Anti-TRBC1 Antibody-Based Flow Cytometric Detection of T-Cell Clonality: Standardization of Sample Preparation and Diagnostic Implementation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients, Controls and Samples
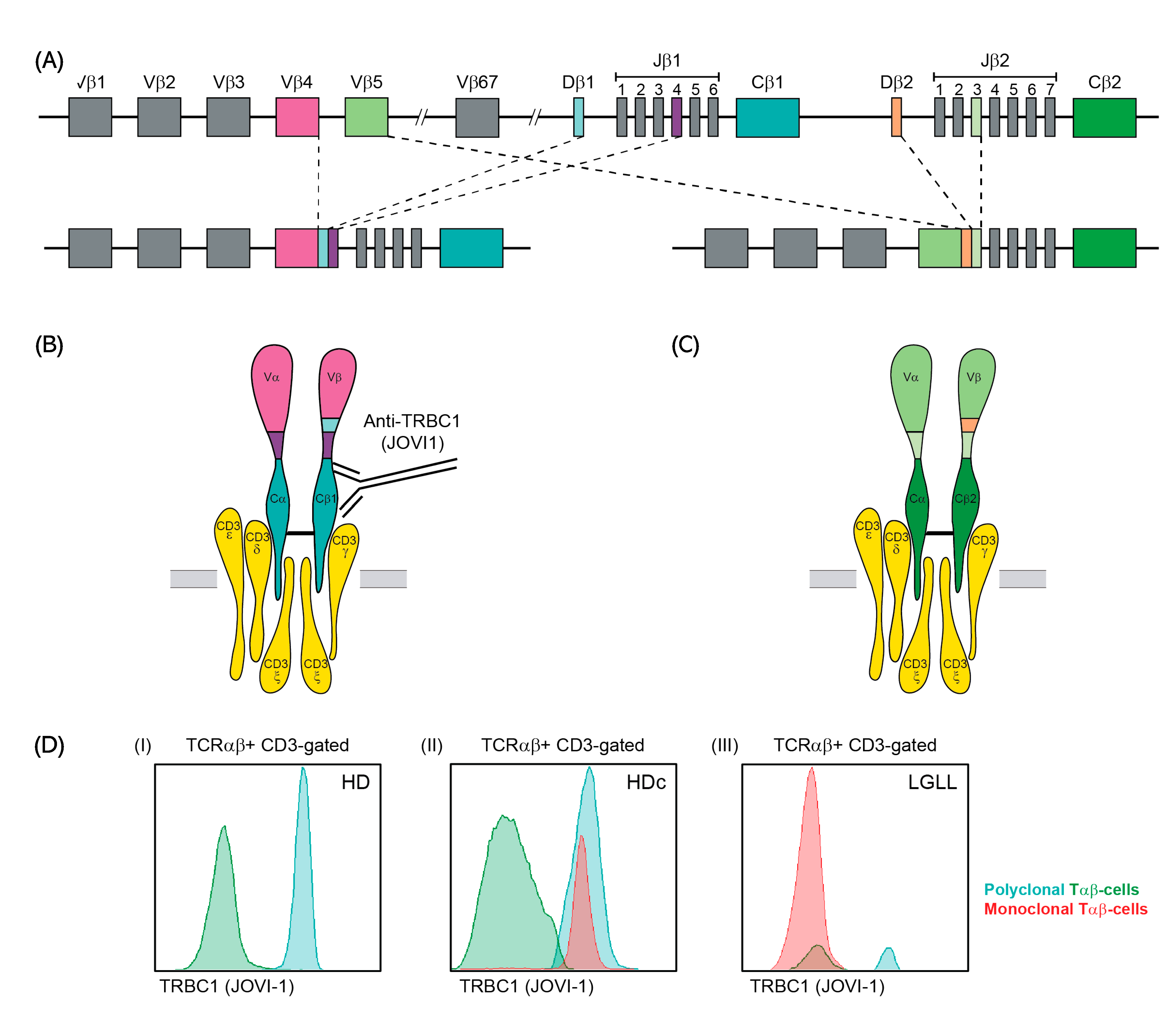
2.2. General Immunophenotypic Approach
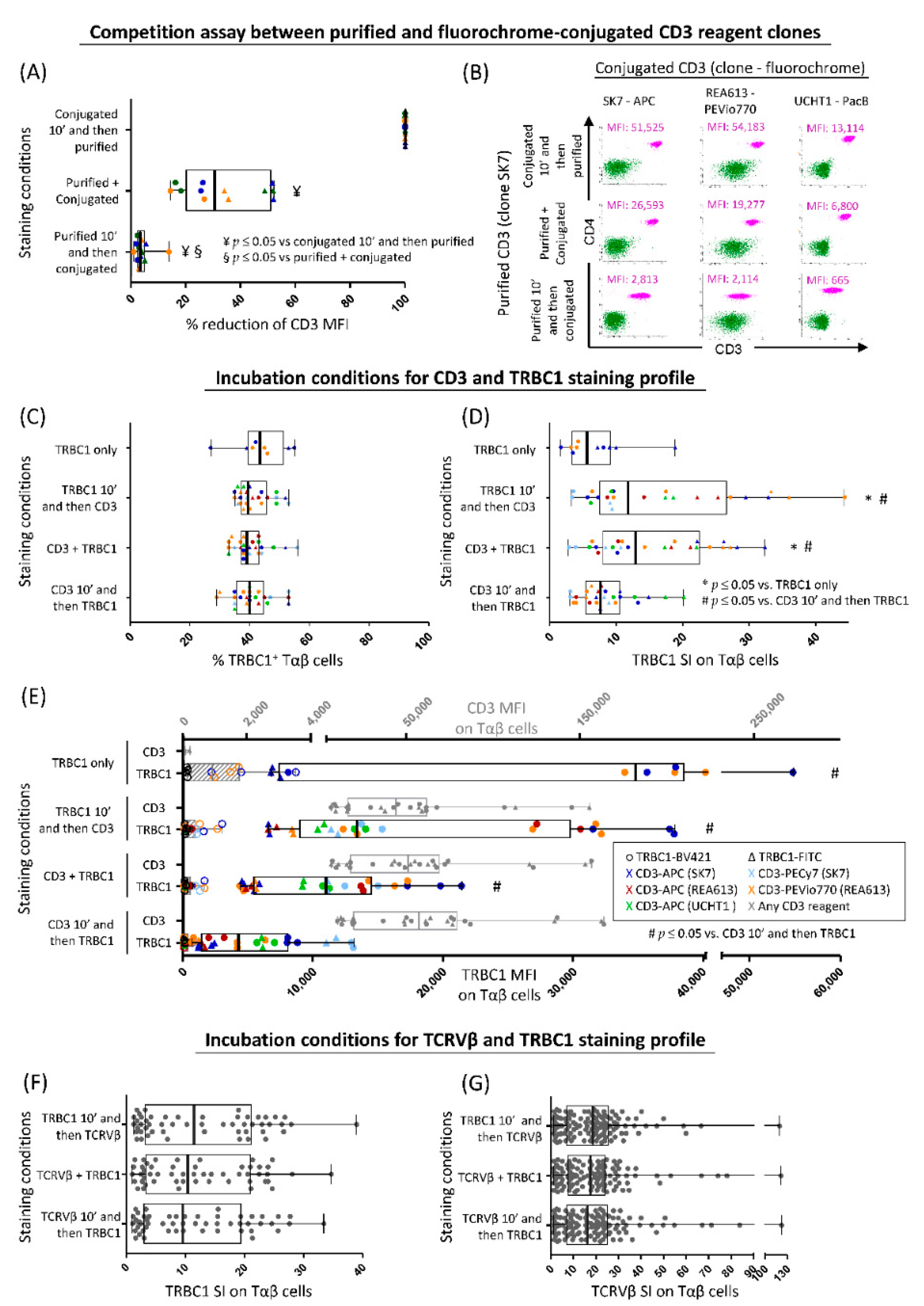
2.3. Optimization of TRBC1 Staining for Flow Cytometry
2.4. PCR-Based Detection of TRBJ1 or TRBJ2 Gene Rearrangements in FACS-Sorted Tαβ-Cell Populations
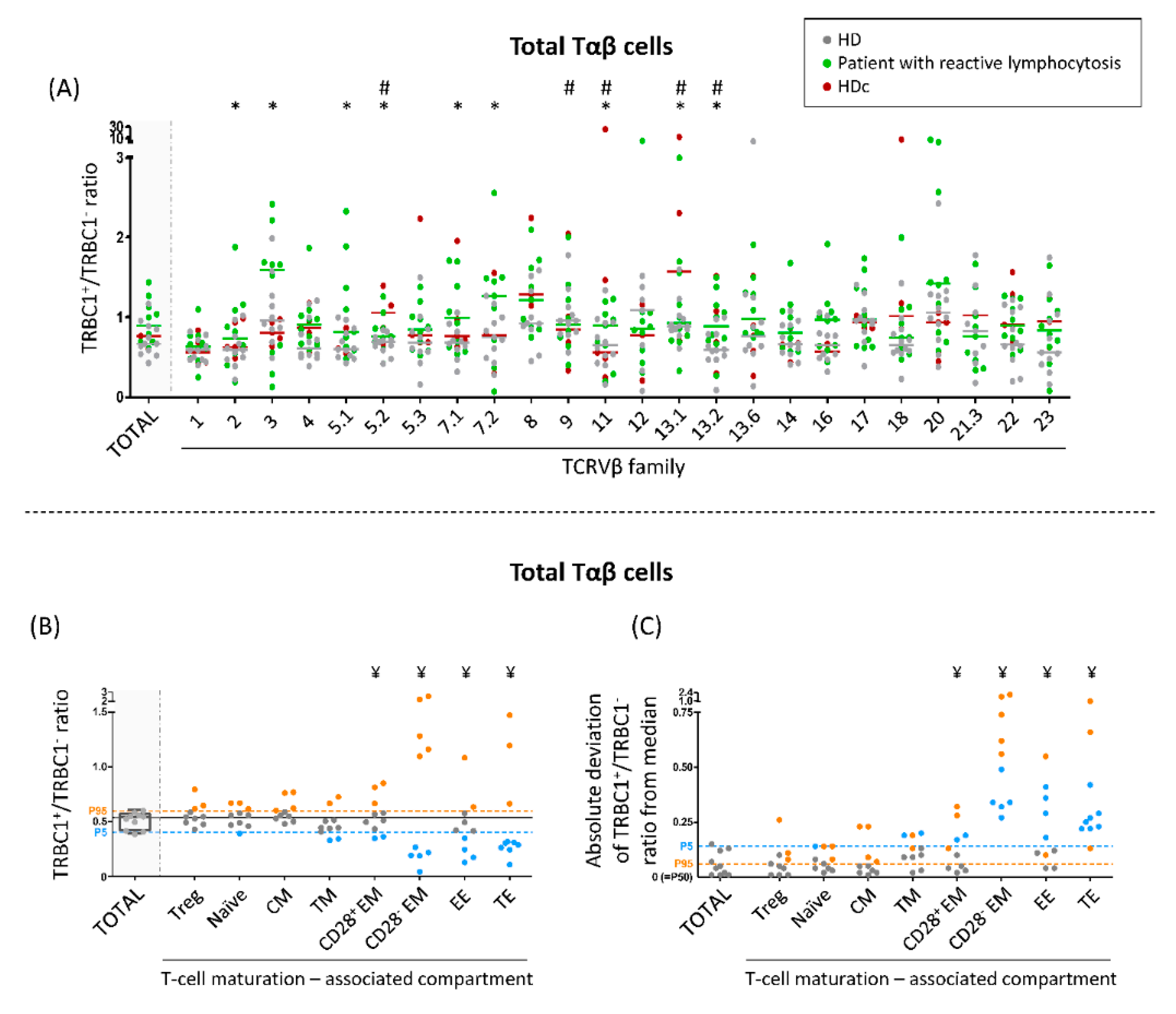
2.5. Analysis of the TRBC1+/TRBC1− Ratio in Distinct Subsets of Normal Tαβ-Cells Defined by the TCRVβ Family Expressed and Their Maturation Stage
2.6. Assessment of T-Cell Clonality on FACS-Sorted Cell Populations for Patients with T-CLPD vs. Reactive Lymphocytosis and Healthy Donors
2.7. Validation of the TRBC1-FCM Assay against Conventional Molecular and FCM Techniques for Detection of Clonal Tαβ-Cells
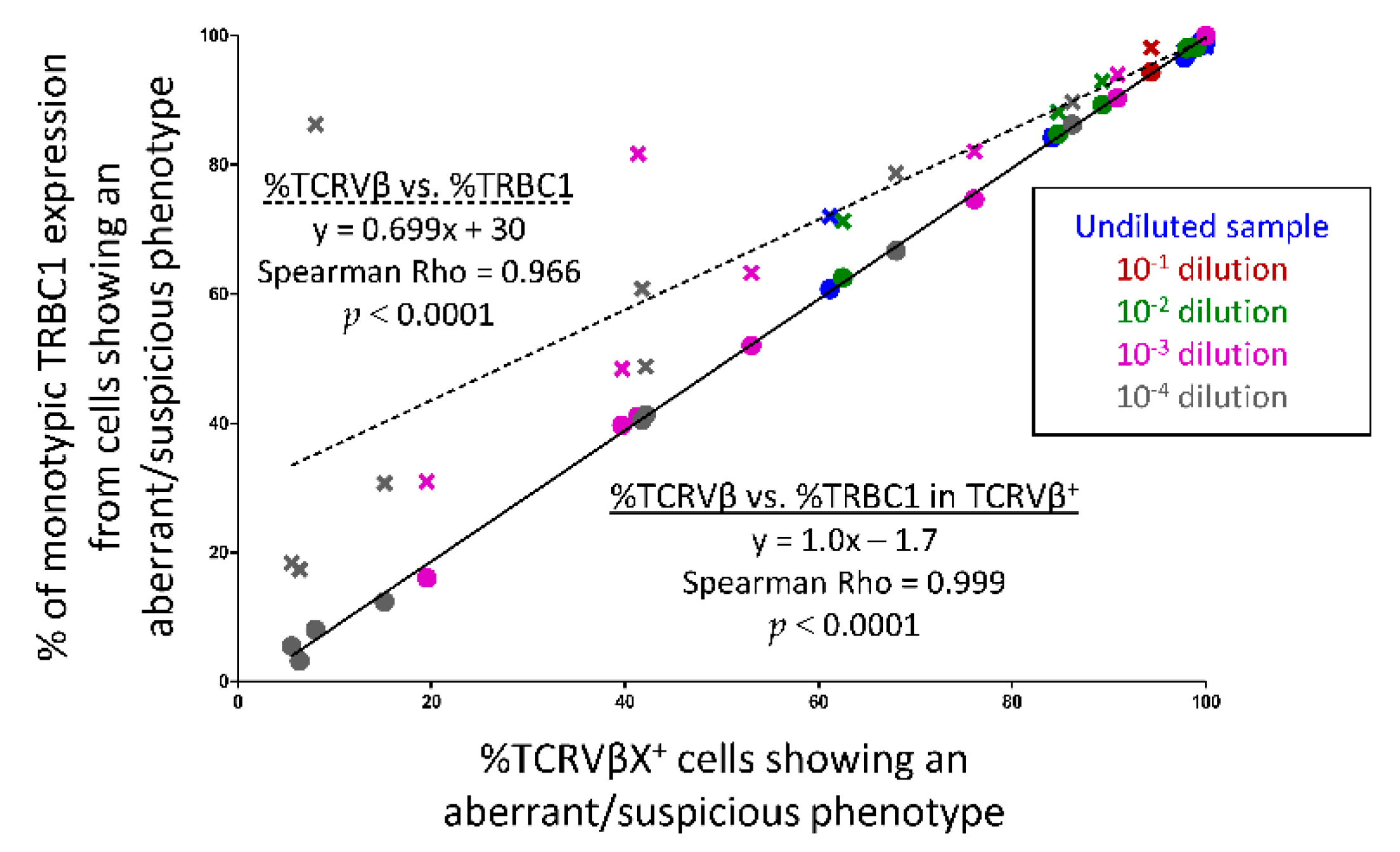
2.8. Serial Dilution Experiments of Pathological Tαβ-Cells in Normal Blood Cells
2.9. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of TRBC1 Staining by FCM
3.2. TRBJ Gene Rearrangements in FACS-Sorted TRBC1+ and/or TRBC1− Tαβ+-Cell Populations
3.3. Ranges for Polyclonal (Normal and Reactive) Tαβ-Cells and Major Tαβ-Cell Populations
3.4. TRBC1+/TRBC1− Ratio of Normal Polyclonal Tαβ-Cells and Their TCRVβ and Maturation-Associated Subsets in Normal Blood
3.5. TRBC1+/TRBC1− Ratio of Polyclonal Tαβ-Cells Expressing Different TCRVβ Families in Patients with Reactive Lymphocytosis and HDc Blood
3.6. Comparison between the TRBC1-FCM Assay and Conventional TCRVβ-FCM and/or Molecular Techniques for Assessment of Tαβ-Cell Clonality
3.7. Utility of TRBC1 for Sensitive FCM Detection of Clonal Tαβ-Cellsi in Serial Dilution Experiments of Pathological Tαβ-Cells in Normal Blood Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J.M. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; Swerdlow, S.H., Ed.; Revised 4 t.; WHO Press: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Armitage, J.O. A clinical evaluation of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood 1997, 89, 3909–3918. [Google Scholar]
