Simple Summary
Abundance of certain proteins such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and their growth factors on cancer cells is in part responsible for their uncontrolled growth. Compounds that selectively bind to such proteins have diagnostic and/or therapeutic implications. EGFR has four binding domains (I-IV). Most anti-EGFR therapeutic antibodies bind to domain III. Compounds that bind to other domains have implications not only for diagnosis but also for monitoring therapy response. We describe the development of a diagnostic agent to be used with positron emission tomography (PET) that binds to domain II of EGFR. We developed 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc antibody PET agent and evaluated its binding characteristics in cancer cells and mouse models. The presence of a domain III-binding antibody such as nimotuzumab did not inhibit the binding of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc, and vice versa. Therefore, 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc PET/CT can be used for diagnosis and monitoring therapy response in the presence of a domain III-binding agent.
Abstract
Epidermal growth factor receptor I (EGFR) is overexpressed in many cancers. The extracellular domain of EGFR has four binding epitopes (domains I- IV). All clinically approved anti-EGFR antibodies bind to domain III. Imaging agents that bind to domains other than domain III of EGFR are needed for accurate quantification of EGFR, patient selection for anti-EGFR therapeutics and monitoring of response to therapies. We recently developed a domain II-specific antibody fragment 8709. In this study, we have evaluated the in vitro and in vivo properties of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc (105 kDa). We conjugated 8709-scFv-Fc with the deferoxamine (DFO) chelator and radiolabeled the DFO-8970-scFv with 89Zr. We evaluated the binding of 89Zr-DFO-8709-scFv-Fc in EGFR positive and negative cell lines DLD-1, MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435, respectively, and in mouse xenograft models. Simultaneously, we have compared the binding of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc with 111In-nimotuzumab, a domain III anti-EGFR antibody. DFO-8709-scFv-Fc displayed similar cell binding specificity as 8709-scFv-Fc. Saturation cell binding assay and immunoreactive fraction showed that radiolabeling did not alter the binding of 8709-scFv-Fc. Biodistribution and microPET showed good uptake of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc in xenografts after 120 h post injection (p.i). and was domain-specific to EGFR domain II. 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc did not compete for binding in vitro and in vivo with a known domain III binder nimotuzumab. The results show that 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc is specific to domain II of EGFR making it favorable for quantification of EGFR in vivo, hence, patient selection and monitoring of response to treatment with anti-EGFR antibodies.
1. Introduction
Epidermal growth factor receptor I (EGFR) is a 170 kDa transmembrane cell-surface glycoprotein which belongs to the ErbB family. EGFR and its family members play a variety of roles in the aberrant growth, oncogenesis and tumor progression in different cancers and cell types [1,2]. Overexpression of EGFR is known to drive a subset of aggressive cancers, including squamous cell head and neck [3], glioma [4], non-small cell lung, colorectal [5], ovarian [2,6], breast [7] and cervical cancers. In addition, a crosstalk of this receptor with many other receptors including those from its subfamily causes resistance to targeted therapies [8,9]. Structurally, EGFR consists of an extracellular ligand-binding, transmembrane, and intracellular domains. The extracellular binding domain has four subdomains, domains I–IV. Ligands of EGFR (epidermal growth factor, amphiregulin, transforming growth factor receptor α) bind to EGFR initiating a homo- and hetero-dimerization which results in downstream signal activation of the receptor(s) [2].
Ex vivo quantification of EGFR using biopsy samples are inherently flawed because of the intra-and inter-lesion heterogeneity of tumors. It is also known that EGFR expression of tumors changes over time [10,11]. In vivo assessment techniques have several advantages over current ex vivo methods, including measuring EGFR expression over the entire tumor volume rather than just a section of the tumor, assessing the biologic availability of EGFR in vivo, evaluating effects of therapy on EGFR expression, and quantifying EGFR expression of all lesions in real time.
EGFR overexpression in a wide range of cancers makes it a validated target for imaging and therapy using monoclonal antibodies. A few anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies such as cetuximab, panitumumab, necitumumab and nimotuzumab are approved for treatment in different countries. These antibodies bind to domain III of EGFR [12,13,14,15]. Some of them have been radiolabeled with different isotopes for use as diagnostics. The clinical utility of 89Zr-cetuximab PET/CT in selecting patients that would benefit from treatment using an EGFR targeted monoclonal antibody was recently demonstrated in colorectal cancer patients by Menke-van der Houven van Oordt et al. [16]. Only patients with positive 89Zr-cetuximab PET/CT lesions showed clinical benefit with the therapeutic monoclonal antibody cetuximab. 89Zr-cetuximab and other domain III imaging agents can only be used for diagnosis and patient selection. They cannot be used to monitor response to treatment using anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies, since the imaging probe will compete for binding with the therapeutic antibody.
Therefore, there is strong interest to develop novel imaging agents that bind to epitopes/domains that are different from that of the therapeutic agent. A domain II binder can find applications in patient selection, diagnosis and monitoring of response to anti-EGFR treatments. For the first time, Miersch et al. recently engineered a domain II (8709-scFv-Fc) specific anti-EGFR antibody using phage display [1]. Anti-EGFR antibody 8709-scFv-Fc inimitably binds to domain II of EGFR with a high affinity and does not interfere with the binding of clinically available anti-EGFR therapeutic antibodies e.g., cetuximab [17]. The expression, purification and optical imaging of the 8709-scFv-Fc antibody fragment has been published [17].
Here, we have evaluated the in vitro and in vivo properties of 8709-scFv-Fc fragment radiolabeled with 89Zr via a deferoxamine (p-SCN-Bn-deferoxamine) chelator in EGFR overexpressing cell lines and mouse xenografts and controls. We present the in vitro cell binding characteristics as well as in vivo biodistribution, pharmacokinetics and microPET imaging in tumor-bearing mice. Our results show that 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc has the potential to be used for diagnosis, patient selection and treatment monitoring of EGFR-positive cancers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Antibody
Anti-EGFR antibody 8709-Fab was identified by phage display and converted to an scFv-Fc (8709-scFv-Fc) its expression, purification and fluorescent imaging has been published [17].
2.2. Cell Lines and Xenografts
EGFR positive DLD-1 (RRID:CVCL_0248) colorectal cancer, breast cancer MDA-MB-231 (RRID:CVCL_0062), and EGFR negative human melanoma MDA-MB-435 (RRID:CVCL_0417) cell lines were obtained from ATCC (Rockville, MD, USA). MDA-MB-435 cells are derived from M14 melanoma cells. Cells were propagated by serial passage in MEM/EBSS medium, supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Biochrom, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2. All human cell lines have been authenticated using STR profiling within the last three years. All experiments were performed with mycoplasma-free cells.
All animals used in imaging experiments were cared for and maintained under the supervision and guidelines of the University of Saskatchewan Animal Care Committee (UACC). All animal studies were approved by UACC in accordance with the guidelines set forth on the Use of Laboratory Animals (protocol # 20170084) [18]. Female CD-1 nude mice were obtained from Charles River Canada (St-Constant, Quebec) at 4 weeks of age and housed in a 12 h light, 12 h dark cycle in a temperature and humidity-controlled vivarium. Animals had libitum access to diet (Lab Diet, St. Louis, MO, USA) and water [18]. After one week of acclimatization, mice were subcutaneously injected with a suspension of 5–10 × 106 DLD-1, MDA-MB-231 or MDA-MB-435 cells in 100 μL of a 1:1 mixture of serum-free MEM/EBSS medium (HyClone Laboratories, Logan, UT, USA) and Matrigel matrix basement membrane (Discovery Laboware, Inc. Bedford, MA, USA) at the hind limb of each mouse. Xenograft was located in the right thigh of the hind leg of the mouse and tumor growth was followed with caliper measurements.
2.3. Conjugation of Antibodies with Bifunctional Chelators
Conjugation of 8709-scFv-Fc (domain I/II binder) was performed as reported earlier [19]. The excess unreacted chelator was removed by centrifugation using an Amicon Ultra-10 K (Burlington, MA, USA) molecular filtration device. The solution of DFO-8709-scFv-Fc was aliquoted and stored at −80 °C until further use after quality control. 8709-scFv-Fc and DFO-8709-scFv-Fc purities were determined using SEC-HPLC (Waters 2796 Bioseparations Module, Waters 2487 Dual λ Absorbance Detector, XBridge BEH 200A SEC 3.5 µm 7.8 × 300 mm column, Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA). The UV-Detector was set at 220 and 280 nm and the solvent system was PBS at a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min. Nimotuzumab (domain III binder) was conjugated with DOTA for labeling with 111In following lab protocol [18].
The analysis of MW and purity of conjugated antibody was performed on an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer using Agilent High Sensitivity Protein 250 Kit using the manufacturer’s protocol. The size and relative peak area were calculated using Agilent 2100 Expert software (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA, cat # 5067-1575).
Binding kinetics between the antibodies and recombinant monomeric EGFR were measure with ForteBio Octet RED384 (PALL Corporation, NY, USA). Antibodies were immobilized on anti-human FAB-CH1 sensors (18-5104, Forte Bio) according to manufacture’s instructions. The equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) was obtained using a 1 to 1 binding model with global fitting. Data analysis and curve fitting was performed using data analysis software 7.1.0.33 (Forte Bio, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Saturation binding flow cytometry was performed as described previously [17].
