Viral Particle-Mediated SAMHD1 Depletion Sensitizes Refractory Glioblastoma to DNA-Damaging Therapeutics by Impairing Homologous Recombination
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
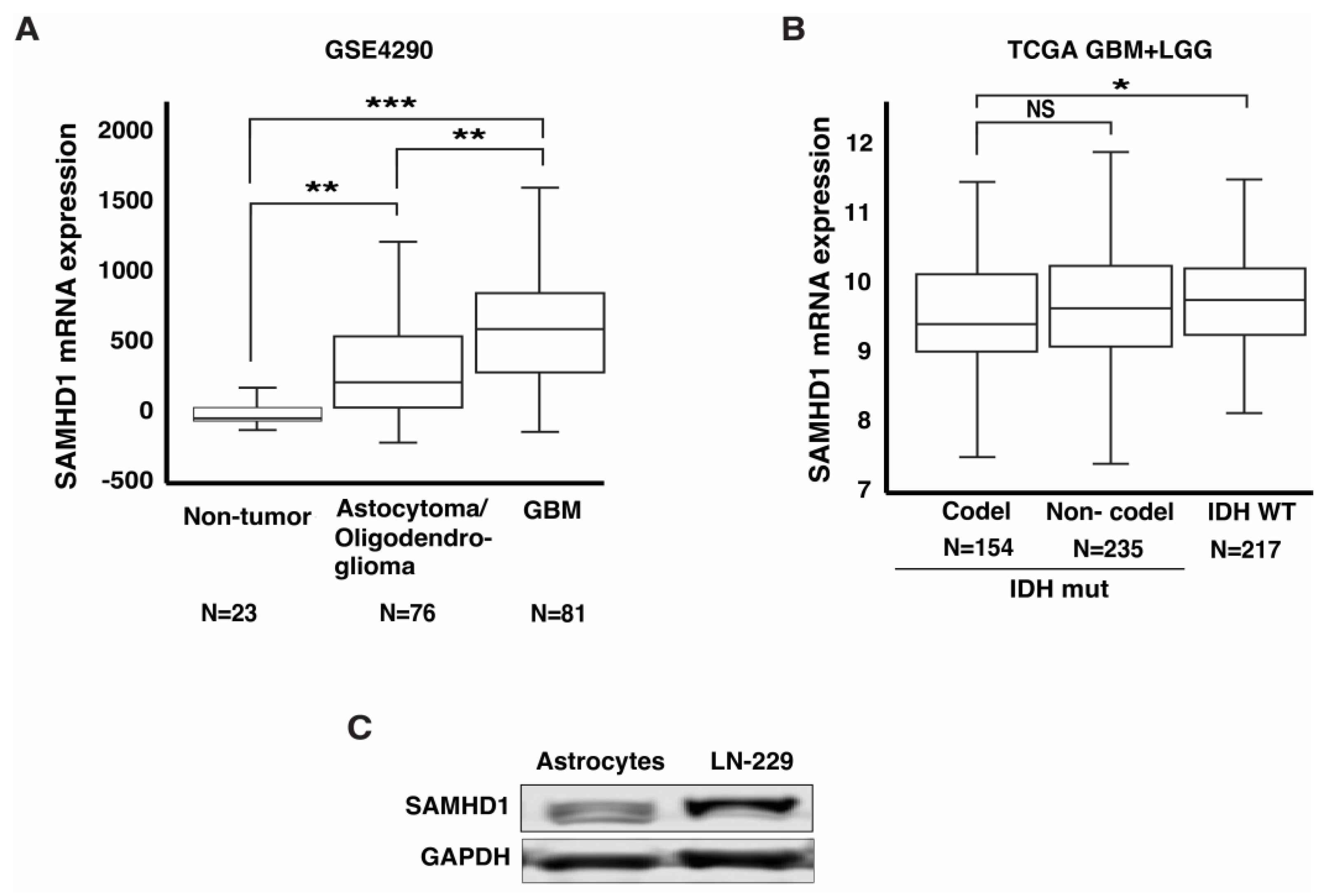
3.1. SAMHD1 Is Highly Expressed in GBM
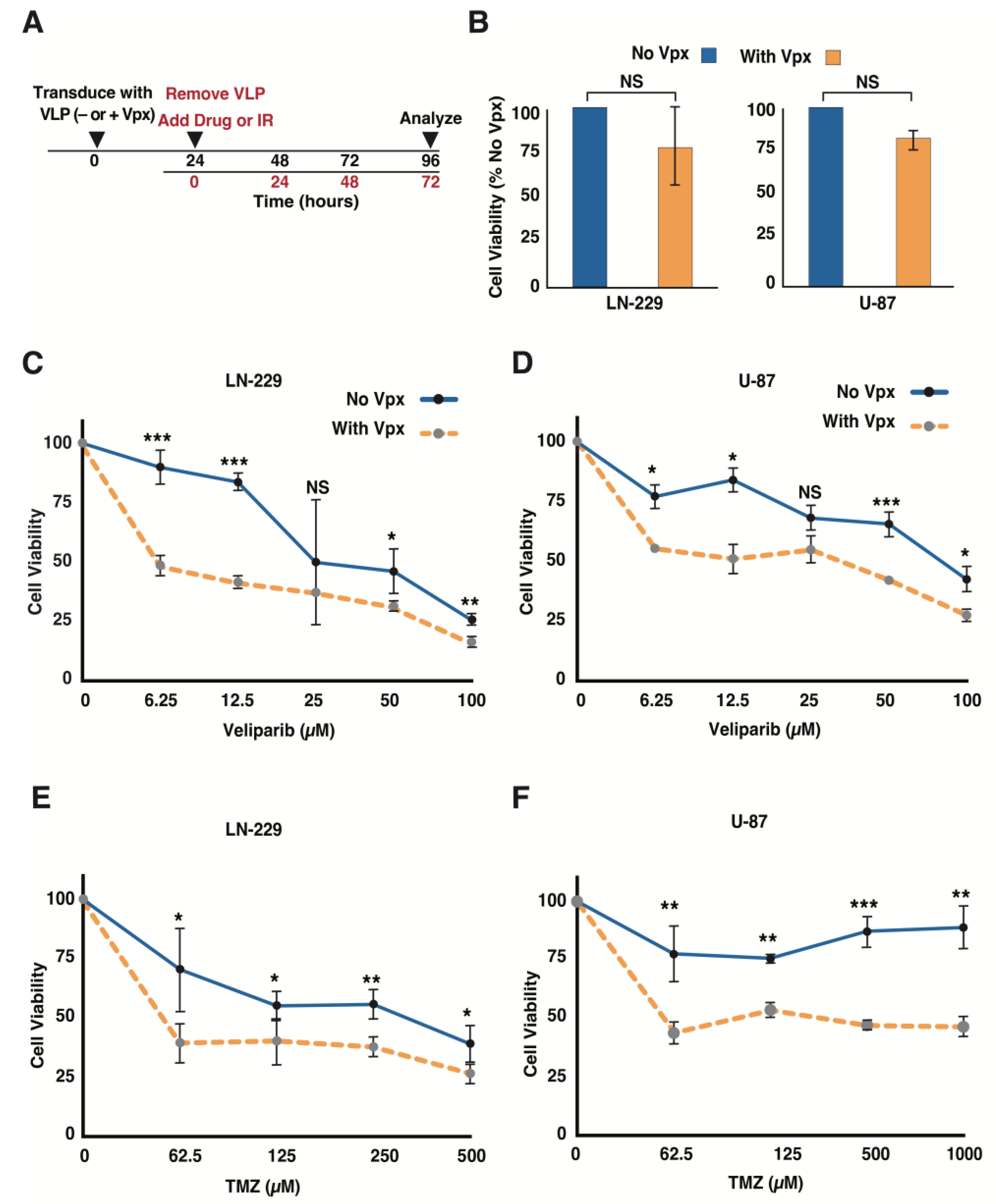
3.2. Vpx-Mediated SAMHD1 Depletion Sensitizes GBM Cells to a PARP Inhibitor and TMZ
3.3. Delivery of Vpx into GBM Cells Causes Dose-Dependent Cell Growth Inhibition
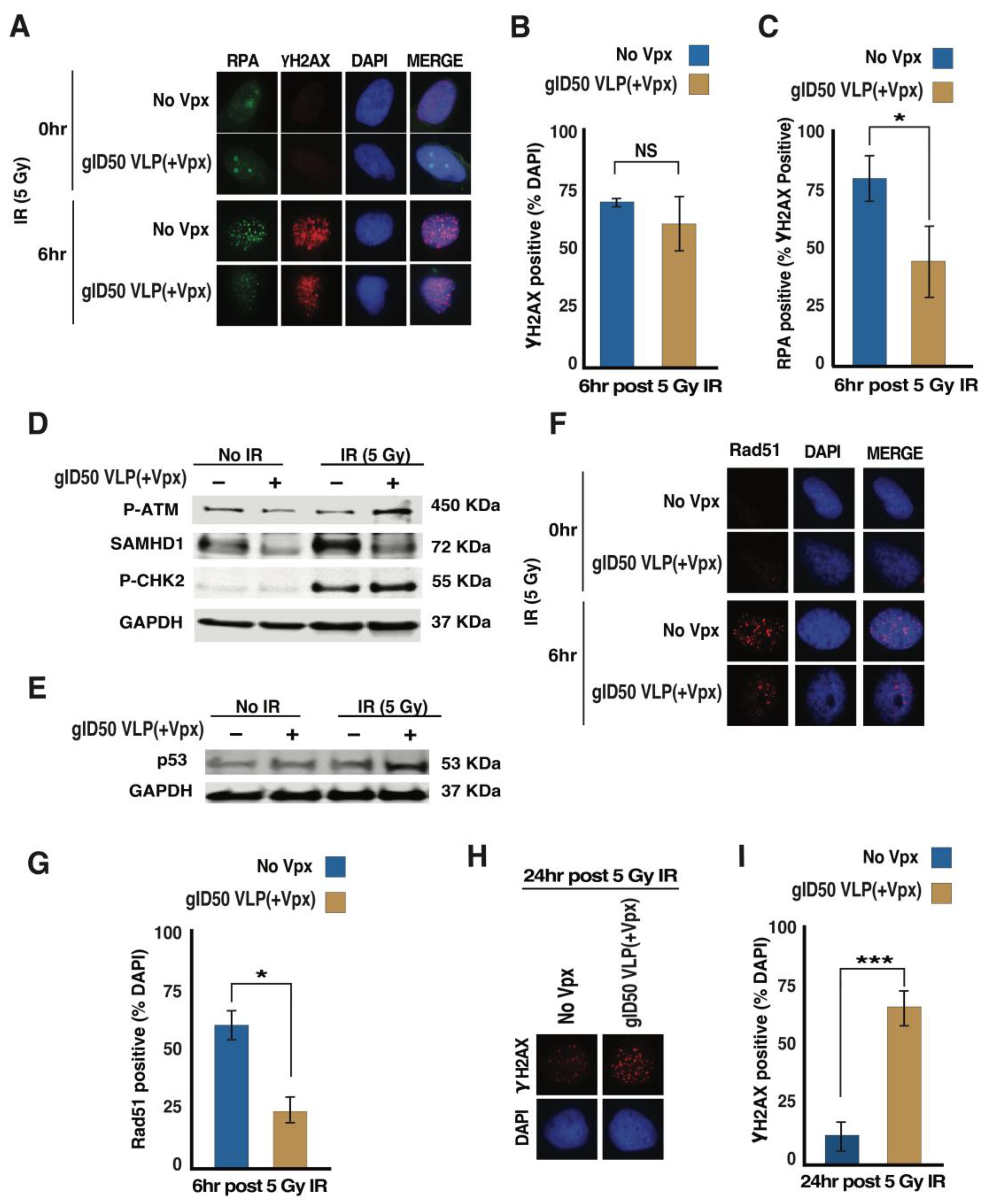
3.4. gID50 VLP(+Vpx)-Induced SAMHD1 Depletion Impairs Cellular DNA Damage Repair Potential
3.5. Exposing Malignant Glioma Cells to gID50 VLP(+Vpx) Enhances Their Sensitivity to TMZ and Ionizing Radiation (IR)
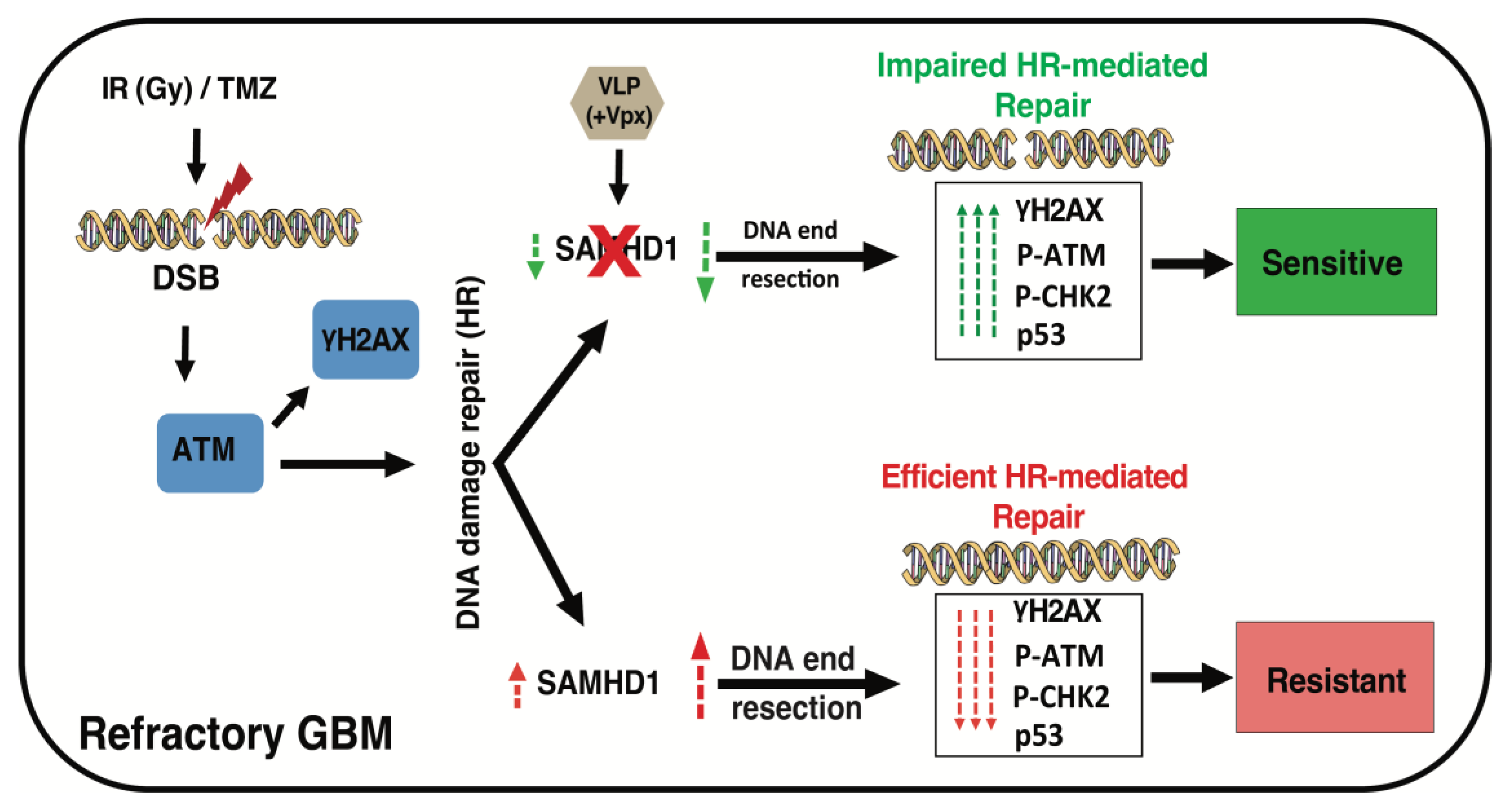
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, J.; Lv, X.; Lu, C.; Ye, X.; Chen, X.; Fu, J.; Luo, C.-H.; Zhao, Y. Prognostic factors of patients with Gliomas—An analysis on 335 patients with Glioblastoma and other forms of Gliomas. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silantyev, A.S.; Falzone, L.; Libra, M.; Gurina, O.I.; Kardashova, K.S.; Nikolouzakis, T.K.; Nosyrev, A.E.; Sutton, C.W.; Mitsias, P.D.; Tsatsakis, A. Current and Future Trends on Diagnosis and Prognosis of Glioblastoma: From Molecular Biology to Proteomics. Cells 2019, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mair, M.J.; Geurts, M.; Bent, M.J.V.D.; Berghoff, A.S. A basic review on systemic treatment options in WHO grade II-III gliomas. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 92, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.D.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Kruchko, C.; Patil, N.; Tihan, T.; Cioffi, G.; Fuchs, H.E.; Waite, K.A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L.; et al. Brain and other central nervous system tumor statistics, 2021. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 381–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzero, G.; Di Stefano, A.L.; Ronchi, S.; Bielle, F.; Villa, C.; Guillerm, E.; Capelle, L.; Mathon, B.; Laurenge, A.; Giry, M.; et al. IDH-wildtype lower-grade diffuse gliomas: The importance of histological grade and molecular assessment for prognostic stratification. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, A.M.; Taylor, J.W.; Wiencke, J.K.; Wrensch, M.R. Genetic and molecular epidemiology of adult diffuse glioma. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, R.; Matsuya, Y.; Yoshii, Y.; Date, H. Estimation of the radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks number by considering cell cycle and absorbed dose per cell nucleus. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 59, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, R.P.; Isogawa, A.; A Paulo, J.; Onizuka, K.; Takahashi, T.; Amunugama, R.; Duxin, J.P.; Fujii, S. Crosstalk between repair pathways elicits double-strand breaks in alkylated DNA and implications for the action of temozolomide. eLife 2021, 10, e69544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarra, G.; Pagano, C.; Pacelli, R.; Crescenzi, E.; Longobardi, E.; Gazzerro, P.; Fiore, D.; Pastorino, O.; Pentimalli, F.; Laezza, C.; et al. N(6)-Isopentenyladenosine Enhances the Radiosensitivity of Glioblastoma Cells by Inhibiting the Homologous Recombination Repair Protein RAD51 Expression. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickoloff, J.A.; Taylor, L.; Sharma, N.; Kato, T.A. Exploiting DNA repair pathways for tumor sensitization, mitigation of resistance, and normal tissue protection in radiotherapy. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021, 4, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.; Pongor, L.; Su, Y.-T.; Xi, L.; Raffeld, M.; Quezado, M.; Trepel, J.; Aldape, K.; Pommier, Y.; Wu, J. MGMT Status as a Clinical Biomarker in Glioblastoma. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohba, S.; Yamashiro, K.; Hirose, Y. Inhibition of DNA Repair in Combination with Temozolomide or Dianhydrogalactiol Overcomes Temozolomide-Resistant Glioma Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Yang, M.; Du, Q.; Wang, R.; Fu, B.; Tan, Y.; Cao, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. Acquired temozolomide resistance in MGMT(low) gliomas is associated with regulation of homologous recombination repair by ROCK2. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Nguyen, L.A.; Daddacha, W.; Hollenbaugh, J.A. Tight interplay among SAMHD1 protein level, cellular dNTP levels, and HIV-1 proviral DNA synthesis kinetics in human primary monocyte-derived macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21570–21574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laguette, N.; Sobhian, B.; Casartelli, N.; Ringeard, M.; Chable-Bessia, C.; Ségéral, E.; Yatim, A.; Emiliani, S.; Schwartz, O.; Benkirane, M. SAMHD1 is the dendritic- and myeloid-cell-specific HIV-1 restriction factor counteracted by Vpx. Nature 2011, 474, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, N.; Rudd, S.; Ljungblad, L.; Sanjiv, K.; Myrberg, I.H.; Paulin, C.B.J.; Heshmati, Y.; Hagenkort, A.; Kutzner, J.; Page, B.D.G.; et al. Targeting SAMHD1 with the Vpx protein to improve cytarabine therapy for hematological malignancies. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Oellerich, T.; Baldauf, H.-M.; Schwarz, S.-M.; Thomas, D.; Flick, R.; Bohnenberger, H.; Kaderali, L.; Stegmann, L.; Cremer, A.; et al. SAMHD1 is a biomarker for cytarabine response and a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yue, W.; Tang, G.; Ye, M.; Yu, J.; Liu, B.; Jiao, L.; Liu, X.; Yin, S.; Chen, J.; et al. SAMHD1 Mutations and Expression in Mantle Cell Lymphoma Patients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 763151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, K.; Majer, C.; Bulashevska, A.; Childs, L.; Schmidt, M.H.H.; Rajalingam, K.; Munder, M.; König, R. SAMHD1 in cancer: Curse or cure? J. Mol. Med. 2022, 100, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquel, F.; Silva, M.