Prognostic, Diagnostic and Predictive Biomarkers in the Barrett’s Oesophagus-Adenocarcinoma Disease Sequence
Abstract
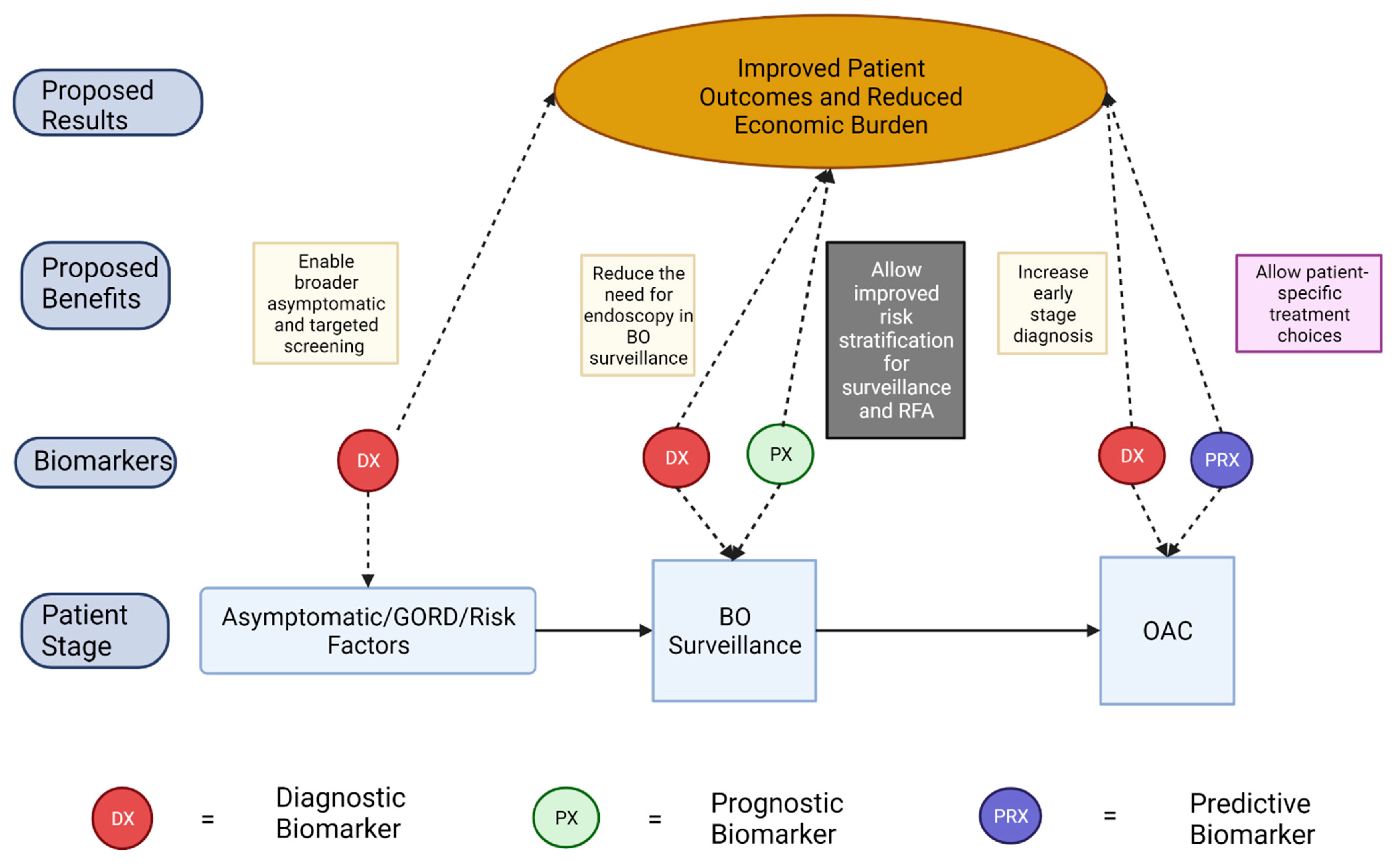
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prognostic Biomarkers of Progression from Barrett’s Oesophagus to Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma
3. Diagnostic Biomarkers of Barret’s Oesophagus and Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma
- (1)
- Early, accurate, and cost-effective diagnosis of BO and OAC
- (2)
- Reduce the need for endoscopy in the surveillance of individuals with low-risk BO
- (3)
- Identification of those with current HGD which would benefit from RFA
- (4)
- Enable broader population screening for those who do not meet the referral criteria for upper endoscopy.
