Radiotherapy for Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis in Breast Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Radiotherapy on Survival
3.2. Whole-Brain Radiotherapy
3.3. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
3.4. Proton Therapy
3.5. Craniospinal Irradiation
3.6. Radiotherapy Guidelines
3.7. Future Perspectives
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Chamberlain, M.C. Neoplastic meningitis and metastatic epidural spinal cord compression. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayson, G.C.; Howell, A.; Harris, M.; Morgenstern, G.; Chang, J.; Ryder, W.D. Carcinomatous meningitis in breast cancer: An aggressive disease variant. Cancer 1994, 74, 3135–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogerd, W.; Hart, A.A.; van der Sande, J.J.; Engelsman, E. Meningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer: Prognostic factors and influence of treatment. Cancer 1991, 67, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Howell, A.; Harris, M.; Bramwell, V.H.; Sellwood, R.A. Carcinomatous meningitis associated with infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 1985, 11, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bendell, J.C.; Domchek, S.M.; Burnstein, H.J.; Harris, L.; Younger, J.; Kuter, I.; Bunnell, C.; Rue, M.; Gelman, R.; Winer, E. Central nervous system metastases in women who receive trastuzumab based therapy for metastatic breast carcinoma. Cancer 2003, 97, 2972–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamovec, J.; Zidar, A. Association of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in carcinoma of the breast with infiltrating lobular carcinoma. An autopsy study. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1991, 115, 507–510. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada, Y.; Fouad, A.; Pickren, J.W.; Lane, W.W. Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma. Autops. Study Cancer 1983, 52, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.T. Breast carcinoma: Pattern of metastasis at autopsy. J. Surg. Oncol. 1983, 23, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.U.; Bello, J.R.; Winer, E.P. CNS metastases in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 3608–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittica, G.; Senetta, R.; Richiardi, L.; Rudà, R.; Coda, R.; Castellano, I.; Sapino, A.; Cassoni, P. Meningeal carcinomatosis underdiagnosis and overestimation: Incidence in a large consecutive and unselected population of breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azevedo, C.R.A.S.; Cruz, M.R.S.; Chinen, L.T.D.; Peres, S.V.; Peterlevitz, M.A.; de Azevedo Pereira, A.E.; Fanelli, M.F.; Gimenes, D.L. Meningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer: Prognostic factors and outcome. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 104, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altundag, K.; Bondy, M.L.; Mirza, N.Q.; Kau, S.W.; Broglio, K.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Rivera, E. Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognostic factors in 420 metastatic breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastasis. Cancer 2007, 110, 2640–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Im, S.A.; Keam, B.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, S.W.; Kim, T.M.; Oh, D.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Chie, E.K.; et al. Clinical outcome of central nervous system metastases from breast cancer: Differences in survival depending on systemic treatment. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 106, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoi, M.A.; Hortobagy, G.N. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in patients with breast cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 135, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.D.; Avkshtol, V.; Baschnagel, A.M.; Meyer, K.; Ye, H.; Grills, I.S.; Chen, P.Y.; Maitz, A.; Olson, R.E.; Pieper, D.R.; et al. Surgical resection of brain metastases and the risk of leptomeningeal recurrence in patients treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, L.K.; Grossman, S.A.; Olivi, A. Neoplastic meningitis following surgical resection of isolated cerebellar metastasis: A potentially preventable complication. J. Neurooncol. 1997, 32, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, N.; Muskens, I.S.; DiRisio, A.C.; Meijer, L.; Briceno, V.; Edress, H.; Aslam, B.; Minhas, S.; Verhoeff, J.C.J.; Kleynen, C.E.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery versus whole-brain radiotherapy after intracranial metastasis resection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.; Elson, P.; Otvos, B.; Rose, J.; Loftus, C.; Rahmathulla, G.; Angelov, L.; Barnett, G.H.; Weil, R.J.; Vogelbaum, M.A. Tumor progression in patients receiving adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy vs localized radiotherapy after surgical resection of brain metastases. Neurosurgery 2015, 76, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R.; Prabhu, R.S.; Kandula, S.; Oliver, D.E.; Kim, S.; Hadjipanayis, C.; Olson, J.J.; Oyesiku, N.; Curran, W.J.; Khan, M.K.; et al. Intracranial control and radiographic changes with adjuvant radiation therapy for resected brain metastases: Whole brain radiotherapy versus stereotactic radiosurgery alone. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 120, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.A.; Lu, V.M.; Himes, B.T.; Burns, T.C.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A.; Chaichana, K.L.; Parney, I.F. Breast brain metastases are associated with increased risk of leptomeningeal disease after stereotactic radiosurgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2020, 37, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifiletti, D.M.; Romano, K.D.; Xu, Z.; Reardon, K.A.; Sheehan, J. Leptomeningeal disease following stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases from breast cancer. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 124, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, M.D. New strategies in the management of leptomeningeal metastases. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Rhun, E.; Rudà, R.; Devos, P.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Brandsma, D.; Pérez Segura, P.; Soffietti, R.; Weller, M. Diagnosis and treatment patterns for patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors across Europe. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, E.; Weller, M.; Brandsma, D.; Van den Bent, M.; de Azambuja, E.; Henriksson, R.; Boulanger, T.; Peters, S.; Watts, C.; Wick, W.; et al. EANO-ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumours. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, iv84–iv99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, M.C. Neoplastic meningitis. In Blue Books of Neurology; Rees, J., Wen, P.Y., Eds.; Neuro-Oncology: Blue Books of Neurology Series; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 333–351. [Google Scholar]