- Vose, J.M.; Neumann, M.; Harris, M.E. International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: Pathology findings and clinical outcomes international T-cell lymphoma project. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4124–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, S.; Picker, L.J.; Aquino, D.B.; McKenna, R.W.; Dawson, D.B.; Kroft, S.H. Immunophenotypic analysis of peripheral T-cell neoplasms: A multiparameter flow cytometric approach. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 116, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorczyca, W.; Weisberger, J.; Liu, Z.; Tsang, P.; Hossein, M.; Wu, C.D.; Dong, H.; Wong, J.Y.L.; Tugulea, S.; Dee, S.; et al. An Approach to Diagnosis of T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders by Flow Cytometry. Clin. Cytom. 2002, 50, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevremovic, D.; Olteanu, H. Flow Cytometry Applications in the Diagnosis of T/NK-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Cytom. Part B - Clin. Cytom. 2019, 96, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Went, P.; Agostinelli, C.; Gallamini, A.; Piccaluga, P.P.; Ascani, S.; Sabattini, E.; Bacci, F.; Falini, B.; Motta, T.; Paulli, M.; et al. Marker expression in peripheral T-cell lymphoma: A proposed clinical-pathologic prognostic score. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Amador, C.; McKeithan, T.W.; Chan, W.C. T-Cell and NK-Cell Lymphomas. From Biology to Novel Therapies - Chapter: Molecular and Genomic Landscape of Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma; Querfeld, C., Zain, J., Rosen, S.T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 9783319997155. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Montero, J.; Grigore, G.; Fluxá, R.; Hernández, J.; Fernandez, P.; Almeida, J.; Muñoz, N.; Böttcher, S.; Sedek, L.; van der Velden, V.; et al. EuroFlow Lymphoid Screening Tube (LST) data base for automated identification of blood lymphocyte subsets. J. Immunol. Methods 2019, 475, 112662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerak, A.W.; van den Beemd, R.; Wolvers-Tettero, I.L.M.; Boor, P.P.C.; van Lochem, E.G.; Hooijkaas, H.; van Dongen, J.J.M. Molecular and flow cytometric analysis of the VB repertoire for clonality assessment in mature TCRab T-cell proliferations. Blood 2001, 98, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morice, W.G.; Kimlinger, T.; Katzmann, J.A.; Lust, J.A.; Heimgartner, P.J.; Halling, K.C.; Hanson, C.A. Flow Cytometric Assessment of TCR-Vβ Expression in the Evaluation of Peripheral Blood Involvement by T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders: A Comparison with Conventional T-Cell Immunophenotyping and Molecular Genetic Techniques. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 121, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, R.C.; Stahl, S.; O’Keefe, C.L.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Theil, K.S.; Hsi, E.D. Detection of Mature T-Cell Leukemias by Flow Cytometry Using Anti-T-Cell Receptor Vβ Antibodies. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 120, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tembhare, P.; Yuan, C.M.; Xi, L.; Morris, J.C.; Liewehr, D.; Venzon, D.; Janik, J.E.; Raffeld, M.; Stetler-Stevenson, M. Flow cytometric immunophenotypic assessment of T-cell clonality by V β repertoire analysis: Detection of T-cell clonality at diagnosis and monitoring of minimal residual disease following therapy. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 135, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerak, A.W.; Groenen, P.J.T.A.; Brüggemann, M.; Beldjord, K.; Bellan, C.; Bonello, L.; Boone, E.; Carter, G.I.; Catherwood, M.; Davi, F.; et al. EuroClonality/BIOMED-2 guidelines for interpretation and reporting of Ig/TCR clonality testing in suspected lymphoproliferations. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2159–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dongen, J.J.M.; Langerak, A.W.; Brüggemann, M.; Evans, P.A.S.; Hummel, M.; Lavender, F.L.; Delabesse, E.; Davi, F.; Schuuring, E.; García-Sanz, R.; et al. Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: Report of the BIOMED-2 concerted action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 2003, 17, 2257–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Raffeld, M. Molecular assessment of clonality in lymphoid neoplasms. Semin. Hematol. 2019, 56, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, J.A.; Duncavage, E.J.; Mosbruger, T.L.; Szankasi, P.M.; Kelley, T.W. A comparison of deep sequencing of TCRG rearrangements vs. traditional capillary electrophoresis for assessment of clonality in t-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 141, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, N.D.; Griffin, G.K.; Dudley, G.; Drew, M.; Rojas-Rudilla, V.; Lindeman, N.I.; Dorfman, D.M. Utility of a simple and robust flow cytometry assay for rapid clonality testing in mature peripheral T-Cell lymphomas. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 151, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciocia, P.M.; Wawrzyniecka, P.A.; Philip, B.; Ricciardelli, I.; Akarca, A.U.; Onuoha, S.C.; Leguţ, M.; Cole, D.K.; Sewell, A.K.; Gritti, G.; et al. Targeting the T cell receptor β-chain constant region for immunotherapy of T cell malignancies. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Jevremovic, D.; Otteson, G.E.; Timm, M.M.; Olteanu, H.; Horna, P. Single Antibody Detection of T-Cell Receptor αβ Clonality by Flow Cytometry Rapidly Identifies Mature T-Cell Neoplasms and Monotypic Small CD8-Positive Subsets of Uncertain Significance. Cytom. Part B - Clin. Cytom. 2020, 98, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, H.; Otteson, G.E.; Corley, H.; Shi, M.; Horna, P.; Jevremovic, D.; Olteanu, H. Flow cytometric evaluation of TRBC1 expression in tissue specimens and body fluids is a novel and specific method for assessment of T-cell clonality and diagnosis of T-cell neoplasms. Cytom. Part B - Clin. Cytom. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewpreedee, P.; Boonrat, P.; Tansiri, Y.; Rowland-Jones, S.L.; Hansasuta, P. Dimorphism in the T-cell receptor constant region affects T-cell function, phenotype and HIV outcome. Aids 2019, 33, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Olteanu, H.; Jevremovic, D.; He, R.; Viswanatha, D.; Corley, H.; Horna, P. T-cell clones of uncertain significance are highly prevalent and show close resemblance to T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia. Implications for laboratory diagnostics. Mod. Pathol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horna, P.; Shi, M.; Jevremovic, D.; Craig, F.E.; Comfere, N.I.; Olteanu, H. Utility of TRBC1 Expression in the Diagnosis of Peripheral Blood Involvement by Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 821–829.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horna, P.; Olteanu, H.; Jevremovic, D.; Otteson, G.E.; Corley, H.; Ding, W.; Parikh, S.A.; Shah, M.V.; Morice, W.G.; Shi, M. Single-Antibody Evaluation of T-Cell Receptor β Constant Chain Monotypia by Flow Cytometry Facilitates the Diagnosis of T-Cell Large Granular Lymphocytic Leukemia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 156, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horna, P.; Shi, M.; Olteanu, H.; Johansson, U. Emerging role of t-cell receptor constant β chain-1 (TRBC1) expression in the flow cytometric diagnosis of t-cell malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dongen, J.J.; Lhermitte, L.; Böttcher, S.; Almeida, J.; van der Velden, V.H.; Flores-Montero, J.; Rawstron, A.; Asnafi, V.; Lécrevisse, Q.; Lucio, P.; et al. EuroFlow antibody panels for standardized n-dimensional flow cytometric immunophenotyping of normal, reactive and malignant leukocytes. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1908–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, T.; Flores-Montero, J.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Martin-Ayuso, M.; Böttcher, S.; Ritgen, M.; Almeida, J.; Lhermitte, L.; Asnafi, V.; Mendonça, A.; et al. EuroFlow standardization of flow cytometer instrument settings and immunophenotyping protocols. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1986–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EuroFlow. Available online: https://www.euroflow.org/ (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Maecker, H.T.; Frey, T.; Nomura, L.E.; Trotter, J. Selecting fluorochrome conjugates for maximum sensitivity. Cytom. Part A 2004, 62, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerak, A.; Wolvers-Tettero, I.; van Dongen, J. Detection of T cell receptor beta (TCRB) gene rearrangement patterns in T cell malignancies by Southern blot analysis. Leukemia 1999, 13, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Droese, J.; Langerak, A.W.; Groenen, P.J.T.A.; Brüggemman, M.; Neumann, P.; Wolvers-Tettero, I.L.M.; van Altena, M.C.; Kneba, M.; van Dongen, J.J.M. Validation of BIOMED-2 multiplex PCR tubes for detection of TCRB gene rearrangements in T-cell malignancies. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-García, N.; Jara-Acevedo, M.; Caldas, C.; Bárcena, P.; López, A.; Puig, N.; Alcoceba, M.; Fernández, P.; Villamor, N.; Flores-Montero, J.A.; et al. STAT3 and STAT5B mutations in T/NK-cell chronic lymphoproliferative disorders of large granular lymphocytes (LGL): Association with disease features. Cancers 2020, 12, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laribi, K.; Lemaire, P.; Sandrini, J.; de Materre, A.B. Advances in the understanding and management of T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 104664–104686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrup, J.; Pedersen, L.; Dietrich, J.; Lauritsen, J.P.H.; Menné, C.; Geisler, C. In vitro production and characterization of partly assembled human CD3 complexes. Scand. J. Immunol. 2002, 56, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morath, A.; Schamel, W.W. αβ and γδ T cell receptors: Similar but different. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, K.; Jiang, J.; May, N.A.; Mage, M.G.; Boyd, L.F.; McShan, A.C.; Sgourakis, N.G.; Bax, A.; Margulies, D.H. The role of molecular flexibility in antigen presentation and T cell receptor-mediated signaling. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunnacliffe, A.; Kefford, R.; Milstein, C.; Forster, A.; Rabbitts, T.H. Sequence and evolution of the human T-cell antigen receptor β-chain genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 5068–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diks, A.M.; Bonroy, C.; Teodosio, C.; Groenland, R.J.; de Mooij, B.; de Maertelaere, E.; Neirynck, J.; Philippé, J.; Orfao, A.; van Dongen, J.J.M.; et al. Impact of blood storage and sample handling on quality of high dimensional flow cytometric data in multicenter clinical research. J. Immunol. Methods 2019, 475, 112616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duby, A.D.; Seidman, J.G. Abnormal recombination products result from aberrant DNA rearrangement of the human T-cell antigen receptor B-chain gene. Immunology 1986, 83, 4890–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TRBC2 Sequence. Available online: http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Gene/Summary?db=core;g=ENSG00000211772;r=7:142801041-142802748;t=ENST00000466254 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- TRBC1 Sequence. Available online: http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Gene/Summary?db=core;g=ENSG00000211751;r=7:142791694-142793368;t=ENST00000633705 (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Katzmann, J.A.; Clark, R.J.; Abraham, R.S.; Bryant, S.; Lymp, J.F.; Bradwell, A.R.; Kyle, R.A. Serum reference intervals and diagnostic ranges for free κ and free λ immunoglobulin light chains: Relative sensitivity for detection of monoclonal light chains. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, W.; Frierson, H.; Innes, D.; Normansell, D. Quantitative criteria for clonality in the diagnosis of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma by flow cytometry. Mod. Pathol. 1993, 6, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Criado, I.; Rodríguez-Caballero, A.; Gutiérrez, M.L.; Pedreira, C.E.; Alcoceba, M.; Nieto, W.; Teodosio, C.; Bárcena, P.; Romero, A.; Fernández-Navarro, P.; et al. Low-count monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis persists after seven years of follow up and is associated with a poorer outcome. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, M.