| Biomarker Name | Disease State Tested | Biomarker Type | Regulation (in Disease State) | Sample Type | Testing Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FER1L4, ZNF671, ST8SIA1, TBX15, ARHGEF4 | OC | Diagnostic | ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ | Plasma | Quantitative Methylation Specific PCR | [30] |
| Acrylonitrile, Carbon disulfide | GORD, OAC | Diagnostic | ↓ ↓ | Plasma | SIFT-MS | [35] |
| Butyric acid, Pentanoic acid, Hexanoic acid, Butanal, Decanal | Oesophagogastric Adenocarcinoma | Diagnostic | ↓ ↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ | Breath | SIFT-MS | [36] |
| RNU6-1/miR-16-5p, miR-25-3p/miR-320a, let-7e-5p/miR-15b-5p, miR-30a-5p/miR-324-5p, miR-17-5p/miR-194-5p | OAC | Diagnostic | ↑ ↑ ↑ ↓ ↓ | Serum | qPCR | [38] |
| miR-92a-3p, miR-151a-5p, miR-362-3p, miR-345-3p, miR-619-3p, miR-1260b, miR-1276, miR-381-3p, miR-502-3p, miR-3615 | NDBO, HGD, OAC | Diagnostic | ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↓ ↓ ↓ | Serum | qPCR | [39] |
| Neutrophil-leukocyte ratio | OAC | Diagnostic | ↑ | Serum | Whole Blood Count | [40] |
| Erythrocyte Mutation Frequency | HGD, OAC | Diagnostic | ↑ | Serum | Phosphatidylinositol glycan class A gene mutation assay (Flow cytometry) | [41] |
| HMGB1 (Nuclear, Cytoplasmic) | Dysplastic BO, OAC | Diagnostic | ↑ ↓ | Tissue Biopsy | IHC | [42] |
4. Predictive Biomarkers of Neoadjuvant Treatment Response in OAC
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AJCC | American Joint Committee on Cancer |
| AOL | Aspergillus Oryzae Lectin |
| AUROC | Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| BO | Barrett’s Oesophagus |
| DFS | Disease-free Survival |
| EMF | Erythrocyte Mutation Frequency |
| FFPE | Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Biopsies |
| FISH | Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| GORD | Gastro-oesophageal Reflux Disease |
| HGD | High Grade Dysplasia |
| HMGB1 | High Mobility Group Box-1 |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| LGD | Low Grade Dysplasia |
| lncRNA | long non-coding RNA |
| miRNA | micro RNAs |
| NA-C | Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy |
| NA-CRT | Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy |
| NA-T | Neoadjuvant Therapy |
| NDBO | Non-Dysplastic Barrett’s Oesophagus |
| NLR | Neutrophil-Leukocyte Ratio |
| OAC | Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma |
| OC | Oesophageal Cancer |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| OSCC | Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| PODXL | Podocalyxin-like Protein |
| RFA | Radiofrequency Ablation |
| TRG | Tumor Regression Grade |
| T-UCR | Transcribed Ultra-Conserved Regions |
| VOC | Volatile Organic Compounds |
References
- Jain, S.; Dhingra, S. Pathology of esophageal cancer and Barrett’s esophagus. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 6, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qumseya, B.; Sultan, S.; Bain, P.; Jamil, L.; Jacobson, B.; Anandasabapathy, S.; Agrawal, D.; Buxbaum, J.L.; Fishman, D.S.; Gurudu, S.R.; et al. ASGE guideline on screening and surveillance of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 90, 335–359.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, R.C.; Di Pietro, M.; Ragunath, K.; Ang, Y.; Kang, J.-Y.; Watson, P.; Trudgill, N.; Patel, P.; Kaye, P.V.; Sanders, S.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the diagnosis and management of Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut 2014, 63, 7–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weusten, B.; Bisschops, R.; Coron, E.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M.; Dumonceau, J.-M.; Esteban, J.