Identification of Gender- and Subtype-Specific Gene Expression Associated with Patient Survival in Low-Grade and Anaplastic Glioma in Connection with Steroid Signaling
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection from the TCGA and CGGA Databases and Normalization
2.2. Selection of Differentially Expressed Genes
2.3. Univariate Analysis
2.4. Survival Analysis
2.5. Gene Expression Correlation Analysis in the TCGA Database
2.6. Validation of Gene Expression Correlations in the CGGA Database
2.7. Functional Annotation
3. Results
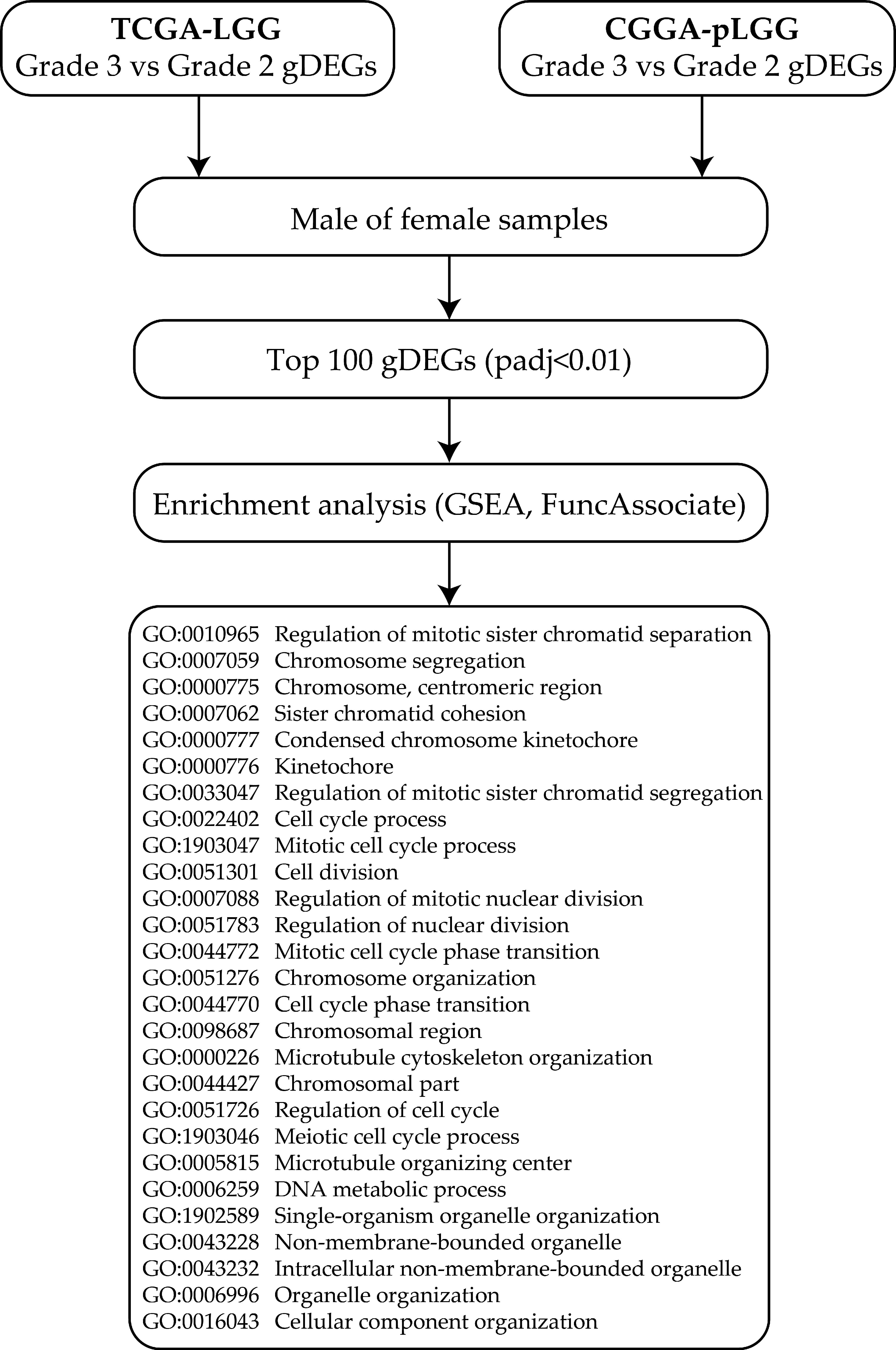
3.1. Grade 3 over Grade 2 Differentially Expressed Genes in Males and Females
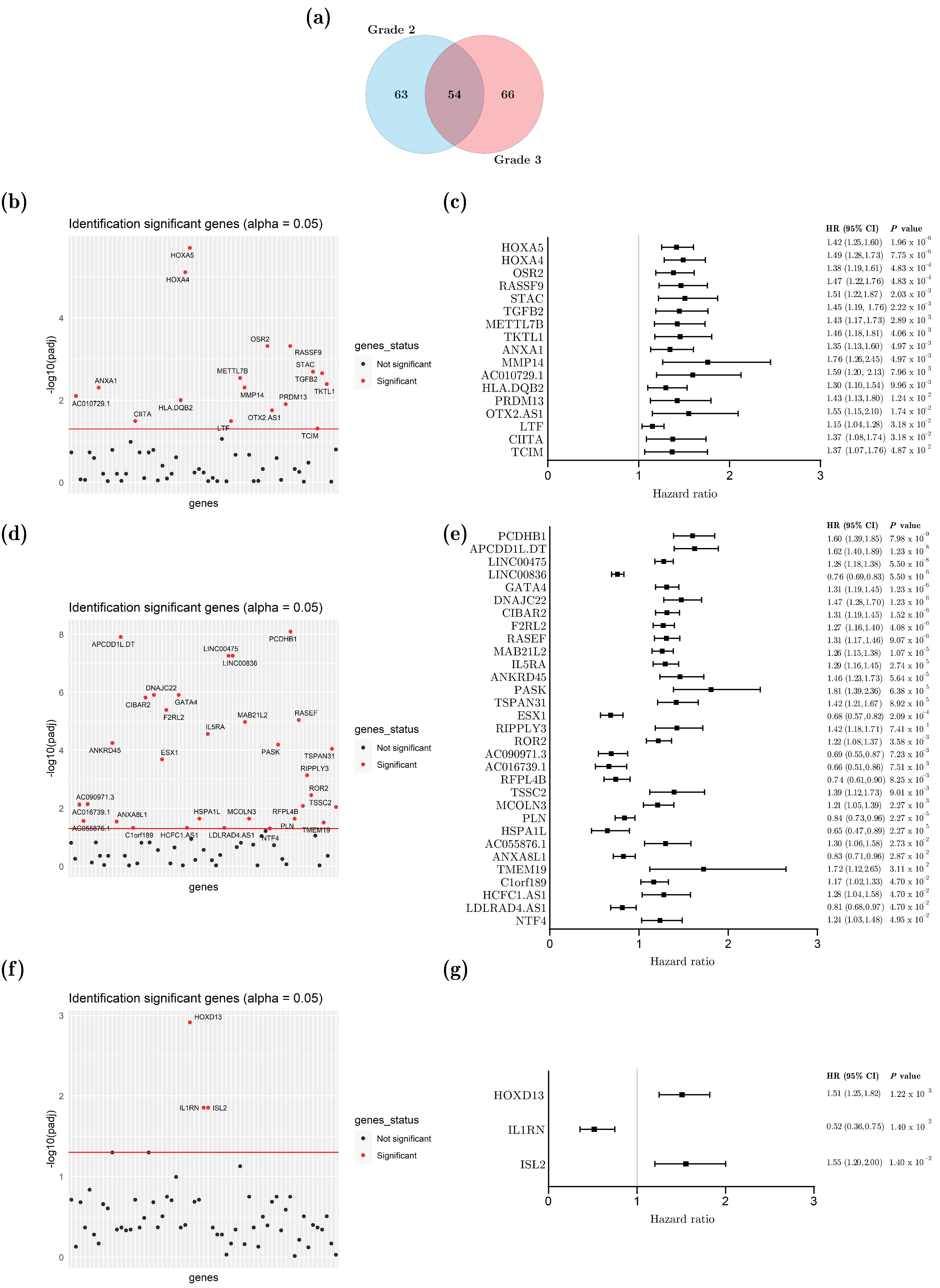
3.2. Male-Over-Female Differentially Expressed Genes in Grade 2 or Grade 3 Gliomas Associated with Patient Overall Survival
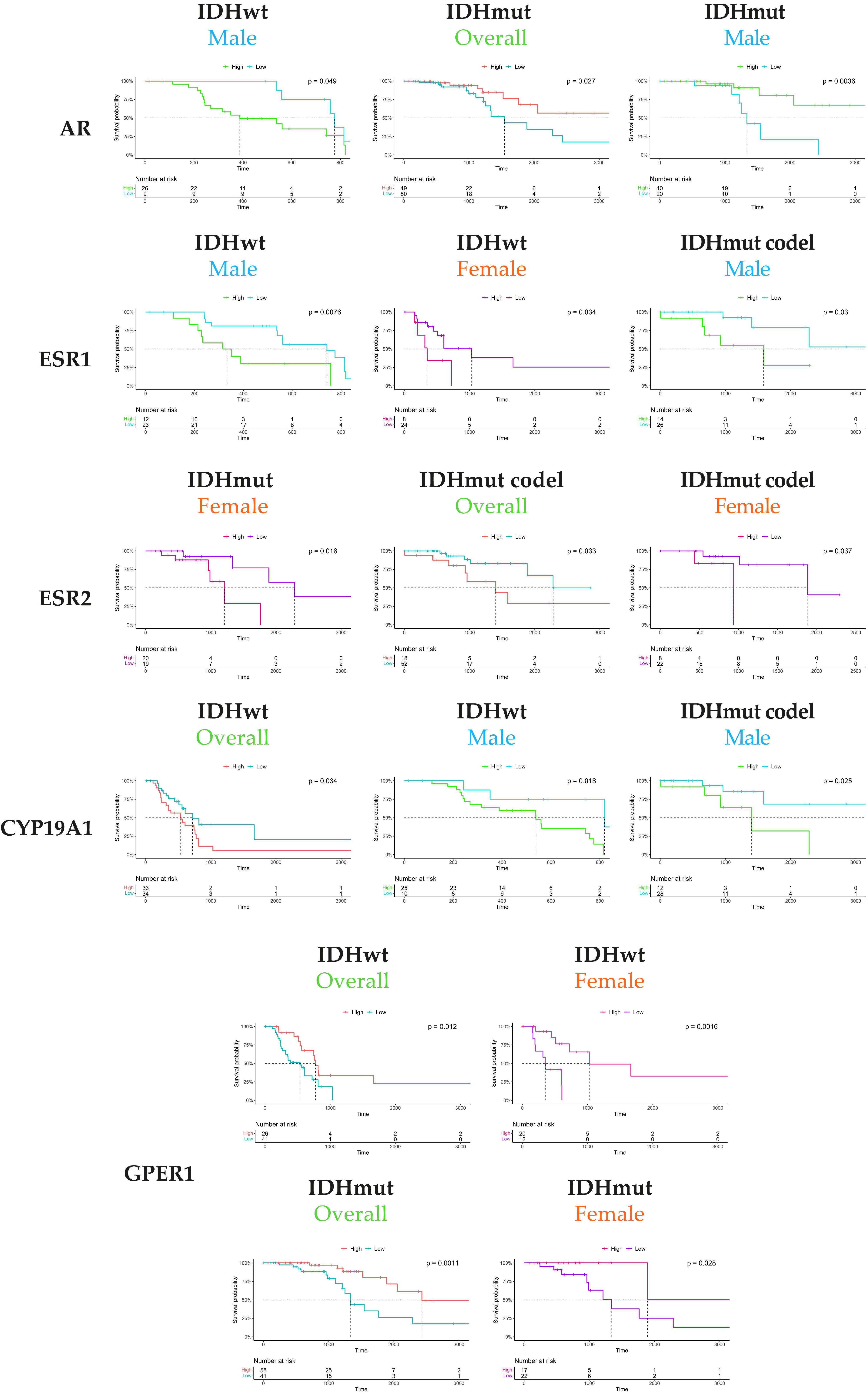
3.3. Expression of Aromatase and Steroid Receptors in Grade 3 Tumors Associated with Patient Overall Survival Depending on Gender and Tumor Type
3.4. Genes Correlated with Aromatase and Steroid Receptor Expression in the Whole Population, Males, and Females, Stratified by Tumor Type
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obara, T.; Blonski, M.; Brzenczek, C.; Mézières, S.; Gaudeau, Y.; Pouget, C.; Gauchotte, G.; Verger, A.; Vogin, G.; Moureaux, J.-M.; et al. Adult Diffuse Low-Grade Gliomas: 35-Year Experience at the Nancy France Neurooncology Unit. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 574679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.J.; Bota, D.A.; van Den Bent, M.J.; Brown, P.D.; Maher, E.; Aregawi, D.; Liau, L.M.; Buckner, J.C.; Weller, M.; Berger, M.S.; et al. Management of Low-Grade Glioma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuro-Oncol. Pract. 2019, 6, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Fulop, J.; Liu, M.; Blanda, R.; Kromer, C.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2008–2012. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, iv1–iv62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.T.; Prajapati, B.; Lakhina, S.; Sharma, M.; Prajapati, S.; Chosdol, K.; Sinha, S. Identification of Gender-Specific Molecular Differences in Glioblastoma (GBM) and Low-Grade Glioma (LGG) by the Analysis of Large Transcriptomic and Epigenomic Datasets. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 699594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirtz, A.; Rech, F.; Dubois-Pot-Schneider, H.; Dumond, H. Astrocytoma: A Hormone-Sensitive Tumor? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, W.; Cong, P.; Ding, Y.; Xiang, L.; Wu, K. Androgen Receptor Signaling Regulates Growth of Glioblastoma Multiforme in Men. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidenfeld, J.; Schiller, H. Metabolism of Steroids by Human Brain Tumors. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 1984, 7, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallud, J.; Mandonnet, E.; Deroulers, C.; Fontaine, D.; Badoual, M.; Capelle, L.; Guillet-May, F.; Page, P.; Peruzzi, P.; Jouanneau, E.; et al. Pregnancy Increases the Growth Rates of World Health Organization Grade II Gliomas. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, S.; Pagès, M.; Gauchotte, G.; Miquel, C.; Cartalat-Carel, S.; Guillamo, J.-S.; Capelle, L.; Delattre, J.-Y.; Beauchesne, P.; Debouverie, M.; et al. Interactions between Glioma and Pregnancy: Insight from a 52-Case Multicenter Series. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, C.; Gomes-Braga, F.; Costa-Silva, D.; Escórcio-Dourado, C.; Borges, U.; Conde-Junior, A.; Barros-Oliveira, M.; Sousa, E.; Barros, L.; Martins, L.; et al. Expression of Estrogen and Progesterone Receptors in Astrocytomas: A Literature Review. Clinics 2016, 71, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueñas Jiménez, J.M.; Candanedo Arellano, A.; Santerre, A.; Orozco Suárez, S.; Sandoval Sánchez, H.; Feria Romero, I.; López-Elizalde, R.; Alonso Venegas, M.; Netel, B.; de la Torre Valdovinos, B.; et al. Aromatase and Estrogen Receptor Alpha MRNA Expression as Prognostic Biomarkers in Patients with Astrocytomas. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 119, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaprico, A.; Silva, T.C.; Olsen, C.; Garofano, L.; Cava, C.; Garolini, D.; Sabedot, T.S.; Malta, T.M.; Pagnotta, S.M.; Castiglioni, I.; et al. TCGAbiolinks: An R/Bioconductor Package for Integrative Analysis of TCGA Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, K.-N.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Chai, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; et al. Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas (CGGA): A Comprehensive Resource with Functional Genomic Data from Chinese Glioma Patients. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Qian, Z.; Sun, Z.; Xu, K.; Wang, K.; Liu, S.; Fan, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; et al. A Radiomic Signature as a Non-Invasive Predictor of Progression-Free Survival in Patients with Lower-Grade Gliomas. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 20, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Meng, F.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, T. Comprehensive RNA-Seq Transcriptomic Profiling in the Malignant Progression of Gliomas. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, T.; You, G.; Peng, X.; Chen, C.; You, Y.; Yao, K.; Wu, C.; Ma, J.; Sha, Z.; et al. Localizing Seizure-Susceptible Brain Regions Associated with Low-Grade Gliomas Using Voxel-Based Lesion-Symptom Mapping. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.K.; Khanna, P.; Kishore, J. Understanding Survival Analysis: Kaplan-Meier Estimate. Int. J. Ayurveda Res. 2010, 1, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berriz, G.F.; Beaver, J.E.; Cenik, C.; Tasan, M.; Roth, F.P. Next Generation Software for Functional Trend Analysis. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 3043–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) Hallmark Gene Set Collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis: A Knowledge-Based Approach for Interpreting Genome-Wide Expression Profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, G.; Miller, J.J. Lower Grade Gliomas. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, C.S.; Le Boiteux, E.; Arnaud, P.; Costa, B.M. HOX Gene Cluster (de)Regulation in Brain: From Neurodevelopment to Malignant Glial Tumours. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 3797–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Boiteux, E.; Court, F.; Guichet, P.; Vaurs-Barrière, C.; Vaillant, I.; Chautard, E.; Verrelle, P.; Costa, B.M.; Karayan-Tapon, L.; Fogli, A.; et al. Widespread Overexpression from the Four DNA Hypermethylated HOX Clusters in Aggressive (IDH Wt) Glioma Is Associated with H3K27me3 Depletion and Alternative Promoter Usage. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1995–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Chen, P.; Bie, P.; Piao, W.; Cheng, Q. HOXA5 Is Recognized as a Prognostic-Related Biomarker and Promotes Glioma Progression Through Affecting Cell Cycle. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 633430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Engrailed 1 Overexpression as a Potential Prognostic Marker in Lower Grade Glioma. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinawi, T.; Hill, V.K.; Krex, D.; Schackert, G.; Gentle, D.; Morris, M.R.; Wei, W.; Cruickshank, G.; Maher, E.R.; Latif, F. DNA Methylation Profiles of Long- and Short-Term Glioblastoma Survivors. Epigenetics 2013, 8, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, M.; Tong, H.; Xue, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, S. A Novel MiR-7156-3p-HOXD13 Axis Modulates Glioma Progression by Regulating Tumor Cell Stemness. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 3200–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Hu, J.; Zheng, W.; Jing, Z. The U2AF2 /CircRNA ARF1/MiR-342–3p/ISL2 Feedback Loop Regulates Angiogenesis in Glioma Stem Cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daftary, G.S.; Taylor, H.S. Endocrine Regulation of HOX Genes. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 331–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbas, G.E.; Song, J.; Taylor, H.S. A HOXA10 Estrogen Response Element (ERE) Is Differentially Regulated by 17 Beta-Estradiol and Diethylstilbestrol (DES). J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preciados, M.; Yoo, C.; Roy, D. Estrogenic Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals Influencing NRF1 Regulated Gene Networks in the Development of Complex Human Brain Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapienza, C.; Issa, J.-P. Diet, Nutrition, and Cancer Epigenetics. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Zuo, Z.; Qu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H. Comprehensive Analysis of Inflammatory Response-Related Genes, and Prognosis and Immune Infiltration in Patients With Low-Grade Glioma. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 748993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.-R.; Weng, J.-C.; Li, C.-B.; Huo, X.-L.; Li, H.; Hao, S.-Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.-T. Prognostic and Predictive Value of an Immune Infiltration Signature in Diffuse Lower-Grade Gliomas. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e133811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sareddy, G.R.; Zhou, M.; Viswanadhapalli, S.; Li, X.; Lai, Z.; Tekmal, R.R.; Brenner, A.; Vadlamudi, R.K. Differential Effects of Estrogen Receptor β Isoforms on Glioblastoma Progression. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3176–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallmann, T.; Zhang, X.-M.; Wallerius, M.; Bolin, S.; Joly, A.-L.; Sobocki, C.; Leiss, L.; Jiang, Y.; Bergh, J.; Holland, E.C.; et al. Microglia Induce PDGFRB Expression in Glioma Cells to Enhance Their Migratory Capacity. iScience 2018, 9, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, J.Y. Differential Expression of PDGFRB and EGFR in Microvascular Proliferation in Glioblastoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 10577–10586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambhore, N.S.; Katragadda, R.; Raju Kalidhindi, R.S.; Thompson, M.A.; Pabelick, C.M.; Prakash, Y.S.; Sathish, V. Estrogen Receptor Beta Signaling Inhibits PDGF Induced Human Airway Smooth Muscle Proliferation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 476, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirtz, A.; Lebourdais, N.; Rech, F.; Bailly, Y.; Vaginay, A.; Smaïl-Tabbone, M.; Dubois-Pot-Schneider, H.; Dumond, H. GPER Agonist G-1 Disrupts Tubulin Dynamics and Potentiates Temozolomide to Impair Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation. Cells 2021, 10, 3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutzauer, J.; Gonzalez de Valdivia, E.; Swärd, K.; Alexandrakis Eilard, I.; Broselid, S.; Kahn, R.; Olde, B.; Leeb-Lundberg, L.M.F. Ligand-Independent G Protein–Coupled Estrogen Receptor/G Protein–Coupled Receptor 30 Activity: Lack of Receptor-Dependent Effects of G-1 and 17 β-Estradiol. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 100, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Lee, S.; Cao, P. The Inhibitive Effect of Sh-HIF1A-AS2 on the Proliferation, Invasion, and Pathological Damage of Breast Cancer via Targeting MiR-548c-3p through Regulating HIF-1α/VEGF Pathway in Vitro and Vivo. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Cui, T.; Dai, J. MicroRNA-548c-3p Inhibits T98G Glioma Cell Proliferation and Migration by Downregulating c-Myb. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3866–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saffari, M.; Ghaderian, S.M.H.; Omrani, M.D.; Afsharpad, M.; Shankaie, K.; Samadaian, N. The Association of MiR-Let 7b and MiR-548 with PTEN in Prostate Cancer. Urol. J. 2018, 16, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormo, E.; Pineda, B.; Serna, E.; Guijarro, A.; Ribas, G.; Fores, J.; Chirivella, E.; Climent, J.; Lluch, A.; Eroles, P. MicroRNA Profile in Response to Doxorubicin Treatment in Breast Cancer. J. Cell Biochem. 2015, 116, 2061–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidu, R.A.; Wu, M.; Su, Z.; Xu, H. Paradoxical Role of High Mobility Group Box 1 in Glioma: A Suppressor or a Promoter? Oncol. Rev. 2017, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lynch, C.; Zhao, J.; Sakamuru, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, R.; Witt, K.; Merrick, B.; Teng, C.; Xia, M. Identification of Compounds That Inhibit Estrogen-Related Receptor Alpha Signaling Using High-Throughput Screening Assays. Molecules 2019, 24, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, H.; Ren, G.; Tang, J.; et al. The Increased Expression of Estrogen-Related Receptor α Correlates with Wnt5a and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Glioma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Correlated Genes (IrhoI > 0.6) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Good Prognosis | Number | Top GO | pval | FDR qval | Genes Associated with Enriched GO (TCGA and CGGA) | |||
| AR | IDH wt | Male | Low | 11 | GO:0006578 | amino-acid betaine biosynthetic process | 8.11.10−7 | 8.44.10−3 | BBOX1 |
| IDH mut | All | High | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Male | High | 19 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| ESR1 | IDH wt | Male | Low | 0 | - | - | - | ||
| Female | Low | 44 | GO:0006955 | immune response | 1.34.10−26 | 1.4.10−22 | CD3G, EOMES, SLAMF1, SLAMF7, CCR4, CD3E, GZMA, CST7, LY9, CD96, FCGR2B, IL2RG, SLAMF6, FASLG, SKAP1 | ||
| GO:0042110 | T cell activation | 1.10−18 | 1.74.10−15 | CD3G, EOMES, CD2, CD3E, LCK | |||||
| IDH mut codel | Male | Low | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| ESR2 | IDH mut | Female | Low | 29 | - | - | - | - | - |
| IDH mut codel | All | Low | 9 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Female | Low | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| CYP19A1 | IDHwt | All | Low | 23 | GO:0022610 | Biological adhesion | 6.7.10−8 | 5.63.10−4 | RAC2, PLAUR, SIGLEC9, SIGLEC7, SPP1, FRMT3, S100A11 |
