Targeting NEDDylation as a Novel Approach to Improve the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Head and Neck Cancer
2. Current Therapeutic Strategies
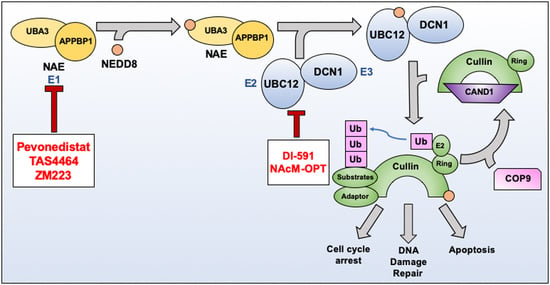
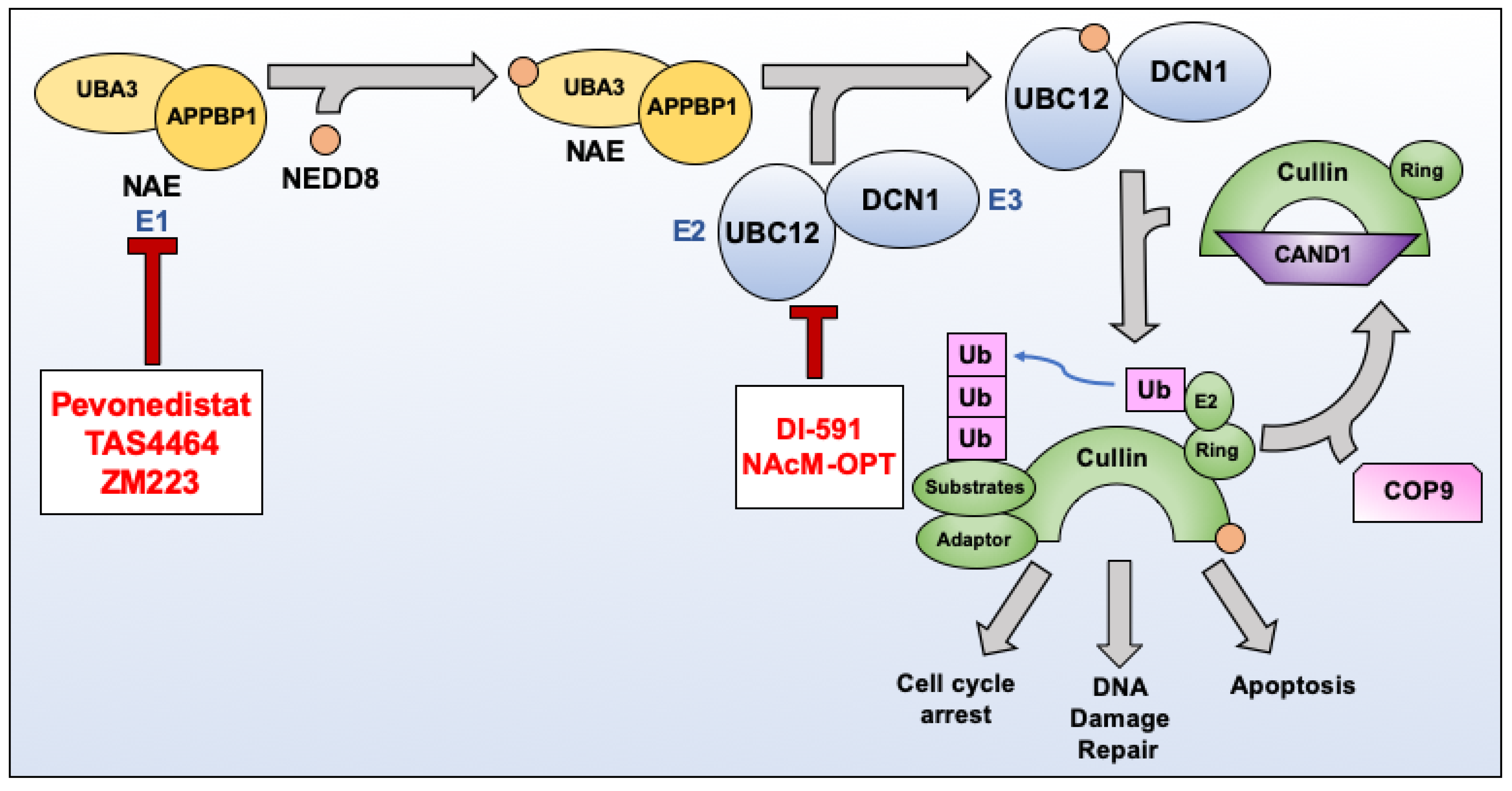
3. NEDDylation as a Therapeutic Target
3.1. Pevonedistat (MLN4924)
3.2. TAS4464
3.3. ZM223
3.4. DI-591
3.5. NAcM-OPT
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HPV | Human Papillomavirus |
| RT | Radiation therapy |
| 5-FU | Fluorouracil |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibody |
| PD-1 | Programmed death receptor-1 |
| RTOG | Radiation Therapy Oncology Group |
| NEDD8 | Neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally-downregulated 8 |
| UBA3 | Ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 3 |
| APPBP1 | NEDD8 activating enzyme E1 regulatory subunit |
| NAE | NEDD8 activating enzyme |
| UBC12 | NEDD8 conjugating enzyme Ubc12 |
| UBE2F | NEDD8 conjugating enzyme 2 |
| RBX1 | RING-box protein 1 |
| RBX2 | RING-box protein 2 |
| COP9 | Constitutive photomorphogenesis 9 |
| CRL | Cullin RING ligase |
| CAND1 | Cullin-associated NEDD8-dissociated protein 1 |
| p21 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 |
| p27 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1b |
| Wee1 | WEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase |
| RING | Really interesting new gene |
| Ub | Ubiquitin |
| PEV | Pevonedistat |
| CDT1 | Chromatin licensing and DNA replication factor 1 |
| PI-FACS | Propidium Iodide-fluorescent activated cell sorting |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| MM | Multiple myeloma |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| NOXA | Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1 |
| BIM | Bcl-2-like protein 11 |
| BH3 | Bcl-2 homology 3 domain |
| TRAIL | Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand |
| CDT2 | Denticleless protein homolog |
| Gy | Gray (unit of radiation) |
| Chk1 | Checkpoint kinase 1 |
| Chk2 | Checkpoint kinase 2 |
| γH2AX | Gamma H2A histone family member X |
| PR | Partial response |
| AUC6 | target area under the concentration-time curve of 6 mg/mL * min |
| ORR | Overall response rate |
| TAS | TAS4464 |
| DCN1 | Defective in Cullin NEDDylation 1 |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alsahafi, E.; Begg, K.; Amelio, I.; Raulf, N.; Lucarelli, P.; Sauter, T.; Tavassoli, M. Clinical update on head and neck cancer: Molecular biology and ongoing challenges. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hobbs, C.G.; Sterne, J.A.; Bailey, M.; Heyderman, R.S.; Birchall, M.A.; Thomas, S.J. Human papillomavirus and head and neck cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2006, 31, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillison, M.L.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Anderson, W.F.; Fakhry, C. Epidemiology of Human Papillomavirus-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3235–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillison, M.L.; Koch, W.M.; Capone, R.B.; Spafford, M.; Westra, W.H.; Wu, L.; Zahurak, M.L.; Daniel, R.W.; Viglione, M.; Symer, D.E.; et al. Evidence for a causal association between human papillomavirus and a subset of head and neck cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.K.; Harris, J.; Wheeler, R.; Weber, R.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Nguyen-Tan, P.F.; Westra, W.H.; Chung, C.H.; Jordan, R.C.; Lu, C.; et al. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ragin, C.C.; Taioli, E. Survival of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in relation to human papillomavirus infection: Review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braakhuis, B.J.