-M.; Hassan, C.; Pech, O.; Repici, A.; Bergman, J.; et al. Endoscopic management of Barrett’s esophagus: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Position Statement. Endoscopy 2017, 49, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaninotto, G.; Bennett, C. Surveillance for Low-Grade Dysplastic Barrett’s Oesophagus: One Size Fits All? World J. Surg. 2015, 39, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoa, K.N.; Van Vilsteren, F.G.I.; Weusten, B.L.A.M.; Bisschops, R.; Schoon, E.J.; Ragunath, K.; Fullarton, G.; Di Pietro, M.; Ravi, N.; Visser, M.; et al. Radiofrequency Ablation vs. Endoscopic Surveillance for Patients With Barrett Esophagus and Low-Grade Dysplasia. JAMA 2014, 311, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, C.; Choi, S.E.; Rubenstein, J.H.; Kong, C.Y.; Nishioka, N.S.; Provenzale, D.T.; Inadomi, J.M. The Cost Effectiveness of Radiofrequency Ablation for Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmberg, D.; Ness-Jensen, E.; Mattsson, F.; El-Serag, H.B.; Lagergren, J. Risk of oesophageal adenocarcinoma in individuals with Barrett’s oesophagus. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 75, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PPicardo, S.L.; O’brien, M.P.; Feighery, R.; O’Toole, D.; Ravi, N.; O’Farrell, N.J.; O’Sullivan, J.N.; Reynolds, J.V. A Barrett’s esophagus registry of over 1000 patients from a specialist center highlights greater risk of progression than population-based registries and high risk of low grade dysplasia. Dis. Esophagus 2015, 28, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coleman, H.G.; Xie, S.-H.; Lagergren, J. The Epidemiology of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.; Soerjomataram, I.; Gavin, A.T.; Rutherford, M.J.; Gatenby, P.; Bardot, A.; Ferlay, J.; Bucher, O.; De, P.; Engholm, G.; et al. International trends in oesophageal cancer survival by histological subtype between 1995 and 2014. Gut 2021, 70, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, J.H.; Shaheen, N.J. Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 302–317.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mansour, N.M.; Groth, S.S.; Anandasabapathy, S. Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: Screening, Surveillance, and Management. Annu. Rev. Med. 2017, 68, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geh, J.I.; Crellin, A.M.; Glynne-Jones, R. Preoperative (neoadjuvant) chemoradiotherapy in oesophageal cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2002, 88, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, J.; Hamdy, S.; McLaughlin, J.; Horne, M.; Ang, Y. Barrett’s oesophagus: A qualitative study of patient burden, care delivery experience and follow-up needs. Health Expect. 2019, 22, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eluri, S.; Shaheen, N.J. Barrett’s esophagus: Diagnosis and management. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 85, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wani, S.; Rubenstein, J.H.; Vieth, M.; Bergman, J. Diagnosis and Management of Low-Grade Dysplasia in Barrett’s Esophagus: Expert Review From the Clinical Practice Updates Committee of the American Gastroenterological Association. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Wel, M.J.; Duits, L.C.; Pouw, R.E.; Seldenrijk, C.A.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Visser, M.; Ten Kate, F.J.; Biermann, K.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Doukas, M.; et al. Improved diagnostic stratification of digitised Barrett’s oesophagus biopsies by p53 immunohistochemical staining. Histopathology 2018, 72, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastelein, F.; Biermann, K.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Verheij, J.; Kalisvaart, M.; Looijenga, L.H.J.; Stoop, H.A.; Walter, L.; Kuipers, E.J.; Spaander, M.C.W.; et al. Aberrant p53 protein expression is associated with an increased risk of neoplastic progression in patients with Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut 2013, 62, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davelaar, A.L.; Calpe, S.; Lau, L.; Timmer, M.R.; Visser, M.; Ten Kate, F.J.; Parikh, K.B.; Meijer, S.L.; Bergman, J.J.; Fockens, P.; et al. Aberrant TP53 detected by combining immunohistochemistry and DNA-FISH improves Barrett’s esophagus progression prediction: A prospective follow-up study. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2015, 54, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachler, M.D.; Camarda, N.D.; Deitrick, C.; Kim, A.; Agoston, A.T.; Odze, R.D.; Hornick, J.L.; Nag, A.; Thorner, A.R.; Ducar, M. Detection of mutations in Barrett’s esophagus before progression to high-grade dysplasia or adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duits, L.C.; Lao-Sirieix, P.; Wolf, W.A.; O’Donovan, M.; Galeano-Dalmau, N.; Meijer, S.L.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Redman, J.; Crawte, J.; Zeki, S.; et al. A biomarker panel predicts progression of Barrett’s esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2019, 32, doy102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmer, M.R.; Martinez, P.; Lau, C.T.; Westra, W.M.; Calpe, S.; Rygiel, A.M.; Rosmolen, W.D.; Meijer, S.L.; Ten Kate, F.J.W.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.W.; et al. Derivation of genetic biomarkers for cancer risk stratification in Barrett’s oesophagus: A prospective cohort study. Gut 2016, 65, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picardo, S.L.; Maher, S.G.; O’Sullivan, J.N.; Reynolds, J.V. Barrett’s to Oesophageal Cancer Sequence: A Model of Inflammatory-Driven Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer. Dig. Surg. 2012, 29, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Farrell, N.J.; Phelan, J.J.; Feighery, R.; Doyle, B.; Picardo, S.L.; Ravi, N.; O’Toole, D.; Reynolds, J.V.; O’Sullivan, J. Differential Expression Profiles of Oxidative Stress Levels, 8-oxo-dG and 4-HNE, in Barrett’s Esophagus Compared to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porter, R.J.; Murray, G.I.; Brice, D.P.; Petty, R.D.; McLean, M.H. Novel biomarkers for risk stratification of Barrett’s oesophagus associated neoplastic progression–epithelial HMGB1 expression and stromal lymphocytic phenotype. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepage, C.; Drouillard, A.; Jouve, J.-L.; Faivre, J. Epidemiology and risk factors for oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Dig. Liver Dis. 2013, 45, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Naik, A.D.; Duan, Z.; Shakhatreh, M.; Helm, A.; Pathak, A.; Hinojosa-Lindsey, M.; Hou, J.; Nguyen, T.; Chen, J.; et al. Surveillance endoscopy is associated with improved outcomes of oesophageal adenocarcinoma detected in patients with Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut 2016, 65, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirst, N.G.; Gordon, L.G.; Whiteman, D.C.; Watson, D.I.; Barendregt, J.J. Is endoscopic surveillance for non-dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus cost-effective? Review of economic evaluations. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvid-Jensen, F.; Pedersen, L.; Drewes, A.M.; Sørensen, H.T.; Funch-Jensen, P. Incidence of Adenocarcinoma among Patients with Barrett’s Esophagus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Wu, C.W.; Taylor, W.R.; Sawas, T.; Burger, K.N.; Mahoney, D.W.; Sun, Z.; Yab, T.C.; Lidgard, G.P.; Allawi, H.T.; et al. Discovery, Validation, and Application of Novel Methylated DNA Markers for Detection of Esophageal Cancer in Plasma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7396–7404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bejerano, G.; Pheasant, M.; Makunin, I.; Stephen, S.; Kent, W.J.; Mattick, J.S.; Haussler, D. Ultraconserved elements in the human genome. Science 2004, 304, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fassan, M.; Dall’Olmo, L.; Galasso, M.; Braconi, C.; Pizzi, M.; Realdon, S.; Volinia, S.; Valeri, N.; Gasparini, P.; Baffa, R. Transcribed ultraconserved noncoding RNAs (T-UCR) are involved in Barrett’s esophagus carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, J.H.; Tieu, A.H.