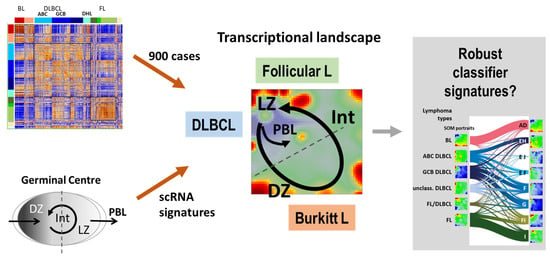
Classifying Germinal Center Derived Lymphomas—Navigate a Complex Transcriptional Landscape
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Lymphoma Data
2.2. Transcriptome Map of Lymphomas and Spot Classifiers
2.3. Reference Classifiers, Gene Set Maps and GSZ-Profiles
3. Results
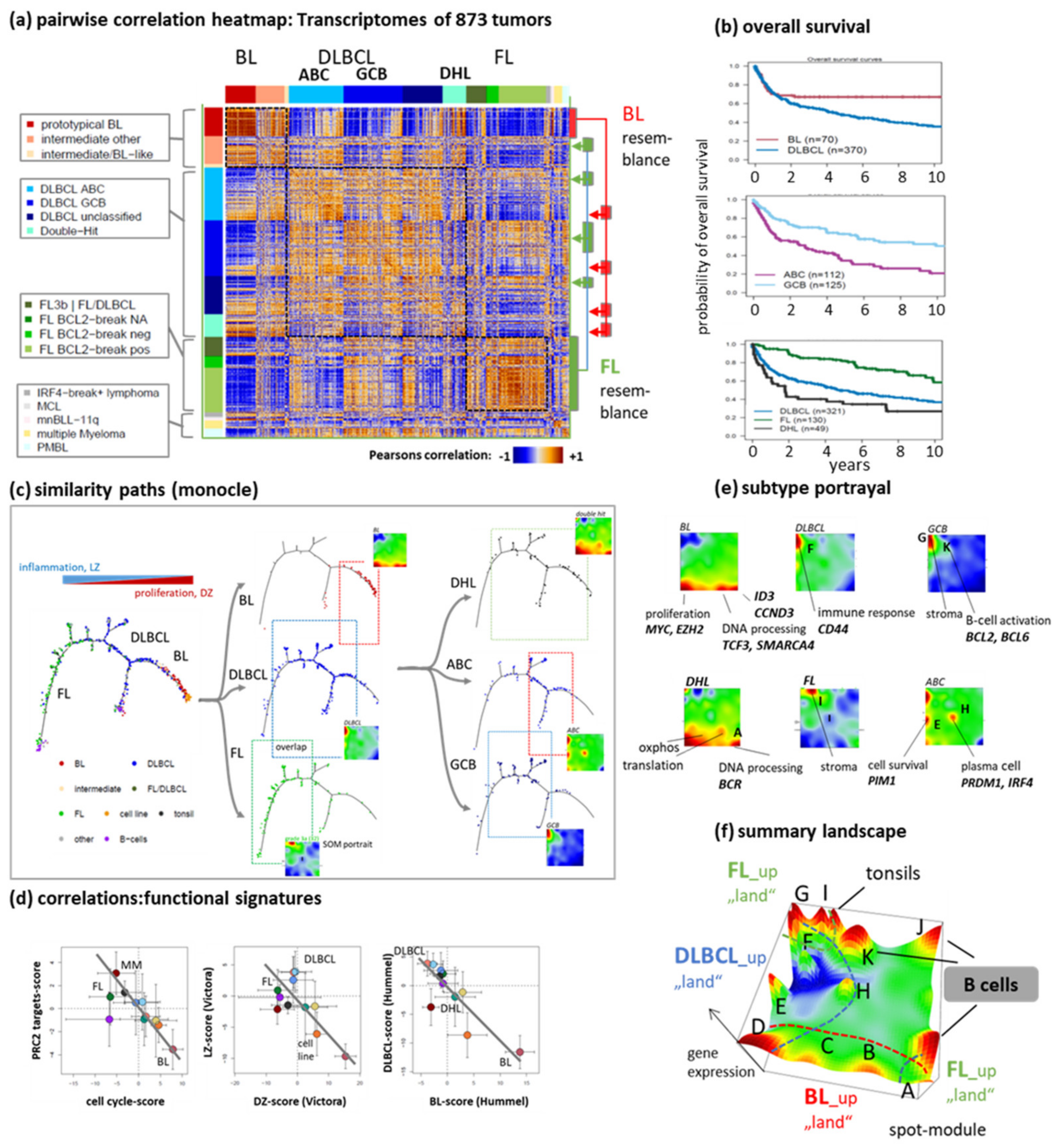
3.1. The Multi-Dimensional Nature of the Lymphoma Transcriptome
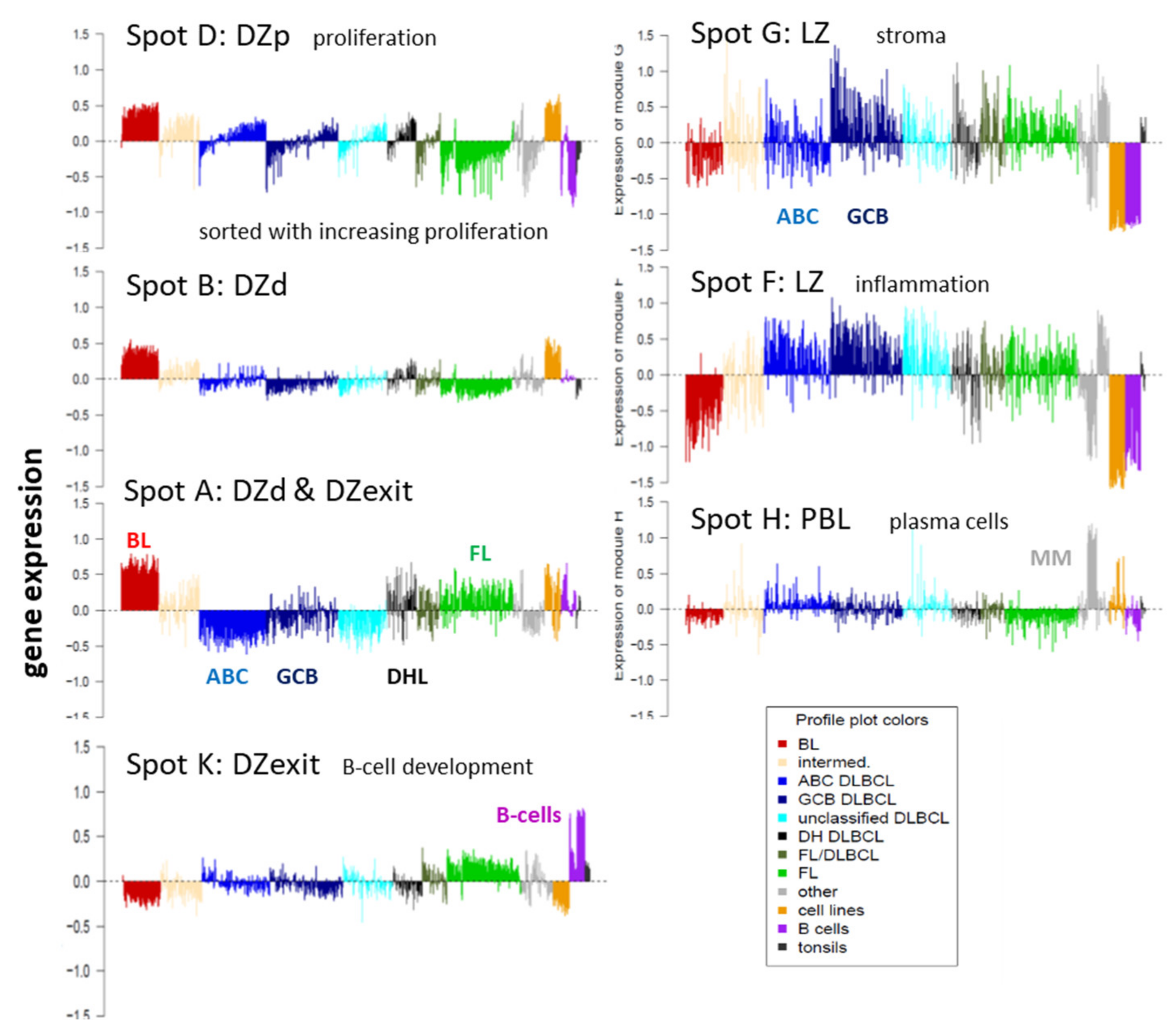
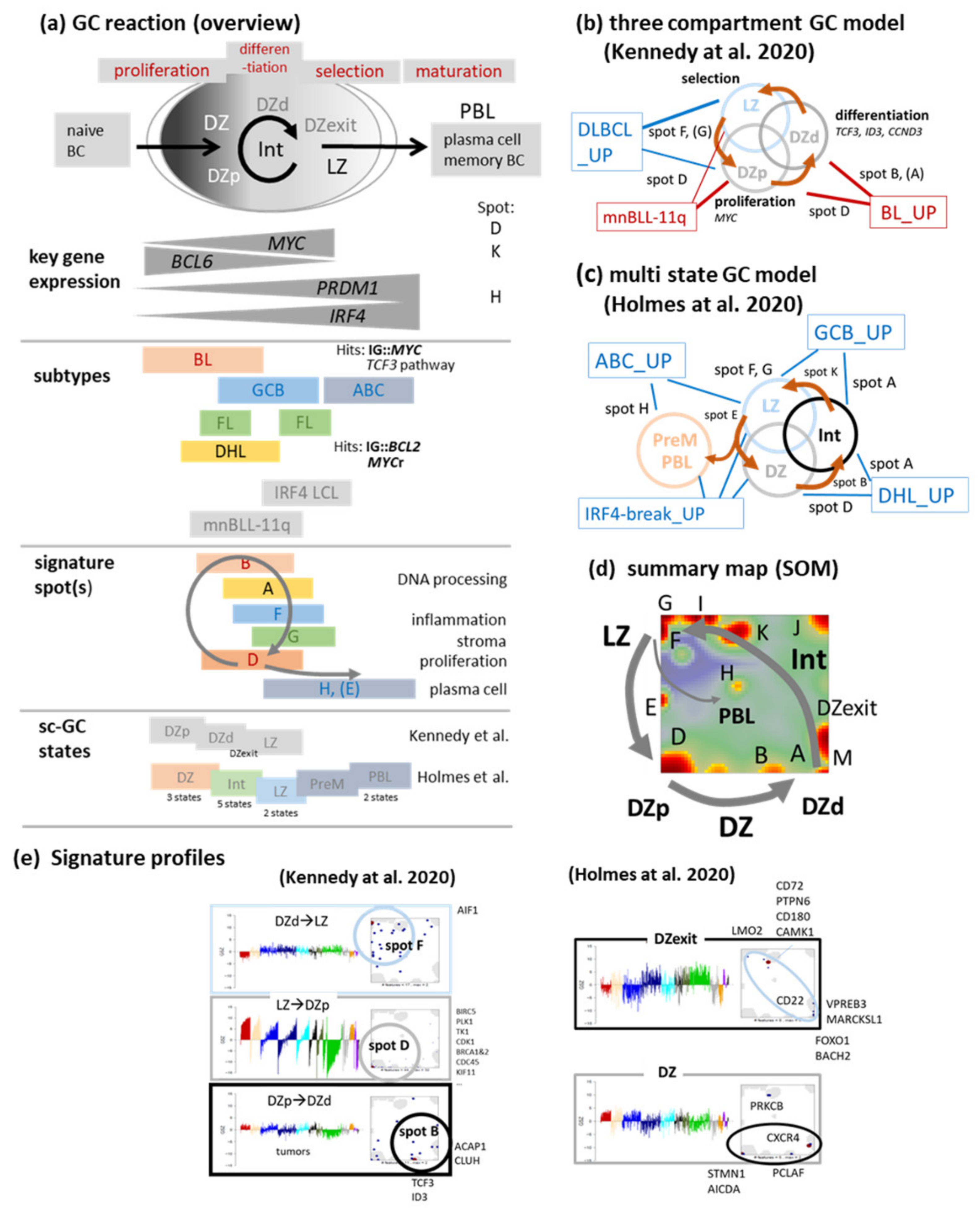
3.2. Beyond the Canonical DZ-LZ Dualism
3.3. Provisonal Genetic Entities: mnBLL-11q, IRF4-Break-LCL and HGBL-DH
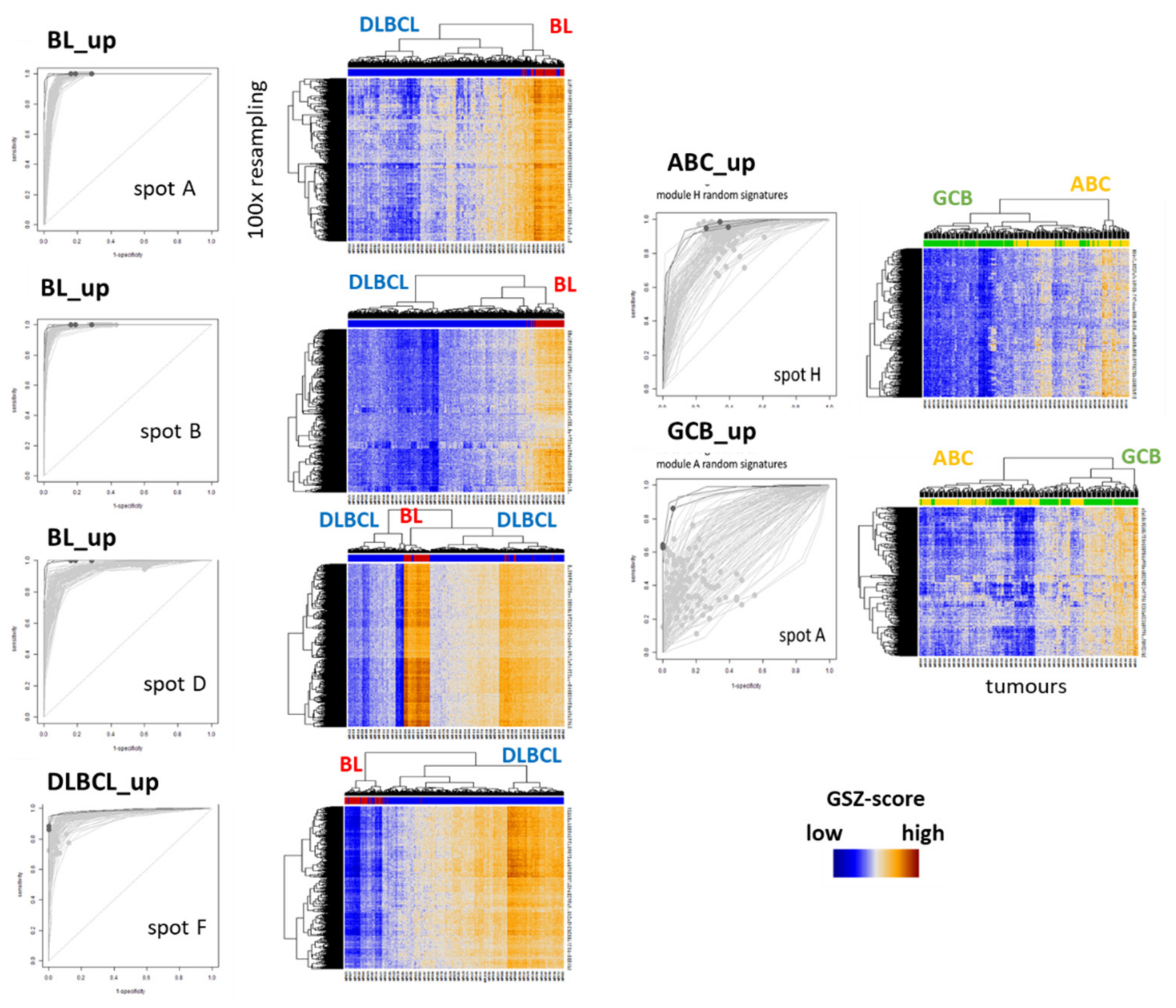
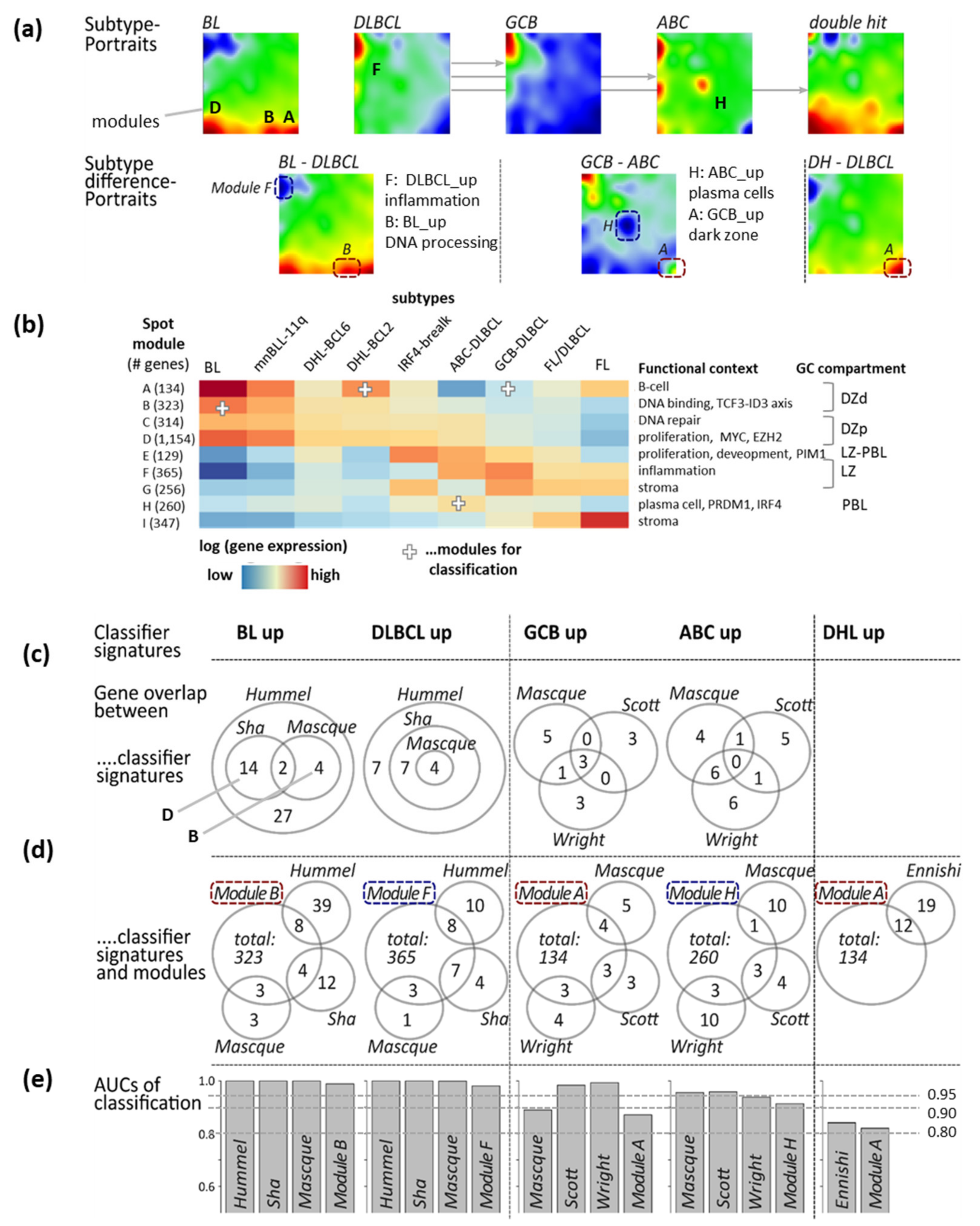
3.4. Gene Expression Classifiers of BL and DLBCL
| Classifier (a),(f) | Reference | Classifier Sets (b) | Sample Size and Platform (c) | Comment (d) | Spot (e) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL-vs-DLBCL (& intermediate) (f) | Hummel et al. [3] | BL_up: 47 DLBCL_up: 18 | BL, DLBCL (N = 221) Array (HG U133A) | Linear model (shrunken centroids [63]) | BL_UP: B DLBCL_UP: F |
| BL-vs-DLBCL | Sha et al. [30] | BL_up: 16 DLBCL_up: 11 | BL, DLBCL (N = 1177) Array (HG U133A, lymphochip) | Support vector machine (SVM) | |
| BL-vs-DLBCL (& intermediate) | Masque-Soler at al. [18] | BL_up: 6 DLBCL_up: 4 | BL, DLBCL (N = 90) Multiplex count (nCounter) | Linear classification | |
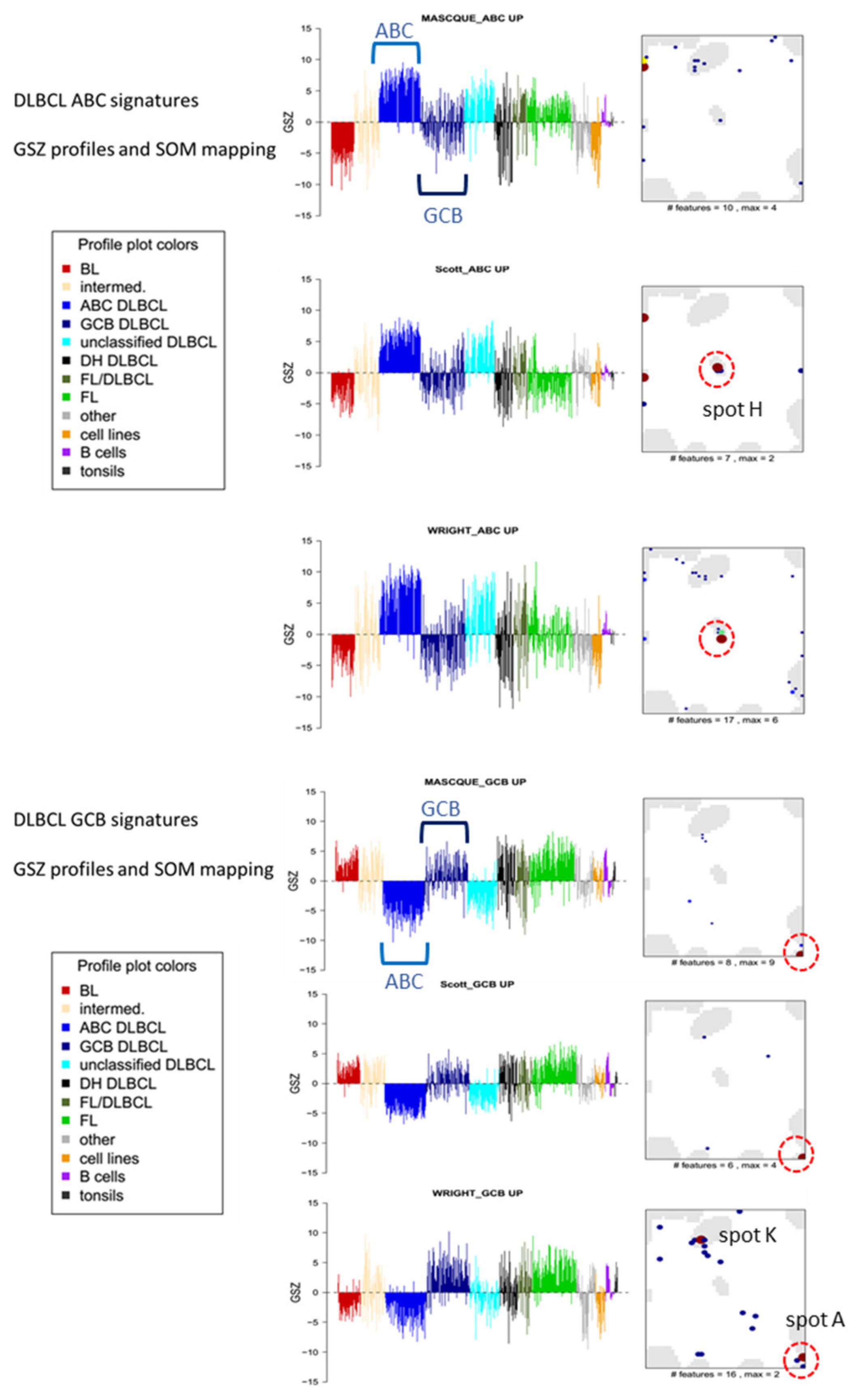
| ABC-vs-GCB (& unclassified) | Masque-Soler at al. [18] | ABC_up: 9 GCB_up: 11 | DLBCL (N = 90) Multiplex count (nCounter) | Linear classification | ABC_UP: H GCB_UP: A |
| ABC-vs-GCB (& unclassified) | Scott et al. [17] | ABC_up: 7 GCB_up: 6 | DLBCL (N = 119) Array (Nanostring) | Weighted average | |
| ABC-vs-GCB (& unclassified) | Wright et al. [31] | ABC_up: 13 GCB_up: 7 | DLBCL (N = 274) Array (HG U133A, Lymphochip) | Linear classification g) | |
| DHL-vs-non DHL (DHL-BCL2) | Ennishi et al. [5] | DHL_up: 31 Non-DHL_up: 47 | GCB DLBCL (N = 157) RNA sequencing | Weighted average | DHL_UP: A n-DHL_UP: F |
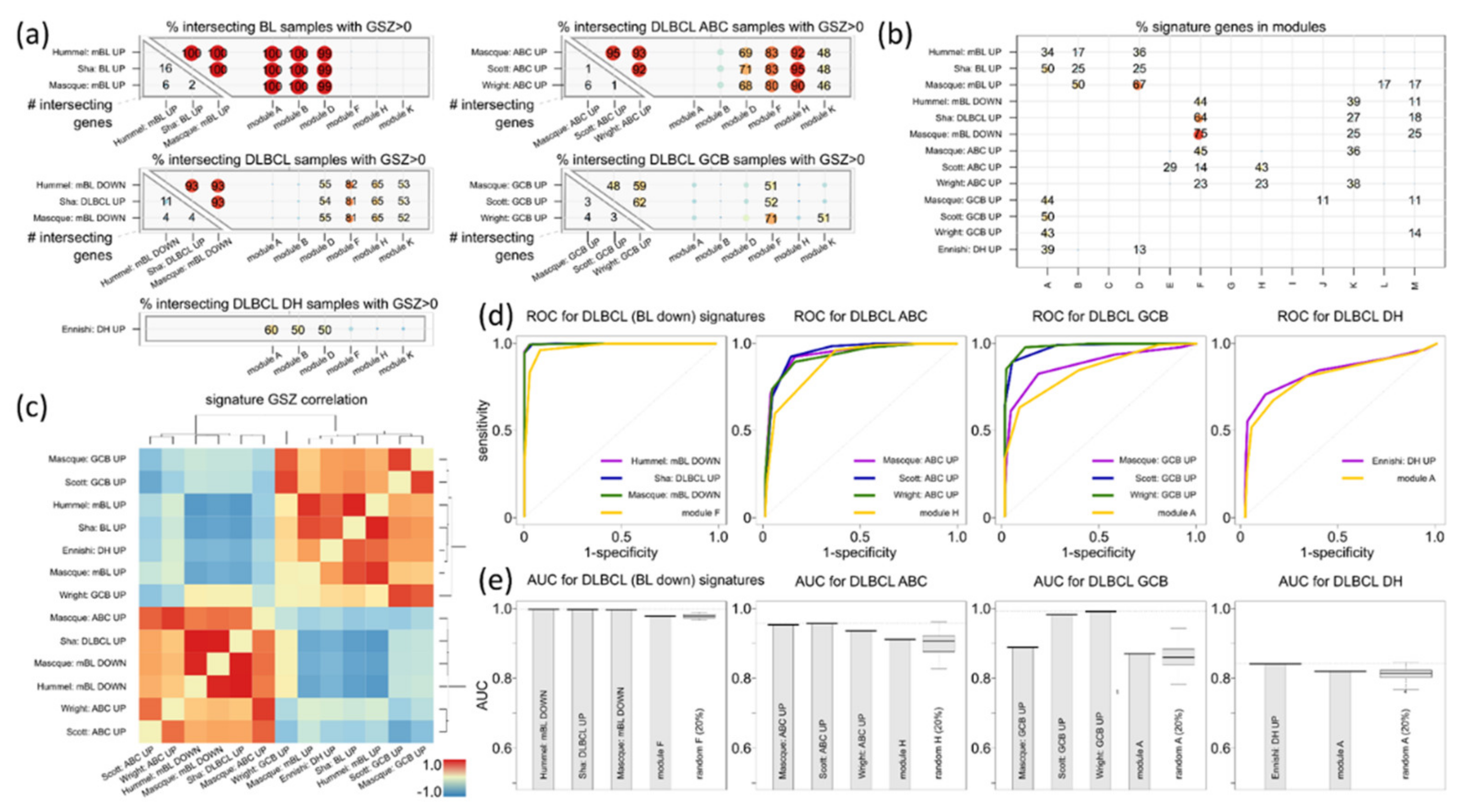
3.5. Distinguishing BL
3.6. Distinguishing DLBCL: ABC, GCB and DHL
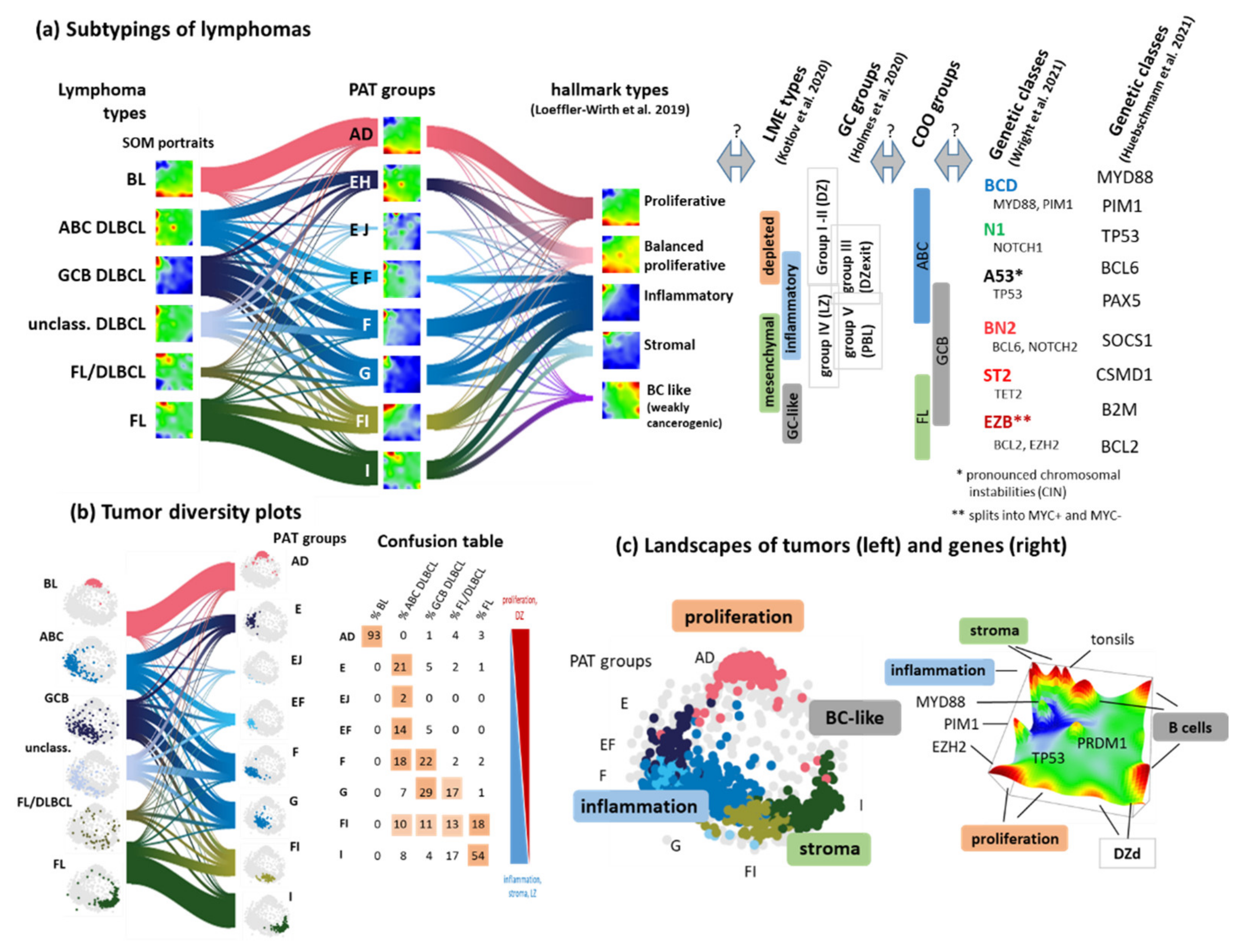
3.7. Pattern Types, Microenvironmental and GC-Related Categories
4. Discussion
4.1. Footprints of the GC Reaction in the Lymphoma Transcriptome
4.2. Navigating a Multidimensional Transcriptional Landscape
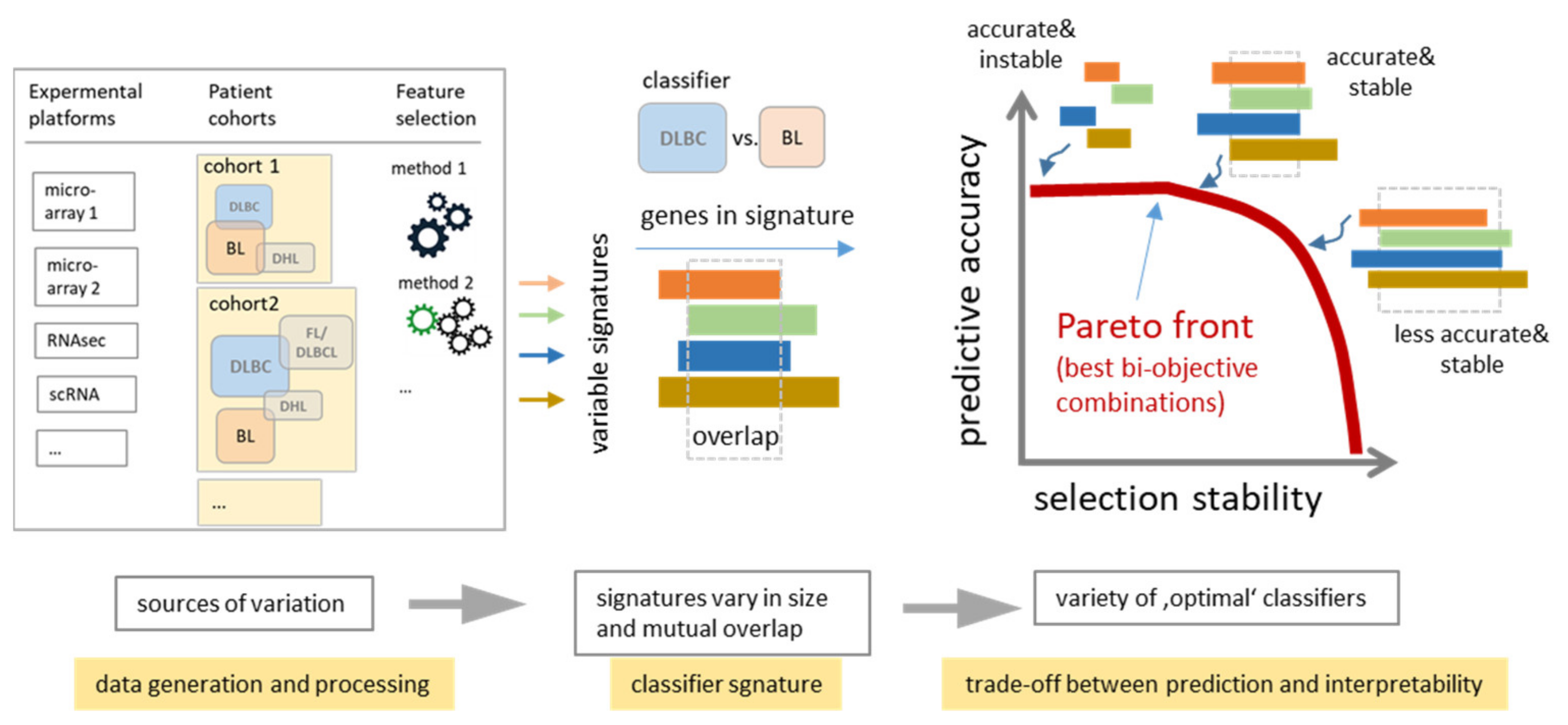
4.3. Consenting Classifiers as a Trade-Off Balancing Accuracy and Stability
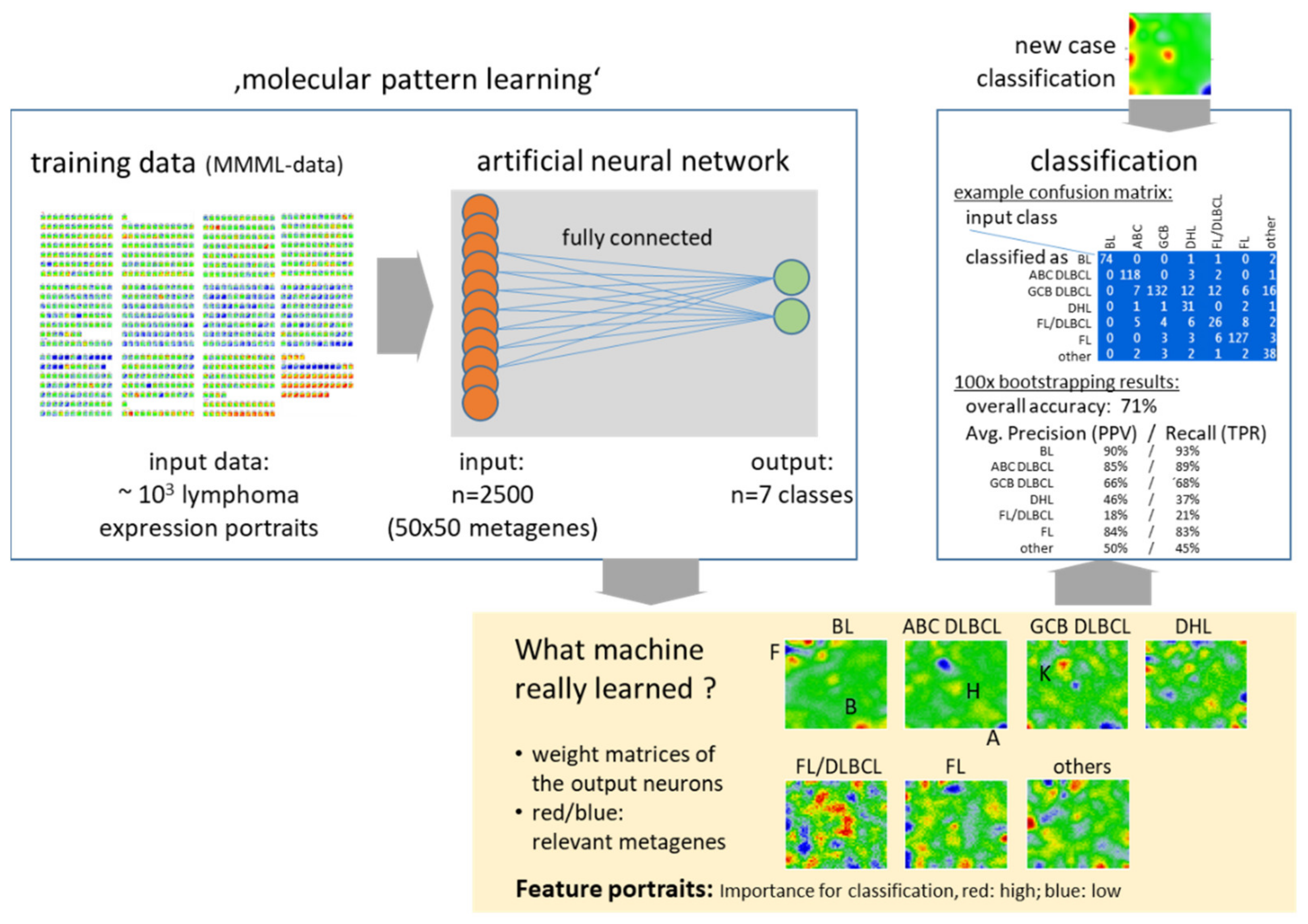
4.4. New Concepts: PATs, Machine Learning of Molecular Portraits and Multiomics Classifiers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| ABC | activated B-cell-like subgroup |
| AUC | area under the (ROC) curve |
| BL | Burkitt lymphoma |
| Chr | chromosome |
| COO | cell of origin |
| DHL | double-hit lymphoma |
| DZ | dark zone of germinal centre |
| DZd | cell state of differentiation in dark zone of germinal centre |
| DZexit | B-cells that just exit the dark zone of germinal centre |
| DZp | cell state of proliferation in dark zone of germinal centre |
| DLBCL | diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| FL | follicular lymphoma |
| GC | germinal center |
| GCB | germinal center B-cell-like subgroup |
| GEP | gene expression profiling |
| GSZ | gene set Z-score |
