Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion in Pediatric Brain Tumors: A Review of Techniques, Quality Control, and Quantification
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. ASL Perfusion Principles and Methods
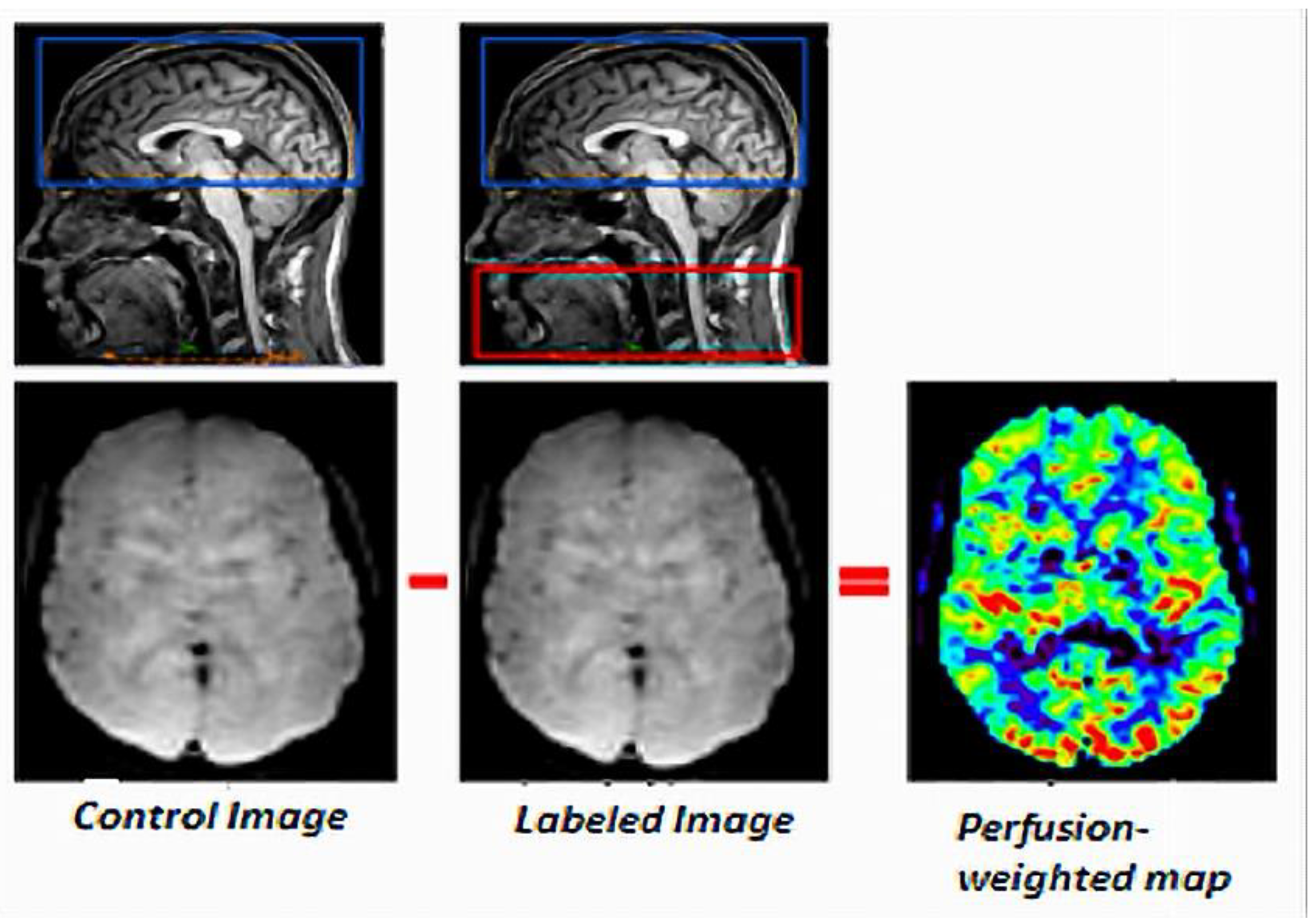
2.1. Principles
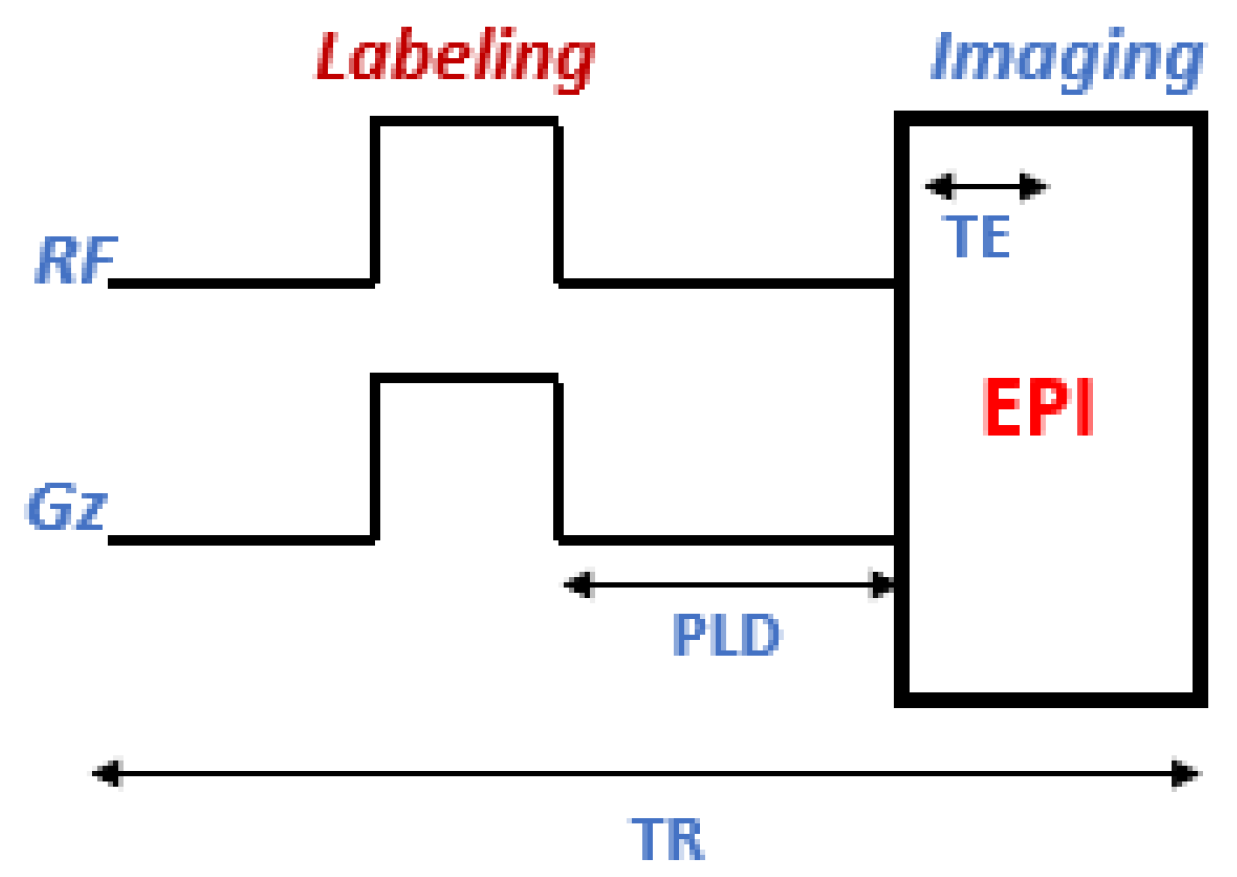
2.2. Techniques
2.2.1. Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling
2.2.2. Pulsed Arterial Spin Labeling
2.2.3. Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling
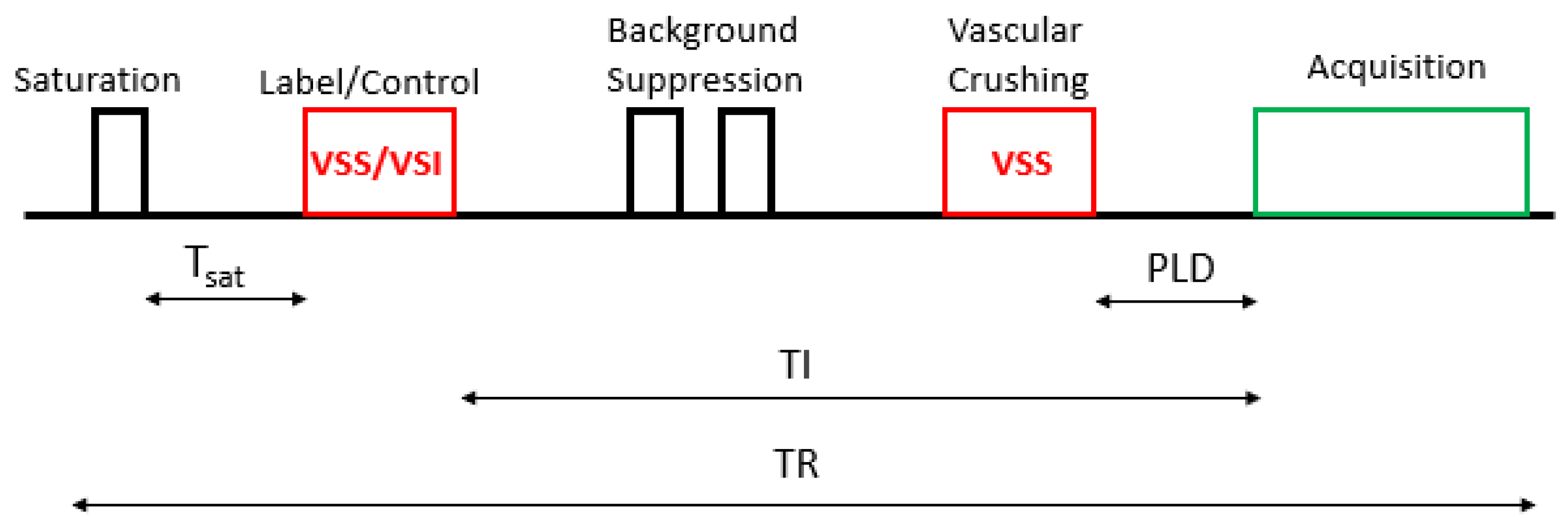
2.2.4. Velocity Selective Arterial Spin Labeling
3. CBF Quantification
- CASL/pCASL
- PASLwhere λ is the brain/blood partition coefficient in mL/g, SIcontrol and SIlabel are the time-averaged signal intensities for the control and labeled images, T1blood (ms) is the longitudinal blood relaxation time, α is labeling efficiency, SI(PD) is the signal intensity of PD images, and τ (ms) is the labeling duration. PLD (ms) is the delay after labeling, TI (ms) is the bolus duration in PASL (i.e., equivalent of labeling duration in CASL/pCASL), and TI1 (ms) is the reversal time in PASL. The factor 6000 converts the mL/g/s unit to mL/100 g/min, as described in the literature.
- VSASLwhere λ is the blood-tissue partition coefficient, ∆S the signal difference between the label and the control images, τ (ms) the time between labeling, and TI (ms) the time between labeling pulse and readout. T1blood (ms) is the T1 value of the blood. SI(PD) is acquired PD and Tsat (ms) the saturation.
- -
- Long TR calibration scan: This method is based on a separately acquired long TR scan that approximates the tissue’s equilibrium magnetization in each voxel.
- -
- ASL control averaging: If no background suppression is used, the SI(PD) map can be estimated by averaging the control images at a fixed TI, which should then be corrected for the amount of T1 relaxation during TI at each voxel, to yield a corrected map of the tissue equilibrium magnetization.
- -
- Control saturation recovery: If no background suppression is used, multiple TIs are sampled, and the acquisition sequence includes pre-saturation. An SI(PD) map can be estimated by fitting a saturation recovery curve to a series of control images.
4. Technical Advances in ASL
4.1. Resting-State fMRI Using ASL
4.2. BOLD fMRI and ASL
5. Quality Control
5.1. Common Artifacts
5.2. Visual and Automated Quality Control
5.3. Quality Control of Negative Values in CBF Maps
6. ASL-CBF Perfusion MRI Quantification
6.1. CBF in Healthy Children
6.2. CBF in Pediatric Brain Tumors
6.2.1. Classification of Tumor Types
6.2.2. Tumor Grading
6.2.3. CBF at Diagnosis
6.2.4. CBF after Treatment
CBF in Children Treated for Ependymoma
CBF in Children Treated for Pilocytic Astrocytoma, Glioblastoma, and Low-Grade Glioma
CBF in Children Treated for Medulloblastoma
7. ASL Perfusion Weighted Map Assessment
7.1. Qualitative Assessment
7.2. Semi-Quantitative Assessment in Pediatric Tumors
8. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jahng, G.-H.; Li, K.-L.; Ostergaard, L.; Calamante, F. Perfusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Comprehensive Update on Principles and Techniques. Korean J. Radiol. 2014, 15, 554–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurel, P. Brain image analysis, arterial spin labeling perfusion images and joint EEG-fMRI neurofeedback. Comput. Sci. Univ. Rennes 1 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.S.; A Detre, J.; Leigh, J.S.; Koretsky, A.P. Magnetic resonance imaging of perfusion using spin inversion of arterial water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yao, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zhu, W. Comparative analysis of arterial spin labeling and dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion imaging for quantitative perfusion measurements of brain tumors. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 2790–2799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banos, J. Intérêt de la Séquence Artérial Spin Labeling (ASL) en IRM dans les Épilepsies Réfractaires de l ’ Enfant; Sciences du Vivant [q-bio]: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yeom, K.W.; Mitchell, L.A.; Lober, R.M.; Barnes, P.D.; Vogel, H.; Fisher, P.G.; Edwards, M.S. Arterial Spin-Labeled Per-fusion of Pediatric Brain Tumors. Pediatrics 2014, 35, 395–401. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Duan, Y.; Peterson, B.S.; Asllani, I.; Zelaya, F.; Lythgoe, D.; Kangarlu, A. Resting state cerebral blood flow with arterial spin labeling MRI in developing human brains. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2018, 22, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.J.J.; Chen, Y.; Fernández-Seara, M.A.; Detre, J.A. Potentials and Challenges for Arterial Spin Labeling in Pharmacological Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 337, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, A.; De Luca, F.; Hanagandi, P.; Van Westen, D.; Delgado, A. Arterial Spin-Labeling in Children with Brain Tumor: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Guerrero, S.; Vargas-Cuellar, M.P.; Charry-Sánchez, J.D.; Talero-Gutiérrez, C. Cognitive sequelae of radiotherapy in primary brain tumors. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2021, 26, 101305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.D.; Forkert, N.D.; Kundu, P.; Ambler, C.; Lober, R.M.; Burns, T.C.; Barnes, P.D.; Gibbs, I.C.; Grant, G.A.; Fisher, P.G.; et al. Brain Perfusion and Diffusion Abnormalities in Children Treated for Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors. J. Pediatr. 2017, 185, 173–180.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, P.; Mutsaerts, H.-J.; Václavů, L.; Ghariq, E.; Pizzini, F.B.; Smits, M.; Acou, M.; Jovicich, J.; Vanninen, R.; Kononen, M.; et al. Variability of physiological brain perfusion in healthy subjects—A systematic review of modifiers. Considerations for multi-center ASL studies. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 38, 1418–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, S.; Zaharchuk, G.; Thomas, D.L.; Lovblad, K.O.; Barkhof, F.; Golay, X. Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion of the Brain. Emerg. Clin. Radiol. 2016, 20, 985–996. [Google Scholar]
- Fallatah, S.M.; Pizzini, F.B.; Gomez-Anson, B.; Magerkurth, J.; De Vita, E.; Bisdas, S.; Jäger, H.R.; Mutsaerts, H.J.M.M.; Golay, X. A visual quality control scale for clinical arterial spin labeling images. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsop, D.C.; Detre, J.A.; Golay, X.; Günther, M.; Hendrikse, J.; Hernandez-Garcia, L.; Lu, H.; MacIntosh, B.; Parkes, L.M.; Smits, M.; et al. Recommended implementation of arterial spin-labeled perfusion MRI for clinical applications: A consensus of the ISMRM perfusion study group and the European consortium for ASL in dementia. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsin-Vu, A.; Corouge, I.; Commowick, O.; Bouzillé, G.; Barillot, C.; Ferré, J.-C.; Proisy, M. Measurement of pediatric regional cerebral blood flow from 6 months to 15 years of age in a clinical population. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 101, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidyasagar, R.; Abernethy, L.; Pizer, B.; Avula, S.; Parkes, L.M. Quantitative measurement of blood flow in paediatric brain tumours-a comparative study of dynamic susceptibility contrast and multi time-point arterial spin labelled MRI. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.; Withey, S.B.; Lateef, S.; MacPherson, L.; Pinkey, B.; Peet, A.C. A comparison of pseudo-continuous arterial spin labelling and dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI with and without contrast agent leakage correction in paediatric brain tumours. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20170872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, N.M. Three-Dimensional Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling Parameters Distinguish Pediatric Medulloblastoma and Pilocytic Astrocytoma. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 8, 598190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yecies, D.; Azad, T.D.; Esparza, R.; Quon, J.L.; Forkert, N.D.; MacEachern, S.J.; Bruckert, L.; Maleki, M.; Edwards, M.S.; Grant, G.A.; et al. Long-Term Supratentorial Radiologic Effects of Surgery and Local Radiation in Children with Infratentorial Ependymoma. World Neurosurg. 2018, 122, e1300–e1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, P.; Monet, P.; de Marco, G.; Saliou, G.; Perrin, M.; Stoquart-Elsankari, S.; Bruniau, A.; Vallée, J. A Comparative Study of Perfusion Measurement in Brain Tumours at 3 Tesla MR: Arterial Spin Labeling versus Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast-Enhanced MRI. Eur. Neurol. 2010, 64, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, J.-C.; Bannier, E.; Raoult, H.; Mineur, G.; Carsin-Nicol, B.; Gauvrit, J.-Y. Perfusion par arterial spin labeling (ASL): Technique et mise en œuvre clinique. J. de Radiol. Diagn. et Interv. 2013, 94, 1208–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallatah, S. Perfusion Imaging in Brain Tumors; Institute of Neurology, University College London: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cuenod, C.-A.; Balvay, D. Imagerie de la perfusion tissulaire et de la perméabilité. J. Radiol. Diagn. Interv. 2013, 94, 1184–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detre, J.A.; Alsop, D. Perfusion magnetic resonance imaging with continuous arterial spin labeling: Methods and clinical applications in the central nervous system. Eur. J. Radiol. 1999, 30, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Alsop, D.; Li, L.; Listerud, J.; Gonzalez-At, J.B.; Schnall, M.D.; Detre, J.A. Comparison of quantitative perfusion imaging using arterial spin labeling at 1.5 and 4.0 Tesla. Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 48, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsop, D.; Detre, J.A. Multisection cerebral blood flow MR imaging with continuous arterial spin labeling. Radiology 1998, 208, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharchuk, G.; Ledden, P.J.; Kwong, K.K.; Reese, T.G.; Rosen, B.R.; Wald, L. Multislice perfusion and perfusion territory imaging in humans with separate label and image coils. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 41, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, K.K.; Chesler, D.A.; Weisskoff, R.M.; Donahue, K.M.; Davis, T.L.; Ostergaard, L.; Campbell, T.A.; Rosen, B.R. MR Perfusion Studies with TI-Weighted Echo Planar Imaging. MRM 1995, 34, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golay, X.; Hendrikse, J.; Lim, C.T. Perfusion Imaging Using Arterial Spin Labeling. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 15, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.C.; Kim, S. Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling Technique for Measuring CBF Dynamics With High Temporal Resolution. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 429, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Alsop, D.C.; Bolar, D.S.; Hernandez-Garcia, L.; Meakin, J.; Liu, D.; Nayak, K.S.; Schmid, S.; van Osch, M.J.P.; Wong, E.C.; et al. Velocity-selective arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI: A review of the state of the art and recommendations for clinical implementation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2022, 34, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, R.B.; Frank, L.R.; Wong, E.C.; Siewert, B.; Warach, S.; Edelman, R.R. A General Kinetic Model for Quantitative Perhsion Imaging with Arterial Spin Labeling. MRM 1998, 19, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.T.; Zimine, I.; Ho, Y.-C.L.; Golay, X. Non-invasive measurement of perfusion: A critical review of arterial spin labelling techniques. Br. J. Radiol. 2006, 79, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.-C.; Lawrence, K.S.S.; Licht, D.J.; Wang, D. Quantification Issues in Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 21, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, M.E.; Frayne, R. Cerebrovascular MRI: A review of state-of-the-art approaches, methods and techniques. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, J.; Chappell, M.A.; Okell, T.W.; Mezue, M.; Segerdahl, A.R.; Tracey, I.; Vilela, P.; Figueiredo, P. Calibration of arterial spin labeling data—Potential pitfalls in post-processing. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 83, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallée, C.; Maurel, P.; Corouge, I.; Barillot, C. Acquisition Duration in Resting-State Arterial Spin Labeling. How Long Is Enough? Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Jann, K.; Wang, D. Characterizing Resting-State Brain Function Using Arterial Spin Labeling. Brain Connect. 2015, 5, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, P.; Hernandez, L.M.; Orient, E. Age-related differences in cerebral blood flow underlie the BOLD fMRI signal in childhood. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, L.; Oliveira, A.; Heij, J.; Priovoulos, N.; Kundu, P.; Leoni, R.F.; van der Zwaag, W. Advances in resting state fMRI acquisitions for functional connectomics. NeuroImage 2021, 243, 118503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Varma, G.; Scheidegger, R.; Alsop, D.C. Quantifying fluctuations of resting state networks using arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borogovac, A.; Habeck, C.; A Small, S.; Asllani, I. Mapping Brain Function Using a 30-Day Interval between Baseline and Activation: A Novel Arterial Spin Labeling fMRI Approach. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 1721–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, D.S.; Park, S.E.; Choi, H.C.; Koh, E.H.; Kim, S.H. Preoperative localization of the sensorimotor cortex and measurement of tumor perfusion in a single acquisition using ASL technique. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 59, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zou, Q.; He, Y.; Yang, Y. Coupling of functional connectivity and regional cerebral blood flow reveals a physiological basis for network hubs of the human brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Childress, A.R.; Detre, J.A.; Wang, Z. Relations between BOLD fMRI-Derived Resting Brain Activity and Cerebral Blood Flow. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Vidorreta, M.; Katchmar, N.; Alsop, D.C.; Wolf, D.; Detre, J.A. Effects of resting state condition on reliability, trait specificity, and network connectivity of brain function measured with arterial spin labeled perfusion MRI. NeuroImage 2018, 173, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, J.M.; Tan, H.; Kraft, R.A.; Whitlow, C.T.; Burdette, J.H.; Maldjian, J.A. Arterial Spin-Labeled MR Perfusion Imaging: Clinical Applications. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2009, 17, 315–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolui, S.; Wolf, R.L.; Nabavizadeh, S.A.; Wolk, D.A.; Detre, J.A. Automated Quality Evaluation Index for 2D ASL CBF Maps. Proc. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 682. [Google Scholar]
- Meurée, C. Arterial Spin Labelling: Quality Control and Super-Resolution. In Medical Imaging; NNT: 2019REN1S016; Université Rennes 1: Rennes, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mutsaerts, H.J.; Richard, E.; Heijtel, D.F.; van Osch, M.J.; Majoie, C.B.; Nederveen, A.J. Gray matter contamination in arterial spin labeling white matter perfusion measurements in patients with dementia. NeuroImage: Clin. 2013, 4, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proisy, M.; Corouge, I.; Legouhy, A.; Nicolas, A.; Charon, V.; Mazille, N.; Leroux, S.; Bruneau, B.; Barillot, C.; Ferré, J.-C. Changes in brain perfusion in successive arterial spin labeling MRI scans in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 24, 101939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Improving cerebral blood flow quantification for arterial spin labeled perfusion MRI by removing residual motion artifacts and global signal fluctuations. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhrara, M.; Lee, D.Y.; Rejimon, A.C.; Bergeron, C.M.; Spencer, R.G. Spatially adaptive unsupervised multispectral nonlocal filtering for improved cerebral blood flow mapping using arterial spin labeling magnetic resonance imaging. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 309, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taki, Y.; Hashizume, H.; Sassa, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Wu, K.; Asano, M.; Asano, K.; Fukuda, H.; Kawashima, R. Correlation between gray matter density-adjusted brain perfusion and age using brain MR images of 202 healthy children. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 32, 1973–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangouloff-Ros, V.; Deroulers, C.; Foissac, F.; Badoual, M.; Shotar, E.; Grévent, D.; Calmon, R.; Pagès, M.; Grill, J.; Dufour, C.; et al. Arterial Spin Labeling to Predict Brain Tumor Grading in Children: Correlations between Histopathologic Vascular Density and Perfusion MR Imaging. Radiology 2016, 281, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisgontier, J.; Fillon, L.; Rutten, C.; Saitovitch, A.; Dufour, C.; Lemaître, H.; Beccaria, K.; Blauwblomme, T.; Levy, R.; Dangouloff-Ros, V.; et al. A CBF decrease in the left supplementary motor areas: New insight into postoperative pediatric cerebellar mutism syndrome using arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2021, 41, 3339–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozsunar, Y.; Mullins, M.E.; Kwong, K.K.; Hochberg, F.H.; Ament, C.; Schaefer, P.W.; Gonzalez, R.G.; Lev, M.H. Glioma Recurrence Versus Radiation Necrosis?: A Pilot Comparison of Arterial Spin-Labeled, Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Enhanced MRI, and FDG-PET Imaging. Acad. Radiol. 2010, 17, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morana, G.; Tortora, D.; Staglianò, S.; Nozza, P.; Mascelli, S.; Severino, M.; Piatelli, G.; Consales, A.; Lequin, M.; Garrè, M.L.; et al. Pediatric astrocytic tumor grading: Comparison between arterial spin labeling and dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI perfusion. Neuroradiology 2018, 60, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, L.M.; Rashid, W.; Chard, D.; Tofts, P. Normal cerebral perfusion measurements using arterial spin labeling: Reproducibility, stability, and age and gender effects. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 51, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, P.W.; Kawadler, J.; Aylett, S.E.; Kirkham, F.; Clark, C.A. Arterial Spin Labeling Characterization of Cerebral Perfusion during Normal Maturation from Late Childhood into Adulthood: Normal ‘Reference Range’ Values and Their Use in Clinical Studies. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, P.W.; D’Arco, F.; Cooper, J.; Pfeuffer, J.; Hargrave, D.; Mankad, K.; Clark, C. Arterial spin labelling and diffusion-weighted imaging in paediatric brain tumours. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 22, 101696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Hiwatashi, A.; Togao, O.; Yamashita, K.; Yoshimoto, K.; Mizoguchi, M.; Suzuki, S.O.; Iwaki, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Honda, H. Correlation between arterial spin-labeling perfusion and histopathological vascular density of pediatric intracranial tumors. J. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 135, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testud, B.; Brun, G.; Varoquaux, A.; Hak, J.F.; Appay, R.; Le Troter, A.; Girard, N.; Stellmann, J.P. Perfusion-weighted techniques in MRI grading of pediatric cerebral tumors: Efficiency of dynamic susceptibility contrast and arterial spin labeling. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudou, E.; Pariente, J.; Péran, P.; Tensaouti, F.; Pollidoro, L.; Meligne, D.; Ducassou, A.; Gros-Dagnac, H.; Arribarat, G.; Desirat, J.-P.; et al. A prospective behavioral and imaging study exploring the impact on long-term memory of radiotherapy delivered for a brain tumor in childhood and adolescence. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 33, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, T.; Ahmeti, H.; Lübbing, I.; Helle, M.; Jansen, O.; Synowitz, M.; Ulmer, S. Intraoperative resection con-trol using arterial spin labeling — Proof of concept, reproducibility of data and initial results. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 15, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Acquisition Parameters | ASL Acquisition | Rs-BOLD fMRI |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition type | CASL | echo-planar gradient |
