Dual Targeting of EGFR with PLK1 Exerts Therapeutic Synergism in Taxane-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma by Suppressing ABC Transporters
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture and Establishment of Paclitaxel-Resistant Cancer Cells
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Fluorometric Caspase 3 Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
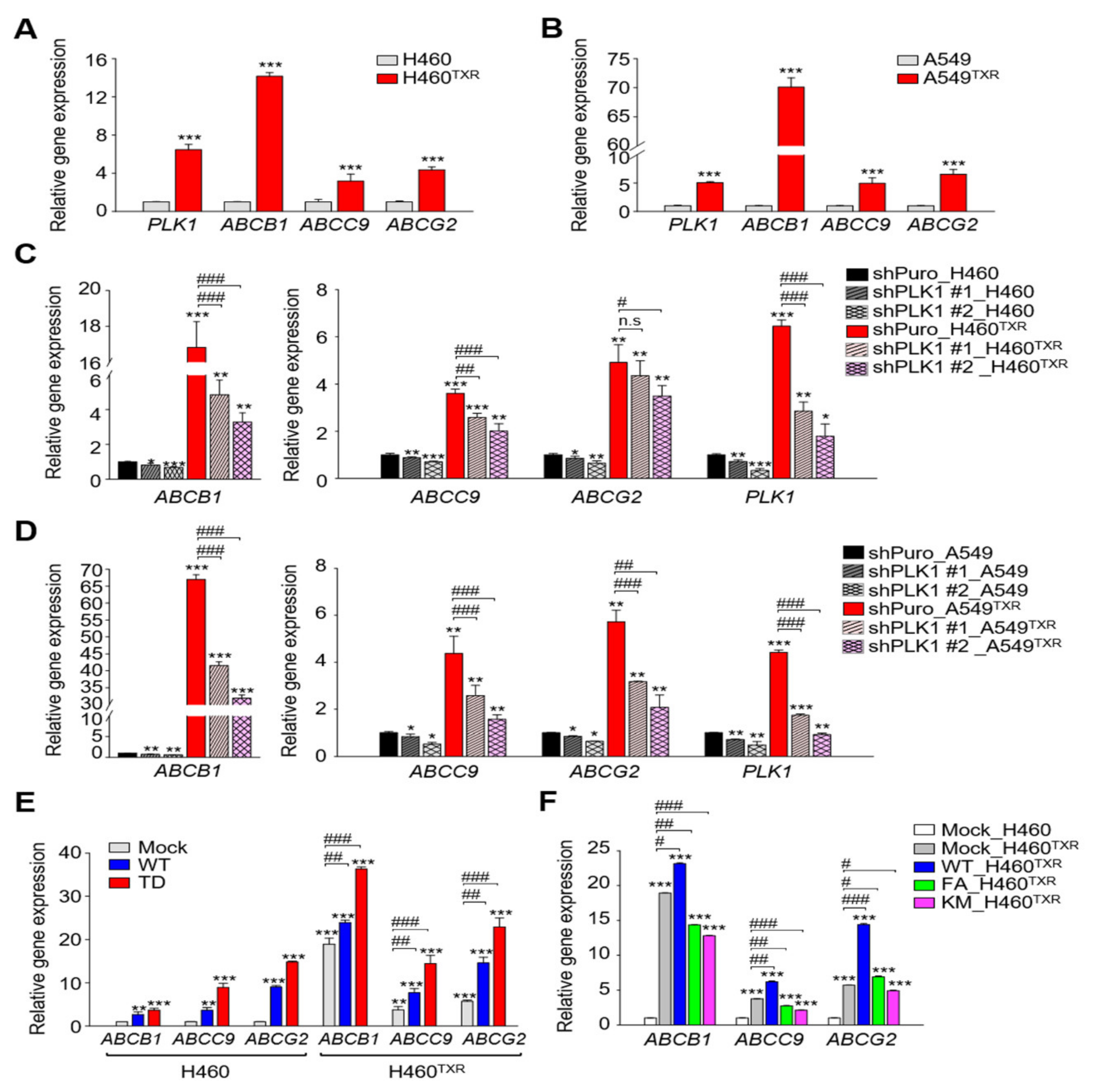
3.1. ABC Transporters Were Regulated by Active PLK1 in Paclitaxel-Resistant LUAD
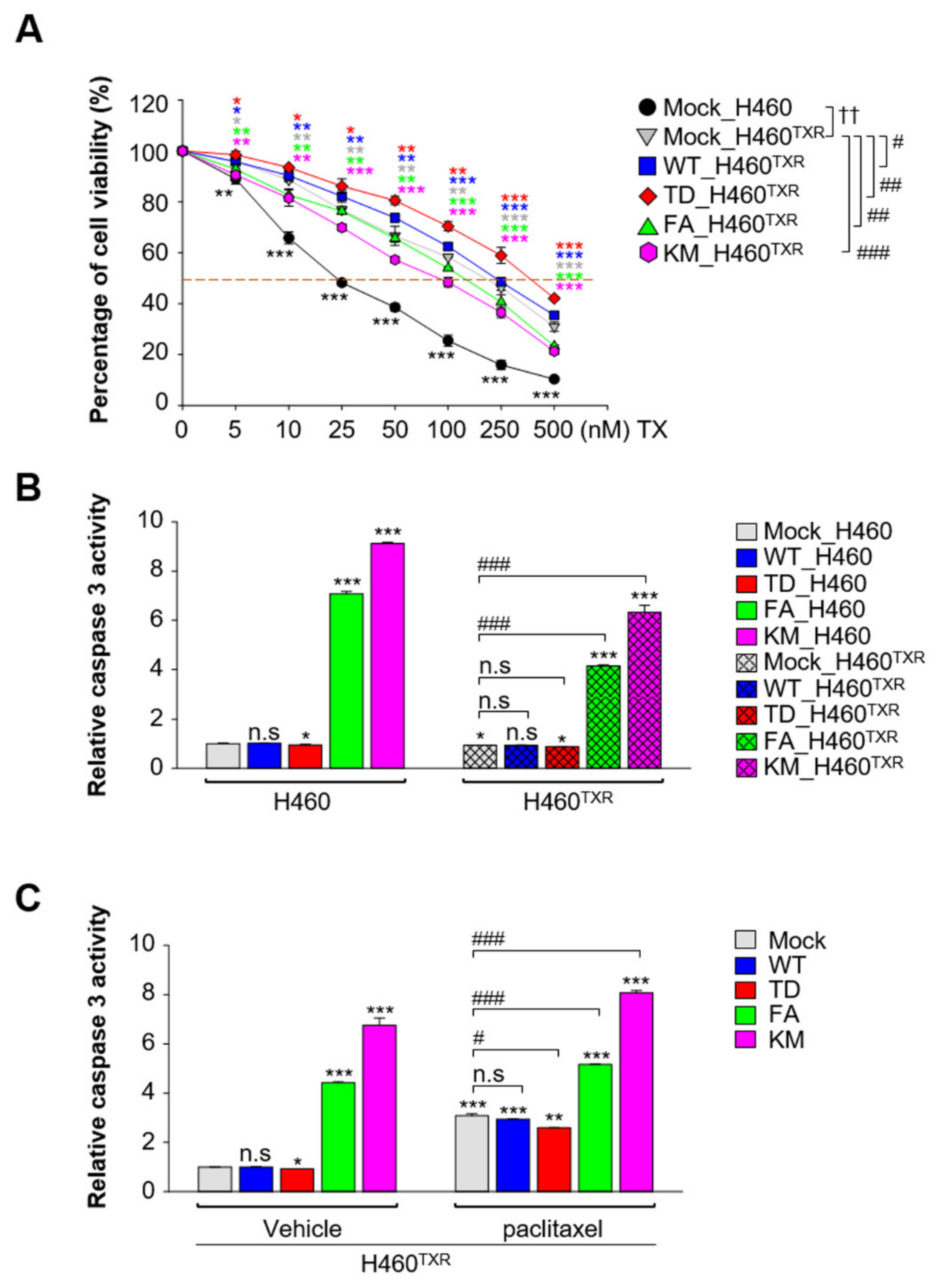
3.2. Paclitaxel-Resistant NCI-H460TXR Lung Cancer Cells Underwent Apoptosis More Easily by Expression of Non-Functional PLK1
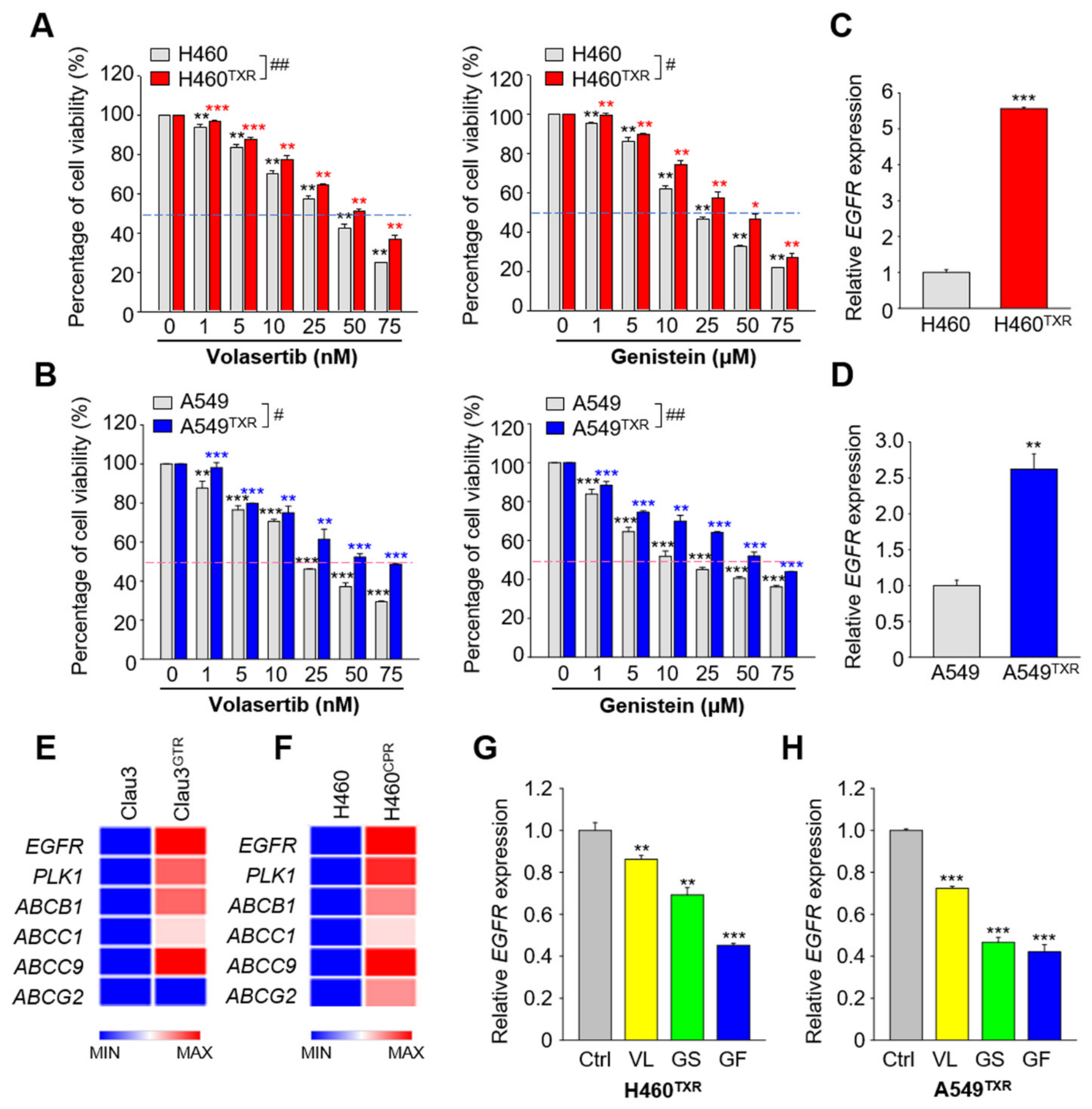
3.3. Paclitaxel-Resistant LUAD Upregulates EGFR Expression, Which Is Suppressed by Treatment with Gefitinib and PLK1 Inhibitors
3.4. Gefitinib Treatment Results in More Effective Apoptotic Cell Death in Paclitaxel-Resistant Lung Cancer Cells Expressing High Levels of ABC Transporters Than in Non-Resistant Lung Cancer
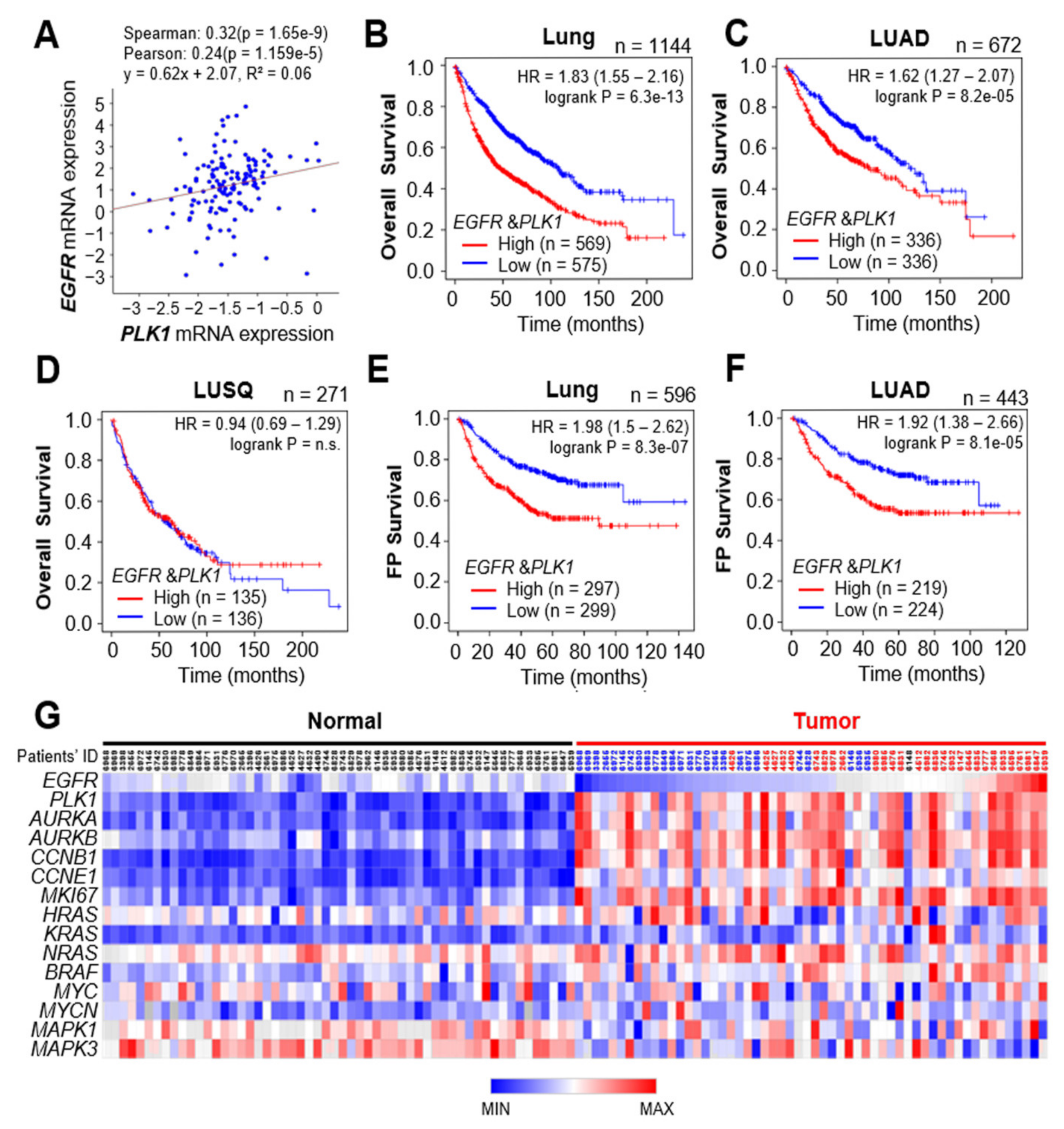
3.5. Clinical Relevance of EGFR and PLK1 in LUAD Cancer Patients
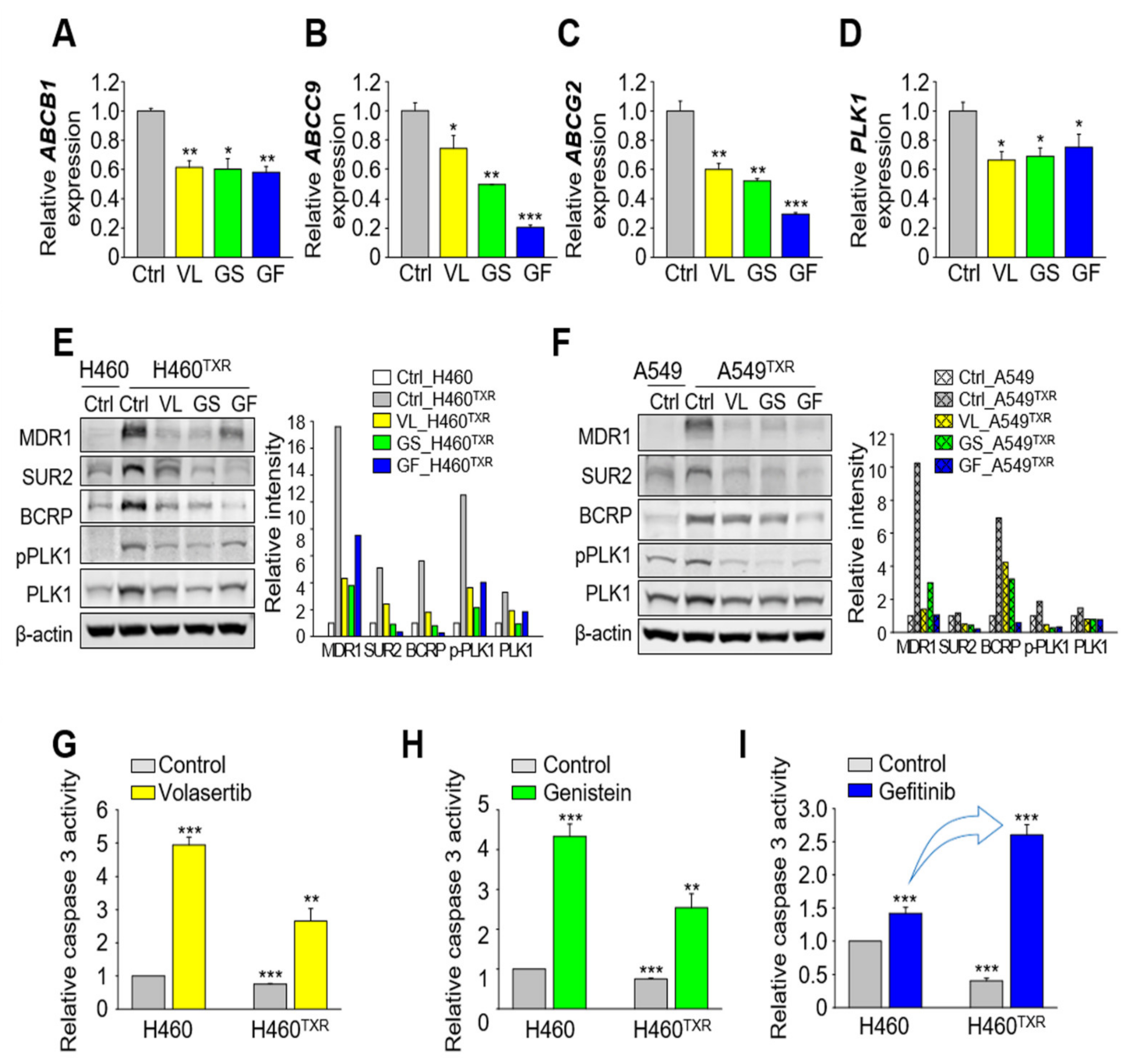
3.6. Combination of Gefitinib and PLK1 Inhibitor Was Effective in Paclitaxel-Resistant NCI-H460TXR Cells
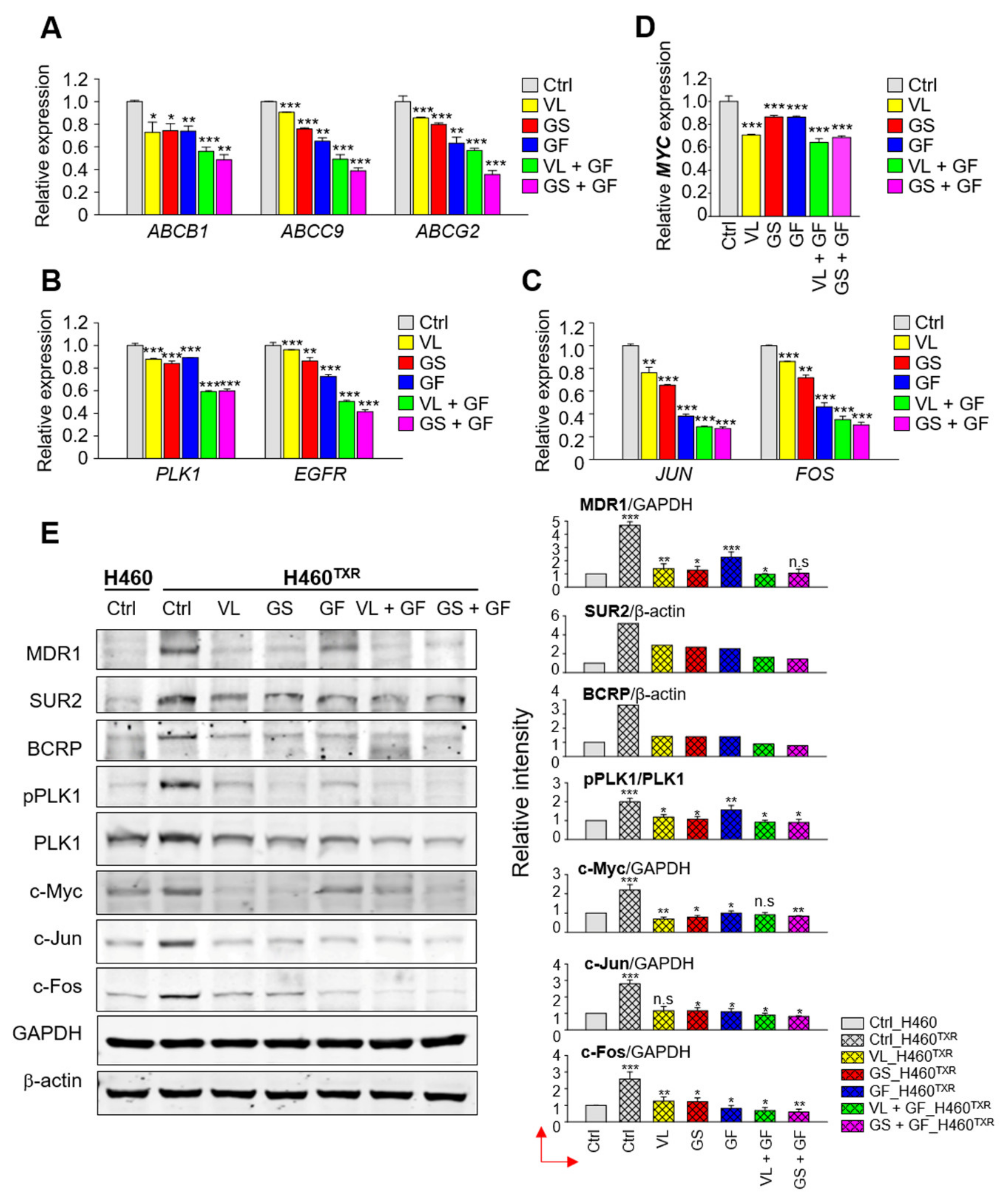
3.7. Inhibition of EGFR and PLK1 Effectively Reduced the Expression of ABC Transporters by Suppressing MYC and FOS/JUN in Paclitaxel-Resistant LUAD Cells
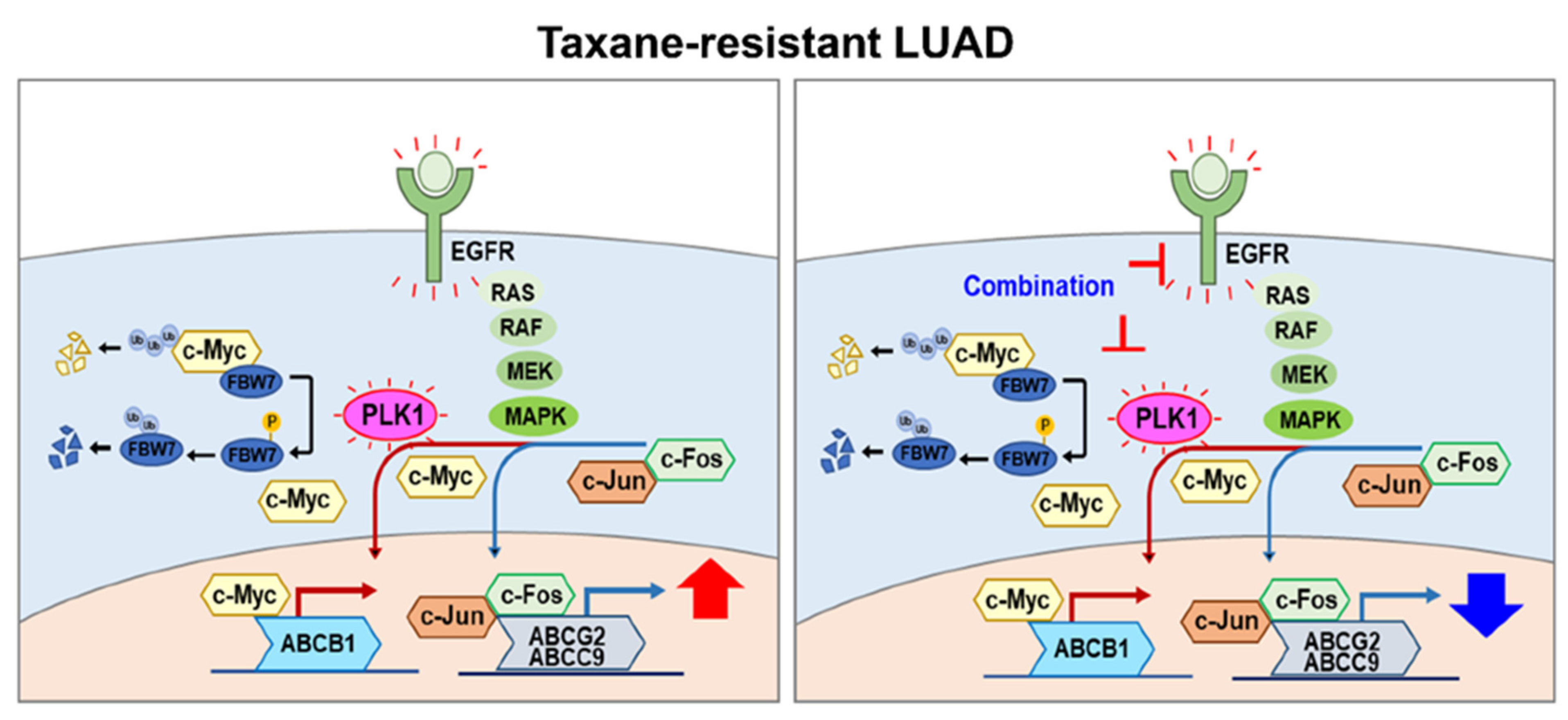
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denisenko, T.V.; Budkevich, I.N.; Zhivotovsky, B. Cell death-based treatment of lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Parkin, D.M.; Steliarova-Foucher, E. Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politi, K.; Herbst, R.S. Lung cancer in the era of precision medicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramanathan, B.; Jan, K.