CD44v6 Defines a New Population of Circulating Tumor Cells Not Expressing EpCAM
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
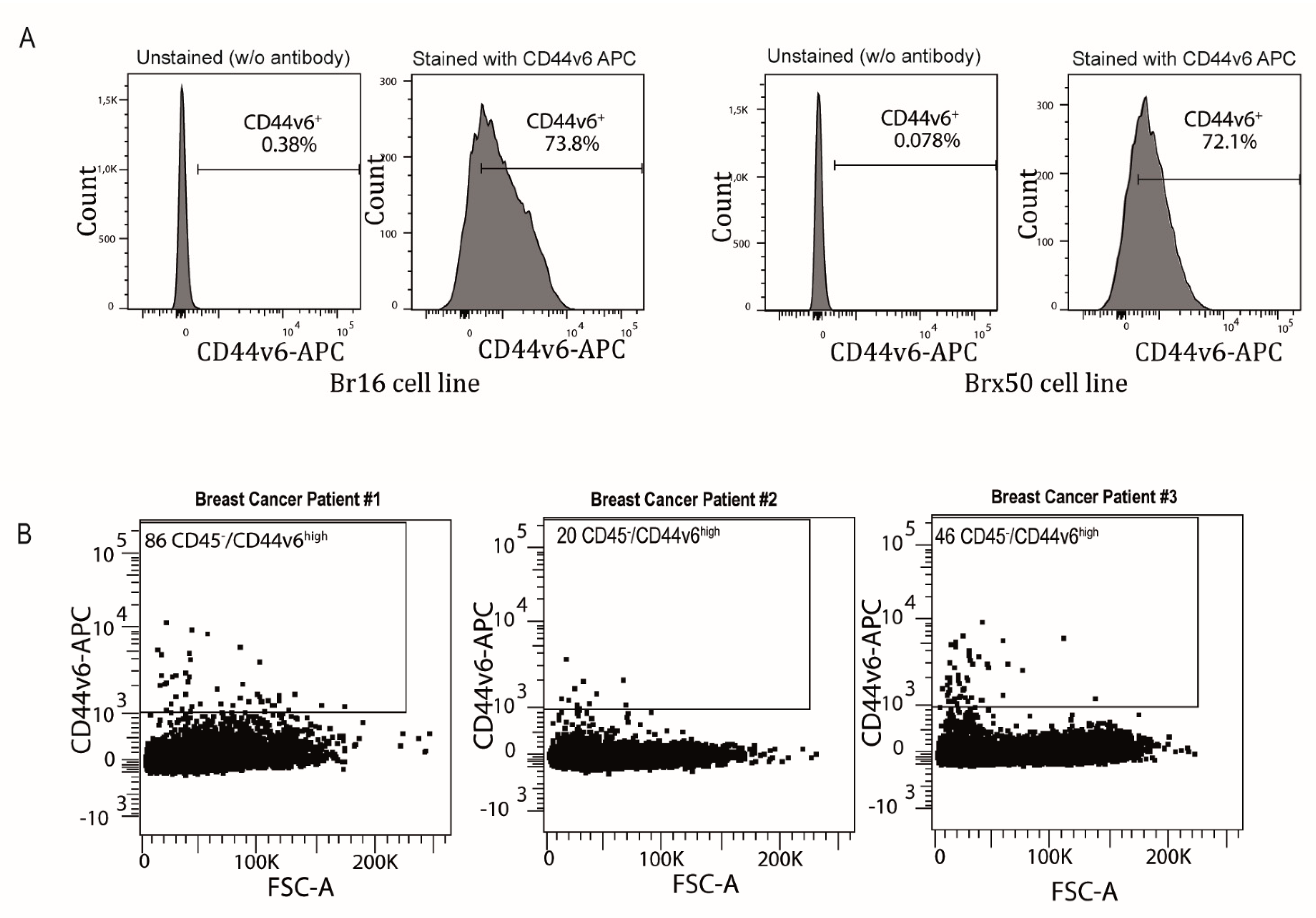
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Relationship of circulating tumor cells to tumor response, progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, G.J.; Goldkorn, A. Development and Application of Liquid Biopsies in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vona, G.; Sabile, A.; Louha, M.; Sitruk, V.; Romana, S.; Schütze, K.; Capron, F.; Franco, D.; Pazzagli, M.; Vekemans, M.; et al. Isolation by size of epithelial tumor cells: A new method for the immunomorphological and molecular characterization of circulatingtumor cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkumur, E.; Shah, A.M.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Emmink, B.L.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Brachtel, E.; Yu, M.; Chen, P.-I.; Morgan, B.; Trautwein, J.; et al. Inertial focusing for tumor antigen-dependent and -independent sorting of rare circulating tumor cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 179ra47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.C.; Robinson, P.S.; Wagner, C.; O’Shannessy, D.J. The ParsortixTM Cell Separation System-A versatile liquid biopsy platform. Cytom. Part J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2018, 93, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, N.; Bardia, A.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Donaldson, M.C.; Wittner, B.S.; Spencer, J.A.; Yu, M.; Pely, A.; Engstrom, A.; Zhu, H.