| PLD | 1000 ms | - |
| Labeling time | 2000 ms | - |
| In-plane resolution | 220 × 220 mm2 | 220 × 220 mm2 |
| TE | 17 ms | 30 ms |
| TR | 3800 ms | 3000 ms |
| Flip angle | 90° | 90° |
| Slice thickness | 7 mm | 3 mm |
| Inter-slice gap | 2.35 mm | - |
| Matrix | 64 × 64 × 12 | 64 × 64 |
| Image number | 50 labeled/control image pairs | 220 images |
| Common Artifacts | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Motion artifacts | Appear as rings or curved lines and can cause artificially high or low CBF values. |
| Signal loss | Results from susceptibility effects with EPI-based playback sequences. These typically occur at air-tissue interfaces, such as near the frontal sinuses or the mastoid bone. |
| Distortions | |
| Bright spots (or macrovascular artifacts) | Are random clusters of very high perfusion voxels caused by the residual vascular signal. |
| Hyper/Hypo-perfusion | Is sometimes visible on perfusion maps, without being either a pathological or acquisition artifact. This constitutes a physiological change in perfusion. |
| Labeling failure | Failure to label incoming blood due to local susceptibility artifacts results in an apparent lack of perfusion throughout the affected vascular territory. |
| Imaging Technique: 3D Pulsed ASL on 1.5T MAGNETOM Aera | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Whole Brain CBF | CBF in GM | CBF in WM |
| 6–11 months | 53.3 ± 7.8 | 58.6 ± 8.3 | 29.2 ± 5.1 |
| 12–23 months | 61.7 ± 3.2 | 68.2 ± 3.5 | 39.3 ± 2.5 |
| 2–3 years | 68.5 ± 4.4 | 76.5 ± 4.9 | 40.2 ± 4.5 |
| 4–5 years | 56.6 ± 3.8 | 64.9 ± 4.3 | 26.0 ± 2.1 |
| 6–7 years | 62.4 ± 3.0 | 71.4 ± 3.1 | 30.5 ± 2.3 |
| 8–9 years | 54.9 ± 2.7 | 63.9 ± 3.1 | 25.8 ± 1.8 |
| 10–11 years | 53.4 ± 5.2 | 62.4 ± 6.1 | 23.9 ± 2.6 |
| 12–13 years | 43.3 ± 2.6 | 51.0 ± 3.0 | 21.7 ± 2.0 |
| 14–15 years | 50.1 ± 2.0 | 59.3 ± 2.5 | 24.8 ± 1.2 |
| Imaging Technique: Axial 3D Pseudo Continuous ASL with 16-Channel Head Coil in a 1.5 T MRI Machine | |
|---|---|
| Tumor Type | CBF |
| Medulloblastoma | 16.02 |
| Pilocytic astrocytoma | 9.28 |
| Imaging Technique: 3D Pseudo Continuous ASL MR Imaging on a GE Signa HDxt 1.5 T System with a 12-Channel Head-Neck-Spine Coil | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age in Years | Brain Structure | Tumor Type | CBF without Treatment |
| 2.3–9.5 | Posterior fossa | Pilocytic astrocytoma | 32 (25–40) |
| 4.6–10.5 | Medulloblastoma | 59 (48–87) | |
| 1.2–2.6 | Grade 3 ependymoma | 82 (47–142) | |
| 2.7–5.6 | Thalamus | Pilocytic astrocytoma | 36 (30–40) |
| 8.9–14.2 | Grade 3 astrocytoma | 73 (64–241) | |
| 6.6–7.4 | Glioblastoma | 94 (90–97) | |
| 4.9–12.7 | Hemispheres | Glioblastoma | 117 (100–130) |
| Imaging Technique: Spin Tagging with Alternating RF Labeling Scheme (STAR) with a Look–Locker Readout on a 3T Philips Achieva | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tumor Type | CBF | |
| CBF in control regions | - | 75 |
| CBF in tumor regions | Low-grade glioma | 87 |
| Medulloblastoma | 111 | |
| Imaging Technique: 3D Pseudo Continuous Labeling on a 3 T MRI Scanner | |
|---|---|
| Brain Structure | p Value |
| White matter | 0.749 |
| Cerebral cortex | 0.742 |
| Thalamus | 0.650 |
| Caudate | 0.050 |
