Comparison of Genomic Profiling Data with Clinical Parameters: Implications for Breast Cancer Prognosis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
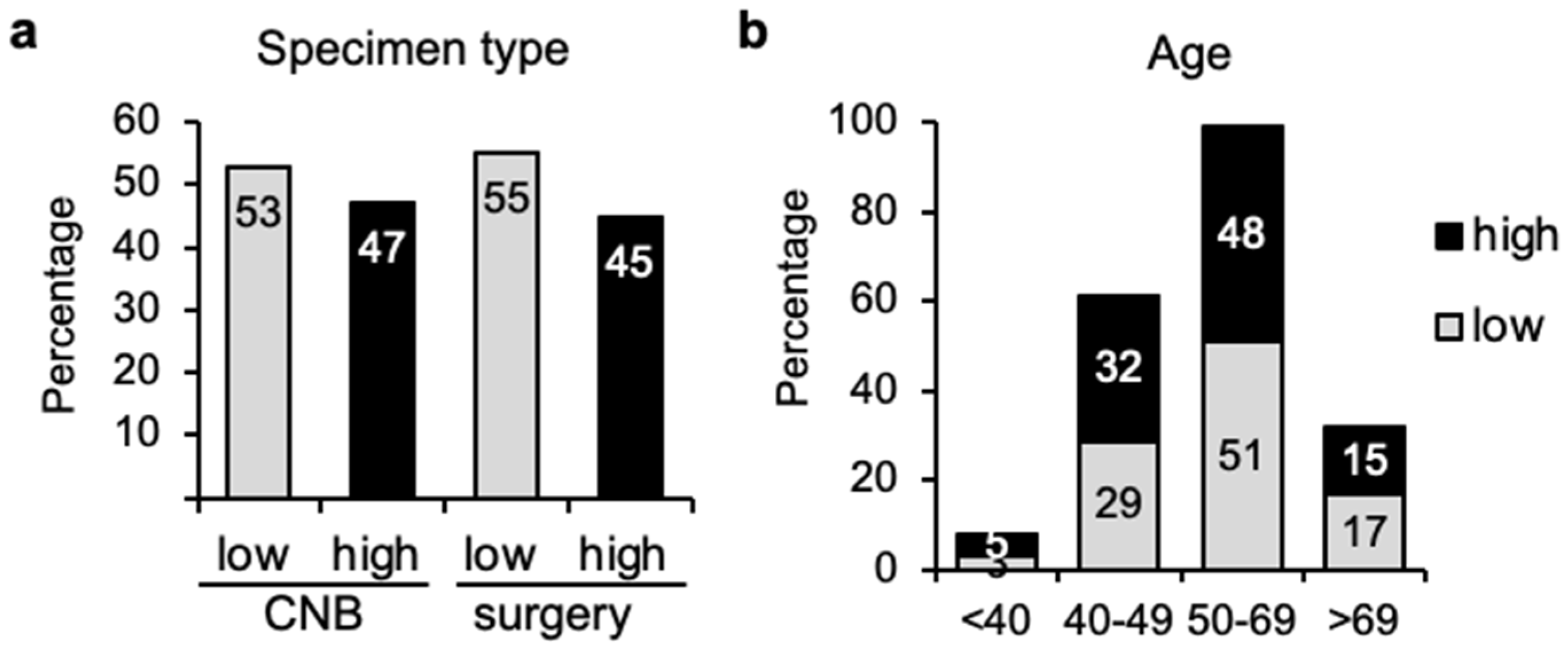
3.1. Similar Distribution of Genomic Risk Independently of Sampling Method or Age
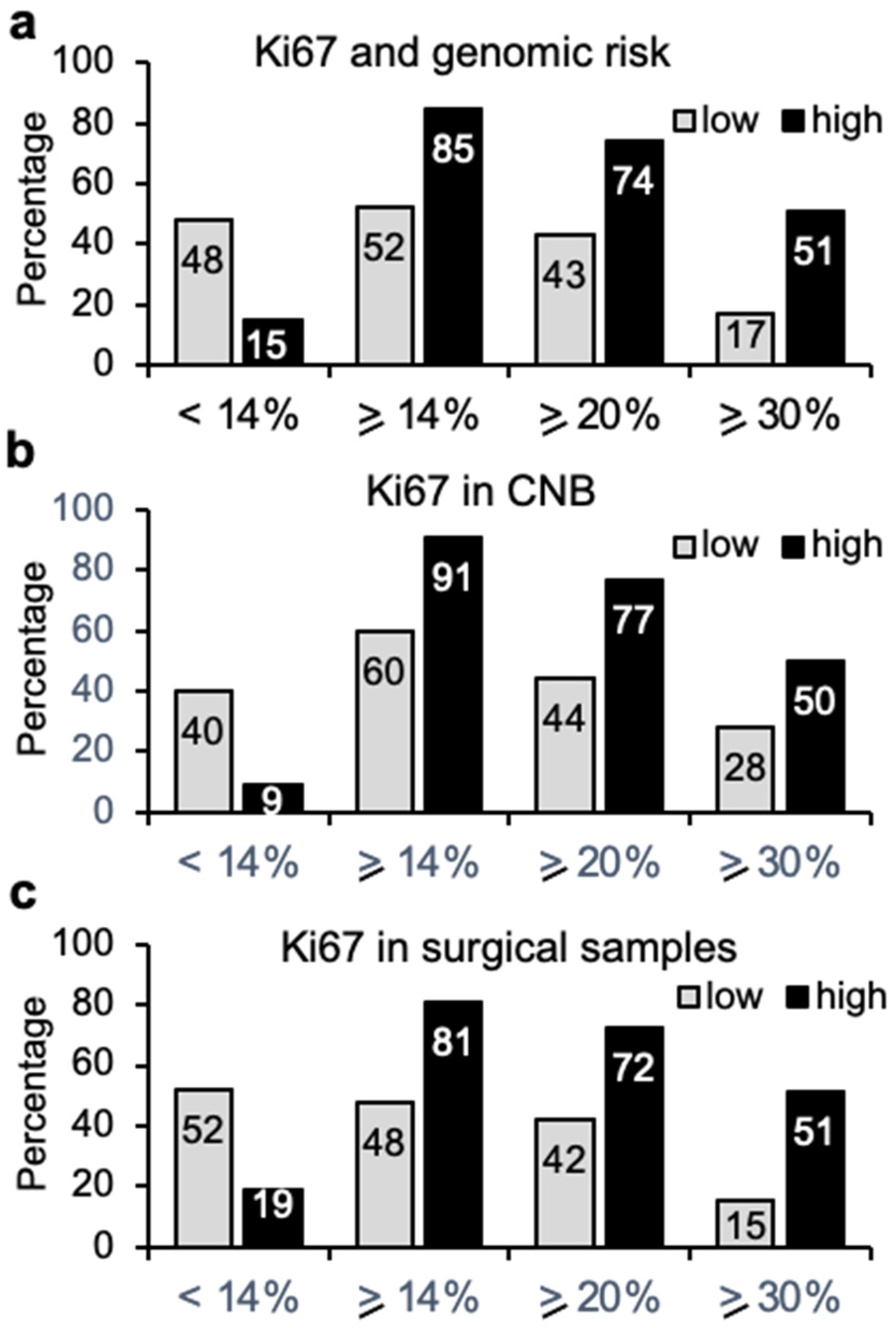
3.2. Immunohistochemical Analysis and Genomic Risk Correlation
3.3. Molecular Subtype Correlation
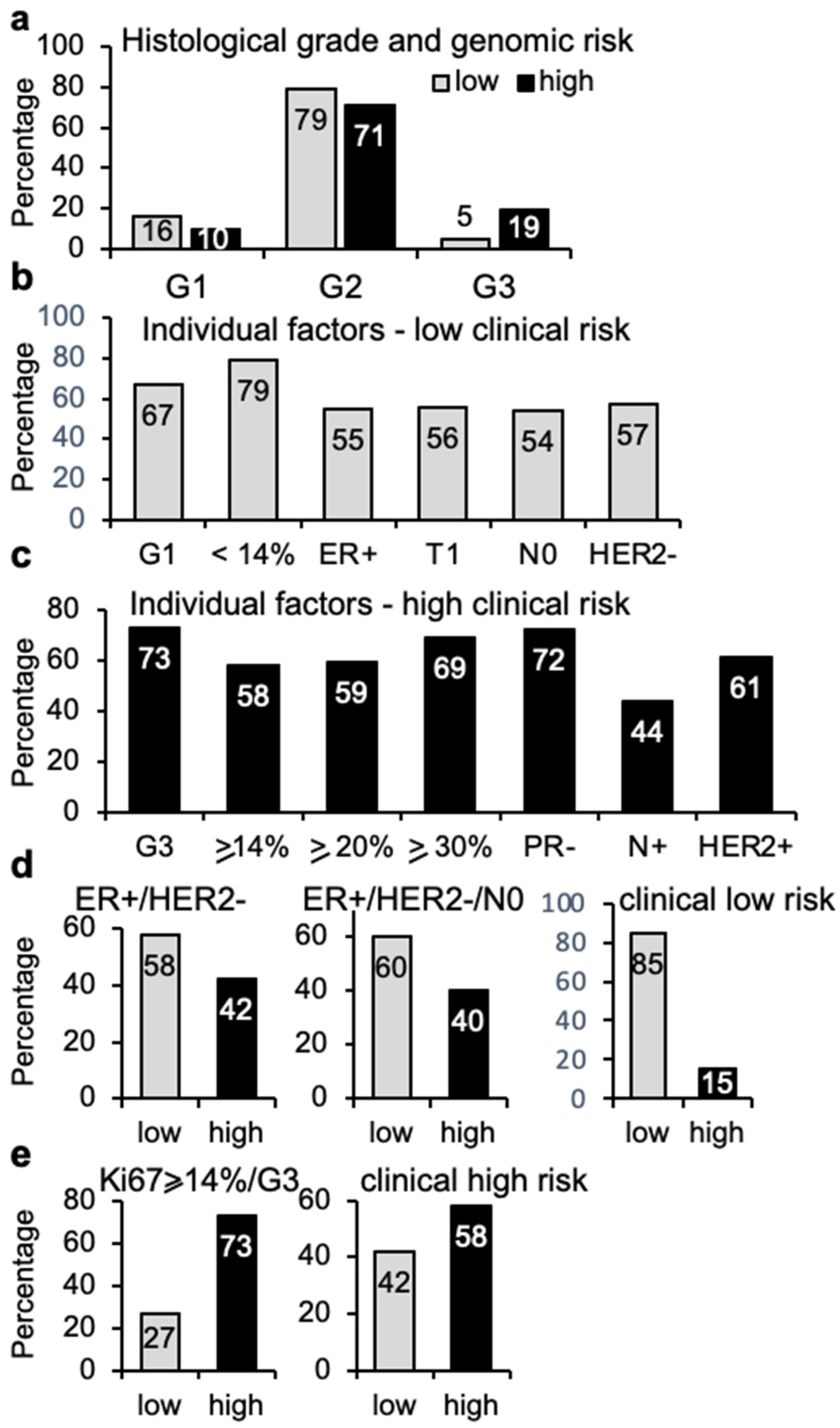
3.4. Clinical Risk vs. Genomic Risk
3.5. Immunohistochemical Analysis and Genomic Risk Correlation
3.6. Histological Grade and Genomic Risk Correlation
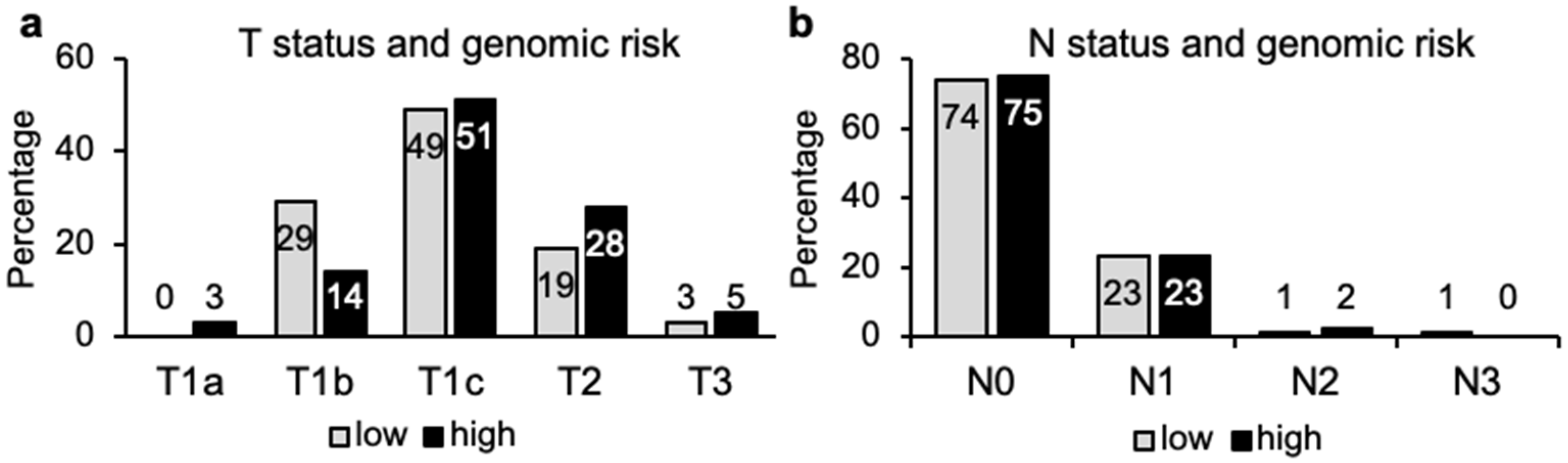
3.7. TN Staging and Genomic Risk Correlation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J.; Harbeck, N.; Nap, M.; Molina, R.; Nicolini, A.; Senkus, E.; Cardoso, F. Clinical use of biomarkers in breast cancer: Updated guidelines from the European Group on Tumor Markers (EGTM). Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 75, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorlie, T.; Perou, C.M.; Tibshirani, R.; Aas, T.; Geisler, S.; Johnsen, H.; Hastie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10869–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drukker, C.A.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, J.M.; Retel, V.P.; van Harten, W.H.; van Tinteren, H.; Wesseling, J.; Roumen, R.M.; Knauer, M.; van‘t Veer, L.J.; Sonke, G.S.; et al. A prospective evaluation of a breast cancer prognosis signature in the observational RASTER study. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; van’t Veer, L.J.; Bogaerts, J.; Slaets, L.; Viale, G.; Delaloge, S.; Pierga, J.Y.; Brain, E.; Causeret, S.; DeLorenzi, M.; et al. 70-Gene Signature as an Aid to Treatment Decisions in Early-Stage Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viale, G.; de Snoo, F.A.; Slaets, L.; Bogaerts, J.; van’t Veer, L.; Rutgers, E.J.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.J.; Stork-Sloots, L.; Glas, A.; Russo, L.; et al. Immunohistochemical versus molecular (BluePrint and MammaPrint) subtyping of breast carcinoma. Outcome results from the EORTC 10041/BIG 3-04 MINDACT trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 167, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, L.; Witteveen, A.; Beumer, I.; Delahaye, L.; Wehkamp, D.; van den Akker, J.; Snel, M.; Chan, B.; Floore, A.; Bakx, N.; et al. Controlling technical variation amongst 6693 patient microarrays of the randomized MINDACT trial. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.A.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; Chang, W.J.; Choi, M.K.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Kil, W.H.; Lee, J.E.; et al. Prognostic relevance of biological subtype overrides that of TNM staging in breast cancer: Discordance between stage and biology. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, J. Diversity of Breast Carcinoma: Histological Subtypes and Clinical Relevance. Clin. Med. Insights Pathol. 2015, 8, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Cho, J.; Kwon, S.Y.; Kang, S.H. Biologic subtype is a more important prognostic factor than nodal involvement in patients with stages I and II breast carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2016, 90, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cserni, G.; Chmielik, E.; Cserni, B.; Tot, T. The new TNM-based staging of breast cancer. Virchows Arch. 2018, 472, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focke, C.M.; Burger, H.; van Diest, P.J.; Finsterbusch, K.; Glaser, D.; Korsching, E.; Decker, T.; German Breast Screening Pathology Initiative. Interlaboratory variability of Ki67 staining in breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 84, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Tse, G.M. Immunohistochemical Surrogates for Molecular Classification of Breast Carcinoma: A 2015 Update. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, L.; Viale, G.; Bria, E.; Lutrino, E.S.; Sperduti, I.; Carbognin, L.; Schiavone, P.; Quaranta, A.; Fedele, P.; Caliolo, C.; et al. Discordance in pathology report after central pathology review: Implications for breast cancer adjuvant treatment. Breast 2016, 30, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccart, M.; van’t Veer, L.J.; Poncet, C.; Lopes Cardozo, J.M.N.; Delaloge, S.; Pierga, J.Y.; Vuylsteke, P.; Brain, E.; Vrijaldenhoven, S.; Neijenhuis, P.A.; et al. 70-gene signature as an aid for treatment decisions in early breast cancer: Updated results of the phase 3 randomised MINDACT trial with an exploratory analysis by age. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes Cardozo, J.M.N.; Drukker, C.A.; Rutgers, E.J.T.; Schmidt, M.K.; Glas, A.M.; Witteveen, A.; Cardoso, F.; Piccart, M.; Esserman, L.J.; Poncet, C.; et al. Outcome of Patients with an Ultralow-Risk 70-Gene Signature in the MINDACT Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendijk, F.H.; Jager, A.; Cardoso, F.; van Deurzen, C.H.M. A nationwide registry-based cohort study of the MammaPrint genomic risk classifier in invasive breast cancer. Breast 2018, 38, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelt, B.; Peterse, J.L.; van’t Veer, L.J. Breast cancer metastasis: Markers and models. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparano, J.A.; Gray, R.J.; Ravdin, P.M.; Makower, D.F.; Pritchard, K.I.; Albain, K.S.; Hayes, D.F.; Geyer, C.E., Jr.; Dees, E.C.; Goetz, M.P.; et al. Clinical and Genomic Risk to Guide the Use of Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2395–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, B.M.; Brase, J.C.; Haufe, F.; Weber, K.E.; Budzies, J.; Petry, C.; Prinzler, J.; Kronenwett, R.; Dietel, M.; Denkert, C. Comparison of the RNA-based EndoPredict multigene test between core biopsies and corresponding surgical breast cancer sections. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Seijen, M.; Mooyaart, A.L.; Mulder, L.; Hoogstraat, M.; Drukker, C.A.; Loo, C.E.; Pouw, B.; Sonke, G.S.; Wesseling, J.; Lips, E.H. Enrichment of high-grade tumors in breast cancer gene expression studies. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 168, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, H.; Shah, V.; Srkalovic, G.; Mahtani, R.; Levine, E.; Mavromatis, B.; Srinivasiah, J.; Kassar, M.; Gabordi, R.; Qamar, R.; et al. MammaPrint guides treatment decisions in breast Cancer: Results of the IMPACt trial. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, C.; Bendahl, P.O.; Borg, A.; Ehinger, A.; Hegardt, C.; Larsson, C.; Loman, N.; Malmberg, M.; Olofsson, H.; Saal, L.H.; et al. Agreement between molecular subtyping and surrogate subtype classification: A contemporary population-based study of ER-positive/HER2-negative primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 178, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polley, M.Y.; Leung, S.C.; Gao, D.; Mastropasqua, M.G.; Zabaglo, L.A.; Bartlett, J.M.; McShane, L.M.; Enos, R.A.; Badve, S.S.; Bane, A.L.; et al. An international study to increase concordance in Ki67 scoring. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonneuve, P.; Disalvatore, D.; Rotmensz, N.; Curigliano, G.; Colleoni, M.; Dellapasqua, S.; Pruneri, G.; Mastropasqua, M.G.; Luini, A.; Bassi, F.; et al. Proposed new clinicopathological surrogate definitions of luminal A and luminal B (HER2-negative) intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, R65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, N.; Nishimura, R.; Osako, T.; Okumura, Y.; Nakano, M.; Fujisue, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Toyozumi, Y. Ki-67 index value and progesterone receptor status can predict prognosis and suitable treatment in node-negative breast cancer patients with estrogen receptor-positive and HER2-negative tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.O.; Leung, S.C.Y.; Rimm, D.L.; Dodson, A.; Acs, B.; Badve, S.; Denkert, C.; Ellis, M.J.; Fineberg, S.; Flowers, M.; et al. Assessment of Ki67 in Breast Cancer: Updated Recommendations From the International Ki67 in Breast Cancer Working Group. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheang, M.C.; Chia, S.K.; Voduc, D.; Gao, D.; Leung, S.; Snider, J.; Watson, M.; Davies, S.; Bernard, P.S.; Parker, J.S.; et al. Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 736–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, L.N.; Jawa, Z.; Szabo, A.; Visotcky, A.; Chitambar, C.R. Relevance of progesterone receptor immunohistochemical staining to Oncotype DX recurrence score. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2016, 9, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Asten, K.; Slembrouck, L.; Olbrecht, S.; Jongen, L.; Brouckaert, O.; Wildiers, H.; Floris, G.; Van Limbergen, E.; Weltens, C.; Smeets, A.; et al. Prognostic Value of the Progesterone Receptor by Subtype in Patients with Estrogen Receptor-Positive, HER-2 