Developing a Predictive Grading Model for Children with Gliomas Based on Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Metrics: Accuracy and Clinical Correlations with Patient Survival
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Data Collection
2.2. Image Acquisition, Preprocessing, and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
- -
- “number of estimators” = 100, which describes the number of trees in the model.
- -
- “maximum depth” = 3, which describes the maximum depth of each tree in the forest.
3. Results
3.1. Patients Features
3.2. DKI Differences between pLGG and pHGG
3.3. Predictive Model Development
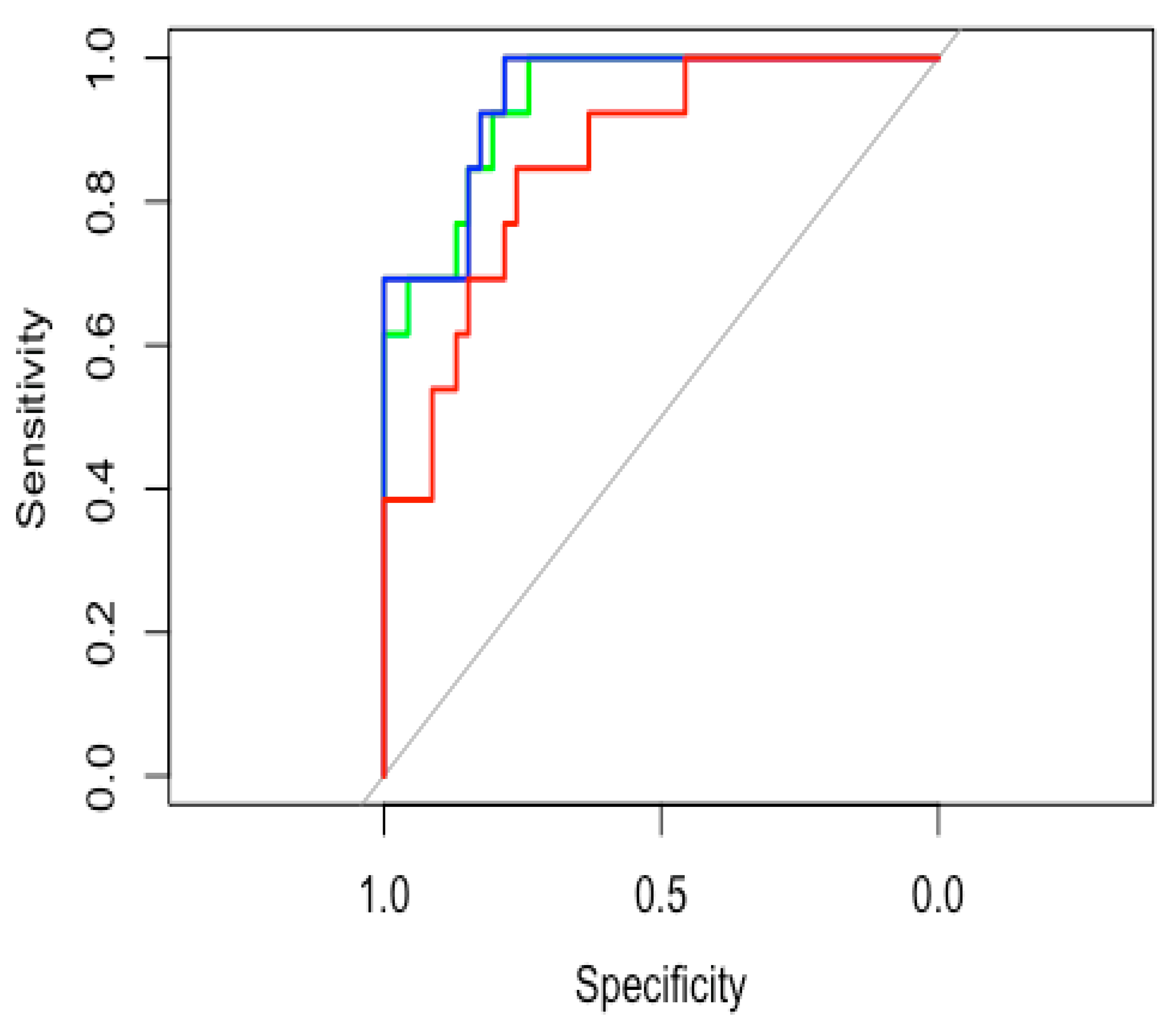
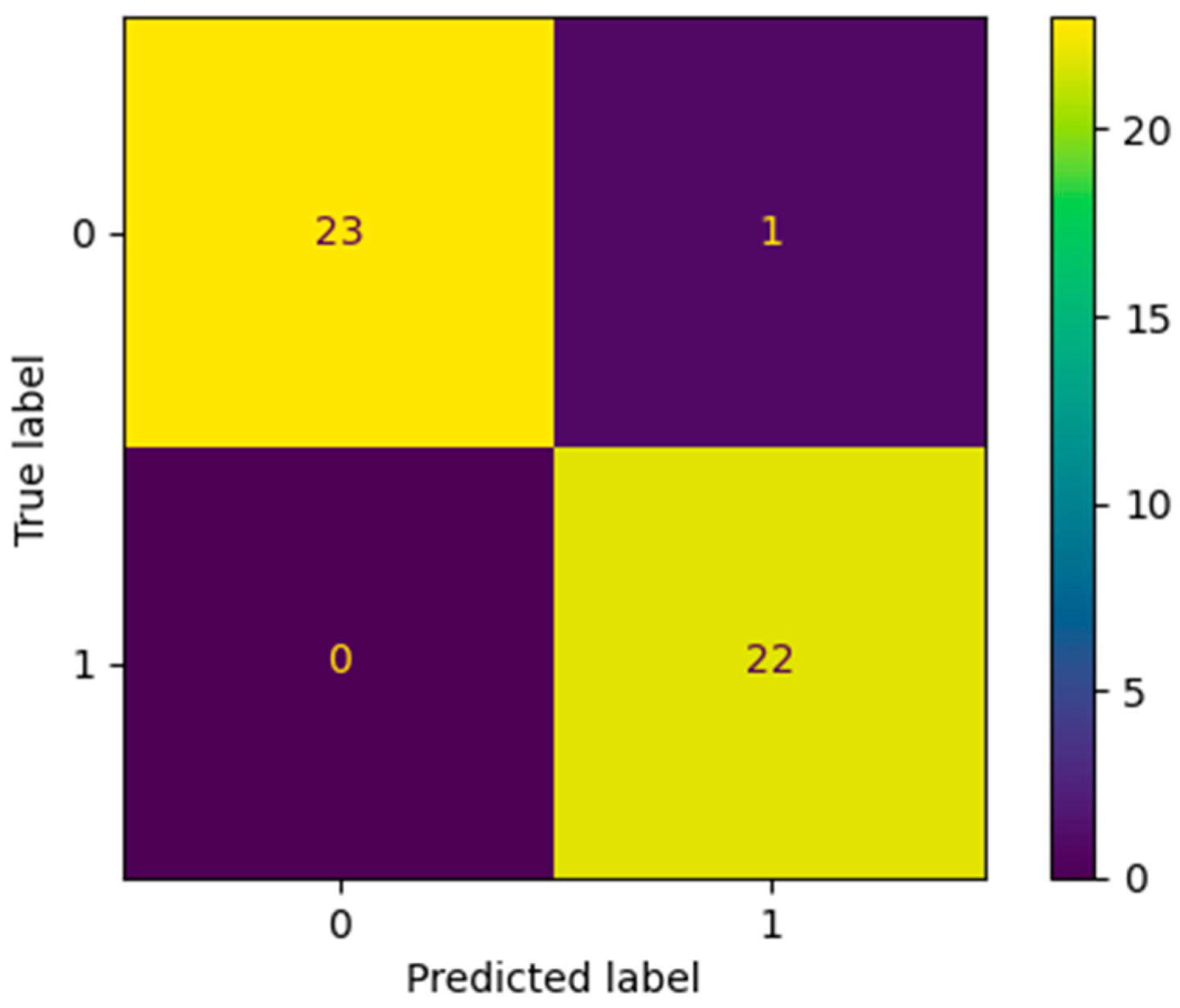
3.4. Model Accuracy Estimation
3.5. SMOTE Analysis
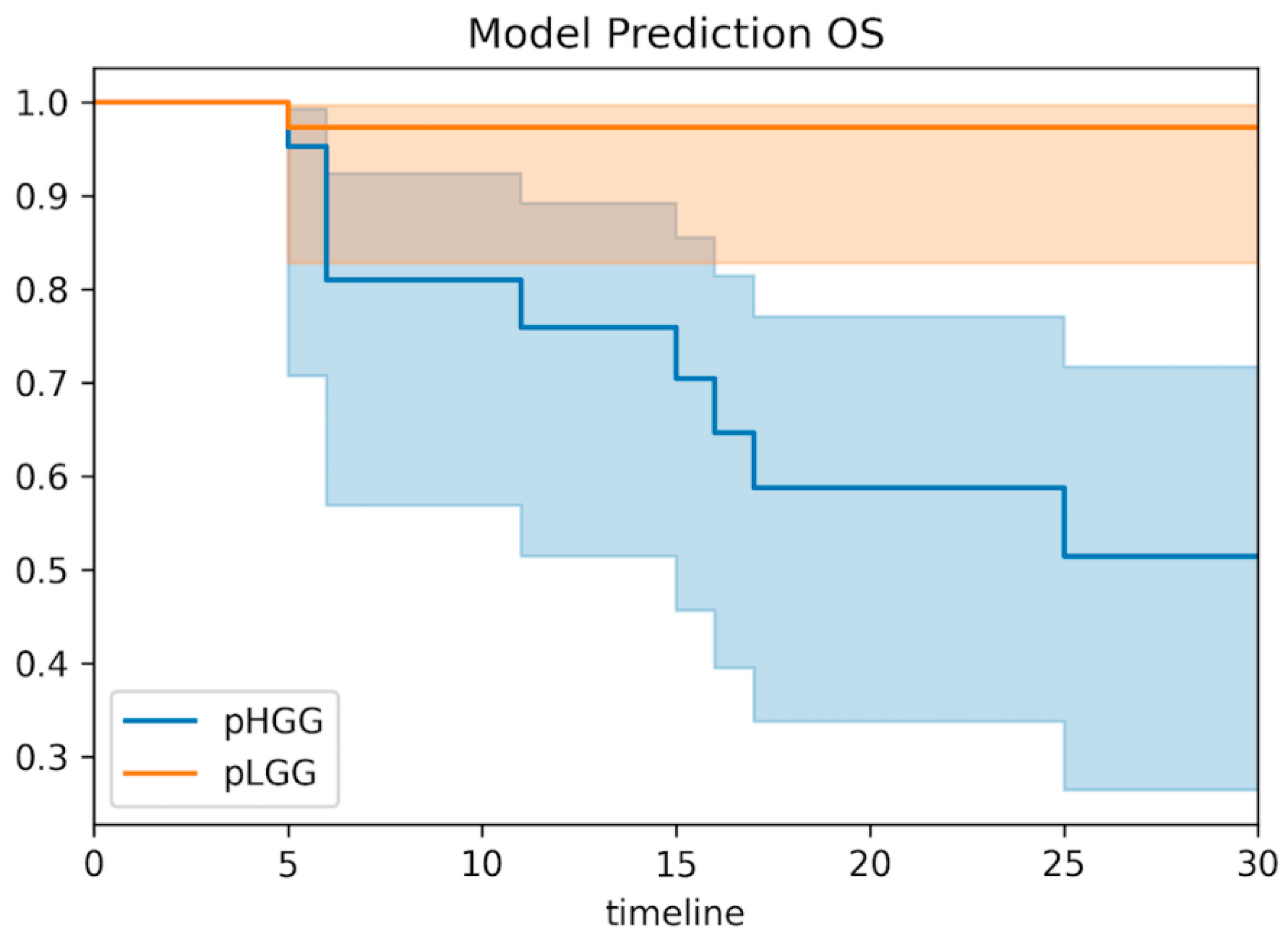
3.6. Clinical Correlations of the Predictive Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DKI | Diffusion kurtosis imaging |
| MK | Mean kurtosis |
| AK | Axial kurtosis |
| RK | Radial kurtosis |
| FA | Fractional anisotropy |
| KFA | Kurtosis fractional anisotropy |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristics |
| SMOTE | Synthetic minority oversampling technique |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| pHGG | Pediatric high-grade gliomas |
| pLGG | Pediatric low-grade gliomas |
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; de Blank, P.M.; Kruchko, C.; Petersen, C.M.; Liao, P.; Finlay, J.L.; Stearns, D.S.; Wolff, J.E.; Wolinsky, Y.; Letterio, J.J.; et al. Alex’s Lemonade Stand Foundation Infant and Childhood Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2007–2011. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 16 (Suppl. S10), x1–x36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Karajannis, M.A.; Jones, D.T.W.; Kieran, M.W.; Monje, M.; Baker, S.J.; Becher, O.J.; Cho, Y.J.; Gupta, N.; Hawkins, C.; et al. Pediatric high-grade glioma: Biologically and clinically in need of new thinking. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paugh, B.S.; Qu, C.; Jones, C.; Liu, Z.; Adamowicz-Brice, M.; Zhang, J.; Bax, D.A.; Coyle, B.; Barrow, J.; Hargrave, D.; et al. Integrated molecular genetic profiling of pediatric high-grade gliomas reveals key differences with the adult disease. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3061–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, D.; Pfister, S.M.; Jones, D.T.W. Pediatric Gliomas: Current Concepts on Diagnosis, Biology, and Clinical Management. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2370–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab, P.; Hattingen, E.; Franz, K.; Zanella, F.E.; Lanfermann, H. Cerebral gliomas: Diffusional kurtosis imaging analysis of microstructural differences. Radiology 2010, 254, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabesh, A.; Jensen, J.H.; Ardekani, B.A.; Helpern, J.A. Estimation of tensors and tensor-derived measures in diffusional kurtosis imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauter, S.; Veraart, J.; Sijbers, J.; Peeters, R.R.; Himmelreich, U.; De Keyzer, F.; Van Gool, S.W.; Van Calenbergh, F.; De Vleeschouwer, S.; Van Hecke, W.; et al. Gliomas: Diffusion kurtosis MR imaging in grading. Radiology 2012, 263, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yao, Y.; Yang, S.; Shi, J.; Shen, N.; Su, C.; et al. Diffusion kurtosis imaging can efficiently assess the glioma grade and cellular proliferation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42380–42393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Falk Delgado, A.; Nilsson, M.; van Westen, D. Glioma Grade Discrimination with MR Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging: A Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy. Radiology 2018, 287, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, D.; Lin, S.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, D. Grading of Pediatric Intracranial Tumors: Are Intravoxel Incoherent Motion and Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Superior to Conventional DWI? AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, S.; Moller, H.E.; Kugel, H.; Muller, D.K.; Deppe, M. Correcting eddy current and motion effects by affine whole-brain registrations: Evaluation of three-dimensional distortions and comparison with slicewise correction. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 64, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, G.R.; Helpern, J.A.; Tabesh, A.; Jensen, J.H. Quantitative assessment of diffusional kurtosis anisotropy. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombo, M.; Gentili, S.; Bozzali, M.; Macaluso, E.; Capuani, S. New insight into the contrast in diffusional kurtosis images: Does it depend on magnetic susceptibility? Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, M.F.; Freund, P.; Draganski, B.; Anderson, E.; Cappelletti, M.; Chowdhury, R.; Diedrichsen, J.; Fitzgerald, T.H.; Smittenaar, P.; Helms, G.; et al. Widespread age-related differences in the human brain microstructure revealed by quantitative magnetic resonance imaging. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1862–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, N.; Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Cox’s Proportional Hazards Model via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Garcia, S.; Herrera, F.; Chawla, N.V. SMOTE for learning from imbalanced data: Progress and challenges, marking the 15-year anniversary. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2018, 61, 863–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E.M.P. Non parametric estimation from incomplete observations. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1958, 53, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.M.; DeWire, M.; Ryall, S.; Buczkowicz, P.; Leach, J.; Miles, L.; Ramani, A.; Brudno, M.; Kumar, S.S.; Drissi, R.; et al. Spatial genomic heterogeneity in diffuse intrinsic pontine and midline high-grade glioma: Implications for diagnostic biopsy and targeted therapeutics. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.H.; Veldhuijzen van Zanten, S.E.; Sanchez Aliaga, E.; Heymans, M.W.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Hargrave, D.; van der Hoeven, E.J.; Gidding, C.E.; de Bont, E.S.; Eshghi, O.S.; et al. Survival prediction model of children with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma based on clinical and radiological criteria. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulo, M.; Panara, V.; Tortora, D.; Mattei, P.A.; Briganti, C.; Pravata, E.; Salice, S.; Cotroneo, A.R.; Tartaro, A. Data-driven grading of brain gliomas: A multiparametric MR imaging study. Radiology 2014, 272, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kickingereder, P.; Neuberger, U.; Bonekamp, D.; Piechotta, P.L.; Gotz, M.; Wick, A.; Sill, M.; Kratz, A.; Shinohara, R.T.; Jones, D.T.W.; et al. Radiomic subtyping improves disease stratification beyond key molecular, clinical, and standard imaging characteristics in patients with glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinci, M.; Burford, A.; Molinari, V.; Kessler, K.; Popov, S.; Clarke, M.; Taylor, K.R.; Pemberton, H.N.; Lord, C.J.; Gutteridge, A.; et al. Functional diversity and cooperativity between subclonal populations of pediatric glioblastoma and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma cells. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.H.; Helpern, J.A. MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis. NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
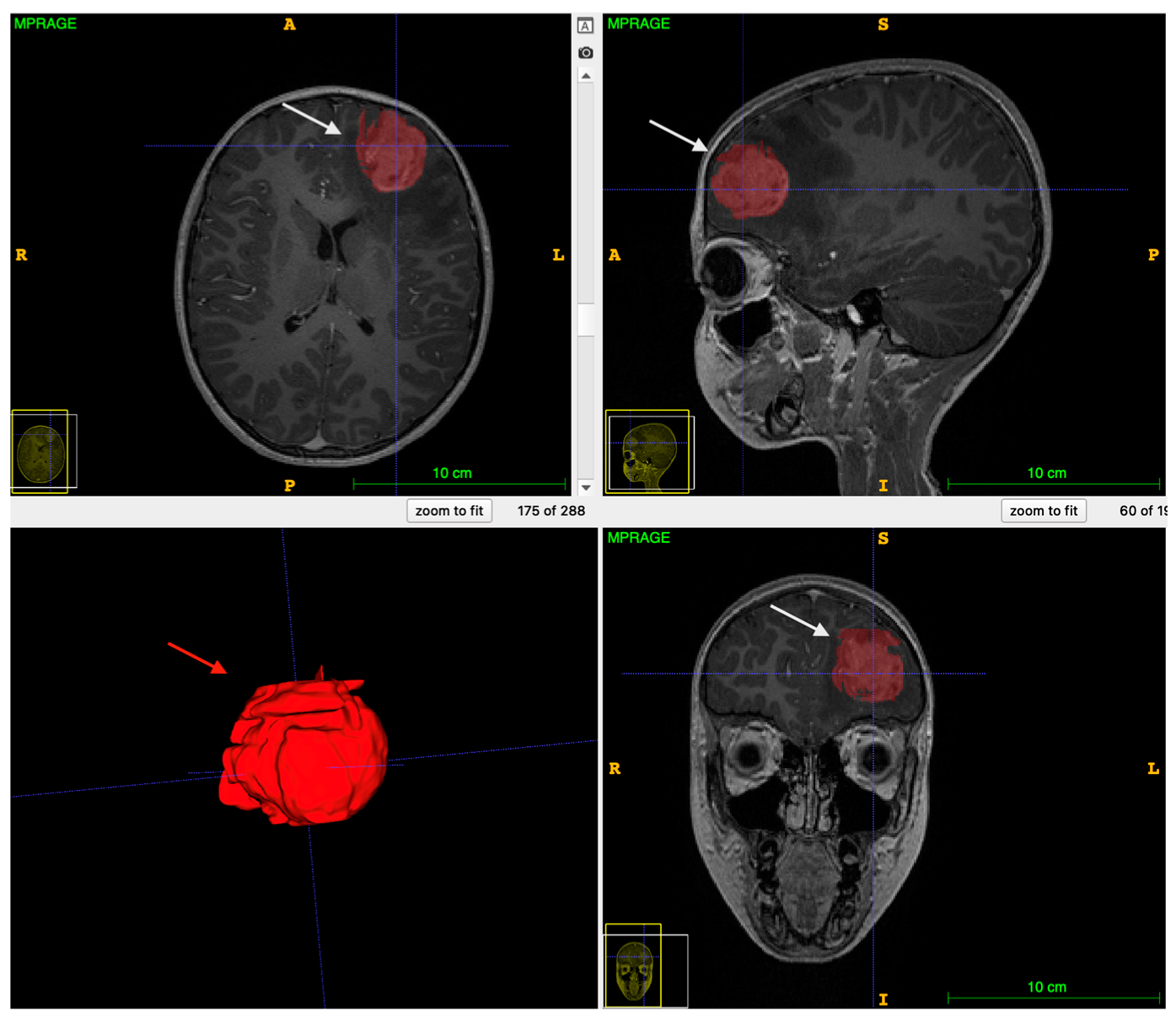


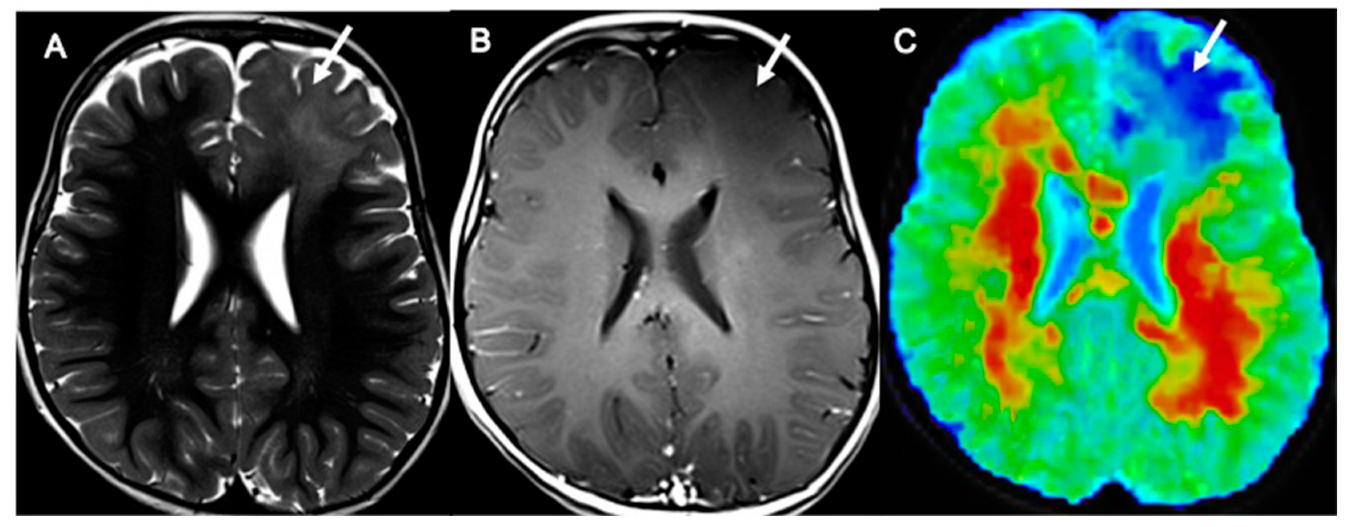
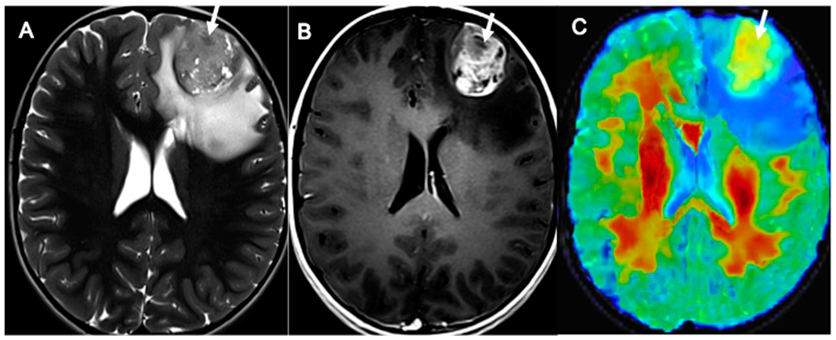
| Patient Characteristic | Number of Patients |
|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics | 59/59 (100%) |
| Median age | 7.2 (5.0–11.5) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 32/59 (55.1%) |
| Female | 26/59 (44.8%) |
| Histologic characteristics | |
| Low-grade gliomas (WHO 1–2) | 46/59 (79.3%) |
| High-grade gliomas (WHO 3–4) | 13/59 (20.7%) |
| Anaplastic astrocytoma (WHO 3) | 2/59 (3.4%) |
| Anaplastic ganglioglioma (WHO 3) | 1/59 (1.7%) |