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Hour, T.C.; Yu, H.J.; Pu, Y.S. Resistance to paclitaxel is proportional to cellular total antioxidant capacity. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 8455–8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marsland, T.A.; Garfield, D.H.; Khan, M.M.; Look, R.M.; Boehm, K.A.; Asmar, L. Sequential versus concurrent paclitaxel and carboplatin for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer in elderly patients and patients with poor performance status: Results of two Phase II, multicenter trials. Lung Cancer 2005, 47, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahreddine, H.; Borden, K.L. Mechanisms and insights into drug resistance in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, M.; Hamon, Y.; Chimini, G. The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. J. Lipid. Res. 2001, 42, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szakacs, G.; Paterson, J.K.; Ludwig, J.A.; Booth-Genthe, C.; Gottesman, M.M. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Balch, C.; Chan, M.W.; Lai, H.C.; Matei, D.; Schilder, J.M.; Yan, P.S.; Huang, T.H.; Nephew, K.P. Identification and characterization of ovarian cancer-initiating cells from primary human tumors. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4311–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lhomme, C.; Joly, F.; Walker, J.L.; Lissoni, A.A.; Nicoletto, M.O.; Manikhas, G.M.; Baekelandt, M.M.; Gordon, A.N.; Fracasso, P.M.; Mietlowski, W.L.; et al. Phase III study of valspodar (PSC 833) combined with paclitaxel and carboplatin compared with paclitaxel and carboplatin alone in patients with stage IV or suboptimally debulked stage III epithelial ovarian cancer or primary peritoneal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2674–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenberg, W.R.; Rue, M.; Blood, E.A.; Dalton, W.S.; Shustik, C.; Larson, R.A.; Sonneveld, P.; Greipp, P.R. Phase III study of PSC-833 (valspodar) in combination with vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone (valspodar/VAD) versus VAD alone in patients with recurring or refractory multiple myeloma (E1A95): A trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Cancer 2006, 106, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, P.L.; Lee, S.J.; Advani, R.; Tallman, M.S.; Sikic, B.I.; Letendre, L.; Dugan, K.; Lum, B.; Chin, D.L.; Dewald, G.; et al. Mitoxantrone, etoposide, and cytarabine with or without valspodar in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: A phase III trial (E2995). J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, T.; Nomizu, T.; Toi, M.; Ito, Y.; Noguchi, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Asaga, T.; Minami, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Aogi, K.; et al. Dofequidar fumarate (MS-209) in combination with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and fluorouracil for patients with advanced or recurrent breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.; Bates, S.E. Tariquidar (XR9576): A P-glycoprotein drug efflux pump inhibitor. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2007, 7, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cripe, L.D.; Uno, H.; Paietta, E.M.; Litzow, M.R.; Ketterling, R.P.; Bennett, J.M.; Rowe, J.M.; Lazarus, H.M.; Luger, S.; Tallman, M.S. Zosuquidar, a novel modulator of P-glycoprotein, does not improve the outcome of older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group 3999. Blood 2010, 116, 4077–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.B.; Woo, S.U.; Yim, H. Cotargeting Plk1 and androgen receptor enhances the therapeutic sensitivity of paclitaxel-resistant prostate cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919846375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, H.; Erikson, R.L. Plk1-targeted therapies in TP53- or RAS-mutated cancer. Mutat. Res. 2014, 761, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sero, V.; Tavanti, E.; Vella, S.; Hattinger, C.M.; Fanelli, M.; Michelacci, F.; Versteeg, R.; Valsasina, B.; Gudeman, B.; Picci, P.; et