BRG1 and NPM-ALK Are Co-Regulated in Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma; BRG1 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in ALCL
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Inhibitors and Antibodies
2.3. Primary Patient Samples and Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Mice
2.5. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
2.6. RNAseq
2.7. Isolation of RNA
2.8. Synthesis of cDNA
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.10. Lentiviral Transduction of shRNA
2.11. Viability and Caspase Assays
3. Results
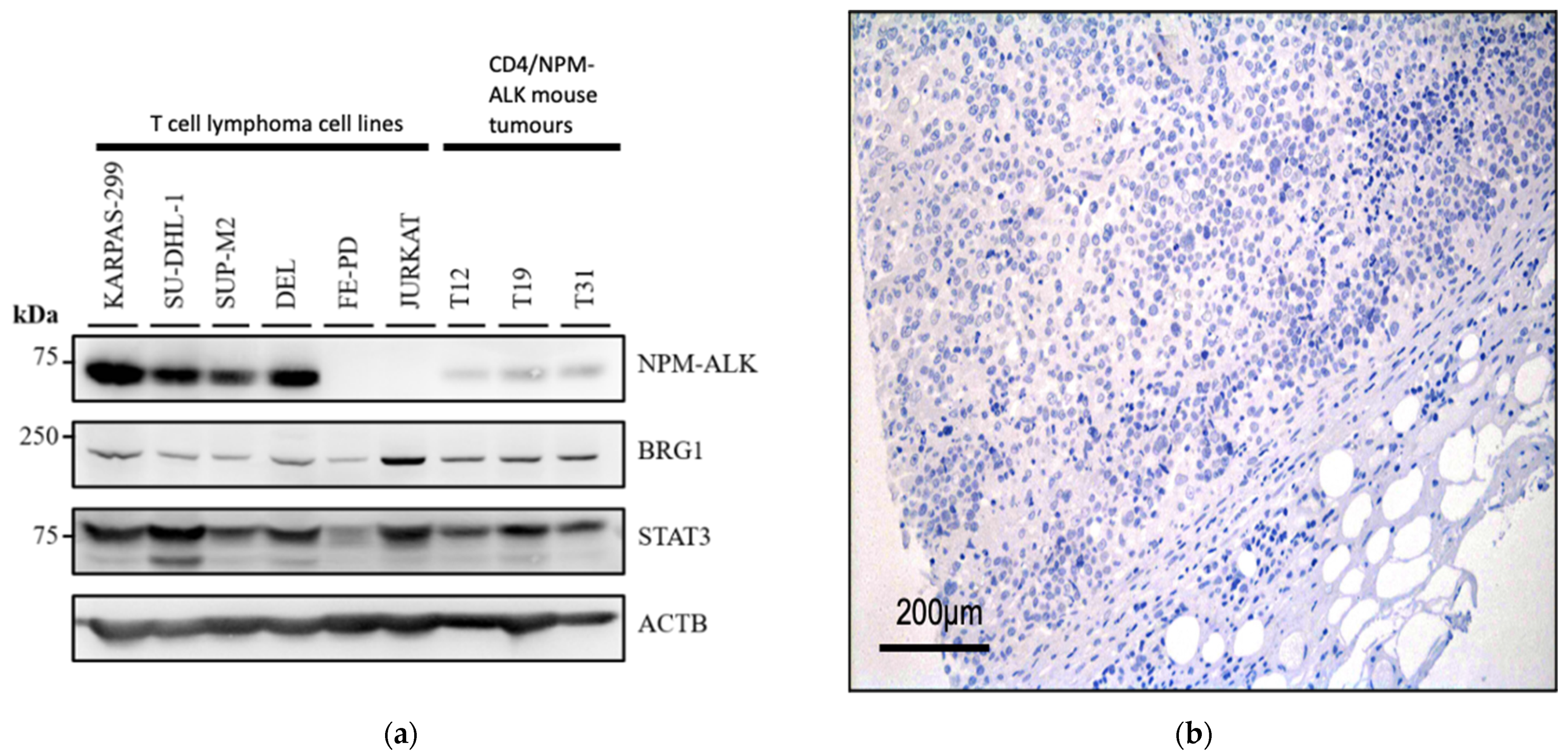
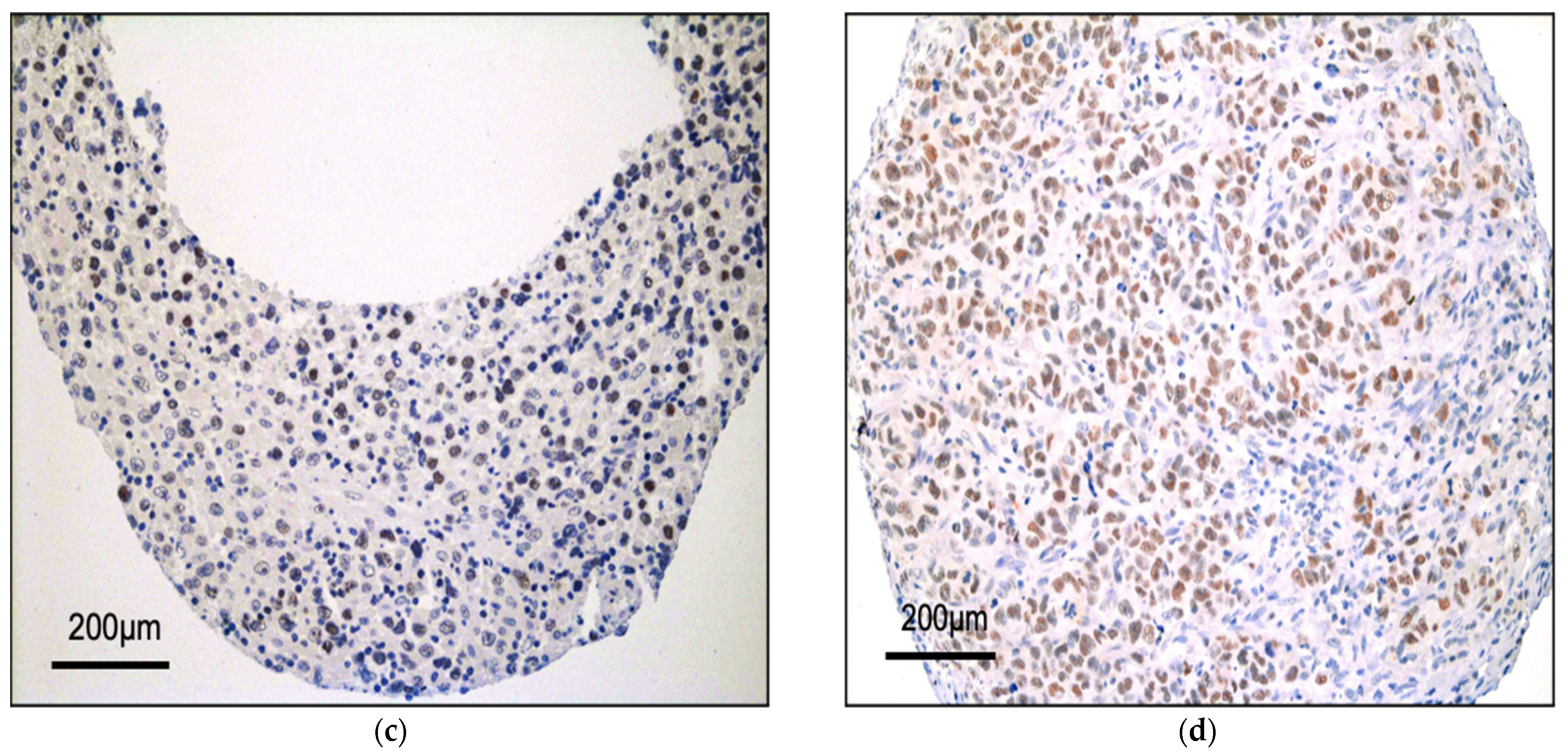
3.1. BRG1 Is Expressed in ALK+ ALCL and Other Peripheral T-Cell Lymphomas
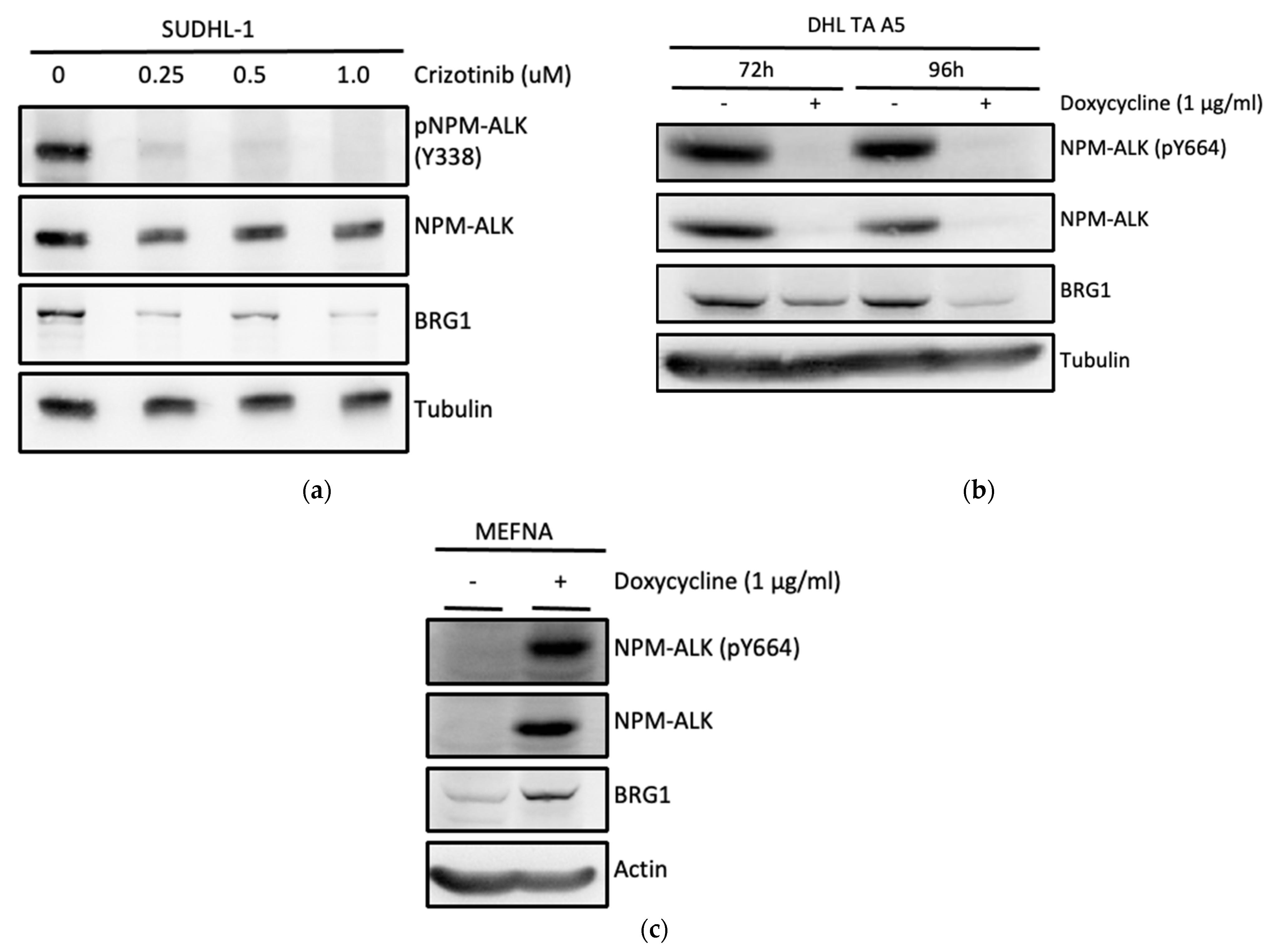
3.2. NPM-ALK Regulates Expression of BRG1 by Protecting It from Proteasomal Degradation
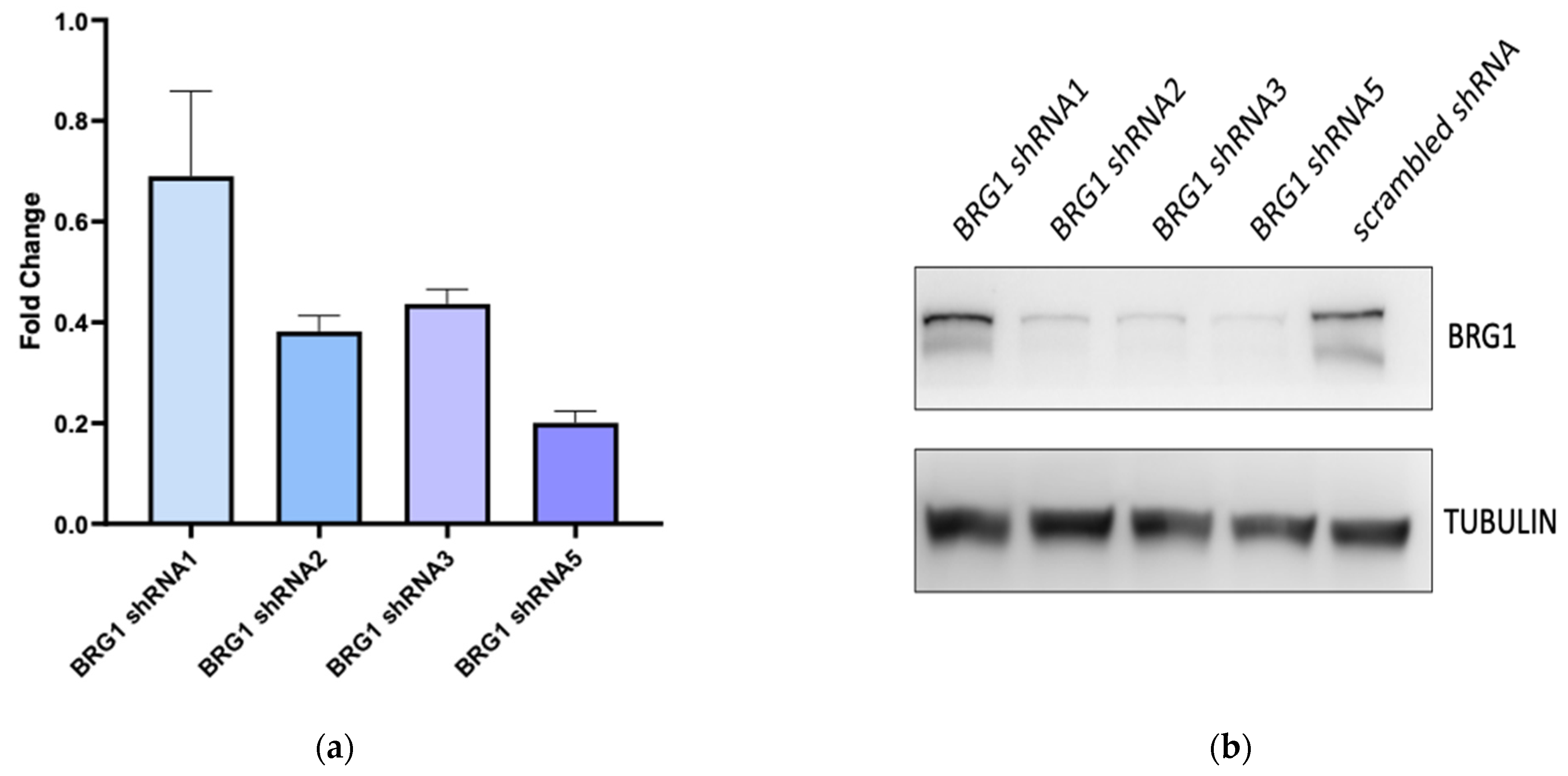
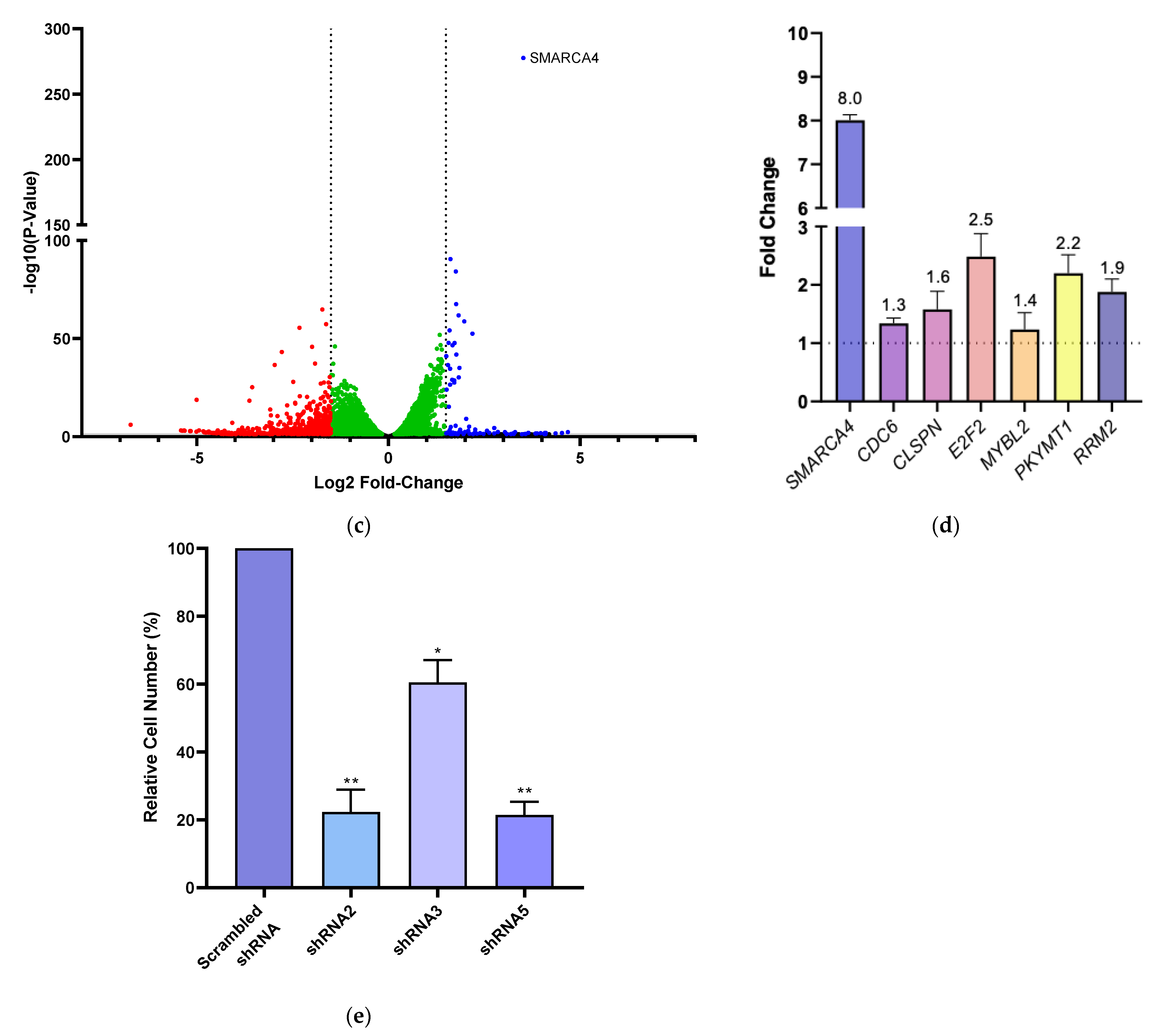
3.3. BRG1 Induces Transcription of Genes Involved in Cell Cycle Progression and Its Inhibition Results in a Loss of Cell Viability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kinney, M.C.; Higgins, R.A.; Medina, E.A. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: Twenty-five years of discovery. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2011, 135, 19–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugières, L.; Le Deley, M.C.; Rosolen, A.; Williams, D.; Horibe, K.; Wrobel, G.; Mann, G.; Zsiros, J.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Marky, I.; et al. Impact of the methotrexate administration dose on the need for intrathecal treatment in children and adolescents with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Results of a randomized trial of the EICNHL Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Deley, M.C.; Rosolen, A.; Williams, D.M.; Horibe, K.; Wrobel, G.; Attarbaschi, A.; Zsiros, J.