CTRP1 Knockout Attenuates Tumor Progression in A549 and HCT116 Cancer Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Proliferation Assay
2.2. Generation of Knockout Cell Lines
2.3. Virus Production and Transduction
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Transwell Invasion Assay
2.7. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.8. Tumor Xenograft
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
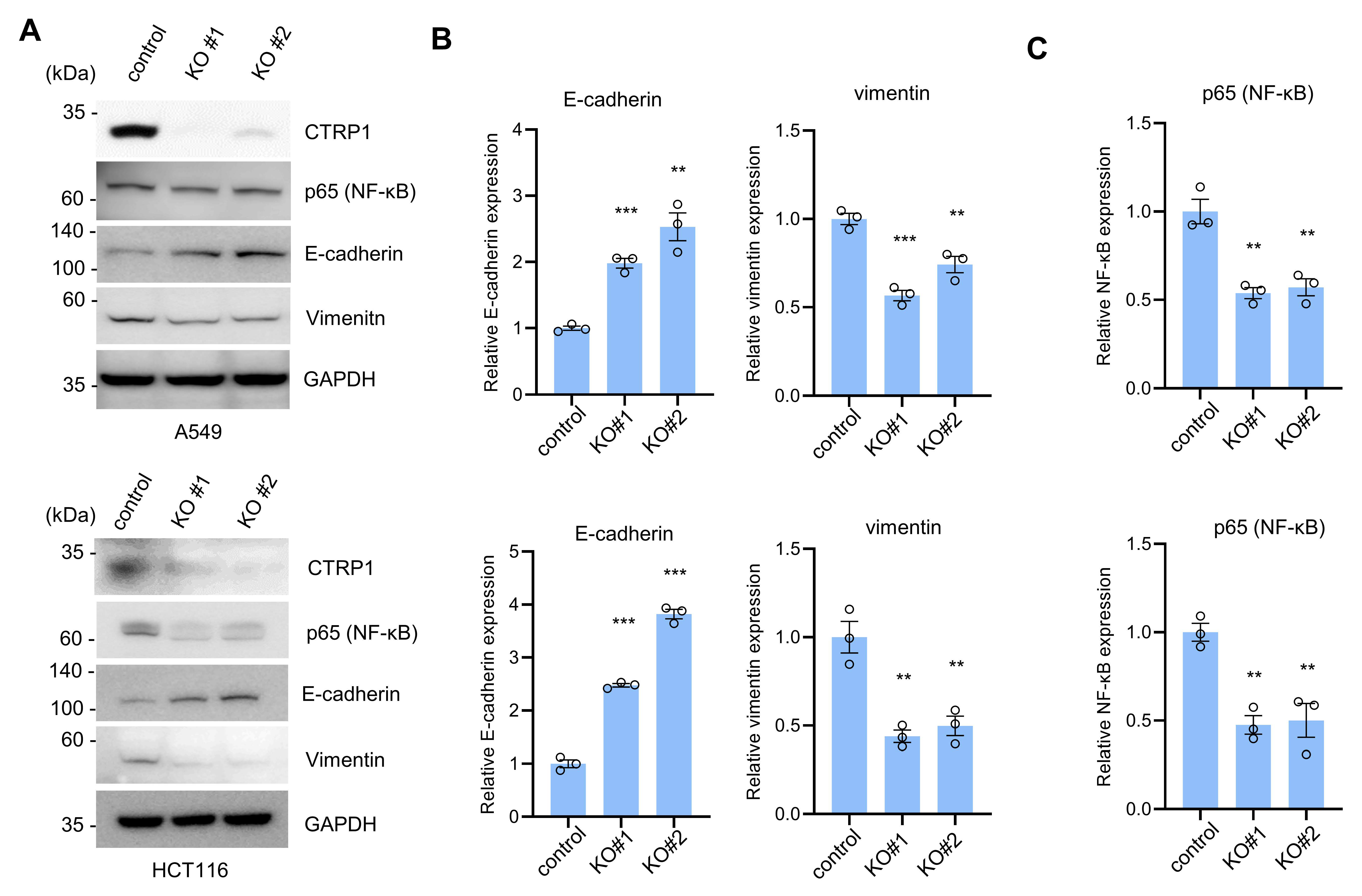
3.1. CTRP1 Knockout Decreases NF-κB and NF-κB-Dependent Transcript Levels
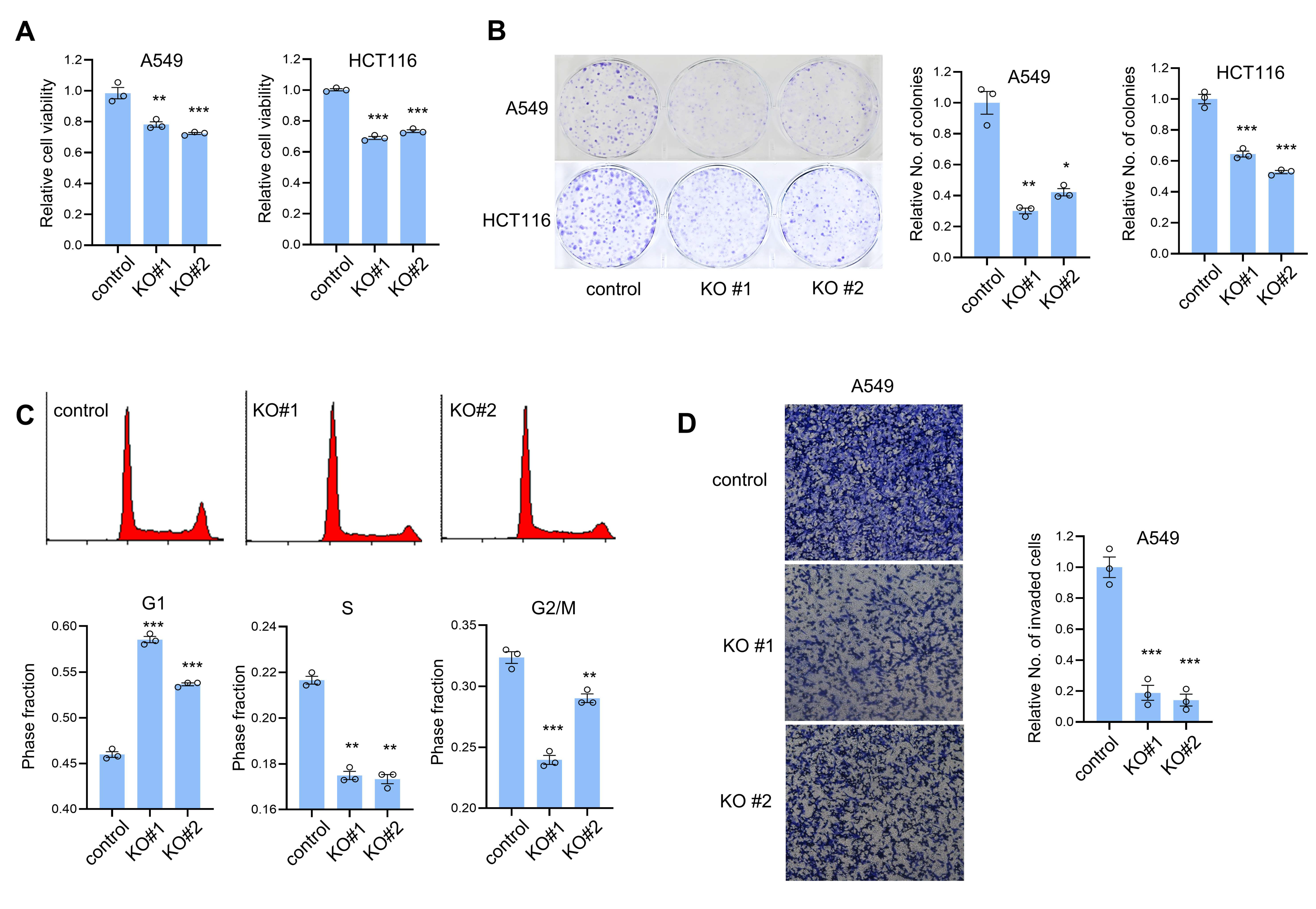
3.2. CTRP1 Knockout Decreases the Cell Proliferation and Invasion and Cell Cycle Progression
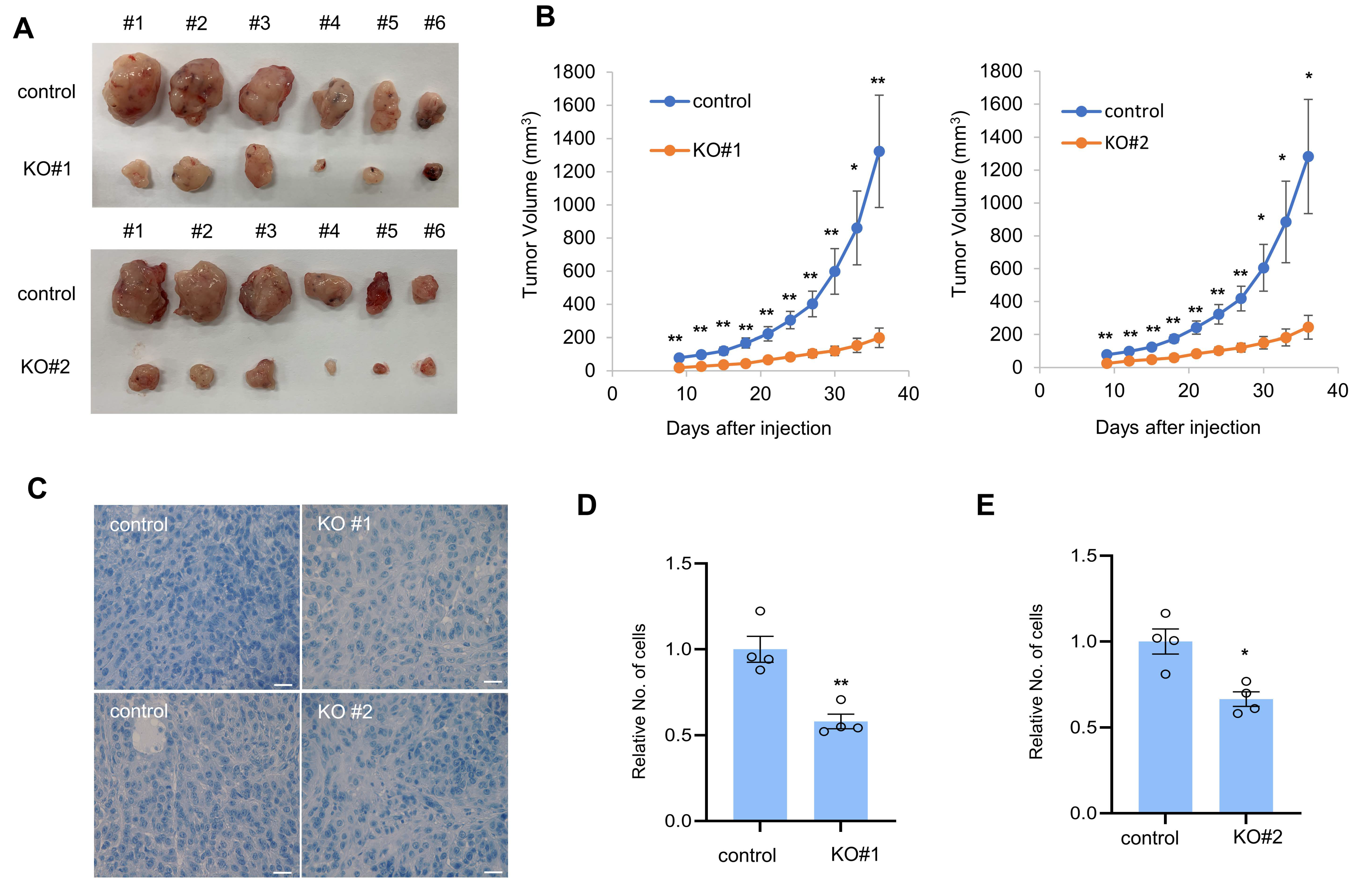
3.3. CTRP1 Contributes to Tumor Formation in Mice
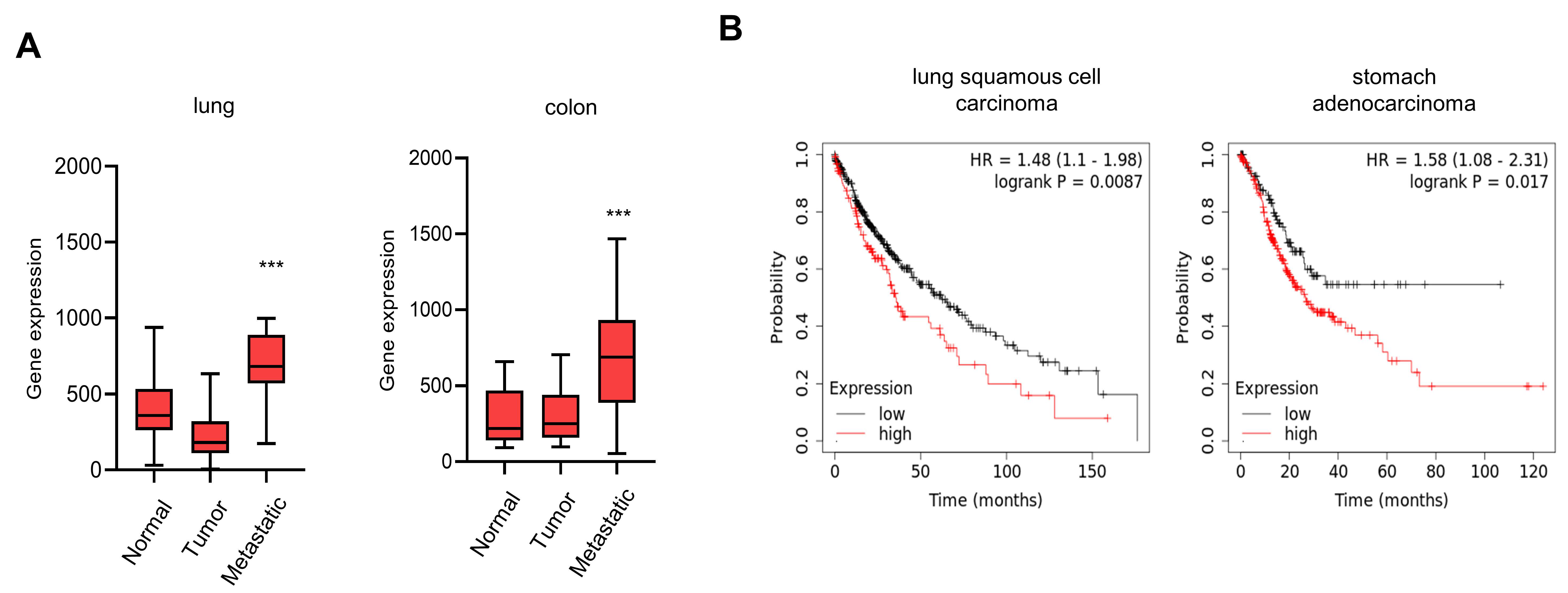
3.4. Elevated Expression of CTRP1 Results in Poor Prognosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M. Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature 2006, 441, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Tchou-Wong, K.M.; Rom, W.N. NF-kappaB in lung tumorigenesis. Cancers 2011, 3, 4258–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Shen, S.; Verma, I.M. NF-κB, an active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Bai, L.; Lin, Y. NF-kappaB in lung cancer, a carcinogenesis mediator and a prevention and therapy target. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2011, 16, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, L.A.; Ali, S.; Banerjee, S.; Munkarah, A.R.; Morris, R.T.; Sarkar, F.H. Sensitization of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by genistein: The role of NF-kappaB. J. Ovarian Res. 2008, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakshatri, H.; Bhat-Nakshatri, P.; Martin, D.A.; Goulet, R.J.; Sledge, G.W. Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB during progression of breast cancer to hormone-independent growth. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 3629–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargou, R.C.; Emmerich, F.; Krappmann, D.; Bommert, K.; Mapara, M.Y.; Arnold, W.; Royer, H.D.; Grinstein, E.; Greiner, A.; Scheidereit, C.; et al. Constitutive nuclear factor-kappaB-RelA activation is required for proliferation and survival of Hodgkin’s disease tumor cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2961–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, I.; Morishita, R.; Tsujimoto, S.; Manda, T.; Tomoi, M.; Tomita, N.; Goto, T.; Ogihara, T.; Kaneda, Y. Intravenous injection of oligodeoxynucleotides to the NF-kappaB binding site inhibits hepatic metastasis of M5076 reticulosarcoma in mice. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pires, B.R.; Mencalha, A.L.; Ferreira, G.M.; de Souza, W.F.; Morgado-Díaz, J.A.; Maia, A.M.; Corrêa, S.; Abdelhay, E.S. NF-kappaB is involved in the regulation of EMT genes in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhaos, J.; Liu, X.; Yan, B.; Chen, D.; Gao, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, C. Activation of NF-B upregulates Snail and consequent repression of E-cadherin in cholangiocarcinoma cell invasion. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2011, 58, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Onder, T.T.; Gupta, P.B.; Mani, S.A.; Yang, J.; Lander, E.S.; Weinberg, R.A. Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3645–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäffler, A.; Buechler, C. CTRP family: Linking immunity to metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seldin, M.M.; Tan, S.Y.; Wong, G.W. Metabolic function of the CTRP family of hormones. Rev. Endocr. Metab Disord. 2014, 15, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.W.; Krawczyk, S.A.; Kitidis-Mitrokostas, C.; Revett, T.; Gimeno, R.; Lodish, H.F. Molecular, biochemical and functional characterizations of C1q/TNF family members: Adipose-tissue-selective expression patterns, regulation by PPAR-γ agonist, cysteine-mediated oligomerizations, combinatorial associations and metabolic functions. Biochem. J. 2008, 416, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Judd, R.L. Adiponectin regulation and function. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1031–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Xie, Y.; Yu, Y. Role of the CTRP family in tumor development and progression [Review]. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Han, S.H.; Lim, J.S.; Cho, D.H.; Lee, M.S.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta increases CTRP1 expression in adipose tissue. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 3953–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Lyu, X.; Wang, C.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Tian, C.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D. Elevated circulating levels of CTRP1, a novel adipokine, in diabetic patients. Endocr. J. 2014, 61, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.; Jang, M.; Park, Y.I.; Park, Y.; Namkoong, S.; Lee, J.I.; Park, J. Elevated levels of CTRP1 in obesity contribute to tumor progression in a p53-dependent manner. Cancers 2021, 13, 3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Su, G. Identification of CTRP1 as a prognostic biomarker and oncogene in human glioblastoma. BioMed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2582416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.M.; Aja, S.; Wei, Z.; Wong, G.W. CTRP1 protein enhances fatty acid oxidation via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Lau, S.H.; Tzang, C.H.; Wen, J.M.; Wang, W.; Xie, D.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.C.; Huang, J.F.; et al. Association of Vimentin Overexpression and hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.L.; Dive, C.; Renehan, A.G. Biological mechanisms linking obesity and cancer risk: New perspectives. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010, 61, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, R.; Park, Y.-I.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.; So, J.; Park, J. CTRP1 Knockout Attenuates Tumor Progression in A549 and HCT116 Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184495
Park R, Park Y-I, Park Y, Lee S, So J, Park J. CTRP1 Knockout Attenuates Tumor Progression in A549 and HCT116 Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2022; 14(18):4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184495
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Rackhyun, Yea-In Park, Yeonjeong Park, Siyun Lee, Jaeyeon So, and Junsoo Park. 2022. "CTRP1 Knockout Attenuates Tumor Progression in A549 and HCT116 Cancer Cells" Cancers 14, no. 18: 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184495
APA StylePark, R., Park, Y.-I., Park, Y., Lee, S., So, J., & Park, J. (2022). CTRP1 Knockout Attenuates Tumor Progression in A549 and HCT116 Cancer Cells. Cancers, 14(18), 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184495






