STAMP2 Expression Mediated by Cytokines Attenuates Their Growth-Limiting Effects in Prostate Cancer Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.2. RNA Interference
2.3. Quantitative PCR
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
2.6. Small-Molecule Inhibitors
2.7. Cell Viability and Colony Formation Assay
2.8. Statistical Analyzes
3. Results
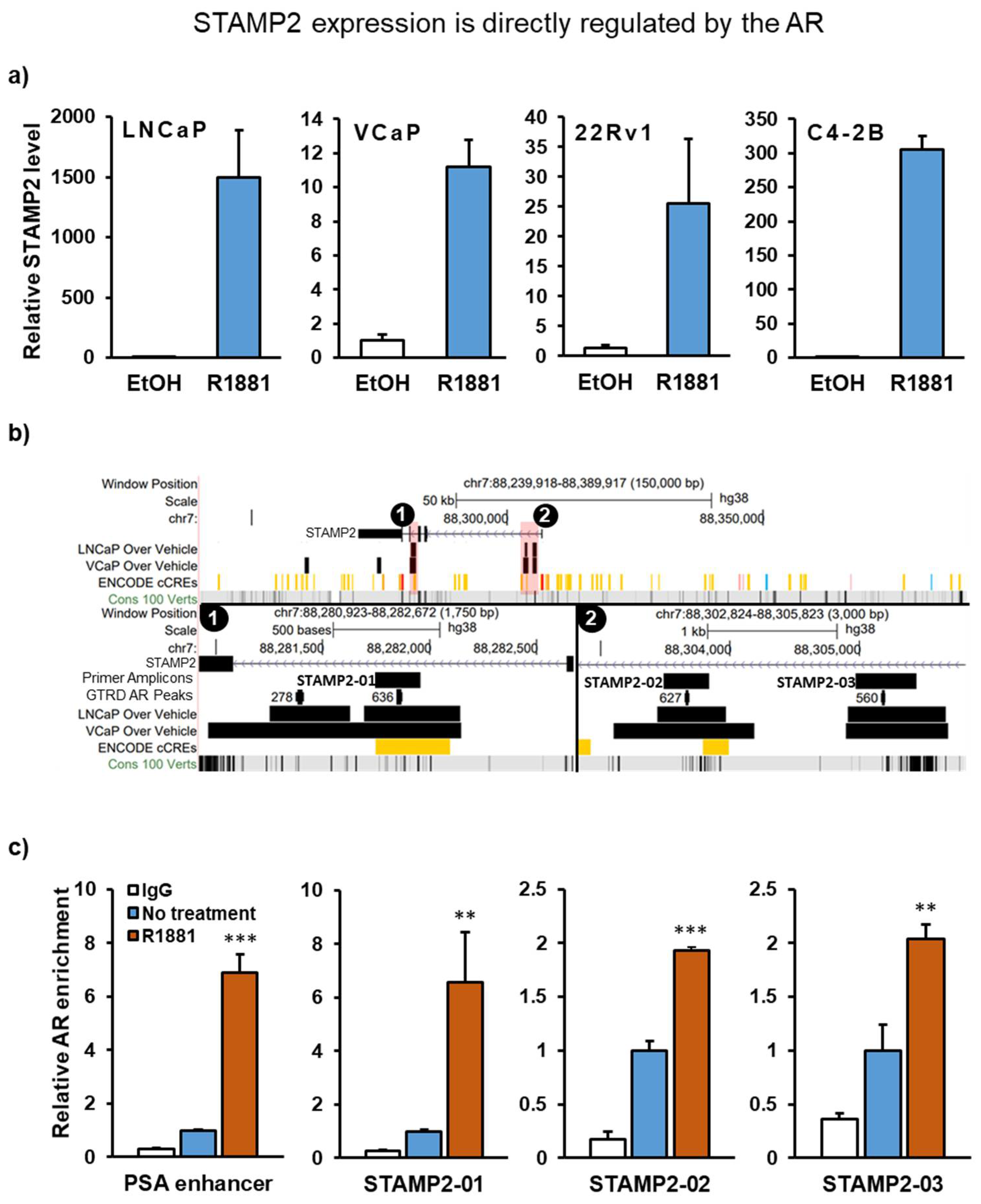
3.1. STAMP2 Is a Direct AR Target Gene in Prostate Cancer Cells
3.2. Temporal Regulation of STAMP2 Expression by Cytokines
3.3. Cytokines and Androgens Synergistically Induce STAMP2 Expression in PCa Cells
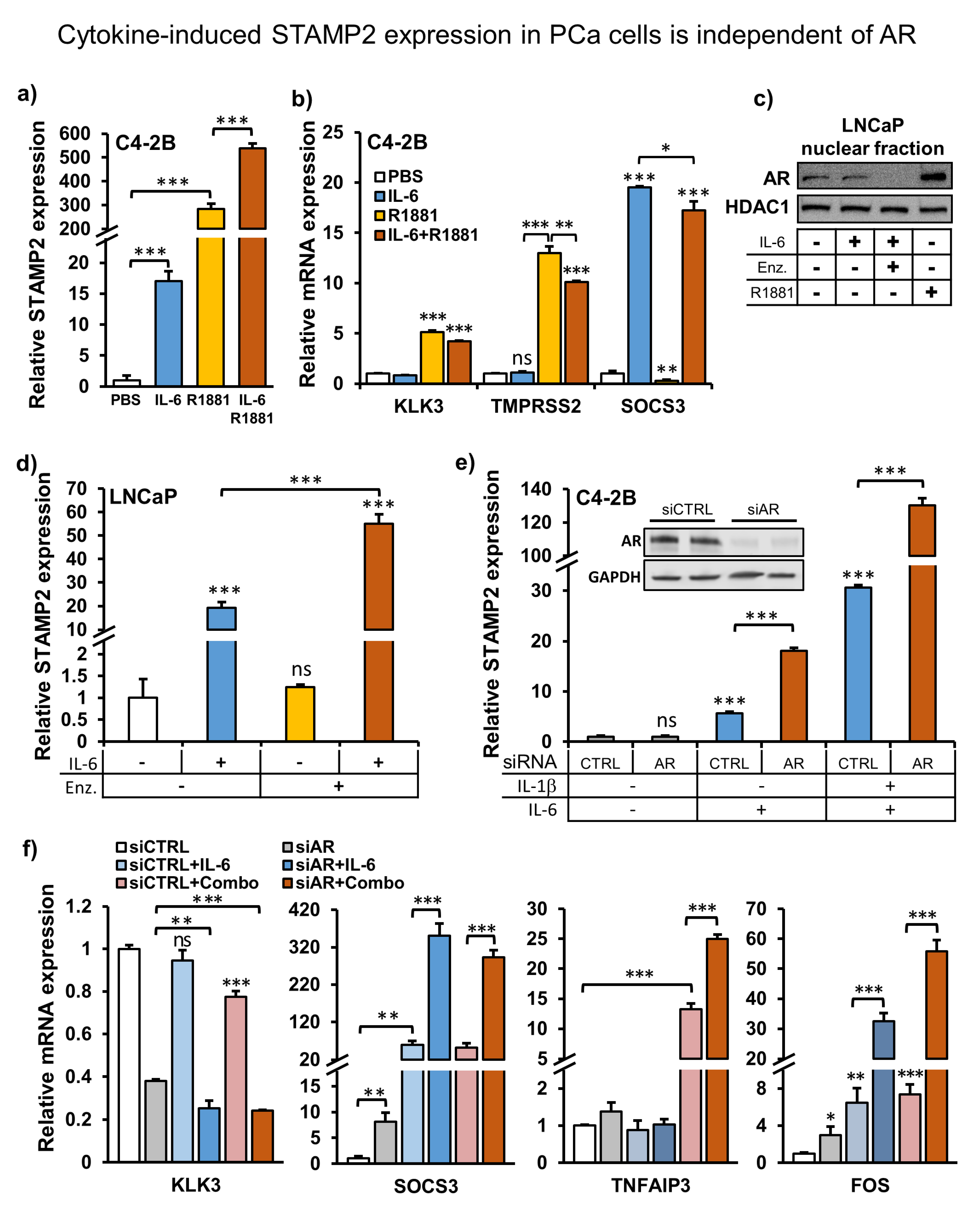
3.4. Cytokine-Induced STAMP2 Expression in PCa Cells Is Independent of AR
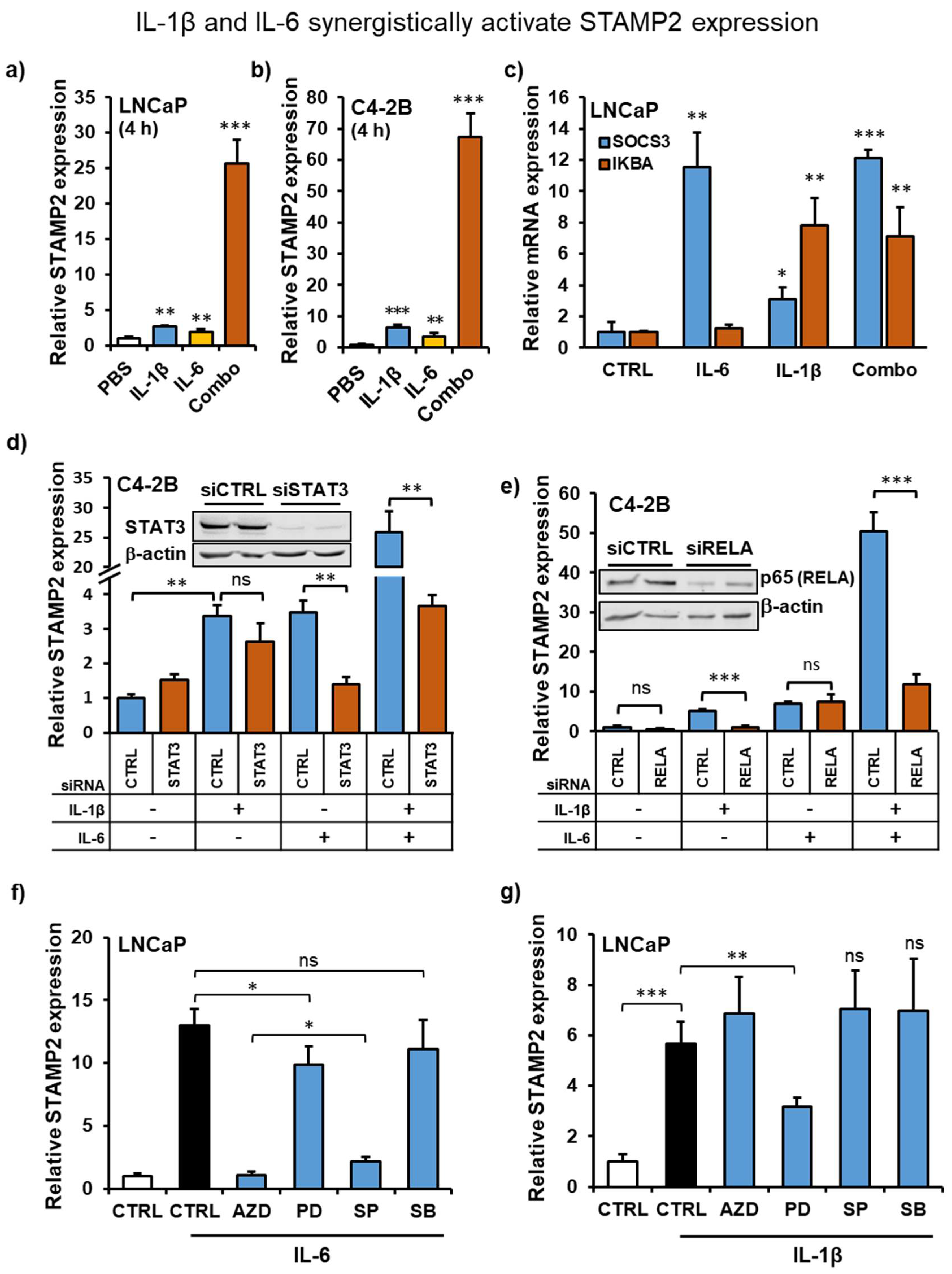
3.5. IL-1β and IL-6 Synergize to Increase STAMP2 Expression
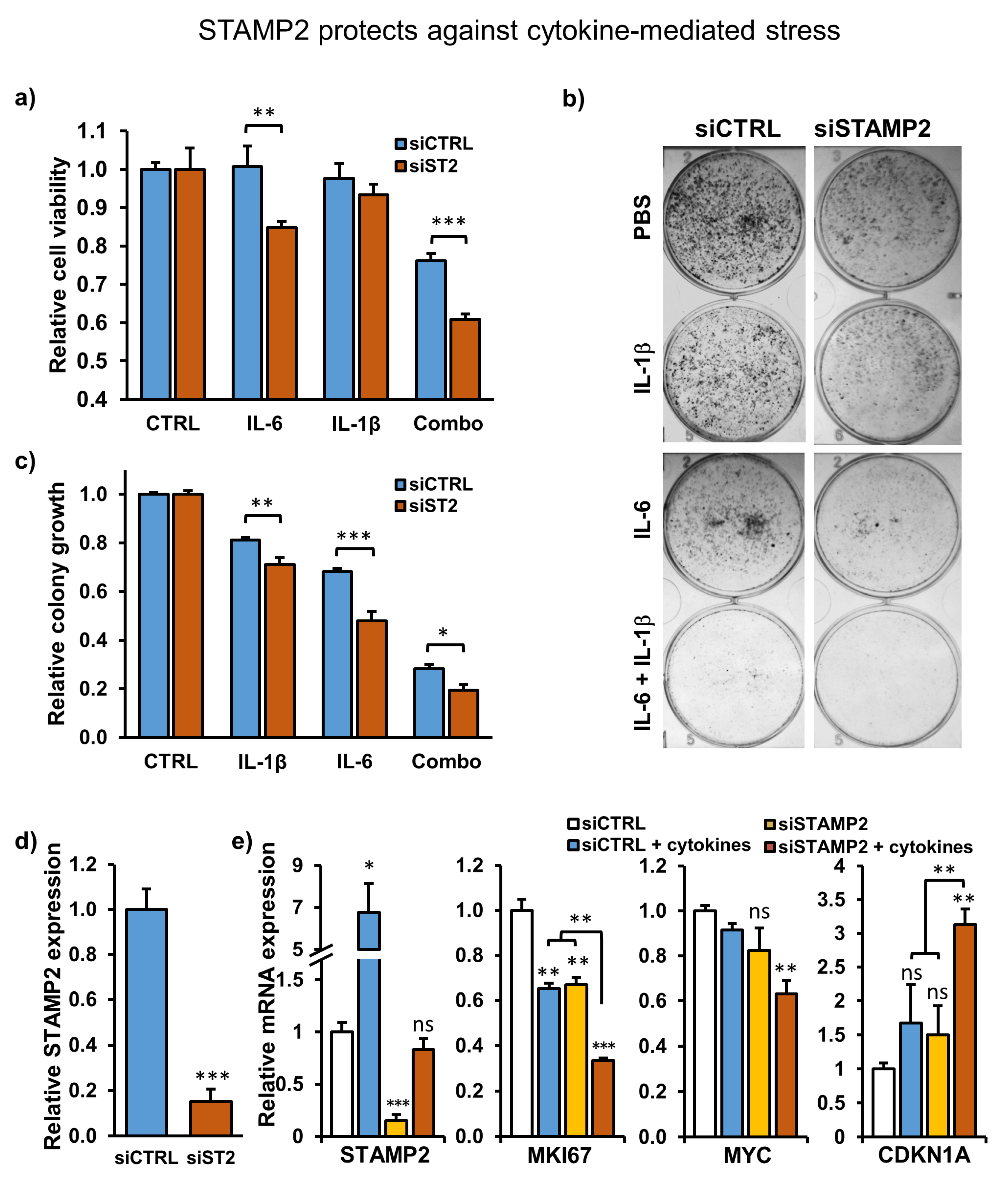
3.6. STAMP2 Expression Attenuates Cytokine-Induced Growth Inhibition in PCa Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, G.; Parker, C.; Eeles, R.A.; Schroder, F.; Tomlins, S.A.; Tannock, I.; Drake, C.G.; de Bono, J.S. Prostate cancer. Lancet 2016, 387, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumanasuriya, S.; de Bono, J. Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer-A Review of Current Therapies and Future Promise. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a030635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bono, J.S.; Guo, C.; Gurel, B.; de Marzo, A.M.; Sfanos, K.S.; Mani, R.S.; Gil, J.; Drake, C.G.; Alimonti, A. Prostate carcinogenesis: Inflammatory storms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.; Santi, R.; Tamanini, I.; Galli, I.C.; Perletti, G.; Bjerklund Johansen, T.E.; Nesi, G. Current Knowledge of the Potential Links between Inflammation and Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasner, A.; Karin, M. Immune Infiltration and Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfanos, K.S.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Nelson, W.G.; de Marzo, A.M. The inflammatory microenvironment and microbiome in prostate cancer development. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLennan, G.T.; Eisenberg, R.; Fleshman, R.L.; Taylor, J.M.; Fu, P.; Resnick, M.I.; Gupta, S. The influence of chronic inflammation in prostatic carcinogenesis: A 5-year followup study. J. Urol. 2006, 176, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellsten, R.; Lilljebjorn, L.; Johansson, M.; Leandersson, K.; Bjartell, A. The STAT3 inhibitor galiellalactone inhibits the generation of MDSC-like monocytes by prostate cancer cells and decreases immunosuppressive and tumorigenic factors. Prostate 2019, 79, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, D.C.; Shevde, L.A. The Tumor Microenvironment Innately Modulates Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouraoui, Y.; Ricote, M.; Garcia-Tunon, I.; Rodriguez-Berriguete, G.; Touffehi, M.; Rais, N.B.; Fraile, B.; Paniagua, R.; Oueslati, R.; Royuela, M. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and prostate-specific antigen in hyperplasia and human prostate cancer. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2008, 32, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, R.; Bryce, S.D.; Roome, C.; Dussupt, V.; Droop, A.; Lang, S.H.; Berry, P.A.; Hyde, C.F.; Lewis, J.L.; Stower, M.J.; et al. Gene expression profiling of human prostate cancer stem cells reveals a pro-inflammatory phenotype and the importance of extracellular matrix interactions. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Kattan, M.W.; Traxel, E.; Andrews, B.; Zhu, K.; Wheeler, T.M.; Slawin, K.M. Association of pre- and postoperative plasma levels of transforming growth factor beta(1) and interleukin 6 and its soluble receptor with prostate cancer progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1992–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, J.; Tachibana, M.; Horiguchi, Y.; Oya, M.; Ohigashi, T.; Asakura, H.; Murai, M. Serum interleukin 6 as a prognostic factor in patients with prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2702–2706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, A.; Herrmann, A.; Cherryholmes, G.; Kowolik, C.; Buettner, R.; Pal, S.; Yu, H.; Muller-Newen, G.; Jove, R. Loss of androgen receptor expression promotes a stem-like cell phenotype in prostate cancer through STAT3 signaling. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiro, N.; Bermudez-Fernandez, S.; Fernandez-Garcia, B.; Atienza, S.; Beridze, N.; Escaf, S.; Vizoso, F.J. Analysis of the expression of interleukins, interferon beta, and nuclear factor-kappa B in prostate cancer and their relationship with biochemical recurrence. J. Immunother. 2014, 37, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staal, J.; Beyaert, R. Inflammation and NF-kappaB Signaling in Prostate Cancer: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Cells 2018, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, C.G.; Korkmaz, K.S.; Kurys, P.; Elbi, C.; Wang, L.; Klokk, T.I.; Hammarstrom, C.; Troen, G.; Svindland, A.; Hager, G.L.; et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of STAMP2, an androgen-regulated six transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4934–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauss, G.H.; Kleven, M.D.; Sendamarai, A.K.; Fleming, M.D.; Lawrence, C.M. The crystal structure of six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 (Steap4), a ferri/cuprireductase, suggests a novel interdomain flavin-binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20668–20682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleven, M.D.; Dlakic, M.; Lawrence, C.M. Characterization of a single b-type heme, FAD, and metal binding sites in the transmembrane domain of six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate (STEAP) family proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 22558–22569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterheert, W.; van Bezouwen, L.S.; Rodenburg, R.N.P.; Granneman, J.; Forster, F.; Mattevi, A.; Gros, P. Cryo-EM structures of human STEAP4 reveal mechanism of iron(III) reduction. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, L.; Qu, S.; Sheng, X.; Kristian, A.; Maelandsmo, G.M.; Pallmann, N.; Yuca, E.; Tekedereli, I.; Gorgulu, K.; et al. STAMP2 increases oxidative stress and is critical for prostate cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Freyhaus, H.; Calay, E.S.; Yalcin, A.; Vallerie, S.N.; Yang, L.; Calay, Z.Z.; Saatcioglu, F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Stamp2 controls macrophage inflammation through nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate homeostasis and protects against atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Xing, X.; Beamer, M.A.; Swindell, W.R.; Sarkar, M.K.; Roberts, L.W.; Voorhees, J.J.