Negative Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2019, 24, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piva, M.; Domenici, G.; Iriondo, O.; Rabano, M.; Simoes, B.M.; Comaills, V.; Barredo, I.; Lopez-Ruiz, J.A.; Zabalza, I.; Kypta, R.; et al. Sox2 promotes tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenici, G.; Aurrekoetxea-Rodriguez, I.; Simoes, B.M.; Rabano, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Millan, J.S.; Comaills, V.; Oliemuller, E.; Lopez-Ruiz, J.A.; Zabalza, I.; et al. A Sox2-Sox9 signalling axis maintains human breast luminal progenitor and breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3151–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Gray, R.; Braybrooke, J.; Davies, C.; Taylor, C.; McGale, P.; Peto, R.; Pritchard, K.I.; Bergh, J.; Dowsett, M.; et al. 20-Year Risks of Breast-Cancer Recurrence after Stopping Endocrine Therapy at 5 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakha, E.A.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Baehner, F.; Dabbs, D.J.; Decker, T.; Eusebi, V.; Fox, S.B.; Ichihara, S.; Jacquemier, J.; Lakhani, S.R.; et al. Breast cancer prognostic classification in the molecular era: The role of histological grade. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donegan, W.L. Tumor-related prognostic factors for breast cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 1997, 47, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi Rossi, P.; Lebeau, A.; Canelo-Aybar, C.; Saz-Parkinson, Z.; Quinn, C.; Langendam, M.; McGarrigle, H.; Warman, S.; Rigau, D.; Alonso-Coello, P.; et al. Recommendations from the European Commission Initiative on Breast Cancer for multigene testing to guide the use of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early breast cancer, hormone receptor positive, HER-2 negative. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Vijver, M.J.; He, Y.D.; van’t Veer, L.J.; Dai, H.; Hart, A.A.; Voskuil, D.W.; Schreiber, G.J.; Peterse, J.L.; Roberts, C.; Marton, M.J.; et al. A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, F.; Ismaila, N.; Henry, N.L.; Somerfield, M.R.; Bast, R.C.; Barlow, W.; Collyar, D.E.; Hammond, M.E.; Kuderer, N.M.; Liu, M.C.; et al. Use of Biomarkers to Guide Decisions on Adjuvant Systemic Therapy for Women with Early-Stage Invasive Breast Cancer: ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline Update-Integration of Results from TAILORx. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1956–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krop, I.; Ismaila, N.; Andre, F.; Bast, R.C.; Barlow, W.; Collyar, D.E.; Hammond, M.E.; Kuderer, N.M.; Liu, M.C.; Mennel, R.G.; et al. Use of Biomarkers to Guide Decisions on Adjuvant Systemic Therapy for Women with Early-Stage Invasive Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2838–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, A.S.; Winer, E.P.; Goldhirsch, A.; Gelber, R.D.; Gnant, M.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.; Thurlimann, B.; Senn, H.J.; Panel, M. Tailoring therapies—Improving the management of early breast cancer: St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2015. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blok, E.J.; Bastiaannet, E.; van den Hout, W.B.; Liefers, G.J.; Smit, V.; Kroep, J.R.; van de Velde, C.J.H. Systematic review of the clinical and economic value of gene expression profiles for invasive early breast cancer available in Europe. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 62, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, B.; Zhang, Y.; Stal, O.; Fornander, T.; Brufsky, A.; Sgroi, D.C.; Schnabel, C.A. Risk stratification with Breast Cancer Index for late distant recurrence in patients with clinically low-risk (T1N0) estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2017, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Retel, V.P.; Byng, D.; Linn, S.C.; Jozwiak, K.; Koffijberg, H.; Rutgers, E.J.; Cardoso, F.; Piccart, M.J.; Poncet, C.; Van’t Veer, L.J.; et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of the 70-gene signature compared with clinical assessment in breast cancer based on a randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 137, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, F.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Patsouris, A.; Droin, N.; Piscuoglio, S.; Carbuccia, N.; Soria, J.C.; Dien, A.T.; Adnani, Y.; Kamal, M.; et al. Genomic characterization of metastatic breast cancers. Nature 2019, 569, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| IHC/FISH/SISH | Nr Cases | TargetPrint | Nr Agree (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ER+ | 47 | ER+ | 46 (98%) |