- Mammoser, A.G.; Groves, M.D. Biology and therapy of neoplastic meningitis. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 12, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clatot, F.; Philippin-Lauridant, G.; Ouvrier, M.-J.; Nakry, T.; Laberge-Le-Couteulx, S.; Guillemet, C.; Veyret, C.; Blot, E. Clinical improvement and survival in breast cancer leptomeningeal metastasis correlate with the cytologic response to intrathecalchemotherapy. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 95, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, A.; Jordan, L.; Rozner, R.; Patil, S.; Boire, A.; Pentsova, E.; Seidman, A.D. Characteristics and outcomes of patients with breast cancer with leptomeningeal metastasis. Clin. Breast Cancer 2017, 17, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwińska, A.; Pogoda, K.; Michalski, W.; Kunkiel, M.; Jagiełło-Gruszfeld, A. Determinants of prolonged survival for breast cancer patient groups with leptomeningeal metastasis (LM). J. Neurooncol. 2018, 138, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, H.; Guilhaume, M.N.; Bidard, F.C.; Pierga, J.Y.; Girre, V.; Cottu, P.H.; Laurence, V.; Livartowski, A.; Mignot, L.; Diéras, V. Survival of breast cancer patients with meningeal carcinomatosis. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 2183–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyerb, S.P.; Thomssenc, C.; Fehmd, T.; Diele, I.; Nitzf, U.; Jannig, W.; Bischoffh, J.; Saueri, R. Clinical Recommendations of DEGRO and AGO on Preferred Standard Palliative Radiotherapy of Bone and Cerebral Metastases, Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression, and Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis in Breast Cancer. Breast Care 2010, 5, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Feyer, P.; Sautter-Bihl, M.L.; Budach, W.; Dunst, J.; Haase, W.; Harms, W.; Sedlmayer, F.; Souchon, R.; Wenz, F.; Sauer, R. DEGRO Practical Guidelines for palliative radiotherapy of breast cancer patients: Brain metastases and leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2010, 186, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwińska, A.; Rudnicka, H.; Murawska, M. Breast cancer leptomeningeal metastasis: Propensity of breast cancer subtypes for leptomeninges and the analysis of factors influencing survival. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnicka, H.; Niwińska, A.; Murawska, M. Breast cancer leptomeningeal metastasis--the role of multimodality treatment. J. Neurooncol. 2007, 84, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingston, B.; Kayhanian, H.; Brooks, C.; Cox, N.; Chaabouni, N.; Redana, S.; Kalaitzaki, E.; Smith, I.; O’Brien, M.; Johnston, S.; et al. Treatment and prognosis of leptomeningeal disease secondary to metastatic breast cancer: A single-centre experience. Breast 2017, 36, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchins, R.N.; Bell, D.R.; Woods, R.L.; Levi, J.A. A prospective randomized trial of single-agent versus combination chemotherapy in meningeal carcinomatosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 1987, 5, c1655–c1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Yang, G.; He, H.; Zhao, G.; Yuan, T.; Li, Y.; Shi, W.; Gao, P.; Dong, L.; Li, Y. Concurrent radiotherapy and intrathecal methotrexate for treating leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors with adverse prognostic factors: A prospective and single-arm study. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, S.A.; Trump, D.L.; Chen, D.C.; Thompson, G.; Camargo, E.E. Cerebrospinal fluid flow abnormalities in patients with neoplastic meningitis. An evaluation using 111indium-DTPA ventriculography. Am. J. Med. 1982, 73, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glantz, M.J.; Hall, W.A.; Cole, B.F.; Chozick, B.S.; Shannon, C.M.; Wahlberg, L.; Akerley, W.; Marin, L.; Choy, H. Diagnosis, management, and survival of patients with leptomeningeal cancer based on cerebrospinal fluid-flow status. Cancer 1995, 75, 2919–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, M.C.; Kormanik, P.A. Prognostic significance of 111indium-DTPA CSF flow studies in leptomeningeal metastases. Neurology 1996, 46, 1674–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, M.C. Radioisotope CSF flow studies in leptomeningeal metastases. J. Neurooncol. 