| HGBL-DH/TH | high-grade B-cell lymphomas with double or triple hits |
| HGBL-NOS | high-grade B-cell lymphomas, not otherwise specified |
| LCL | large cell lymphoma |
| LME | lymphoma microenvironment |
| LRP | layer-wise relevance propagation |
| LZ | light zone of germinal center |
| MCL | mantle cell lymphoma |
| mnBLL-11q | MYC-negative Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration |
| MM | multiple myeloma |
| MMML | ‘Molecular Mechanisms of Malignant Lymphoma’ consortium |
| mRNA | messenger ribonucleic acid (RNA) |
| PAT | pattern types |
| PBL | plasmablast |
| PMBL | primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma |
| PrePC | precursors of plasma cells |
| PreM | precursors of memory B-cells |
| ROC | receiver operator curve |
| SHL | single hit lymphoma |
| SOM | self-organizing map |
| THL | triple hit lymphoma |
| WES | whole-exome sequencing |
| WGS | whole-genome sequencing |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
Appendix A. Additional Methods
Appendix A.1. Transcriptome Map of Lymphoma
Appendix A.2. GSZ Profiles of Classifier Signatures and ROC Characteristics
Appendix A.3. oposSOM Browser of the MMML Lymphoma Data Set
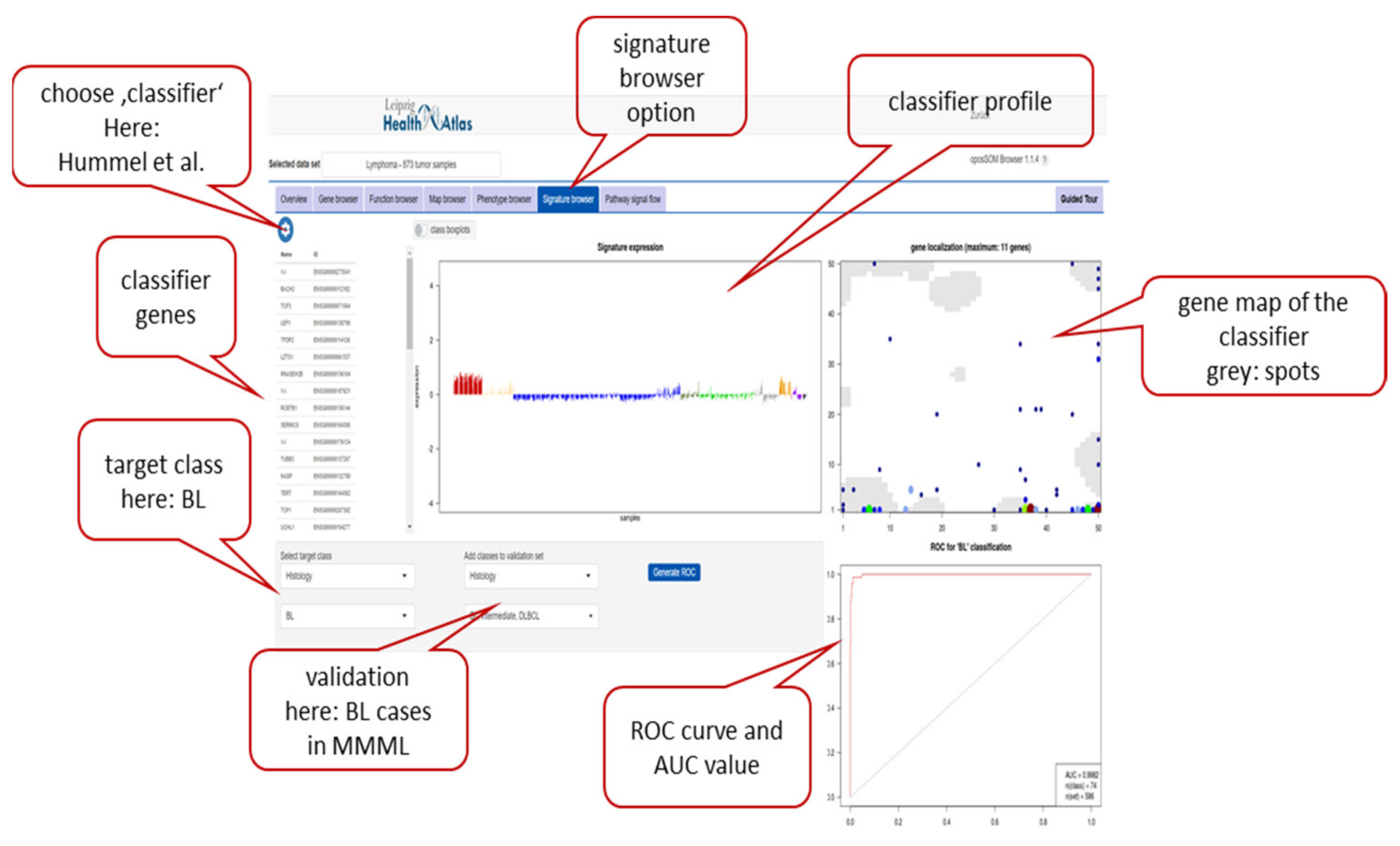
Appendix A.4. Machine Learning of Transcriptonal Portraits
Appendix B. Additional Figures
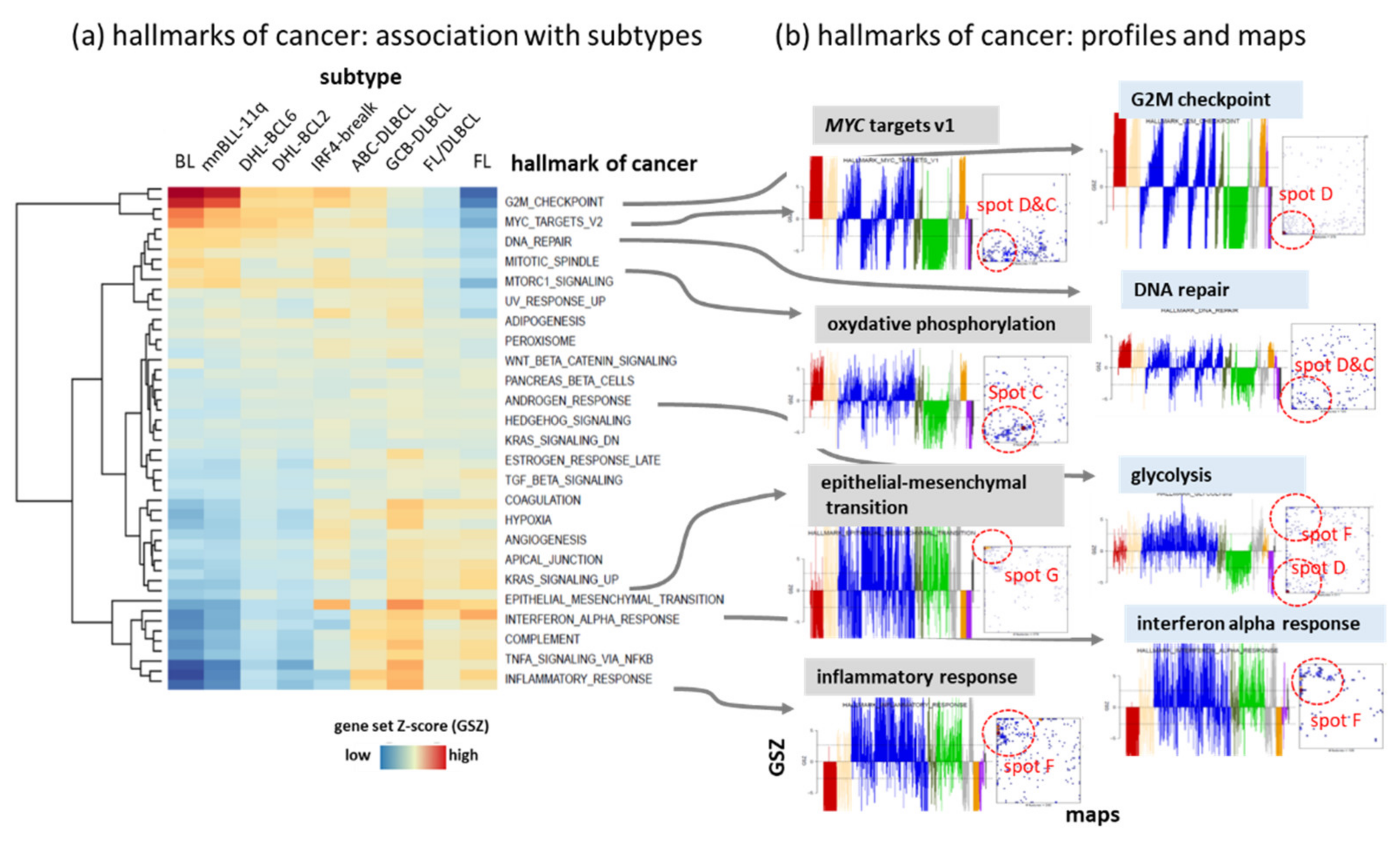
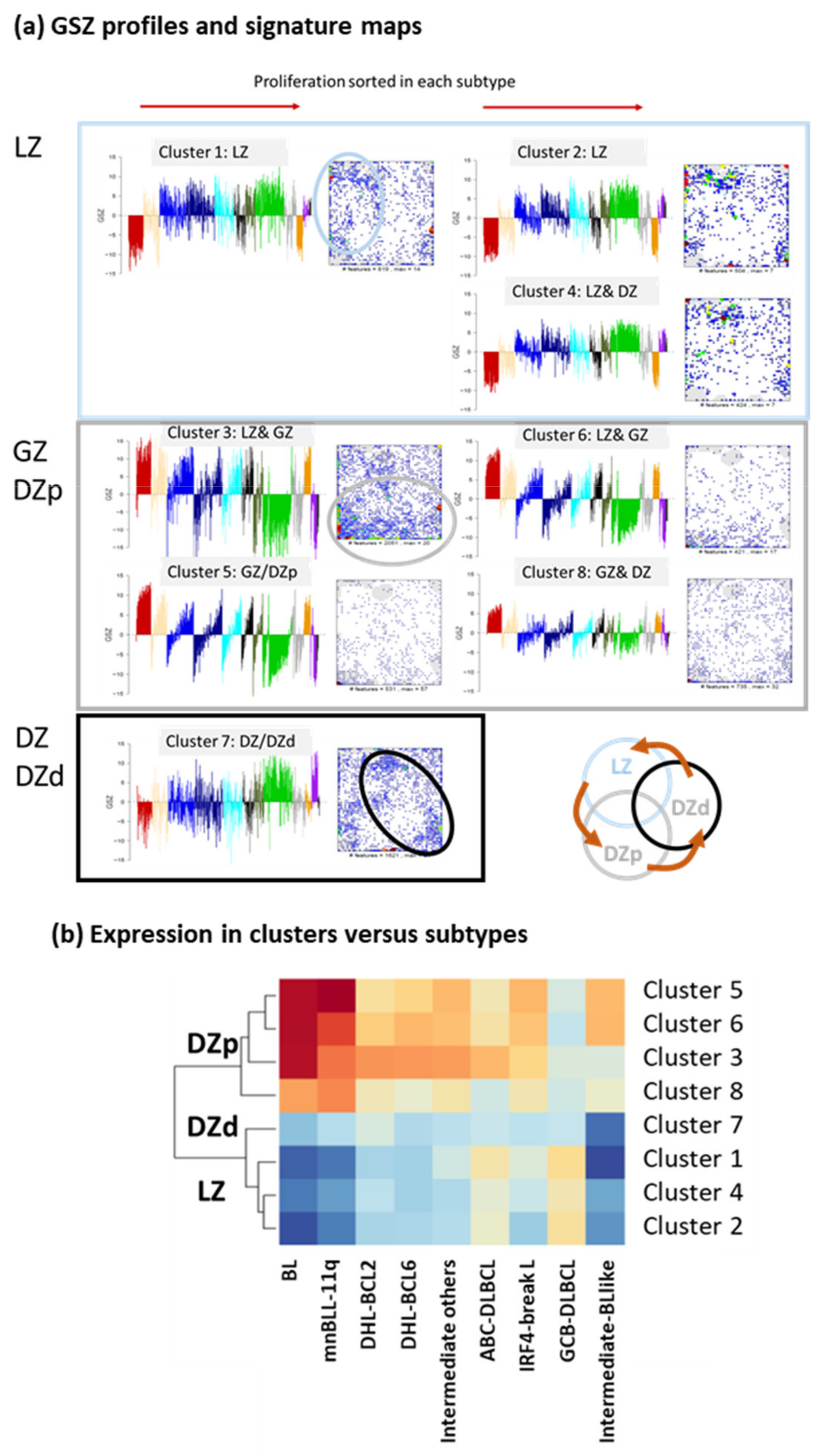
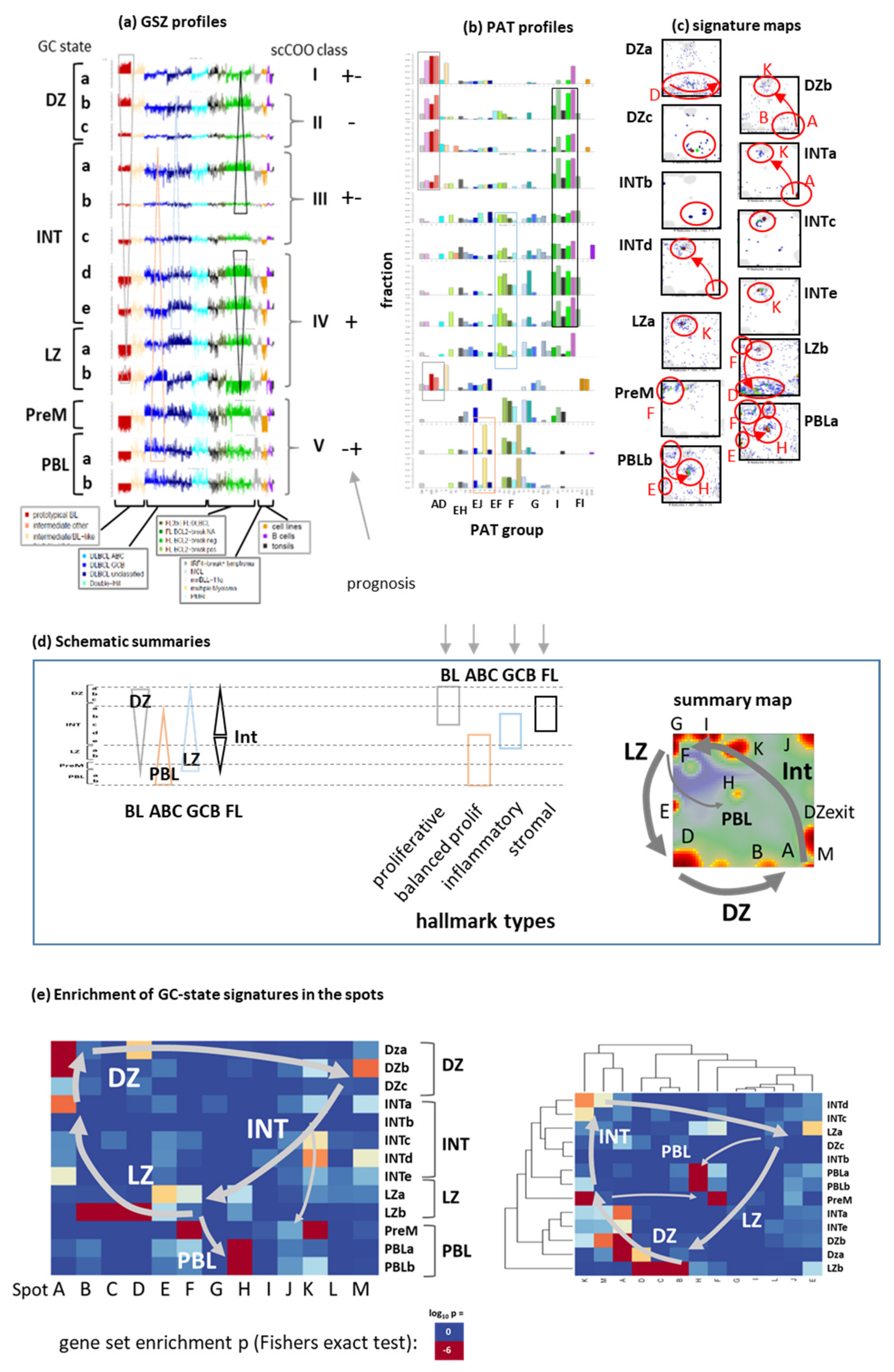
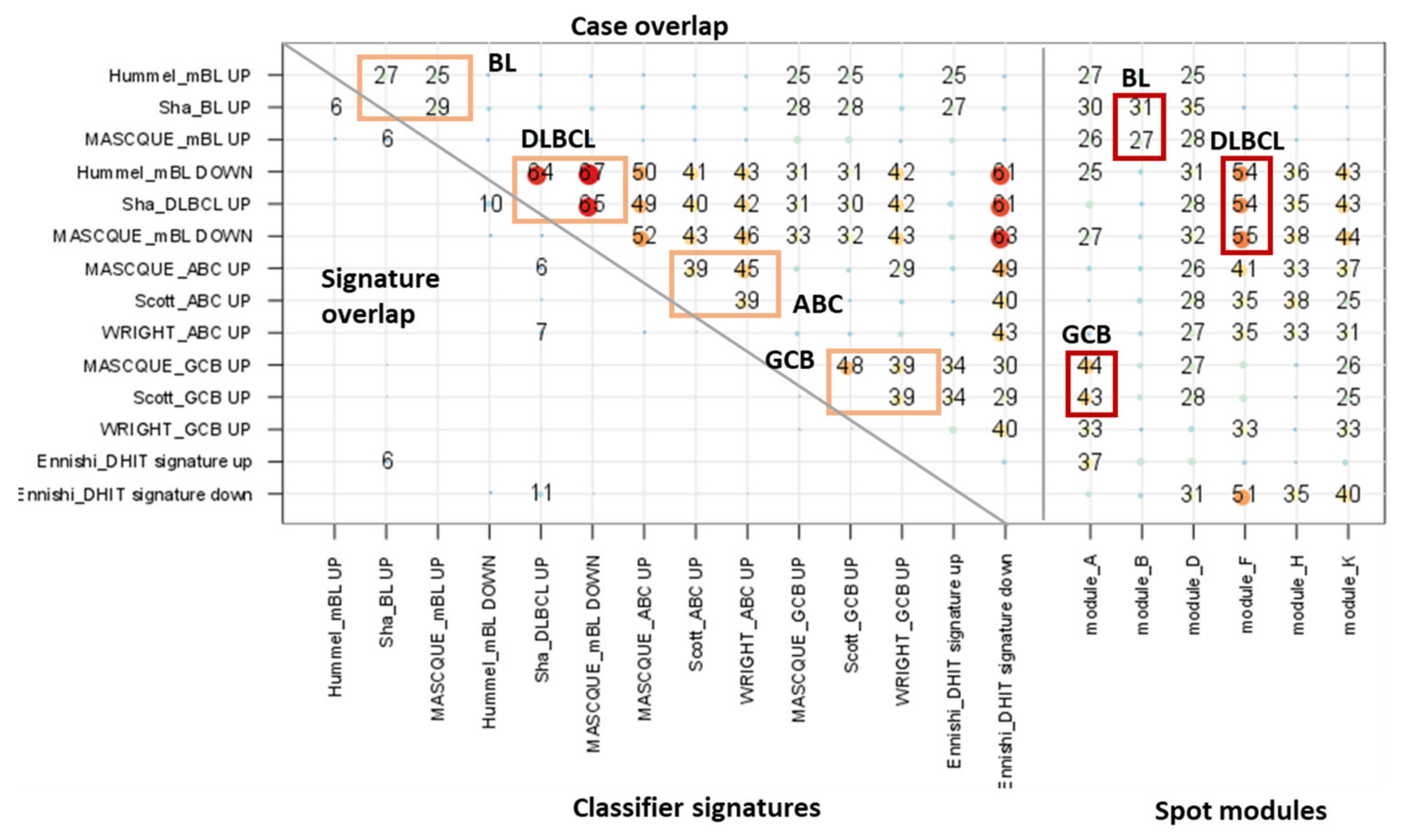


References
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Leval, L.; Jaffe, E.S. Lymphoma Classification. Cancer J. 2020, 26, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, M.; Bentink, S.; Berger, H.; Klapper, W.; Wessendorf, S.; Barth, T.F.E. The Molecular Mechanisms in Malignant Lymphomas Network Project of the Deutsche Krebshilfe, A Biologic Definition of Burkitt’s Lymphoma from Transcriptional and Genomic Profiling. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Kreuz, M.; Hopp, L.; Arakelyan, A.; Haake, A.; Cogliatti, S.B.; Feller, A.C.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Lenze, D. A modular transcriptome map of mature B cell lymphomas. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ennishi, D.; Jiang, A.; Boyle, M.; Collinge, B.; Grande, B.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rushton, C.; Tang, J.; Thomas, N.; Slack, G.W.; et al. Double-Hit Gene Expression Signature Defines a Distinct Subgroup of Germinal Center B-Cell-Like Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukema, S.M.; Siebert, R.; Schuuring, E.; van Imhoff, G.W.; Kluin-Nelemans, H.C.; Boerma, E.-J.; Kluin, P.M. Double-hit B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2011, 117, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosolowski, M.; Läuter, J.; Abramov, D.; Drexler, H.G.; Hummel, M.; Klapper, W.; MacLeod, R.A.; Pellissery, S.; Horn, F.; Siebert, R.; et al. Massive Transcriptional Perturbation in Subgroups of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentink, S.; Wessendorf, S.; Schwaenen, C.; Rosolowski, M.; Klapper, W.; Rosenwald, A.; Ott, G.; Banham, A.H.; Berger, H.; Feller, A.C.; et al. Pathway activation patterns in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caro, P.; Kishan, A.U.; Norberg, E.; Stanley, I.A.; Chapuy, B.; Ficarro, S.B.; Polak, K.; Tondera, D.; Gounarides, J.; Yin, H.; et al. Metabolic Signatures Uncover Distinct Targets in Molecular Subsets of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monti, S. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood 2005, 105, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Shipp, M.A. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roschewski, M.; Phelan, J.D.; Wilson, W.H. Molecular Classification and Treatment of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma. Cancer J. 2020, 26, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wienand, K.; Chapuy, B. Molecular classification of aggressive lymphomas—Past, present, future. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Eisen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.W.; Wright, G.W.; Williams, P.M.; Lih, C.-J.; Walsh, W.; Jaffe, E.; Rosenwald, A.; Campo, E.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Determining cell-of-origin subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using gene expression in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Blood 2014, 123, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, N.M.; Szczepanowski, M.; Kohler, C.W.; Spang, R.; Klapper, W. Molecular classification of mature aggressive B-cell lymphoma using digital multiplexed gene expression on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded biopsy specimens. Blood 2013, 122, 1985–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopp, L.; Lembcke, K.; Binder, H.; Wirth, H. Portraying the Expression Landscapes of B-CellLymphoma-Intuitive Detection of Outlier Samples and of Molecular Subtypes. Biology 2013, 2, 1411–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlov, N.; Bagaev, A.; Revuelta, M.V.; Phillip, J.M.; Cacciapuoti, M.T.; Antysheva, Z.; Svekolkin, V.; Tikhonova, E.; Miheecheva, N.; Kuzkina, N.; et al. Clinical and Biological Subtypes of B-cell Lymphoma Revealed by Microenvironmental Signatures. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1468–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybkær, K.; Bøgsted, M.; Falgreen, S.; Bødker, J.S.; Kjeldsen, M.K.; Schmitz, A.; Johnsen, H.E. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Classification System That Associates Normal B-Cell Subset Phenotypes With Prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Groot, F.A.; de Groen, R.A.L.; Berg, A.V.D.; Jansen, P.M.; Lam, K.H.; Mutsaers, P.G.N.J.; van Noesel, C.J.M.; Chamuleau, M.E.D.; Stevens, W.B.C.; Plaça, J.R.; et al. Biological and Clinical Implications of Gene-Expression Profiling in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Proposal for a Targeted BLYM-777 Consortium Panel as Part of a Multilayered Analytical Approach. Cancers 2022, 14, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, S.; Tesson, B.; Mareschal, S.; Viailly, P.-J.; Bohers, E.; Ruminy, P.; Etancelin, P.; Peyrouze, P.; Copie-Bergman, C.; Fabiani, B.; et al. Refining diffuse large B-cell lymphoma subgroups using integrated analysis of molecular profiles. eBio Med. 2019, 48, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holmes, A.B.; Corinaldesi, C.; Shen, Q.; Kumar, R.; Compagno, N.; Wang, Z.; Nitzan, M.; Grunstein, E.; Pasqualucci, L.; Dalla-Favera, R.; et al. Single-cell analysis of germinal-center B cells informs on lymphoma cell of origin and outcome. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20200483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.E.; Okoreeh, M.; Maienschein-Cline, M.; Ai, J.; Veselits, M.; McLean, K.; Dhungana, Y.; Wang, H.; Peng, J.; Chi, H.; et al. Novel specialized cell state and spatial compartments within the germinal center. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macon, W.R. Twenty years later: Has cell of origin testing in diffuse large B cell lymphoma run its course? J. Hematop. 2020, 13, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunz, M.; Löffler-Wirth, H.; Dannemann, M.; Willscher, E.; Doose, G.; Kelso, J.; Kottek, T.; Nickel, B.; Hopp, L.; Landsberg, J.; et al. RNA-seq analysis identifies different transcriptomic types and developmental trajectories of primary melanomas. Oncogene 2018, 37, 6136–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, H.; Willscher, E.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Hopp, L.; Jones, D.T.W.; Pfister, S.M.; Kreuz, M.; Gramatzki, D.; Fortenbacher, E.; Hentschel, B.; et al. DNA methylation, transcriptome and genetic copy number signatures of diffuse cerebral WHO grade II/III gliomas resolve cancer heterogeneity and development. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binder, H.; Hopp, L.; Schweiger, M.R.; Hoffmann, S.; Jühling, F.; Kerick, M.; Timmermann, B.; Siebert, S.; Grimm, C.; Nersisyan, L.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic heterogeneity of colorectal tumours arising in Lynch syndrome. J. Pathol. 2017, 243, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, C.; Barrans, S.; Cucco, F.; Bentley, M.A.; Care, M.A.; Cummin, T.; Kennedy, H.; Thompson, J.S.; Uddin, R.; Worrillow, L.; et al. Molecular High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma: Defining a Poor-Risk Group That Requires Different Approaches to Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.; Tan, B.; Rosenwald, A.; Hurt, E.H.; Wiestner, A.; Staudt, L.M. A gene expression-based method to diagnose clinically distinct subgroups of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9991–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.D.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopp, L.; Nersisyan, L.; Löffler-Wirth, H.; Arakelyan, A.; Binder, H. Epigenetic Heterogeneity of B-Cell Lymphoma: Chromatin Modifiers. Genes 2015, 6, 1076–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hopp, L.; Wirth-Loeffler, H.; Binder, H. Epigenetic heterogeneity of B-cell lymphoma: DNA-methylation, gene expression and chromatin states. Genes 2015, 6, 812–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.; Dave, S.S.; Xiao, W.; Powell, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Tan, B.; Goldschmidt, N.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Stromal Gene Signatures in Large-B-Cell Lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trapnell, C.; Cacchiarelli, D.; Grimsby, J.; Pokharel, P.; Li, S.; Morse, A.M.; Lennon, N.J.; Livak, K.J.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Rinn, J.L. The dynamics and regulators of cell fate decisions are revealed by pseudotemporal ordering of single cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben-Porath, I.; Thomson, M.W.; Carey, V.J.; Ge, R.; Bell, G.W.; Regev, A.; Weinberg, R.A. An embryonic stem cell–like gene expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human tumors. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victora, G.D.; Dominguez-Sola, D.; Holmes, A.B.; Deroubaix, S.; Dalla-Favera, R.