2.4. Production and Characterization of 89Zr-Oxalate
89Zr-oxalate was produced at the Saskatchewan Centre for Cyclotron Sciences (SCCS), University of Saskatchewan. Yttrium coated (10 mm diameter and 200 µm thickness) on the coin shaped niobium (24 mm diameter and 1 mm thickness) target supplied by ACSI, was irradiated with an incident beam energy of 17.8 MeV providing a degraded transmitted energy through an aluminum degrader of 12.8 MeV and a current of 40 µA for 2 h on an in-house beam-line on TR-24 cyclotron to produce 89Zr via the natY(p, n)89Zr reaction. During irradiation the target was cooled on the frontal side by Helium gas and on the back side by chilled water. After the irradiation, the target left on the target station for 2–3 h to allow decay of short-lived isotopes. Then target was released in the lead pig and transported to the hot cells in the lead shielded cart.
89Zr was separated as 89Zr-oxalate from the irradiated yttrium coin as described by Queern et al. [20]. Briefly, to a dissolution vessel charged with the irradiated target 2 N trace metal HCl (4 mL) was added slowly. The resulting solution was warmed to 80 °C for 20 min and cooled to room temperature before loading onto a pre-conditioned column of hydroxamate resin (100 mg). A dissolution vessel and target body rinsed with 2 N trace metal HCl (2 mL) and loaded onto hydroxamate resin. Then hydroxamate resin was rinsed with 2N HCl (14 mL) followed by traceselect water (10 mL). Finally, 89Zr was eluted with 1.5 mL of 1.0 M Oxalic acid
89Zr-oxalate was characterized for activity amount, half-life, radionuclidic purity, elemental impurities and specific activity. The final activity of purified 89Zr-oxalate was measured in the Capintec dose calibrator (CRC-55t PET). Specific activity was determined using a published method by Holland et al. [21] and the specific activity was found to be in the range of 673-1161 MBq/µmol. The 89Zr-oxalate solutions were tested for radionuclidic identity and purity using a high purity germanium (HPGe) detector (Ortec, Oak Ridge, TN, USA). The radiochemical purity was 99.99% and the identity was confirmed by the presence of 909 keV and 511 keV peaks. The ICP-MS analysis of 89Zr-oxalate solutions were performed at Saskatchewan Research Council, Saskatoon and elemental impurity levels were found to be always below 30 ppm and all batches met the QC release specifications.
2.5. Radiolabeling and Characterization of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc and 111In-Nimotuzumab
Radiolabeling of DFO-8709 conjugate with 89Zr-oxalate was performed as per the standard lab protocol [19]. After radiolabeling the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and an aliquot was injected onto SEC-HPLC (the same HPLC and solvent system as above) for radiochemical quality control and radiolabeling efficiency determination. Oxalate, HEPES and other impurities (less than 30 kDa) were removed from the crude reaction mixture by single centrifugation in spin columns (Amicon Ultra-4 Centrifugal Filter 30K NMCO, 4 mL, EMD Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) and sterilized by filtration with 0.22 µm hydrophilic PTFE membrane filter (Ultrafree-CL Centrifugal filter 4 mL, Millipore). The final solution was formulated in PBS. The recovery of the radiolabeled product was 60% for 89Zr-DFO-8709-scFv-Fc with a radiochemical purity of > 95% was used for in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Radiolabeling of DOTA-nimotuzumab conjugate with 111InCl3 was performed as per the standard lab protocol [18]. After labeling, the reaction was monitored using iTLC strip with 100 mM sodium citrate buffer (pH 5.0) as the mobile phase and analyzed using ScanRam (LabLogic, Brandon, FL, USA). 111In-labeled conjugates were purified using Amicon Ultra-4 centrifugal filters (10K, EMD Millipore) with PBS. The purity of the radiolabeled immunoconjugates were determined using size exclusion radio-HPLC and iTLC. A radiochemical purity (RCP) of more than 95% was considered good for in vitro and in vivo experiments.
2.6. In Vitro Binding
The in vitro saturation binding, immunoreactivity and domain specific binding of 89Zr-DFO-8709-scFv-Fc was determined in EGFR positive DLD-1 cells. A saturation radioligand binding assay was performed by incubating 0.5 million cells with increasing concentrations of radioimmunoconjugates (0.2–95 nmol/L in 100 μL PBS) for 4 h at 4 °C. Non-specific binding (NSB) was determined in a similar assay but in the presence of a 50-fold molar excess of unlabeled 8709-scFv-Fc (relative to the highest concentration of the radioimmunoconjugates). A non-linear regression analysis with one-site binding equation was used to determine KD using GraphPad Prism 6 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). The immunoreactive fraction of the radioimmunoconjugate was determined as described in Lindmo et al. [22].
Domain II specific binding was determined by a competitive binding experiment. Briefly, one million DLD-1 cells were transferred in 3 vials and incubated with 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc, but with slight modifications. The first vial was incubated only with 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc, second vial was initially incubated with cold 8709-scFv-Fc whose concentration was 50× the concentration of radiolabeled 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc. After 2 h of pre-incubation with unlabeled 8709-scFv-Fc, 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc was added to these cells. The third vial was incubated with unlabeled nimotuzumab whose concentration was 50 × the concentration of radiolabeled 89Zr8709-scFv-Fc. After 2 h pre-incubation with nimotuzumab, 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc was added to these cells. After incubation, the cells were centrifuged at 1200 rpm and supernatant was collected separately. This process was repeated 3 times to ensure complete removal of unbound 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc. After centrifugation the pellet was re-dissolved in PBS and samples were measured using gamma counter. Experiments were performed in triplicate using three different concentrations (50, 5 and 0.5 nM) of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc.
2.7. Biodistribution and Pharmacokinetics
Biodistribution studies were performed in athymic CD-1 nude mice bearing EGFR positive DLD-1, and EGFR negative MDA-MB-435 (control) xenografts (n = 3/group). Each mouse received a dose of with 10 ± 0.2 MBq of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc (20 µg, specific activity of 0.5 MBq/µg). Animals were sacrificed at 24 and 168 h post injection (p.i.) and different organs were harvested (blood, lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys, bladder, muscle, heart, brain, bones, thymus, pancreas, stomach, small, and large intestine) for biodistribution. The activity in the organs was measured using a gamma counter (2480 Perkin Elmer, Waltham MA, USA) and the tissue uptake was expressed as percentage of injected activity per gram (% IA/g).
The pharmacokinetics was determined in healthy Balb/c mice (n = 5/group). The animals were injected with 10 ± 0.0.1 MBq of the 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc via a tail vein and blood was collected at various time points from a saphenous vein in heparinized capillary tubes. Activity in the capillary tube was measured using a gamma counter and the blood volume was determined using a digital caliper, assuming the internal diameter of the tube. Radioactivity in blood activity was expressed as % IA/mL). All relevant pharmacokinetic parameters were determined using an exponential decay curve fitting from sigma plot using GraphPad Prism 6.
2.8. EGFR Domain Specific Imaging Using 111In-Nimotuzumab and 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc
In vivo evaluation of domain III binding of 111In-nimotuzumab was studied with two groups of mice (n = 3), one group bearing EGFR positive DLD-1 xenografts and other bearing EGFR negative MDA-MB-435 xenografts. Mice were injected with 15 ± 0.2 MBq of 111In-nimotuzumab (0.5 MBq/µg) via tail vein injection. Imaging was performed in mice injected with EGFR positive DLD-1 and EGFR negative MDA-MB-435 (control) xenografts. Imaging was performed at three different time points 24 h, 48 h, and 120 h p.i.
In vivo evaluation of domain II binding of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc was also studied with two groups of mice (n = 3), one group bearing EGFR positive DLD-1 xenograft and other bearing EGFR negative MDA-MB-435 xenograft. Mice were injected with 9 ± 0.2 MBq of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc via a tail vein. Imaging was performed at three different time points 24 h, 48 h, and 120 h p.i.
To understand site-specific domain II binding of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc, one group (n = 3) of mice were initially injected with 250 µg of non-radiolabeled nimotuzumab to block the domain III of EGFR leaving domain II available for 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc binding.
Simultaneously imaging of domain III and domain II was also studied following simultaneous injection of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc and 111In-nimotuzumab. Two groups of mice (n = 3) one group bearing EGFR positive DLD-1 xenograft and other bearing EGFR negative MDA-MB-435 xenograft were simultaneously injected with 9 ± 0.2 MBq of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc and 15 ± 0.2 MBq of 111In-nimotuzumab via tail vein injection.
To confirm domain II specificity, groups of mice (n = 3) bearing EGFR positive DLD-1 or MDA-MB-231 xenograft was initially injected with 250 ug (therapeutic dose) of unlabeled nimotuzumab to block domain III, followed by simultaneous injection with 9 ± 0.2 MBq of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc and/or 15 ± 0.2 MBq of 111In-nimotuzumab and microPET/SPECT/CT imaging.
PET/CT images were acquired at 24 h, 48 h, and 120 h p.i. using the Vector4CT scanner (MILabs B.V., Utrecht, The Netherlands). PET scans were acquired in a list-mode data format with a high-energy ultra-high resolution (HE-UHR-1.0 mm) mouse/rat pinhole collimator. Corresponding CT scans were acquired and images were reconstructed using a pixel-based order-subset expectation maximization (POS-EM) algorithm that included resolution recovery and compensation for distance-dependent pinhole sensitivity and were registered on CT and quantified using PMOD 3.8 software (PMOD Technologies Ltd., Zurich, Switzerland). SPECT/CT images were acquired using collimator and detector settings as described previously [19].