| Anaplastic Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma (WHO 3) | 1/59 (1.7%) |
| Astroblastoma (WHO 1) | 1/59 (1.7%) |
| Diffuse midline glioma, H3K27Maltered (WHO 4) | 2/59 (3.4%) |
| Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor DNET (WHO 1) | 1/59 (1.7%) |
| Ganglioglioma (WHO 1) | 14/59 (23.7%) |
| Glioblastoma, IDH wild type (WHO 4) | 5/59 (8.5%) |
| Low-grade Astrocytoma (WHO 2) | 4/59 (6.8%) |
| Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma (WHO 2) | 1/59 (1.7%) |
| Pilocytic Astrocytoma (WHO 1) | 14/59 (23.7%) |
| PLNTY (Polymorphous low-grade neuroepithelial tumor of the young, WHO 1) | 2/59 (3.4%) |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of directions | 30 |
| B values (s/mm2) | 0, 1000, 2000 |
| Repetition Time TR (ms) | 7400 |
| Echo Time TE (ms) | 113 |
| Acquisition matrix | 128 × 128 |
| Resolution (mm3) | 2 × 2 × 2 |
| Average slice number | 36 |
| GRAPPA | 2 |
| Reference lines | 38 |
| Acquisition time (min:s) | 12.00 |
| Bandwidth (hz/px) | 1562 |
| Acceleration Factor | 2 |
| Model Coefficients for DKI Predictive Grading. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Feature Name | DTI | DKI | DTI + DKI |
| Intercept | 1.574 | −9.699 | −11.412 |
| Fractional anisotropy (FA) | 2.743 | - | 3.927 |
| Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) | −2.484 | - | −0.275 |
| Radial Kurtosis (RK) | - | −5.952 | −5.474 |
| Mean Kurtosis (MK) | - | 24.046 | 19.904 |