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Identification of human germinal center light and dark zone cells and their relationship to human B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2012, 120, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Victora, G.D.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Germinal Centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 429–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesin, L.; Ersching, J.; Victora, G.D. Germinal Center B Cell Dynamics. Immunity 2016, 45, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basso, K.; Dalla-Favera, R. Germinal centres and B cell lymphomagenesis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, K. Biology of Germinal Center B Cells Relating to Lymphomagenesis. Hema Sphere 2021, 5, e582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milpied, P.; Cervera-Marzal, I.; Mollichella, M.-L.; Tesson, B.; Brisou, G.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Salles, G.; Spinelli, L.; Nadel, B. Human germinal center transcriptional programs are de-synchronized in B cell lymphoma. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Melnick, A. The Epigenetic Basis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Semin. Hematol. 2015, 52, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corinaldesi, C.; Holmes, A.B.; Shen, Q.; Grunstein, E.; Pasqualucci, L.; Dalla-Favera, R.; Basso, K. Tracking Immunoglobulin Repertoire and Transcriptomic Changes in Germinal Center B Cells by Single-Cell Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 818758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaf, N.; Baaklini, S.; Binet, L.; Milpied, P. Heterogeneity of germinal center B cells: New insights from single-cell studies. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.E.; Clark, M.R. Compartments and Connections Within the Germinal Center. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.; Papenhausen, P.; Shao, H. The Role of c-MYC in B-Cell Lymphomas: Diagnostic and Molecular Aspects. Genes 2017, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohde, M.; Bonn, B.R.; Zimmermann, M.; Lange, J.; Möricke, A.; Klapper, W.; Oschlies, I.; Szczepanowski, M.; Nagel, I.; Schrappe, M.; et al. Relevance of ID3-TCF3-CCND3 pathway mutations in pediatric aggressive B-cell lymphoma treated according to the non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster protocols. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mlynarczyk, C.; Fontán, L.; Melnick, A. Germinal center-derived lymphomas: The darkest side of humoral immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 288, 214–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salaverria, I.; Philipp, C.; Oschlies, I.; Kohler, C.W.; Kreuz, M.; Szczepanowski, M.; Burkhardt, B.; Trautmann, H.; Gesk, S.; Andrusiewicz, M.; et al. Translocations activating IRF4 identify a subtype of germinal center-derived B-cell lymphoma affecting predominantly children and young adults. Blood 2011, 118, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H. Diagnosis of ‘double hit’ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between DLBCL and Burkitt lymphoma: When and how, FISH versus IHC. Hematology 2014, 2014, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campo, E. MYC in DLBCL: Partners matter. Blood 2015, 126, 2439–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Khiabanian, H.; Fangazio, M.; Vasishtha, M.; Messina, M.; Holmes, A.B.; Ouillette, P.; Trifonov, V.; Rossi, D.; Tabbò, F.; et al. Genetics of Follicular Lymphoma Transformation. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aukema, S.M.; Van Pel, R.; Nagel, I.; Bens, S.; Siebert, R.; Rosati, S.; Berg, E.V.D.; Bosga-Bouwer, A.G.; Kibbelaar, E.R.; Hoogendoorn, M.; et al. MYC expression and translocation analyses in low-grade and transformed follicular lymphoma. Histopathology 2017, 71, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, K.; Maienschein-Cline, M.; Simonetti, G.; Chen, J.; Rosenthal, R.; Brink, R.; Chong, A.S.; Klein, U.; Dinner, A.R.; Singh, H.; et al. Transcriptional Regulation of Germinal Center B and Plasma Cell Fates by Dynamical Control of IRF4. Immunity 2013, 38, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salaverria, I.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; Wagener, R.; Kreuz, M.; Kohler, C.W.; Richter, J.; Siebert, R. A recurrent 11q aberration pattern characterizes a subset of MYC-negative high-grade B-cell lymphomas resembling Burkitt lymphoma. Blood 2014, 123, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagener, R.; Seufert, J.; Raimondi, F.; Bens, S.; Kleinheinz, K.; Nagel, I.; Altmüller, J.; Thiele, H.; Hübschmann, D.; Kohler, C.W.; et al. The mutational landscape of Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration is distinct from that of Burkitt lymphoma. Blood 2019, 133, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanca, G.-F.; Joan Enric, R.-Z.; Julia, S.-V.; Olga, B.; Verónica, C.; Jaime, V.-A.; Itziar, S. Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration: A germinal center-derived lymphoma genetically unrelated to Burkitt lymphoma. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1822–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Healy, J.A.; Nugent, A.; Rempel, R.E.; Moffitt, A.B.; Davis, N.S.; Jiang, X.; Shingleton, J.R.; Zhang, J.; Love, C.; Datta, J.; et al. GNA13 loss in germinal center B cells leads to impaired apoptosis and promotes lymphoma in vivo. Blood 2016, 127, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Desai, P.; Lin, P.; Yin, C.C.; Tang, G.; Wang, X.J.; Konoplev, S.N.; Khoury, J.D.; Bueso-Ramos, E.C.; Medeiros, L.J. MYC/BCL6double-hit lymphoma (DHL): A tumour associated with an aggressive clinical course and poor prognosis. Histopathology 2015, 68, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Reikowski, J.; Hakobyan, S.; Wagner, J.; Binder, H. oposSOM-Browser: An interactive tool to explore omics data landscapes in health science. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibshirani, R.; Hastie, T.; Narasimhan, B.; Chu, G. Diagnosis of multiple cancer types by shrunken centroids of gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6567–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, D.W. Cell-of-Origin in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Are the Assays Ready for the Clinic? Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2015, 35, e458–e466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hübschmann, D.; Kleinheinz, K.; Wagener, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; López, C.; Toprak, U.H.; Sungalee, S.; Ishaque, N.; Kretzmer, H.; Kreuz, M.; et al. Mutational mechanisms shaping the coding and noncoding genome of germinal center derived B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2002–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Binder, H. Developmental scRNAseq Trajectories in Gene- and Cell-State Space—The Flatworm Example. Genes 2020, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.A.M.; Mortensen, L.S.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Kosnopfel, C.; Krohn, K.; Binder, H.; Kunz, M. Single-cell trajectories of melanoma cell resistance to targeted treatment. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 18, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoghosyan, M.; Schmidt, M.; Margaryan, K.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Arakelyan, A.; Binder, H. SOMmelier—Intuitive Visualization of the Topology of Grapevine Genome Landscapes Using Artificial Neural Networks. Genes 2020, 11, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Arshad, M.; Bernhart, S.H.; Hakobyan, S.; Arakelyan, A.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Binder, H. The Evolving Faces of the SARS-CoV-2 Genome. Viruses 2021, 13, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lee, V.; Ng, M.K.; Yan, H.; Bijlsma, M.F. Molecular subtyping of cancer: Current status and moving toward clinical applications. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 20, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, V.; Dupont, P. An Importance Weighted Feature Selection Stability Measure. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 22, 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Stein-O’Brien, G.L.; Arora, R.; Culhane, A.C.; Favorov, A.V.; Garmire, L.X.; Greene, C.S.; Goff, L.A.; Li, Y.; Ngom, A.; Ochs, M.F.; et al. Enter the Matrix: Factorization Uncovers Knowledge from Omics. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 790–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.; Zhang, J.; Davis, N.S.; Moffitt, A.; Love, C.L.; Waldrop, A.; Leppä, S.; Pasanen, A.; Meriranta, L.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.-L.; et al. Genetic and Functional Drivers of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cell 2017, 171, 481–494.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richter, J.; Schlesner, M.; Hoffmann, S.; Kreuz, M.; Leich, E.; Burkhardt, B. Recurrent mutation of the ID3 gene in Burkitt lymphoma identified by integrated genome, exome and transcriptome sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Coccaro, N.; Anelli, L.; Zagaria, A.; Perrone, T.; Specchia, G.; Albano, F. Molecular Complexity of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Can It Be a Roadmap for Precision Medicine? Cancers 2020, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wirth, H.; von Bergen, M.; Binder, H. Mining SOM expression portraits: Feature selection and integrating concepts of molecular function. Bio. Data Min. 2012, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Gong, D.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Huang, S.; Yang, M.; Yang, X.; et al. Deep learning-based model for detecting 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia on high-resolution computed tomography. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Sánchez, C.I.; Timofeeva, N.; Hermsen, M.; Nagtegaal, I.; Kovacs, I.