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Marky, I.M.; Lamant, L.; et al. Vinblastine in children and adolescents with high-risk anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Results of the randomized ALCL99-vinblastine trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3987–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, K.J.; Harris, N.L.; Vose, J.M.; Ullrich, F.; Jaffe, E.S.; Connors, J.M.; Rimsza, L.; Pileri, S.A.; Chhanabhai, M.; Gascoyne, R.D.; et al. ALK- anaplastic large-cell lymphoma is clinically and immunophenotypically different from both ALK+ ALCL and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: Report from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood 2008, 111, 5496–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischof, D.; Pulford, K.; Mason, D.Y.; Morris, S.W. Role of the nucleophosmin (NPM) portion of the non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma-associated NPM-anaplastic lymphoma kinase fusion protein in oncogenesis. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 2312–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.G.; Shapiro, D.N.; Saltman, D.L.; Look, A.T. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 1994, 263, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.D.; Merz, H.; Yeung, D.; Alexander, D.R. CD2 promoter regulated nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase in transgenic mice causes B lymphoid malignancy. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 3275–3279. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, S.D.; Tooze, R.; Maclennan, K.; Alexander, D.R. Vav-promoter regulated oncogenic fusion protein NPM-ALK in transgenic mice causes B-cell lymphomas with hyperactive Jun kinase. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7750–7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuriato, S.; Foisseau, M.; Dejean, E.; Felsher, D.W.; Al Saati, T.; Demur, C.; Ragab, A.; Kruczynski, A.; Schiff, C.; Delsol, G.; et al. Conditional TPM3-ALK and NPM-ALK transgenic mice develop reversible ALK-positive early B-cell lymphoma/leukemia. Blood 2010, 115, 4061–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, R.; Hahne, J.; Jacob, A.; Egert, A.; Schenkel, J.; Wernert, N.; Schorle, H.; Wellmann, A. Mice transgenic for NPM-ALK develop non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 3191–3196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiarle, R.; Gong, J.Z.; Guasparri, I.; Pesci, A.; Cai, J.; Liu, J.; Simmons, W.J.; Dhall, G.; Howes, J.; Piva, R.; et al. NPM-ALK transgenic mice spontaneously develop T-cell lymphomas and plasma cell tumors. Blood 2003, 101, 1919–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducray, S.P.; Natarajan, K.; Garland, G.D.; Turner, S.D.; Egger, G. The Transcriptional Roles of ALK Fusion Proteins in Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2019, 11, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Messa, C.; Pogliani, E.M. Crizotinib in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 775–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crockett, D.K.; Lin, Z.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.S.; Lim, M.S. Identification of NPM-ALK interacting proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2617–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcolm, T.I.; Villarese, P.; Fairbairn, C.J.; Lamant, L.; Trinquand, A.; Hook, C.E.; Burke, G.A.; Brugieres, L.; Hughes, K.; Payet, D.; et al. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma arises in thymocytes and requires transient TCR expression for thymic egress. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokoph, N.; Probst, N.A.; Lee, L.C.; Monahan, J.M.; Matthews, J.D.; Liang, H.C.; Bahnsen, K.; Montes-Mojarro, I.A.; Karaca-Atabay, E.; Sharma, G.G.; et al. IL10RA Modulates Crizotinib Sensitivity in NPM1-ALK-positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2020, 136, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, A.D.