ADC Values of Cytologically Benign and Cytologically Malignant 18 F-FDG PET-Positive Lymph Nodes of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. FDG PET-CT Imaging
2.3. DW-MRI Imaging
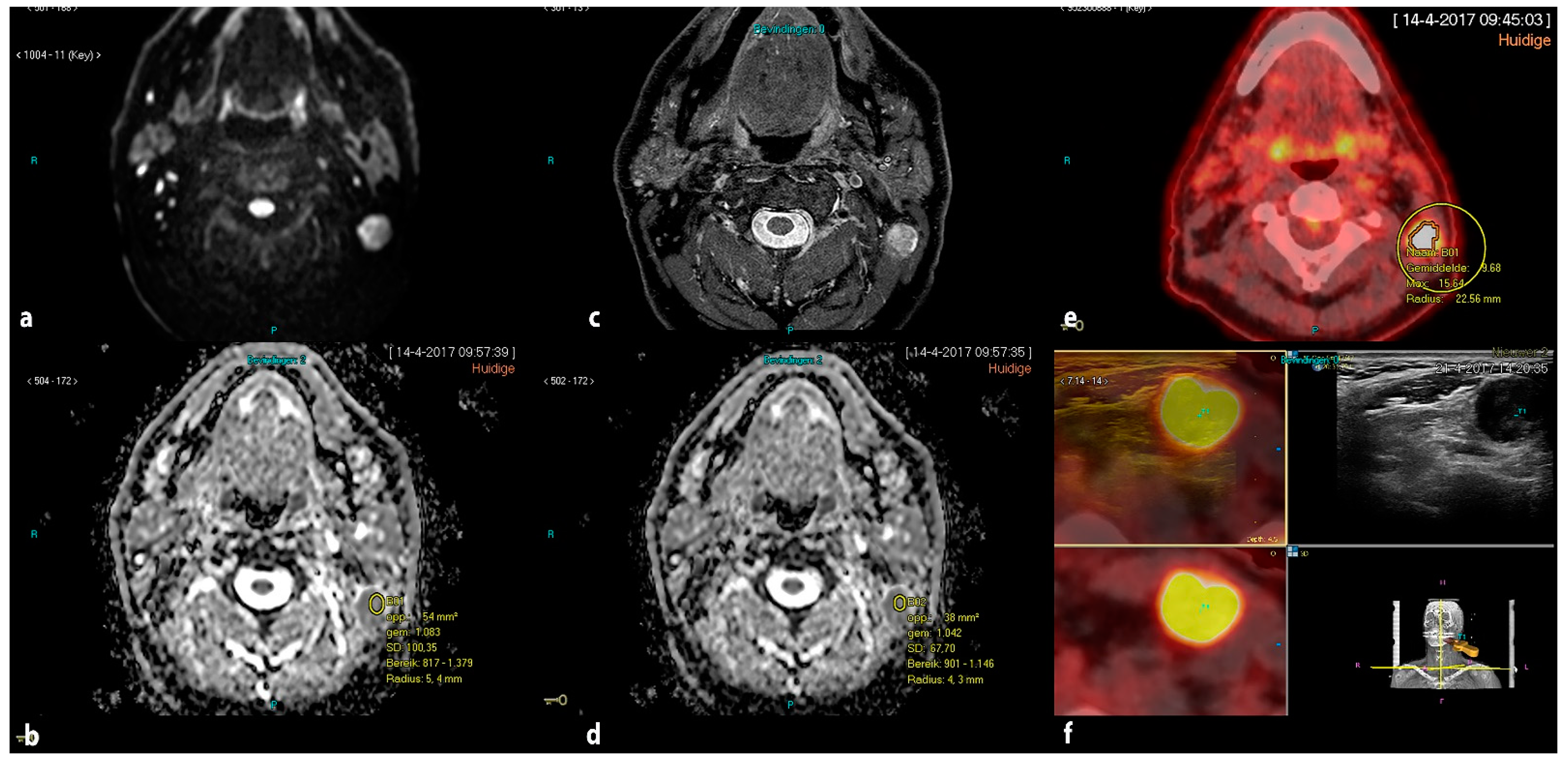
2.4. Ultrasound, Real-Time Image Fusion with FDG PET-CT and Real-Time Fused Guided FNAC
2.5. Pathology
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, P.; Contente, M.; Bennett, B.; Hall, J.; Bailey, H.; Bailey, A.; Zarrelli, L.; Sanchez, C.P. Real-World Treatment Patterns and Outcomes in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: Point-in-Time Survey of Oncologists in Italy and Spain. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 4722–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, H.R.; Curtin, H.D. Chapter 2 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck—Imaging Evaluation of Regional Lymph Nodes and Implications for Management. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2017, 38, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodder, W.; Pameijer, F.; Rasch, C.; Brekel, M.V.D.; Balm, A. Prognostic significance of radiologically determined neck node volume in head and neck cancer: A systematic review. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Brekel, M.W.; Castelijns, J.A. What the clinician wants to know: Surgical perspective and ultrasound for lymph node imaging of the neck. Cancer Imaging 2005, 5, S41–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, L.-J.; Lo, W.-C.; Hsu, W.-L.; Wang, C.-T.; Lai, M.-S. Detection of cervical lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer patients with clinically N0 neck—A meta-analysis comparing different imaging modalities. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Datta, S.; Arya, S.; Rangarajan, V.; Kane, S.V.; Nair, D.; Nair, S.V.; Chaukar, D.A.; Pai, P.S.; Pantvaidya, G.; et al. Prospective study of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology and sentinel node biopsy in the staging of clinically negative T1 and T2 oral cancer. Head Neck 2014, 37, 1504–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bondt, R.; Nelemans, P.; Hofman, P.; Casselman, J.; Kremer, B.; van Engelshoven, J.; Beets-Tan, R. Detection of lymph node metastases in head and neck cancer: A meta-analysis comparing US, USgFNAC, CT and MR imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2007, 64, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brekel, M.W. Lymph node metastases: CT and MRI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2000, 33, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekel, M.W.V.D.; Stel, H.V.; Castelijns, J.A.; Nauta, J.J.; Van Der Waal, I.; Valk, J.; Meyer, C.J.; Snow, G.B. Cervical lymph node metastasis: Assessment of radiologic criteria. Radiology 1990, 177, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, M.; Ahuja, A.T.; Metreweli, C. Diagnostic accuracy of sonographic criteria for evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy. J. Ultrasound Med. 1998, 17, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brekel, M.W.; Castelijns, J.A.; Snow, G.B. The size of lymph nodes in the neck on sonograms as a radiologic criterion for metastasis: How reliable is it? Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1998, 19, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chammas, M.C.; Macedo, T.A.A.; Lo, V.W.; Gomes, A.C.; Juliano, A.; Cerri, G.G. Predicting malignant neck lymphadenopathy using color duplex sonography based on multivariate analysis. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2016, 44, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyzas, P.A.; Evangelou, E.; Denaxa-Kyza, D.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography to Evaluate Cervical Node Metastases in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-analysis. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Koekkoek-Doll, P.; Maas, M.; Vogel, W.; Castelijns, J.; Smit, L.; Zavrakidis, I.; Beets-Tan, R.; Brekel, M.V.D. Real-Time Ultrasound Image Fusion with FDG-PET/CT to Perform Fused Image-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration in Neck Nodes: Feasibility and Diagnostic Value. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Koekkoek-Doll, P.K.; Vogel, W.; Maas, M.; Castelijns, J.; Smit, L.; Zavrakidis, J.; Beets-Tan, R.; van den Brekel, M. SUVmax values at FDG PET-CT to predict malignancy in lymph nodes aspirated by real time image fused USgFNAC in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sant, I.V.; Van Eden, W.J.; Engbersen, M.; Kok, N.F.M.; Woensdregt, K.; Lambregts, D.M.J.; Shanmuganathan, S.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Aalbers, A.G.J.; Lahaye, M.J. Diffusion-weighted MRI assessment of the peritoneal cancer index before cytoreductive surgery. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 106, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Beets, G. MRI for assessing and predicting response to neoadjuvant treatment in rectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandecaveye, V.; De Keyzer, F.; Poorten, V.V.; Dirix, P.; Verbeken, E.; Nuyts, S.; Hermans, R. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Value of Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging for Nodal Staging. Radiology 2009, 251, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barchetti, F.; Pranno, N.; Giraldi, G.; Sartori, A.; Gigli, S.; Barchetti, G.; Mele, L.L.; Marsella, L.T. The Role of 3 Tesla Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign versus Malignant Cervical Lymph Nodes in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 532095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajo, M.; Nakajo, M.; Kajiya, Y.; Tani, A.; Kamiyama, T.; Yonekura, R.; Fukukura, Y.; Matsuzaki, T.; Nishimoto, K.; Nomoto, M.; et al. FDG PET/CT and diffusion-weighted imaging of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Comparison of prognostic significance between primary tumor standardized uptake value and apparent diffusion coefficient. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 37, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Hisamatsu, K.; Suzui, N.; Hara, A.; Tomita, H.; Miyazaki, T. A Review of HPV-Related Head and Neck Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kendi, A.T.K.; Magliocca, K.; Corey, A.; Nickleach, D.C.; Galt, J.; Higgins, K.; Beitler, J.J.; El-Deiry, M.W.; Wadsworth, J.T.; Hudgins, P.A.; et al. Do 18F-FDG PET/CT Parameters in Oropharyngeal and Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinomas Indicate HPV Status? Clin. Nucl. Med. 2015, 40, e196–e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Payabvash, S.; Chan, A.; Maralani, P.J.; Malhotra, A. Quantitative diffusion magnetic resonance imaging for prediction of human papillomavirus status in head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroradiol. J. 2019, 32, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Tang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C. 18FDG-PET/CT for the detection of regional nodal metastasis in patients with head and neck cancer: A meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yongkui, L.; Jian, L.; Wang, H.; Jingui, L. 18FDG-PET/CT for the detection of regional nodal metastasis in patients with primary head and neck cancer before treatment: A meta-analysis. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 22, e11–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Pak, K.; Kim, K. Diagnostic accuracy of F-18 FDG PET or PET/CT for detection of lymph node metastasis in clinically node negative head and neck cancer patients. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Med. Surg. 2019, 40, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülbül, H.M.; Bülbül, O.; Sarıoğlu, S.; Özdoğan, Ö.; Doğan, E.; Karabay, N. Relationships Between DCE-MRI, DWI, and 18F-FDG PET/CT Parameters with Tumor Grade and Stage in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Imaging Radionucl. Ther. 2021, 30, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, T.; Meng, Z.; Huang, C.; Chen, X.; Lu, J.; Xian, J. Correlation between apparent diffusion coefficients and metabolic parameters in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: A prospective study with integrated PET/MRI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 129, 109070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruehwald-Pallamar, J.; Czerny, C.; Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Halpern, B.S.; Eder-Czembirek, C.; Brunner, M.; Schuetz, M.; Weber, M.; Fruehwald, L.; Herneth, A.M. Functional imaging in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Correlation of PET/CT and diffusion-weighted imaging at 3 Tesla. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011, 38, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.; Choi, Y.; Baek, J.H.; Lee, J. The Diagnostic Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Differentiating Metastatic Lymph Nodes of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1889–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medeiros, L.D.; Ioachim, H.L. Ioachim’s Lymph Node Pathology, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-1-45-119357-2. [Google Scholar]
| Diagnosis | n Patient | % Patient |
|---|---|---|
| scc unknown primary | 8 | 10.3% |
| scc oral cavity | 19 | 24.4% |
| scc oropharyngeal | 32 | 41.0% |
| scc hypopharyngeal | 4 | 5.1% |
| scc laryngeal | 8 | 10.3% |
| scc nasal cavity paranasal sinuses | 3 | 3.8% |
| scc nasopharyngeal | 2 | 2.6% |
| scc cutaneous | 2 | 2.6% |
| total | 78 | 100.0% |
| ADC | Malignant Nodes | Benign Nodes | Significance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Measurement | N | Mean (sd) | N | Mean (sd) | p 1 |
| Full | ADC 1 2 | 12 | 0.444 (0.186) | 12 | 0.562 (0.179) | 0.138 |
| ADC 2 3 | 79 | 0.645 (0.188) | 64 | 0.625 (0.201) | 0.620 | |
| ADC 3 4 | 78 | 0.625 (0.199) | 64 | 0.609 (0.172) | 0.666 | |
| No HPV | ADC 1 2 | 2 | 0.381 (0.078) | 0 | ||
| ADC 2 3 | 13 | 0.570 (0.239) | 10 | 0.645 (0.204) | 0.086 | |
| ADC 3 4 | 13 | 0.554 (0.236) | 10 | 0.665 (0.200) | 0.031 | |
| HPV | ADC 1 2 | 2 | 0.587 (0.163) | 4 | 0.439 (0.157) | 0.132 |
| ADC 2 3 | 34 | 0.654 (0.177) | 17 | 0.660 (0.214) | 0.996 | |
| ADC 3 4 | 34 | 0.640 (0.199) | 17 | 0.605 (0.174) | 0.434 | |
| ADC | Malignant Nodes | Benign Nodes | Significance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Measurement | N | Mean (sd) | N | Mean (sd) | p 1 |
| Full | ADC 1 2 | 12 | 0.721 (0.229) | 12 | 0.842 (0.154) | 0.400 |
| ADC 2 3 | 79 | 0.834 (0.206) | 64 | 0.847 (0.201) | 0.605 | |
| ADC 3 4 | 78 | 0.817 (0.185) | 64 | 0.806 (0.198) | 0.747 | |
| No HPV | ADC 1 2 | 2 | 0.602 (0.069) | 0 | ||
| ADC 2 3 | 13 | 0.780 (0.293) | 10 | 0.920 (0.213) | 0.018 | |
| ADC 3 4 | 13 | 0.772 (0.298) | 10 | 0.852 (0.199) | 0.132 | |
| HPV | ADC 1 2 | 2 | 0.753 (0.227) | 4 | 0.761 (0.125) | 0.256 |
| ADC 2 3 | 34 | 0.842 (0.215) | 17 | 0.819 (0.217) | 0.683 | |
| ADC 3 4 | 34 | 0.838 0.169 | 17 | 0.770 (0.182) | 0.174 | |
| ADC | Malignant Nodes | Benign Nodes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Measurement | N | Difference 1, Mean (sd) | p 2 | N | Difference, Mean (sd) | p 2 |
| Full | ADC 1 3 | 12 | −0.164 (0.291) | 0.192 | 12 | −0.089 (0.286) | 0.301 |
| ADC 2 4 | 79 | −0.063 (0.279) | 0.050 | 64 | −0.095 (0.275) | 0.018 | |
| ADC 3 5 | 78 | −0.044(0.278) | 0.083 | 64 | −0.088 (0.277) | 0.016 | |
| No HPV | ADC 1 3 | 2 | −0.706 (0.078) | 0.140 | 0 | ||
| ADC 2 4 | 13 | −0.236 (0.384) | 0.155 | 10 | −0.127 (0.198) | 0.275 | |
| ADC 3 5 | 13 | −0.113 (0.273) | 0.301 | 10 | 0.035 (0.194) | 0.601 | |