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters Are Oligoclonal Precursors of Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cell 2014, 158, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szczerba, B.M.; Castro-Giner, F.; Vetter, M.; Krol, I.; Gkountela, S.; Landin, J.; Scheidmann, M.C.; Donato, C.; Scherrer, R.; Singer, J.; et al. Neutrophils Escort Circulating Tumour Cells to Enable Cell Cycle Progression. Nature 2019, 566, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, A.; McCulloch, P.G. Detection and enumeration of circulating tumour cells in colorectal cancer. Br. J. Surg. 1993, 80, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkersma, L.R.; Gómez, C.O.; Manso, L.S.J.; De Castro, S.V.; Romo, I.G.; Lázaro, M.V.; De La Orden, G.V.; Fernández, M.A.; Diaz-Rubio, E.; Moyano, A.S.; et al. Immunomagnetic quantification of circulating tumoral cells in patients with prostate cancer: Clinical and pathological correlation. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2010, 63, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Allard, W.J.; Terstappen, L.W.; et al. Circulating tumor cells, disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, X.; Brabletz, T.; Kang, Y.; Longmore, G.D.; Nieto, M.A.; Stanger, B.Z.; Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Upholding a role for EMT in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2017, 547, E1–E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lee, D.K.; Feng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Bu, W.; Li, Y.; Liao, L.; Xu, J. Breast tumor