| GO:0002274 | Myeloid leukocyte activation | 1.84.10−7 | 5.63.10−4 | RAC2, FCER1G, HMOX1 | |||||
| Male | Low | 22 | GO:0022610 | Biological adhesion | 3.27.10−6 | 3.4.10−2 | RAC2, PLAUR, SIGLEC9, SIGLEC7, CSTA, IL4I1, SPP1 | ||
| IDH mut codel | Male | Low | 66 | GO:0045087 | Innate immune response | 2.42.10−19 | 4.19.10−16 | C1R, APOL1, HLA-E | |
| GPER1 | IDH wt | All | High | 50 | GO:0001944 | vasculature development | 3.9.10−19 | 4.06.10−15 | FLT4, TIE1, ACVRL1, CLEC14A, PDGFRB, ADGRA2, ROBO4, NOTCH4, ANPEP, CDH5, ECM1, RASIP1, TMEM204, ARHGEF15 |
| Female | High | 85 | GO:0001944 | Vasculature development | 3.53.10−15 | 3.67.10−11 | FLT4, NOTCH4, ACVR1L, CLEC14A, RASIP1, EGFL7, ROBO4, CLDN5 | ||
| IDH mut | All | High | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Female | High | 191 | GO:0016070 | RNA metabolic process | 5.32.10−10 | 1.47.10−6 | ZNF333, ZNF254, TFDP2, MGA, SETD5, ZFP69, SRSF11, PNN, HNRNPH1, TRIT1, ZNF326 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hirtz, A.; Lebourdais, N.; Thomassin, M.; Rech, F.; Dumond, H.; Dubois-Pot-Schneider, H. Identification of Gender- and Subtype-Specific Gene Expression Associated with Patient Survival in Low-Grade and Anaplastic Glioma in Connection with Steroid Signaling. Cancers 2022, 14, 4114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174114
Hirtz A, Lebourdais N, Thomassin M, Rech F, Dumond H, Dubois-Pot-Schneider H. Identification of Gender- and Subtype-Specific Gene Expression Associated with Patient Survival in Low-Grade and Anaplastic Glioma in Connection with Steroid Signaling. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174114
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirtz, Alex, Nolwenn Lebourdais, Magalie Thomassin, Fabien Rech, Hélène Dumond, and Hélène Dubois-Pot-Schneider. 2022. "Identification of Gender- and Subtype-Specific Gene Expression Associated with Patient Survival in Low-Grade and Anaplastic Glioma in Connection with Steroid Signaling" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174114
APA StyleHirtz, A., Lebourdais, N., Thomassin, M., Rech, F., Dumond, H., & Dubois-Pot-Schneider, H. (2022). Identification of Gender- and Subtype-Specific Gene Expression Associated with Patient Survival in Low-Grade and Anaplastic Glioma in Connection with Steroid Signaling. Cancers, 14(17), 4114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174114