| Putamen | 0.124 |
| Globus pallidus | 0.029 |
| Imaging Technique: Pseudo-Continuous ASL Sequence on a Philips Achieva 3T TX System (Best, The Netherlands) Using a 32-Channel Head Coil | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years) | Brain Structure | Tumor Type | Absolute CBF Value |
| 11.3 | Thalamus | Pilocytic astrocytoma | 79.49 |
| 4.8 | Optic chiasm | Pilocytic astrocytoma | 86.12 |
| 3.9 | Optic chiasm | Pilocytic astrocytoma | 56.03 |
| 2.8 | Optic chiasm | Pilocytic astrocytoma | 52.50 (chemotherapy only) |
| 5.6 | Optic pathway | Pilocytic astrocytoma | 48.21 (chemotherapy only) |
| 2.1 | Left hemisphere | Glioblastoma | 10.94 |
| 5.3 | Optic pathway | Low grade glioma | 82.62 (chemotherapy only) |
| Imaging Technique: 3D Pseudo-Continuous Labeling on a 3T MRI Scanner | ||
|---|---|---|
| Brain Structure | Absolute CBF Values in Healthy Controls | Absolute CBF Values in Patients with Medulloblastoma |
| White matter | 45.6–49.2 | 37.9–44.4 |
| Cerebral cortex | 64.2–69.7 | 47.8–57.9 |
| Thalamus | 53.4–58.2 | 38.6–47.3 |
| Caudate | 53.1–56.8 | 43.8–50.6 |
| Putamen | 54.9–58.6 | 44.6–51.4 |
| Globus pallidus | 42.3–45.9 | 32.9–39.4 |
| Hippocampus | 52.2–56.5 | 41.1–49 |
| Amygdala | 49–53.2 | 37.4–44.9 |
| Nucleus accumbens | 56.5–60.6 | 49.1–56.7 |
| Tumor Type | Mean Age (Years) | Tumor Location | rTBF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glioblastoma | 13 ± 8.5 | Cerebrum | 3.70 ± 1.89 |
| Anaplastic astrocytoma | 11 | Cerebrum | 3.60 |
| Medulloblastoma | 6.1 ± 3.7 | Posterior fossa | 2.87 ± 1.74 |
| Pilocytic astrocytoma | 9.4 ± 6.1 | Cerebrum, Cerebellum, Brainstem | 1.05 ± 0.19 |
| Ependymoma | 3 | Posterior fossa | 1.82 |
| Histopathology | Age (Years) | Sex | rTBF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pilocytic astrocytoma | 3 | Male | 0.54 |
| Pilocytic astrocytoma | 3 | Female | 0.29 |
| Pilocytic astrocytoma | 6 | Male | 0.36 |
| Pilocytic astrocytoma | 11 | Female | 0.53 |
| Glioblastomas | 9 | Female | 0.78 |
| Anaplastic ependymoma | 2 | Female | 2.00 |
| Anaplastic ependymoma | 3 | Male | 1.44 |
| Anaplastic ependymoma | 6 | Female | 1.98 |
| Medulloblastoma | 9 | Male | 3.59 |
| Medulloblastoma | 11 | Male | 0.82 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Troudi, A.; Tensaouti, F.; Baudou, E.; Péran, P.; Laprie, A. Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion in Pediatric Brain Tumors: A Review of Techniques, Quality Control, and Quantification. Cancers 2022, 14, 4734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194734
Troudi A, Tensaouti F, Baudou E, Péran P, Laprie A. Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion in Pediatric Brain Tumors: A Review of Techniques, Quality Control, and Quantification. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194734
Chicago/Turabian StyleTroudi, Abir, Fatima Tensaouti, Eloise Baudou, Patrice Péran, and Anne Laprie. 2022. "Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion in Pediatric Brain Tumors: A Review of Techniques, Quality Control, and Quantification" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194734
APA StyleTroudi, A., Tensaouti, F., Baudou, E., Péran, P., & Laprie, A. (2022). Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion in Pediatric Brain Tumors: A Review of Techniques, Quality Control, and Quantification. Cancers, 14(19), 4734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194734