Tracer uptake was expressed as percentage injected activity (% IA) per cc of tissue volume (% IA/cc). All quantification data was reported as mean ± standard deviation within one animal study group. After imaging all mice were sacrificed for biodistribution. Activity in the organs was analyzed as percent injected activity per gram (% IA/g).
2.9. Statistical Analysis
All data was expressed as the mean ± SD or SEM of at least three independent experiments. Statistical comparisons between the experimental groups were performed by a t-test. Graphs were prepared and p values were calculated using GraphPad Prism (version 5.03). p values of less than 0.5 were considered significant.
2.10. Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
3. Results
3.1. Conjugation and Quality Control of Immunoconjugates
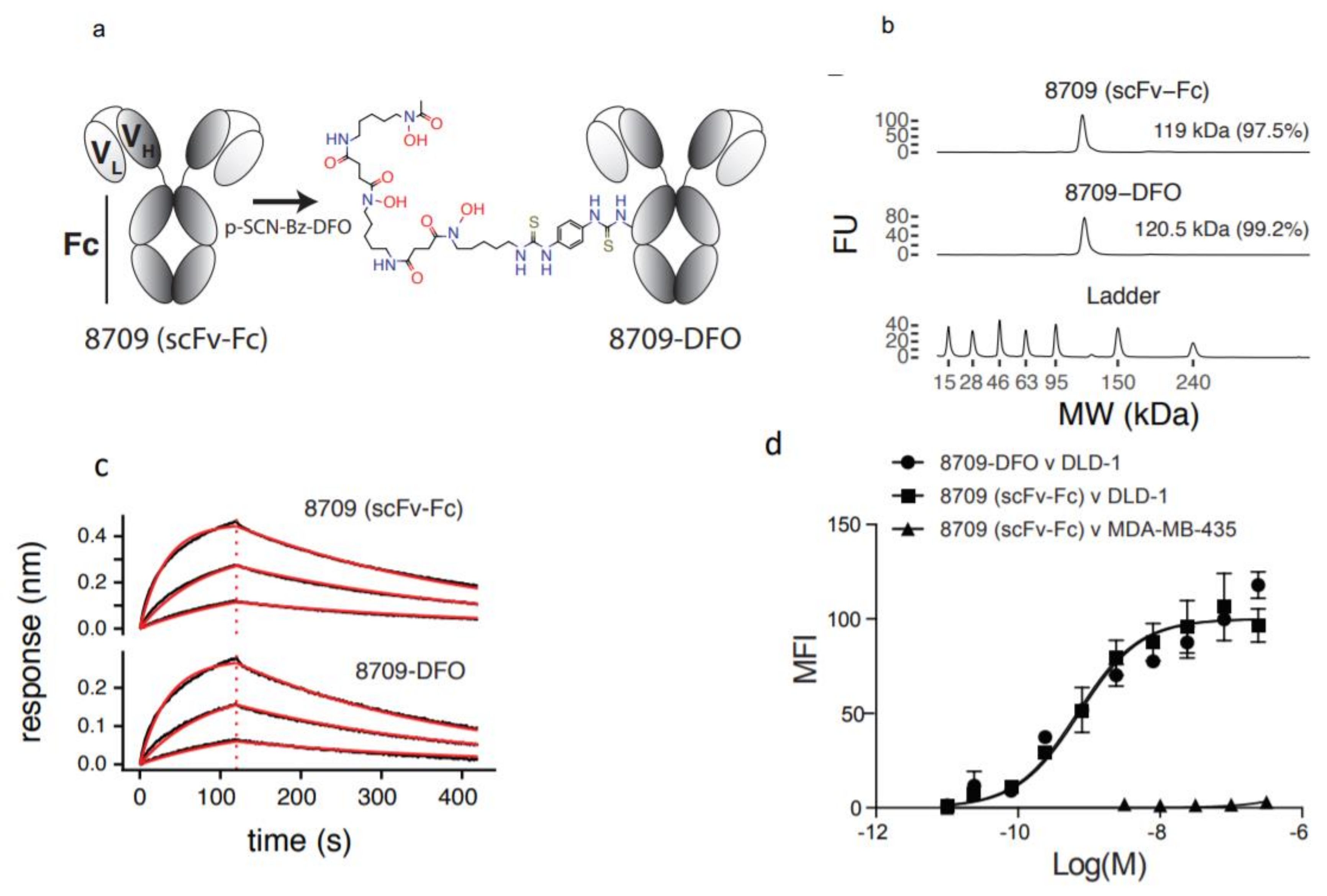
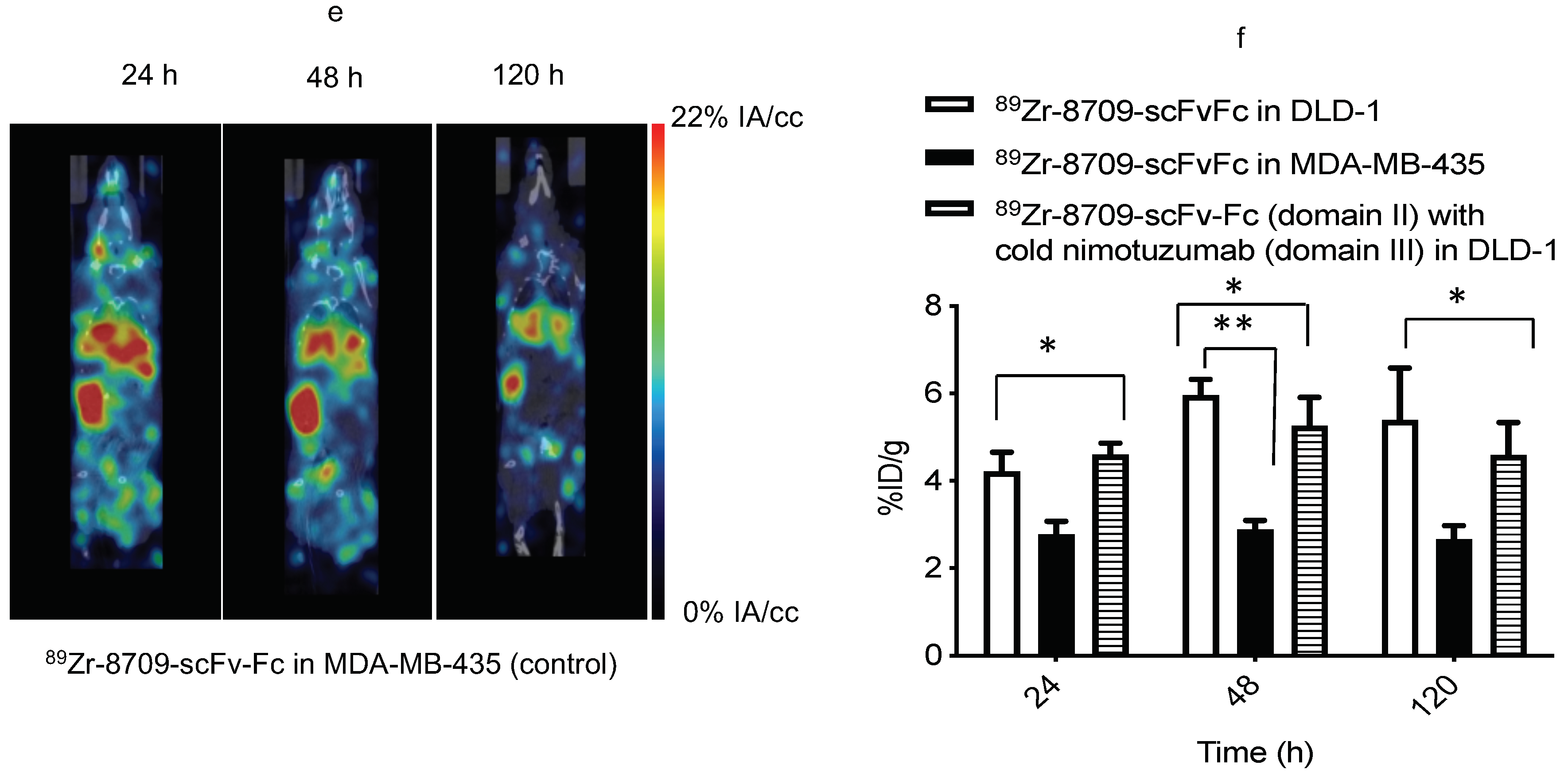
8709-scFv-Fc was conjugated to p-SCN-Bz-deferoxamine (DFO) resulting in 8709-DFO (Figure 1a). The resulting 8709-DFO was >99% pure, conjugation increased the molecular weight of the parent compound from 119 kDa to 120.5 kDa representing the incorporation of an average of 2 DFO molecules per antibody (Figure 1b). Binding to recombinant human EGFR was 1.5 fold worse when conjugated to DFO (KDBLI(8709) = 55 ± 1 nM versus KDBLI(8709-DFO) = 83 ± 10 nM) (Figure 1c). The binding constant to DLD-1 cells was not significantly affected by conjugation with DFO (KDflow(8709) = 72 ± 5 nM, KDflow(8709-DFO) = 97 ± 15 nM, p-value > 0.5) (Figure 1d). 8709 bound the control cell-line MDA-MB-435 with less than 3 ± 2% (Figure 1d).
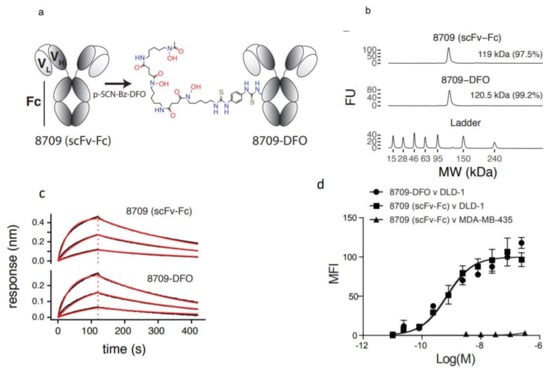
Figure 1.
