Vocal Fold Leukoplakia: Which of the Classifications of White Light and Narrow Band Imaging Most Accurately Predicts Laryngeal Cancer Transformation? Proposition for a Diagnostic Algorithm
Abstract
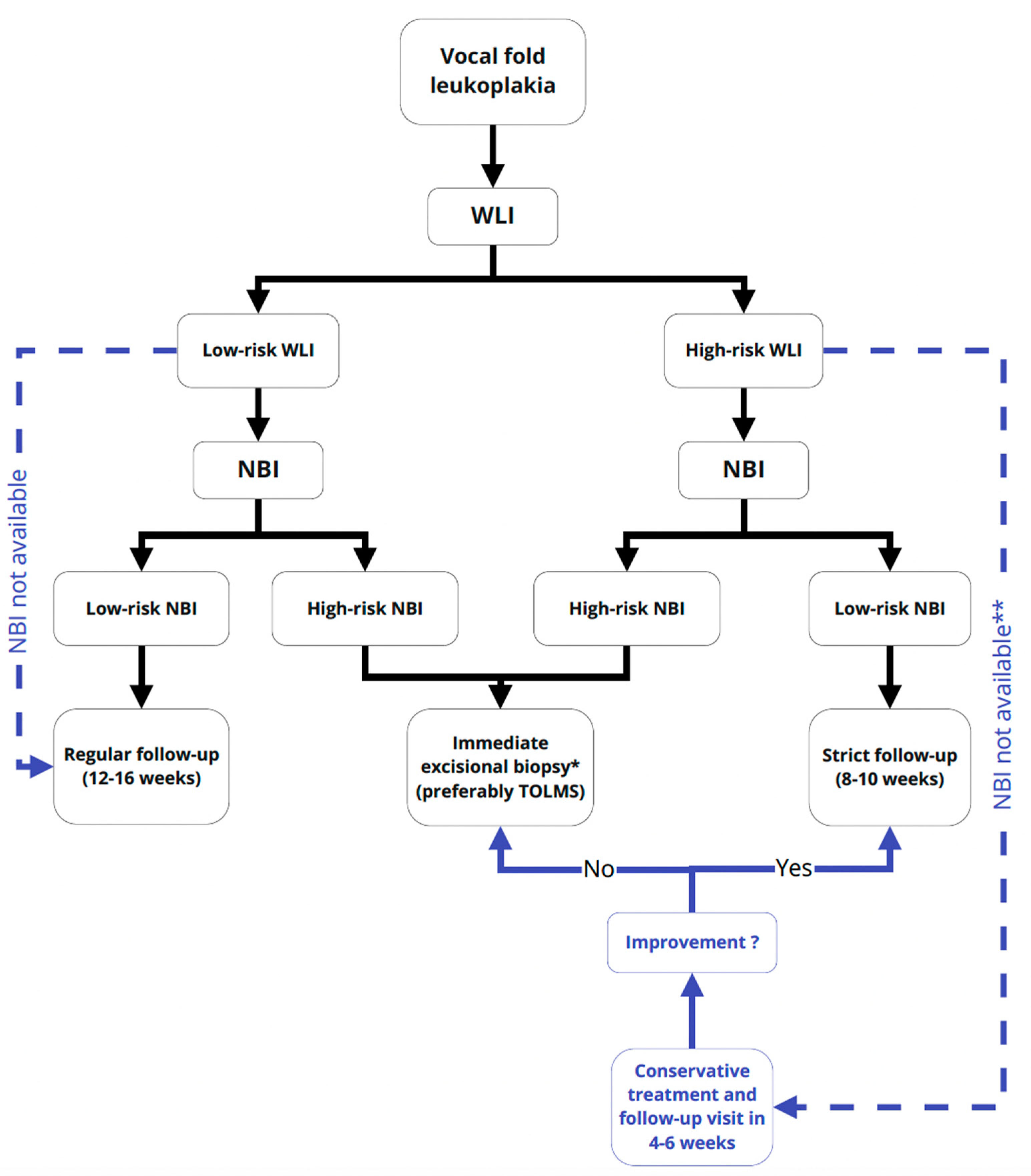
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Endoscopic Examination Procedure
2.3. White Light Imaging (WLI)
2.4. Narrow Band Imaging (NBI)
2.4.1. Assessment of the Immediate Surrounding of Leukoplakia Plaque According to Ni 2011 Classification
2.4.2. Assessment of the Microvascular Features of Leukoplakia According to 2015 ELS Guidelines
2.4.3. Assessment of Vocal Fold Leukoplakia According to the NBI Endoscopic Classification by Ni et al. 2019
2.5. Histopathological Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. WLI Classifications
4.2. NBI Classifications
4.3. Combination of WLI and NBI Classifications
4.4. The Limitations and Strengths of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NBI | narrow band imaging |
| WLI | white light imaging |
| VF | vocal fold |
| VFL | vocal fold leukoplakia |
| HP | histopathology |
| ELS | European Laryngological Society |
| IPCLs | Intraepithelial papillary capillary loops |
| CT | conservative treatment |
| TOLMS | Transoral Laser Microsurgery |
References
- Gale, N.; Michaels, L.; Luzar, B.; Poljak, M.; Zidar, N.; Fischinger, J.; Cardesa, A. Current review on squamous intraepithelial lesions of the larynx. Histopathology 2009, 54, 639–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Jiang, T.; Chen, X. Differences in gene expression profile between vocal cord Leukoplakia and normal larynx mucosa by gene chip. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, A.; Wang, L.; Slaughter, J.C.; Nguyen, A.M.; Ossoff, R.H.; Francis, D.O. Serial full-thickness excision of dysplastic vocal fold leukoplakia: Diagnostic or therapeutic? Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouquot, J.E.; Gnepp, D.R. Laryngeal precancer: A review of the literature, commentary, and comparison with oral leukoplakia. Head Neck 1991, 13, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Cheng, L.; Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Shi, F. A new classification of vocal fold leukoplakia by morphological appearance guiding the treatment. Acta Otolaryngol. 2018, 138, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.J.; Lin, W.N.; Lee, L.Y.; Young, C.K.; Lee, L.A.; Chang, K.P.; Liao, C.T.; Li, H.Y.; Yen, T.C. Classification of vocal fold leukoplakia by clinical scoring. Head Neck 2016, 38 (Suppl. 1), E1998–E2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wu, H. A morphological classification for vocal fold leukoplakia. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 85, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.-J.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Ye, J.-Y.; Xu, W.; Yang, Q.-W. Clinical classification and treatment of leukokeratosis of the vocal cords. Chin. Med. J. (Engl). 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenberg, J.S.; Crozier, D.L.; Dailey, S.H. Institutional and comprehensive review of laryngeal leukoplakia. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2008, 117, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimza, H.; Jackowska, J.; Tokarski, M.; Piersiala, K.; Wierzbicka, M. Narrow-band imaging (NBI) for improving the assessment of vocal fold leukoplakia and overcoming the umbrella effect. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0180590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, G.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Q.; Song, X. Endoscopic diagnosis value of narrow band imaging Ni classification in vocal fold leukoplakia and early glottic cancer. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42, 102904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.G.; Wang, G.Q.; Hu, F.Y.; Xu, X.M.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, X.S.; Liu, L.; Ren, X.L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Clinical utility and effectiveness of a training programme in the application of a new classification of narrow-band imaging for vocal cord leukoplakia: A multicentre study. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2019, 44, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Eun, Y.-G.; Park, I.-S. The Value of I-Scan Image-Enhanced Endoscopy in the Diagnosis of Vocal Cord Leukoplakia. J. Korean Soc. Laryngol. Phoniatr. Logop. 2018, 29, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Xu, W.; Yang, Q.; Hu, R. Clinicopathological parameters associated with histological background and recurrence after surgical intervention of vocal cord leukoplakia. Medicine (United States) 2017, 96, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannelli, G.; Cecconi, L.; Gallo, O. Laryngeal preneoplastic lesions and cancer: Challenging diagnosis. Qualitative literature review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 106, 64–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Han, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X. Diagnostic Performance of Narrow Band Imaging for Laryngeal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, R.S.; Heckman, W.W.; Isenberg, J.; Thibeault, S.L.; Dailey, S.H. Genetic characterization of vocal fold lesions: Leukoplakia and Carcinoma. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Yoon, T.M.; Lee, J.K.; Lim, S.C. Predictive factors of recurrence and malignant transformation in vocal cord leukoplakia. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 272, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoffel-Havakuk, H.; Lahav, Y.; Meidan, B.; Haimovich, Y.; Warman, M.; Hain, M.; Hamzany, Y.; Brodsky, A.; Landau-Zemer, T.; Halperin, D. Does narrow band imaging improve preoperative detection of glottic malignancy? A matched comparison study. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, J. TOLUIDINE blue. Whats. New 1950, 150, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.; Nilakantan, A.; Sahai, K.; Sethi, A.; Singh, S.; Datta, R. Contact Endoscopy - A promising tool for evaluation of laryngeal mucosal lesions. J. Laryngol. Voice 2012, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.G.; He, S.; Xu, Z.G.; Gao, L.; Lu, N.; Yuan, Z.; Lai, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.M.; Yi, J.L.; Wang, X.L.; et al. Endoscopic diagnosis of laryngeal cancer and precancerous lesions by narrow band imaging. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2011, 125, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arens, C.; Piazza, C.; Andrea, M.; Dikkers, F.G.; Tjon Pian Gi, R.E.A.; Voigt-Zimmermann, S.; Peretti, G. Proposal for a descriptive guideline of vascular changes in lesions of the vocal folds by the committee on endoscopic laryngeal imaging of the European Laryngological Society. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2016, 273, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.G.; Zhu, J.Q.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhang, B.G.; Wang, G.Q. Diagnosis of vocal cord leukoplakia: The role of a novel narrow band imaging endoscopic classification. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Chhetri, D.K. Triological Best Practice: When Is Surgical Intervention Indicated for Vocal Fold Leukoplakia? Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 1362–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fluss, R.; Faraggi, D.; Reiser, B. Estimation of the Youden Index and its associated cutoff point. Biom. J. 2005, 47, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piazza, C.; Cocco, D.; Del Bon, F.; Mangili, S.; Nicolai, P.; Majorana, A.; Bolzoni Villaret, A.; Peretti, G. Narrow band imaging and high definition television in evaluation of oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer: A prospective study. Oral Oncol. 2010, 46, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrens, M.J. Five Ways to Look at Cohen’s Kappa. J. Psychol. Psychother. 2015, 5, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. Landis amd Koch1977_agreement of categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Naggar, A.K. Squamous cell carcinoma. In WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumors; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017; ISBN 978-92-832-2438-9. [Google Scholar]
- Campo, F.; Ralli, M.; Di Stadio, A.; Greco, A.; Pellini, R.; de Vincentiis, M. Role of Narrow Band Imaging Endoscopy in Preoperative Evaluation of Laryngeal Leukoplakia: A Review of the Literature. Ear Nose Throat J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.K.; Lin, W.N.; Lee, L.Y.; Lee, L.A.; Hsin, L.J.; Liao, C.T.; Li, H.Y.; Chen, I.H.; Fang, T.J. Laryngoscopic characteristics in vocal leukoplakia: Inter-rater reliability and correlation with histology grading. Laryngoscope 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzepakowska, A.; Sobol, M.; Sielska-Badurek, E.; Niemczyk, K.; Osuch-Wójcikiewicz, E. Morphology, Vibratory Function, and Vascular Pattern for Predicting Malignancy in Vocal Fold Leukoplakia. J. Voice 2020, 34, 812.e9–812.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irjala, H.; Matar, N.; Remacle, M.; Georges, L. Pharyngo-laryngeal examination with the narrow band imaging technology: Early experience. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2011, 268, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šifrer, R.; Rijken, J.A.; Leemans, C.R.; Eerenstein, S.E.J.; van Weert, S.; Hendrickx, J.J.; Bloemena, E.; Heuveling, D.A.; Rinkel, R.N.P.M. Evaluation of vascular features of vocal cords proposed by the European Laryngological Society. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2018, 275, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ansari, U.H.; Wong, E.; Smith, M.; Singh, N.; Palme, C.E.; Smith, M.C.; Riffat, F. Validity of narrow band imaging in the detection of oral and oropharyngeal malignant lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2019, 41, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.D.; Nankivell, P.C.; McConkey, C.; Paleri, V.; Mehanna, H.M. The risk and interval to malignancy of patients with laryngeal dysplasia; a systematic review of case series and meta-analysis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2010, 35, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staníková, L.; Šatanková, J.; Kučová, H.; Walderová, R.; Zeleník, K.; Komínek, P. The role of narrow-band imaging (NBI) endoscopy in optical biopsy of vocal cord leukoplakia. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2017, 274, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Yu, J.; Zhang, F.; He, C.; Li, S.; Shao, J. The usefulness of narrow-band imaging for the diagnosis and treatment of vocal fold leukoplakia. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popek, B.; Bojanowska-Poźniak, K.; Tomasik, B.; Fendler, W.; Jeruzal-Świątecka, J.; Pietruszewska, W. Clinical experience of narrow band imaging (NBI) usage in diagnosis of laryngeal lesions. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2019, 73, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlum, C.S.; Rosenberg, T.; Dyrvig, A.K.; Groentved, A.M.; Kjaergaard, T.; Godballe, C. Can the Ni classification of vessels predict neoplasia? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missale, F.; Taboni, S.; Carobbio, A.L.C.; Mazzola, F.; Berretti, G.; Iandelli, A.; Fragale, M.; Mora, F.; Paderno, A.; Del Bon, F.; et al. Validation of the European Laryngological Society classification of glottic vascular changes as seen by narrow band imaging in the optical biopsy setting. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, B.; Rasid, N.S.A.; Lazim, N.M.; Volgger, V.; Betz, C.S.; Mohammad, Z.W.; Hassan, N.F.H.N. Ni endoscopic classification for Storz Professional Image Enhancement System (SPIES) endoscopy in the detection of upper aerodigestive tract (UADT) tumours. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Laryngeal Light Endoscopy | Classification | Benign Leukoplakia | Malignant Leukoplakia |
|---|---|---|---|
| White Light Endoscopy | two-tier classification | thin white plaque of a uniform color and a flat surface | thick white plaque, a rough surface, and congestive vocal fold mucosa |
| three-tier classification acc. to Chen 2019 |
|
| |
| Narrow Band Imaging | Ni 2011 classification: cut-off point 4 | 1+2
| 4+5 4. IPCLs recognized as small dots 5a. IPCLs appear as solid or hollow, with a brownish, speckled pattern and various shapes 5b. IPCLs appear as irregular, tortuous, line-like shapes 5c. IPCLs appear as brownish speckles or tortuous, line-like shapes with irregular distribution, scattered on the tumour surface. |
| Ni 2011 classification: cut-off point 5 | 1+2+4 | 5 | |
| ELS classification |
|
| |
| Ni 2019 classification: cut-off point 4 | 1+2+3
| 4+5+6
| |
