Machine Learning to Discern Interactive Clusters of Risk Factors for Late Recurrence of Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results
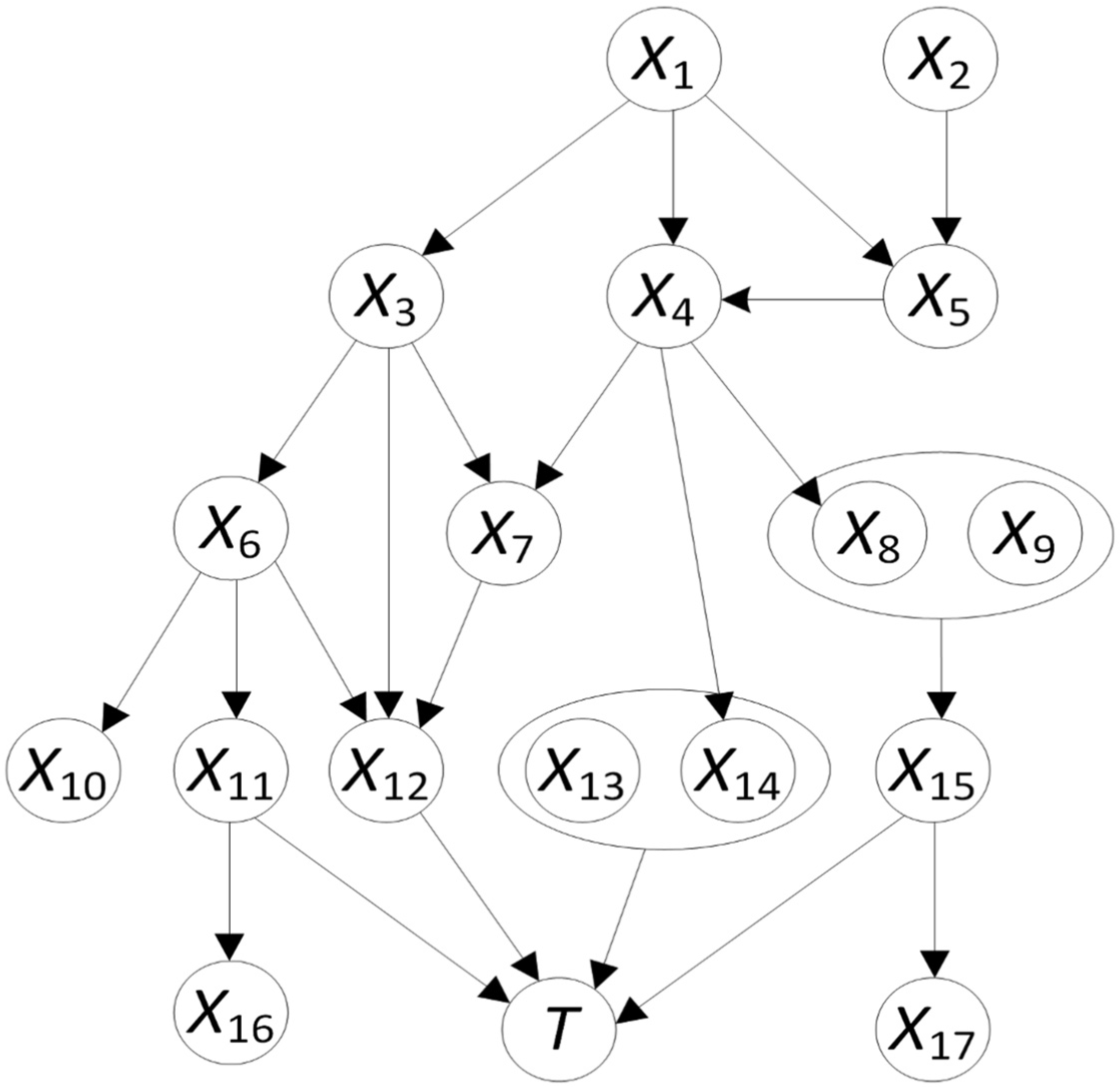
3.1. Causal Sets of Metastases
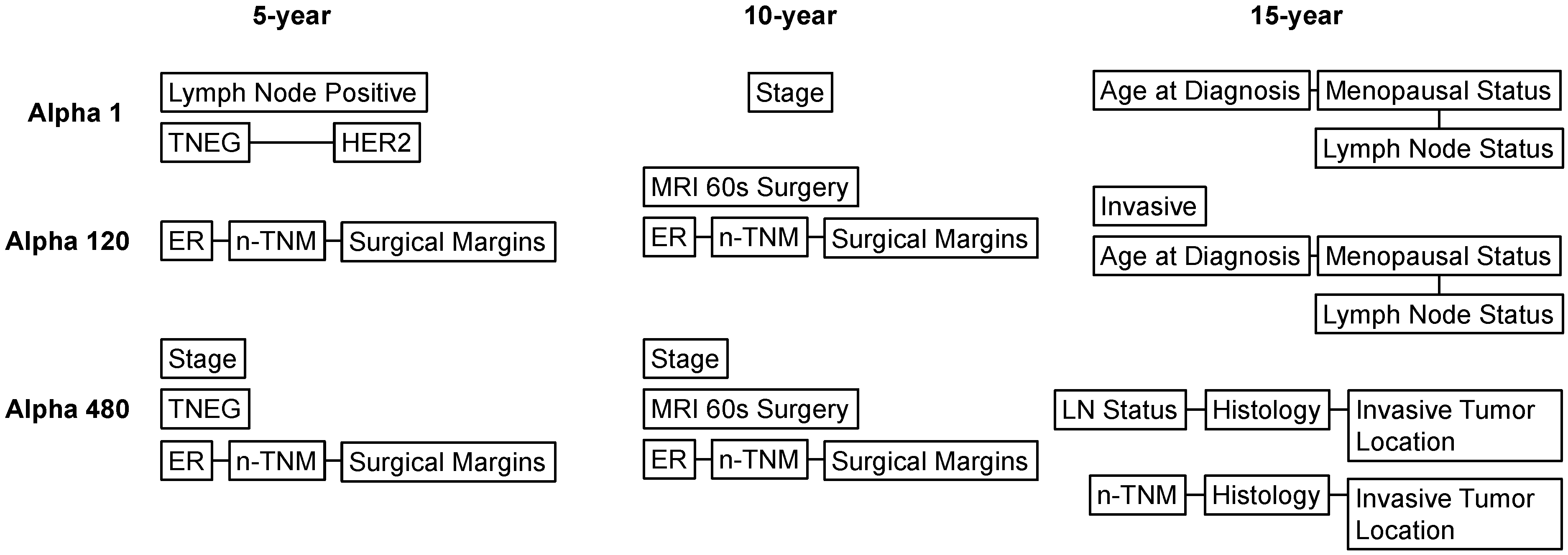
3.2. Learned Interactions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sopik, V.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Predictors of time to death after distant recurrence in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 173, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sestak, I.; Cuzick, J. Markers for the identification of late breast cancer recurrence. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, C.; Pan, H.; Godwin, J.; Gray, R.; Arriagada, R.; Raina, V.; Abraham, M.; Medeiros Alencar, V.H.; Badran, A.; Bonfill, X.; et al. Long-term effects of continuing adjuvant tamoxifen to 10 years versus stopping at 5 years after diagnosis of oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: ATLAS, a randomised trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, H.; Gray, R.; Braybrooke, J.; Davies, C.; Taylor, C.; McGale, P.; Peto, R.; Pritchard, K.I.; Bergh, J.; Dowsett, M.; et al. 20-Year Risks of Breast-Cancer Recurrence after Stopping Endocrine Therapy at 5 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhutiani, N.; Egger, M.E.; Ajkay, N.; Scoggins, C.R.; Martin, R.C., 2nd; McMasters, K.M. Multigene Signature Panels and Breast Cancer Therapy: Patterns of Use and Impact on Clinical Decision Making. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2018, 226, 406–412.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodilsen, A.; Bjerre, K.; Offersen, B.V.; Vahl, P.; Amby, N.; Dixon, J.M.; Ejlertsen, B.; Overgaard, J.; Christiansen, P. Importance of margin width in breast-conserving treatment of early breast cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 113, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskins, K.F.; Danciu, O.C.; Ko, N.Y.; Calip, G.S. Association of Race/Ethnicity and the 21-Gene Recurrence Score with Breast Cancer–Specific Mortality Among US Women. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Wells, A.; Brufsky, A.; Shetty, D.; Shajihan, K.; Neapolitan, R.E. Leveraging Bayesian networks and information theory to learn risk factors for breast cancer metastasis. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Jao, J.; Neapolitan, R. Learning Predictive Interactions Using Information Gain and Bayesian Network Scoring. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Z.; Jiang, X.; Neapolitan, R.E. Discovering causal interactions using Bayesian network scoring and information gain. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Wells, A.; Brufsky, A.; Neapolitan, R. A clinical decision support system learned from data to personalize treatment recommendations towards preventing breast cancer metastasis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neapolitan, R.E. Probabilistic Reasoning in Expert Systems: Theory and Algorithms; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990; p. xiii. 433p. [Google Scholar]
- Neapolitan, R.E.; Jiang, X. Contemporary Artificial Intelligence, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2012; 500p. [Google Scholar]
- Neapolitan, R.E. Learning Bayesian Networks; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004; p. xv. 674p. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, G.F.; Herskovits, E. A Bayesian method for the induction of probabilistic networks from data. Mach. Learn. 1992, 9, 309–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckerman, D.; Geiger, D.; Chickering, D.M. Learning Bayesian Networks: The Combination of Knowledge and Statistical Data. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 197–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arpino, G.; Milano, M.; De Placido, S. Features of aggressive breast cancer. Breast 2015, 24, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, K.; Cole, S.R.; Tse, C.-K.; Perou, C.; Carey, L.A.; Foulkes, W.; Dressler, L.G.; Geradts, J.; Millikan, R.C. Intrinsic Breast Tumor Subtypes, Race, and Long-Term Survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 6100–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nechuta, S.; Chen, W.Y.; Cai, H.; Poole, E.M.; Kwan, M.L.; Flatt, S.W.; Patterson, R.E.; Pierce, J.P.; Caan, B.; Shu, X.O. A pooled analysis of post-diagnosis lifestyle factors in association with late estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer prognosis. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ekholm, M.; Bendahl, P.; Fernö, M.; Nordenskjöld, B.; Stål, O.; Rydén, L. Effects of adjuvant tamoxifen over three decades on breast cancer–free and distant recurrence–free interval among premenopausal women with oestrogen receptor–positive breast cancer randomised in the Swedish SBII:2pre trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 110, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wangchinda, P.; Ithimakin, S. Factors that predict recurrence later than 5 years after initial treatment in operable breast cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sammut, S.