Solitary Fibrous Tumor/Hemangiopericytoma Metastasizes Extracranially, Associated with Altered Expression of WNT5A and MMP9
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Gene Expression Assay Using the NanoString nCounter Analysis System
2.3. Pathway Dysregulation and Differentially Expressed Gene Analysis
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Selected SFT/HPC Cases
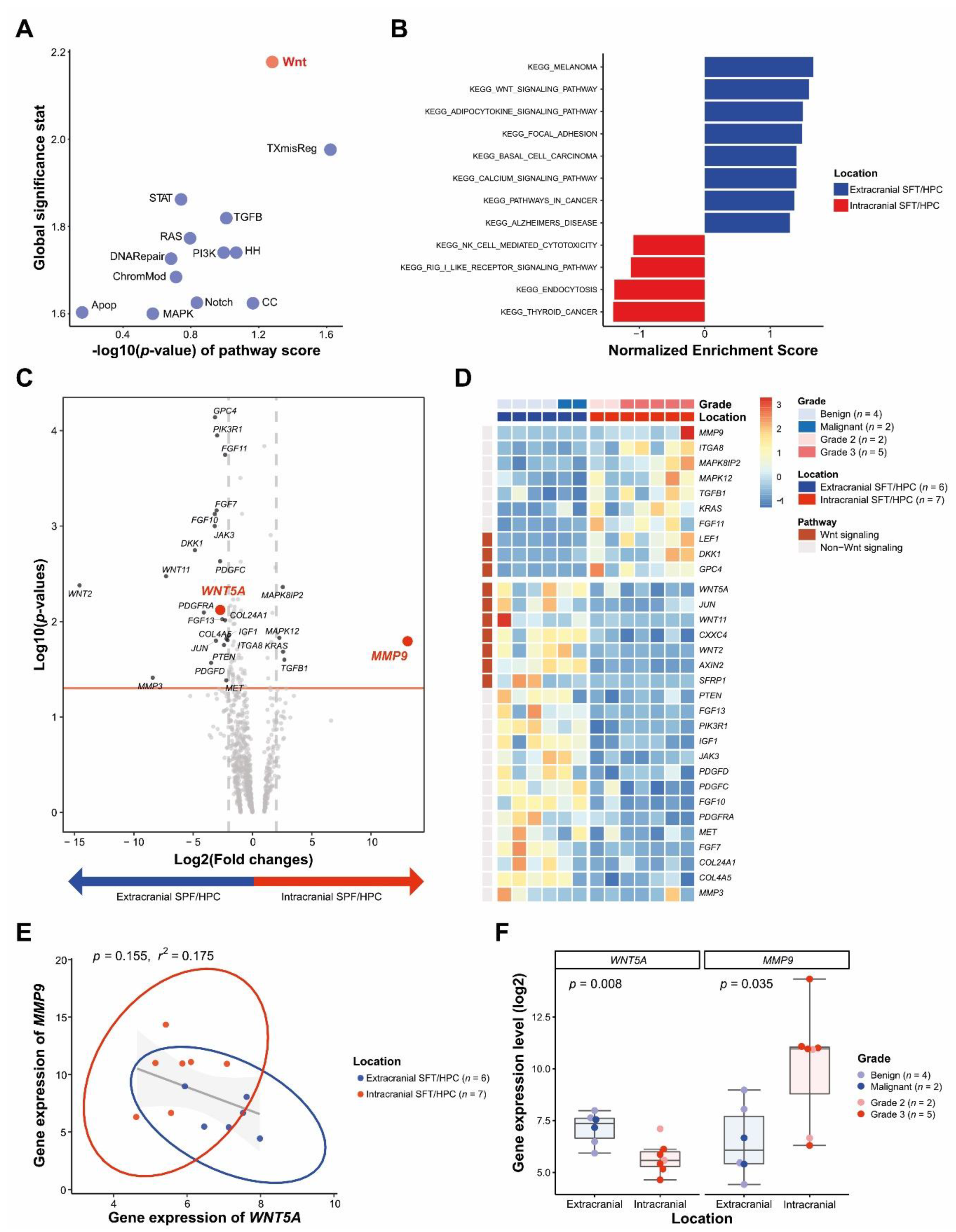
3.2. DEGs between icSFT/HPC and exSFT/HPC by Pan-Cancer Pathway Panel Assay
3.3. Differential WNT5A and MMP9 Protein Levels in icSFT/HPC and exSFT/HPC
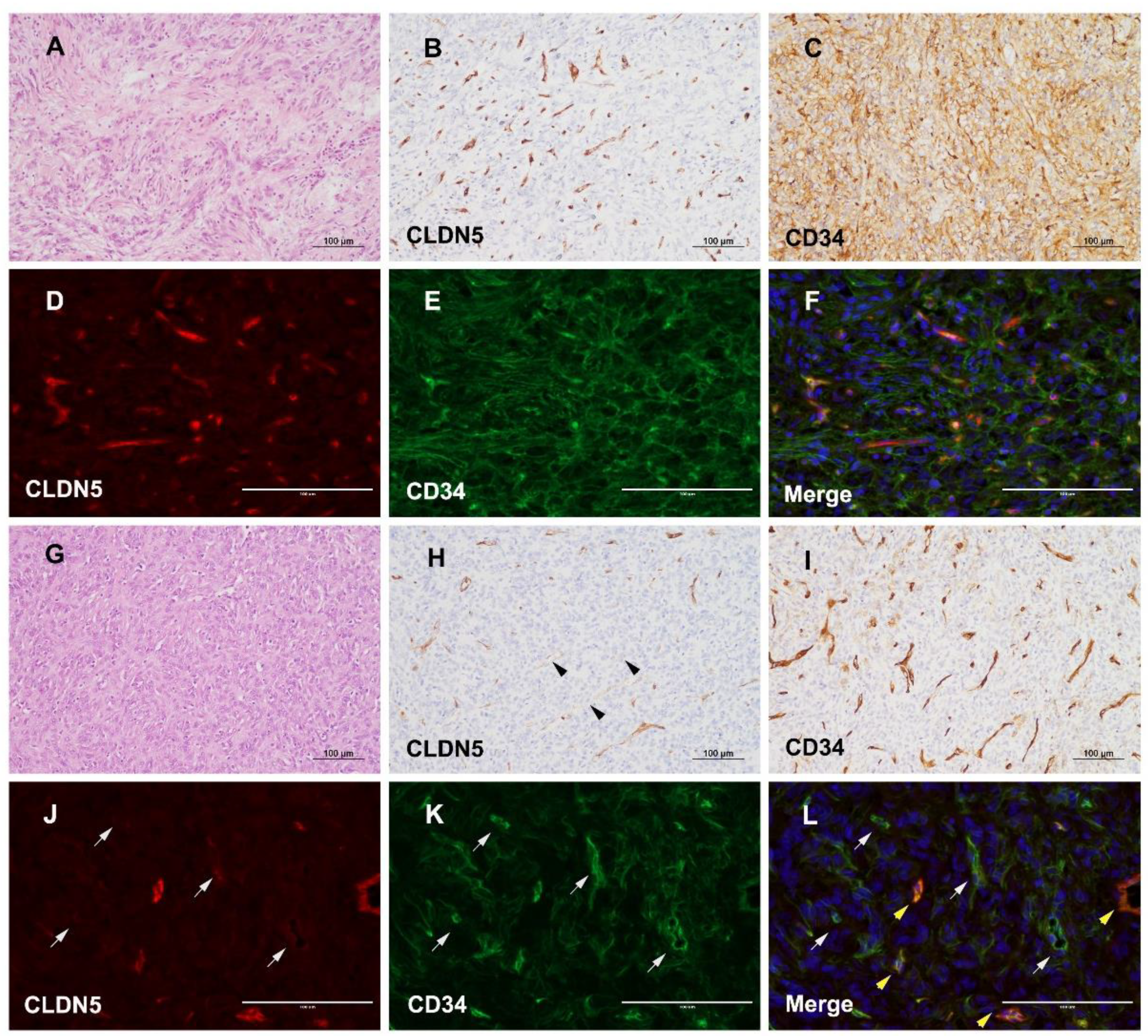
3.4. Different Expression of CLDN5 and CD34 in icSFT/HPC and exSFT/HPC
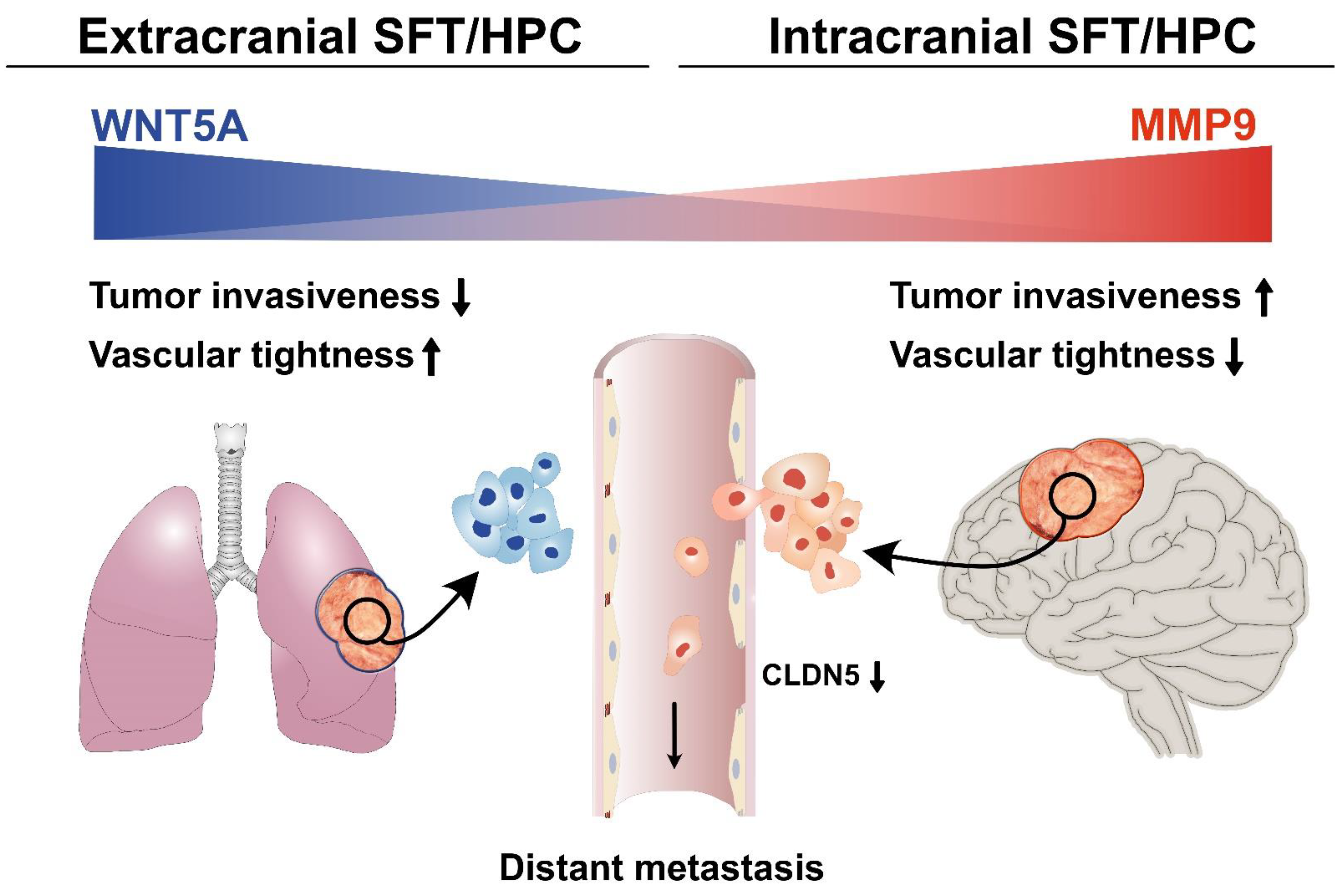
3.5. Reduced and Enhanced Expression of WNT5A and MMP9 in Extracranial Metastatic Lesions of icSFT/HPC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Claudin-5 | CLDN5 |
| Differentially expressed genes | DEG |
| Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded | FFPE |
| Gene set enrichment analysis | GSEA |
| Immunohistochemistry | IHC |
| Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes | KEGG |
| Matrix metalloproteinase-9 | MMP9 |
| Solitary fibrous tumor/hemangiopericytoma | SFT/HPC |
References
- Dilani, L.; Valerie, A.W.; Ian, A.C. Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours. In WHO Classification of Tumours, 5th ed.; Antonescu, C.R., Bridge, J.A., Cunha, I.W., Dei Tos, A.P., Fletcher, C.D., Folpe, A.L., Goldblum, J.R., Hornick, J.L., Miettinen, M., Oda, Y., Eds.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2020; pp. 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- De Saint Aubain Somerhausen, N.; Rubin, B.P.; Fletcher, C.D. Myxoid solitary fibrous tumor: A study of seven cases with emphasis on differential diagnosis. Mod. Pathol. 1999, 12, 463–471. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Han, A. Fat-forming solitary fibrous tumor of the kidney: A case report and literature review. Int J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 8632–8635. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guillou, L.; Gebhard, S.; Coindre, J.M. Orbital and extraorbital giant cell angiofibroma: A giant cell-rich variant of solitary fibrous tumor? Clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of a series in favor of a unifying concept. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2000, 24, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collini, P.; Negri, T.; Barisella, M.; Palassini, E.; Tarantino, E.; Pastorino, U.; Gronchi, A.; Stacchiotti, S.; Pilotti, S. High-grade sarcomatous overgrowth in solitary fibrous tumors: A clinicopathologic study of 10 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, J.M.; Fletcher, C.D. Expanding the spectrum of malignant progression in solitary fibrous tumors: A study of 8 cases with a discrete anaplastic component—Is this dedifferentiated SFT? Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009, 33, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thway, K.; Hayes, A.; Ieremia, E.; Fisher, C. Heterologous osteosarcomatous and rhabdomyosarcomatous elements in dedifferentiated solitary fibrous tumor: Further support for the concept of dedifferentiation in solitary fibrous tumor. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 17, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, P.C.; Scheithauer, B.W. 10. Tumors and tumor-like lesions of mesenchymal tissue. In Tumors of the Central Nervous System: AFIP Atlas of Tumor Pathology, 1st ed.; Burger, P.C., Scheithauer, B.W., Eds.; American Registry of Pathology: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 363–408. [Google Scholar]
- Pierscianek, D.; Michel, A.; Hindy, N.E.; Keyvani, K.; Dammann, P.; Oezkan, N.; Mueller, O.; Sure, U.; Zhu, Y. Activation of multiple angiogenic signaling pathways in hemangiopericytoma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2016, 33, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demicco, E.G.; Wani, K.; Fox, P.S.; Bassett, R.L.; Young, E.D.; Lev, D.; Aldape, K.D.; Lazar, A.J.; Wang, W.L. Histologic variability in solitary fibrous tumors reflects angiogenic and growth factor signaling pathway alterations. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatva, E.; Böhling, T.; Jääskeläinen, J.; Persico, M.G.; Haltia, M.; Alitalo, K. Vascular growth factors and receptors in capillary hemangioblastomas and hemangiopericytomas. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 148, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perry, A.