cell-specific knockout of Twist1 inhibits cancer cell plasticity, dissemination, and lung metastasis in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11494–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krebs, A.M.; Mitschke, J.; Losada, M.L.; Schmalhofer, O.; Boerries, M.; Busch, H.; Böttcher, M.; Mougiakakos, D.; Reichardt, W.; Bronsert, P.; et al. The EMT-activator Zeb1 is a key factor for cell plasticity and promotes metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cegan, M.; Kolostova, K.; Matkowski, R.; Broul, M.; Schraml, J.; Fiutowski, M.; Bobek, V. In vitro culturing of viable circulating tumor cells of urinary bladder cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 7164–7171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bobek, V.; Gurlich, R.; Eliasova, P.; Kolostova, K. Circulating tumor cells in pancreatic cancer patients: Enrichment and cultivation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17163–17170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgkinson, C.L.; Morrow, C.J.; Li, Y.; Metcalf, R.L.; Rothwell, D.; Trapani, F.; Polanski, R.; Burt, D.J.; Simpson, K.L.; Morris, K.; et al. Tumorigenicity and genetic profiling of circulating tumor cells in small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Bardia, A.; Aceto, N.; Bersani, F.; Madden, M.W.; Donaldson, M.C.; Desai, R.; Zhu, H.; Comaills, V.