-J.; Crispin-Ortuzar, M.; Chin, S.-F.; Provenzano, E.; Bardwell, H.A.; Ma, W.; Cope, W.; Dariush, A.; Dawson, S.-J.; Abraham, J.E.; et al. Multi-omic machine learning predictor of breast cancer therapy response. Nature 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz, A.E.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Boone, S.D. Healthy lifestyle impact on breast cancer-specific and all-cause mortality. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 167, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwan, M.L.; Kushi, L.; Weltzien, E.; Tam, E.K.; Castillo, A.; Sweeney, C.; Caan, B. Alcohol Consumption and Breast Cancer Recurrence and Survival Among Women with Early-Stage Breast Cancer: The Life After Cancer Epidemiology Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4410–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Variables Included | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Race | Race of patient | White, Black, Asian, American Indian or Alaskan native, native Hawaiian or other Pacific islander |
| Ethnicity | Ethnicity of patient | Not Hispanic, Hispanic |
| Smoking | Smoking history of patient | Ex-smoker, non-smoker, cigarettes, chewing tobacco, cigar |
| Alcohol usage | Alcohol usage of patient | Moderate, no use, use but not otherwise specified former user, heavy user |
| Family history | Family history of cancer | Cancer, no cancer, breast cancer, other cancer, cancer but not otherwise specified |
| Age_at_diagnosis | Age at diagnosis of the disease | 0–49, 50–69, >69 |
| Menopausal_status | Inferred menopausal status | Pre-, post- |
| Side | Side of tumor | Left, right |
| TNEG | Triple negative status in terms of patient being ER-, PR- and HER2-negative | Yes, no |
| ER | Estrogen receptor expression | Neg, pos, low pos |
| ER_percent | Percent of cell stain pos for ER receptors | 0–20, 20–90, 90–100 |
| PR | Progesterone receptor expression | Neg, pos, low pos |
| PR_percent | Percent of cell stain pos for PR receptors | 0–20, 20–90, 90–100 |
| P53 | Whether P53 is mutated | Neg, pos, low pos |
| HER2 | HER2 expression | Neg, pos |
| t_tnm_stage | Prime tumor stage in TNM system | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, IS, 1 mic, X |
| n_tnm_stage | Number of nearby cancerous lymph nodes | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, X |