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Harms, P.W.; Johnston, A.; et al. Six-transmembrane epithelial antigens of the prostate comprise a novel inflammatory nexus in patients with pustular skin disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Matsumoto, I.; Iwanami, K.; Inoue, A.; Minami, R.; Umeda, N.; Kanamori, A.; Ochiai, N.; Miyazawa, K.; Sugihara, M.; et al. Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate4 (STEAP4) is a tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein that regulates IL-6, IL-8, and cell proliferation in synovium from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2012, 22, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Matsumoto, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Umeda, N.; Takai, C.; Kawaguchi, H.; Ebe, H.; Yoshida, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Segawa, S.; et al. TIARP attenuates autoantibody-mediated arthritis via the suppression of neutrophil migration by reducing CXCL2/CXCR2 and IL-6 expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralisch, S.; Sommer, G.; Weise, S.; Lipfert, J.; Lossner, U.; Kamprad, M.; Schrock, K.; Bluher, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Fasshauer, M. Interleukin-1beta is a positive regulator of TIARP/STAMP2 gene and protein expression in adipocytes in vitro. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, A.; Matsumoto, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Iwanami, K.; Kanamori, A.; Ochiai, N.; Goto, D.; Ito, S.; Sumida, T. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced adipose-related protein expression in experimental arthritis and in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellen, K.E.; Fucho, R.; Gregor, M.F.; Furuhashi, M.; Morgan, C.; Lindstad, T.; Vaillancourt, E.