Molecular Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Wnt–Hippo Signaling Pathway-Related Genes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Liver Samples
2.2. RNA Extraction and RNA-Seq
2.3. RNA-Seq Data Analysis
2.4. Molecular Classification of HCC
2.5. Cell Enrichment Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
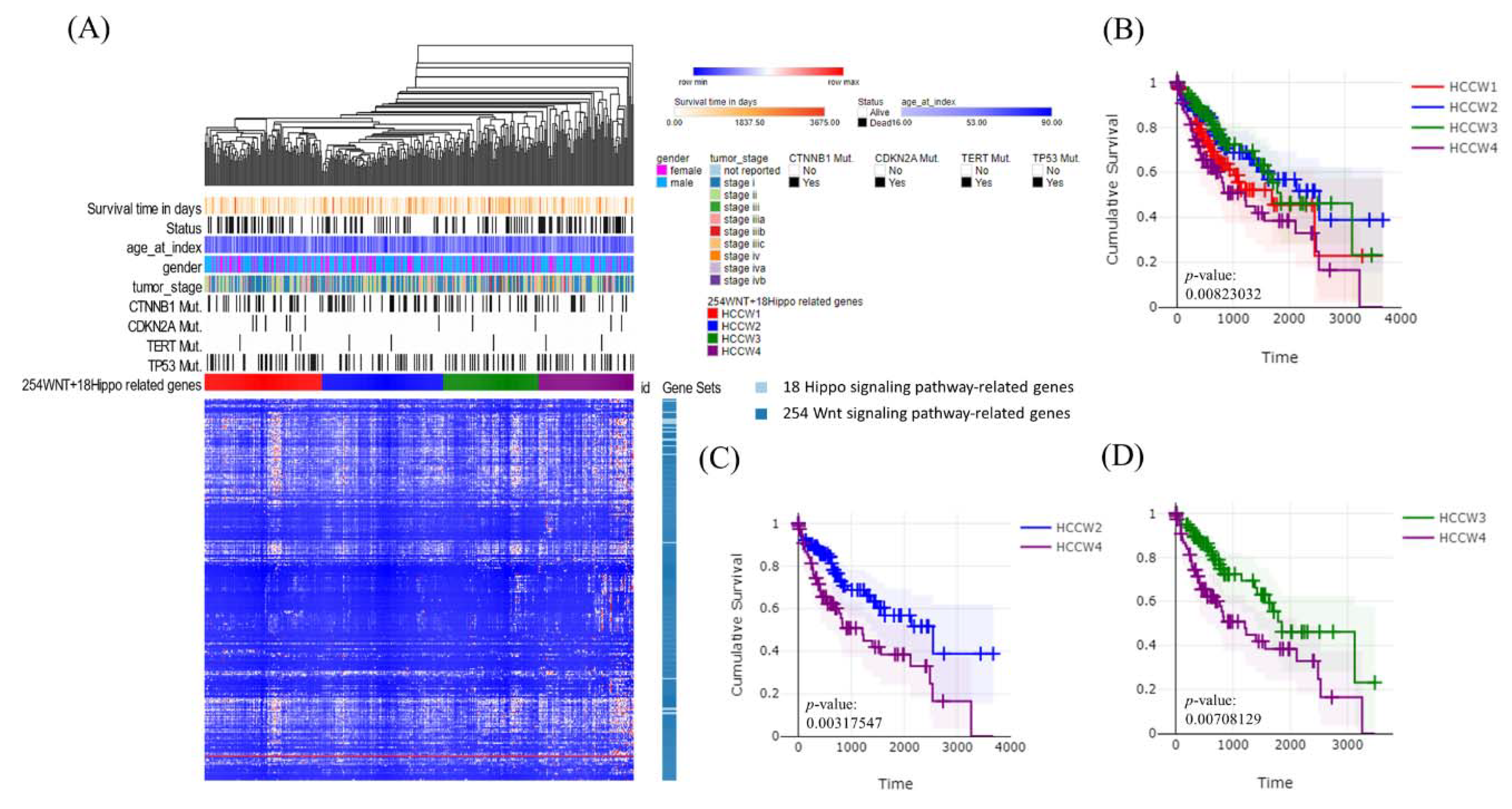
3.1. Molecular Subtypes of Taiwanese HCC Based on the Expression Profiles of 254 Wnt Pathway Genes
3.2. Molecular Subtypes of Taiwanese HCC Based on the Expression Profiles of 18 Hippo Pathway Genes
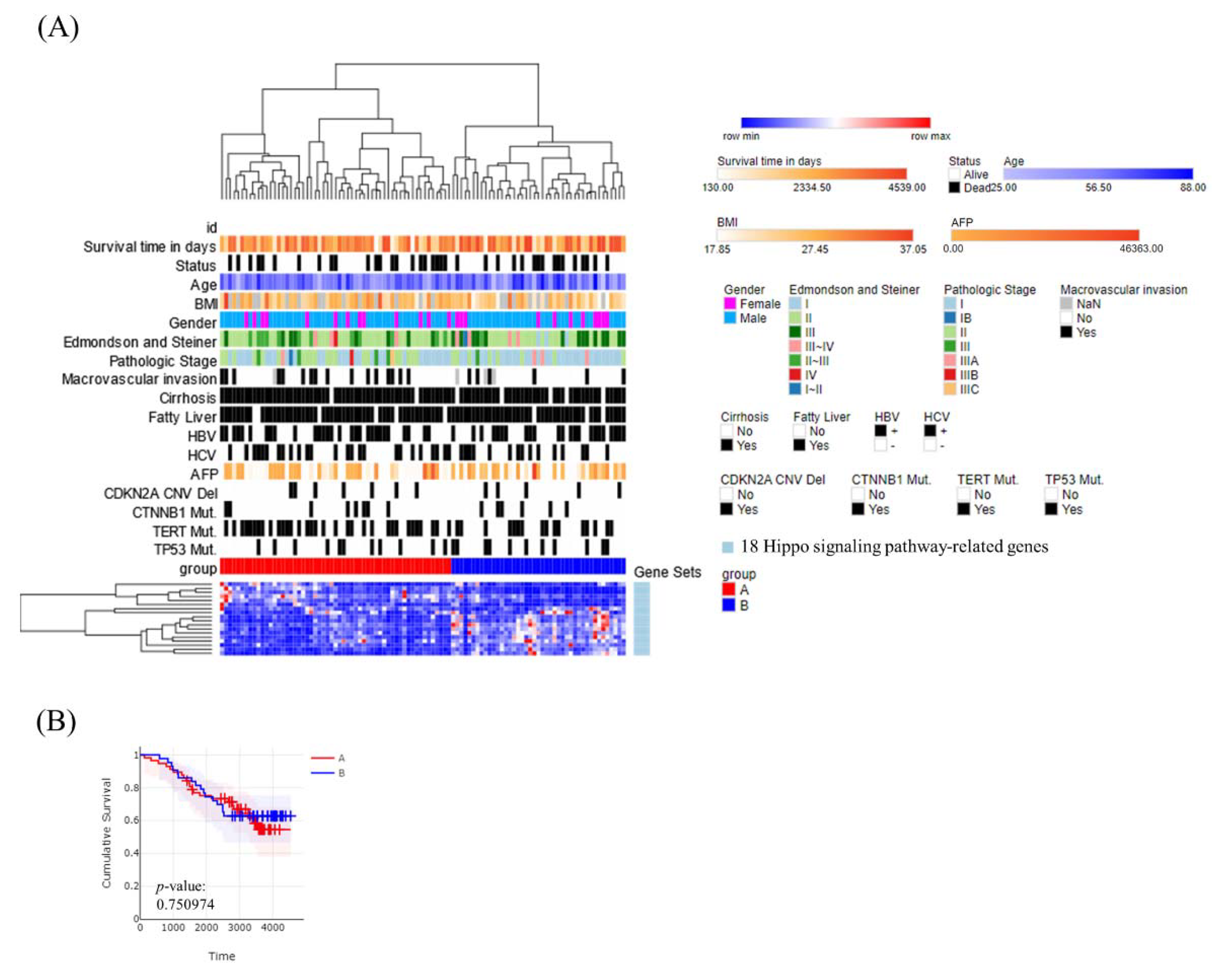
3.3. Molecular Subtypes of Taiwanese HCC Based on the Expression Profiles of 272 Wnt–Hippo Pathways Genes
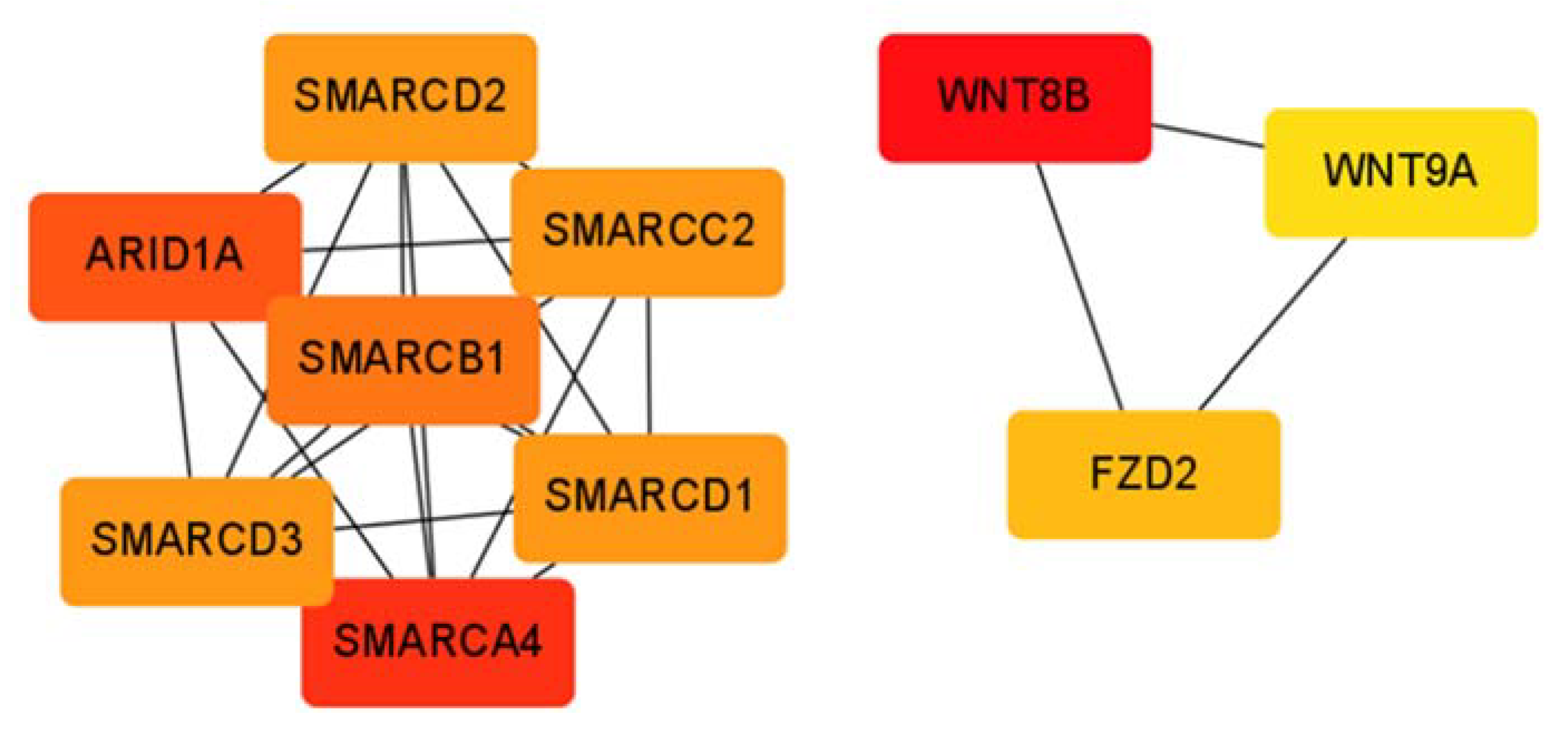
3.4. Transcriptomes of the HCC Subclasses
3.5. Correlation of HCC Subclasses with Immune Infiltration
3.6. Correlation of the HCC Subclasses with Clinical Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73 (Suppl. 1), 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.W.; Lin, C.L.; Liu, C.J.; Yang, S.H.; Tseng, Y.L.; Wu, C.F. Influence of Metabolic Risk Factors on Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Liver-Related Death in Men with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Large Cohort Study. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1006–1017.e1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Reeves, H.L.; Kotsiliti, E.; Govaere, O.; Heikenwalder, M. From NASH to HCC: Current concepts and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.; Bird, T.G.; Nault, J.C. The landscape of gene mutations in cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letouze, E.; Shinde, J.; Renault, V.; Couchy, G.; Blanc, J.F.; Tubacher, E.; Bayard, Q.; Bacq, D.; Meyer, V.; Semhoun, J.; et al. Mutational signatures reveal the dynamic interplay of risk factors and cellular processes during liver tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive and Integrative Genomic Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell 2017, 169, 1327–1341.e1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candia, J.; Bayarsaikhan, E.; Tandon, M.; Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Tovuu, L.O.; Tudev, U.; Lack, J.; Chao, A.; Chinburen, J.; et al. The genomic landscape of Mongolian hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Fujita, M.; Li, R.; Yan, S.M.; Ong, C.K.; Liao, X.; Gao, Q.; Sasagawa, S.