Characterization of DFO-8709-scFv-Fc. (a) Conjugation of 8709-scFv-Fc to DFO, (b) Bioanalyzer analysis for 8709-scFv-Fc and 8709-scFv-Fc-DFO, Bioanalyzer shows ladder (L), 8709-scFv-Fc, DFO-8709-scFv-Fc (c) biolayer interferometry (BLI) (d) Flow cytometry analysis of 8709-scFv-Fc and DFO-8709-scFv-Fc in EGFR positive DLD-1 and EGFR negative MDA-MB-435 cell lines.
3.2. Radiolabeling of 89Zr-DFO-8709 ScFv-Fc and 111In-Nimotuzumab
Radiolabeling of 8709-scFv-Fc with 89Zr and nimotuzumab with 111In was performed as per the standard laboratory protocol [18,19]. Radiolabeling was monitored after 30 min using iTLC. Radiochemical yield of >95% was obtained for 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc within 2 h. The radiochemical purity for 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc was >98% as observed by iTLC. Purity of radiolabeled conjugates was analysed using SEC-HPLC (Figure S1).
3.3. In Vitro Binding
Effect of radiolabeling on binding of radioimmunoconjugates to EGFR was analysed using saturation binding assay towards EGFR positive DLD-1 cells. It was observed that 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc displayed good specific binding (Figure S2) which was evident from dissociation constant KD value of 34.39 ± 4.02 nM. 111In-nimotuzumab also had good binding affinity towards EGFR positive DLD-1 with a KD value of 14 nM. The immunoreactive fraction assay was performed to determine the fraction of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc that binds to DLD-1 cells. The immunoreactive fraction of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc was 0.73. A similar value was reported for 111In-nimotuzumab by our group [18].
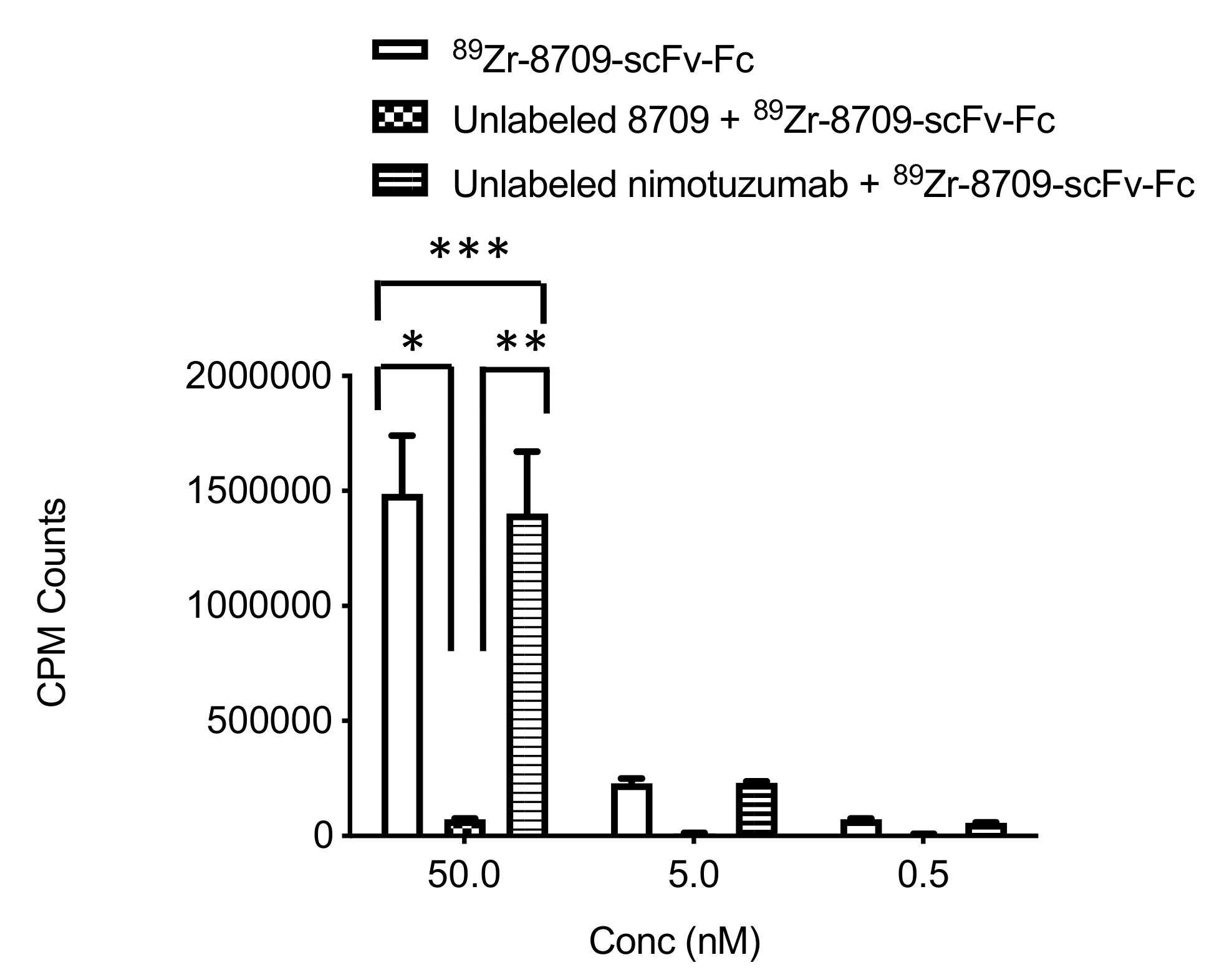
To confirm the specific binding of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc to domain II of EGFR, competitive binding experiment was performed. 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc specifically bound to domain II (Figure 2). In the presence of cold 8709-scFv-Fc no binding was observed, while in the presence of cold nimotuzumab (domain III binder), there was no reduction of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc binding confirming specificity of domain binding of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc.
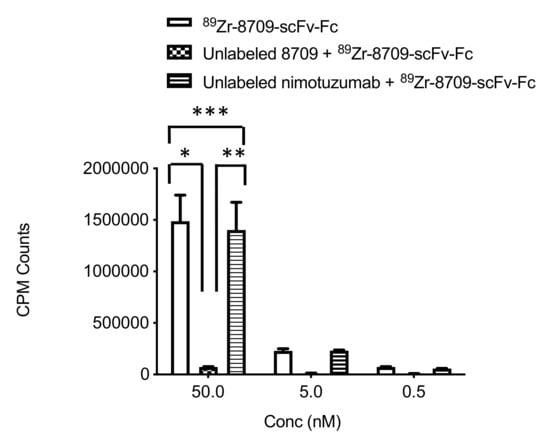
Figure 2.
Competitive binding assay of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc in EGFR positive DLD-1 cells at different concentration 50 nM, 5 nM and 0.5 nM in the presence of unlabeled 8709-scFv-Fc or unlabeled nimotuzumab (domain III binder). p < 0.05 for * and ** indicating statistical significance, while p > 0.05 for *** at 50 nM concentration, and as well at 5 and 0.5 nM.