| ER− | 1 | ||
| ER− | 1 | ER− | 1 (100%) |
| PR+ | 44 | PR+ | 39 (89%) |
| PR− | 5 | ||
| PR− | 4 | PR− | 4 (100%) |
| HER2+ | 8 | HER2+ | 4 (50%) |
| HER2− | 4 | ||
| HER2− | 40 | HER2− | 38 (95%) |
| HER2+ | 2 | ||
| IHC/FISH/SISH | Nr Cases (%) | BluePrint | Nr Agree (%) |
| LuminalA | 44 (33%) | Luminal A | 35 (80%) |
| Luminal B | 8 (18%) | ||
| Basal | 1 (2%) | ||
| Luminal B | 88 (65%) | Luminal B | 47 (53%) |
| Luminal A | 35 (40%) | ||
| HER2 | 5 (6%) | ||
| Basal | 1 (1%) | ||
| Basal | 3 (2%) | Basal | 2 (67%) |
| Luminal A | 1 (33%) | ||
| HER2+ | 0 | ||
| IHC/FISH/SISH | Nr Cases (%) | TargetPrint/BluePrint | Nr Agree (%) |
| HER2+ | 23 (16%) | HER2+ | 12 (52%) |
| HER2− | 11 (48%) | ||
| HER2− | 114 | HER2− | 111 (97%) |
| HER2+ | 3 (3%) | ||
| Clinical risk | Nr Cases (%) | MammaPrint | Nr Agree (%) |
| High | 95 (67%) | High | 55 (58%) |
| Low | 40 (42%) | ||
| Low | 46 (33%) | Low | 37 (80%) |
| High | 9 (20%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Ruiz, J.A.; Mieza, J.A.; Zabalza, I.; Vivanco, M.d.M. Comparison of Genomic Profiling Data with Clinical Parameters: Implications for Breast Cancer Prognosis. Cancers 2022, 14, 4197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174197
López-Ruiz JA, Mieza JA, Zabalza I, Vivanco MdM. Comparison of Genomic Profiling Data with Clinical Parameters: Implications for Breast Cancer Prognosis. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174197
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Ruiz, José A., Jon A. Mieza, Ignacio Zabalza, and María d. M. Vivanco. 2022. "Comparison of Genomic Profiling Data with Clinical Parameters: Implications for Breast Cancer Prognosis" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174197
APA StyleLópez-Ruiz, J. A., Mieza, J. A., Zabalza, I., & Vivanco, M. d. M. (2022). Comparison of Genomic Profiling Data with Clinical Parameters: Implications for Breast Cancer Prognosis. Cancers, 14(17), 4197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174197