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.; Bult, P.; Van Ginneken, B.; Van Der Laak, J. Deep learning as a tool for increased accuracy and efficiency of histopathological diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syrykh, C.; Abreu, A.; Amara, N.; Siegfried, A.; Maisongrosse, V.; Frenois, F.X.; Martin, L.; Rossi, C.; Laurent, C.; Brousset, P. Accurate diagnosis of lymphoma on whole-slide histopathology images using deep learning. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Bledsoe, J.R.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Bi, K.; Liang, A.; Li, S. A deep learning diagnostic platform for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with high accuracy across multiple hospitals. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiderska-Chadaj, Z.; Hebeda, K.M.; Brand, M.V.D.; Litjens, G. Artificial intelligence to detect MYC translocation in slides of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Virchows Arch. 2020, 479, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuschkin, S.; Wäldchen, S.; Binder, A.; Montavon, G.; Samek, W.; Müller, K.-R. Unmasking Clever Hans predictors and assessing what machines really learn. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whitfield, M.L.; Sherlock, G.; Saldanha, A.J.; Murray, J.I.; Ball, C.A.; Alexander, K.E.; Matese, J.C.; Perou, C.M.; Hurt, M.M.; Brown, P.O.; et al. Identification of Genes Periodically Expressed in the Human Cell Cycle and Their Expression in Tumors. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 1977–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database Hallmark Gene Set Collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Previous Nomenclature (This Paper) | New Nomenclature (WHO 2022) | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| DHL MYC + BCL2 | DLBCL/HGBL MYC/BCL2 | |
| THL MYC + BCL2 + BCL6 | DLBCL/HGBL MYC/BCL2 and BCL6 | BCL6 rearrangement is not considered as “hit“ defining an entity |
| DHL MYC + BCL6 | DLBCL or HGBL, NOS | |
| MYC-negative Burkitt-like lymphomas with Chr. 11q aberration pattern (mnBLL-11q) | High-grade B-cell lymphoma with 11q aberration (HGBL-11q) | Reference to BL is removed |
| IRF4-rearranged large cell lymphoma (IRF4-LCL) | Large B-cell lymphoma with IRF4 rearrangement |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Kreuz, M.; Schmidt, M.; Ott, G.; Siebert, R.; Binder, H. Classifying Germinal Center Derived Lymphomas—Navigate a Complex Transcriptional Landscape. Cancers 2022, 14, 3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143434
Loeffler-Wirth H, Kreuz M, Schmidt M, Ott G, Siebert R, Binder H. Classifying Germinal Center Derived Lymphomas—Navigate a Complex Transcriptional Landscape. Cancers. 2022; 14(14):3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143434
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoeffler-Wirth, Henry, Markus Kreuz, Maria Schmidt, German Ott, Reiner Siebert, and Hans Binder. 2022. "Classifying Germinal Center Derived Lymphomas—Navigate a Complex Transcriptional Landscape" Cancers 14, no. 14: 3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143434
APA StyleLoeffler-Wirth, H., Kreuz, M., Schmidt, M., Ott, G., Siebert, R., & Binder, H. (2022). Classifying Germinal Center Derived Lymphomas—Navigate a Complex Transcriptional Landscape. Cancers, 14(14), 3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143434