3.4. Biodistribution and Pharmacokinetics
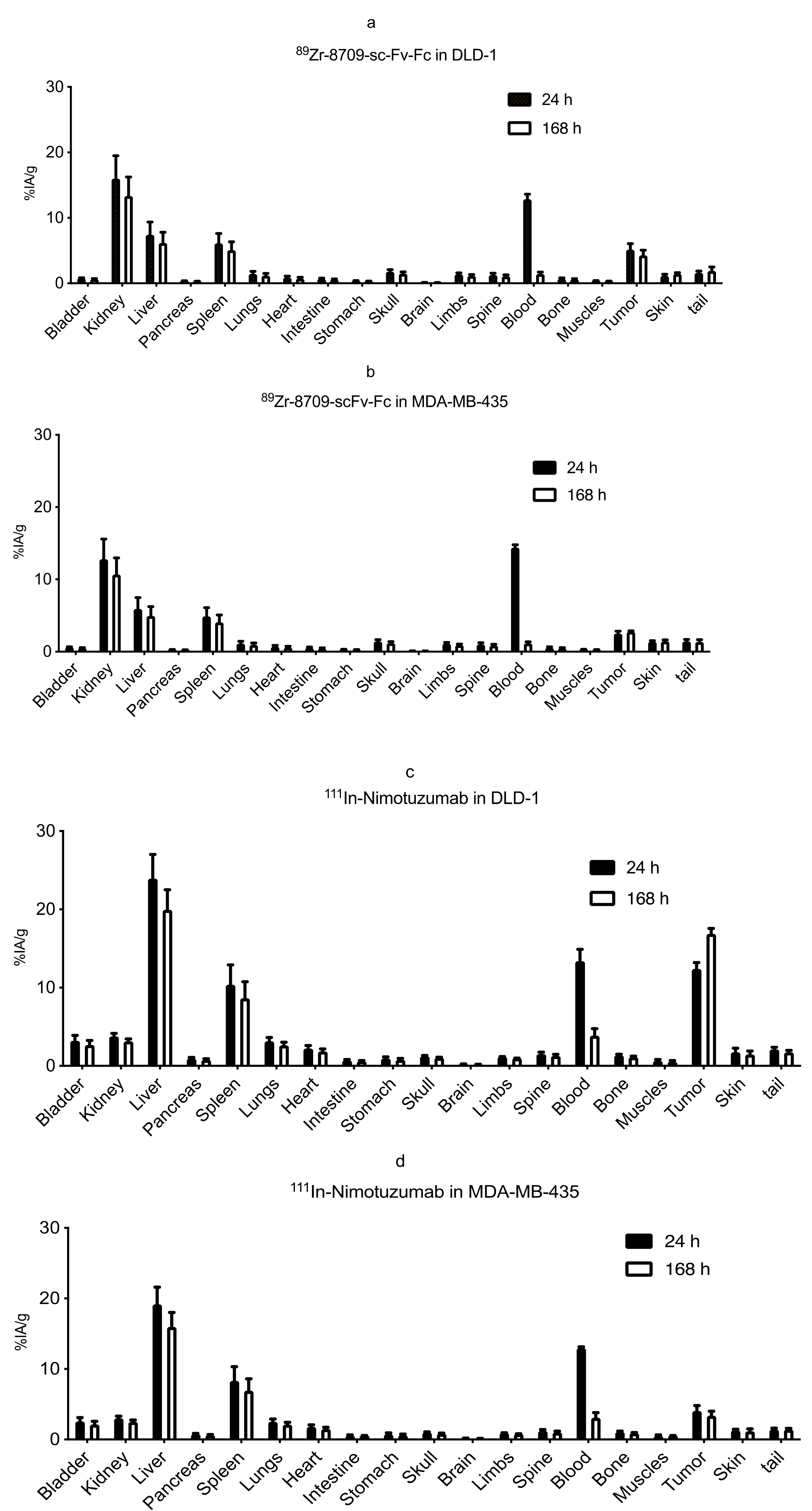
Biodistribution of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc and 111In-nimotuzumab was analysed at 24 and 168 h p.i. (Figure 3) in mice bearing xenografts with high EGFR expression (DLD-1) and an EGFR negative control (MDA-MB-435). There was no significant difference in tumor uptake of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc at 24 h (5.1 ± 1.6 %IA/g) and at 168 h (4.3 ± 1.4 %IA/g) (Figure 3a). Uptake of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc in control xenograft MDA-MB-435 was less (2.5 ± 0.6 %IA/g) indicating specificity of 8709-scFv-Fc towards EGFR (Figure 3b). Tumor uptake of 111In-nimotuzumab followed a similar trend with high uptake (12.4 ± 1.3 %IA/g) in EGFR positive DLD-1 xenograft (Figure 3c) and less uptake (3.4 ± 1.1 %IA/g) in EGFR negative MDA-MB-435 xenograft (Figure 3d). Tumor-to-blood ratios for 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc was 0.4 and 3.1 in DLD-1 xenograft at 24 h and 168 h post injection, respectively, and was 0.9 and 4.3 in the same xenograft at 24 h and 168 h post injection, respectively for 111In-nimotuzumab.
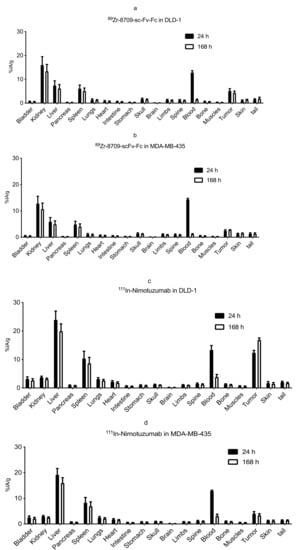
Figure 3.
(a–d). Biodistribution of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc in athymic CD-1 nude mice bearing EGFR positive xenograft DLD-1 (a) and EGFR negative MDA-MB-435 model (b) at 24 h and 120 h post injection (p.i.). Biodistribution of 111In-nimotuzumab in athymic CD-1 nude mice bearing EGFR positive xenograft DLD-1 (c) and EGFR negative MDA-MB-435 model (d) at 24 and 120 h p.i. Tissue uptake was expressed as % injected activity per gram (% IA/g) +/− SEM.
89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc exhibited a bi-phasic clearance with a fast (distribution) half-life t1/2α of 1.5 ± 1.2 h and a slow clearance t1/2β of 134.1 ± 1.3 h (Figure S3 and Table 1).

Table 1.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc ± SD.
3.5. MicroPET/SPECT/CT Imaging Using 111In-Nimotuzumab and 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc
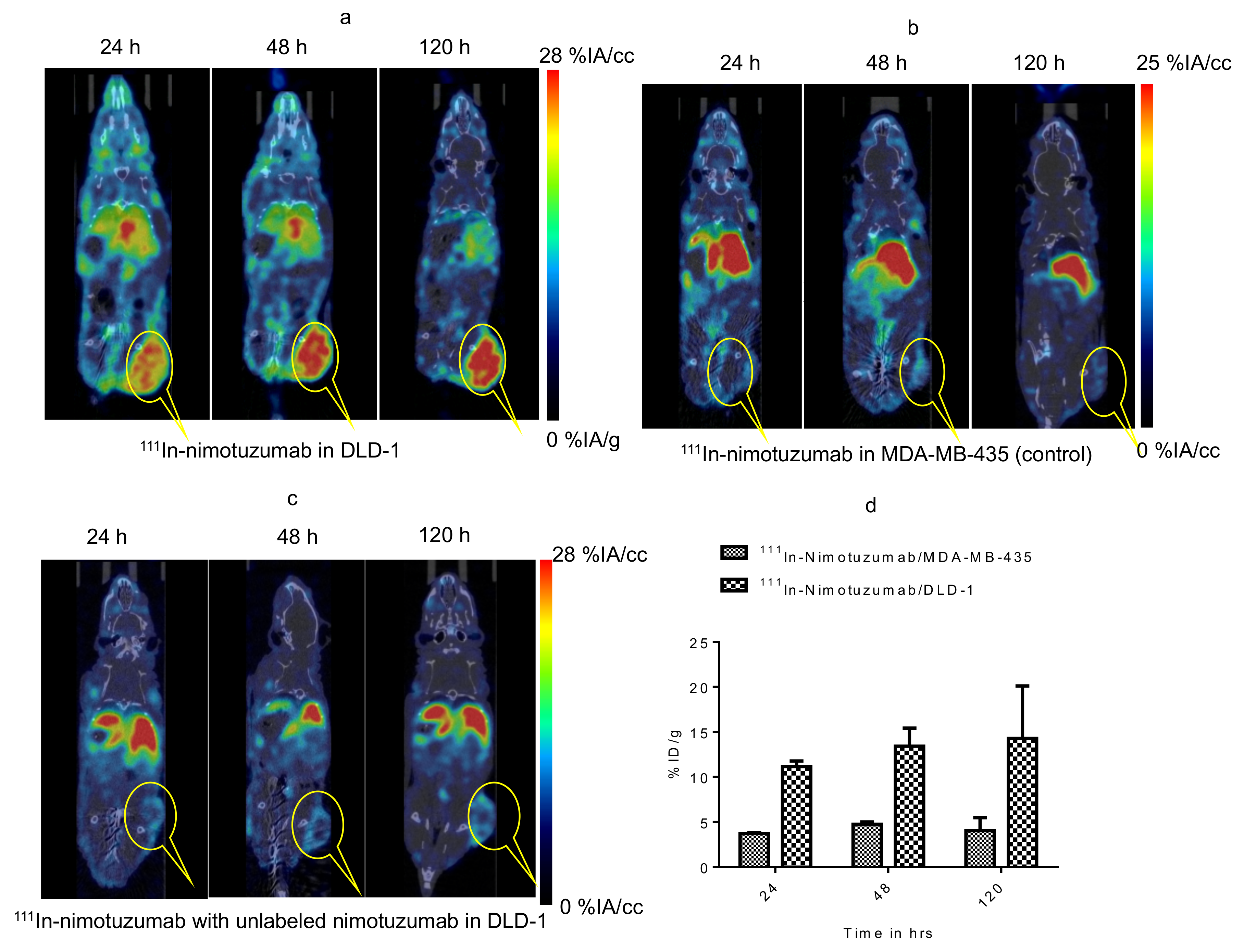
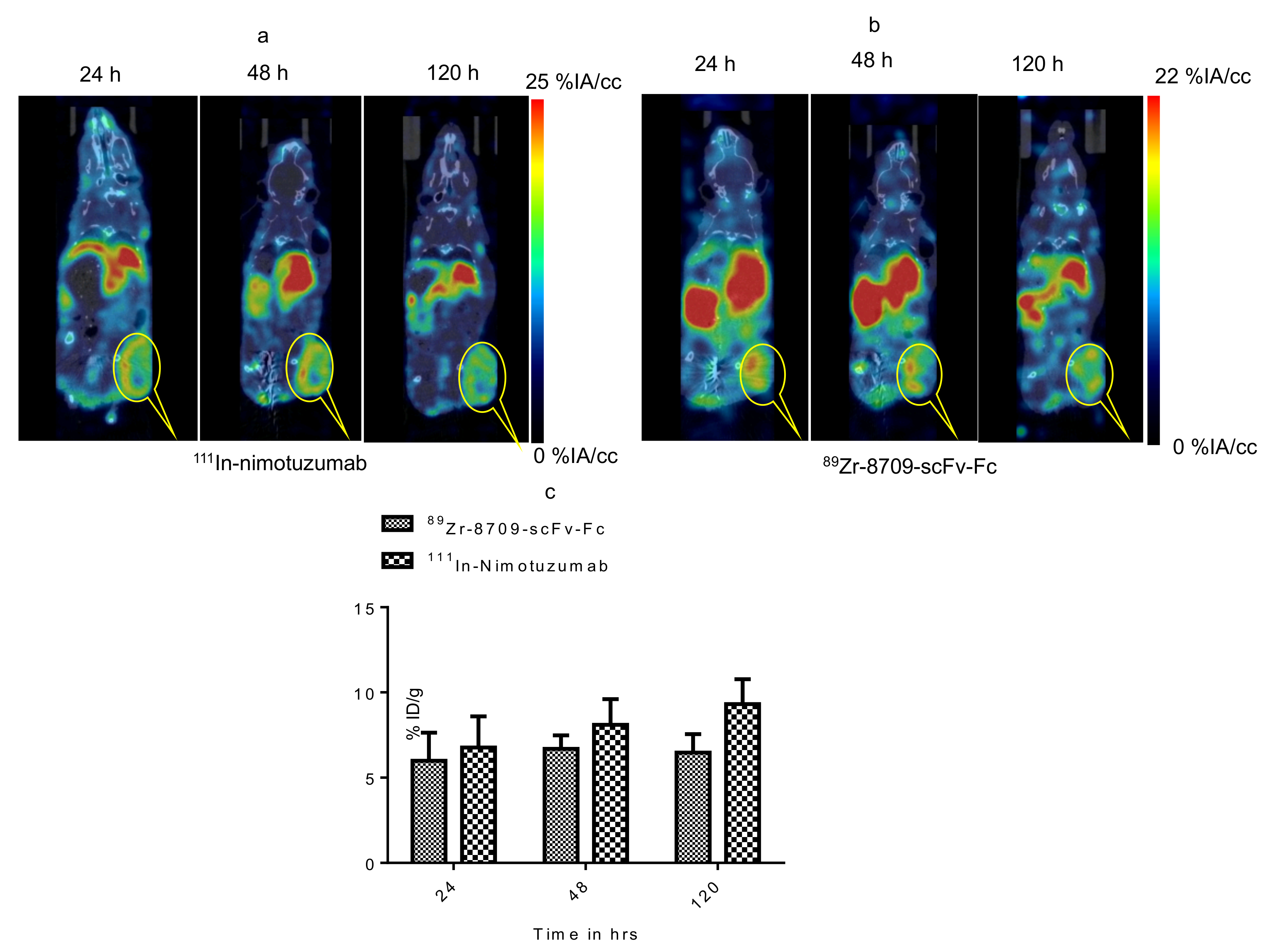