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Profiling of Combined Hepatocellular and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Reveals Distinct Molecular Subtypes. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 932–947.e938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisaingmongkol, J.; Budhu, A.; Dang, H.; Rabibhadana, S.; Pupacdi, B.; Kwon, S.M.; Forgues, M.; Pomyen, Y.; Bhudhisawasdi, V.; Lertprasertsuke, N.; et al. Common Molecular Subtypes Among Asian Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 57–70.e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.W.; Lin, C.C.; Mo, L.R.; Chang, C.Y.; Perng, D.S.; Hsu, C.C.; Lo, G.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Yen, Y.C.; Hu, J.T.; et al. Heavy alcohol consumption increases the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.H.; You, S.L.; Chen, C.J.; Liu, C.J.; Lai, M.W.; Wu, T.C.; Wu, S.F.; Lee, C.M.; Yang, S.S.; Chu, H.C.; et al. Long-term Effects of Hepatitis B Immunization of Infants in Preventing Liver Cancer. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 472–480.e471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.H.; Chen, C.L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chien, K.L.; Kao, J.H.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, T.H.; Chen, C.H. Long-term effectiveness of population-wide multifaceted interventions for hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Lin, M.H.; Lee, C.P.; Tsan, Y.T.; Lai, M.N.; Yang, H.Y.; Ho, W.C.; Chen, P.C.; Health Data Analysis in Taiwan Research Group. Herbal medicine containing aristolochic acid and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyda Seydel, G.; Kucukoglu, O.; Altinbasv, A.; Demir, O.O.; Yilmaz, S.; Akkiz, H.; Otan, E.; Sowa, J.P.; Canbay, A. Economic growth leads to increase of obesity and associated hepatocellular carcinoma in developing countries. Ann. Hepatol. 