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Cancer therapy. Ex vivo culture of circulating breast tumor cells for individualized testing of drug susceptibility. Science 2014, 345, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grillet, F.; Bayet, E.; Villeronce, O.; Zappia, L.; Lagerqvist, E.L.; Lunke, S.; Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Pham, K.; Molck, C.; Rolland, N.; et al. Circulating tumour cells from patients with colorectal cancer have cancer stem cell hallmarks in ex vivo culture. Gut 2017, 66, 1802–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Todaro, M.; Gaggianesi, M.; Catalano, V.; Benfante, A.; Iovino, F.; Biffoni, M.; Apuzzo, T.; Sperduti, I.; Volpe, S.; Cocorullo, G.; et al. CD44v6 is a marker of constitutive and reprogrammed cancer stem cells driving colon cancer metastasis. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Rana, S.; Giese, N.; Büchler, M.W.; Zöller, M. Tspan8, CD44v6 and alpha6beta4 are biomarkers of migrating pancreatic cancer-initiating cells. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Wu, J.; Lai, X.; Ai, H.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, B.; Huang, L. CD44 and CD44v6 Are Correlated With Gastric Cancer Progression and Poor Patient Prognosis: Evidence From 42 Studies. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 40, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Zhao, W.; Shao, W. Prognostic Value of CD44 and CD44v6 Expression in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Meta-Analysis. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 7383–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-J.; Li, X.-D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Ning, Z.-H.; Yin, Y.