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Saatcioglu, F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Coordinated regulation of nutrient and inflammatory responses by STAMP2 is essential for metabolic homeostasis. Cell 2007, 129, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klokk, T.I.; Kilander, A.; Xi, Z.; Waehre, H.; Risberg, B.; Danielsen, H.E.; Saatcioglu, F. Kallikrein 4 is a proliferative factor that is overexpressed in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5221–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, X.; Nenseth, H.Z.; Qu, S.; Kuzu, O.F.; Frahnow, T.; Simon, L.; Greene, S.; Zeng, Q.; Fazli, L.; Rennie, P.S.; et al. IRE1alpha-XBP1s pathway promotes prostate cancer by activating c-MYC signaling. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massie, C.E.; Lynch, A.; Ramos-Montoya, A.; Boren, J.; Stark, R.; Fazli, L.; Warren, A.; Scott, H.; Madhu, B.; Sharma, N.; et al. The androgen receptor fuels prostate cancer by regulating central metabolism and biosynthesis. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 2719–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleutjens, K.B.; van der Korput, H.A.; van Eekelen, C.C.; van Rooij, H.C.; Faber, P.W.; Trapman, J. An androgen response element in a far upstream enhancer region is essential for high, androgen-regulated activity of the prostate-specific antigen promoter. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonen-Korkmaz, C.; Sevin, G.; Gokce, G.; Arun, M.Z.; Yildirim, G.; Reel, B.; Kaymak, A.; Ogut, D. Analysis of tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced and nuclear factor kappaB-silenced LNCaP prostate cancer cells by RT-qPCR. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Wang, L.H.; Farrar, W.L. Interleukin 6 activates androgen receptor-mediated gene expression through a signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-dependent pathway in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2132–2135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.A.; Patel, V.; Gwede, M.; Morgado, M.; Tomasevich, K.; Fong, E.L.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Delk, N.A. IL-1beta induces p62/SQSTM1 and represses androgen receptor expression in prostate cancer cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2014, 115, 2188–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.; Lee, O.Y.; Park, Y.; Seo, M.W.; Lee, D.S. IL-1beta induces IL-6 production and increases invasiveness and