| Axial Kurtosis (AK) | - | −3.164 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voicu, I.P.; Napolitano, A.; Caulo, M.; Dotta, F.; Piccirilli, E.; Vinci, M.; Diomedi-Camassei, F.; Lattavo, L.; Carboni, A.; Miele, E.; et al. Developing a Predictive Grading Model for Children with Gliomas Based on Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Metrics: Accuracy and Clinical Correlations with Patient Survival. Cancers 2022, 14, 4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194778
Voicu IP, Napolitano A, Caulo M, Dotta F, Piccirilli E, Vinci M, Diomedi-Camassei F, Lattavo L, Carboni A, Miele E, et al. Developing a Predictive Grading Model for Children with Gliomas Based on Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Metrics: Accuracy and Clinical Correlations with Patient Survival. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194778
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoicu, Ioan Paul, Antonio Napolitano, Massimo Caulo, Francesco Dotta, Eleonora Piccirilli, Maria Vinci, Francesca Diomedi-Camassei, Lorenzo Lattavo, Alessia Carboni, Evelina Miele, and et al. 2022. "Developing a Predictive Grading Model for Children with Gliomas Based on Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Metrics: Accuracy and Clinical Correlations with Patient Survival" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194778
APA StyleVoicu, I. P., Napolitano, A., Caulo, M., Dotta, F., Piccirilli, E., Vinci, M., Diomedi-Camassei, F., Lattavo, L., Carboni, A., Miele, E., Cacchione, A., Carai, A., Tomà, P., Mastronuzzi, A., & Colafati, G. S. (2022). Developing a Predictive Grading Model for Children with Gliomas Based on Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Metrics: Accuracy and Clinical Correlations with Patient Survival. Cancers, 14(19), 4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194778