1998, 38, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, J.V.; Saha, S.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Hullett, C.R.; Ian Robins, H. Management of leptomeningeal metastases: Prognostic factors and associated outcomes. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 27, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gani, C.; Müller, A.C.; Eckert, F.; Schroeder, C.; Bender, B.; Pantazis, G.; Bamberg, M.; Berger, B. Outcome after whole brain radiotherapy alone in intracranial leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from solid tumors. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2012, 188, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogerd, W.; van den Bent, M.J.; Koehler, P.J.; Heimans, J.J.; van der Sande, J.J.; Aaronson, N.K.; Hart, A.A.; Benraadt, J.; Vecht, C.J. The relevance of intraventricular chemotherapy for leptomeningeal metastasis in breast cancer: A randomised study. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 2726–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boogerd, W.; vd Sande, J.J.; Moffie, D. Acute fever and delayed leukoencephalopathy following low dose intraventricular methotrexate. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Abe, T.; Shinozaki, M.; Tanaka, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Hiromichi, G.; Kanemaki, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Kojima, Y. Evaluation of imaging findings and prognostic factors after whole-brain radiotherapy for carcinomatous meningitis from breast cancer: A retrospective analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e21333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Central Nervous System Cancers, Version 2.2021—8 September 2021. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cns.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2021).
- Specht, H.M.; Combs, S.E. Stereotactic radiosurgery of brain metastases. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2016, 60, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.; Donahue, B.; Silverman, J.S.; Chachoua, A.; Lee, J.K.; Kondziolka, D. Stereotactic radiosurgery for focal leptomeningeal disease in patients with brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 134, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekovic, G.; Drazin, D.; Mak, A.C.; Schwartz, M.S. Cyberknife Radiosurgery and Concurrent Intrathecal Chemotherapy for Leptomeningeal Metastases: Case Report of Prolonged Survival of a HER2+ Breast Cancer Patient Status-Post Craniospinal Irradiation. Cureus 2016, 8, e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, B.; Hültenschmidt, B.; Sautter-Bihl, M.L. Radiotherapy of theneuroaxis for palliative treatment of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2001, 177, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, H.M.; Mitsuya, K.; Asakura, K.; Ogawa, H.; Onoe, T.; Kawashiro, S.; Sumita, K.; Murayama, S.; Fuji, H.; Nakasu, Y.; et al. Cranio-spinal irradiation for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis: A pilot study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, S310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shafie, R.A.; Böhm, K.; Weber, D.; Lang, K.; Schlaich, F.; Adeberg, S.; Paul, A.; Haefner, M.F.; Katayama, S.; Sterzing, F.; et al. Outcome and prognostic factors following palliative craniospinal irradiation for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.P.; Barney, C.L.; Grosshans, D.R.; McAleer, M.F.; de Groot, J.F.; Puduvalli, V.K.; Tucker, S.L.; Crawford, C.N.; Khan, M.; Khatua, S.; et al. Proton beam craniospinal irradiation reduces acute toxicity for adults with medulloblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 86, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.J.; Wijetunga, N.A.; Yamada, J.; Wolden, S.; Mehallow, M.; Goldman, D.A.; Zhang, Z.; Young, R.J.; Kris, M.G.; Yu, H.A.; et al. Clinical Trial of Proton Craniospinal Irradiation for Leptomeningeal Metastases. Neuro. Oncol. 