estrogen-independent growth in a TG2-dependent manner in human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spooren, A.; Mestdagh, P.; Rondou, P.; Kolmus, K.; Haegeman, G.; Gerlo, S. IL-1beta potently stabilizes IL-6 mRNA in human astrocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, S.; Chosa, N.; Ishisaki, A.; Naruishi, K. Enhancement of gingival inflammation induced by synergism of IL-1beta and IL-6. Biomed. Res. 2013, 34, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culig, Z.; Puhr, M. Interleukin-6 and prostate cancer: Current developments and unsolved questions. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2018, 462, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebe, C.; Ghiringhelli, F. Interleukin-1beta and Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Bredell, B.X.; Anderson, E.R.; Martin, A.; Mays, C.; Nagao-Kitamoto, H.; Huang, S.; Gyorffy, B.; Greenson, J.K.; Hardiman, K.; et al. Quantitative proteomics identifies STEAP4 as a critical regulator of mitochondrial dysfunction linking inflammation and colon cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9608–E9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallmann, N.; Livgard, M.; Tesikova, M.; Zeynep Nenseth, H.; Akkus, E.; Sikkeland, J.; Jin, Y.; Koc, D.; Kuzu, O.F.; Pradhan, M.; et al. Regulation of the unfolded protein response through ATF4 and FAM129A in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6301–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkeland, J.; Sheng, X.; Jin, Y.; Saatcioglu, F. STAMPing at the crossroads of normal physiology and disease states. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2016, 425, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y.; Arya, A.; Naema, A.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Looi, C.Y. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STATs) Proteins in Cancer and Inflammation: Functions and Therapeutic Implication. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.L.; Thaper, D.; Zoubeidi, A. The Multifaceted Roles of STAT3 Signaling in the Progression of Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2014, 6, 829–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, D.; Ozen, M.; Ittmann, M. Interleukin-6 is an autocrine growth factor in human prostate cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culig, Z.; Bartsch, G.; Hobisch, A. Interleukin-6 regulates androgen receptor activity and prostate cancer cell growth. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2002, 197, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handle, F.; Puhr, M.; Schaefer, G.; Lorito, N.; Hoefer, J.; Gruber, M.; Guggenberger, F.; Santer, F.R.; Marques, R.B.; van Weerden, W.M.; et al. The STAT3 Inhibitor Galiellalactone Reduces IL6-Mediated AR Activity in Benign and Malignant Prostate Models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 2722–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lou, W.; Cui, Y.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C. Inhibition of constitutively active Stat3 reverses enzalutamide resistance in LNCaP derivative prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2014, 74, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Bruchovsky, N.; Sadar, M.D. Activation of the androgen receptor N-terminal domain by interleukin-6 via MAPK and STAT3 signal transduction pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 7076–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traish, A.; Bolanos, J.; Nair, S.; Saad, F.; Morgentaler, A. Do Androgens Modulate the Pathophysiological Pathways of Inflammation? Appraising the Contemporary Evidence. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debelec-Butuner, B.; Alapinar, C.; Varisli, L.; Erbaykent-Tepedelen, B.; Hamid, S.M.; Gonen-Korkmaz, C.; Korkmaz, K.S. Inflammation-mediated abrogation of androgen signaling: An in vitro model of prostate cell inflammation. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinen, M.; Niskanen, E.A.; Kaikkonen, M.U.; Palvimo, J.J. Crosstalk between androgen and pro-inflammatory signaling remodels androgen receptor and NF-kappaB cistrome to reprogram the prostate cancer cell transcriptome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, K.; Fang, L.Y.; Mizokami, A.; Namiki, M.; Li, L.; Lin, W.J.; Chang, C. Targeting the androgen receptor with siRNA promotes prostate cancer metastasis through enhanced macrophage recruitment via CCL2/CCR2-induced STAT3 activation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1383–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tong, D.; Liu, G.; Xu, J.; Do, K.; Geary, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Metformin reverses prostate cancer resistance to enzalutamide by targeting TGF-beta1/STAT3 axis-regulated EMT. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Don-Doncow, N.; Marginean, F.; Coleman, I.; Nelson, P.S.; Ehrnstrom, R.; Krzyzanowska, A.; Morrissey, C.; Hellsten, R.; Bjartell, A. Expression of STAT3 in Prostate Cancer Metastases. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.; Wasiliew, P.; Kracht, M. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) pathway. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, cm1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobisch, A.; Ramoner, R.; Fuchs, D.; Godoy-Tundidor, S.; Bartsch, G.; Klocker, H.; Culig, Z. Prostate cancer cells (LNCaP) generated after long-term interleukin 6 (IL-6) treatment express IL-6 and acquire an IL-6 partially resistant phenotype. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 2941–2948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pihlstrøm, N.; Jin, Y.; Nenseth, Z.; Kuzu, O.F.; Saatcioglu, F. STAMP2 Expression Mediated by Cytokines Attenuates Their Growth-Limiting Effects in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071579
Pihlstrøm N, Jin Y, Nenseth Z, Kuzu OF, Saatcioglu F. STAMP2 Expression Mediated by Cytokines Attenuates Their Growth-Limiting Effects in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2021; 13(7):1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071579
Chicago/Turabian StylePihlstrøm, Nicklas, Yang Jin, Zeynep Nenseth, Omer F. Kuzu, and Fahri Saatcioglu. 2021. "STAMP2 Expression Mediated by Cytokines Attenuates Their Growth-Limiting Effects in Prostate Cancer Cells" Cancers 13, no. 7: 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071579
APA StylePihlstrøm, N., Jin, Y., Nenseth, Z., Kuzu, O. F., & Saatcioglu, F. (2021). STAMP2 Expression Mediated by Cytokines Attenuates Their Growth-Limiting Effects in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancers, 13(7), 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071579