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; Dvorkin, S.; Meimei, M.; Poon, L.; Lam, N.; Kumar, B.V.; Louzoun, Y.; Prak, E.T.L.; et al. Maintenance of the human memory T cell repertoire by subset and tissue site. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Montero, J.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Paiva, B.; Puig, N.; García-Sánchez, O.; Böttcher, S.; Van Der Velden, V.H.J.; Pérez-Morán, J.J.; Vidriales, M.B.; García-Sanz, R.; et al. Next Generation Flow for highly sensitive and standardized detection of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, B.; Risberg, B.; Berner, A.; Smeland, E.B.; Torlakovic, E. Evaluation of lymphoid cell populations in cytology specimens using flow cytometry and polymerase chain reaction. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 1999, 8, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Diagnosis | n. of Cases |
|---|---|
| T-PLL | 10 |
| PCTCL-SS | 16 |
| PCTCL-MF | 6 |
| PCTCL-NOS | 1 |
| PTCL-AITL | 2 |
| Extranodal NK/T-lymphoma, nasal type | 1 |
| PCTCLPD-small/medium CD4 | 2 |
| Hemophagocytic syndrome | 1 |
| PTCL-NOS | 2 |
| T-LGLL | 40 |
| T-CLPD not classified | 6 |
| TRBC1 Expression by FCM | Clonality Status of TRBC1 Stained Cell Populations 1 | TRBJ Rearrangement | |
|---|---|---|---|
| JB1 | JB1+JB2 | ||
| Positive (n = 47) | Monoclonal (n = 4) | 4 | 0 |
| Oligoclonal (n = 3) | 3 | 0 | |
| Polyclonal (n = 40) | 37 | 3 | |
| TOTAL | 44/47 (94%) | 3/47 (6%) | |
| Negative (n = 48) | Monoclonal (n = 3 2) | 0 | 3 |
| Oligoclonal (n = 4) | 0 | 4 | |
| Polyclonal (n = 41) | 0 | 41 | |
| TOTAL | 0 | 48/48 (100%) | |
| Tαβ-Cell Subset | % TRBC1+ Cells * | TRBC1+/TRBC1− Ratio | Probability (%) of Finding A Clonal Tαβ Expansion When TRBC1+/TRBC1− Ratio is Outside the Range Mean ± 3 SD (ρ-Value) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± 1 SD | Range (Mean ± 3 SD) | Mean ± 1 SD | Range (Mean ± 3 SD) | ||
| Tαβ cells | 40 ± 6.7 | 20–60 | 0.66 ± 0.071 | 0.25–1.4 | 99.73% (<0.001) |
| Tαβ CD4+ | 43 ± 6.3 | 24–62 | 0.75 ± 0.067 | 0.31–1.6 | |
| Tαβ CD8+ | 35 ± 8.8 | 8.3–61 | 0.53 ± 0.096 | 0.091–1.6 | |
| Tαβ DP | 36 ± 12 | 1.6–71 | 0.57 ± 0.13 | 0.016–2.5 | |
| Tαβ DN | 29 ± 10 | 0-61 | 0.41 ± 0.12 | 0–1.5 | |
| Clonality Status by Other Techniques * | TRBC1 Expression Pattern by FCM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polytypic (n = 23) | Monotypic (n = 94) | ||