| Stage | Composite of size and number of positive nodes | 0, 1, 2, 3 |
| Lymph_nodes_removed | Number of lymph nodes removed | 0–11, 12–22, >22 |
| Lymph_nodes_positive | Number of positive lymph nodes | 0, 1–8, >8 |
| Lymph_node_status | Whether patient has any positive lymph nodes | Neg, pos |
| Histology | Tumor histology | Lobular, ductal |
| Size | Size of tumor in mm | 0–32, 32–70, >70 |
| Grade | Grade of disease | 1, 2, 3 |
| Invasive | Whether tumor is invasive | Yes, no |
| Histology2 | Tumor histology subtypes | IDC, DCIS, ILC, NC |
| Invasive_tumor_location | Where invasive tumor is located | Mixed duct and lobular, duct, lobular, none |
| DCIS_level | Type of ductal carcinoma in situ | Solid, apocrine, cribriform, dcis, comedo, papillary, micropapillary |
| Re_excision | Removal of an additional margin of tissue | Yes, no |
| Surgical_margins | Whether there are any residual tumors | Residual tumor, no residual tumor, no primary site surgery |
| MRIs_60_surgery | MRIs within 60 days of surgery | Yes, no |
| Alpha 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Interacts with | n Times | Years after DG | Total | % |
| ER | n-TNM | 2 | 5, 10 | 6 | 33.33% |
| ER | HER2 | 2 | 5, 15 | 6 | 33.33% |
| ER | LN positive | 2 | 15, 15 | 6 | 33.33% |
| TNEG | HER2 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 14.29% |
| TNEG | Age at DG | 1 | 15 | 7 | 14.29% |
| TNEG | LN positive/status | 2 | 15 | 7 | 28.57% |
| TNEG | Ethnicity | 1 | 15 | 7 | 14.29% |
| TNEG | Stage | 1 | 15 | 7 | 14.29% |
| TNEG | Re_excision | 1 | 15 | 7 | 14.29% |
| HER2 | Stage | 6 | 5, 5, 10, 10, 10, 15 | 23 | 26.09% |
| HER2 | MRIs_60_surgery | 1 | 5 | 23 | 4.35% |
| HER2 | ER_percent | 1 | 5 | 23 | 4.35% |
| HER2 | TNEG | 1 | 5 | 23 | 4.35% |
| HER2 | Histology | 3 | 5, 10, 10 | 23 | 13.04% |
| HER2 | Grade | 2 | 5, 5 | 23 | 8.70% |
| HER2 | Invasive tumor location | 2 | 5, 10 | 23 | 8.70% |
| HER2 | ER | 1 | 5, 15 | 23 | 4.35% |
| HER2 | PR | 2 | 5, 10 | 23 | 8.70% |
| HER2 | LN positive/status | 3 | 10, 10, 15 | 23 | 13.04% |
| HER2 | Surgical margins | 1 | 10 | 23 | 4.35% |
| Race/ethnicity | Histology | 1 | 5 | 8 | 12.50% |
| Race/ethnicity | Grade | 1 | 5 | 8 | 12.50% |
| Race/ethnicity | ER_percent | 1 | 10 | 8 | 12.50% |
| Race/ethnicity | n-TNM | 1 | 10 | 8 | 12.50% |
| Race/ethnicity | Side | 1 | 10 | 8 | 12.50% |
| Race/ethnicity | LN positive/status | 1 | 10 | 8 | 12.50% |
| Race/ethnicity | TNEG | 1 | 15 | 8 | 12.50% |
