p21-Activated Kinase: Role in Gastrointestinal Cancer and Beyond
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure and Activation of PAK
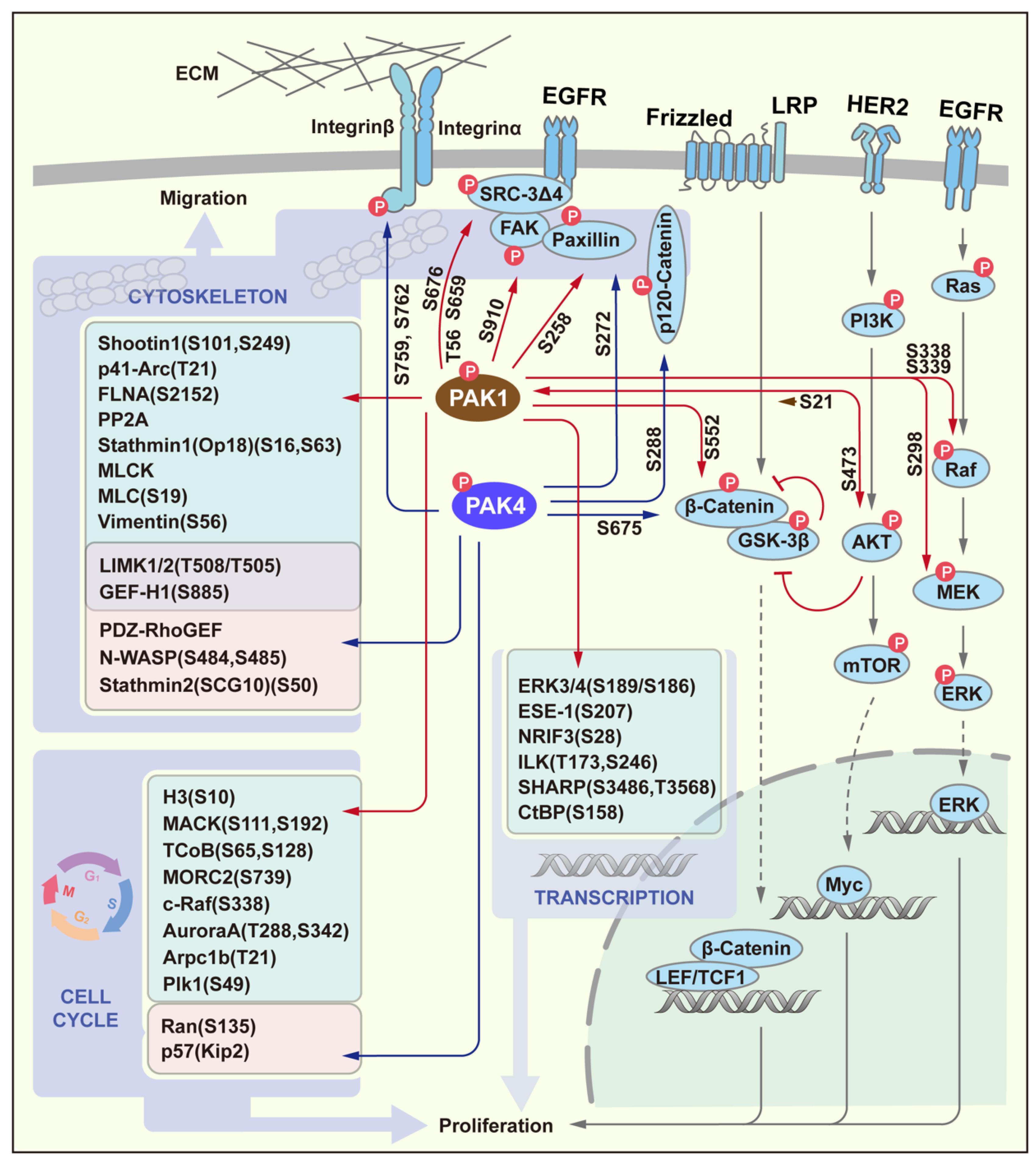
3. PAK Signaling in Proliferation and Migration
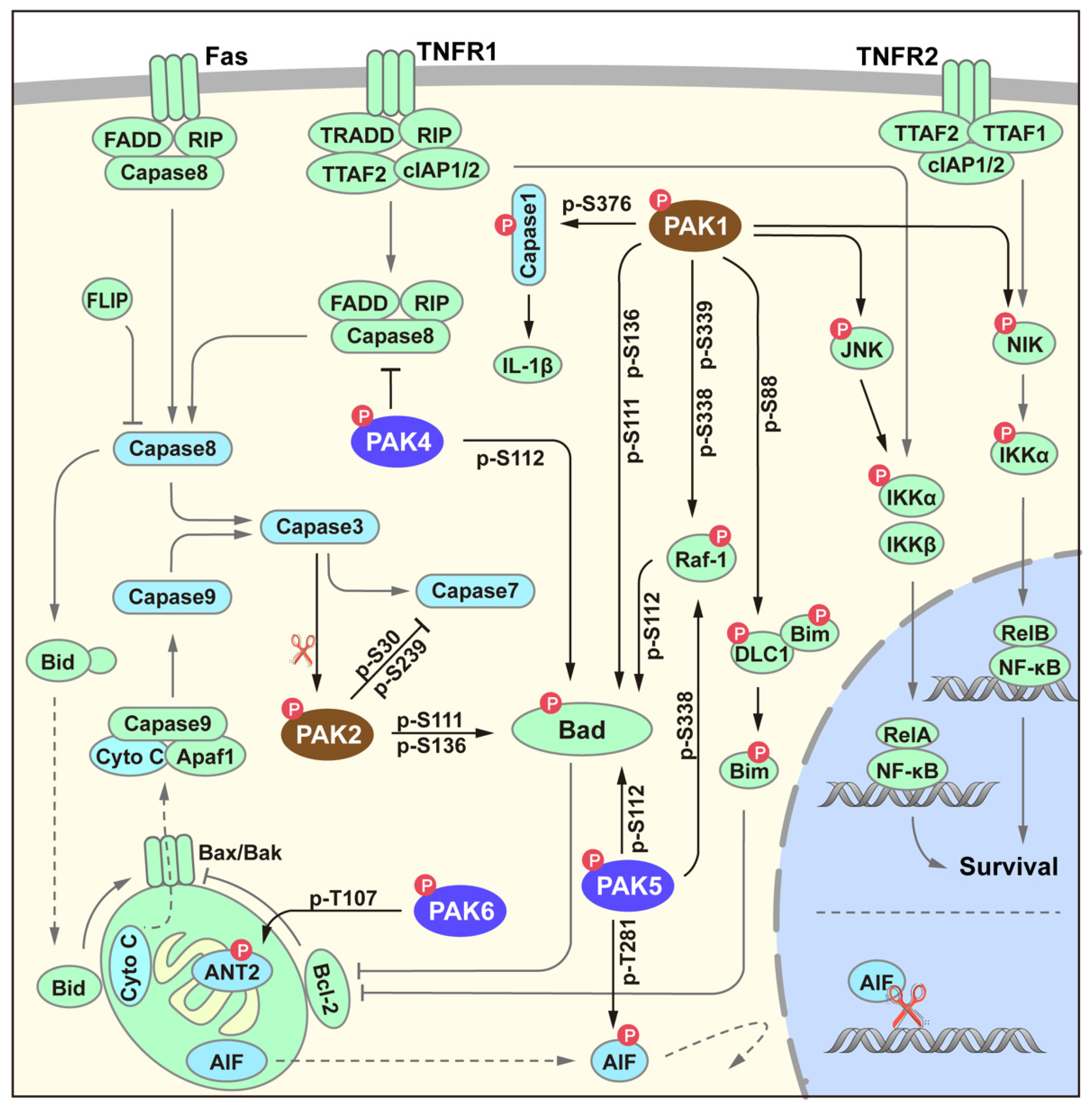
4. PAK Signaling in Survival
5. PAK Signaling in Plasticity
6. PAK Regulation of Tumor Microenvironment
7. PAK Profile in Cancer
8. Positive Role of PAK in Gastrointestinal Cancer
9. PAK in Other Cancers
10. PAK in Breast Cancer
11. PAK in Lung Cancer
12. PAK in Prostate Cancer
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manser, E.; Leung, T.; Salihuddin, H.; Zhao, Z.S.; Lim, L. A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature 1994, 367, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaus, U.G.; Morris, S.; Dong, H.J.; Chernoff, J.; Bokoch, G.M. Regulation of human leukocyte p21-activated kinases through G protein--coupled receptors. Science 1995, 269, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.A.; Bollag, G.; McCormick, F.; Abo, A. A novel serine kinase activated by rac1/CDC42Hs-dependent autophosphorylation is related to PAK65 and STE20. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagrodia, S.; Taylor, S.J.; Creasy, C.L.; Chernoff, J.; Cerione, R.A. Identification of a mouse p21Cdc42/Rac activated kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 22731–22737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.R.; Song, C.; Yang, Z.; Kumar, R. Nuclear localization and chromatin targets of p21-activated kinase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 18130–18137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shao, Y.; Tong, Y.; Shen, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Gu, H.; Li, F. Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of PAK4 modulates beta-catenin intracellular translocation and signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotteret, S.; Chernoff, J. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of Pak5 regulates its antiapoptotic properties. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 3215–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sells, M.A.; Chernoff, J. Emerging from the Pak: The p21-activated protein kinase family. Trends Cell Biol. 1997, 7, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokoch, G.M. Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 743–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Gururaj, A.E.; Barnes, C.J. p21-activated kinases in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, M.; Semenova, G.; Kosoff, R.; Chernoff, J. PAK signalling during the development and progression of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, Y.P.; Leong, V.Y.; Wong, C.M.; Kung, H.F. Identification of an autoinhibitory domain of p21-activated protein kinase 5. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 33621–33624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskaran, Y.; Ng, Y.W.; Selamat, W.; Ling, F.T.; Manser, E. Group I and II mammalian PAKs have different modes of activation by Cdc42. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirruccello, M.; Sondermann, H.; Pelton, J.G.; Pellicena, P.; Hoelz, A.; Chernoff, J.; Wemmer, D.E.; Kuriyan, J. A dimeric kinase assembly underlying autophosphorylation in the p21 activated kinases. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 361, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Lu, W.; Meng, W.; Parrini, M.C.; Eck, M.J.; Mayer, B.J.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of PAK1 in an autoinhibited conformation reveals a multistage activation switch. Cell 2000, 102, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strochlic, T.I.; Viaud, J.; Rennefahrt, U.E.; Anastassiadis, T.; Peterson, J.R. Phosphoinositides are essential coactivators for p21-activated kinase 1. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwald, G.; Hostinova, E.; Rudolph, M.G.; Kraemer, A.; Sickmann, A.; Meyer, H.E.; Scheffzek, K.; Wittinghofer, A. Conformational switch and role of phosphorylation in PAK activation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 5179–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, B.H.; Davis, M.J.; Chen, C.; Lou, H.J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, R.; Krauthammer, M.; Halaban, R.; Schlessinger, J.; Turk, B.E.; et al. Type II p21-activated kinases (PAKs) are regulated by an autoinhibitory pseudosubstrate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16107–16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, L.C.; Shaw, P.E. PAK1 primes MEK1 for phosphorylation by Raf-1 kinase during cross-cascade activation of the ERK pathway. Oncogene 2002, 21, 2236–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Jaffer, Z.M.; Huang, Y.; Volden, P.; Chernoff, J.; Liang, Q. Regulation of Akt/PKB activity by P21-activated kinase in cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2008, 44, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrenson, B.; Dissanayake, W.C.; Hu, F.; Lee, K.L.; Shepherd, P.R. A role for PAK1 mediated phosphorylation of beta-catenin Ser552 in the regulation of insulin secretion. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, K.; Dong, Z. The Role of p21-Activated Kinases in Cancer and Beyond: Where Are We Heading? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 641381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Li, C.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; He, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. P21-Activated Kinase 1: Emerging biological functions and potential therapeutic targets in Cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9741–9766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, E.A.; Ilic, D.; Han, Q.; Hauck, C.R.; Jin, F.; Kawakatsu, H.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Damsky, C.H. Matrix survival signaling: From fibronectin via focal adhesion kinase to c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, M.; Foryst-Ludwig, A.; Klar, S.; Schweitzer, K.; Naumann, M. The PAK1 autoregulatory domain is required for interaction with NIK in Helicobacter pylori-induced NF-kappaB activation. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnesutta, N.; Minden, A. Death receptor-induced activation of initiator caspase 8 is antagonized by serine/threonine kinase PAK4. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 7838–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.Z.; Jin, S.; Zhuo, Y.; Field, J. p21-Activated kinase 1 (Pak1) phosphorylates BAD directly at serine 111 in vitro and indirectly through Raf-1 at serine 112. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wen, W.; Rayala, S.K.; Chen, M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, M.; Kumar, R. Serine 88 phosphorylation of the 8-kDa dynein light chain 1 is a molecular switch for its dimerization status and functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 4004–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobi, R.; Moertl, E.; Koeppel, M.A. p21-activated protein kinase gamma-PAK suppresses programmed cell death of BALB3T3 fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 16624–16634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnesutta, N.; Qu, J.; Minden, A. The serine/threonine kinase PAK4 prevents caspase activation and protects cells from apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 14414–14419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotteret, S.; Jaffer, Z.M.; Beeser, A.; Chernoff, J. p21-Activated kinase 5 (Pak5) localizes to mitochondria and inhibits apoptosis by phosphorylating BAD. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 5526–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, T.; Li, F. Mitochondrial PAK6 inhibits prostate cancer cell apoptosis via the PAK6-SIRT4-ANT2 complex. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2571–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, B.; Han, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Jin, F.; et al. PAK5-mediated AIF phosphorylation inhibits its nuclear translocation and promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Rayala, S.; Nguyen, D.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Chen, S.; Kumar, R. Pak1 phosphorylation of snail, a master regulator of epithelial-to-mesenchyme transition, modulates snail's subcellular localization and functions. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3179–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.J.; Park, M.H.; Oh, E.H.; Soung, N.K.; Lee, S.J.; Jung, J.K.; Lee, O.J.; Yun, S.J.; Kim, W.J.; Shin, E.Y.; et al. The p21-activated kinase 4-Slug transcription factor axis promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and worsens prognosis in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5147–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavathi, B.; Rayala, S.K.; Kumar, R. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of stability and transforming potential of ETS transcriptional factor ESE-1 by p21-activated kinase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 19820–19830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.J.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Jacobson, R.H.; Li, F.; Kumar, R. Functional inactivation of a transcriptional corepressor by a signaling kinase. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadlamudi, R.K.; Manavathi, B.; Singh, R.R.; Nguyen, D.; Li, F.; Kumar, R. An essential role of Pak1 phosphorylation of SHARP in Notch signaling. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4591–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhong, M.; Ye, Z.; Wu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. PAK3 promotes the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating EMT process. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesanakurti, D.; Maddirela, D.; Banasavadi-Siddegowda, Y.K.; Lai, T.H.; Qamri, Z.; Jacob, N.K.; Sampath, D.; Mohanam, S.; Kaur, B.; Puduvalli, V.K. A novel interaction of PAK4 with PPARgamma to regulate Nox1 and radiation-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in glioma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5309–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Liu, W.; Menezes, S.; Yue, F.; Zheng, M.; Kovacevic, Z.; Richardson, D.R. The metastasis suppressor NDRG1 modulates the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of beta-catenin through mechanisms involving FRAT1 and PAK4. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 3116–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Pan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Fang, X. PAK5 Induces EMT and Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion by Activating the PI3K/AKT Pathway in Ovarian Cancer. Anal. Cell Pathol. 2018, 2018, 8073124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, F.C.; Pan, Y.J.; Li, T.T.; Mou, J.; Pei, D.S. PAK5 promotes the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells by phosphorylating SATB1. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Li, X.; Guo, B.; Ke, Q.; Dong, M.; Li, F. PAK5-mediated E47 phosphorylation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of colon cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1943–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ke, Q.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, G.; Li, Y.; Geng, N.; Jin, F.; Li, F. GATA1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells through PAK5 oncogenic signaling. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4345–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; An, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xu, J. p21-activated kinase 1 determines stem-like phenotype and sunitinib resistance via NF-kappaB/IL-6 activation in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, S.L.; Lee, D.S. The PAK1-Stat3 Signaling Pathway Activates IL-6 Gene Transcription and Human Breast Cancer Stem Cell Formation. Cancers 2019, 11, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, N.; Marimuthu, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, A.P.; McClellan, S.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S. p-21 activated kinase 4 (PAK4) maintains stem cell-like phenotypes in pancreatic cancer cells through activation of STAT3 signaling. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.J.; Wu, D.W.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, H. PAK1 confers chemoresistance and poor outcome in non-small cell lung cancer via beta-catenin-mediated stemness. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Yang, M.C.; Ding, L.Y.; Chen, C.S.; Chu, P.C. p21-Activated kinase 3 promotes cancer stem cell phenotypes through activating the Akt-GSK3beta-beta-catenin signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2019, 456, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfarouk, K.O.; Muddathir, A.K.; Shayoub, M.E. Tumor acidity as evolutionary spite. Cancers 2011, 3, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Drake, C.G.; Pardoll, D.M. Immune checkpoint blockade: A common denominator approach to cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abril-Rodriguez, G.; Torrejon, D.Y.; Liu, W.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Nowicki, T.S.; Tsoi, J.; Puig-Saus, C.; Baselga-Carretero, I.; Medina, E.; Quist, M.J.; et al. PAK4 inhibition improves PD-1 blockade immunotherapy. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konig, S.; Nimtz, M.; Scheiter, M.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Bryceson, Y.T.; Jansch, L. Kinome analysis of receptor-induced phosphorylation in human natural killer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, F.; Zhang, D.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L.; Dorsey, J.F.; Binder, Z.A.; O’Rourke, D.M.; et al. Targeting PAK4 to reprogram the vascular microenvironment and improve CAR-T immunotherapy for glioblastoma. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhan, Y.; Huynh, N.; Dumesny, C.; Wang, X.; Asadi, K.; Herrmann, D.; Timpson, P.; Yang, Y.; Walsh, K.; et al. Inhibition of PAK1 suppresses pancreatic cancer by stimulation of anti-tumour immunity through down-regulation of PD-L1. Cancer Lett. 2020, 472, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; He, K.Y.; Li, C.; Ni, Y.Y.; Li, M.N.; Chen, L.; Hou, M.