| HPV | ADC 1 3 | 2 | −0.128 (0.152) | 0.355 | 4 | −0.169 (0.278) | 0.227 |
| ADC 2 4 | 34 | −0.002 (0.233) | 0.721 | 17 | −0.161 (0.377) | 0.184 | |
| ADC 3 5 | 34 | 0.002 (0.275) | 0.637 | 17 | −0.208 (0.280) | 0.030 | |
| ADC | Malignant Nodes | Benign Nodes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Measurement | N | Difference 1, Mean (sd) | p 2 | N | Difference 1, Mean (sd) | p 2 |
| Full | ADC 1 3 | 12 | −0.166 (0.366) | 0.201 | 12 | −0.102 (0.196) | 0.189 |
| ADC 2 4 | 79 | −0.151 (0.289) | <0.001 | 64 | −0.102 (0.263) | 0.004 | |
| ADC 3 5 | 78 | −0.117 (0.277) | 0.003 | 64 | −0.101 (0.288) | 0.007 | |
| No HPV | ADC 1 3 | 2 | −0.860 (0.069) | 0.101 | 0 | ||
| ADC 2 4 | 13 | −0.258 (0.382) | 0.125 | 10 | −0.022 (0.217) | 0.953 | |
| ADC 3 5 | 13 | −0.163 (0.347) | 0.247 | 10 | −0.013 (0.191) | 0.893 | |
| HPV | ADC 1 3 | 2 | −0.134 (0.153) | 0.341 | 4 | −0.090 (0.067) | 0.135 |
| ADC 2 4 | 34 | −0.099 (0.284) | 0.087 | 17 | −0.248 (0.326) | 0.010 | |
| ADC 3 5 | 34 | −0.049 (0.252) | 0.257 | 17 | −0.255 (0.316) | 0.011 | |
| Variable 1 | Variable 2 | Pearson Correlation | Pearson Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum ADC | Mean ADC | ||
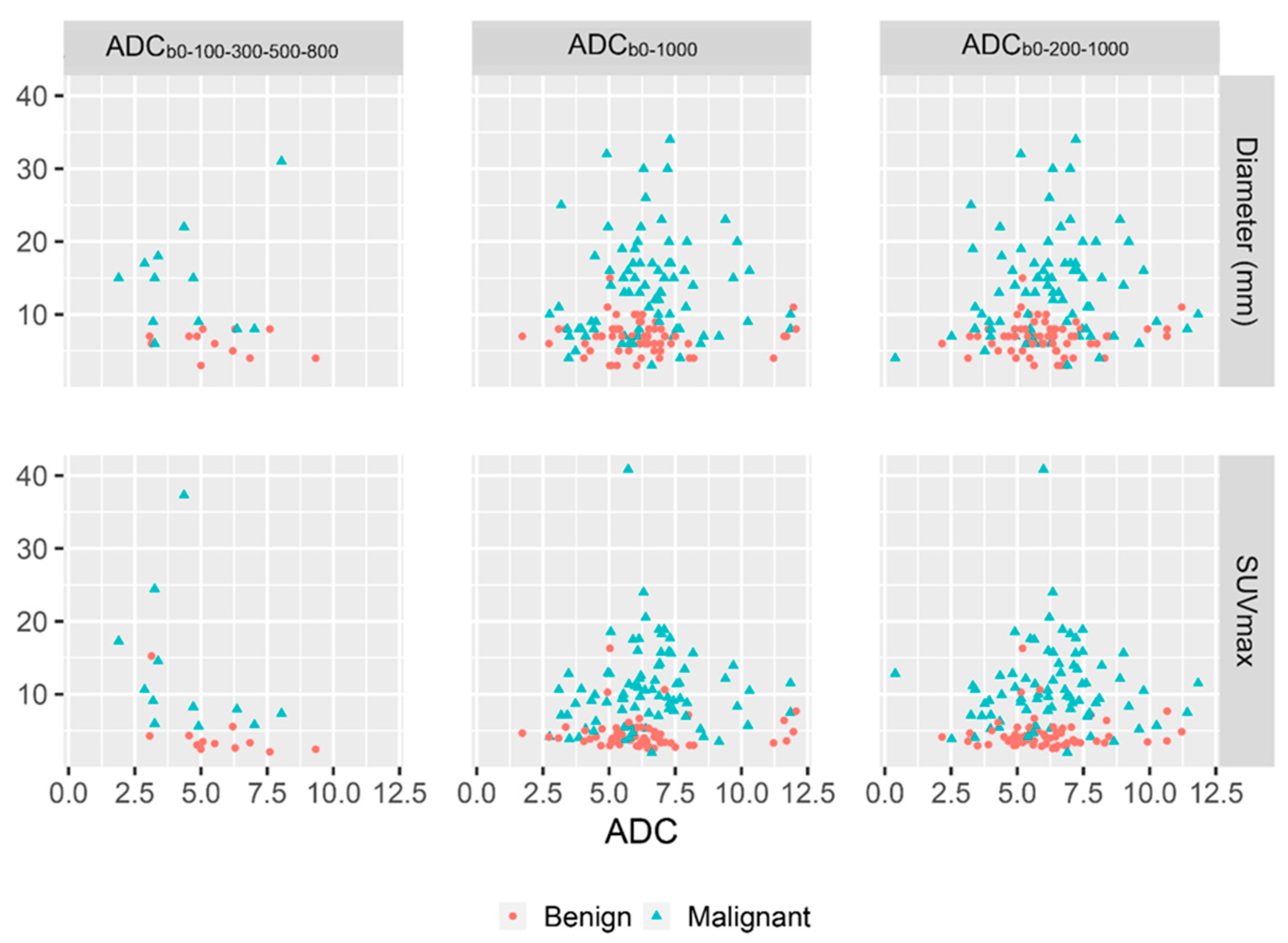
| ADC 1 1 | SUVmax | −0.45 | −0.30 |
| ADC 2 2 | SUVmax | 0.07 | −0.06 |
| ADC 3 3 | SUVmax | 0.06 | −0.04 |
| ADC 1 | Diameter | −0.12 | −0.18 |
| ADC 2 | Diameter | 0.07 | −0.04 |
| ADC 3 | Diameter | 0.09 | −0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Koekkoek-Doll, P.K.; Roberti, S.; Smit, L.; Vogel, W.V.; Beets-Tan, R.; van den Brekel, M.W.; Castelijns, J. ADC Values of Cytologically Benign and Cytologically Malignant 18 F-FDG PET-Positive Lymph Nodes of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 4019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14164019
de Koekkoek-Doll PK, Roberti S, Smit L, Vogel WV, Beets-Tan R, van den Brekel MW, Castelijns J. ADC Values of Cytologically Benign and Cytologically Malignant 18 F-FDG PET-Positive Lymph Nodes of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2022; 14(16):4019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14164019
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Koekkoek-Doll, Petra K., Sander Roberti, Laura Smit, Wouter V. Vogel, Regina Beets-Tan, Michiel W. van den Brekel, and Jonas Castelijns. 2022. "ADC Values of Cytologically Benign and Cytologically Malignant 18 F-FDG PET-Positive Lymph Nodes of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 14, no. 16: 4019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14164019
APA Stylede Koekkoek-Doll, P. K., Roberti, S., Smit, L., Vogel, W. V., Beets-Tan, R., van den Brekel, M. W., & Castelijns, J. (2022). ADC Values of Cytologically Benign and Cytologically Malignant 18 F-FDG PET-Positive Lymph Nodes of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 14(16), 4019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14164019