al. Targeting polo-like kinase 1 by NMS-P937 in osteosarcoma cell lines inhibits tumor cell growth and partially overcomes drug resistance. Invest. New Drugs 2014, 32, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, D.S.; Henry, S.M.; Shubin, A.D.; Hoffman, A.S.; Stayton, P.S. pH-responsive polymeric sirna carriers sensitize multidrug resistant ovarian cancer cells to doxorubicin via knockdown of polo-like kinase 1. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gutteridge, R.E.; Ndiaye, M.A.; Liu, X.; Ahmad, N. Plk1 Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy: From Laboratory to Clinics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.B.; Jang, H.R.; Xu, R.; Won, J.Y.; Yim, H. Active PLK1-driven metastasis is amplified by TGF-beta signaling that forms a positive feedback loop in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 767–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lei, M.; Erikson, R.L. Normal cells, but not cancer cells, survive severe Plk1 depletion. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 2093–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.B.; Woo, S.U.; Chin, Y.W.; Jang, Y.J.; Yim, H. Sensitivity of TP53-Mutated Cancer Cells to the Phytoestrogen Genistein Is Associated With Direct Inhibition of Plk1 Activity. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 2818–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Verdier-Pinard, P.; Fernandez-Fuentes, N.; Burd, B.; Angeletti, R.; Fiser, A.; Horwitz, S.B.; Orr, G.A. Insights into the mechanism of microtubule stabilization by Taxol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10166–10173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orr, G.A.; Verdier-Pinard, P.; McDaid, H.; Horwitz, S.B. Mechanisms of Taxol resistance related to microtubules. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7280–7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.B.; Kim, C.H.; Jang, H.R.; Yim, H. Combination of Inhibitors of USP7 and PLK1 has a Strong Synergism against Paclitaxel Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Ishida, J.; Nakagawa, S.; Ogawara, H.; Watanabe, S.; Itoh, N.; Shibuya, M.; Fukami, Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 5592–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooker, P.; Yen, W.C.; Ng, S.C.; Negro-Vilar, A.; Hermann, T.W. Bexarotene (LGD1069, Targretin), a selective retinoid X receptor agonist, prevents and reverses gemcitabine resistance in NSCLC cells by modulating gene amplification. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 4425–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurz, E.U.; Cole, S.P.; Deeley, R.G. Identification of DNA-protein interactions in the 5′ flanking and 5′ untranslated regions of the human multidrug resistance protein (MRP1) gene: Evaluation of a putative antioxidant response element/AP-1 binding site. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cripe, L.D.; Gelfanov, V.M.; Smith, E.A.; Spigel, D.R.; Phillips, C.A.; Gabig, T.G.; Jung, S.H.; Fyffe, J.; Hartman, A.D.; Kneebone, P.; et al. Role for c-jun N-terminal kinase in treatment-refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML): Signaling to multidrug-efflux and hyperproliferation. Leukemia 2002, 16, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey-Dell, K.J.; Hassel, B.; Doyle, L.A.; Ross, D.D. Promoter characterization and genomic organization of the human breast cancer resistance protein (ATP-binding cassette transporter G2) gene. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1520, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, N.; Schooley, J.F., Jr.; Claycomb, W.C.; Flagg, T.P. Promoter DNA methylation regulates murine SUR1 (Abcc8) and SUR2 (Abcc9) expression in HL-1 cardiomyocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porro, A.; Haber, M.; Diolaiti, D.; Iraci, N.; Henderson, M.; Gherardi, S.; Valli, E.; Munoz, M.A.; Xue, C.; Flemming, C.; et al. Direct and coordinate regulation of ATP-binding cassette