2021, 23, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.T.; Wijetunga, N.A.; Pentsova, E.; Wolden, S.; Young, R.J.; Correa, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Steckler, A.; Bucwinska, W.; et al. Randomized phase II trial of proton craniospinal irradiation versus photon involved-field radiotherapy for patients with solid tumor leptomeningeal metastasis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, JCO2201148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devecka, M.; Duma, M.N.; Wilkens, J.J.; Kampfer, S.; Borm, K.J.; Münch, S.; Straube, C.; Combs, S.E. Craniospinal irradiation (CSI) in patients with leptomeningeal metastases: Risk-benefit-profile and development of a prognostic score for decision making in the palliative setting. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiopu, S.R.; Habl, G.; Haefner, M.; Katayama, S.; Herfarth, K.; Debus, J.; Sterzing, F. Helical tomotherapy in patients with leptomeningeal metastases. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 11, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, J.K.; Yaraskavitch, M.; Henning, J.W.; Graham, D.; Logie, N. Craniospinal Irradiation for Leptomeningeal Disease in Recurrent Breast Cancer. Appl. Rad. Oncol. 2021, 10, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Maillie, L.; Salgado, L.R.; Lazarev, S. A systematic review of craniospinal irradiation for leptomeningeal disease: Past, present, and future. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 2109–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.M.; Baselga, J.; Kim, S.B.; Ro, J.; Semiglazov, V.; Campone, M.; Ciruelos, E.; Ferrero, J.M.; Schneeweiss, A.; Heeson, S.; et al. Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagouri, F.; Zoumpourlis, P.; Le Rhun, E.; Bartsch, R.; Zografos, E.; Apostolidou, K.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Preusser, M. Intrathecal administration of anti-HER2 treatment for the treatment of meningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer: A metanalysis with meta-regression. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 88, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saura, C.; Oliveira, M.; Feng, Y.H.; Dai, M.S.; Chen, S.W.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Kim, S.B.; Moy, B.; Delaloge, S.; Gradishar, W.; et al. NALA Investigators. Neratinib Plus Capecitabine Versus Lapatinib Plus Capecitabine in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Previously Treated with ≥ 2 HER2-Directed Regimens: Phase III NALA Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3138–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, R.K.; Loi, S.; Okines, A.; Paplomata, E.; Hamilton, E.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Lin, N.U.; Borges, V.; Abramson, V.; Anders, C.; et al. Tucatinib, Trastuzumab, and Capecitabine for HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exman, P.; Mallery, R.M.; Lin, N.U.; Parsons, H.A. Response to Olaparib in a Patient with Germline BRCA2 Mutation and Breast Cancer Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis. NPJ Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.V.; Searle, K.; Jerzak, K.J. Central nervous system-specific efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitors in randomized controlled trials for metastatic breast cancer. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 6317–6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolaney, S.M.; Sahebjam, S.; Le Rhun, E.; Bachelot, T.; Kabos, P.; Awada, A.; Yardley, D.; Chan, A.; Conte, P.; Diéras, V.; et al. A Phase II Study of Abemaciclib in Patients with Brain Metastases Secondary to Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5310–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Lee, E.Q.; Cohen, J.V.; Tolaney, S.M.; Lin, N.U.; Wang, N.; Chukwueke, U.; White, M.D.; Nayyar, N.; Kim, A.; et al. Single-arm, open-label phase 2 trial of pembrolizumab in patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, M.; Junck, L.; Brandsma, D.; Soffietti, R.; Rudà, R.; Raizer, J.; Boogerd, W.; Taillibert, S.; Groves, M.D.; Le Rhun, E.; et al. Leptomeningeal metastases: A RANO proposal for response criteria. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Rhun, E.; Devos, P.; Winklhofer, S.; Lmalem, H.; Brandsma, D.; Gállego Pérez-Larraya, J.; Castellano, A.; Compter, A.; Dhermain, F.; Franceschi, E.; et al. NIMG-01. Interobserver variability of the revised imaging scorecard for leptomeningeal metastasis: A joint EORTC and brain tumor group and RANO effort. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23 (Suppl. S6), vi126–vi127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, E.; Devos, P.; Weller, J.; Seystahl, K.; Mo, F.; Compter, A.; Berghoff, A.S.; Jongen, J.L.M.; Wolpert, F.; Rudà, R.; et al. Prognostic validation and clinical implications of the EANO ESMO classification of leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors. Neuro. Oncol. 2021, 23, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
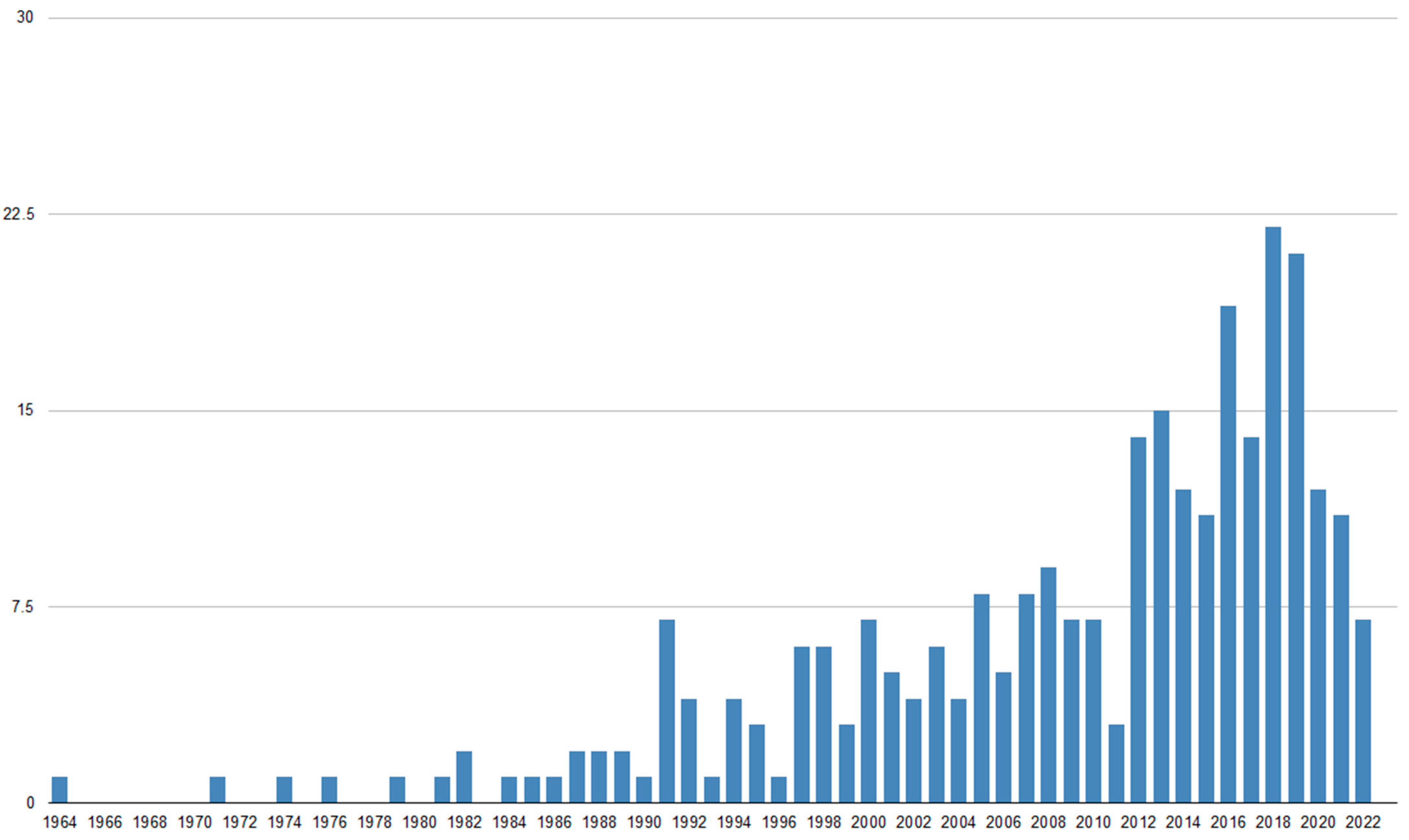
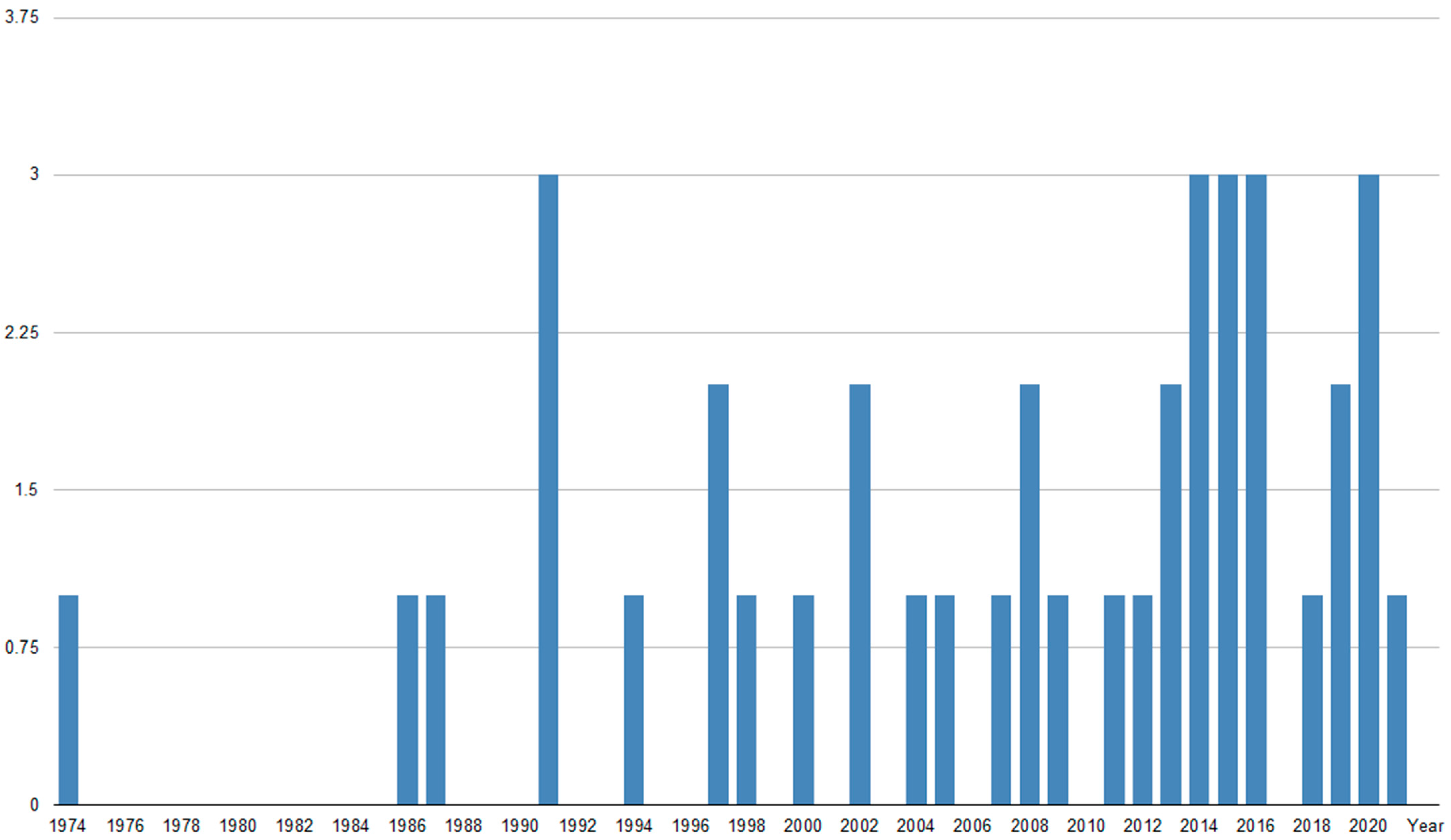
| Authors | Number of Patients (BC) | Study Type | Treatment | Major Results | Toxicity (Including All Treatment Methods) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Niwińska et al. [33] | 118 (118) | Prospective | Treatment of physicians’ choice ChT-68% ITC-79% WBRT-56% spinal cord RT-24% | Brain RT-prolongs survival in univariate analysis (p = 0.017), not confirmed in multivariate analysis (p = 0.817); No OS benefit of spinal cord RT (p = 0.894) | |
| Rudnicka et al. [34] | 67 (67) | Prospective | Treatment of physicians’ choice ITC 85% ChT 61% WBRT 49% Spinal cord RT 15% | Brain RT-prolongs survival in univariate analysis (p = 0.004), not confirmed in multivariate analysis (p = 0.156); No OS benefit of spinal cord RT (p = 0.989) | |
| Niwińska et al. [29] | 187 (187) | Prospective | Treatment of physicians’ choice ITC 68% ChT 56% WBRT 35% spinal cord RT 8% WBRT + spinal cord RT 13% | Multivariate analysis: RT improves survival (p < 0.001) | |
| Kingston et al. [35] | 182 (182) | Retrospective | Treatment of physicians’ choice ITC 7.7% ChT 25% RT 34% best supportive care 20.3% | Longer OS (median 6.1 mo.) and PFS (median 5.8 mo.) with RT compared to ITC or palliative care alone | |
| Hitchins et al. [36] | 44 (11) | Prospective, randomized | Arm A: ITC MTX Arm B: ITC MTX + Ara-C ChT 68% RT 50% (WBRT n = 17, spinal RT n = 4, neuroaxis n = 1) | Improved OS with concurrent ITC and WBRT (p = 0.003) compared to ITC alone RR 73% and 35%, with and without RT, respectively, (p < 0.05) Median OS of 4 mo. and 1.8 mo., with and without RT, respectively | Nausea and vomiting: 45% Meningitis: 14% Septicemia, neutropenia: 12% Mucositis: 12% Pancytopenia: 10% |
| Pan et al. [37] | 59 (11) | Prospective, single-arm | Induction, concomitant and consolidation ITC (MTX) + IF-RT (40–50 Gy/20 fx) | Univariate analysis: longer OS in patients achieving clinical response (p = 0.013) and administered a complete course of concomitant (ITC + RT) therapy (p = 0.016) | Acute cerebral meningitis: 2% Chronic encephalopathy: 5% Radiculitis: 27% Bone marrow depression: 22% Mucositis: 20% Leukodystrophy: 68% Encephalopathy: 19% |