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Leemans, C.R. Treatment choice for locally advanced head and neck cancers on the basis of risk factors: Biological risk factors. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23 (Suppl. 10), x173–x177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, J.D.; Burtness, B.; Le, Q.T.; Ferris, R.L. The changing therapeutic landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiris, A.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Raben, D.; Ferris, R.L. Head and neck cancer. Lancet 2008, 371, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, D.G.; Spencer, S.; Brizel, D.M.; Burtness, B.; Busse, P.M.; Caudell, J.J.; Cmelak, A.J.; Colevas, A.D.; Dunphy, F.; Eisele, D.W.; et al. Head and neck cancers, Version 2.2014. Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2014, 12, 1454–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forastiere, A.A.; Zhang, Q.; Weber, R.S.; Maor, M.H.; Goepfert, H.; Pajak, T.F.; Morrison, W.; Glisson, B.; Trotti, A.; Ridge, J.A.; et al. Long-term results of RTOG 91–11: A comparison of three nonsurgical treatment strategies to preserve the larynx in patients with locally advanced larynx cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posner, M.R.; Hershock, D.M.; Blajman, C.R.; Mickiewicz, E.; Winquist, E.; Gorbounova, V.; Tjulandin, S.; Shin, D.M.; Cullen, K.; Ervin, T.J.; et al. Cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or with docetaxel in head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, N.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, L. A meta-analysis comparing cisplatin-based to carboplatin-based chemotherapy in moderate to advanced squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck (SCCHN). Oncotarget 2016, 7, 7110–7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pendleton, K.P.; Grandis, J.R. Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy Options for Recurrent and/or Metastatic Squamous Cell Cancer of the Head and Neck. Clin. Med. Insights 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamitani, T.; Kito, K.; Nguyen, H.P.; Yeh, E.T. Characterization of NEDD8, a developmentally down-regulated ubiquitin-like protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 28557–28562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, L.; Yeh, E.T. Identification of the activating and conjugating enzymes of the NEDD8 conjugation pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 12036–12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohnsack, R.N.; Haas, A.L. Conservation in the mechanism of Nedd8 activation by the human AppBp1-Uba3 heterodimer. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 26823–26830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walden, H.; Podgorski, M.S.; Huang, D.T.; Miller, D.W.; Howard, R.J.; Minor, D.L., Jr.; Holton, J.M.; Schulman, B.A. The structure of the APPBP1-UBA3-NEDD8-ATP complex reveals the basis for selective ubiquitin-like protein activation by an E1. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1427–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.T.; Ayrault, O.; Hunt, H.W.; Taherbhoy, A.M.; Duda, D.M.; Scott, D.C.; Borg, L.A.; Neale, G.; Murray, P.J.; Roussel, M.F.; et al. E2-RING expansion of the NEDD8 cascade confers specificity to cullin modification. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, D.C.; Sviderskiy, V.O.; Monda, J.K.; Lydeard, J.R.; Cho, S.E.; Harper, J.W.; Schulman, B.A. Structure of a RING E3 trapped in action reveals ligation mechanism for the ubiquitin-like protein NEDD8. Cell 2014, 157, 1671–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hori, T.; Osaka, F.; Chiba, T.; Miyamoto, C.; Okabayashi, K.; Shimbara, N.; Kato, S.; Tanaka, K. Covalent modification of all members of human cullin family proteins by NEDD8. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6829–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petroski, M.D.; Deshaies, R.J. Function and regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baek, K.; Scott, D.C.; Schulman, B.A. NEDD8 and ubiquitin ligation by cullin-RING E3 ligases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2021, 67, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubiel, W.; Chaithongyot, S.; Dubiel, D.; Naumann, M. The COP9 Signalosome: A Multi-DUB Complex. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydeard, J.R.; Schulman, B.A.; Harper, J.W. Building and remodelling Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases. EMBO Rep. 2013, 14, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Furukawa, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Xiong, Y. NEDD8 modification of CUL1 dissociates p120(CAND1), an inhibitor of CUL1-SKP1 binding and SCF ligases. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yang, X.; Harrell, J.M.; Ryzhikov, S.; Shim, E.-H.; Lykke-Andersen, K.; Wei, N.; Sun, H.; Kobayashi, R.; Zhang, H. CAND1 Binds to Unneddylated CUL1 and Regulates the Formation of SCF Ubiquitin E3 Ligase Complex Despite the importance of cullins in controlling many essential biological processes, the mechanism that reg-ulates the cullin-containing ubiquitin E3 ligases. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.M.; Redon, C.E.; Thakur, B.L.; Bahta, M.K.; Aladjem, M.I. Regulation of cell cycle drivers by Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1637–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podust, V.N.; Brownell, J.E.; Gladysheva, T.B.; Luo, R.S.; Wang, C.; Coggins, M.B.; Pierce, J.W.; Lightcap, E.S.; Chau, V. A Nedd8 conjugation pathway is essential for proteolytic targeting of p27Kip1 by ubiquitination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4579–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, N.; Arai, H.; Nishihara, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Watanabe, N.; Hunter, T.; Osada, H. M-phase kinases induce phospho-dependent ubiquitination of somatic Wee1 by SCFbeta-TrCP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4419–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y. Cullin-RING Ligases and Protein Neddylation: Introduction; Sun, Y., Wei, W., Jin, J., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 1217. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, J.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, X.; Lu, Y. Targeting the neddylation pathway in cells as a potential therapeutic approach for diseases. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2018, 81, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulatov, E.; Ciulli, A. Targeting Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases for drug discovery: Structure, assembly and small-molecule modulation. BioChem. J. 2015, 467, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, P.; Yang, J.P.; Cao, Y.; Peng, L.X.; Zheng, L.S.; Sun, R.; Meng, D.F.; Wang, M.Y.; Mei, Y.; Qiang, Y.Y.; et al. Promoting tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, NEDD8 serves as a potential theranostic target. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.; Hunter, T. Ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of the p21(Cip1), p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2) CDK inhibitors. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 2342–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehan, E.; Bassermann, F.; Guardavaccaro, D.; Vasiliver-Shamis, G.; Cohen, M.; Lowes, K.N.; Dustin, M.; Huang, D.C.; Taunton, J.; Pagano, M. betaTrCP- and Rsk1/2-mediated degradation of BimEL inhibits apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liakopoulos, D.; Busgen, T.; Brychzy, A.; Jentsch, S.; Pause, A. Conjugation of the ubiquitin-like protein NEDD8 to cullin-2 is linked to von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5510–5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cullinan, S.B.; Gordan, J.D.; Jin, J.; Harper, J.W.; Diehl, J.A. The Keap1-BTB protein is an adaptor that bridges Nrf2 to a Cul3-based E3 ligase: Oxidative stress sensing by a Cul3-Keap1 ligase. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 8477–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, C.M.; Pang, L.Y.; Chen, H.A.; Wu, P.R.; Lin, M.Y.; Jiang, S.T.; Tsai, T.F.; et al. Cul3-KLHL20 Ubiquitin Ligase Governs the Turnover of ULK1 and VPS34 Complexes to Control Autophagy Termination. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitani, H.; Sugimoto, N.; Roukos, V.; Nakanishi, Y.; Saijo, M.; Obuse, C.; Tsurimoto, T.; Nakayama, K.I.; Nakayama, K.; Fujita, M.; et al. Two E3 ubiquitin ligases, SCF-Skp2 and DDB1-Cul4, target human Cdt1 for proteolysis. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugasawa, K. The CUL4 enigma: Culling DNA repair factors. Mol. Cell 2009, 34, 403–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Xu, J.; Li, H.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z.J.; Wei, W.; Pan, Z.; Sun, Y. Neddylation E2 UBE2F Promotes the Survival of Lung Cancer Cells by Activating CRL5 to Degrade NOXA via the K11 Linkage. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiong, X.; Sun, Y. Cullin-RING Ligase 5: Functional characterization and its role in human cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 67, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Miao, H.; Wan, X.; Huang, J.; Mao, X.; Chen, C. CUL7 promotes cancer cell survival through promoting Caspase-8 ubiquitination. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xiong, Y. Cytoplasmic E3 ubiquitin ligase CUL9 controls cell proliferation, senescence, apoptosis and genome integrity through p53. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5212–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soucy, T.A.; Smith, P.G.; Milhollen, M.A.; Berger, A.J.; Gavin, J.M.; Adhikari, S.; Brownell, J.E.; Burke, K.E.; Cardin, D.P.; Critchley, S.; et al. An inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme as a new approach to treat cancer. Nature 2009, 458, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownell, J.E.; Sintchak, M.D.; Gavin, J.M.; Liao, H.; Bruzzese, F.J.; Bump, N.J.; Soucy, T.A.; Milhollen, M.A.; Yang, X.; Burkhardt, A.L.; et al. Substrate-assisted inhibition of ubiquitin-like protein-activating enzymes: The NEDD8 E1 inhibitor MLN4924 forms a NEDD8-AMP mimetic in situ. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, H.; Tang, Z.; Jin, H.; Sun, Y. Neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 suppresses growth and migration of human gastric cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, S.; Si, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Xie, P.; Jiang, W. MLN4924 (Pevonedistat), a protein neddylation inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and migration of human clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Milhollen, M.A.; Smith, P.G.; Narayanan, U.; Dutta, A. NEDD8-targeting drug MLN4924 elicits DNA rereplication by stabilizing Cdt1 in S phase, triggering checkpoint activation, apoptosis, and senescence in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10310–10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nawrocki, S.T.; Kelly, K.R.; Smith, P.G.; Espitia, C.M.; Possemato, A.; Beausoleil, S.A.; Milhollen, M.; Blakemore, S.; Thomas, M.; Berger, A.; et al. Disrupting protein NEDDylation with MLN4924 is a novel strategy to target cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3577–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nawrocki, S.T.; Kelly, K.R.; Smith, P.G.; Keaton, M.; Carraway, H.; Sekeres, M.A.