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, K.; Akshintala, V.S.; Simsek, C.; Prasath, V.; Shin, E.J.; Ngamruengphong, S.; Khashab, M.A. Novel long noncoding RNA miR205HG functions as an esophageal tumor-suppressive hedgehog inhibitor. Cancers 2021, 13, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Han, G.; Sun, C.; Pizzi, M.P.; Huo, L.; Scott, A.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L. LncRNA PVT1 up-regulation is a poor prognosticator and serves as a therapeutic target in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, A.; Parsi, M.A.; Stevens, T.; Gabbard, S.; Kumaravel, A.; Jang, S.; Grove, D.; Lopez, R.; Murthy, S.; Vargo, J.J.; et al. Volatile organic compounds in plasma for the diagnosis of esophageal adenocarcinoma: A pilot study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 84, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markar, S.R.; Wiggins, T.; Antonowicz, S.; Chin, S.-T.; Romano, A.; Nikolic, K.; Evans, B.; Cunningham, D.; Mughal, M.; Lagergren, J.; et al. Assessment of a Noninvasive Exhaled Breath Test for the Diagnosis of Oesophagogastric Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Sen, S. MicroRNA as biomarkers and diagnostics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiam, K.; Wang, T.; Watson, D.I.; Mayne, G.C.; Irvine, T.S.; Bright, T.; Smith, L.; White, I.A.; Bowen, J.M.; Keefe, D.; et al. Circulating Serum Exosomal miRNAs As Potential Biomarkers for Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2015, 19, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fassan, M.; Realdon, S.; Cascione, L.; Hahne, J.C.; Munari, G.; Guzzardo, V.; Arcidiacono, D.; Lampis, A.; Brignola, S.; Dal Santo, L.; et al. Circulating microRNA expression profiling revealed miR-92a-3p as a novel biomarker of Barrett’s carcinogenesis. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, V.J.; Mazzini, G.S.; Juchem, J.F.; Gurski, R.R. Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Marker of Progression from Non-Dysplastic Barrett’s Esophagus to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haboubi, H.N.; Lawrence, R.L.; Rees, B.; Williams, L.; Manson, J.M.; Al-Mossawi, N.; Bodger, O.; Griffiths, P.; Thornton, C.; Jenkins, G.J. Developing a blood-based gene mutation assay as a novel biomarker for oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januszewicz, W.; Tan, W.K.; Lehovsky, K.; Debiram-Beecham, I.; Nuckcheddy, T.; Moist, S.; Kadri, S.; Di Pietro, M.; Boussioutas, A.; Shaheen, N.J. Safety and acceptability of esophageal cytosponge cell collection device in a pooled analysis of data from individual patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 647–656.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smyth, E.C.; Lagergren, J.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Lordick, F.; Shah, M.A.; Lagergren, P.; Cunningham, D. Oesophageal cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, K.L.; Weber, J.M.; Turaga, K.K.; Siegel, E.M.; McLoughlin, J.; Hoffe, S.; Marcovalerio, M.; Shah, N.; Kelley, S.; Karl, R. Pathologic Response after Neoadjuvant Therapy is the Major Determinant of Survival in Patients with Esophageal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, O.M.; Lord, S.J.; Falkenback, D.; Clemons, N.J.; Eslick, G.D.; Lord, R.V. The prognostic value of TP53 mutations in oesophageal adenocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2017, 66, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandioler, D.; Schoppmann, S.F.; Zwrtek, R.; Kappel, S.; Wolf, B.; Mittlböck, M.; Kührer, I.; Hejna, M.; Pluschnig, U.; Ba-Ssalamah, A.; et al. The biomarker TP53 divides patients with neoadjuvantly treated esophageal cancer into 2 subgroups with markedly different outcomes. A p53 Research Group study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 2280–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powell, A.G.M.T.; Chin, C.; Coxon, A.H.; Chalishazar, A.; Christian, A.; Roberts, S.A.; Lewis, W.G. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and survival in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. BJS Open 2020, 4, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, F.; Hopkins, J.; Curtis, N.; Kelly, J.J.; Bailey, I.S.; Byrne, J.P.; Bateman, A.C.; Bateman, A.R.; Underwood, T.J. The role of systemic inflammatory and nutritional blood-borne markers in predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and survival in oesophagogastric cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, H.D.; Lee, J.H.; Bhutani, M.S.; Weston, B.; Hofstetter, W.; Komaki, R.; Shiozaki, H.; Wadhwa, R.; Sudo, K.; Elimova, E.; et al. A validated miRNA profile predicts response to therapy in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2014, 120, 3635–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, B.A.S.; Reynolds, J.V.; Maher, S.G. MicroRNA-330-5p as a Putative Modulator of Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Sensitivity in Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiam, K.; Mayne, G.C.; Watson, D.I.; Woodman, R.J.; Bright, T.F.; Michael, M.Z.; Karapetis, C.S.; Irvine, T.; Phillips, W.A.; Hummel, R.; et al. Identification of microRNA Biomarkers of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Using Next Generation Sequencing. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, S.G.; McDowell, D.T.; Collins, B.C.; Muldoon, C.; Gallagher, W.M.; Reynolds, J.V. Serum Proteomic Profiling Reveals That Pretreatment Complement Protein Levels are Predictive of Esophageal Cancer Patient Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation. Ann. Surg. 2011, 254, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynam-Lennon, N.; Bibby, B.A.S.; Mongan, A.M.; Marignol, L.; Paxton, C.N.; Geiersbach, K.; Bronner, M.P.; O’Sullivan, J.; Reynolds, J.V.; Maher, S.G. Low MiR-187 Expression Promotes Resistance to Chemoradiation Therapy In Vitro and Correlates with Treatment Failure in Patients with Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macgregor, T.P.; Carter, R.; Gillies, R.S.; Findlay, J.M.; Kartsonaki, C.; Castro-Giner, F.; Sahgal, N.; Wang, L.M.; Chetty, R.; Maynard, N.D.; et al. Translational study identifies XPF and MUS81 as predictive biomarkers for oxaliplatin-based peri-operative chemotherapy in patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borg, D.; Larsson, A.H.; Hedner, C.; Nodin, B.; Johnsson, A.; Jirström, K. Podocalyxin-like protein as a predictive biomarker for benefit of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in resectable gastric and esophageal adenocarcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, D.; Hedner, C.; Nodin, B.; Larsson, A.; Johnsson, A.; Eberhard, J.; Jirström, K. Expression of podocalyxin-like protein is an independent prognostic biomarker in resected esophageal and gastric adenocarcinoma. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2016, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kukar, M.; Alnaji, R.M.; Jabi, F.; Platz, T.A.; Attwood, K.; Nava, H.; Ben-David, K.; Mattson, D.; Salerno, K.; Malhotra, U.; et al. Role of Repeat18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Examination in Predicting Pathologic Response Following Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy for Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. JAMA Surg. 2015, 150, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynam-Lennon, N.; Maher, S.G.; Maguire, A.; Phelan, J.; Muldoon, C.; Reynolds, J.V.; O’Sullivan, J. Altered Mitochondrial Function and Energy Metabolism Is Associated with a Radioresistant Phenotype in Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.; Cockburn, J.; Smith, R.A.; Wardle, J. A perspective from countries using organized screening programs. Cancer Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 2004, 101, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Alnaji, R.M.; Du, W.; Gabriel, E.; Singla, S.; Attwood, K.; Nava, H.; Malhotra, U.; Hochwald, S.N.; Kukar, M. Pathologic Complete Response Is an Independent Predictor of Improved Survival Following Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation for Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2016, 20, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, F.; Lloyd, M.A.; Turkington, R.; Griffiths, E.; O’Donovan, M.; O’Neill, J.R.; Mercer, S.; Parsons, S.L.