Kv1.3 Controls Mitochondrial Dynamics during Cell Cycle Progression
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Lentiviral Infection
2.3. Cell Cycle Analysis by Flow Cytometry
2.4. Proliferation, Viability and Cell Size Assays
- A = absorbance of the test wells
- A° = absorbance of the control wells
2.5. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Purification of Mitochondria
2.7. Immunocytochemistry, Confocal Microscopy and Image Analysis
2.8. Cell Death Assay and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Measurement
2.9. Oil Red Staining
2.10. Glucose Uptake
2.11. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.12. Statistics
3. Results
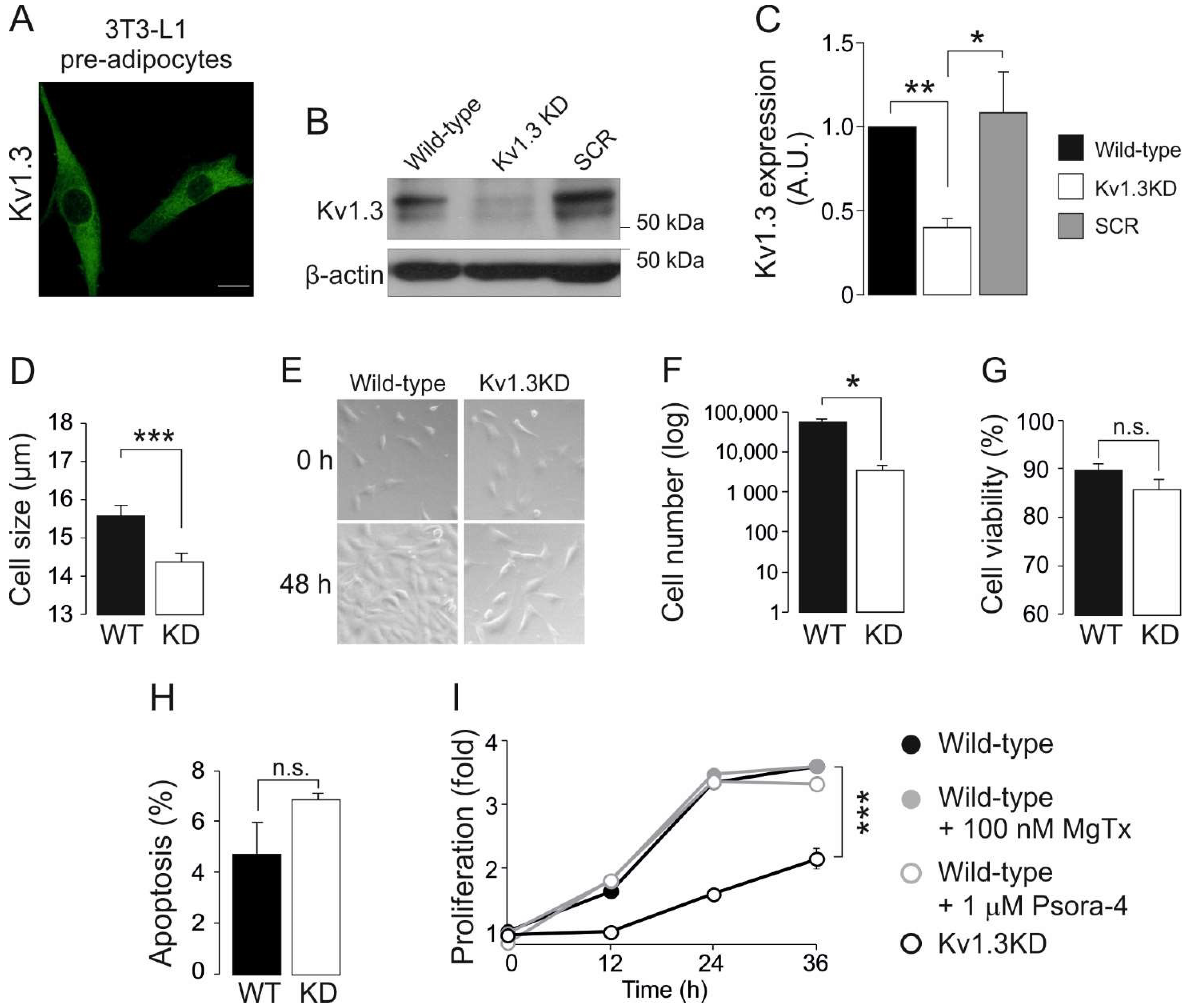
3.1. Kv1.3 Participates in the Proliferation and Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes
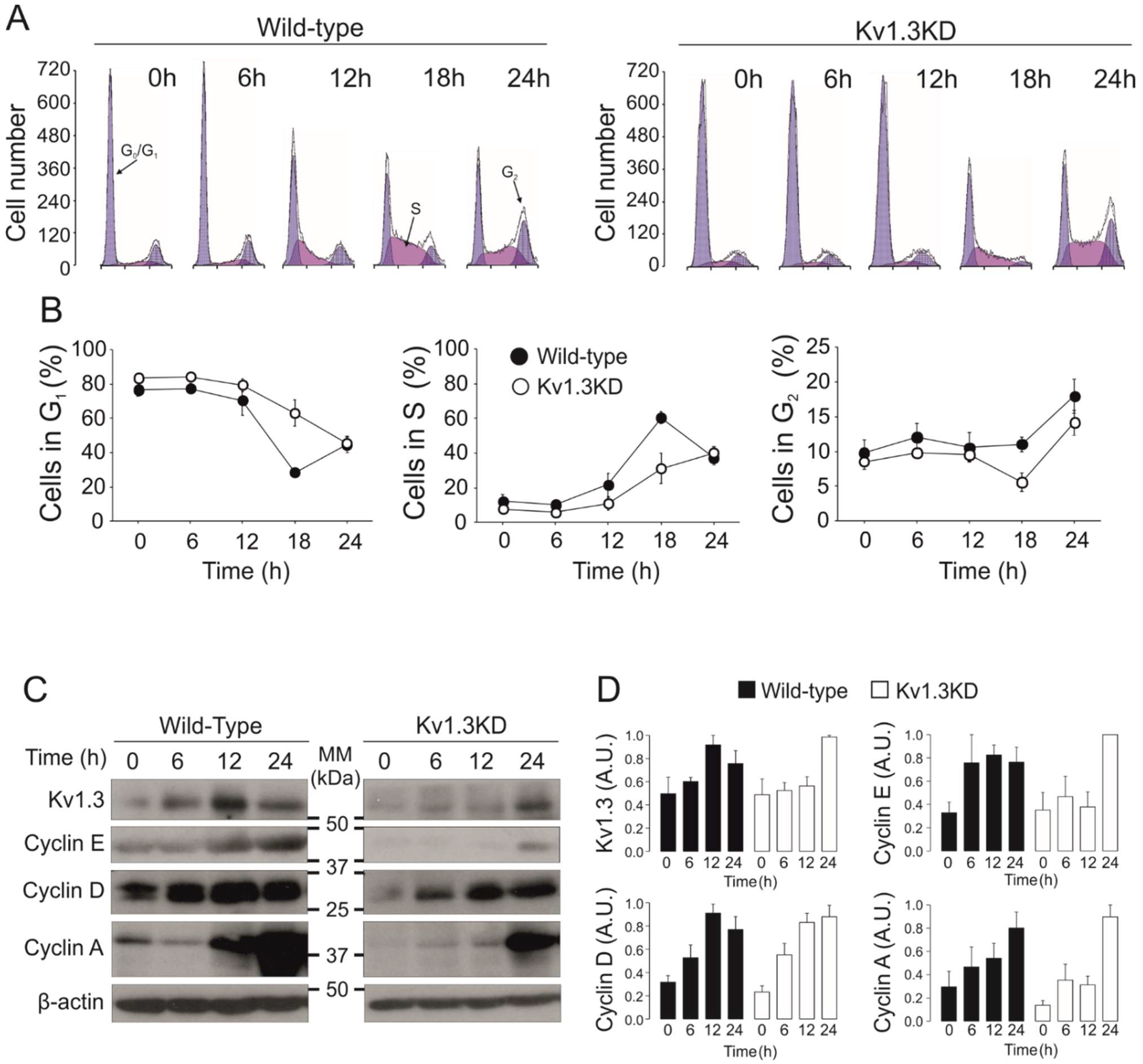
3.2. Kv1.3 Expression Facilitates the G1/S Transition
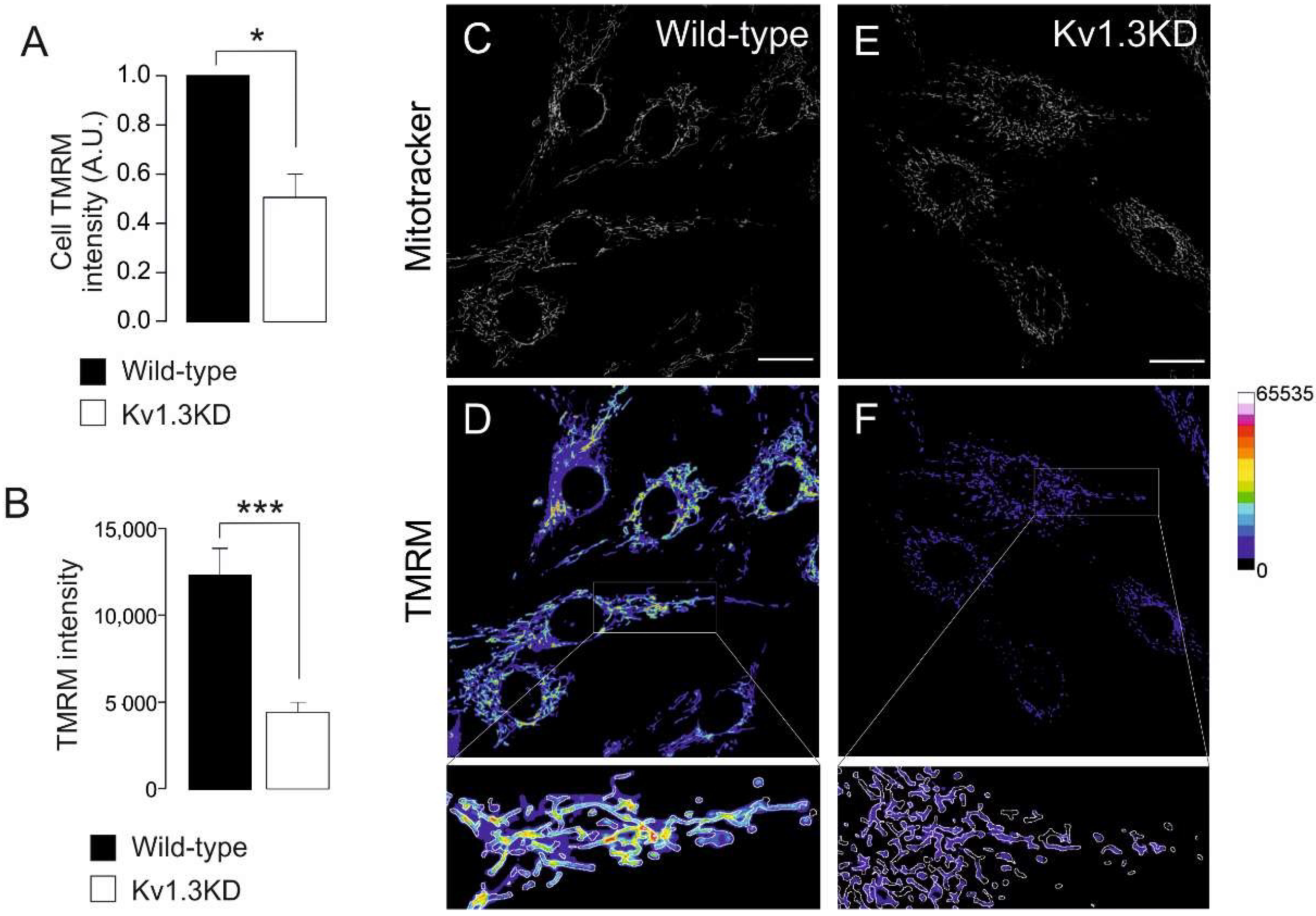
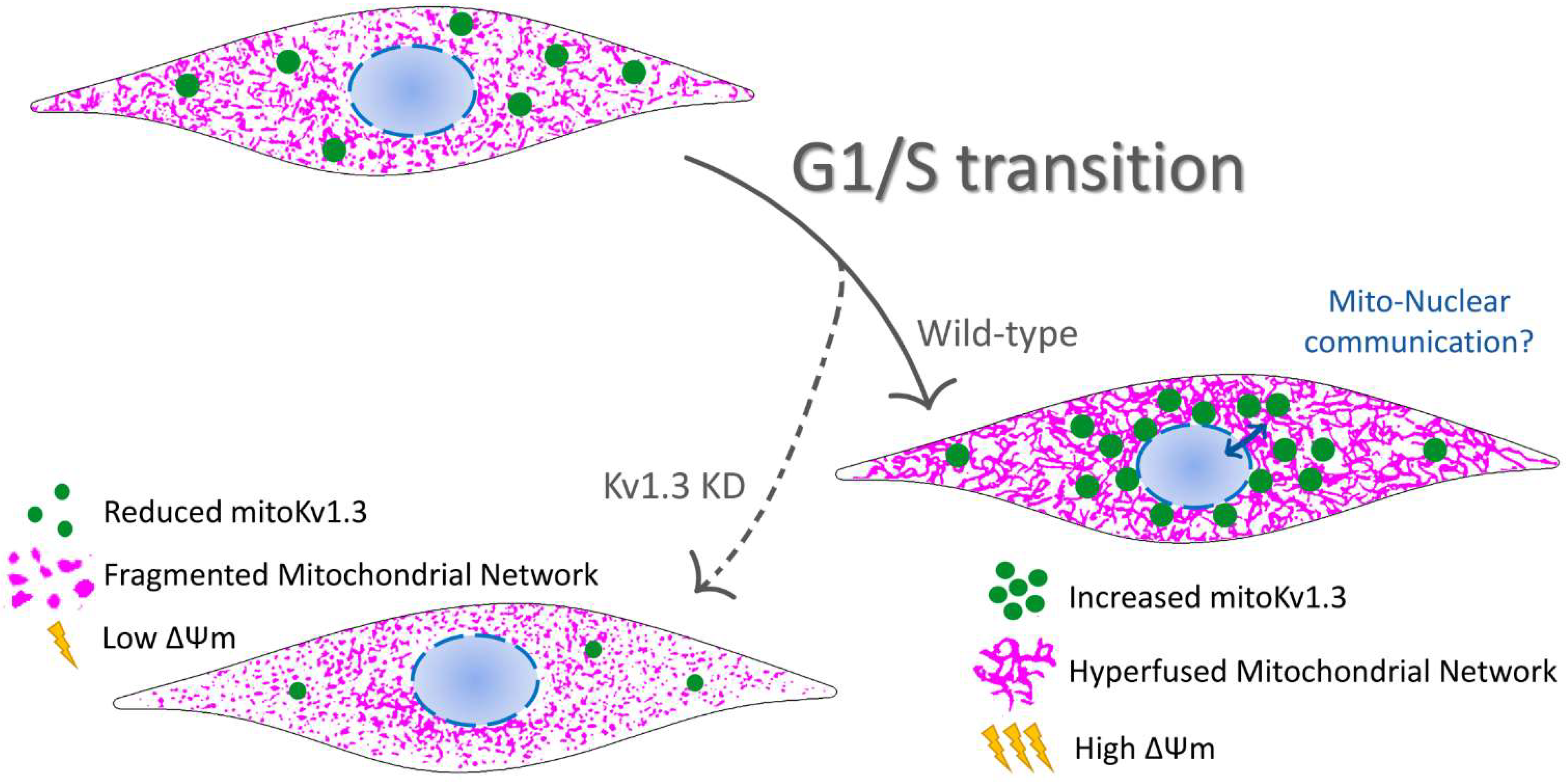
3.3. Cell Cycle-Dependent Mitochondrial Kv1.3 Targeting
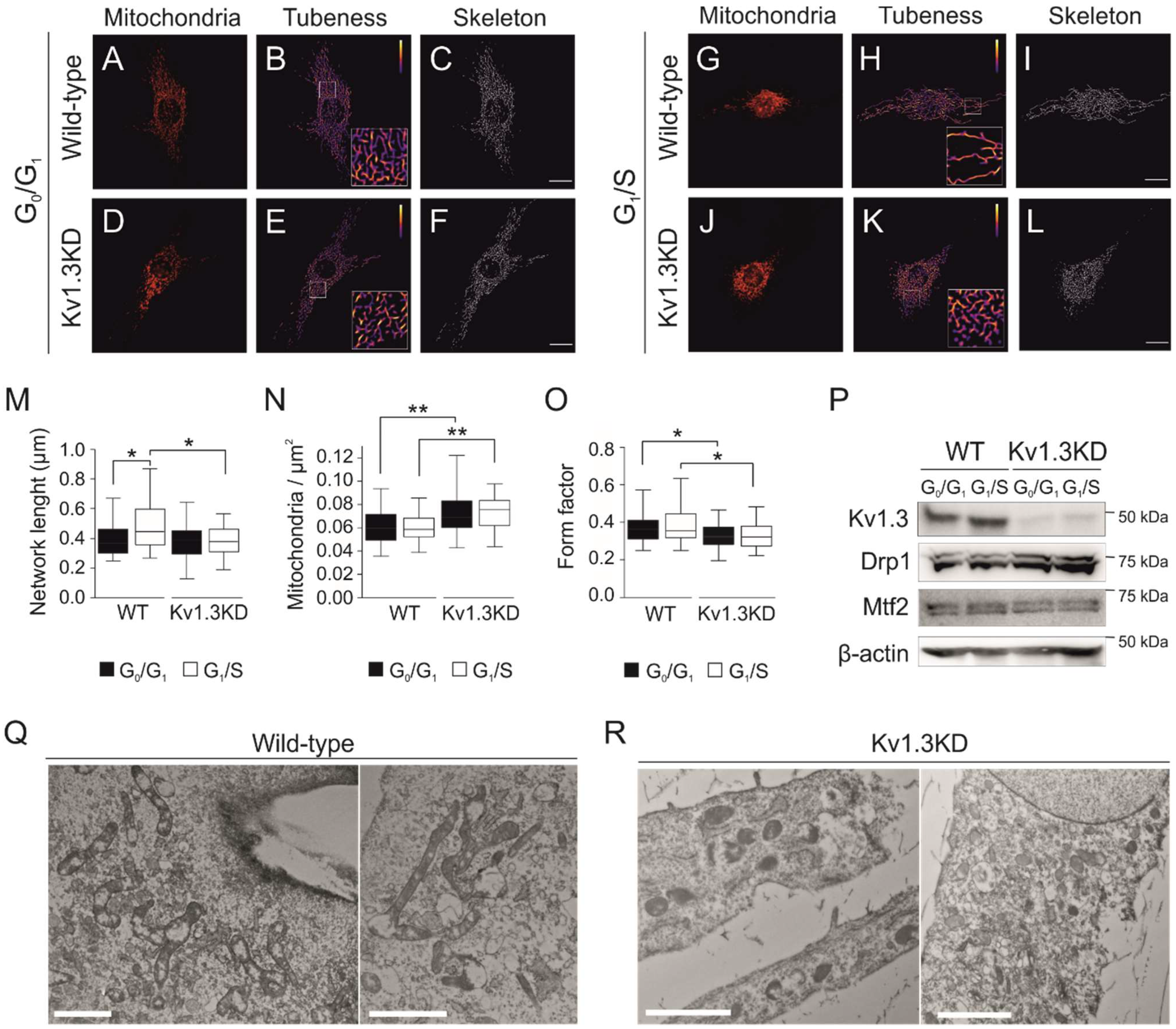
3.4. Kv1.3 Promotes Hyperfusion of the Mitochondrial Network during the G1/S Transition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muir, L.A.; Baker, N.A.; Washabaugh, A.R.; Neeley, C.K.; Flesher, C.G.; DelProposto, J.B.; Geletka, L.M.; Ghaferi, A.A.; Finks, J.F.; Singer, K.; et al. Adipocyte hypertrophy-hyperplasia balance contributes to weight loss after bariatric surgery. Adipocyte 2017, 6, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, L.A.; Neeley, C.K.; Meyer, K.A.; Baker, N.A.; Brosius, A.M.; Washabaugh, A.R.; Varban, O.A.; Finks, J.F.; Zamarron, B.F.; Flesher, C.G.; et al. Adipose tissue fibrosis, hypertrophy, and