| Race/ethnicity | Stage | 1 | 15 | 8 | 12.50% |
| Alcohol/smoking | LN positive/status | 1 | 15 | 1 | 100.00% |
| Alpha 120 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Interacts with | n Times | Years after DG | Total | % |
| ER | n-TNM | 9 | 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 10, 15 | 30 | 30.00% |
| ER | Surgical margins | 4 | 5, 5, 10, 15 | 30 | 13.33% |
| ER | Family history | 2 | 5, 10 | 30 | 6.67% |
| ER | LN positive/status | 4 | 5, 10, 15, 15 | 30 | 13.33% |
| ER | HER2 | 1 | 5 | 30 | 3.33% |
| ER | MRIs_60_surgery | 1 | 5 | 30 | 3.33% |
| ER | Race/ethnicity | 3 | 5, 15, 15 | 30 | 10.00% |
| ER | Histology | 1 | 5 | 30 | 3.33% |
| ER | Invasive tumor location | 1 | 5 | 30 | 3.33% |
| ER | Size | 1 | 5 | 30 | 3.33% |
| ER | Side | 1 | 5 | 30 | 3.33% |
| ER | DCIS_level | 2 | 5, 10 | 30 | 6.67% |
| TNEG | n-TNM | 4 | 5, 5, 10, 15 | 8 | 50.00% |
| TNEG | Surgical margins | 2 | 10, 15 | 8 | 25.00% |
| TNEG | Smoking | 1 | 5 | 8 | 12.50% |
| TNEG | Invasive tumor location | 1 | 5 | 8 | 12.50% |
| HER2 | ER | 1 | 5 | 12 | 8.33% |
| HER2 | n-TNM | 1 | 5 | 12 | 8.33% |
| HER2 | Stage | 5 | 5, 10, 10, 10, 15 | 12 | 41.67% |
| HER2 | Surgical margins | 2 | 5, 10 | 12 | 16.67% |
| HER2 | Histology | 1 | 10 | 12 | 8.33% |
| HER2 | Grade | 1 | 15 | 12 | 8.33% |
| HER2 | PR | 1 | 10 | 12 | 8.33% |
| Race/ethnicity | ER | 3 | 5, 15, 15 | 17 | 17.65% |
| Race/ethnicity | n-TNM | 3 | 5, 10, 15 | 17 | 17.65% |
| Race/ethnicity | Stage | 3 | 5, 15, 15 | 17 | 17.65% |
| Race/ethnicity | Surgical margins | 1 | 5 | 17 | 5.88% |
| Race/ethnicity | ER_percent | 1 | 10 | 17 | 5.88% |
| Race/ethnicity | Grade | 1 | 15 | 17 | 5.88% |
| Race/ethnicity | LN positive/status | 3 | 15 | 17 | 17.65% |
| Race/ethnicity | Re_excision | 1 | 15 | 17 | 5.88% |
| Race/ethnicity | PR_percent | 1 | 15 | 17 | 5.88% |
| Smoking/alcohol | TNEG | 1 | 5 | 4 | 25.00% |
| Smoking/alcohol | n-TNM | 1 | 5 | 4 | 25.00% |
| Smoking/alcohol | Stage | 1 | 10 | 4 | 25.00% |
| Smoking/alcohol | Histology | 1 | 10 | 4 | 25.00% |
| Alpha 480 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Interacts with | n Times | Years after DG | Total | % |
| ER | n-TNM | 6 | 5, 5, 5, 10, 10, 10 | 19 | 31.58% |
| ER | Surgical margins | 3 | 5, 5, 10 | 19 | 15.79% |
| ER | Race | 3 | 5, 10, 15 | 19 | 15.79% |
| ER | Size | 1 | 5 | 19 | 5.26% |
| ER | Smoking | 1 | 5 | 19 | 5.26% |
| ER | Family history | 1 | 10 | 19 | 5.26% |
| ER | LN positive/status | 1 | 10 | 19 | 5.26% |
| ER | Stage | 1 | 10 | 19 | 5.26% |