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Nascimento, A.G. The immunophenotypic spectrum of meningeal hemangiopericytoma: A comparison with fibrous meningioma and solitary fibrous tumor of meninges. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1997, 21, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, E.; Kurimoto, M.; Fukuda, O.; Takahashi, C.; Nagai, S.; Oya, T.; Endo, S. Recurrent intracranial solitary fibrous tumor initially diagnosed as hemangiopericytoma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2007, 24, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shidoh, S.; Yoshida, K.; Takahashi, S.; Mikami, S.; Mukai, M.; Kawase, T. Parasagittal solitary fibrous tumor resembling hemangiopericytoma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2010, 27, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielecki, J.; Crago, A.M.; Rosenberg, M.; O’Connor, R.; Walker, S.R.; Ambrogio, L.; Auclair, D.; McKenna, A.; Heinrich, M.C.; Frank, D.A.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies a recurrent NAB2-STAT6 fusion in solitary fibrous tumors. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.R.; Wu, Y.M.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Cao, X.; Lonigro, R.J.; Sung, Y.S.; Chen, C.L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Su, F.; et al. Identification of recurrent NAB2-STAT6 gene fusions in solitary fibrous tumor by integrative sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, V.Y.; Fletcher, C.D. WHO classification of soft tissue tumours: An update based on the 2013 (4th) edition. Pathology 2014, 46, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, C.; Rushing, E.J.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Bouvier, C.; Figarella-Branger, D.; von Deimling, A.; Wesseling, P.; Antonescu, C.R. Solitary fibrous tumor/hemangiopericytoma. In WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System, 4th ed.; Louis, D.N., Ohgaki, H., Wiestler, O.D., Cavenee, W.K., Eds.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2016; pp. 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, C.; Kang, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, K.P.