2016, 15, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.F.; Chang, I.C.; Hong, C.C.; Yen, T.C.; Chen, C.L.; Wu, C.C.; Tsai, C.C.; Ho, M.C.; Lee, W.C.; Yu, H.C.; et al. Metabolic risk factors are associated with non-hepatitis B non-hepatitis C hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan, an endemic area of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Tang, S. WNT/beta-catenin signaling in the development of liver cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Hepatic Hippo signaling inhibits development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, B.H.; Shim, J.J.; Kim, S.B.; Jang, K.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, J.E.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.C.; et al. Inactivation of Hippo Pathway Is Significantly Associated with Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeini, A.; Torrecilla, S.; Tovar, V.; Montironi, C.; Andreu-Oller, C.; Peix, J.; Higuera, M.; Pfister, D.; Ramadori, P.; Pinyol, R.; et al. An Immune Gene Expression Signature Associated with Development of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Identifies Mice That Respond to Chemopreventive Agents. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1383–1397.e1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidkhori, G.; Benfeitas, R.; Klevstig, M.; Zhang, C.; Nielsen, J.; Uhlen, M.; Boren, J.; Mardinoglu, A. Metabolic network-based stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma reveals three distinct tumor subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11874–E11883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshida, Y.; Nijman, S.M.; Kobayashi, M.; Chan, J.A.; Brunet, J.P.; Chiang, D.Y.; Villanueva, A.; Newell, P.; Ikeda, K.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Integrative transcriptome analysis reveals common molecular subclasses of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7385–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Montal, R.; Sia, D.; Finn, R.S. Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Tu, S.J.; Yen, J.C.; Lee, Y.T.; Fang, H.Y.; Chang, J.G. The Fusion Gene Landscape in Taiwanese Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Tu, S.J.; Chiang, H.S.; Yen, J.C.; Lee, Y.T.; Fang, H.Y.; Chang, J.G. Genome-Wide Analysis of Prognostic Alternative Splicing Signature and Splicing Factors in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Genes 2020, 11, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaka, S.; Zimin, A.V.; Pertea, G.M.; Razaghi, R.; Salzberg, S.L.; Pertea, M. Transcriptome assembly from long-read RNA-seq alignments with StringTie2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouillard, A.D.; Gundersen, G.W.; Fernandez, N.F.; Wang, Z.; Monteiro, C.D.; McDermott, M.G.; Ma’ayan, A. The harmonizome: A collection of processed datasets gathered to serve and mine knowledge about genes and proteins. Database 2016, 2016, baw100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Chen, J.; Dang, X.; Chen, C.; Huang, Z.; Shen, W.; Shi, X.; Dai, C.; Chen, C. Hippo Pathway Core Genes Based Prognostic Signature and Immune Infiltration Patterns in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 680918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8 (Suppl. 4), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aran, D.; Hu, Z.; Butte, A.J. xCell: Digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
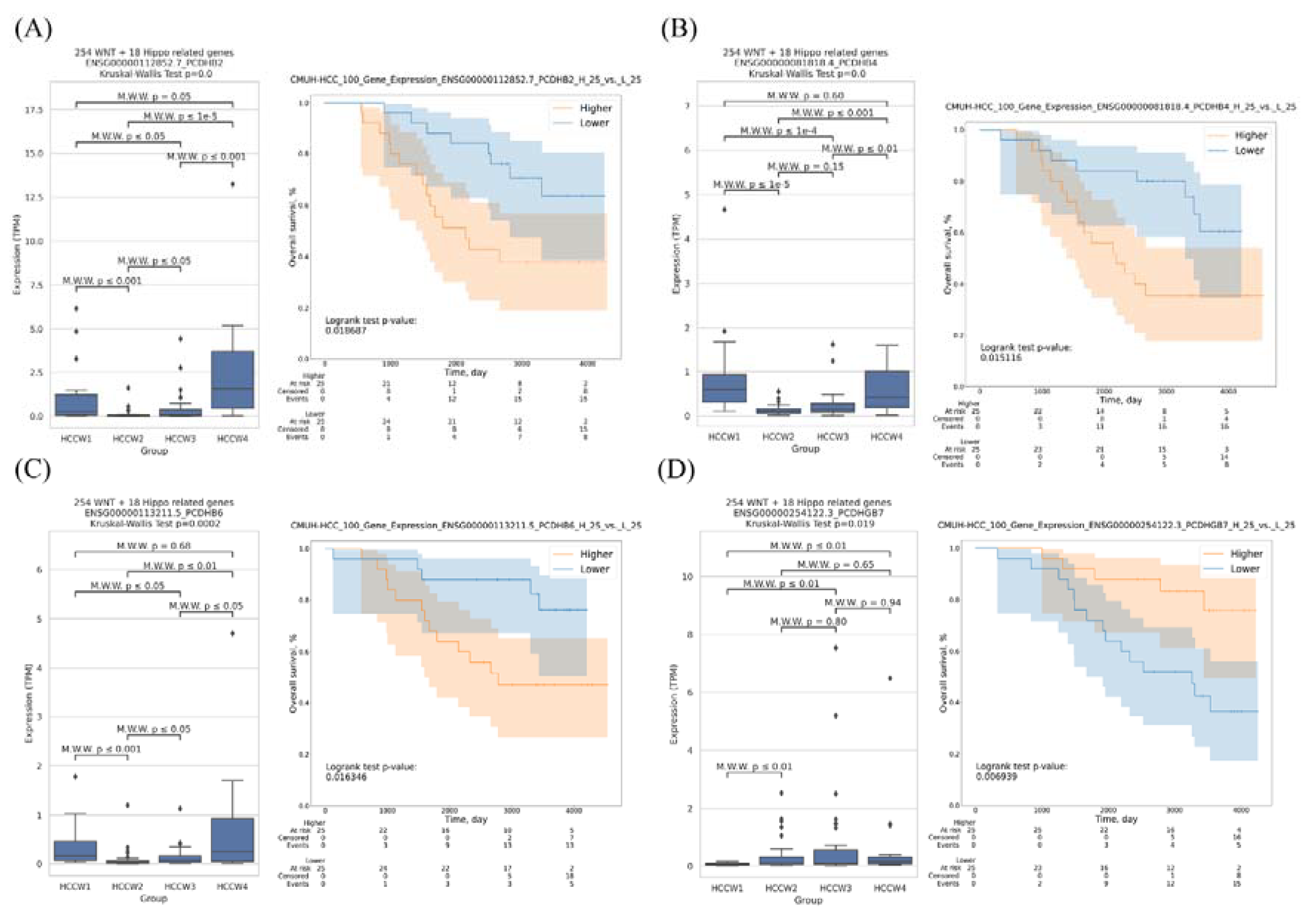
- Pancho, A.; Aerts, T.; Mitsogiannis, M.D.; Seuntjens, E. Protocadherins at the Crossroad of Signaling Pathways. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, P.; Mannisto, V.; de Mello, V.D.; Vaittinen, M.; Perfilyev, A.; Hanhineva, K.; Ling, C.; Pihlajamaki, J. Liver DNA methylation of FADS2 associates with FADS2 genotype. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Li, H.; Seng, T.J.; Langford, C.; Srivastava, G.; Tsao, S.W.; Putti, T.; Murray, P.; Chan, A.T.; Tao, Q. Functional epigenetics identifies a protocadherin PCDH10 as a candidate tumor suppressor for nasopharyngeal, esophageal and multiple other carcinomas with frequent methylation. Oncogene 2006, 25, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Huang, S.F.; Cao, J.; Wen, Y.A.; Zhang, L.P.; Ren, G.S. Silencing of PCDH10 in hepatocellular carcinoma via de novo DNA methylation independent of HBV infection or HBX expression. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 13, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Guan, G.; Chen, T.; Jin, J.; Zhang, L.; Yao, M.; Qi, X.; Zou, J.; Chen, J.; Lu, F.; et al. Methylation of PCDH19 predicts poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 14, e352–e358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, Z.; Shangguan, J.; Zhang, C.; Hu, P.; Ren, Y.; Lv, Z.; Xiang, H.; Wang, X. Loss of protocadherin-17 (PCDH-17) promotes metastasis and invasion through hyperactivation of EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Zhu, P.; Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Chen, X.; Lu, F. PCDH20 functions as a tumour-suppressor gene through antagonizing the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlen, M.; Zhang, C.; Lee, S.; Sjostedt, E.; Fagerberg, L.; Bidkhori, G.; Benfeitas, R.; Arif, M.; Liu, Z.; Edfors, F.; et al. A pathology atlas of the human cancer transcriptome. Science 2017, 357, eaan2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsberry, W.N.; Londono, A.; Randall, T.D.; Norian, L.A.; Arend, R.C. A Review of the Role of Wnt in Cancer Immunomodulation. Cancers 2019, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Alam, A.; Pant, R.; Chattopadhyay, S. Wnt Signaling and Its Significance within the Tumor Microenvironment: Novel Therapeutic Insights. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, A.; Hussein, M.S.; Prasad, P.D.; Manicassamy, S. Wnt Signaling Cascade in Dendritic Cells and Regulation of Anti-tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz de Galarreta, M.; Bresnahan, E.; Molina-Sanchez, P.; Lindblad, K.E.; Maier, B.; Sia, D.; Puigvehi, M.; Miguela, V.; Casanova-Acebes, M.; Dhainaut, M.; et al. beta-Catenin Activation Promotes Immune Escape and Resistance to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1124–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugorria, M.J.; Olaizola, P.; Labiano, I.; Esparza-Baquer, A.; Marzioni, M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Bujanda, L.; Banales, J.M. Wnt-beta-catenin