| ER | DCIS_level | 1 | 10 | 19 | 5.26% |
| ER | Age at DG | 1 | 10 | 19 | 5.26% |
| TNEG | n-TNM | 1 | 10 | 2 | 50.00% |
| TNEG | Surgical margins | 1 | 10 | 2 | 50.00% |
| HER2 | Stage | 2 | 5, 10 | 7 | 28.57% |
| HER2 | Surgical margins | 4 | 5, 5, 10 | 7 | 57.14% |
| HER2 | t-TNM | 1 | 5 | 7 | 14.29% |
| Race/ethnicity | Stage | 6 | 5, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15 | 22 | 27.27% |
| Race/ethnicity | Surgical margins | 2 | 5, 5 | 22 | 9.09% |
| Race/ethnicity | ER | 3 | 5, 10, 15 | 22 | 13.64% |
| Race/ethnicity | n-TNM | 3 | 5, 10, 10 | 22 | 13.64% |
| Race/ethnicity | Family history | 1 | 10 | 22 | 4.55% |
| Race/ethnicity | LN positive/status | 1 | 10 | 22 | 4.55% |
| Race/ethnicity | ER_percent | 1 | 10 | 22 | 4.55% |
| Race/ethnicity | Grade | 1 | 15 | 22 | 4.55% |
| Race/ethnicity | Invasive tumor location | 1 | 15 | 22 | 4.55% |
| Race/ethnicity | Re-excision | 1 | 15 | 22 | 4.55% |
| Race/ethnicity | Alcohol | 1 | 15 | 22 | 4.55% |
| Race/ethnicity | Histology2 | 1 | 15 | 22 | 4.55% |
| Smoking/alcohol | t-TNM | 2 | 5, 5 | 12 | 16.67% |
| Smoking/alcohol | n-TNM | 3 | 5, 5, 5 | 12 | 25.00% |
| Smoking/alcohol | Stage | 3 | 5, 10, 15 | 12 | 25.00% |
| Smoking/alcohol | Surgical margins | 2 | 5, 10 | 12 | 16.67% |
| Smoking/alcohol | ER | 1 | 5 | 12 | 8.33% |
| Smoking/alcohol | race | 1 | 15 | 12 | 8.33% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomez Marti, J.L.; Brufsky, A.; Wells, A.; Jiang, X. Machine Learning to Discern Interactive Clusters of Risk Factors for Late Recurrence of Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010253
Gomez Marti JL, Brufsky A, Wells A, Jiang X. Machine Learning to Discern Interactive Clusters of Risk Factors for Late Recurrence of Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(1):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010253
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomez Marti, Juan Luis, Adam Brufsky, Alan Wells, and Xia Jiang. 2022. "Machine Learning to Discern Interactive Clusters of Risk Factors for Late Recurrence of Metastatic Breast Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 1: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010253
APA StyleGomez Marti, J. L., Brufsky, A., Wells, A., & Jiang, X. (2022). Machine Learning to Discern Interactive Clusters of Risk Factors for Late Recurrence of Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancers, 14(1), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010253