| Poly/oligoclonal (n = 24) | 21/24 (87%) | 3/24 (13%) | <0.0001 |
| Monoclonal (n = 93) | 2/93 (2%) | 91/93 (98%) | |
| WHO 2017 Diagnosis | TRBC1+ (n = 52) | TRBC1− (n = 37) |
|---|---|---|
| T-PLL (n = 10) | 3/10 (30%) | 7/10 (70%) |
| PCTCL-SS (n = 15) | 12/15 (80%) | 3/15 (20%) |
| PCTCL-MF (n = 6) | 3/6 (50%) | 3/6 (50%) |
| PCTCL-NOS (n = 1) | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) |
| PTCL-AITL (n = 2) | 0/2 (0%) | 2/2 (100%) |
| Extranodal NK/T-lymphoma, nasal type (n = 1) | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) |
| PCTCLPD-small/medium CD4 (n = 2) | 2/2 (100%) | 0/2 (0%) |
| Hemophagocytic syndrome (n = 1) | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) |
| PTCL-NOS (n = 2) | 1/2 (50%) | 1/2 (50%) |
| T-LGLL (n = 39) | 22/39 (56%) | 17/39 (44%) |
| HDc * (n = 10) | 9/10 (90%) | 1/10 (10%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-García, N.; Lima, M.; Villamor, N.; Morán-Plata, F.J.; Barrena, S.; Mateos, S.; Caldas, C.; Balanzategui, A.; Alcoceba, M.; Domínguez, A.; et al. Anti-TRBC1 Antibody-Based Flow Cytometric Detection of T-Cell Clonality: Standardization of Sample Preparation and Diagnostic Implementation. Cancers 2021, 13, 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174379
Muñoz-García N, Lima M, Villamor N, Morán-Plata FJ, Barrena S, Mateos S, Caldas C, Balanzategui A, Alcoceba M, Domínguez A, et al. Anti-TRBC1 Antibody-Based Flow Cytometric Detection of T-Cell Clonality: Standardization of Sample Preparation and Diagnostic Implementation. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174379
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-García, Noemí, Margarida Lima, Neus Villamor, F. Javier Morán-Plata, Susana Barrena, Sheila Mateos, Carolina Caldas, Ana Balanzategui, Miguel Alcoceba, Alejandro Domínguez, and et al. 2021. "Anti-TRBC1 Antibody-Based Flow Cytometric Detection of T-Cell Clonality: Standardization of Sample Preparation and Diagnostic Implementation" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174379
APA StyleMuñoz-García, N., Lima, M., Villamor, N., Morán-Plata, F. J., Barrena, S., Mateos, S., Caldas, C., Balanzategui, A., Alcoceba, M., Domínguez, A., Gómez, F., Langerak, A. W., van Dongen, J. J. M., Orfao, A., & Almeida, J. (2021). Anti-TRBC1 Antibody-Based Flow Cytometric Detection of T-Cell Clonality: Standardization of Sample Preparation and Diagnostic Implementation. Cancers, 13(17), 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174379