| Authors | Study Type | Number of patients (BC) | RT Dose | Percentage of Patients Receiving RT | Percentage of Patients Receiving ChT/ITC | Major Findings | Toxicity of Radiotherapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broewer et al. [42] | Retrospective | 124 (22) | Median 30 Gy/10 fx. (range 24–40 Gy) | 54.5% | 31.4%/7.4% | A complete course of WBRT was predictive of prolonged survival in a multivariate analysis (p = 0.019) | |
| Gani et al. [43] | Retrospective | 27 (20) | Median 30 Gy/10 fx. (range 24–40 Gy) | 100% | 0%/0% | 6-mo. OS 26%, 12-mo. OS 15% Median OS 2 mo. Improvement of neurological deficits: 11% | Grade 1 (erythema, alopecia, nausea, headache, fatigue—26% Grade 2 (tinnitus, alopecia, somnolence)—11.1% No grade 3 or 4 toxicity |
| Boogerd et al. [44] | Prospective, randomized | 35 (35) | 30 Gy/10 fx. | 43% | 46%/49% | WBRT with ITC is feasible and safe | DNL in one patient six mo. after WBRT and 3 patients without WBRT |
| Boogerd et al. [45] | Retrospective | 14 (14) | (range 17.5–42 Gy) | 29% | 0%/100% | DNL occurred in 100% of irradiated patients and in 50% of patients without RT | DNL in all patients with WBRT and 50% of patients without WBRT |
| Okada et al. [46] | Retrospective | 31 (31) | Median 30 Gy/10 fx. (range 20–37.5 Gy) | 100% | 0%/0% | Median OS for patients treated with 30 Gy in <10 fx. −0.6 mo. Median OS for patients treated with 30 Gy in ≥10 fx. −2.6 mo. (p < 0.1) |
| Authors | Number of Patients (BC) | Technique | Median Dose (Gy)/Fractions (N) | Clinical Response | Median OS (Mo.) | Grade 3–4 Toxicity (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hermann et al. [51] | 16 (9) | 2D | 36/20 | 68% improvement 12% stable | Entire group-2.8 CSI-1.84 CSI + ITC-3.7 | Myelosuppression (5) |
| Harada et al. [52] | 17 (6) | 2D | 41.4/23 | 70% improvement | 8.8 | Leukopenia (7) Thrombocytopenia (6) Fatigue, Nausea, Anorexia (4) Anemia (1) 1 toxic death |
| El Shafie et al. [53] | 25 (15) | HTT | 35.2/20 | 28% improvement 40% stable | 4.8 | Myelosuppression (8) |
| Devecka et al. [57] | 19 (5) | 2D until 2007, then HTT | 30.6/19; boost to 37.6 | 58% improvement | 34 (4.7 in BC) | Leukopenia (7) Thrombocytopenia (7) 1 toxic death-thrombosis |
| Schiopu et al. [58] | 15 (6) | HTT | 32.4/18 | 53% improvement (67% in BC) | 3.0 (6.0 in BC) | Leukopenia (8) Thrombocytopenia (7) Anemia (5) Other (6) 3 toxic deaths (1 pulmonary embolism, 2 infections) |
| Author | Title | Evidence | SRS | CSI | WBRT | IF-RT | Publication Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) [47] | NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) Central Nervous System Cancers | Expert consensus | Preferred option. Recommended in case of focal mass obstructing CSF flow | Not recommended due to high toxicity. Should be used only in highly selected patients (e.g., leukemia, lymphoma) | Preferred option | May be considered for palliation to neurologically symptomatic or painful sites (including spine and intracranial disease) | Version 2.2021—8 September 2021 |
| European Association of Neuro-oncology (EANO)-European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) [24] | EANO–ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors | Expert consensus | Should be considered for extensive nodular or symptomatic linear LC | Should be considered for circumscribed, notably symptomatic lesions. | 1 July 2017 | ||