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Allen, J.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Azov, A.G.; Bennett, R.; et al. Ensembl 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D682–D688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piva, R.; Pellegrino, E.; Mattioli, M.; Agnelli, L.; Lombardi, L.; Boccalatte, F.; Costa, G.; Ruggeri, B.A.; Cheng, M.; Chiarle, R.; et al. Functional validation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase signature identifies CEBPB and BCL2A1 as critical target genes. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3171–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, R.; Chiarle, R.; Manazza, A.D.; Taulli, R.; Simmons, W.; Ambrogio, C.; D’Escamard, V.; Pellegrino, E.; Ponzetto, C.; Palestro, G.; et al. Ablation of oncogenic ALK is a viable therapeutic approach for anaplastic large-cell lymphomas. Blood 2006, 107, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofaro, M.F.D.; Betz, B.L.; Rorie, C.J.; Reisman, D.N.; Wang, W.; Weissman, B.E. Characterization of SWI/SNF protein expression in human breast cancer cell lines and other malignancies. J. Cell. Physiol. 2001, 186, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisman, D.N.; Sciarrotta, J.; Wang, W.; Funkhouser, W.K.; Weissman, B.E. Loss of BRG1/BRM in human lung cancer cell lines and primary lung cancers: Correlation with poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laimer, D.; Dolznig, H.; Kollmann, K.; Vesely, P.W.; Schlederer, M.; Merkel, O.; Schiefer, A.I.; Hassler, M.R.; Heider, S.; Amenitsch, L.; et al. IPDGFR blockade is a rational and effective therapy for NPM-ALK-driven lymphomas. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, J.; Fujii, T.; Shih, J.H.; Dracheva, T.; Meerzaman, D.; Player, A.; Hong, K.; Settnek, S.; Gupta, A.; Buetow, K.; et al. Chromatin remodeling factors and BRM/BRG1 expression as prognostic indicators in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4314–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisman, D.N.; Strobeck, M.W.; Betz, B.L.; Sciariotta, J.; Funkhouser, W., Jr.; Murchardt, C.; Yaniv, M.; Sherman, L.S.; Knudsen, E.S.; Weissman, B.E. Concomitant down-regulation of BRM and BRG1 in human tumor cell lines: Differential effects on RB-mediated growth arrest vs CD44 expression. Oncogene 2002, 21, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bultman, S.J.; Herschkowitz, J.I.; Godfrey, V.; Gebuhr, T.C.; Yaniv, M.; Perou, C.M.; Magnuson, T. Characterization of mammary tumors from Brg1 heterozygous mice. Oncogene 2008, 27, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultman, S.; Gebuhr, T.; Yee, D.; La Mantia, C.; Nicholson, J.; Gilliam, A.; Randazzo, F.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P.; Crabtree, G.; et al. A Brg1 null mutation in the mouse reveals functional differences among mammalian SWI/SNF complexes. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaros, S.; Cirrincione, G.M.; Palanca, A.; Metzger, D.; Reisman, D. Targeted knockout of BRG1 potentiates lung cancer development. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisman, D.N.; Sciarrotta, J.; Bouldin, T.W.; Weissman, B.E.; Funkhouser, W.K. The expression of the SWI/SNF ATPase subunits BRG1 and BRM in normal human tissues. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2005, 13, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, S.R.; Love, I.M.; Imbalzano, A.N.; Grossman, S.R.; Androphy, E.J. The SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling subunit BRG1 is a critical regulator of p53 necessary for proliferation of malignant cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tando, T.; Ishizaka, A.; Watanabe, H.; Ito, T.; Iida, S.; Haraguchi, T.; Mizutani, T.; Izumi, T.; Isobe, T.; Akiyama, T.; et al. Requiem protein links RelB/p52 and the Brm-type SWI/SNF complex in a noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 21951–21960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motegi, A.; Fujimoto, J.; Kotani, M.; Sakuraba, H.; Yamamoto, T. ALK receptor tyrosine kinase promotes cell growth and neurite outgrowth. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 3319–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazot, P.; Cazes, A.; Dingli, F.; Degoutin, J.; Irinopoulou, T.; Boutterin, M.C.; Lombard, B.; Loew, D.; Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H.; et al. Internalization and down-regulation of the ALK receptor in neuroblastoma cell lines upon monoclonal antibodies treatment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Molavi, O.; Zhang, H.; Gupta, N.; Alshareef, A.; Bone, K.M.; Gopal, K.; Wu, F.; Lewis, J.T.; Douglas, D.N.; et al. STAT1 is phosphorylated and downregulated by the oncogenic tyrosine kinase NPM-ALK in ALK-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonvini, P.; Dalla Rosa, H.; Vignes, N.; Rosolen, A. Ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase induced by 17-allylamino-demethoxygeldanamycin: Role of the co-chaperone carboxyl heat shock protein 70-interacting protein. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3256–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Primer | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| BRG1 Forward | TGCTGCGGCCCTTCTTGCTC |
| BRG1 Reverse | GGTGCCGCCTTTGCCCTTCT |
| CDC6 Forward | ACCTATGCAACACTCCCCATT |
| CDC6 Reverse | TGGCTAGTTCTCTTTTGCTAGGA |
| CLSPN Forward | AAGACAGTGATTCCGAAACAGAG |
| CLSPN Reverse | TGCGCTTCAAGATTTTCCTGA |
| E2F2 Forward | CGTCCCTGAGTTCCCAACC |
| E2F2 Reverse | GCGAAGTGTCATACCGAGTCTT |
| MYBL2 Forward | CCGGAGCAGAGGGATAGCA |