transporter genes by Myc factors generates specific transcription signatures that significantly affect the chemoresistance phenotype of cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 19532–19543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porro, A.; Chrochemore, C.; Cambuli, F.; Iraci, N.; Contestabile, A.; Perini, G. Nitric oxide control of MYCN expression and multi drug resistance genes in tumours of neural origin. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porro, A.; Iraci, N.; Soverini, S.; Diolaiti, D.; Gherardi, S.; Terragna, C.; Durante, S.; Valli, E.; Kalebic, T.; Bernardoni, R.; et al. c-MYC oncoprotein dictates transcriptional profiles of ATP-binding cassette transporter genes in chronic myelogenous leukemia CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Ma, C.; Huang, Y.; Luo, J.; Huang, C. Differential requirement of EGF receptor and its tyrosine kinase for AP-1 transactivation induced by EGF and TPA. Oncogene 2003, 22, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, D.; Yue, M.; Su, H.; Ren, P.; Jiang, J.; Li, F.; Hu, Y.; Du, H.; Liu, H.; Qing, G. Polo-like Kinase-1 Regulates Myc Stabilization and Activates a Feedforward Circuit Promoting Tumor Cell Survival. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.; Bi, C.; Zhao, X.; Lwin, T.; Wang, C.; Yuan, J.; Silva, A.S.; Shah, B.D.; Fang, B.; Li, T.; et al. PLK1 stabilizes a MYC-dependent kinase network in aggressive B cell lymphomas. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 128, 5517–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Li, Z.; Lee, P.L.; Guan, P.; Aau, M.Y.; Lee, S.T.; Feng, M.; Lim, C.Z.; Lee, E.Y.; Wee, Z.N.; et al. PDK1 signaling toward PLK1-MYC activation confers oncogenic transformation, tumor-initiating cell activation, and resistance to mTOR-targeted therapy. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 1156–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Dobi, A.; Mohamed, A.; Li, H.; Thangapazham, R.L.; Furusato, B.; Shaheduzzaman, S.; Tan, S.H.; Vaidyanathan, G.; Whitman, E.; et al. TMPRSS2-ERG fusion, a common genomic alteration in prostate cancer activates C-MYC and abrogates prostate epithelial differentiation. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5348–5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gasca, J.; Flores, M.L.; Giraldez, S.; Ruiz-Borrego, M.; Tortolero, M.; Romero, F.; Japon, M.A.; Saez, C. Loss of FBXW7 and accumulation of MCL1 and PLK1 promote paclitaxel resistance in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52751–52765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reda, M.; Ngamcherdtrakul, W.; Gu, S.; Bejan, D.S.; Siriwon, N.; Gray, J.W.; Yantasee, W. PLK1 and EGFR targeted nanoparticle as a radiation sensitizer for non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 467, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Singh, R.; Wang, L.; Nilsson, M.; Goonatilake, R.; Tong, P.; Li, L.; Giri, U.; Villalobos, P.; Mino, B.; et al. Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition diminishes acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer with T790M mutations. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 47998–48010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
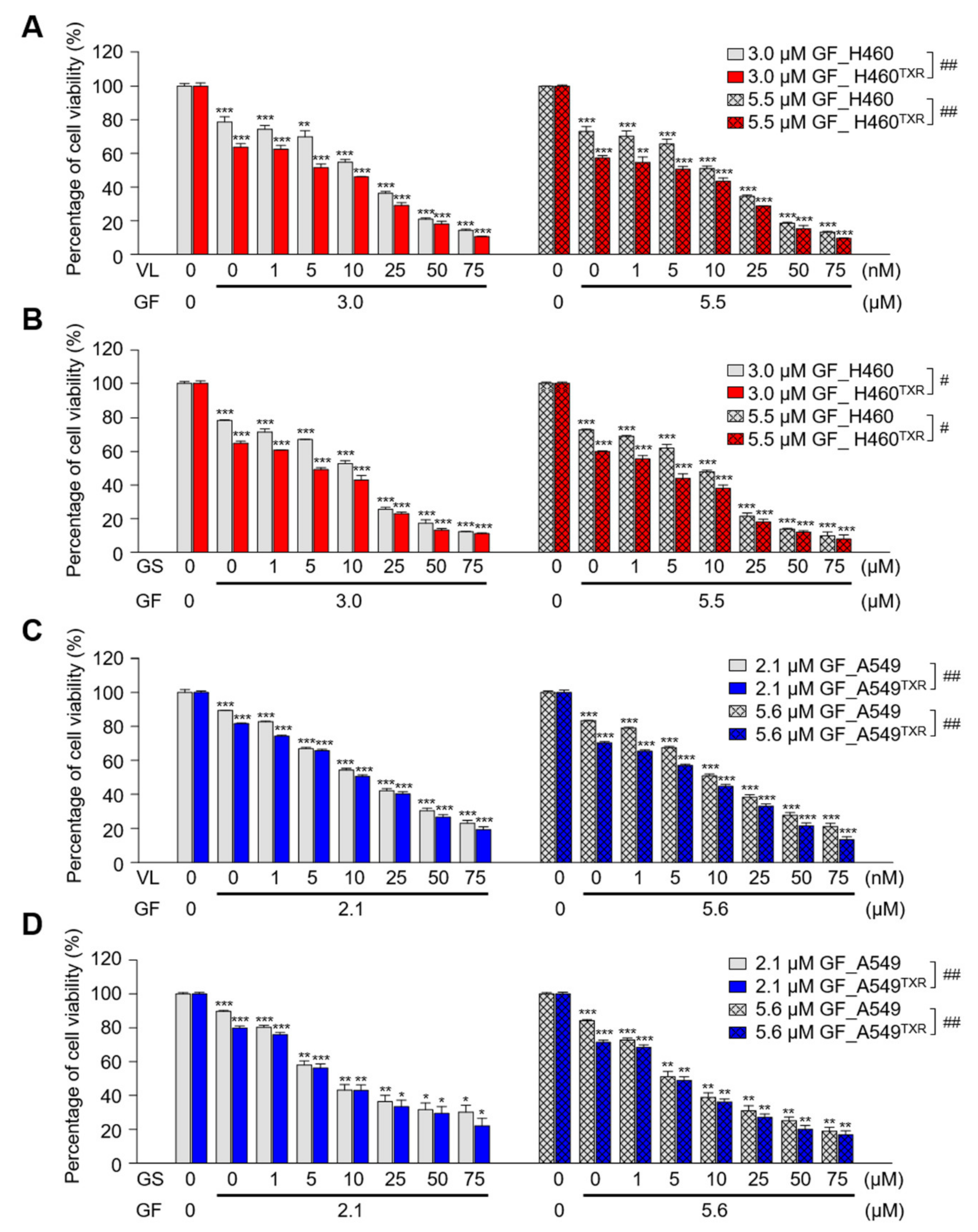
| Compounds | NCI-H460 | NCI-H460TXR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | CI | IC50 | CI | |
| Gefitinib (µM) | 16.68 | - | 12.06 | - |
| Volasertib (nM) | 30.16 | - | 51.39 | - |
| Volasertib (in combination 3.0 µM Gefitinib) | 12.79 | 0.604 | 6.41 | 0.374 |
| Volasertib (in combination 5.5 µM Gefitinib) | 10.85 | 0.690 | 5.85 | 0.570 |
| Genistein (µM) | 23.16 | - | 37.84 | - |
| Genistein (in combination 3.0 µM Gefitinib) | 10.78 | 0.645 | 4.02 | 0.355 |
| Genistein (in combination 5.5 µM Gefitinib) | 8.85 | 0.712 | 2.54 | 0.523 |
| Compounds | A549 | A549TXR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | CI | IC50 | CI | |
| Gefitinib (µM) | 19.91 | - | 43.17 | - |
| Volasertib (nM) | 21.63 | - | 67.27 | - |