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Underwood, T.J.; et al. Multicentre cohort study to define and validate pathological assessment of response to neoadjuvant therapy in oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Surg. 2017, 104, 1816–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shapiro, J.; van Hagen, P.; Lingsma, H.F.; Wijnhoven, B.P.; Biermann, K.; ten Kate, F.J.; Steyerberg, E.W.; van der Gaast, A.; van Lanschot, J.J.B.; Group, C.S. Prolonged time to surgery after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy increases histopathological response without affecting survival in patients with esophageal or junctional cancer. Ann. Surg. 2014, 260, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Biomarker Name | Disease Progression Assessed | Biomarker Type | Regulation (in Progressors) | Sample Type | Testing Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aberrant P53 expression | NDBO/LGD-HGD/OAC | Prognostic | ↑ | FFPE Biopsy | IHC, FISH, NGS | [19,20,21] |
| Panel of abnormal P53 expression, abnormal AOL expression and diagnosis of LGD | NDBO/LGD-HGD/OAC | Prognostic | ↑ | FFPE Biopsy | IHC, pathologist review | [22] |
| MYC gain, p16 loss, aneusomy, age, circumferential BO length | NDBO-HGD/OAC | Prognostic | ↑ | Brush cytology specimens | FISH | [23] |
| 8-oxo-dG | NDBO-HGD/OAC | Prognostic | ↓ | Tissue Biopsy | IHC | [25] |
| Biomarker Name | Disease | Therapy Type | Relative Regulation (Good Responders) | Sample Type | Testing Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P53 | OAC | NA-C | Not mutated | Tumor Biopsy | Gene Sequencing | [47] |
| Neutrophil-Leukocyte Ratio | OAC | NA-C | ↓←→ | Serum | Whole Blood Count | [48,49] |
| mir-505*, mir-99b, mir-451, mir-145* | OAC | NA-CRT | ↓ | Tumor Biopsy | qPCR | [50] |
| Mir-330-5p | OAC | NA-CRT | ↑ | Tumor Biopsy | qPCR | [51] |
| miR-4521/miR-340-5p, miR-101-3p/miR-451a | OAC | NA-CRT | ↑ | Tumor Biopsy | qPCR | [52] |
| C3A, C4A | OC | NA-CRT | ↓ | Serum (Ig and albumin depleted) | SELDI-TOF-MS | [53] |
| mir-187 | OAC | NA-CRT | ↑ | Tumor Biopsy | RT-PCR | [54] |
| XPF, MUS81 | OAC | NA-CRT | ↓ | Tumor Biopsy | IHC | [55] |
| Podocalyxin-like protein | OAC | NA-C | ↑ | Tumor Biopsy | IHC | [56] |
| ATP5B | OAC | NA-CRT | ↓ | Tumor Biopsy | IHC, RT-PCR | [59] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Dowd, D.; O’Sullivan, J.; Marcone, S. Prognostic, Diagnostic and Predictive Biomarkers in the Barrett’s Oesophagus-Adenocarcinoma Disease Sequence. Cancers 2022, 14, 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143427
O’Dowd D, O’Sullivan J, Marcone S. Prognostic, Diagnostic and Predictive Biomarkers in the Barrett’s Oesophagus-Adenocarcinoma Disease Sequence. Cancers. 2022; 14(14):3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143427
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Dowd, Darragh, Jacintha O’Sullivan, and Simone Marcone. 2022. "Prognostic, Diagnostic and Predictive Biomarkers in the Barrett’s Oesophagus-Adenocarcinoma Disease Sequence" Cancers 14, no. 14: 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143427
APA StyleO’Dowd, D., O’Sullivan, J., & Marcone, S. (2022). Prognostic, Diagnostic and Predictive Biomarkers in the Barrett’s Oesophagus-Adenocarcinoma Disease Sequence. Cancers, 14(14), 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143427