-M.; Tian, Y. Clinical significance of CD44s, CD44v3 and CD44v6 in breast cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2015, 43, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, G.-L.; Song, L.-N.; Deng, Z.-F.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.-J. Prognostic value of CD44v6 expression in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 5451–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, S.; Okabe, H.; Watanabe, M.; Ishimoto, T.; Iwatsuki, M.; Baba, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Kurashige, J.; Miyamoto, Y.; Baba, H. CD44v6 expression is related to mesenchymal phenotype and poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.-L.; Su, W.-Y.; Lin, Y.-W.; Xiong, H.; Chen, Y.-X.; Xu, J.; Fang, J.-Y. CD44v6 Overexpression Related to Metastasis and Poor Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 12866–12876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Dong, L.; Chang, P. CD44v6 engages in colorectal cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Zhang, D.S.; Zheng, J. Expression of CD44v6 Gene in Normal Human Peripheral Blood. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkountela, S.; Castro-Giner, F.; Szczerba, B.M.; Vetter, M.; Landin, J.; Scherrer, R.; Krol, I.; Scheidmann, M.C.; Beisel, C.; Stirnimann, C.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clustering Shapes DNA Methylation to Enable Metastasis Seeding. Cell 2019, 176, 98–112.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolazzo, C.; Loreni, F.; Caponnetto, S.; Magri, V.; Vestri, A.R.; Zamarchi, R.; Gradilone, A.; Facchinetti, A.; Rossi, E.; Cortesi, E.; et al. Baseline CD44v6-positive circulating tumor cells to predict first-line treatment failure in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 4115–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, D.; Denis, M.G.; Lustenberger, P. Limitations of CD44v6 amplification for the detection of tumour cells in the blood of colorectal cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueo, H.; Sugimachi, K.; Gorges, T.M.; Bartkowiak, K.; Yokobori, T.; Müller, V.; Shinden, Y.; Ueda, M.; Mori, M.; Kuwano, H.; et al. Circulating tumour cell-derived plastin3 is a novel marker for predicting long-term prognosis in patients with breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lankiewicz, S.; Rother, E.; Zimmermann, S.; Hollmann, C.; Korangy, F.; Greten, T.F. Tumour-associated transcripts and EGFR deletion variants in colorectal cancer in primary tumour, metastases and circulating tumour cells. Cell. Oncol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cell. Oncol. 2008, 30, 463–471. [Google Scholar]
- Zieglschmid, V.; Hollmann, C.; Gutierrez, B.; Krehan, A.; Kaul, S.; Böcher, O. Heterogeneous expression of tumor-associated genes in disseminated breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Agerbæk, M.Ø.; Bang-Christensen, S.R.; Yang, M.H.; Clausen, T.M.; Pereira, M.A.; Sharma, S.; Ditlev, S.B.; Nielsen, M.A.; Choudhary, S.; Gustavsson, T.; et al. The VAR2CSA malaria protein efficiently retrieves circulating tumor cells in an EpCAM-independent manner. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
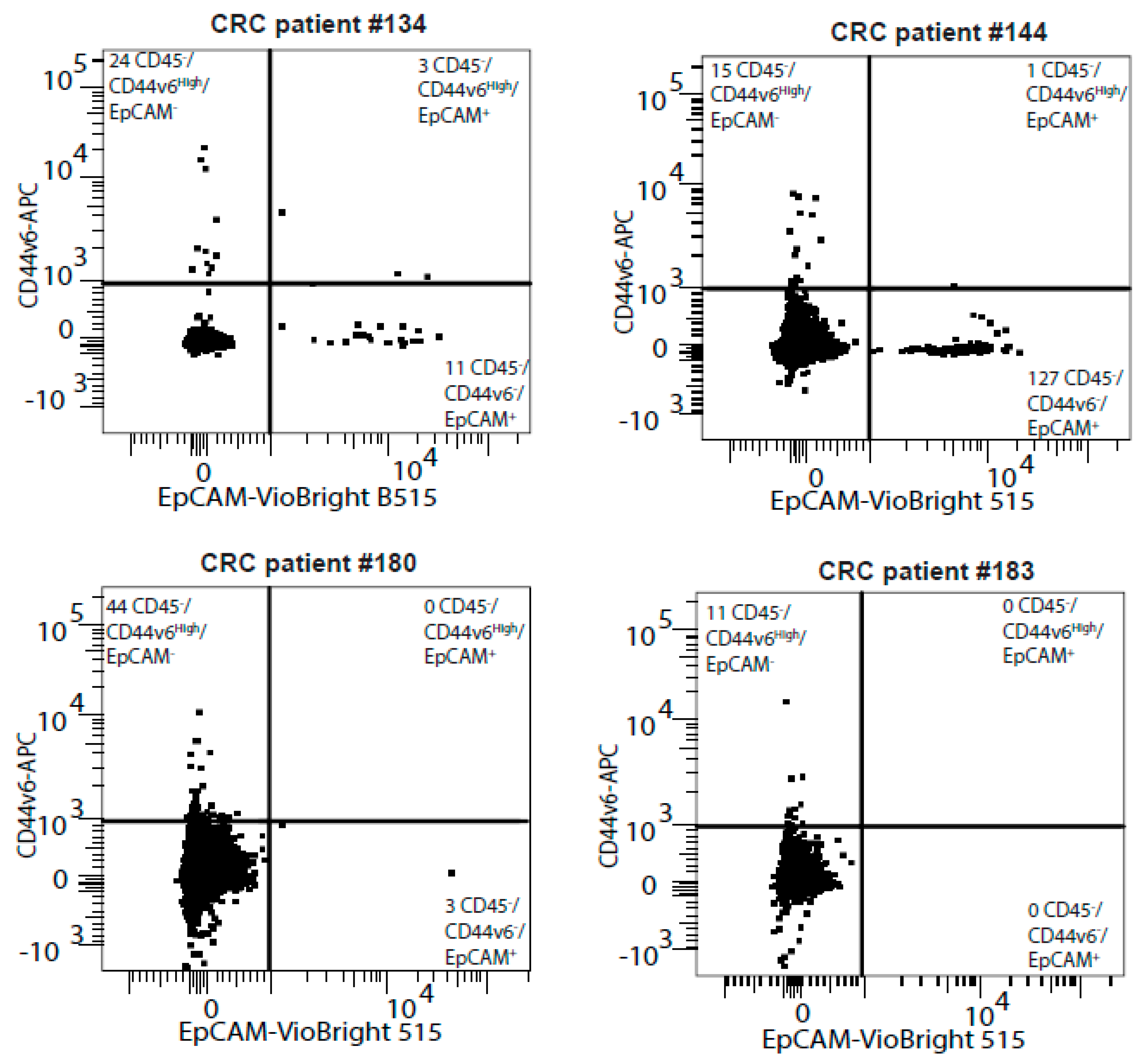
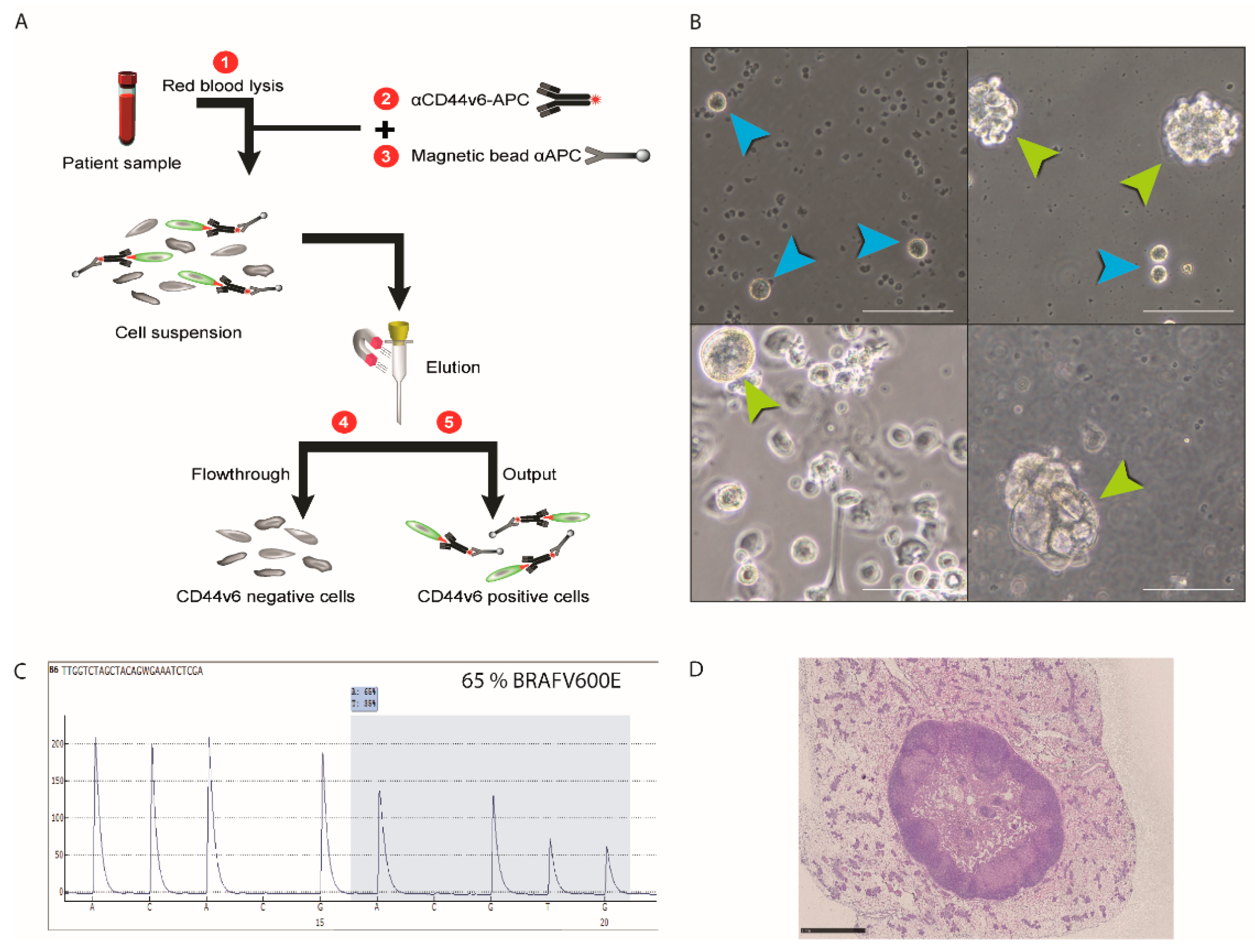