MicroSPECT/CT imaging confirms the specific binding of 111In-nimotuzumab to EGFR (Figure 4a). The tumor-to-muscle ratio was found to increase from 4.8 ± 1.73 to 6.6 ± 2.20 by the end of 120 h. Tumor uptake in mice bearing control MDA-MB-435 xenografts was low (4.0 ± 1.44%IA/cc) at the end of 120 h (Figure 4b) which confirms specific uptake 111In-nimotuzumab to EGFR positive DLD-1 xenograft model. Tumor uptake of 111In-nimotuzumab was blocked when mice were pre-injected with a therapeutic dose of unlabeled nimotuzumab prior to SPECT imaging with the tracer (Figure 4c). Mice bearing DLD-1 xenografts, had high tumor uptake (14.2 ± 6%IA/cc) at 120 h p.i. (Figure 4d).
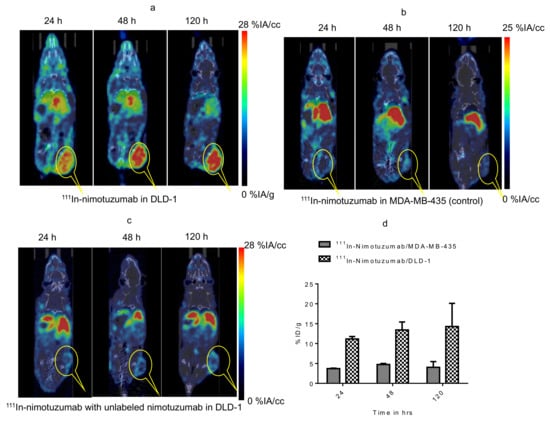
Figure 4.
Micro SPCET/CT imaging of Domain III binding of 111In-nimotuzumab in CD-1 nude mice bearing (a) EGFR positive DLD-1, (b) control MDA-MB-435 and (c) Pre-blocking with cold nimotuzumab followed by administration of 111In-nimotuzumab and at 24, 48, and 120 h p.i. A group of mice was initially pre-injected with 250 µg of unlabeled nimotuzumab to block domain III, and was followed by a tail vein injection of 111In-nimotuzumab c (domain III specific). (d) Quantification of tumor uptake presented as %IA/g +/− SEM.
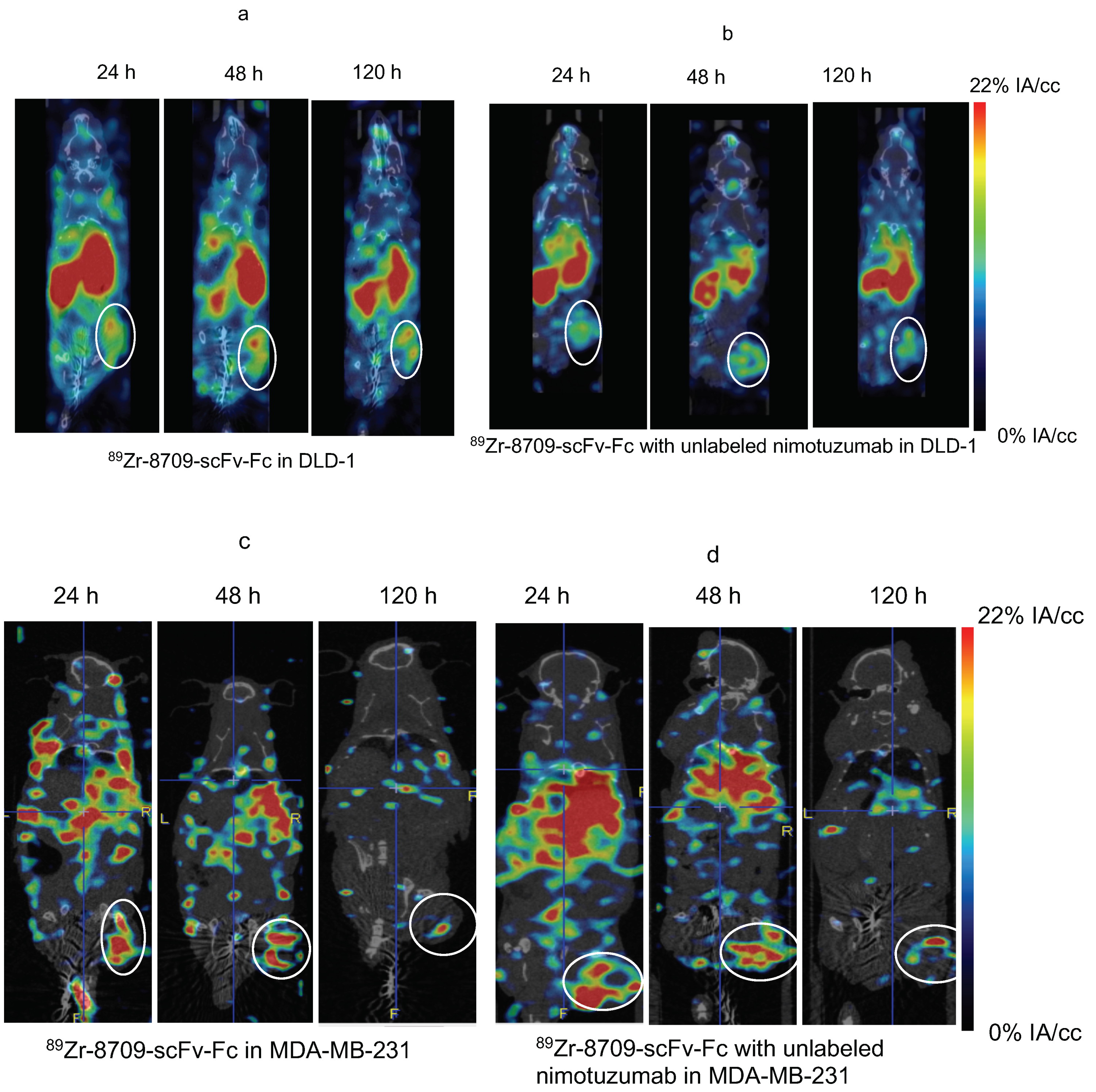
Binding of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc to domain II of EGFR was studied using PET imaging at different time points 24, 48, and 120 h p.i. (Figure 4 and Figure 5). Tumor uptake of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc gradually increased from 4.2 ± 0.7 % at 24 h p.i. to 6.0 ± 0.6 %IA/cc at 48 h (Figure 5a). Groups of mice pre-injected with unlabeled nimotuzumab before the injection of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc also showed similar tumor uptake at 24 h and 120 h p.i. (Figure 5b), confirming that a blocking dose of unlabeled nimotuzumab (domain III binder) did not alter the binding of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc (domain II binder) to EGFR. A similar trend in tumor uptake observed in DLD-1 xenograft was seen in EGFR positive MDA-MB-231 which has medium EGFR expression (Figure 5c,d). Mice bearing control MDA-MB-435 xenografts displayed lower tumor uptake of 3.1 %IA/cc at the end of 120 h (Figure 5e). Quantification of this uptake is presented in the supplementary section (Figure 5f and Figure S4) and shows no statistical difference.
