouland, J.-P.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Brennan, C.; Tabar, V.; et al. Interrogation of the Microenvironmental Landscape in Brain Tumors Reveals Disease-Specific Alterations of Immune Cells. Cell 2020, 181, 1643–1660.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Walle, T.; Cornish, A.E.; Basu, S.; Anandhan, S.; Fernandez, I.; Vence, L.; Blando, J.; Zhao, H.; Yadav, S.S.; et al. Immune profiling of human tumors identifies CD73 as a combinatorial target in glioblastoma. Nat. Med. 2019, 26, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebel, E.; Kapolou, K.; Unger, S.; Núñez, N.G.; Utz, S.; Rushing, E.J.; Regli, L.; Weller, M.; Greter, M.; Tugues, S.; et al. Single-Cell Mapping of Human Brain Cancer Reveals Tumor-Specific Instruction of Tissue-Invading Leukocytes. Cell 2020, 181, 1626–1642.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyonteck, S.M.; Akkari, L.; Schuhmacher, A.J.; Bowman, R.L.; Sevenich, L.; Quail, D.F.; Olson, O.C.; Quick, M.L.; Huse, J.T.; Teijeiro, V.; et al. CSF-1R inhibition alters macrophage polarization and blocks glioma progression. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Kohanbash, G.; Fellows-Mayle, W.; Hamilton, R.L.; Komohara, Y.; Decker, S.A.; Ohlfest, J.R.; Okada, H. COX-2 Blockade Suppresses Gliomagenesis by Inhibiting Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2664–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalper, K.A.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Diez-Valle, R.; López-Janeiro, A.; Porciuncula, A.; Idoate, M.A.; Inogés, S.; De Andrea, C.; De Cerio, A.L.-D.; Tejada, S.; et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab modifies the tumor immune microenvironment in resectable glioblastoma. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, L.; Molinaro, A.M.; Peters, K.B.; Clarke, J.L.; Jordan, J.T.; de Groot, J.F.; Nghiemphu, P.L.; Kaley, T.J.; Colman, H.; McCluskey, C.; et al. Randomized Phase II and Biomarker Study of Pembrolizumab plus Bevacizumab versus Pembrolizumab Alone for Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omuro, A.; Vlahovic, G.; Lim, M.; Sahebjam, S.; Baehring, J.; Cloughesy, T.; Voloschin, A.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Ligon, K.L.; Latek, R.; et al. Nivolumab with or without ipilimumab in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: Results from exploratory phase I cohorts of CheckMate 143. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouzlani, A.; Kandoussi, S.; Tall, M.; Reddy, K.P.; Rafii, S.; Badou, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Human Glioma Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 679425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsson, V.; Gibbs, D.L.; Brown, S.D.; Wolf, D.; Bortone, D.S.; Ou Yang, T.-H.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Gao, G.F.; Plaisier, C.L.; Eddy, J.A.; et al. The Immune Landscape of Cancer. Immunity 2018, 48, 812–830.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, S.; Zenklusen, J.-C.; Kotliarov, Y.; Sahni, H.; Fine, H.A.; Buetow, K. Rembrandt: Helping Personalized Medicine Become a Reality through Integrative Translational Research. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoentong, P.; Finotello, F.; Angelova, M.; Mayer, C.; Efremova, M.; Rieder, D.; Hackl, H.; Trajanoski, Z. Pan-cancer Immunogenomic Analyses Reveal Genotype-Immunophenotype Relationships and Predictors of Response to Checkpoint Blockade. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Waldner, M.; Obenauf, A.C.; Angell, H.; Fredriksen, T.; Lafontaine, L.; Berger, A.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Intratumoral Immune Cells Reveal the Immune Landscape in Human Cancer. Immunity 2013, 39, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Deng, C.; Pang, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Liao, G.; Yuan, H.; Cheng, P.; Li, F.; Long, Z.; et al. TIP: A Web Server for Resolving Tumor Immunophenotype Profiling. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6575–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Yan, X.; Sun, F.; Li, L.M. Inferring activity changes of transcription factors by binding association with sorted expression profiles. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varn, F.S.; Tafe, L.J.; Amos, C.I.; Cheng, C. Computational immune profiling in lung adenocarcinoma reveals reproducible prognostic associations with implications for immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1431084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varn, F.S.; Wang, Y.; Mullins, D.W.; Fiering, S.; Cheng, C. Systematic Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals Immune Cell Interactions in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olah, M.; Menon, V.; Habib, N.; Taga, M.F.; Ma, Y.; Yung, C.J.; Cimpean, M.; Khairallah, A.; Coronas-Samano, G.; Sankowski, R.; et al. Single cell RNA sequencing of human microglia uncovers a subset associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, T.R.; Dufort, C.; Dissing-Olesen, L.; Giera, S.; Young, A.; Wysoker, A.; Walker, A.J.; Gergits, F.; Segel, M.; Nemesh, J.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of Microglia throughout the Mouse Lifespan and in the Injured Brain Reveals Complex Cell-State Changes. Immunity 2019, 50, 253–271.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boeck, A.; Ahn, B.Y.; D’Mello, C.; Lun, X.; Menon, S.V.; Alshehri, M.M.; Szulzewsky, F.; Shen, Y.; Khan, L.; Dang, N.H.; et al. Glioma-derived IL-33 orchestrates an inflammatory brain tumor microenvironment that accelerates glioma progression. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durinck, S.; Spellman, P.T.; Birney, E.; Huber, W. Mapping identifiers for the integration of genomic datasets with the R/Bioconductor package biomaRt. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.H.; Espinosa, I.; Edris, B.; Li, R.; Montgomery, K.; Zhu, S.; Varma, S.; Marinelli, R.J.; van de Rijn, M.; West, R.B. The Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor 1 Response Signature in Breast Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, E.R.; Chitu, V. CSF-1 Receptor Signaling in Myeloid Cells. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a021857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankowski, R.; Böttcher, C.; Masuda, T.; Geirsdottir, L.; Sagar; Sindram, E.; Seredenina, T.; Muhs, A.; Scheiwe, C.; Shah, M.J.; et al. Mapping microglia states in the human brain through the integration of high-dimensional techniques. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 2098–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanisch, U.-K.; Kettenmann, H. Microglia: Active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sarkar, S.; Cua, R.; Zhou, Y.; Hader, W.; Yong, V.W. A dialog between glioma and microglia that promotes tumor invasiveness through the CCL2/CCR2/interleukin-6 axis. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive, Integrative Genomic Analysis of Diffuse Lower-Grade Gliomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2481–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, K.; Shahmoradgoli, M.; Martínez, E.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Trevino, V.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Levine, D.A.; et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Liu, S.; Qi, F.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Feng, J.; Zheng, Y. Screening TCGA database for prognostic genes in lower grade glioma microenvironment. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schaafsma, E.; Jiang, C.; Nguyen, T.; Zhu, K.; Cheng, C. Microglia-Based Gene Expression Signature Highly Associated with Prognosis in Low-Grade Glioma. Cancers 2022, 14, 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194802
Schaafsma E, Jiang C, Nguyen T, Zhu K, Cheng C. Microglia-Based Gene Expression Signature Highly Associated with Prognosis in Low-Grade Glioma. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194802
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchaafsma, Evelien, Chongming Jiang, Thinh Nguyen, Kenneth Zhu, and Chao Cheng. 2022. "Microglia-Based Gene Expression Signature Highly Associated with Prognosis in Low-Grade Glioma" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194802
APA StyleSchaafsma, E., Jiang, C., Nguyen, T., Zhu, K., & Cheng, C. (2022). Microglia-Based Gene Expression Signature Highly Associated with Prognosis in Low-Grade Glioma. Cancers, 14(19), 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194802