-J.; Técher, H.; Zadorozhny, K.; Sharma, S.; Nieminuszczy, J.; Mettling, C.; Dardillac, E.; Barthe, A.; Schmitz, A.-L.; et al. SAMHD1 acts at stalled replication forks to prevent interferon induction. Nature 2018, 557, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Ryoo, J.; Jeong, H.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Ahn, J.; Kim, D.; Moon, H.C.; Baek, D.; et al. Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome-associated gene SAMHD1 preserves genome integrity by preventing R-loop formation at transcription-replication conflict regions. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, R.; Louis, T.; Robbe, P.; Ackroyd, S.; Burns, A.; Timbs, A.T.; Colopy, G.W.; Dreau, H.; Sigaux, F.; Judde, J.G.; et al. SAMHD1 is mutated recurrently in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is involved in response to DNA damage. Blood 2014, 123, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daddacha, W.; Koyen, A.E.; Bastien, A.J.; Head, P.S.E.; Dhere, V.R.; Nabeta, G.N.; Connolly, E.C.; Werner, E.; Madden, M.Z.; Daly, M.B.; et al. SAMHD1 Promotes DNA End Resection to Facilitate DNA Repair by Homologous Recombination. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, N.; Shen, S.; Yu, X.-F.; Wei, W. Determinants of lentiviral Vpx-CRL4 E3 ligase-mediated SAMHD1 degradation in the substrate adaptor protein DCAF1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllery, S.A.; Ahlenstiel, C.L.; Suzuki, K.; Symonds, G.P.; Kelleher, A.D.; Turville, S.G. The feasibility of incorporating Vpx into lentiviral gene therapy vectors. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2016, 5, 16066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, R.; Subramanian, G.; Silayeva, L.; Newkirk, I.; Doctor, D.; Chawla, K.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Chandra, D.; Chilukuri, N.; Betapudi, V. Gene Therapy Leaves a Vicious Cycle. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munis, A.M. Gene Therapy Applications of Non-Human Lentiviral Vectors. Viruses 2020, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gao, F.