| Volasertib (in combination 2.1 µM Gefitinib) | 14.16 | 0.760 | 10.42 | 0.204 |
| Volasertib (in combination 5.6 µM Gefitinib) | 10.33 | 0.759 | 7.48 | 0.241 |
| Genistein (µM) | 17.10 | - | 54.42 | - |
| Genistein (in combination 2.1 µM Gefitinib) | 7.16 | 0.524 | 6.71 | 0.172 |
| Genistein (in combination 5.6 µM Gefitinib) | 4.92 | 0.569 | 4.09 | 0.205 |
| Compounds | NCI-H460TXR | |
|---|---|---|
| IC50 | CI | |
| Gefitinib (µM) | 12.06 | - |
| Volasertib (nM) | 51.39 | - |
| Genistein (µM) | 37.84 | - |
| Volasertib (in combination 1.5 µM Gefitinib) | 8.13 | 0.283 |
| Genistein (in combination 1.5 µM Gefitinib) | 6.86 | 0.306 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, S.-B.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, D.-E.; Aldonza, M.B.D.; Kim, Y.; Yim, H. Dual Targeting of EGFR with PLK1 Exerts Therapeutic Synergism in Taxane-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma by Suppressing ABC Transporters. Cancers 2021, 13, 4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174413
Shin S-B, Kim D-H, Kim D-E, Aldonza MBD, Kim Y, Yim H. Dual Targeting of EGFR with PLK1 Exerts Therapeutic Synergism in Taxane-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma by Suppressing ABC Transporters. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174413
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Sol-Bi, Dae-Hoon Kim, Da-Eun Kim, Mark Borris D. Aldonza, Yoosik Kim, and Hyungshin Yim. 2021. "Dual Targeting of EGFR with PLK1 Exerts Therapeutic Synergism in Taxane-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma by Suppressing ABC Transporters" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174413
APA StyleShin, S.-B., Kim, D.-H., Kim, D.-E., Aldonza, M. B. D., Kim, Y., & Yim, H. (2021). Dual Targeting of EGFR with PLK1 Exerts Therapeutic Synergism in Taxane-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma by Suppressing ABC Transporters. Cancers, 13(17), 4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174413