hyperplasia: Correlations with diabetes in human obesity. Obesity 2016, 24, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drolet, R.; Richard, C.; Sniderman, A.D.; Mailloux, J.; Fortier, M.; Huot, C.; Rheaume, C.; Tchernof, A. Hypertrophy and hyperplasia of abdominal adipose tissues in women. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2008, 32, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalding, K.L.; Arner, E.; Westermark, P.O.; Bernard, S.; Buchholz, B.A.; Bergmann, O.; Blomqvist, L.; Hoffstedt, J.; Naslund, E.; Britton, T.; et al. Dynamics of fat cell turnover in humans. Nature 2008, 453, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Koni, P.A.; Wang, P.; Li, G.; Kaczmarek, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Flavell, R.A.; Desir, G.V. The voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 regulates energy homeostasis and body weight. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, K.; Overton, J.M.; Fadool, D.A. Kv1.3 gene-targeted deletion alters longevity and reduces adiposity by increasing locomotion and metabolism in melanocortin-4 receptor-null mice. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2008, 32, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Verdaguer, M.; Capera, J.; Serrano-Novillo, C.; Estadella, I.; Sastre, D.; Felipe, A. The voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 is a promising multitherapeutic target against human pathologies. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.K.; Eckel-Mahan, K.L.; Mirbolooki, M.R.; Tjong, I.; Griffey, S.M.; Schmunk, G.; Koehne, A.; Halbout, B.; Iadonato, S.; Pedersen, B.; et al. Selective Kv1.3 channel blocker as therapeutic for obesity and insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2239–E2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, K.; Overton, J.M.; Fadool, D.A. Diet-induced obesity resistance of Kv1.3−/− mice is olfactory bulb dependent. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2012, 24, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahalan, M.D.; Chandy, K.G. The functional network of ion channels in T lymphocytes. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 231, 59–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, R.; Escalada, A.; Coma, M.; Fuster, G.; Sanchez-Tillo, E.; Lopez-Iglesias, C.; Soler, C.; Solsona, C.; Celada, A.; Felipe, A. Differential voltage-dependent K+ channel responses during proliferation and activation in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46307–46320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Kaczmarek, L.K.; Wu, Y.; Koni, P.A.; Flavell, R.A.; Desir, G.V. The voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 regulates peripheral insulin sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3112–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Verdaguer, M.; Capera, J.; Ortego-Dominguez, M.; Bielanska, J.; Comes, N.; Montoro, R.J.; Camps, M.; Felipe, A. Caveolar targeting links Kv1.3 with the insulin-dependent adipocyte physiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2018, 75, 4059–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Novillo, C.; Capera, J.; Colomer-Molera, M.; Condom, E.; Ferreres, J.C.; Felipe, A. Implication of Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Neoplastic Cell Proliferation. Cancers 2019, 11, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCoursey, T.E.; Chandy, K.G.; Gupta, S.; Cahalan, M.D. Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes: A role in mitogenesis? Nature 1984, 307, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Garcia, M.T.; Cidad, P.; Lopez-Lopez, J.R. The secret life of ion channels: Kv1.3 potassium channels and proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2018, 314, C27–C42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittajallu, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Ghiani, C.A.; Heckman, T.; McBain, C.J.; Gallo, V. Regulation of Kv1 subunit expression in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and their role in G1/S phase progression of the cell cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2350–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Perez, L.; Cidad, P.; Alvarez-Miguel, I.; Santos-Hipolito, A.; Torres-Merino, R.; Alonso, E.; de la Fuente, M.A.; Lopez-Lopez, J.R.; Perez-Garcia, M.T. Molecular Determinants of Kv1.3 Potassium Channels-induced Proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 3569–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cidad, P.; Jimenez-Perez, L.; Garcia-Arribas, D.; Miguel-Velado, E.; Tajada, S.; Ruiz-McDavitt, C.; Lopez-Lopez, J.R.; Perez-Garcia, M.T. Kv1.3 channels can modulate cell proliferation during phenotypic switch by an ion-flux independent mechanism. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzo, R.; Mattarei, A.; Romio, M.; Paradisi, C.; Zoratti, M.; Szabo, I.; Leanza, L. Regulation of Proliferation by a Mitochondrial Potassium Channel in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leanza, L.; Henry, B.; Sassi, N.; Zoratti, M.; Chandy, K.G.; Gulbins, E.; Szabo, I. Inhibitors of mitochondrial Kv1.3 channels induce Bax/Bak-independent death of cancer cells. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Munoz, E.; Lopez-Iglesias, C.; Calvo, M.; Palacin, M.; Zorzano, A.; Camps, M. Caveolin-1 loss of function accelerates glucose transporter 4 and insulin receptor degradation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 3493–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalonga, N.; Martinez-Marmol, R.; Roura-Ferrer, M.; David, M.; Valenzuela, C.; Soler, C.; Felipe, A. Cell cycle-dependent expression of Kv1.5 is involved in myoblast proliferation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo-Gracia, A.; Bielanska, J.; Hernandez-Losa, J.; Castellvi, J.; Ruiz-Marcellan, M.C.; Ramon y Cajal, S.; Condom, E.; Manils, J.; Soler, C.; Comes, N.; et al. Emerging role for the voltage-dependent K+ channel Kv1.5 in B-lymphocyte physiology: Expression associated with human lymphoma malignancy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastre, D.; Estadella, I.; Bosch, M.; Felipe, A. Triple-Colocalization Approach to Assess Traffic Patterns and Their Modulation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2040, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, N.M.; Chi, H. Hallmarks of T-cell Exit from Quiescence. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros-Baro, A.; Lopez-Iglesias, C.; Peiro, S.; Bellido, D.; Palacin, M.; Zorzano, A.; Camps, M. Lipid rafts are required for GLUT4 internalization in adipose cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12050–12055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar-Roa, M.; Malumbres, M. Fueling the Cell Division Cycle. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesa, M.; Van der Bliek, A.; Shirihai, O.S. To Fis or not to Fuse? This is the question! EMBO J. 2019, 38, e101839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Marmol, R.; Comes, N.; Styrczewska, K.; Perez-Verdaguer, M.; Vicente, R.; Pujadas, L.; Soriano, E.; Sorkin, A.; Felipe, A. Unconventional EGF-induced ERK1/2-mediated Kv1.3 endocytosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2016, 73, 1515–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Ponce, M.P.; Mateos, J.C.; Bellido, J.A. Insulin increases the density of potassium channels in white adipocytes: Possible role in adipogenesis. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 174, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Szabo, I.; Bock, J.; Jekle, A.; Soddemann, M.; Adams, C.; Lang, F.; Zoratti, M.; Gulbins, E. A novel potassium channel in lymphocyte mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 12790–12798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leanza, L.; Romio, M.; Becker, K.A.; Azzolini, M.; Trentin, L.; Manago, A.; Venturini, E.; Zaccagnino, A.; Mattarei, A.; Carraretto, L.; et al. Direct Pharmacological Targeting of a Mitochondrial Ion Channel Selectively Kills Tumor Cells In Vivo. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 516–531.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, A.; Pasche, M.; Junker, C.; Al-Ansary, D.; Rieger, H.; Kummerow, C.; Nunez, L.; Villalobos, C.; Meraner, P.; Becherer, U.; et al. Calcium microdomains at the immunological synapse: How ORAI channels, mitochondria and calcium pumps generate local calcium signals for efficient T-cell activation. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3895–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raturi, A.; Simmen, T. Where the endoplasmic reticulum and the mitochondrion tie the knot: The mitochondria-associated membrane (MAM). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S.F.; Flinck, M.; Pardo, L. The interplay between dysregulated ion transport and mitochondrial architecture as a dangerous liaison in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiros, P.M.; Mottis, A.; Auwerx, J. Mitonuclear communication in homeostasis and stress. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mehdi, A.B.; Pastukh, V.M.; Swiger, B.M.; Reed, D.J.; Patel, M.R.; Bardwell, G.C.; Pastukh, V.V.; Alexeyev, M.F.; Gillespie, M.N. Perinuclear mitochondrial clustering creates an oxidant-rich nuclear domain required for hypoxia-induced transcription. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.W.; Staples, O.; Turmaine, M.; Ashcroft, M. CHCHD4 Regulates Intracellular Oxygenation and Perinuclear Distribution of Mitochondria. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemurro, C.; Vadrevu, S.; Gurlo, T.; Butler, A.E.; Vongbunyong, K.E.; Petcherski, A.; Shirihai, O.S.; Satin, L.S.; Braas, D.; Butler, P.C.; et al. Cell cycle-related metabolism and mitochondrial dynamics in a replication-competent pancreatic beta-cell line. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 2086–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, K.; Wunder, C.; Roysam, B.; Lin, G.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. A hyperfused mitochondrial state achieved at G1-S regulates cyclin E buildup and entry into S phase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11960–11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.H.