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Martinez-Ledesma, E.; Ezhilarasan, R.; Ding, J.; Li, X.; Feng, N.; Multani, A.; et al. EGFR Amplification Induces Increased DNA Damage Response and Renders Selective Sensitivity to Talazoparib (PARP Inhibitor) in Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Smith, E.J.; Mladek, A.C.; Tian, S.; Decker, P.A.; Kizilbash, S.H.; Kitange, G.J.; Sarkaria, J.N. PARP Inhibitors for Sensitization of Alkylation Chemotherapy in Glioblastoma: Impact of Blood-Brain Barrier and Molecular Heterogeneity. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, G.; Durand, S.; Goujon, C.; Nguyen, X.-N.; Cordeil, S.; Darlix, J.-L.; Cimarelli, A. A simple, versatile and efficient method to genetically modify human monocyte-derived dendritic cells with HIV-1-derived lentiviral vectors. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hui, A.-M.; Su, Q.; Vortmeyer, A.; Kotliarov, Y.; Pastorino, S.; Passaniti, A.; Menon, J.; Walling, J.; Bailey, R.; et al. Neuronal and glioma-derived stem cell factor induces angiogenesis within the brain. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravendeel, L.A.; Kouwenhoven, M.C.; Gevaert, O.; de Rooi, J.J.; Stubbs, A.P.; Duijm, J.E.; Daemen, A.; Bleeker, F.E.; Bralten, L.B.; Kloosterhof, N.K.; et al. Intrinsic gene expression profiles of gliomas are a better predictor of survival than histology. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 9065–9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, C.; Weterings, E.; Mahadevan, D.; Sanan, A.; Weinand, M.; Stea, B. Expression Levels of RAD51 Inversely Correlate with Survival of Glioblastoma Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; He, D.; Yang, P.; He, J.; Zhang, Y. Genome-wide expression profiling of glioblastoma using a large combined cohort. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, M.; Barthel, F.P.; Malta, T.M.; Sabedot, T.S.; Salama, S.R.; Murray, B.A.; Morozova, O.; Newton, Y.; Radenbaugh, A.; Pagnotta, S.M.; et al. Molecular Profiling Reveals Biologically Discrete Subsets and Pathways of Progression in Diffuse Glioma. Cell 2016, 164, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooraei, S.; Bahrulolum, H.; Hoseini, Z.S.; Katalani, C.; Hajizade, A.; Easton, A.J.; Ahmadian, G. Virus-like particles: Preparation, immunogenicity and their roles as nanovaccines and drug nanocarriers. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keung, M.; Wu, Y.; Vadgama, J. PARP Inhibitors as a Therapeutic Agent for Homologous Recombination Deficiency in Breast Cancers. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, E.S.; Antonarakis, E.S. PARP inhibitors for homologous recombination-deficient prostate cancer. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2018, 23, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jue, T.R.; Nozue, K.; Lester, A.J.; Joshi, S.; Schroder, L.B.W.; Whittaker, S.P.; Nixdorf, S.; Rapkins, R.W.; Khasraw, M.; McDonald, K.L. Veliparib in combination with radiotherapy for the treatment of MGMT unmethylated glioblastoma. J Transl Med 2017, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.D. Biological Basis for Threshold Responses to Methylating Agents. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 2219–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, Z.D.; Kitange, G.J.; Gupta, S.K.; Joughin, B.A.; Chaim, I.A.; Mazzucato, P.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Samson, L.D. DNA Repair Capacity in Multiple Pathways Predicts Chemoresistance in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, H.; Logue, E.C.; Bloch, N.; Daddacha, W.; Polsky, S.B.; Schultz, M.L.; Kim, B.; Landau, N.R. The Vpx lentiviral accessory protein targets SAMHD1 for degradation in the nucleus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12552–12560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Bergström, T.; Jiang, Y.; Johansson, P.; Marinescu, V.D.; Lindberg, N.; Segerman, A.; Wicher, G.; Niklasson, M.; Baskaran, S.; et al. The