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Z.P.; Ji, M.J. P21 activated kinase-1 (PAK1) in macrophages is required for promotion of Th17 cell response during helminth infection. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 14325–14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hagan, K.L.; Miller, S.D.; Phee, H. Pak2 is essential for the function of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells through maintaining a suppressive Treg phenotype. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.B.; Yang, L.; Xie, G.Q.; Zhou, X.C.; Shen, X.B.; Xu, Q.L.; Ma, Z.Y.; Guo, X.D. The modulation relationship of genomic pattern of intratumor heterogeneity and immunity microenvironment heterogeneity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Qi, D.; Guan, X.; Jiang, G.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Li, N.; Wu, M. c-Abl tyrosine kinase regulates neutrophil crawling behavior under fluid shear stress via Rac/PAK/LIMK/cofilin signaling axis. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 2806–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koranova, T.; Dvoracek, L.; Grebenova, D.; Roselova, P.; Obr, A.; Kuzelova, K. PAK1 and PAK2 in cell metabolism regulation. J Cell Biochem. 2021, 123, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gururaj, A.; Barnes, C.J.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Kumar, R. Regulation of phosphoglucomutase 1 phosphorylation and activity by a signaling kinase. Oncogene 2004, 23, 8118–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalom-Barak, T.; Knaus, U.G. A p21-activated kinase-controlled metabolic switch up-regulates phagocyte NADPH oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 40659–40665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Ajith, A.; Singh, S.; Panday, R.K.; Samaiya, A.; Shukla, S. PAK2-c-Myc-PKM2 axis plays an essential role in head and neck oncogenesis via regulating Warburg effect. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Shao, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, G.; Li, F. PAK4 regulates G6PD activity by p53 degradation involving colon cancer cell growth. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosset, E.; Ilmjarv, S.; Dutoit, V.; Elliott, K.; von Schalscha, T.; Camargo, M.F.; Reiss, A.; Moroishi, T.; Seguin, L.; Gomez, G.; et al. Glut3 Addiction Is a Druggable Vulnerability for a Molecularly Defined Subpopulation of Glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 856–868.e855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Gao, Y.; Yu, Q.H.; Li, M.; Cheng, X.; Hu, S.B.; Song, Z.F.; Zheng, Q.C. P-21-activated kinase 1 contributes to tumor angiogenesis upon photodynamic therapy via the HIF-1alpha/VEGF pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goc, A.; Al-Azayzih, A.; Abdalla, M.; Al-Husein, B.; Kavuri, S.; Lee, J.; Moses, K.; Somanath, P.R. P21 activated kinase-1 (Pak1) promotes prostate tumor growth and microinvasion via inhibition of transforming growth factor beta expression and enhanced matrix metalloproteinase 9 secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3025–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscher, C.; Gaonac’h-Lovejoy, V.; Delisle, C.; Gratton, J.P. Polarization and sprouting of endothelial cells by angiopoietin-1 require PAK2 and paxillin-dependent Cdc42 activation. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2019, 30, 2227–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, M.; Lyle, K.; Hoeflich, K.P.; Villamar-Cruz, O.; Koeppen, H.; Chernoff, J. p21-Activated Kinase 2 Regulates Endothelial Development and Function through the Bmk1/Erk5 Pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 3990–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, V.L.; Simon, B.; Draheim, K.M.; Calderwood, D.A. Serine phosphorylation of the small phosphoprotein ICAP1 inhibits its nuclear accumulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 3269–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, S.; Swaroop, S.S.; Roy, J.; Inemai, E.; Murugan, S.; Rayala, S.K.; Venkatraman, G. p21 activated kinase-1 and tamoxifen-A deadly nexus impacting breast cancer outcomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1877, 188668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ma, X.; Chao, X.; Wang, F.; Cai, L.; Yan, Z.; Xie, L.; Guo, X. Systemic analysis of the expression and prognostic significance of PAKs in breast cancer. Genomics 2020, 112, 2433–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.C.; Jubb, A.M.; Haverty, P.M.; Zhou, W.; Tran, V.; Truong, T.; Turley, H.; O’Brien, T.; Vucic, D.; Harris, A.L.; et al. Targeting p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) to induce apoptosis of tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7177–7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Son, B.S.; Kim, D.; Hwang, C.; Shin, D.; Noh, S.G.; Han, J.H.; Kim, D.K.; et al. Upregulation of P21-Activated Kinase 1 (PAK1)/CREB Axis in Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, F.; Lu, J.; Phan, R.; Lewis, M.; Trinidad, K.; Aljilani, A.; Pezeshkpour, G.; Tamanoi, F. Significance of KRAS/PAK1/Crk pathway in non-small cell lung cancer oncogenesis. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.H.; Kim, T.; Kang, Y.J.; Yoon, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.K.; Son, J.H.; Son, B.; Kim, D.H. PAK1 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Male Smokers with EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Molecules 2020, 25, 5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Xia, L.; Oyang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Luo, X.; Liao, Q.; Liang, J. Overexpression of PAK1 Correlates with Aberrant Expression of EMT Markers and Poor Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Zhu, G.; Tang, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Fu, J.; Huang, C.; Fan, S.; Sun, Y.; Lv, J.; et al. Whole genome gene copy number profiling of gastric cancer identifies PAK1 and KRAS gene amplification as therapy targets. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014, 53, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.F.; Qin, S.H.; Ruan, X.Z.; Wang, X. p120-catenin participates in the progress of gastric cancer through regulating the Rac1 and Pak1 signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qing, H.; Gong, W.; Che, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, L.; Liang, Y.; Wang, W.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, B. PAK1-dependent MAPK pathway activation is required for colorectal cancer cell proliferation. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Wang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, Z. P21-activated kinase 1 and 4 were associated with colorectal cancer metastasis and infiltration. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 196, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadeeshan, S.; Krishnamoorthy, Y.R.; Singhal, M.; Subramanian, A.; Mavuluri, J.; Lakshmi, A.; Roshini, A.; Baskar, G.; Ravi, M.; Joseph, L.D.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of fibronectin by p21-activated kinase-1 modulates pancreatic tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2015, 34, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Jubb, A.M.; Lyle, K.; Xiao, Q.; Ong, C.C.; Desai, R.; Fu, L.; Gnad, F.; Song, Q.; Haverty, P.M.; et al. PAK1 mediates pancreatic cancer cell migration and resistance to MET inhibition. J. Pathol. 2014, 234, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Ma, T.; Pang, L.; Xie, R. Activation of P21-activated protein kinase 2 is an independent prognostic predictor for patients with gastric cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Tong, L.; Li, L.; Xu, J.; Xie, S.; Ji, L.; Fu, J.; Liu, Q.; Shen, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Loss of Smad4 promotes aggressive lung cancer metastasis by de-repression of PAK3 via miRNA regulation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.F.; Xu, H.W.; Chen, M.; Xian, Z.R.; Wen, X.F.; Chen, M.N.; Du, C.W.; Huang, W.H.; Wu, J.D.; Zhang, G.J. Activated-PAK4 predicts worse prognosis in breast cancer and promotes tumorigenesis through activation of PI3K/AKT signaling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17573–17585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.D.F.; Zhuang, T.; Lorent, J.; Turco, E.; Olofsson, H.; Masia-Balague, M.; Zhao, M.; Rabieifar, P.; Robertson, N.; Kuiper, R.; et al. PAK4 suppresses RELB to prevent senescence-like growth arrest in breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Tian, M.; Le, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Qu, J.; Hao, M. Study on the expression of PAK4 and P54 protein in breast cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Ye, Z.; Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Weng, Y.; Lao, S.; Wei, H.; Li, L. Overexpression of P21-activated kinase 4 is associated with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer and promotes migration and invasion. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Inokuchi, M.; Takagi, Y.; Otsuki, S.; Fujimori, Y.; Sato, Y.; Yanaka, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Aburatani, T.; Tomii, C.; et al. Prognostic significance of PAK4 expression in gastric cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Qu, X.; Liu, Y. Activated Pak4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in human gastric cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 9431–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Auletta, T.; Dovirak, O.; Hutter, C.; Kuntz, K.; El-ftesi, S.; Kendall, J.; Han, H.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Ashfaq, R.; et al. Copy number alterations in pancreatic cancer identify recurrent PAK4 amplification. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlamaki, E.H.; Kauraniemi, P.; Monni, O.; Wolf, M.; Hautaniemi, S.; Kallioniemi, A. High-resolution genomic and expression profiling reveals 105 putative amplification target genes in pancreatic cancer. Neoplasia 2004, 6, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmelman, A.C.; Hezel, A.F.; Aguirre, A.J.; Zheng, H.; Paik, J.H.; Ying, H.; Chu, G.C.; Zhang, J.X.; Sahin, E.; Yeo, G.; et al. Genomic alterations link Rho family of GTPases to the highly invasive phenotype of pancreas cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19372–19377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, N.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, A.P.; McClellan, S.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S. p-21 activated kinase 4 promotes proliferation and survival of pancreatic cancer cells through AKT- and ERK-dependent activation of NF-kappaB pathway. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8778–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Huo, F.C.; Wei, L.L.; Gong, C.C.; Pan, Y.J.; Mou, J.; Pei, D.S. PAK5-mediated phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB-p65 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xu, X.; He, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pan, W.; Xu, L.; Ma, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gao, J.; Qi, Y.; et al. P21-activated kinase 7 (PAK7) interacts with and activates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in breast cancer. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawdar, S.; Trotter, E.W.; Li, Y.; Stephenson, N.L.; Hanke, F.; Marusiak, A.A.; Edwards, Z.C.; Ientile, S.; Waszkowycz, B.; Miller, C.J.; et al. Targeted genetic dependency screen facilitates identification of actionable mutations in FGFR4, MAP3K9, and PAK5 in lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12426–12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Tong, F.; Bin, Y.; Peng, L.; Gao, X.; Xia, X.; Yi, X.; Dong, X. The Predictive Value of PAK7 Mutation for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Therapy in Non-Small Cell Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 834142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Li, K.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Q.; Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Mu, J.; Wen, H.; et al. A role for p21-activated kinase 7 in the development of gastric cancer. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Mulder, K.; Spratlin, J. How prognostic and predictive biomarkers are transforming our understanding and management of advanced gastric cancer. Oncologist 2014, 19, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburatani, T.; Inokuchi, M.; Takagi, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Okuno, K.; Gokita, K.; Tomii, C.; Tanioka, T.; Murase, H.; Otsuki, S.; et al. High expression of P21-activated kinase 5 protein is associated with poor survival in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Cui, X.; Tu, S.; You, L.; Fu, J.; Chen, Z.; Hu, W.; et al. PAK5 facilitates the proliferation, invasion and migration in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4777–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; An, Z.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Fang, W.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, H. P21-activated kinase 5 is overexpressed during colorectal cancer progression and regulates colorectal carcinoma cell adhesion and migration. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, T.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; Xi, S.; Wen, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, C.; et al. Prognostic and Predictive Value of p21-activated Kinase 6 Associated Support Vector Machine Classifier in Gastric Cancer Treated by 5-fluorouracil/Oxaliplatin Chemotherapy. EBioMedicine 2017, 22, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapatero, A.; Morente, M.; Nieto, S.; Martin de Vidales, C.; Lopez, C.; Adrados, M.; Arellano, R.; Artiga, M.J.; Garcia-Vicente, F.; Herranz, L.M.; et al. Predictive value of PAK6 and PSMB4 expression in patients with localized prostate cancer treated with dose-escalation radiation therapy and androgen deprivation therapy. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, H.; Yan, D.; Cui, F.; Wang, X.; Yu, F.; Xue, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; et al. PAK6 increase chemoresistance and is a prognostic marker for stage II and III colon cancer patients undergoing 5-FU based chemotherapy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Song, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, F.; Cai, X.; Miao, Z.; Xu, H.; Xu, H.; et al. PAK1-mediated MORC2 phosphorylation promotes gastric tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 9877–9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, G.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, L.; et al. Oncogenic PAK4 regulates Smad2/3 axis involving gastric tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3473–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Cheng, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Xu, H.; Li, F. A Novel Pak1/ATF2/miR-132 Signaling Axis Is Involved in the Hematogenous Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 8, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Han, Y.; Miao, Z.; Li, F. PAK1 regulates RUFY3-mediated gastric cancer cell migration and invasion. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nheu, T.; He, H.; Hirokawa, Y.; Walker, F.; Wood, J.; Maruta, H. PAK is essential for RAS-induced upregulation of cyclin D1 during the G1 to S transition. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Cai, X.; Du, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, F. Downregulation of p21-activated kinase-1 inhibits the growth of gastric cancer cells involving cyclin B1. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 2511–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Su, N.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Miao, Z.; Wang, G.; Cheng, M.; Xu, H.; Cao, L.; Li, F. PAK4 kinase-mediated SCG10 phosphorylation involved in gastric cancer metastasis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3277–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ke, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhu, G.; Li, F. DGCR6L, a novel PAK4 interaction protein, regulates PAK4-mediated migration of human gastric cancer cell via LIMK1. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, M.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J.; Li, F. CORO1C, a novel PAK4 binding protein, recruits phospho-PAK4 serine 99 to the leading edge and promotes the migration of gastric cancer cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2022, 54, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shin, S.H.; Chen, H.; Liu, T.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C.; Kim, D.J.; Liu, K.; et al. CDK12 and PAK2 as novel therapeutic targets for human gastric cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 6201–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, M.; Wessler, S.; Bartsch, C.; Wieland, B.; Covacci, A.; Haas, R.; Meyer, T.F. Activation of activator protein 1 and stress response kinases in epithelial cells colonized by Helicobacter pylori encoding the cag pathogenicity island. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31655–31662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foryst-Ludwig, A.; Naumann, M. p21-activated kinase 1 activates the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B)-inducing kinase-Ikappa B kinases NF-kappa B pathway and proinflammatory cytokines in Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39779–39785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Baek, K.E.; Kim, I.K.; Park, S.M.; Choi, Y.L.; Nam, I.K.; Park, S.H.; Im, M.J.; Yoo, J.M.; Ryu, K.J.; et al. Proteomics-based strategy to delineate the molecular mechanisms of RhoGDI2-induced metastasis and drug resistance in gastric cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Feng, J.; Zeng, D.; Ding, Y.; Yu, C.; Yang, B. PAK4 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells via PI3K/Akt- and MEK/ERK-dependent pathways. Biosci. Rep. 2014, 34, e00094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.Z.; Wang, J.; Li, X.D.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, F.N.; Cheng, M.S.; Li, F. Curcumin suppresses proliferation and invasion in human gastric cancer cells by downregulation of PAK1 activity and cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, J.; You, L.H.; Zhou, R.Z.; Zhao, D.M.; Cheng, M.S.; Li, F. GL-1196 Suppresses the Proliferation and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells via Targeting PAK4 and Inhibiting PAK4-Mediated Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Hao, C.Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, M.S.; Zhao, D.M.; Li, F. LC-0882 targets PAK4 and inhibits PAK4-related signaling pathways to suppress the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2736–2747. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, H.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, D.; Li, F. LCH-7749944, a novel and potent p21-activated kinase 4 inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and invasion in human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2012, 317, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Du, R.; Jia, X.; Liu, K.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yao, N.; Yang, L.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; et al. CDK15 promotes colorectal cancer progression via phosphorylating PAK4 and regulating beta-catenin/MEK-ERK signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Cheng, M. PB-10, a thiazolo[4,5-d] pyrimidine derivative, targets p21-activated kinase 4 in human colorectal cancer cells. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 126807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baba, C.; Mahadevan, V.; Fahlbusch, F.B.; Mohan, S.S.; Rau, T.T.; Gali-Muhtasib, H.; Schneider-Stock, R. Thymoquinone-induced conformational changes of PAK1 interrupt prosurvival MEK-ERK signaling in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabusa, H.; Brooks, T.; Massey, A.J. Knockdown of PAK4 or PAK1 inhibits the proliferation of mutant KRAS colon cancer cells independently of RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.H.; Huynh, N.; Patel, O.; Shulkes, A.; Baldwin, G.; He, H. P21-activated kinase 1 promotes colorectal cancer survival by up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Cancer Lett. 2013, 340, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gong, W.; Qing, H.; Geng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, L.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, B. p21-activated kinase 5 inhibits camptothecin-induced apoptosis in colorectal carcinoma cells. Tumour Biol. 2010, 31, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, H. Disheveled-associated activator of morphogenesis 2 promotes invasion of colorectal cancer by activating PAK1 and promoting MMP7 expression. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, N.; Shulkes, A.; Baldwin, G.; He, H. Up-regulation of stem cell markers by P21-activated kinase 1 contributes to 5-fluorouracil resistance of colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Baldwin, G.S.; Nikfarjam, M.; He, H. p21-activated kinase signalling in pancreatic cancer: New insights into tumour biology and immune modulation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3709–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.C.; Ebeling, M.C.; Maher, D.M.; Koch, M.D.; Watanabe, A.; Aburatani, H.; Lio, Y.; Jaggi, M. MUC13 mucin augments pancreatic tumorigenesis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singhal, M.; Chopra, C.; Srinivasan, S.; Surabhi, R.P.; Kanumuri, R.; Tentu, S.; Jagadeeshan, S.; Sundaram, S.; Ramanathan, K.; et al. Threonine 209 phosphorylation on RUNX3 by Pak1 is a molecular switch for its dualistic functions. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4857–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.; Thillai, K.; Whale, A.; Arumugam, P.; Eldaly, H.; Kocher, H.M.; Wells, C.M. PAK4 interacts with p85 alpha: Implications for pancreatic cancer cell migration. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, D.; Phillips, P.; Baldwin, G.S.; He, H.; Nikfarjam, M. Inhibition of group 1 p21-activated kinases suppresses pancreatic stellate cell activation and increases survival of mice with pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboukameel, A.; Muqbil, I.; Senapedis, W.; Baloglu, E.; Landesman, Y.; Shacham, S.; Kauffman, M.; Philip, P.A.; Mohammad, R.M.; Azmi, A.S. Novel p21-Activated Kinase 4 (PAK4) Allosteric Modulators Overcome Drug Resistance and Stemness in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Huynh, N.; Wang, X.; Pajic, M.; Parkin, A.; Man, J.; Baldwin, G.S.; Nikfarjam, M.; He, H. PAK inhibition by PF-3758309 enhanced the sensitivity of multiple chemotherapeutic reagents in patient-derived pancreatic cancer cell lines. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 3353–3364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yeo, D.; Huynh, N.; Beutler, J.A.; Christophi, C.; Shulkes, A.; Baldwin, G.S.; Nikfarjam, M.; He, H. Glaucarubinone and gemcitabine synergistically reduce pancreatic cancer growth via down-regulation of P21-activated kinases. Cancer Lett. 2014, 346, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, D.; He, H.; Patel, O.; Lowy, A.M.; Baldwin, G.S.; Nikfarjam, M. FRAX597, a PAK1 inhibitor, synergistically reduces pancreatic cancer growth when combined with gemcitabine. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.U.; Kim, J.W.; Sung, J.H.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, S.H.; Chang, H.; Lee, J.O.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, J.H.; et al. p21-Activated Kinase 4 (PAK4) as a Predictive Marker of Gemcitabine Sensitivity in Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 47, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, J.H.; Choi, Y.R.; et al. Prognostic value of p21-activated kinase 4 in resected pancreatic cancer. APMIS 2017, 125, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohneis, P.; Sinn, M.; Bischoff, S.; Juhling, A.; Pelzer, U.; Wislocka, L.; Bahra, M.; Sinn, B.V.; Denkert, C.; Oettle, H.; et al. Cytotoxic tumour-infiltrating T lymphocytes influence outcome in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 83, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayala, S.K.; Talukder, A.H.; Balasenthil, S.; Tharakan, R.; Barnes, C.J.; Wang, R.A.; Aldaz, C.M.; Khan, S.; Kumar, R. P21-activated kinase 1 regulation of estrogen receptor-alpha activation involves serine 305 activation linked with serine 118 phosphorylation. Cancer Res 2006, 66, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukder, A.H.; Li, D.Q.; Manavathi, B.; Kumar, R. Serine 28 phosphorylation of NRIF3 confers its co-activator function for estrogen receptor-alpha transactivation. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5233–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saldivar-Ceron, H.I.; Villamar-Cruz, O.; Wells, C.M.; Oguz, I.; Spaggiari, F.; Chernoff, J.; Patino-Lopez, G.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Montecillo-Aguado, M.; Rivera-Pazos, C.M.; et al. p21-Activated Kinase 1 Promotes Breast Tumorigenesis via Phosphorylation and Activation of the Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 759259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, N.; Cui, X.; Zheng, X.; Deng, L.; Price, S.; Karantza, V.; Minden, A. The protein kinase Pak4 disrupts mammary acinar architecture and promotes mammary tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2010, 29, 5883–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Adam, L.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Zhou, H.; Sen, S.; Chernoff, J.; Mandal, M.; Kumar, R. p21-activated kinase 1 interacts with and phosphorylates histone H3 in breast cancer cells. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Pan, D.; Zhen, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; He, Z. Ferulin C triggers potent PAK1 and p21-mediated anti-tumor effects in breast cancer by inhibiting Tubulin polymerization in vitro and in vivo. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, Y.; Schafer, E.J.; Boehm, J.S.; Thomas, S.R.; He, F.; Du, J.; Wang, S.; Barretina, J.; Weir, B.A.; Zhao, J.J.; et al. PAK1 is a breast cancer oncogene that coordinately activates MAPK and MET signaling. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightcap, C.M.; Sun, S.; Lear, J.D.; Rodeck, U.; Polenova, T.; Williams, J.C. Biochemical and structural characterization of the Pak1-LC8 interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27314–27324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumdar, A.; Kumar, R. Estrogen regulation of Pak1 and FKHR pathways in breast cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2003, 535, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadlamudi, R.K.; Bagheri-Yarmand, R.; Yang, Z.; Balasenthil, S.; Nguyen, D.; Sahin, A.A.; den Hollander, P.; Kumar, R. Dynein light chain 1, a p21-activated kinase 1-interacting substrate, promotes cancerous phenotypes. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Q.; Chen, H.N.; Wang, K.; Yuan, K.; Lei, Y.; Li, K.; Lan, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xie, N.; et al. Ivermectin Induces Cytostatic Autophagy by Blocking the PAK1/Akt Axis in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4457–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Romero, L.E.; Villamar-Cruz, O.; Huang, M.; Hoeflich, K.P.; Chernoff, J. Pak1 kinase links ErbB2 to beta-catenin in transformation of breast epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3671–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Dai, W.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, F. P21-activated kinase 4 regulates the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p57(kip2) in human breast cancer. Anat. Rec. 2013, 296, 1561–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, A.; Diakonova, M. Tyrosyl phosphorylated serine-threonine kinase PAK1 is a novel regulator of prolactin-dependent breast cancer cell motility and invasion. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 846, 97–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, M.N.; Yu, X.T.; Tang, J.; Zhou, C.X.; Wang, C.L.; Yin, Q.Q.; Gong, X.F.; He, M.; He, J.R.; Chen, G.Q.; et al. MicroRNA-494 inhibits breast cancer progression by directly targeting PAK1. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dart, A.E.; Box, G.M.; Court, W.; Gale, M.E.; Brown, J.P.; Pinder, S.E.; Eccles, S.A.; Wells, C.M. PAK4 promotes kinase-independent stabilization of RhoU to modulate cell adhesion. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 211, 863–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, L.; Oladimeji, P.; Diakonova, M. PAK1 regulates breast cancer cell invasion through secretion of matrix metalloproteinases in response to prolactin and three-dimensional collagen IV. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 1048–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Ma, D.; Cao, Y.; Hu, L.; Liu, S.; Yan, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; et al. SphK2/S1P Promotes Metastasis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Through the PAK1/LIMK1/Cofilin1 Signaling Pathway. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 598218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, Y.; Tang, L.; Ning, K.; Geng, N.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, F. A novel PAK4-CEBPB-CLDN4 axis involving in breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 511, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lundin, L.; Thullberg, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Stromblad, S. p21-activated kinase 4 phosphorylation of integrin beta5 Ser-759 and Ser-762 regulates cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 23699–23710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Gao, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Li, F. PAK4 phosphorylating RUNX1 promotes ERalpha-positive breast cancer-induced osteolytic bone destruction. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2235–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Cheng, Z.; Tang, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; et al. A mandatory role of nuclear PAK4-LIFR axis in breast-to-bone metastasis of ERalpha-positive breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2019, 38, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Gomez, A.; Kedward, T.; Simoes, B.M.; Dragoni, I.; NicAmhlaoibh, R.; Trivier, E.; Sabin, V.; Gee, J.M.; Sims, A.H.; Howell, S.J.; et al. PAK4 regulates stemness and progression in endocrine resistant ER-positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 458, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Awasthi, S.; Peterson, J.R.; Hamburger, A.W. Regulation of tamoxifen sensitivity by a PAK1-EBP1 signalling pathway in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladimeji, P.; Skerl, R.; Rusch, C.; Diakonova, M. Synergistic Activation of ERalpha by Estrogen and Prolactin in Breast Cancer Cells Requires Tyrosyl Phosphorylation of PAK1. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2600–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroto, B.; Ye, M.B.; von Lohneysen, K.; Schnelzer, A.; Knaus, U.G. P21-activated kinase is required for mitotic progression and regulates Plk1. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4900–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, J.A.; Swantek, J.L.; Stippec, S.; Yin, M.J.; Gaynor, R.; Cobb, M.H. Stimulation of NFkappa B activity by multiple signaling pathways requires PAK1. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 19693–19699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Song, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Nan, X.; Wang, J. Blockage of PAK1 alleviates the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells via inhibiting ERK and AKT signaling activity. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, H.; Tan, S.; Yuan, B.; Huang, X.; Jiang, J.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, R. Therapeutic potential of IBP as an autophagy inducer for treating lung cancer via blocking PAK1/Akt/mTOR signaling. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 20, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettig, M.; Trinidad, K.; Pezeshkpour, G.; Frost, P.; Sharma, S.; Moatamed, F.; Tamanoi, F.; Mortazavi, F. PAK1 kinase promotes cell motility and invasiveness through CRK-II serine phosphorylation in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.; Jeon, B.T.; Jeong, E.A.; Kim, E.J.; Kang, D.; Lee, J.S.; Jeong, B.G.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, B.H.; Lee, J.E.; et al. Pak1/LIMK1/Cofilin Pathway Contributes to Tumor Migration and Invasion in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomas and Cell Lines. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 16, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Li, L.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y.; Xie, F.; Li, H.; Cao, J.; Liu, M.; Wu, D.; He, L.; et al. PAK1-cofilin phosphorylation mediates human lung adenocarcinoma cells migration induced by apelin-13. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016, 43, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, T.; Liang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, Q.; Ma, C.M.; Zhuo, L.; Guo, D.; Zheng, K.; Zhou, C.; et al. PAK4 Phosphorylates Fumarase and Blocks TGFbeta-Induced Cell Growth Arrest in Lung Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Youn, H.; Kwon, T.; Son, B.; Kang, J.; Yang, H.J.; Seong, K.M.; Kim, W.; Youn, B. PAK1 tyrosine phosphorylation is required to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition and radioresistance in lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5520–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.W.; Wu, T.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, H. PAK1 Is a Novel Therapeutic Target in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma Activated by the PI3K/AKT Signaling Regardless of EGFR Mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5370–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.W.; Hu, J.; Wang, R.; Han, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Cytoplasmic P120ctn Promotes Gefitinib Resistance in Lung Cancer Cells by Activating PAK1 and ERK Pathway. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2021, 29, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.J.; Wu, D.W.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, H. Author Correction: PAK1 confers chemoresistance and poor outcome in non-small cell lung cancer via beta-catenin-mediated stemness. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.J.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.H.; Heo, J.N.; Choi, S.W.; Yeon, J.T.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; et al. PF-3758309, p21-activated kinase 4 inhibitor, suppresses migration and invasion of A549 human lung cancer cells via regulation of CREB, NF-kappaB, and beta-catenin signalings. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2014, 389, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.M.; Gimbrone, N.T.; Sarcar, B.; Percy, T.R.; Gordian, E.R.; Kinose, F.; Sumi, N.J.; Rix, U.; Cress, W.D. CDK4/6 inhibition synergizes with inhibition of P21-Activated Kinases (PAKs) in lung cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Azayzih, A.; Gao, F.; Somanath, P.R. P21 activated kinase-1 mediates transforming growth factor beta1-induced prostate cancer cell epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Peng, S.; Yao, K.; Chen, J.; Tao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Cai, W.; et al. The metastatic promoter DEPDC1B induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation via Rac1-PAK1 signaling. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Artham, S.; Alwhaibi, A.; Adil, M.S.; Cummings, B.S.; Somanath, P.R. PAK1 inhibitor IPA-3 mitigates metastatic prostate cancer-induced bone remodeling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 113943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whale, A.D.; Dart, A.; Holt, M.; Jones, G.E.; Wells, C.M. PAK4 kinase activity and somatic mutation promote carcinoma cell motility and influence inhibitor sensitivity. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, C.M.; Whale, A.D.; Parsons, M.; Masters, J.R.; Jones, G.E. PAK4: A pluripotent kinase that regulates prostate cancer cell adhesion. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, E.M.; Sun, X.; Olberding, J.R.; Ha, B.H.; Boggon, T.J.; Calderwood, D.A. PAK6 targets to cell-cell adhesions through its N-terminus in a Cdc42-dependent manner to drive epithelial colony escape. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Chen, R.; Li, X.; Cai, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Peng, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Downregulation of microRNA-23a suppresses prostate cancer metastasis by targeting the PAK6-LIMK1 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3904–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Gu, H.; Zhu, G.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; Li, F. p21-Activated kinase 6 (PAK6) inhibits prostate cancer growth via phosphorylation of androgen receptor and tumorigenic E3 ligase murine double minute-2 (Mdm2). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3359–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.H.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, C.S.; You, S.T.; Kim, D.J.; Park, B.H.; Kang, M.J.; Heo, W.D.; Shin, E.Y.; Schwartz, M.A.; et al. p21-Activated kinase 4 promotes prostate cancer progression through CREB. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, S.; Arora, S.; Tyagi, N.; Andrews, J.; McClellan, S.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, A.P. CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling counteracts docetaxel-induced microtubule stabilization via p21-activated kinase 4-dependent activation of LIM domain kinase 1. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 11490–11500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Li, X.; Liao, B.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yuan, X.; Ouyang, B.; Sun, Q.; Gao, X. Knockdown of p21-activated kinase 6 inhibits prostate cancer growth and enhances chemosensitivity to docetaxel. Urology 2009, 73, 1407–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, C.M.; Lund, P.J.; Huang, A.C.; Davis, M.M.; Bertozzi, C.R.; Pitteri, S.J. Mapping and Quantification of Over 2000 O-linked Glycopeptides in Activated Human T Cells with Isotope-Targeted Glycoproteomics (Isotag). Mol. Cell Proteom. 2018, 17, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Features | PAK1 | PAK2 | PAK3 | PAK4 | PAK5 | PAK6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Similarity | To PAK1 | 100% | 78.68% | 81.87% | 43.08% | 41.40% | 39.02% |
| To PAK4 | 100% | 62.29% | 55.64% | ||||
| Chemical Mass (kDa) | 61 | 58 | 62 | 64 | 81 | 75 | |
| Crystal Structure | 74–109aa 183–204aa 249–545aa | 121–136aa | 261–559aa | 2–591aa | 425–719aa | 11–45aa 94–104aa 385–681aa | |
| Localization signals | Nucleus (NLS) | 243–246aa [5] | 245–251aa | Not available | 4–7aa, 158–161aa [6] | 5–10aa [7] | Not available |
| Mitochondria | 30–83aa, 401–411aa [7] | ||||||
| Cleavage site * | 212–213aa | ||||||
| Modification | Acetylation | N-Acetylation (Ser2) | N-Acetylation (Ser2) | ||||
| Methylation | Methylation (K78) | ||||||
| Myristate | Myristate-(G213) | ||||||
| Glycosylation ** | N-Glycosylation (Asn111) | O-GlcNAcylation (Thr169,178) | N-Glycosylation (Asn22,121) | O-GlcNAcylation |
| PAK | Cancer Type | Alteration | Prognosis | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAK1 | Breast cancer | Amplification Protein overexpression | decreased the relapse-free survival | [72,73] |
| Lung cancer | Amplification Protein overexpression Over-activation | decreased the relapse-free survival | [74,75,76,77,78] | |
| Gastric cancer | Amplification Protein overexpression | [79,80] | ||
| Prostate cancer | Protein overexpression | [68] | ||
| Colon cancer | Protein overexpression | poor prognosis | [81,82] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | Protein overexpression | [83,84] | ||
| PAK2 | Breast cancer | Protein overexpression | [73] | |
| Gastric cancer | Protein overexpression | [85] | ||
| PAK3 | Lung cancer | Protein overexpression | [86] | |
| PAK4 | Breast cancer | Protein overexpression | decreased the relapse-free survival | [73,87,88,89] |
| Lung cancer | Protein overexpression | decreased the relapse-free survival | [90] | |
| Gastric cancer | Protein overexpression Over-activation | decreased relapse-free survival | [91,92] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | Amplification Protein overexpression | [48,93,94,95,96] | ||
| PAK5 | Breast cancer | Protein overexpression | poor prognosis | [33,97,98] |
| Lung cancer | Mutation | Overall survival Immune-microenvironment | [99,100] | |
| Gastric cancer | Protein overexpression | poor prognosis | [101,102,103] | |
| Colon cancer | Protein overexpression | [104,105] | ||
| PAK6 | Breast cancer | mRNA upregulation | [73] | |
| Gastric cancer | Protein overexpression | poor prognosis | [106] | |
| Prostate cancer | Protein overexpression | [107] | ||
| Colon cancer | Protein overexpression | Decreased overall survival | [108] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Li, F. p21-Activated Kinase: Role in Gastrointestinal Cancer and Beyond. Cancers 2022, 14, 4736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194736
Li X, Li F. p21-Activated Kinase: Role in Gastrointestinal Cancer and Beyond. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194736
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaodong, and Feng Li. 2022. "p21-Activated Kinase: Role in Gastrointestinal Cancer and Beyond" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194736
APA StyleLi, X., & Li, F. (2022). p21-Activated Kinase: Role in Gastrointestinal Cancer and Beyond. Cancers, 14(19), 4736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194736