| MYBL2 Reverse | CAGTGCGGTTAGGGAAGTGG |
| PKYMT2 Forward | GCCTGCCAACATCTTCCTG |
| PKYMT2 Reverse | CCCAGACTGAACACATCCGC |
| RRM2 Forward | CACGGAGCCGAAAACTAAAGC |
| RRM2 Reverse | TCTGCCTTCTTATACATCTGCCA |
| NPM-ALK Forward | CTGTACAGCCAACGGTTTCCC |
| NPM-ALK Reverse | GGCCCAGACCCGAATGAGG |
| GAPDH Forward | CCACTCCTCCACCTTTGAC |
| GAPDH Reverse | ACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCA |
| Mouse GAPDH Forward | CATCACTGCCACCCAGAAGACTG |
| Mouse GAPDH Reverse | ATGCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAG |
| Mouse BRG1 Forward | GAAAGTGGCTCTGAAGAGGAGG |
| Mouse BRG1 Reverse | TCCACCTCAGAGACATCATCGC |
| Mouse HPRT Forward | CTGGTGAAAAGGACCTCTCGAAG |
| Mouse HPRT Reverse | CCAGTTTCACTAATGACACAAACG |
| Brg1 shRNA | TRC Construct | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TRCN0000015548 | CCATATTTATACAGCAGAGAACTCGAGTTCTCTGCTGTATAAATATGG |
| 2 | TRCN0000015549 | CCGGCCCGTGGACTTCAAGAAGATACTCGAGTATCTTCTTGAAGTCCACGGG |
| 3 | TRCN0000015550 | CCGGGCCAAGCAAGATGTCGATGATCTCGAGATCATCGACATCTTGCTTGGCTTTTT |
| 5 | TRCN0000015552 | CCGGCGGCAGACACTGTGATCATTTCTCGAGAAATGATCACAGTGTCTGCCGTTTTT |
| Pathway | Gene Count | Entities Total |
|---|---|---|
| Cell cycle | 12 | 734 |
| Cell cycle, mitotic | 10 | 596 |
| Cell cycle checkpoints | 6 | 280 |
| Mitotic G1 phase and G1/S transition | 8 | 173 |
| G2/M checkpoints | 5 | 154 |
| G1/S checkpoints | 5 | 150 |
| DNA replication | 3 | 142 |
| DNA replication pre-initiation | 3 | 88 |
| Apoptotic execution phase | 3 | 54 |
| Transcriptional regulation by E2F6 | 2 | 46 |
| Pathway | Gene Count | Entities Total |
|---|---|---|
| Reproduction | 8 | 123 |
| HDAC deacetylase histones | 7 | 67 |
| Amyloid fibre formation | 7 | 88 |
| Meiosis | 7 | 92 |
| RNA polymerase I promoter opening | 6 | 34 |
| DNA methylation | 6 | 36 |
| PRC2 methylates histones and DNA | 6 | 44 |
| SIRT1 negatively regulated rRNA expression | 6 | 45 |
| ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression | 6 | 48 |
| Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of Androgen Receptor (AR) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 | 6 | 49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garland, G.D.; Ducray, S.P.; Jahangiri, L.; Pucci, P.; Amos Burke, G.A.; Monahan, J.; Lai, R.; Merkel, O.; Schiefer, A.-I.; Kenner, L.; et al. BRG1 and NPM-ALK Are Co-Regulated in Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma; BRG1 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in ALCL. Cancers 2022, 14, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010151
Garland GD, Ducray SP, Jahangiri L, Pucci P, Amos Burke GA, Monahan J, Lai R, Merkel O, Schiefer A-I, Kenner L, et al. BRG1 and NPM-ALK Are Co-Regulated in Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma; BRG1 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in ALCL. Cancers. 2022; 14(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010151
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarland, Gavin D., Stephen P. Ducray, Leila Jahangiri, Perla Pucci, G. A. Amos Burke, Jack Monahan, Raymond Lai, Olaf Merkel, Ana-Iris Schiefer, Lukas Kenner, and et al. 2022. "BRG1 and NPM-ALK Are Co-Regulated in Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma; BRG1 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in ALCL" Cancers 14, no. 1: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010151
APA StyleGarland, G. D., Ducray, S. P., Jahangiri, L., Pucci, P., Amos Burke, G. A., Monahan, J., Lai, R., Merkel, O., Schiefer, A.-I., Kenner, L., Bannister, A. J., & Turner, S. D. (2022). BRG1 and NPM-ALK Are Co-Regulated in Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma; BRG1 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in ALCL. Cancers, 14(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010151