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Hong, S.M.; Hwang, J.J.; Jeong, S.Y.; Hwang, S.; Kim, K.H.; et al. Multiplexed gene expression profiling identifies the FGFR4 pathway as a novel biomarker in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38592–38601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstrale, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, M.G.; Oh, S.J.; Ahn, E.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, T.Y.; Jung, S.; Kim, K.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Moon, K.S. Prognostic significance of E-cadherin and N-cadherin expression in Gliomas. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Ahn, E.J.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, O.; Joo, Y.E.; Bae, J.A.; Yoon, S.; Ryu, H.H.; Jung, S.; Kim, K.K.; et al. KITENIN promotes glioma invasiveness and progression, associated with the induction of EMT and stemness markers. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3240–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asem, M.S.; Buechler, S.; Wates, R.B.; Miller, D.L.; Stack, M.S. Wnt5a Signaling in Cancer. Cancers 2016, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wend, P.; Holland, J.D.; Ziebold, U.; Birchmeier, W. Wnt signaling in stem and cancer stem cells. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mlodzik, M. Wnt-Frizzled/planar cell polarity signaling: Cellular orientation by facing the wind (Wnt). Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 31, 623–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, C.A.; Jones, M.L.; Bernabeu, M.O.; Vion, A.C.; Barbacena, P.; Fan, J.; Mathivet, T.; Fonseca, C.G.; Ragab, A.; Yamaguchi, T.P.; et al. Non-canonical Wnt signalling modulates the endothelial shear stress flow sensor in vascular remodelling. Elife 2016, 5, e07727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, C.; Scholz, B.; Hu, J.; Srivastava, K.; Wojtarowicz, J.; Arnsperger, T.; Adams, R.H.; Boutros, M.; Augustin, H.G.; Augustin, I. Endothelial cell-derived non-canonical Wnt ligands control vascular pruning in angiogenesis. Development 2014, 141, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, I.; Suzuki, H.; Onishi, N.; Takada, R.; Kani, S.; Ohkawara, B.; Koshida, I.; Suzuki, K.; Yamada, G.; Schwabe, G.C.; et al. The receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 is involved in non-canonical Wnt5a/JNK signalling pathway. Genes Cells 2003, 8, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirone, P.; Lin, S.; Griesbach, H.L.; Zhang, Y.; Slusarski, D.C.; Crews, C.M. A role for planar cell polarity signaling in angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 2008, 11, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masckauchán, T.N.; Agalliu, D.; Vorontchikhina, M.; Ahn, A.; Parmalee, N.L.; Li, C.M.; Khoo, A.; Tycko, B.; Brown, A.M.; Kitajewski, J. Wnt5a signaling induces proliferation and survival of endothelial cells in vitro and expression of MMP-1 and Tie-2. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 5163–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.R.; Fortunato, I.C.; Fonseca, C.G.; Pezzarossa, A.; Barbacena, P.; Dominguez-Cejudo, M.A.; Vasconcelos, F.F.; Santos, N.C.; Carvalho, F.A.; Franco, C.A. Non-canonical Wnt signaling regulates junctional mechanocoupling during angiogenic collective cell migration. Elife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, E.; Visioli, A.; Giani, F.; Trivieri, N.; Palumbo, O.; Restelli, S.; Dezi, F.; Mazza, T.; Fusilli, C.; Legnani, F.; et al. Wnt5a Drives an Invasive Phenotype in Human Glioblastoma Stem-like Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuse, M.; Hirase, T.; Itoh, M.; Nagafuchi, A.; Yonemura, S.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S. Occludin: A novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M.; Itoh, M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artus, C.; Glacial, F.; Ganeshamoorthy, K.; Ziegler, N.; Godet, M.; Guilbert, T.; Liebner, S.; Couraud, P.O. The Wnt/planar cell polarity signaling pathway contributes to the integrity of tight junctions in brain endothelial cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piontek, J.; Winkler, L.; Wolburg, H.; Müller, S.L.; Zuleger, N.; Piehl, C.; Wiesner, B.; Krause, G.; Blasig, I.E. Formation of tight junction: Determinants of homophilic interaction between classic claudins. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandooren, J.; Van den Steen, P.E.; Opdenakker, G. Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9): The next decade. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 222–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a Cancer Biomarker and MMP-9 Biosensors: Recent Advances. Sensors 2018, 18, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Cui, J.; Brown, S.; Fridman, R.; Mobashery, S.; Strongin, A.Y.; Lipton, S.A. A highly specific inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-9 rescues laminin from proteolysis and neurons from apoptosis in transient focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6401–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Estrada, E.Y.; Thompson, J.F.; Liu, W.; Rosenberg, G.A. Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Ohashi, N.; Li, W.; Eckman, C.; Nguyen, J.H. Disruptions of occludin and claudin-5 in brain endothelial cells in vitro and in brains of mice with acute liver failure. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1914–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, J.-H.; Noh, M.-G.; Akanda, M.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.H.; Jung, T.-Y.; Jung, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Rhee, J.H.; Kim, K.-K.; et al. Solitary Fibrous Tumor/Hemangiopericytoma Metastasizes Extracranially, Associated with Altered Expression of WNT5A and MMP9. Cancers 2021, 13, 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051142
Hong J-H, Noh M-G, Akanda MR, Kim YJ, Kim SH, Jung T-Y, Jung S, Lee J-H, Rhee JH, Kim K-K, et al. Solitary Fibrous Tumor/Hemangiopericytoma Metastasizes Extracranially, Associated with Altered Expression of WNT5A and MMP9. Cancers. 2021; 13(5):1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051142
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Jong-Hwan, Myung-Giun Noh, Md Rashedunnabi Akanda, Yeong Jin Kim, Se Hoon Kim, Tae-Young Jung, Shin Jung, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Joon Haeng Rhee, Kyung-Keun Kim, and et al. 2021. "Solitary Fibrous Tumor/Hemangiopericytoma Metastasizes Extracranially, Associated with Altered Expression of WNT5A and MMP9" Cancers 13, no. 5: 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051142
APA StyleHong, J.-H., Noh, M.-G., Akanda, M. R., Kim, Y. J., Kim, S. H., Jung, T.-Y., Jung, S., Lee, J.-H., Rhee, J. H., Kim, K.-K., Kim, S. S., Lee, K.-H., & Moon, K.-S. (2021). Solitary Fibrous Tumor/Hemangiopericytoma Metastasizes Extracranially, Associated with Altered Expression of WNT5A and MMP9. Cancers, 13(5), 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051142