| Ni 2019 classification: cut-off point 5 | 1+2+3+4 | 5+6 |
| Endoscopic Light Imaging. | Clinical Classification | Proposed Cut-Off Point | AUC (95% CI) | Youden’s Index | Accuracy % | Sensitivity % | Specificity % | PPV % | NPV % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WLI | two-tier classification | 2 | 0.734 (0.675; 0.793) | 0.47 | 72.0 | 78.9 | 67.9 | 58.9 | 84.7 |
| three-tier classification acc. to Chen 2019 | 2 | 0.806 (0.751; 0.861) | 0.46 | 70.9 | 81.7 | 64.7 | 57.4 | 85.8 | |
| 3 | 0.806 (0.751; 0.861) | 0.53 | 80.4 | 60.6 | 92.0 | 81.5 | 80.0 | ||
| NBI | ELS classification | 2 | 0.787 (0.729; 0.844) | 0.57 | 80.1 | 73.4 | 84.0 | 72.7 | 84.4 |
| Ni 2011 classification | 4 | 0.856 (0.809; 0.902) | 0.56 | 77.4 | 81.7 | 74.9 | 65.4 | 87.5 | |
| 5 | 0.856 (0.809; 0.902) | 0.59 | 83.1 | 65.1 | 93.6 | 85.5 | 82.2 | ||
| Ni 2019 classification | 4 | 0.869 (0.826; 0.912) | 0.61 | 80.7 | 79.8 | 81.3 | 71.3 | 87.4 | |
| 5 | 0.869 (0.826; 0.912) | 0.62 | 84.1 | 68.8 | 93.0 | 85.2 | 83.7 |
| Laryngeal Endoscopy | Clinical Classification | Cut-Off Point | Low-Risk VFL Cases | High-Risk VFL Cases | Cohens Kappa (κ) Coefficient Value | Bowker’s Test for Symmetry (p Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Light Imaging | two-tier classification | 2 | 150 | 146 | 0.44 | <0.001 |
| three-tier classification acc. to Chen 2019 | 2 | 141 | 155 | 0.43 | <0.001 | |
| 3 | 215 | 81 | 0.56 | <0.001 | ||
| Narrow Band Imaging | ELS classification | 2 | 186 | 110 | 0.57 | 0.896 |
| Ni 2011 classification | 4 | 181 | 115 | 0.63 | <0.001 | |
| 5 | 211 | 85 | 0.62 | 0.404 | ||
| Ni 2019 classification | 4 | 176 | 120 | 0.58 | 0.152 | |
| 5 | 208 | 88 | 0.68 | <0.001 | ||
| Total VFL cases in HP | 187 | 109 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietruszewska, W.; Morawska, J.; Rosiak, O.; Leduchowska, A.; Klimza, H.; Wierzbicka, M. Vocal Fold Leukoplakia: Which of the Classifications of White Light and Narrow Band Imaging Most Accurately Predicts Laryngeal Cancer Transformation? Proposition for a Diagnostic Algorithm. Cancers 2021, 13, 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133273
Pietruszewska W, Morawska J, Rosiak O, Leduchowska A, Klimza H, Wierzbicka M. Vocal Fold Leukoplakia: Which of the Classifications of White Light and Narrow Band Imaging Most Accurately Predicts Laryngeal Cancer Transformation? Proposition for a Diagnostic Algorithm. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133273
Chicago/Turabian StylePietruszewska, Wioletta, Joanna Morawska, Oskar Rosiak, Agata Leduchowska, Hanna Klimza, and Małgorzata Wierzbicka. 2021. "Vocal Fold Leukoplakia: Which of the Classifications of White Light and Narrow Band Imaging Most Accurately Predicts Laryngeal Cancer Transformation? Proposition for a Diagnostic Algorithm" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133273
APA StylePietruszewska, W., Morawska, J., Rosiak, O., Leduchowska, A., Klimza, H., & Wierzbicka, M. (2021). Vocal Fold Leukoplakia: Which of the Classifications of White Light and Narrow Band Imaging Most Accurately Predicts Laryngeal Cancer Transformation? Proposition for a Diagnostic Algorithm. Cancers, 13(13), 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133273