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Kung, C.P.; Weber, J.D.; Patti, G.J. Mitochondrial fusion supports increased oxidative phosphorylation during cell proliferation. eLife 2019, 8, e41351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, T.; Hwang, P.M. The Krebs cycle meets the cell cycle: Mitochondria and the G1-S transition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11825–11826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styles, F.L.; Al-Owais, M.M.; Scragg, J.L.; Chuntharpursat-Bon, E.; Hettiarachchi, N.T.; Lippiat, J.D.; Minard, A.; Bon, R.S.; Porter, K.; Sukumar, P.; et al. Kv1.3 voltage-gated potassium channels link cellular respiration to proliferation through a non-conducting mechanism. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovach, C.P.; Al Koborssy, D.; Huang, Z.; Chelette, B.M.; Fadool, J.M.; Fadool, D.A. Mitochondrial Ultrastructure and Glucose Signaling Pathways Attributed to the Kv1.3 Ion Channel. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Capera, J.; Pérez-Verdaguer, M.; Navarro-Pérez, M.; Felipe, A. Kv1.3 Controls Mitochondrial Dynamics during Cell Cycle Progression. Cancers 2021, 13, 4457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174457
Capera J, Pérez-Verdaguer M, Navarro-Pérez M, Felipe A. Kv1.3 Controls Mitochondrial Dynamics during Cell Cycle Progression. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174457
Chicago/Turabian StyleCapera, Jesusa, Mireia Pérez-Verdaguer, María Navarro-Pérez, and Antonio Felipe. 2021. "Kv1.3 Controls Mitochondrial Dynamics during Cell Cycle Progression" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174457
APA StyleCapera, J., Pérez-Verdaguer, M., Navarro-Pérez, M., & Felipe, A. (2021). Kv1.3 Controls Mitochondrial Dynamics during Cell Cycle Progression. Cancers, 13(17), 4457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174457