signalling in liver development, health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Khan, S.K.; Gvozdenovic-Jeremic, J.; Kim, Y.; Dahlman, J.; Kim, H.; Park, O.; Ishitani, T.; Jho, E.H.; Gao, B.; et al. Hippo signaling interactions with Wnt/beta-catenin and Notch signaling repress liver tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manmadhan, S.; Ehmer, U. Hippo Signaling in the Liver—A Long and Ever-Expanding Story. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.V.; Asch, A.S.; Yamada, H.Y. Frequently mutated genes/pathways and genomic instability as prevention targets in liver cancer. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Wang, F.; Wu, E. Alterations of TP53 are associated with a poor outcome for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 2328–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, B.H.; Soong, R.; Grieu, F.; Robbins, P.D.; House, A.K.; Iacopetta, B.J. p53 accumulation and mutation are prognostic indicators of poor survival in human gastric carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 69, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, A.; Bourgmayer, A.; Kurtz, J.E.; Mellitzer, G.; Gaiddon, C. Isoforms of the p53 Family and Gastric Cancer: A Menage a Trois for an Unfinished Affair. Cancers 2021, 13, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Hao, Q.; Vadgama, J.; Wu, Y. Wild-Type TP53 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Gastric Cancer. J. Cancer Sci. Clin Ther 2021, 5, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syn, W.K.; Oo, Y.H.; Pereira, T.A.; Karaca, G.F.; Jung, Y.; Omenetti, A.; Witek, R.P.; Choi, S.S.; Guy, C.D.; Fearing, C.M.; et al. Accumulation of natural killer T cells in progressive nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable | HCCW1 | HCCW2 | HCCW3 | HCCW4 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edmondson–Steiner grade | I, II | 13 | 28 | 21 | 8 | 0.0007 |
| III, IV | 5 | 2 | 13 | 10 | 0.0203 | |
| Pathologic stage | I, II | 16 | 27 | 31 | 15 | >0.05 |