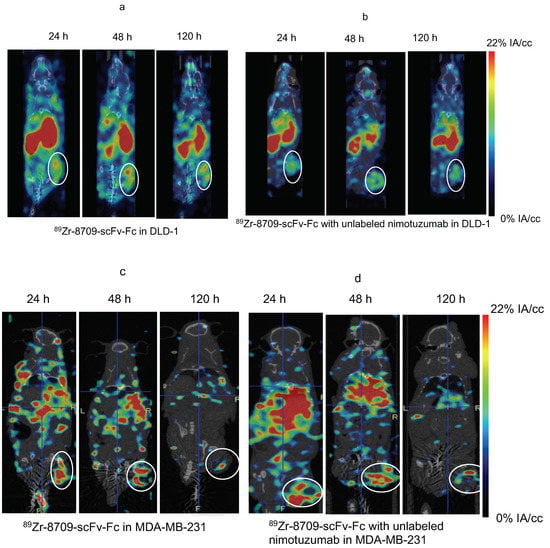
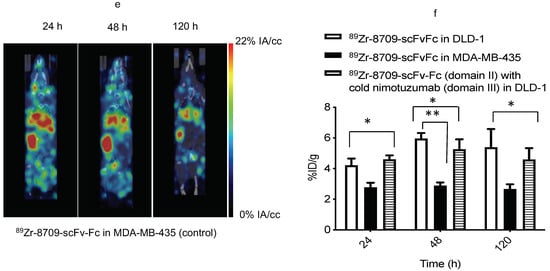
Figure 5.
MicroPET imaging of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc (domain II binder) in CD-1 nude mice bearing (a) EGFR positive DLD-1, (b) Pre-blocking DLD-1 tumor bearing mice with cold nimotuzumab followed by administration of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc, (c) EGFR positive MDA-MB-231, (d) Pre-blocking MDA-MB-231 tumor bearing mice with cold nimotuzumab followed by administration of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc, (e) control MDA-MB-435 xenografts at 24, 48, and 120 h p.i., and (f) Quantification of tumor uptake presented as %IA/g +/− SEM. Mice was initially pre-injected with 250 µg of unlabeled nimotuzumab to block domain III, and was followed by a tail vein injection of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc (domain II specific). * indicates no statistical difference between 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc vs unlabeled nimotuzumab + 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc. ** indicates significant difference between EGFR positive DLD-1 and control MDA-MB-453 xenografts.
Simultaneous targeting of domain III and domain II of EGFR was studied by dual tracer imaging following simultaneous administration of 111In-nimotuzumab and 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc in mice bearing EGFR positive DLD-1 xenograft. Tumor uptake was 9.3 %IA/cc and 6.5 %IA/cc at 120 h p.i. for 111In-nimotuzumab and 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc, respectively (Figure 6a–c). These values were not significantly different from those observed with single tracer imaging studies. Tumor-to-normal organ ratios for 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc are presented (Figure S5A–C).
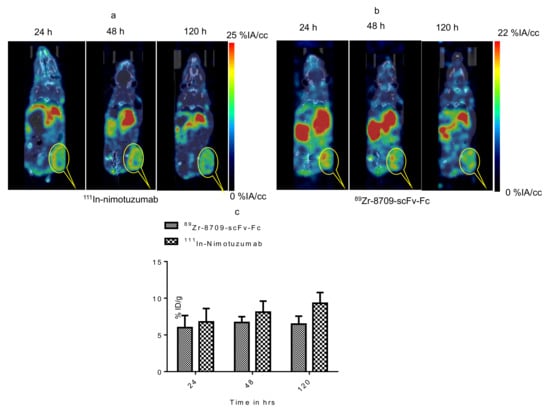
Figure 6.
Simultaneous dual tracer (111In-nimotuzumab and 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc) imaging of EGFR domain III and domain II in athymic CD-1 nude mice bearing DLD-1 xenograft. (a) 111In-nimotuzumab window, (b) 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc window and (c). Bar graph representing the tumor uptake for 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc window and 111In-nimotuzumab window.
4. Discussion
Molecular imaging agents such as 89Zr-cetuximab and 89Zr-panitumumab have been developed and evaluated in clinical trials [16]. However, because these agents bind to the same epitope (mostly domain III) as the anti-EGFR therapeutic antibody, they cannot be used to monitor response to treatment of the same antibody. Approved anti-EGFR antibodies e.g., cetuximab, panitumumab, nimotuzumab and more recently necitumumab bind to domain III leaving the dimerization loop of EGFR (domain II) available for binding to other molecules. Therefore, a monoclonal antibody that binds to a domain other than domain III is needed for comprehensive diagnosis, monitoring of response to anti-EGFR antibody therapy and potentially as a biparatopic anti-EGFR therapeutic agent. For the first time we have developed an immunoPET agent that binds to epitope II of EGFR.
Using phage display we have screened and engineered antibodies and antibody fragments that bind to domain II of EGFR [1]. We recently reported a near-infrared (NIR) fluorescently labeled IRDye800CW-8909 antibody and antibody fragments of this antibody [17]. 8907-scFv-Fc emerged as the best fragment for imaging domain II of EGFR [17]. The expression of 8907-scFv-Fc (50 mg/mL) was at least four-fold better than the other fragments and IgG. In addition, NIR showed that tumor uptake and target to organ ratios of 8907-scFv-Fc was better than all other fragments including the IgG. Here, we report the initial evaluation of a 89Zr-labeled 8907-scFv-Fc fragment of the antibody fragment for potential use in non-invasive diagnosis, patient selection and monitoring of response to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody treatment by PET.
Conjugation of 8709-scFv-Fc resulted in an average of two molecules of DFO attached to 8709-scFv-Fc which was evident from bioanalyzer. Bioanalyzer results show that there was a slight difference in the molecular weight of 8709-scFv-Fc and DFO-8709-scFv-Fc. Flow cytometry data suggests that, binding affinity of DFO-8709-scFv-Fc was not significantly (72 nM vs 97 nM for 8709-scFv-Fc and DFO-8709-scFv-Fc, respectively in DLD-1 cells) altered by conjugation, indicating conjugation and chemicals used in the reaction did not alter the characteristics of the antibody fragment.
The strategy to develop an antibody imaging agent that binds to a different epitope from the therapeutic antibody has already been investigated using anti-HER2 antibodies pertuzumab (domain II) and trastuzumab (domain IV) [23,24,25]. Pertuzumab (Perjeta) and trastuzumab (Herceptin) are approved for treating HER2 positive breast cancer [26]. A number of authors have developed radiolabeled derivatives of pertuzumab for imaging and monitoring of response to trastuzumab [23,25]. Marquez et al. [23] evaluated 89Zr-pertuzumab in mice bearing HER2 positive xenografts with or without the administration of unlabeled trastuzumab. It was shown that the administration of unlabeled trastuzumab 5–60 min before the administration of 89Zr-pertuzumab led to an increase in tumor uptake of 89Zr-pertuzumab compared to mice without pre-administration of unlabeled trastuzumab suggesting treatment with unlabeled trastuzumab may affect the quantification of HER2, despite the fact that both antibodies bind to unique epitopes of the receptor. This observation remains unclear and should be interpreted with caution given the large standard deviation seen in that study. On the other hand, Scheuer et al. [27] showed that the binding of near infrared labeled pertuzumab was not affected by the presence of unlabeled trastuzumab. Assuming this data by Marquez et al. were reliable, 89Zr-pertuzumab would have limited value in monitoring response to trastuzumab treatment. Here, we showed that anti-EGFR nimotuzumab (domain III) did not alter the in vitro binding (Figure 2) and tumor uptake in vivo (Figure 5 and Figure S4) of anti-EGFR 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc. Similarly, the presence of 8709-scFv-Fc did not alter the binding of 111In-nimotuzumab in vitro and in vivo. We also previously showed using near infrared labeled 8709 antibody fragments did not bind cells overexpressing mutant EGFRvIII which has all of domain I and most of domain II deleted [17].
Our in vivo studies show a rather low tumor uptake of the 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc imaging agent. The highest tumor uptake was 6.5 %IA/cc by microPET which was almost two-fold less that for 89Zr-nimotuzumab seen in this model in a previous study [19]. This rather low tumor uptake may be attributed to the high KD of 8709-scFv-Fc fragment (72 nM) compared with nimotuzumab (14 nM). The pharmacokinetics of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc was similar to 89Zr-nimotuzumab, indicating that it is not the reason for the observed differences in tumor uptake of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc versus 89Zr-nimotuzumab [19]. In addition, we observed a rather higher than normal kidney uptake for 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc. Since the size of scFv-Fc is greater than the kidney cutoff this high uptake maybe suggestive of in vivo proteolysis. Additional studies are needed to investigate the stability of this fragment. Strategies such as affinity maturation could be employed in the future to improve the binding and therefore tumor uptake of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc.
5. Conclusions
Necitumumab is the first anti-EGFR therapeutic antibody that is indicated only in squamous NSCLC patients whose cancer is positive for EGFR by immunohistochemistry [28]. Given the inherent issues associated with EGFR determination by immunohistochemistry, better strategies to diagnose, select patients for anti-EGFR treatments and monitor response are needed. Agents that bind to the same epitope as the therapeutic agent would have limited value, hence the need for those that bind to different epitopes. Here, we presented an anti-EGFR domain II PET imaging agent 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc. The domain specificity of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc indicates that this immunoPET agent may find applications for diagnosis, patient selection and monitoring of response to anti-EGFR treatments. In its current form, translation of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc will be limited by the rather low tumor uptake shown in these studies, which is due in part by the high KD (72 nM). Most therapeutic antibodies in this class are pico–low nanomolar affinities. Ongoing engineering studies on affinity maturation of 8709-scFv-Fc/8709-IgG would improve tumor uptake and hence imaging characteristics of the imaging agent(s).