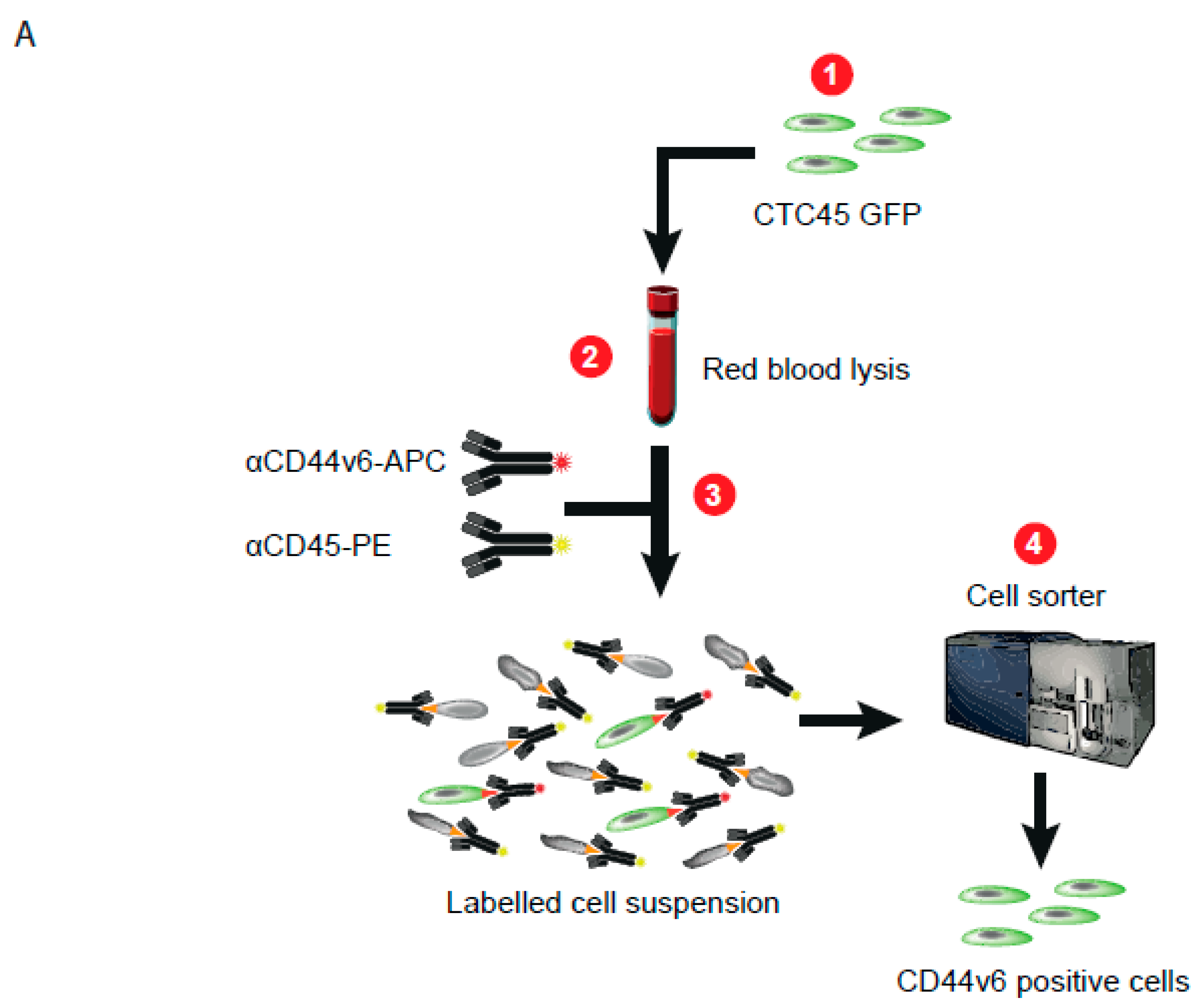
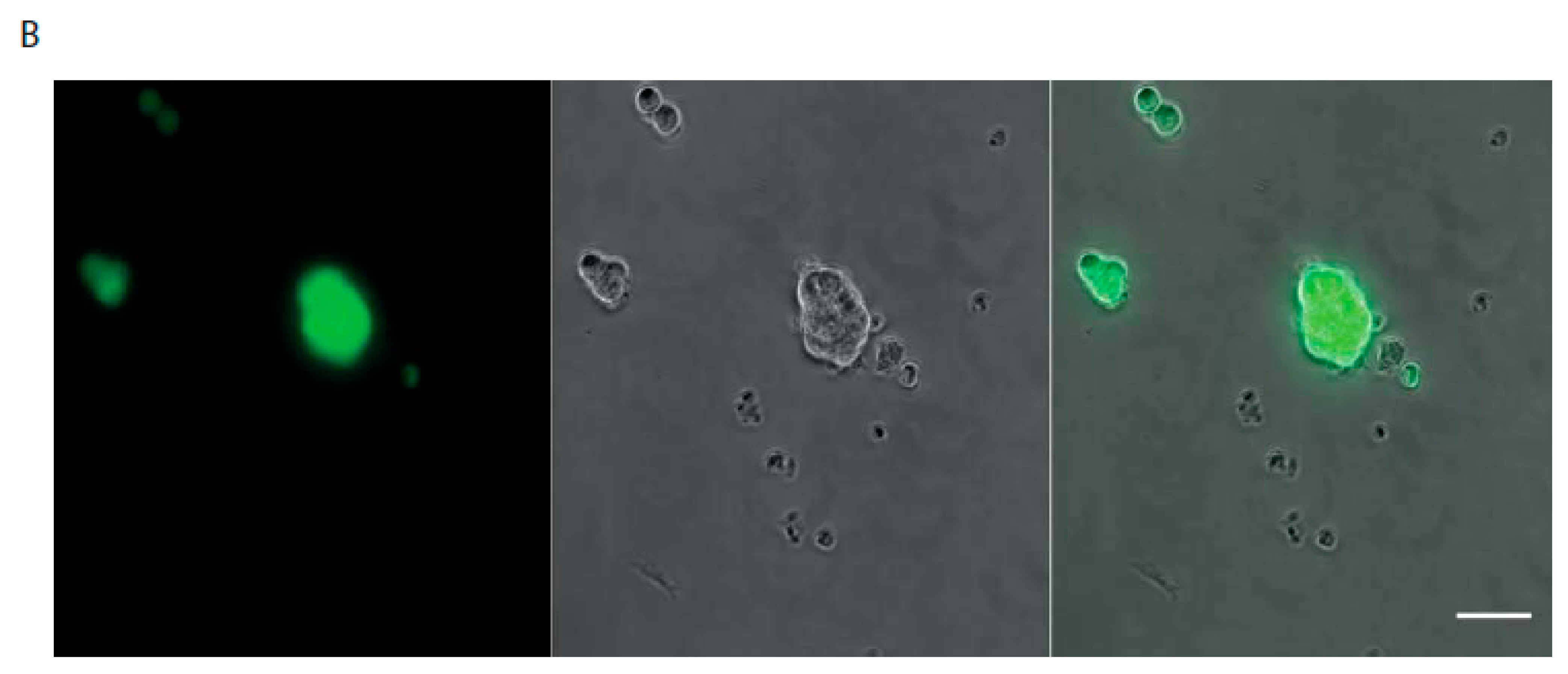

| Patient # | Sex | Age | Primary Tumor Localization | Identified Mutations | Method | Metastatic Sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99 | Male | 61 | Caecum | Kras G13D | ctDNA | Peritoneum |
| 124 | Male | 40 | Transverse colon | Kras G12V | ctDNA | Peritoneum and liver |
| 129 | Male | 79 | Right colon | Kras G12V | NGS on primary tumor biopsy | Liver |
| 130 | Female | 43 | Rectum | no | NGS on primary tumor biopsy | Liver and anal canal |
| 134 | Female | 62 | Right colic flexure | Braf V600G | NGS on primary tumor biopsy | Liver and Lung |
| 143 | Male | 73 | Sigmoid colon | no | NGS on primary tumor biopsy | Liver |
| 144 | Male | 70 | Transverse colon | Kras G12V | ctDNA | Liver and Lung |
| 149 | Male | 62 | Right colon | Kras G12V | NGS on primary tumor biopsy | Liver |
| 170 | Female | 48 | Right colon | Kras G12D | PCR and sequencing | Liver and bones |
| 174 | Female | 59 | Transverse colon | STK11 | NGS | Peritoneum and liver |
| 178 | Female | 55 | Rectum | Kras G12C | PCR and sequencing | Liver and Lung |
| 180 | Female | 69 | Rectum | Kras G12V and PTEN | NGS | Lung |
| 183 | Male | 71 | Right colon | BRAFV600E and IDH1 | NGS | Peritoneum |
| Patient #99 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genes | Locus | Location | Genotype | Type | Amino Acid Change | % Frequency | Variant Effect |
| ERBB4 | chr2: 21228869 | ERBB4: exonic:NM_005235.2 | G/A | SNV | p.Thr926Met | 54.65 | missense |