| III, IV | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Macrovascular invasion | No | 16 | 22 | 24 | 12 | >0.05 |
| Yes | 2 | 8 | 9 | 3 | ||
| Cirrhosis | No | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | >0.05 |
| Yes | 15 | 30 | 32 | 16 | ||
| Fatty liver | No | 3 | 0 | 2 | 3 | >0.05 |
| Yes | 15 | 30 | 32 | 15 | ||
| HBV | No | 7 | 18 | 13 | 10 | >0.05 |
| Yes | 11 | 12 | 21 | 8 | ||
| HCV | No | 12 | 17 | 21 | 10 | >0.05 |
| Yes | 6 | 13 | 13 | 8 | ||
| AFP | Normal | 5 | 8 | 7 | 3 | >0.05 |
| Abnormal | 13 | 22 | 27 | 15 | ||
| CTNNB1 | Wild-type | 16 | 29 | 26 | 15 | 0.0586 |
| Mutation | 2 | 1 | 8 | 3 | ||
| TERT | Wild-type | 11 | 11 | 20 | 9 | >0.05 |
| Mutation | 7 | 19 | 14 | 9 | ||
| TP53 | Wild-type | 12 | 21 | 32 | 13 | 0.0049 |
| Mutation | 6 | 9 | 2 | 5 | ||
| Hoshida | S3 | 18 | 11 | 25 | 5 | 0.0526 |
| S1, S2 | 0 | 19 | 9 | 13 | 0.0039 | |
| Bidkhor | iHCC1, 2 | 30 | 30 | 33 | 12 | <0.0001 |
| iHCC3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y.-S.; Chou, Y.-P.; Chung, C.-C.; Lee, Y.-T.; Yen, J.-C.; Jeng, L.-B.; Chang, J.-G. Molecular Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Wnt–Hippo Signaling Pathway-Related Genes. Cancers 2022, 14, 4580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194580
Chang Y-S, Chou Y-P, Chung C-C, Lee Y-T, Yen J-C, Jeng L-B, Chang J-G. Molecular Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Wnt–Hippo Signaling Pathway-Related Genes. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194580
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Ya-Sian, Yu-Pao Chou, Chin-Chun Chung, Ya-Ting Lee, Ju-Chen Yen, Long-Bin Jeng, and Jan-Gowth Chang. 2022. "Molecular Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Wnt–Hippo Signaling Pathway-Related Genes" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194580
APA StyleChang, Y.-S., Chou, Y.-P., Chung, C.-C., Lee, Y.-T., Yen, J.-C., Jeng, L.-B., & Chang, J.-G. (2022). Molecular Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Wnt–Hippo Signaling Pathway-Related Genes. Cancers, 14(19), 4580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194580