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/13/3/560/s1, Figure S1: Saturation radioligand binding assay of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc in EGFR positive DLD-1 cells. (B) Immunoreactive assay for 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc in EGFR positive DLD-1 cells. Figure S2: Pharmacokinetics of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc in healthy Balb-C mice. Blood values were expressed as % injected activity per mL (% IA/mL) +/− SEM. Figure S3: Tumor ROI quantification of microPET/CT images of mice pre-injected with nimotuzumab (domain III) prior to administration of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc. (a) DLD-1 tumor bearing mice pre-dosed with nimotuzumab followed by 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc, and (b) MDA-MB-231 tumor bearing mice pre-dosed with nimotuzumab followed by 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc. Figure S4: Tumor to normal organ ratios of 89Zr-8709-scFv-Fc at different times post-injection (using microPET/CT image analysis (A,B) and biodistribution data (C)). (A) Tumor/muscle ratio. (B) Tumor/liver ratios. (C) Tumor/blood (data from biodistribution).
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, W.B.; Funding acquisition, C.R.G. and H.F.; Investigation, E.A., V.R.S., V.G., W.B., C.G. and K.B.; Methodology, E.A., K.B.A.A., V.R.S., V.G., A.M., C.G. and K.B.; Project administration, K.B. and C.R.G.; Resources, K.B. and A.C.; Supervision, C.R.G. and H.F.; Writing—original draft, E.A. and K.B.A.A. Writing—review & editing, H.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by a grant from the Saskatchewan Health Research Foundation (No. 3554) and Canadian Institute for Health Research (CIHR, Grant # 408132).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Saskatchewan (UACC) (protocol # 20170084 approved in 31 August 2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare there are no conflict of interests.
Abbreviations
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| SPECT | Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| 89Zr | Zirconium-89 |
| 111In | Indium-111 |
| DFO | Deferoxamine |
| HPLC | High Pressure Liquid Chromatography |
| SEC-HPLC | Size Exclusion HPLC |
| iTLC | Instant Thin Layer Chromatography |
| BLI | Biolayer interferometry |
| KD | Binding Constant |
| %IA/g | % Injected Activity per Gram |
References
- Miersch, S.; Maruthachalam, B.V.; Geyer, C.R.; Sidhu, S.S. Structure-directed and tailored diversity synthetic antibody libraries yield novel anti-egfr antagonists. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwak, D.R.; Carey, M.; Hennessy, B.T.; Nguyen, C.T.; McGahren Murray, M.J.; Nolden, L.; Mills, G.B. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in epithelial ovarian cancer: Current knowledge and future challenges. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.H.; Ely, K.; McGavran, L.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Parker, J.; Parker, N.; Jarrett, C.; Carter, J.; Murphy, B.A.; Netterville, J.; et al. Increased epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4170–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshenawy, H.A. Immunohistochemical expression of epidermal growth factor receptor, e-cadherin, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in ovarian epithelial cancer and relation to patient deaths. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2010, 14, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; Humblet, Y.; Siena, S.; Khayat, D.; Bleiberg, H.; Santoro, A.; Bets, D.; Mueser, M.; Harstrick, A.; Verslype, C.; et al. Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimova, I.; Zaharieva, B.; Raitcheva, S.; Dimitrov, R.; Doganov, N.; Toncheva, D. Tissue microarray analysis of egfr and erbb2 copy number changes in ovarian tumors. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2006, 16, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giltnane, J.M.; Ryden, L.; Cregger, M.; Bendahl, P.O.; Jirstrom, K.; Rimm, D.L. Quantitative measurement of epidermal growth factor receptor is a negative predictive factor for tamoxifen response in hormone receptor positive premenopausal breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 3007–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, M.; Wilken, J.A.; Harris, L.N.; Baron, A.T.; Kimbler, K.D.; Maihle, N.J. Trastuzumab-induced her reprogramming in “resistant” breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, R.; Zhang, J.; Nhonthachit, P.; Penuel, E.; Petropoulos, C.; Parry, G. Egfr over-expression and activation in high her2, er negative breast cancer cell line induces trastuzumab resistance. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 122, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.S.; Koppula, S.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, D.K. Analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor related gene expression changes in a cellular and animal model of parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, J.N.; Sorensen, J.B. Intratumor heterogeneity and chemotherapy-induced changes in egfr status in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 69, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A.J.; de Silva, R.A.; Lapi, S.E. Development and characterization of 89zr-labeled panitumumab for immuno-positron emission tomographic imaging of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol. Imaging 2013, 12, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fasih, A.; Fonge, H.; Cai, Z.; Leyton, J.V.; Tikhomirov, I.; Done, S.J.; Reilly, R.M. 111In-Bn-DTPA-nimotuzumab with/without modification with nuclear translocation sequence (NLS) peptides: An auger electron-emitting radioimmunotherapeutic agent for egfr-positive and trastuzumab (Herceptin)-resistant breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 135, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garousi, J.; Andersson, K.G.; Mitran, B.; Pichl, M.L.; Stahl, S.; Orlova, A.; Lofblom, J.; Tolmachev, V. Pet imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor expression in tumours using 89Zr-labelled zegfr:2377 affibody molecules. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loon, J.; Even, A.J.G.; Aerts, H.; Ollers, M.; Hoebers, F.; van Elmpt, W.; Dubois, L.; Dingemans, A.C.; Lalisang, R.I.; Kempers, P.; et al. Pet imaging of zirconium-89 labelled cetuximab: A phase i trial in patients with head and neck and lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 122, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Houven van Oordt, M.-C.W.; Gootjes, E.C.; Huisman, M.C.; Vugts, D.J.; Roth, C.; Luik, A.M.; Mulder, E.R.; Schuit, R.C.; Boellaard, R.; Hoekstra, O.S.; et al. 89Zr-cetuximab pet imaging in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 30384–30393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, W.; El-Sayed, A.; Barreto, K.; Gonzalez, C.; Fonge, H.; Geyer, C.R. Near infrared imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor positive xenografts in mice with domain i/ii specific antibody fragments. Theranostics 2019, 9, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartimath, S.V.; Alizadeh, E.; Solomon, V.R.; Chekol, R.; Bernhard, W.; Hill, W.; Parada, A.C.; Barreto, K.; Geyer, C.R.; Fonge, H. Preclinical evaluation of (111) in-labeled pegylated maytansine nimotuzumab drug conjugates in egfr-positive cancer models. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekol, R.; Solomon, V.R.; Alizadeh, E.; Bernhard, W.; Fisher, D.; Hill, W.; Barreto, K.; de Coteau, J.F.; Parada, A.C.; Geyer, C.R.; et al. 89Zr-nimotuzumab for immunopet imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor i. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17117–17132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queern, S.L.; Aweda, T.A.; Massicano, A.V.F.; Clanton, N.A.; el Sayed, R.; Sader, J.A.; Zyuzin, A.; Lapi, S.E. Production of Zr-89 using sputtered yttrium coin targets 89Zr using sputtered yttrium coin targets. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2017, 50, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.P.; Sheh, Y.; Lewis, J.S. Standardized methods for the production of high specific-activity zirconium-89. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2009, 36, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindmo, T.; Bunn, P.A., Jr. Determination of the True Immunoreactive Fraction of Monoclonal Antibodies After Radiolabeling. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; Volume 121, pp. 678–691. [Google Scholar]
- Marquez, B.V.; Ikotun, O.F.; Zheleznyak, A.; Wright, B.; Hari-Raj, A.; Pierce, R.A.; Lapi, S.E. Evaluation of (89) Zr-pertuzumab in breast cancer xenografts. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3988–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.; Chan, C.; Reilly, R.M. Development and Preclinical Studies of 64Cu-Nota-Pertuzumab F(Ab’)2 For Imaging Changes in Tumor Her2 Expression Associated with Response to Trastuzumab by PET/Ct. In MAbs; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 151–164. [Google Scholar]
- Massicano, A.V.F.; Lee, S.; Crenshaw, B.K.; Aweda, T.A.; El Sayed, R.; Super, I.; Bose, R.; Marquez-Nostra, B.V.; Lapi, S.E. Imaging of her2 with 89Zr-pertuzumab in response to t-dm1 therapy. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2019, 34, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Minckwitz, G.; Procter, M.; de Azambuja, E.; Zardavas, D.; Benyunes, M.; Viale, G.; Suter, T.; Arahmani, A.; Rouchet, N.; Clark, E.; et al. Adjuvant pertuzumab and trastuzumab in early her2-positive breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheuer, W.; Friess, T.; Burtscher, H.; Bossenmaier, B.; Endl, J.; Hasmann, M. Strongly enhanced antitumor activity of trastuzumab and pertuzumab combination treatment on her2-positive human xenograft tumor models. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 9330–9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatcher, N.; Hirsch, F.R.; Luft, A.V.; Szczesna, A.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Dediu, M.; Ramlau, R.; Galiulin, R.K.; Balint, B.; Losonczy, G.; et al. Necitumumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin versus gemcitabine and cisplatin alone as first-line therapy in patients with stage iv squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (squire): An open-label, randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).