| FGFR1 | chr8: 38285930 | FGFR1: exonic:NM_001174067.1 | CATC/C | INDEL | p.Asp160del | CAT = 0.00, C = 3.38 | non frameshift deletion |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belthier, G.; Homayed, Z.; Grillet, F.; Duperray, C.; Vendrell, J.; Krol, I.; Bravo, S.; Boyer, J.-C.; Villeronce, O.; Vitre-Boubaker, J.; et al. CD44v6 Defines a New Population of Circulating Tumor Cells Not Expressing EpCAM. Cancers 2021, 13, 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13194966
Belthier G, Homayed Z, Grillet F, Duperray C, Vendrell J, Krol I, Bravo S, Boyer J-C, Villeronce O, Vitre-Boubaker J, et al. CD44v6 Defines a New Population of Circulating Tumor Cells Not Expressing EpCAM. Cancers. 2021; 13(19):4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13194966
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelthier, Guillaume, Zeinab Homayed, Fanny Grillet, Christophe Duperray, Julie Vendrell, Ilona Krol, Sophie Bravo, Jean-Christophe Boyer, Olivia Villeronce, Jihane Vitre-Boubaker, and et al. 2021. "CD44v6 Defines a New Population of Circulating Tumor Cells Not Expressing EpCAM" Cancers 13, no. 19: 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13194966
APA StyleBelthier, G., Homayed, Z., Grillet, F., Duperray, C., Vendrell, J., Krol, I., Bravo, S., Boyer, J.-C., Villeronce, O., Vitre-Boubaker, J., Heaug-Wane, D., Macari-Fine, F., Smith, J., Merlot, M., Lossaint, G., Mazard, T., Portales, F., Solassol, J., Ychou, M., ... Pannequin, J. (2021). CD44v6 Defines a New Population of Circulating Tumor Cells Not Expressing EpCAM. Cancers, 13(19), 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13194966