Human Glioblastoma Cell Culture Resource: Validated Cell Models Representing All Molecular Subtypes. eBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, N.K.; A Yap, T.; Koul, D.; Balasubramaniyan, V.; Li, X.; Khan, S.; Gandy, K.S.; Yung, W.K.A.; de Groot, J.F. The promise of DNA damage response inhibitors for the treatment of glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Rhee, J.G.; Song, X.; Prochownik, E.V.; Spitz, D.R.; Lee, Y.J. Breast cancer stem cell-like cells are more sensitive to ionizing radiation than non-stem cells: Role of ATM. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.-A.; Kim, E.-J.; Kwak, S.-J.; Juhnn, Y.-S. cAMP signaling inhibits radiation-induced ATM phosphorylation leading to the augmentation of apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Prim, J.; Endara-Coll, M.; Bonath, F.; Jimeno, S.; Prados, R.; Friedländer, M.R.; Huertas, P.; Visa, N. EXOSC10 is required for RPA assembly and controlled DNA end resection at DNA double-strand breaks. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Tang, G.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, Y.; Li, H.; Fu, X.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, X. Expression Profile Analysis Identifies a Novel Five-Gene Signature to Improve Prognosis Prediction of Glioblastoma. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifati, S.; Daly, M.B.; Gelais, C.S.; Kim, S.H.; Hollenbaugh, J.A.; Shepard, C.; Kennedy, E.M.; Kim, D.H.; Schinazi, R.F.; Kim, B.; et al. SAMHD1 controls cell cycle status, apoptosis and HIV-1 infection in monocytic THP-1 cells. Virology 2016, 495, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminario, M.C.; Precht, P.; Bunnell, S.C.; Warren, S.E.; Morris, C.M.; Taub, D.; Wange, R.L. PTEN permits acute increases in D3-phosphoinositide levels following TCR stimulation but inhibits distal signaling events by reducing the basal activity of Akt. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 3165–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy, P.; Wang, X.; Linder, S. Deubiquitinase inhibition as a cancer therapeutic strategy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 147, 32–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, M.; Ohoka, N.; Shibata, N.; Tsukumo, Y. Targeted Protein Degradation by Chimeric Small Molecules, PROTACs and SNIPERs. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cingöz, O.; Arnow, N.D.; Torrents, M.P.; Bannert, N. Vpx enhances innate immune responses independently of SAMHD1 during HIV-1 infection. Retrovirology 2021, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daddacha, W.; Monroe, D.; Carver, K.; Usoro, E.R.; Alptekin, A.; Xu, H.; Osuka, S.; Arbab, A.S.; Sakamuro, D. Viral Particle-Mediated SAMHD1 Depletion Sensitizes Refractory Glioblastoma to DNA-Damaging Therapeutics by Impairing Homologous Recombination. Cancers 2022, 14, 4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184490
Daddacha W, Monroe D, Carver K, Usoro ER, Alptekin A, Xu H, Osuka S, Arbab AS, Sakamuro D. Viral Particle-Mediated SAMHD1 Depletion Sensitizes Refractory Glioblastoma to DNA-Damaging Therapeutics by Impairing Homologous Recombination. Cancers. 2022; 14(18):4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184490
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaddacha, Waaqo, Dominique Monroe, Kristen Carver, Edidiong R. Usoro, Ahmet Alptekin, Hongyan Xu, Satoru Osuka, Ali S. Arbab, and Daitoku Sakamuro. 2022. "Viral Particle-Mediated SAMHD1 Depletion Sensitizes Refractory Glioblastoma to DNA-Damaging Therapeutics by Impairing Homologous Recombination" Cancers 14, no. 18: 4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184490
APA StyleDaddacha, W., Monroe, D., Carver, K., Usoro, E. R., Alptekin, A., Xu, H., Osuka, S., Arbab, A. S., & Sakamuro, D. (2022). Viral Particle-Mediated SAMHD1 Depletion Sensitizes Refractory Glioblastoma to DNA-Damaging Therapeutics by Impairing Homologous Recombination. Cancers, 14(18), 4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184490