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Carew, J.S. The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 disrupts nucleotide metabolism and augments the efficacy of cytarabine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Yan, Z.; Dong, C.; Zeng, M.S.; Zhong, Q.; Liu, X.K.; Yu, J.; et al. The Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 (TAK-924/Pevonedistat) induces apoptosis via c-Myc-Noxa axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Tan, M.; Wang, G.; Sun, Y. The p21-dependent radiosensitization of human breast cancer cells by MLN4924, an investigational inhibitor of NEDD8 activating enzyme. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yue, P.; Lonial, S.; Khuri, F.R.; Sun, S.Y. The NEDD8-Activating Enzyme Inhibitor, MLN4924, Cooperates with TRAIL to Augment Apoptosis through Facilitating c-FLIP Degradation in Head and Neck Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanderdys, V.; Allak, A.; Guessous, F.; Benamar, M.; Read, P.W.; Jameson, M.J.; Abbas, T. The Neddylation Inhibitor Pevonedistat (MLN4924) Suppresses and Radiosensitizes Head and Neck Squamous Carcinoma Cells and Tumors. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swords, R.T.; Erba, H.P.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Bixby, D.L.; Altman, J.K.; Maris, M.; Hua, Z.; Blakemore, S.J.; Faessel, H.; Sedarati, F.; et al. Pevonedistat (MLN4924), a First-in-Class NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndromes: A phase 1 study. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swords, R.T.; Coutre, S.; Maris, M.B.; Zeidner, J.F.; Foran, J.M.; Cruz, J.; Erba, H.P.; Berdeja, J.G.; Tam, W.; Vardhanabhuti, S.; et al. Pevonedistat, a first-in-class NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, combined with azacitidine in patients with AML. Blood 2018, 131, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lockhart, A.C.; Bauer, T.M.; Aggarwal, C.; Lee, C.B.; Harvey, R.D.; Cohen, R.B.; Sedarati, F.; Nip, T.K.; Faessel, H.; Dash, A.B.; et al. Phase Ib study of pevonedistat, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, in combination with docetaxel, carboplatin and paclitaxel, or gemcitabine, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest. New Drugs 2019, 37, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kathawala, R.J.; Espitia, C.M.; Jones, T.M.; Islam, S.; Gupta, P.; Zhang, Y.K.; Chen, Z.S.; Carew, J.S.; Nawrocki, S.T. ABCG2 Overexpression Contributes to Pevonedistat Resistance. Cancers 2020, 12, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochiiwa, H.; Ailiken, G.; Yokoyama, M.; Yamagata, K.; Nagano, H.; Yoshimura, C.; Muraoka, H.; Ishida, K.; Haruma, T.; Nakayama, A.; et al. TAS4464, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, activates both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways via c-Myc-mediated regulation in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, C.; Muraoka, H.; Ochiiwa, H.; Tsuji, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Kazuno, H.; Nakagawa, F.; Komiya, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Takenaka, T.; et al. TAS4464, A Highly Potent and Selective Inhibitor of NEDD8-Activating Enzyme, Suppresses Neddylation and Shows Antitumor Activity in Diverse Cancer Models. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muraoka, H.; Yoshimura, C.; Kawabata, R.; Tsuji, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Ochiiwa, H.; Nakagawa, F.; Fujioka, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Ohkubo, S. Activity of TAS4464, a novel NEDD8 activating enzyme E1 inhibitor, against multiple myeloma via inactivation of nuclear factor kappaB pathways. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 3802–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- A Dose Finding Study Followed by a Safety and Efficacy Study for Patients with Multiple Myeloma or Lymphoma. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02978235. (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Xu, G.W.; Toth, J.I.; da Silva, S.R.; Paiva, S.L.; Lukkarila, J.L.; Hurren, R.; Maclean, N.; Sukhai, M.A.; Bhattacharjee, R.N.; Goard, C.A.; et al. Mutations in UBA3 confer resistance to the NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 in human leukemic cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Bernard, D.; Yang, C.Y.; Fernandez-Salas, E.; Chinnaswamy, K.; Layton, S.; Stuckey, J.; Yu, Q.; et al. A potent small-molecule inhibitor of the DCN1-UBC12 interaction that selectively blocks cullin 3 neddylation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.C.; Hammill, J.T.; Min, J.; Rhee, D.Y.; Connelly, M.; Sviderskiy, V.O.; Bhasin, D.; Chen, Y.; Ong, S.S.; Chai, S.C.; et al. Blocking an N-terminal acetylation-dependent protein interaction inhibits an E3 ligase. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammill, J.T.; Bhasin, D.; Scott, D.C.; Min, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, L.; Kim, H.S.; Connelly, M.C.; Hammill, C.; et al. Discovery of an Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of Defective in Cullin Neddylation 1 (DCN1)-Mediated Cullin Neddylation. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2694–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Li, X.; Yan, F.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, X. Cyclin-dependent kinases phosphorylate human Cdt1 and induce its degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17283–17288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panagopoulos, A.; Taraviras, S.; Nishitani, H.; Lygerou, Z. CRL4(Cdt2): Coupling Genome Stability to Ubiquitination. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, Y. Anticancer drug discovery by targeting cullin neddylation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 746–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukkarila, J.L.; da Silva, S.R.; Ali, M.; Shahani, V.M.; Xu, G.W.; Berman, J.; Roughton, A.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Schimmer, A.D.; Gunning, P.T. Identification of NAE Inhibitors Exhibiting Potent Activity in Leukemia Cells: Exploring the Structural Determinants of NAE Specificity. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, P.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xia, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Y. A novel NAE/UAE dual inhibitor LP0040 blocks neddylation and ubiquitination leading to growth inhibition and apoptosis of cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 154, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Statsyuk, A.V. An inhibitor of ubiquitin conjugation and aggresome formation. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 5235–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Zhuang, C.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Min, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Miao, Z. Discovery of benzothiazole derivatives as novel non-sulfamide NEDD8 activating enzyme inhibitors by target-based virtual screening. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 133, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.T.; Miller, D.W.; Mathew, R.; Cassell, R.; Holton, J.M.; Roussel, M.F.; Schulman, B.A. A unique E1-E2 interaction required for optimal conjugation of the ubiquitin-like protein NEDD8. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, T.; Ozlu, N.; Rudolf, F.; O’Rourke, S.M.; Luke, B.; Hofmann, K.; Hyman, A.A.; Bowerman, B.; Peter, M. The conserved protein DCN-1/Dcn1p is required for cullin neddylation in C. elegans and S. cerevisiae. Nature 2005, 435, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, T.; Chou, Y.C.; Willems, A.R.; Meyer-Schaller, N.; Hecht, M.L.; Tyers, M.; Peter, M.; Sicheri, F. Dcn1 functions as a scaffold-type E3 ligase for cullin neddylation. Mol. Cell 2008, 29, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.C.; Monda, J.K.; Bennett, E.J.; Harper, J.W.; Schulman, B.A. N-terminal acetylation acts as an avidity enhancer within an interconnected multiprotein complex. Science 2011, 334, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keuss, M.J.; Thomas, Y.; McArthur, R.; Wood, N.T.; Knebel, A.; Kurz, T. Characterization of the mammalian family of DCN-type NEDD8 E3 ligases. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarkaria, I.; O-charoenrat, P.; Talbot, S.G.; Reddy, P.G.; Ngai, I.; Maghami, E.; Patel, K.N.; Lee, B.; Yonekawa, Y.; Dudas, M.; et al. Squamous cell carcinoma related oncogene/DCUN1D1 is highly conserved and activated by amplification in squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9437–9444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Estilo, C.L.; O-Charoenrat, P.; Ngai, I.; Patel, S.G.; Reddy, P.G.; Dao, S.; Shaha, A.R.; Kraus, D.H.; Boyle, J.O.; Wong, R.J.; et al. The role of novel oncogenes squamous cell carcinoma-related oncogene and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p110alpha in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2300–2306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Sun, J.; Huang, G.; Liu, J.C.; Kaufman, A.; Ryan, R.J.; Ramanathan, S.Y.; Venkatesh, T.; Singh, B. Squamous Cell Carcinoma-related Oncogene (SCCRO) Family Members Regulate Cell Growth and Proliferation through Their Cooperative and Antagonistic Effects on Cullin Neddylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 6200–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| CRL | Key Targets | References |
|---|---|---|
| Cullin-1 | BIM-EL, p21, p27, Wee1 | [33,38,39] |
| Cullin-2 | HIF1α | [40] |
| Cullin-3 | Nrf2, Beclin1, ULK1 | [41,42] |
| Cullin-4A/4B | XPC, CDT1, p21 | [43,44] |
| Cullin-5 | NOXA, ATM | [45,46] |
| Cullin-7 | Caspase-8 | [47] |
| Cullin-9 | Regulates p53 localization | [48] |
| Compound | Target | Development Stage | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pevonedistat (MLN4924) | NAE | Clinical Trial: Phase III (AML); Phase II (Advanced Solid Tumors) | [49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63] |
| TAS4464 | NAE | Clinical Trial: Phase I/II (Multiple Myeloma, Lymphoma) | [64,65,66,67] |
| ZM223 | NAE | Preclinical (Osteosarcoma) | [68] |
| DI-591 | UBC12/DCN1 | Preclinical—No Cytotoxicity | [69] |
| NAcM-OPT | UBC12/DCN1 | Preclinical (Lung) | [70,71] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, T.M.; Carew, J.S.; Bauman, J.E.; Nawrocki, S.T. Targeting NEDDylation as a Novel Approach to Improve the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133250
Jones TM, Carew JS, Bauman JE, Nawrocki ST. Targeting NEDDylation as a Novel Approach to Improve the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133250
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Trace M., Jennifer S. Carew, Julie E. Bauman, and Steffan T. Nawrocki. 2021. "Targeting NEDDylation as a Novel Approach to Improve the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133250
APA StyleJones, T. M., Carew, J. S., Bauman, J. E., & Nawrocki, S. T. (2021). Targeting NEDDylation as a Novel Approach to Improve the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers, 13(13), 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133250