| The German Society of Radiation Oncology (DEGRO) [31,32] | DEGRO Practical Guidelines for Palliative Radiotherapy of Breast Cancer Patients: Brain Metastases and Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis | Systematic review | Due to its myelotoxicity, should be considered only in selected cases, such as multiple circumscript plaques or nodules | Recommended for bulky disease or symptomatic regions | Recommended for bulky disease or symptomatic regions | 26 January 2010 |
| ClinicalTrials.Gov Identifier | Recruitment Status | Intervention | Phase | Estimated Enrollment | Radiotherapy | RT Dose | RT Details | Primary Endpoint | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03719768 | Active, not recruiting | Avelumab + RT | 1 | 23 | WBRT | 30 Gy | Not reported | Safety and DLT | - |
| NCT03507244 | Completed | IT pemetrexed + RT | 1,2 | 34 | WBRT, IF-RT | 40 Gy/20 fx or 40–50 Gy/20–25 fx for spinal canal | Planning volume involves sites of symptomatic disease, bulky disease on MRI, WBRT and/or segment of the spinal canal | Incidence of treatment-related adverse events | [50] |
| NCT03520504 | Active, not recruiting | Proton CSI | 1 | 24 | Proton | 30 Gy (RBE)/10 fx or 25 Gy (RBE)/10 fx | Planning volume: brain, spinal cord, space containing CSF | Number of patients with DLT | - |
| NCT04192981 | Recruiting | GDC-0084 + RT | 1 | 36 | WBRT | 30 Gy/10fx | Not reported | MTD | - |
| NCT03082144 | Completed | RT + IT MTX or RT + IT AraC | 2 | 53 | WBRT, IF-RT | 40 Gy/20 fx or 40–50 Gy/20–25 fx for spinal canal | The sites of symptomatic disease, bulky disease at MRI, including the whole brain and cranial base and/or segment of spinal canal | Clinical response rate | - |
| NCT04588545 | Recruiting | RT + IT trastuzumab/ pertuzumab | 1,2 | 39 | WBRT, IF-RT | 30 Gy/10 fx or 20 Gy/5 fx | WBRT or focal brain/spine RT | Phase 1: MTD, Phase 2: OS | - |
| NCT04343573 | Active, not recruiting | RT | 2 | 111 | Arm 1: Proton Arm 2: Photon | 30 Gy/10 fx | Arm 1: Proton CSI Arm 2: Involved field photon RT including WBRT and/or focal spine RT | CNS progression-free survival | - |
| NCT04178343 | Completed | RT | 2 | 103 | Tomotherapy | WBRT: 40 Gy/20 fx with SIB 60 Gy; WBRT: 50Gy/25 fx, depending on BM presence | Boost of the leptomeningeal metastases. WBRT of 50 Gy with hippocampus and brainstem sparing | OS | - |
| NCT00854867 | Completed | WBRT + IT liposomal cytarabine | 1 | 18 | WBRT | 38.4 Gy/20 fx | First two fx of 3 Gy, then 1.8 Gy/fx | The safety of WBRT concomitant with liposomal cytarabine | - |
| NCT05305885 | Recruiting | IT pemetrexed +/− RT | Not applicable | 100 | WBRT, IF-RT | 40 Gy/20 fx | Planning volume: sites of symptomatic disease, bulky disease on MRI, WBRT, and/or segment of the spinal canal | Clinical response rate |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pawłowska, E.; Romanowska, A.; Jassem, J. Radiotherapy for Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis in Breast Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 3899. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163899
Pawłowska E, Romanowska A, Jassem J. Radiotherapy for Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis in Breast Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review. Cancers. 2022; 14(16):3899. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163899
Chicago/Turabian StylePawłowska, Ewa, Anna Romanowska, and Jacek Jassem. 2022. "Radiotherapy for Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis in Breast Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review" Cancers 14, no. 16: 3899. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163899
APA StylePawłowska, E., Romanowska, A., & Jassem, J. (2022). Radiotherapy for Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis in Breast Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review. Cancers, 14(16), 3899. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163899







