Quadruplex Ligands in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
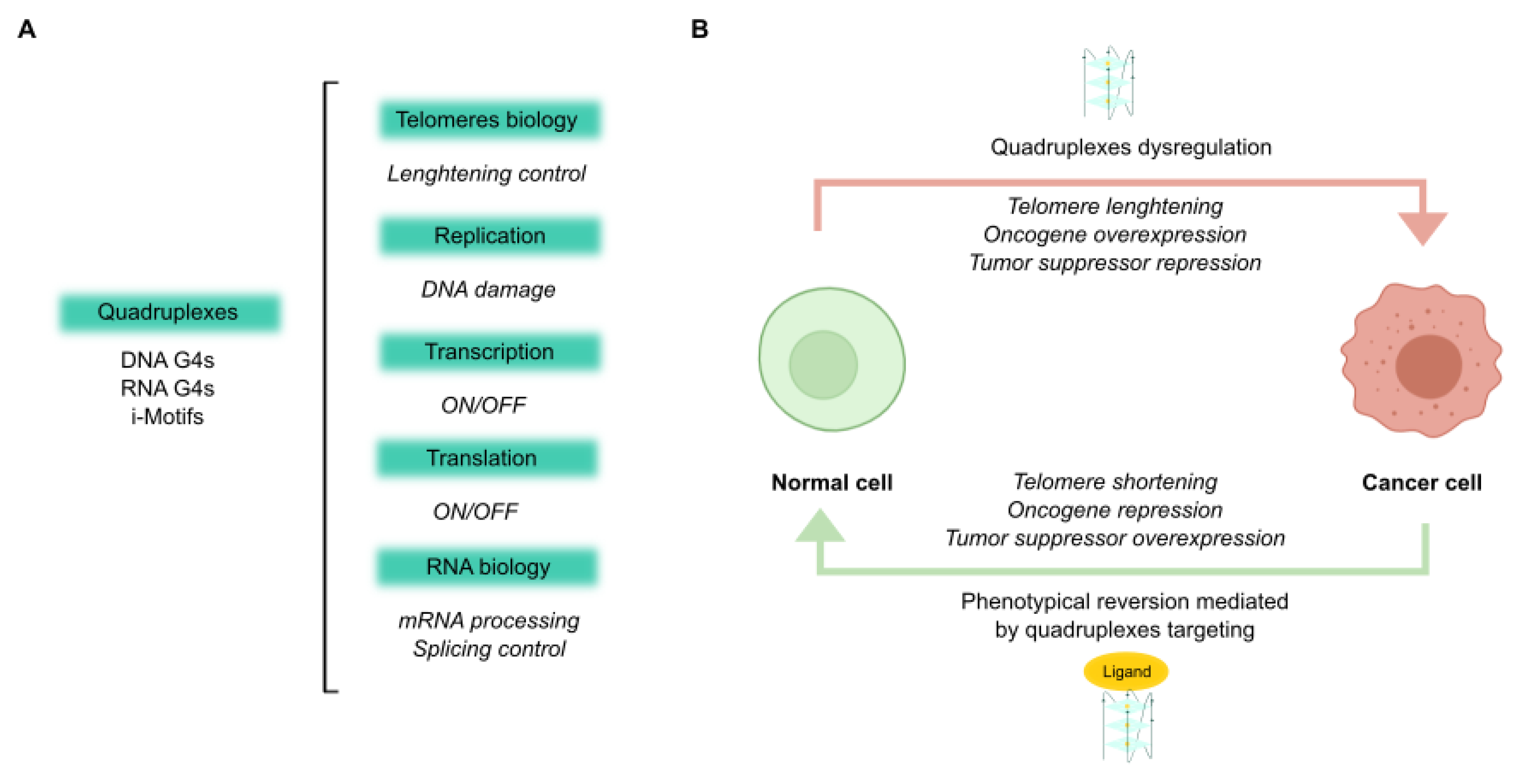
1. Introduction
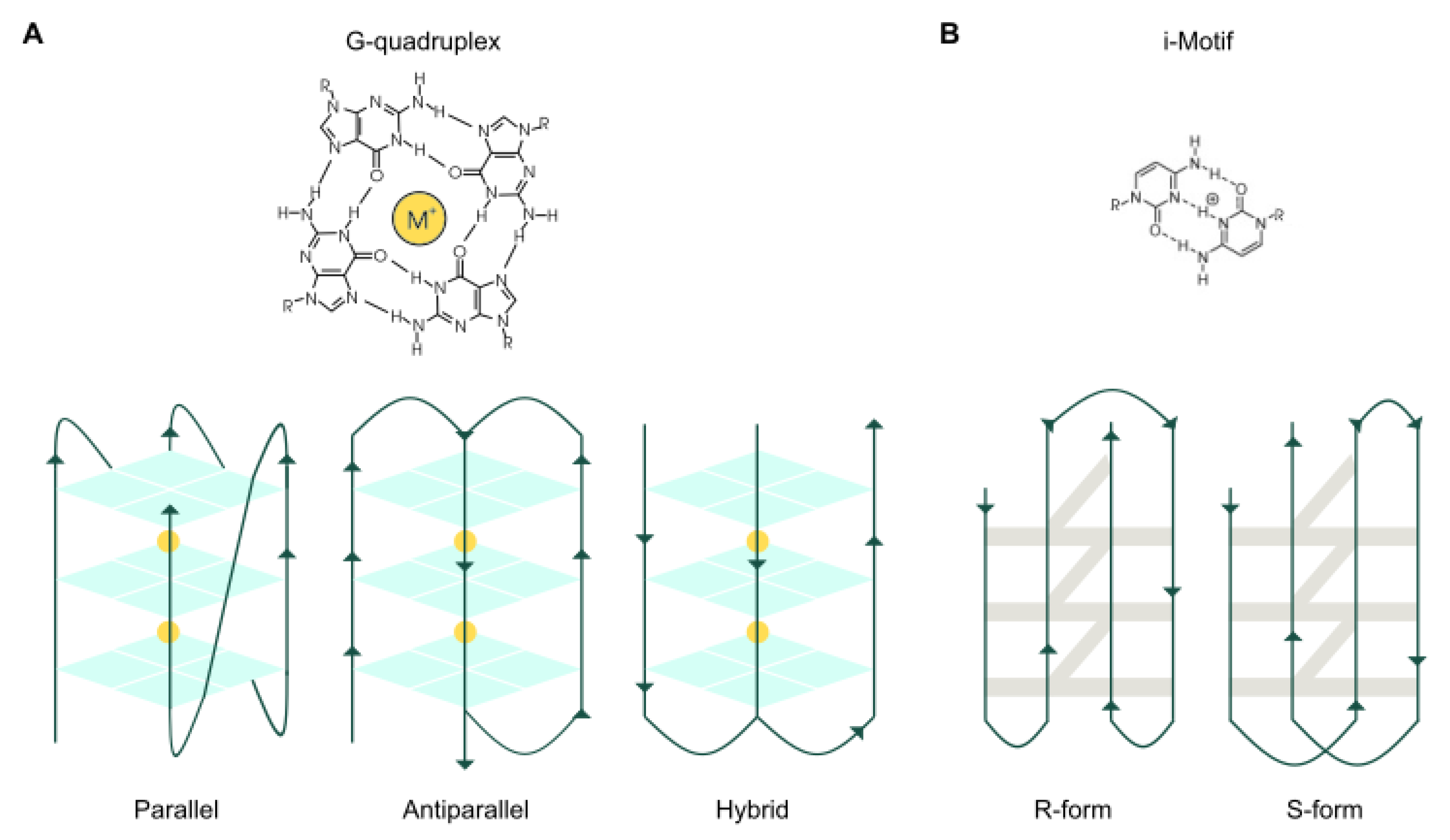
2. Quadruplex Ligands
2.1. DNA G4 Ligands
2.1.1. Classical G4 Ligands
2.1.2. Chemo-Families of G4 Ligands
2.1.3. Selective G4 Ligands
2.2. RNA G4 Ligands
2.2.1. 5′UTR G4 Ligands
2.2.2. Splicing Site G4 Ligands
2.2.3. miRNA G4 Ligands
2.3. I-Motif Ligands
2.3.1. Telomeric i-Motif Ligands
2.3.2. Extratelomeric i-Motif Ligands
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Choi, J.; Majima, T. Conformational changes of non-B DNA. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5893–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burge, S.; Parkinson, G.N.; Hazel, P.; Todd, A.K.; Neidle, S. Quadruplex DNA: Sequence, topology and structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5402–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Di Antonio, M.; Balasubramanian, S. DNA G-quadruplexes in the human genome: Detection, functions and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachimi, A.; Benz, A.; Hartig, J.S. A comparison of DNA and RNA quadruplex structures and stabilities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6811–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gehring, K.; Leroy, J.-L.; Guéron, M. A tetrameric DNA structure with protonated cytosine-cytosine base pairs. Nature 1993, 363, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.S.; Waller, Z.A.E. Tricky Topology: Persistence of Folded Human Telomeric i-Motif DNA at Ambient Temperature and Neutral pH. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bugaut, A.; Balasubramanian, S. A sequence-independent study of the influence of short loop lengths on the stability and topology of intramolecular DNA G-quadraplexes. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, C.D.; Shibata, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Xu, Y. An intramolecular antiparallel G-quadruplex formed by human telomere RNA. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3944–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. Prevalence of quadruplexes in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2908–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varizhuk, A.; Ischenko, D.; Tsvetkov, V.; Novikov, R.; Kulemin, N.; Kaluzhny, D.; Vlasenok, M.; Naumov, V.; Smirnov, I.; Pozmogova, G. The expanding repertoire of G4 DNA structures. Biochimie 2017, 135, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergny, J.L.; Lacroix, L. UV melting of G-quadruplexes. Curr. Protoc. Nucleic Acid Chem. 2009, 17, Unit 17.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, M.; Heddi, B.; Phan, A.T. NMR spectroscopy of G-quadruplexes. Methods 2012, 57, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Spiegel, J.; Marsico, G.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. Genome-wide mapping of endogenous G-quadruplex DNA structures by chromatin immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, C.K.; Marsico, G.; Sahakyan, A.B.; Chambers, V.S.; Balasubramanian, S. RG4-seq reveals widespread formation of G-quadruplex structures in the human transcriptome. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzine, F.; Wojtowicz, D.; Baranello, L.; Yamane, A.; Nelson, S.; Resch, W.; Kieffer-Kwon, K.R.; Benham, C.J.; Casellas, R.; Przytycka, T.M.; et al. Permanganate/S1 Nuclease Footprinting Reveals Non-B DNA Structures with Regulatory Potential across a Mammalian Genome. Cell Syst. 2017, 4, 344–356.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williamson, J.R.; Raghuraman, M.K.; Cech, T.R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: The G-quartet model. Cell 1989, 59, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, K.A.; Merino, E.J.; Weeks, K.M. Selective 2′-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension (SHAPE): Quantitative RNA structure analysis at single nucleotide resolution. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1610–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.U.; Bartel, D.P. RNA G-quadruplexes are globally unfolded in eukaryotic cells and depleted in bacteria. Science 2016, 353, aaf5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biffi, G.; Tannahill, D.; McCafferty, J.; Balasubramanian, S. Quantitative visualization of DNA G-quadruplex structures in human cells. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffi, G.; Di Antonio, M.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. Visualization and selective chemical targeting of RNA G-quadruplex structures in the cytoplasm of human cells. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraati, M.; Langley, D.B.; Schofield, P.; Moye, A.L.; Rouet, R.; Hughes, W.E.; Bryan, T.M.; Dinger, M.E.; Christ, D. I-motif DNA structures are formed in the nuclei of human cells. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Varshney, D.; Simeone, A.; Zhang, X.; Adhikari, S.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. Promoter G-quadruplex folding precedes transcription and is controlled by chromatin. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, J.; Adhikari, S.; Balasubramanian, S. The Structure and Function of DNA G-Quadruplexes. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Hurley, L.H.; Neidle, S. Targeting G-quadruplexes in gene promoters: A novel anticancer strategy? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De, S.; Michor, F. DNA secondary structures and epigenetic determinants of cancer genome evolution. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Martin, V.; Lopez-Pujante, C.; Soriano-Rodriguez, M.; Garcia-Salcedo, J.A. An updated focus on quadruplex structures as potential therapeutic targets in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, E.; Hardin, C.C.; Walk, S.K.; Tinoco, I.; Blackburn, E.H. Telomeric DNA oligonucleotides form novel intramolecular structures containing guanine·guanine base pairs. Cell 1987, 51, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsen, R.C.; DeLeeuw, L.; Dean, W.L.; Gray, R.D.; Sabo, T.M.; Chakravarthy, S.; Chaires, J.B.; Trent, J.O. The hTERT core promoter forms three parallel G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 5720–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martadinata, H.; Heddi, B.; Lim, K.W.; Phan, A.T. Structure of long human telomeric RNA (TERRA): G-quadruplexes formed by four and eight UUAGGG repeats are stable building blocks. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 6455–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.; Lamarteleur, T.; Lacroix, L.; Mailliet, P.; Mergny, J.L.; Riou, J.F. Telomerase downregulation induced by the G-quadruplex ligand 12459 in A549 cells is mediated by hTERT RNA alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rouleau, S.; Glouzon, J.P.S.; Brumwell, A.; Bisaillon, M.; Perreault, J.P. 3′ UTR G-quadruplexes regulate miRNA binding. RNA 2017, 23, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcel, V.; Tran, P.L.T.; Sagne, C.; Martel-Planche, G.; Vaslin, L.; Teulade-Fichou, M.P.; Hall, J.; Mergny, J.L.; Hainaut, P.; van Dyck, E. G-quadruplex structures in TP53 intron 3: Role in alternative splicing and in production of p53 mRNA isoforms. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandey, S.; Agarwala, P.; Jayaraj, G.G.; Gargallo, R.; Maiti, S. The RNA Stem-Loop to G-Quadruplex Equilibrium Controls Mature MicroRNA Production inside the Cell. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 7067–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolski, P.; Nieszporek, K.; Panczyk, T. G-Quadruplex and I-Motif Structures within the Telomeric DNA Duplex. A Molecular Dynamics Analysis of Protonation States as Factors Affecting Their Stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, T.A.; Kendrick, S.; Hurley, L. Making sense of G-quadruplex and i-motif functions in oncogene promoters. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 3459–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neidle, S. Quadruplex nucleic acids as targets for anticancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, O.; Bourdoncle, A.; Boulé, J.B.; Brosh, R.M.; Mergny, J.L. G-quadruplexes and helicases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asamitsu, S.; Bando, T.; Sugiyama, H. Ligand Design to Acquire Specificity to Intended G-Quadruplex Structures. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raje, S.; Pandav, K.; Barthwal, R. Binding of anticancer drug adriamycin to parallel G-quadruplex DNA [d-(TTAGGGT)]4 comprising human telomeric DNA leads to thermal stabilization: A multiple spectroscopy study. J. Mol. Recognit. 2020, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Local, A.; Zhang, H.; Benbatoul, K.D.; Folger, P.; Sheng, X.; Tsai, C.Y.; Howell, S.B.; Rice, W.G. APTO-253 stabilizes G-quadruplex DNA, inhibits MYC expression, and induces DNA damage in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLuckie, K.I.E.; Waller, Z.A.E.; Sanders, D.A.; Alves, D.; Rodriguez, R.; Dash, J.; McKenzie, G.J.; Venkitaraman, A.R.; Balasubramanian, S. G-Quadruplex-Binding benzo[a]phenoxazines down-regulate c-KIT expression in human gastric carcinoma cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2658–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, S.D.; Pal, N.; Singh, M.K.; Shweta, H.; Khan, M.F.; Sen, S. Understanding ligand interaction with different structures of g-quadruplex DNA: Evidence of kinetically controlled ligand binding and binding-mode assisted quadruplex structure alteration. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7218–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, K.M.; Saunders, L.B.; Simmons, J.K.; Leon, E.; Calabrese, D.R.; Zhang, S.; Michalowski, A.; Gareiss, P.; Mock, B.A.; Schneekloth, J.S. Small Molecule Microarrays Enable the Identification of a Selective, Quadruplex-Binding Inhibitor of MYC Expression. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganthi, S.; Sivaraj, R.; Enoch, I.V.M.V. Molecular encapsulation of berberine by a modified β-cyclodextrin and binding of host: Guest complex to G-quadruplex DNA. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2019, 38, 858–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.N.; Xie, M.X. Spectroscopic investigation of the interaction between G-quadruplex of KRAS promoter sequence and three isoquinoline alkaloids. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 171, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Chaires, J.B. Sequence and structural selectivity of nucleic acid binding ligands. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 16067–16075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, M.; Harrison, R.J.; Romagnoli, B.; Tanious, F.A.; Gowan, S.H.; Reszka, A.P.; Wilson, W.D.; Kelland, L.R.; Neidle, S. Structure-based design of selective and potent G quadruplex-mediated telomerase inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4844–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panda, D.; Debnath, M.; Mandal, S.; Bessi, I.; Schwalbe, H.; Dash, J. A Nucleus-Imaging Probe That Selectively Stabilizes a Minor Conformation of c-MYC G-quadruplex and Down-regulates c-MYC Transcription in Human Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, B.X.; She, M.T.; Long, W.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Huang, X.H.; Liu, W.; Hou, J.Q.; Wong, W.L.; Lu, Y.J. A small-sized benzothiazole-indolium fluorescent probe: The study of interaction specificity targeting c-MYC promoter G-quadruplex structures and live cell imaging. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 15016–15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Lin, D.; Tang, Y.; Fei, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J. A light-up probe targeting for Bcl-2 2345 G-quadruplex DNA with carbazole TO. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 191, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, M.; Yuan, G. Formation, recognition and bioactivities of a novel G-quadruplex in the STAT3 gene. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 5987–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamitsu, S.; Obata, S.; Phan, A.T.; Hashiya, K.; Bando, T.; Sugiyama, H. Simultaneous Binding of Hybrid Molecules Constructed with Dual DNA-Binding Components to a G-Quadruplex and Its Proximal Duplex. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 4428–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, R.; Barua, A.; Das, A.; Chatterjee, T.; Pathak, A.; Choudhury, P.; Sen, S.; Saha, P.; Bhattacharyya, M. Porphyrins to restrict progression of pancreatic cancer by stabilizing KRAS G-quadruplex: In silico, in vitro and in vivo validation of anticancer strategy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 125, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Di Antonio, M.; McKinney, S.; Mathew, V.; Ho, B.; O’Neil, N.J.; Dos Santos, N.; Silvester, J.; Wei, V.; Garcia, J.; et al. CX-5461 is a DNA G-quadruplex stabilizer with selective lethality in BRCA1/2 deficient tumours. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschin, M.; Rossetti, L.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Schirripa, S.; Bianco, A.; Ortaggi, G.; Savino, M.; Schultes, C.; Neidle, S. Natural and synthetic G-quadruplex interactive berberine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 1707–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, J.; Pereira, E.; Marquevielle, J.; Campello, M.P.C.; Mergny, J.L.; Paulo, A.; Salgado, G.F.; Queiroz, J.A.; Cruz, C. Fluorescent light-up acridine orange derivatives bind and stabilize KRAS-22RT G-quadruplex. Biochimie 2018, 144, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aria, F.; D’Amore, V.M.; Di Leva, F.S.; Amato, J.; Caterino, M.; Russomanno, P.; Salerno, S.; Barresi, E.; De Leo, M.; Marini, A.M.; et al. Targeting the KRAS oncogene: Synthesis, physicochemical and biological evaluation of novel G-Quadruplex DNA binders. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 149, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.N.; Chevret, E.; Desplat, V.; Rubio, S.; Mergny, J.L.; Guillon, J. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new substituted diquinolinyl-pyridine ligands as anticancer agents by targeting G-Quadruplex. Molecules 2018, 23, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Wen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Wei, C. Promoting the formation and stabilization of human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA, inhibition of telomerase and cytotoxicity by phenanthroline derivatives. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 2648–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Thompson, B.; Cathers, B.E.; Salazar, M.; Kerwin, S.M.; Trent, J.O.; Jenkins, T.C.; Neidle, S.; Hurley, L.H. Inhibition of human telomerase by a G-Quadruplex-Interactive compound. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 2113–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.H.; Lin, X.T.; Liu, B.; Tan, J.H. Dimeric aryl-substituted imidazoles may inhibit ALT cancer by targeting the multimeric G-quadruplex in telomere. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 186, 111891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hagan, M.P.; Ramos-Soriano, J.; Haldar, S.; Sheikh, S.; Morales, J.C.; Mulholland, A.J.; Galan, M.C. Visible-light photoswitching of ligand binding mode suggests G-quadruplex DNA as a target for photopharmacology. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 5186–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raje, S.; Pandav, K.; Barthwal, R. Dual mode of binding of anti cancer drug epirubicin to G-quadruplex [d-(TTAGGGT)]4 containing human telomeric DNA sequence induces thermal stabilization. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 115131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, J.; Pagano, A.; Capasso, D.; Di Gaetano, S.; Giustiniano, M.; Novellino, E.; Randazzo, A.; Pagano, B. Targeting the BCL2 Gene Promoter G-Quadruplex with a New Class of Furopyridazinone-Based Molecules. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.V.; Danford, F.L.; Gokhale, V.; Hurley, L.H.; Brooks, T.A. Demonstration that drug-targeted down-regulation of MYC in non-Hodgkins lymphoma is directly mediated through the promoter G-quadruplex. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 41018–41027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, R.V.; Wang, T.; Chappeta, V.R.; Wu, G.; Onel, B.; Chawla, R.; Quijada, H.; Camp, S.M.; Chiang, E.T.; Lassiter, Q.R.; et al. The Consequences of Overlapping G-Quadruplexes and i-Motifs in the Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor β Core Promoter Nuclease Hypersensitive Element Can Explain the Unexpected Effects of Mutations and Provide Opportunities for Selective Targeting of both structures by small molecules to downregulate gene expression. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7456–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.J.; Cui, Y.; Yin, H.; Scheid, A.; Hendricks, W.P.D.; Schmidt, J.; Sekulic, A.; Kong, D.; Trent, J.M.; Gokhale, V.; et al. A Pharmacological Chaperone Molecule Induces Cancer Cell Death by Restoring Tertiary DNA Structures in Mutant hTERT Promoters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13673–13692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavrado, J.; Borralho, P.M.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Castro, R.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Moreira, R.; Dos Santos, D.J.V.A.; Neidle, S.; Paulo, A. Synthesis, G-quadruplex stabilisation, docking studies, and effect on cancer cells of indolo[3,2-b]quinolines with one, two, or three basic side chains. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 1648–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Funke, A.; Dickerhoff, J.; Weisz, K. Towards the Development of Structure-Selective G-Quadruplex-Binding Indolo[3,2-b]quinolines. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 3170–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zan, L.P.; Wang, X.D.; Lu, Y.J.; Ou, T.M.; Lin, J.; Huang, Z.S.; Gu, L.Q. Stabilization of VEGF G-quadruplex and inhibition of angiogenesis by quindoline derivatives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 2970–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejugam, M.; Sewitz, S.; Shirude, P.S.; Rodriguez, R.; Shahid, R.; Balasubramanian, S. Trisubstituted isoalloxazines as a new class of G-quadruplex binding ligands: Small molecule regulation of c-kit oncogene expression. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12926–12927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, M.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Yu, Z.Y.; Hu, L.N.; Ou, T.M.; Chen, S.B.; Huang, Z.S.; Tan, J.H. Discovery of a New Four-Leaf Clover-Like Ligand as a Potent c-MYC Transcription Inhibitor Specifically Targeting the Promoter G-Quadruplex. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2447–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.H.; Chen, S.B.; Wang, B.; Ou, T.M.; Gu, L.Q.; Tan, J.H.; Huang, Z.S. Specific targeting of telomeric multimeric G-quadruplexes by a new triaryl-substituted imidazole. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 1606–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Tan, W.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, G. Investigation of G-quadruplex formation in the FGFR2 promoter region and its transcriptional regulation by liensinine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, T.P.; Tripathi, S.; Barthwal, R. Molecular recognition of parallel quadruplex [d-(TTGGGGT)]4 by mitoxantrone: Binding with 1:4 stoichiometry leads to telomerase inhibition. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 71652–71661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazaey Zidanloo, S.; Hosseinzadeh Colagar, A.; Ayatollahi, H.; Bagheryan, Z. G-quadruplex forming region within WT1 promoter is selectively targeted by daunorubicin and mitoxantrone: A possible mechanism for anti-leukemic effect of drugs. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.X.; Zhu, L.N.; Wu, B.; Huo, Y.F.; Duan, N.N.; Kong, D.M. Two cationic porphyrin isomers showing different multimeric G-quadruplex recognition specificity against monomeric G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8719–8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunaratnam, M.; Collie, G.W.; Reszka, A.P.; Todd, A.K.; Parkinson, G.N.; Neidle, S. A naphthalene diimide G-quadruplex ligand inhibits cell growth and down-regulates BCL-2 expression in an imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal cancer cell line. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2958–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, C.; Minarini, A.; Tumiatti, V.; Moraca, F.; Parrotta, L.; Alcaro, S.; Rigo, R.; Sissi, C.; Gunaratnam, M.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; et al. Macrocyclic naphthalene diimides as G-quadruplex binders. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3819–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, S.; Nadai, M.; Ruggiero, E.; Tassinari, M.; Marušič, M.; Tosoni, B.; Frasson, I.; Cernilogar, F.M.; Pirota, V.; Doria, F.; et al. The MDM2 inducible promoter folds into four-tetrad antiparallel G-quadruplexes targetable to fight malignant liposarcoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Martin, V.; Schneider, D.A.; Ortiz-Gonzalez, M.; Soriano-Lerma, A.; Linde-Rodriguez, A.; Perez-Carrasco, V.; Gutierrez-Fernandez, J.; Cuadros, M.; González, C.; Soriano, M.; et al. Targeting ribosomal G-quadruplexes with naphthalene-diimides as RNA polymerase I inhibitors for colorectal cancer treatment. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca, F.; Greciano, O.; Gunaratnam, M.; Haider, S.; Munnur, D.; Nanjunda, R.; Wilson, W.D.; Neidle, S. Tri- and tetra-substituted naphthalene diimides as potent G-quadruplex ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, L.; Ren, J.; Xu, Y.; Qu, X. Targeting human telomeric higher-order DNA: Dimeric G-quadruplex units serve as preferred binding site. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18786–18789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Fu, M.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Chiral metallo-supramolecular complexes selectively recognize human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 5695–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tera, M.; Ishizuka, H.; Takagi, M.; Suganuma, M.; Shin-Ya, K.; Nagasawa, K. Macrocyclic hexaoxazoles as sequence- and mode-selective G-quadruplex binders. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 5557–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tera, M.; Iida, K.; Ishizuka, H.; Takagi, M.; Suganuma, M.; Doi, T.; Shin-Ya, K.; Nagasawa, K. Synthesis of a potent G-quadruplex-binding macrocyclic heptaoxazole. ChemBioChem 2009, 10, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, M.; Ghosh, S.; Chauhan, A.; Paul, R.; Bhattacharyya, K.; Dash, J. Preferential targeting of i-motifs and G-quadruplexes by small molecules. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 7448–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. Synthesis and binding studies of novel di-substituted phenanthroline compounds with genomic promoter and human telomeric DNA G-quadruplexes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, J.E.; Neidle, S.; Vilar, R. Stabilisation of human telomeric quadruplex DNA and inhibition of telomerase by a platinum-phenanthroline complex. Chem. Commun. 2007, 42, 4366–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, W.J.; Heddi, B.; Hamon, F.; Teulade-Fichou, M.P.; Phan, A.T. Solution structure of a G-quadruplex bound to the bisquinolinium compound phen-DC3. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cian, A.; DeLemos, E.; Mergny, J.L.; Teulade-Fichou, M.P.; Monchaud, D. Highly efficient G-quadruplex recognition by bisquinolinium compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1856–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taka, T.; Joonlasak, K.; Huang, L.; Randall Lee, T.; Chang, S.W.T.; Tuntiwechapikul, W. Down-regulation of the human VEGF gene expression by perylene monoimide derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterino, M.; D’Aria, F.; Kustov, A.V.; Belykh, D.V.; Khudyaeva, I.S.; Starseva, O.M.; Berezin, D.B.; Pylina, Y.I.; Usacheva, T.; Amato, J.; et al. Selective binding of a bioactive porphyrin-based photosensitizer to the G-quadruplex from the KRAS oncogene promoter. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Das, T.; Debnath, M.; Chauhan, A.; Dash, J. G-Quadruplex-Binding Small Molecule Induces Synthetic Lethality in Breast Cancer Cells by Inhibiting c-MYC and BCL2 Expression. ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.H.; Wu, T.Y.; Huang, Q.; Jin, G. New substituted quinoxalines inhibit triple-negative breast cancer by specifically downregulating the c-MYC transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10529–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnarasi, S.; Radhika, R.; Vijayakumar, S.; Shankar, R. Structural insights into the anti-cancer activity of quercetin on G-tetrad, mixed G-tetrad, and G-quadruplex DNA using quantum chemical and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, C.X.; Yan, J.W.; Hou, J.Q.; Chen, S.B.; Ou, T.M.; Gu, L.Q.; Huang, Z.S.; Tan, J.H. Synthesis and evaluation of quinazolone derivatives as a new class of c-KIT G-quadruplex binding ligands. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jamroskovic, J.; Doimo, M.; Chand, K.; Obi, I.; Kumar, R.; Brännström, K.; Hedenström, M.; Nath Das, R.; Akhunzianov, A.; Deiana, M.; et al. Quinazoline Ligands Induce Cancer Cell Death through Selective STAT3 Inhibition and G-Quadruplex Stabilization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2876–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, Y.J.; Kumarasamy, V.; Camacho, D.; Sun, D. Involvement of G-quadruplex structures in regulation of human RET gene expression by small molecules in human medullary thyroid carcinoma TT cells. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowan, S.M.; Heald, R.; Stevens, M.F.G.; Kelland, L.R. Potent inhibition of telomerase by small-molecule pentacyclic acridines capable of interacting with G-quadruplexes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillard, M.; Weynand, J.; Bonnet, H.; Loiseau, F.; Decottignies, A.; Dejeu, J.; Defrancq, E.; Elias, B. Flexible RuII Schiff Base Complexes: G-Quadruplex DNA Binding and Photo-Induced Cancer Cell Death. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 13849–13860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Liu, W.J.; Guo, K.; Rusche, J.J.; Ebbinghaus, S.; Gokhale, V.; Hurley, L.H. The proximal promoter region of the human vascular endothelial growth factor gene has a G-quadruplex structure that can be targeted by G-quadruplex-interactive agents. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, T.; Chen, S.B.; Tu, J.L.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.P.; Ou, T.M.; et al. Discovery of Novel Schizocommunin Derivatives as Telomeric G-Quadruplex Ligands That Trigger Telomere Dysfunction and the Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Damage Response. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3436–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hagan, M.P.; Peñalver, P.; Gibson, R.S.L.; Morales, J.C.; Galan, M.C. Stiff-Stilbene Ligands Target G-Quadruplex DNA and Exhibit Selective Anticancer and Antiparasitic Activity. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 6224–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, J.; Platella, C.; Iachettini, S.; Zizza, P.; Musumeci, D.; Cosconati, S.; Pagano, A.; Novellino, E.; Biroccio, A.; Randazzo, A.; et al. Tailoring a lead-like compound targeting multiple G-quadruplex structures. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Pan, Y.; Joshi, K.; Purohit, D.; Hu, B.; Demir, H.; Mazumder, S.; Okabe, S.; Yamori, T.; Viapiano, M.; et al. Telomestatin impairs glioma stem cell survival and growth through the disruption of telomeric G-quadruplex and inhibition of the proto-oncogene, c-Myb. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1268–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.Y.; Vankayalapati, H.; Shin-Ya, K.; Wierzba, K.; Hurley, L.H. Telomestatin, a potent telomerase inhibitor that interacts quite specifically with the human telomeric intramolecular G-quadruplex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 2098–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, D.; Debnath, M.; Müller, D.; Paul, R.; Das, T.; Bessi, I.; Schwalbe, H.; Dash, J. Cell penetrating thiazole peptides inhibit c-MYC expression via site-specific targeting of c-MYC G-quadruplex. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 5355–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.H.; Nagesh, N.; Lewis, E.A. Bcl-2 Promoter Sequence G-Quadruplex Interactions with Three Planar and Non-Planar Cationic Porphyrins: TMPyP4, TMPyP3, and TMPyP2. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grand, C.L.; Han, H.; Mũnoz, R.M.; Weitman, S.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Hurley, L.H.; Bearss, D.J. The cationic porphyrin TMPyP4 down-regulates c-MYC and human telomerase reverse transcriptase expression and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paramasivam, M.; Membrino, A.; Cogoi, S.; Fukuda, H.; Nakagama, H.; Xodo, L.E. Protein hnRNP A1 and its derivative Up1 unfold quadruplex DNA in the human KRAS promoter: Implications for transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 2841–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Rezler, E.M.; Gokhale, V.; Sun, D.; Hurley, L.H. Characterization of the G-quadruplexes in the duplex nuclease hypersensitive element of the PDGF-A promoter and modulation of PDGF-A promoter activity by TMPyP4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7698–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheelhouse, R.T.; Sun, D.; Han, H.; Han, F.X.; Hurley, L.H. Cationic porphyrins as telomerase inhibitors: The interaction of tetra- (N-methyl-4-pyridyl)porphine with quadruplex DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 3261–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Guo, K.; Rusche, J.J.; Hurley, L.H. Facilitation of a structural transition in the polypurine/polypyrimidine tract within the proximal promoter region of the human VEGF gene by the presence of potassium and G-quadruplex-interactive agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 6070–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhou, J.; Xu, M.; Yuan, G. Exploration of G-quadruplex function in c-Myb gene and its transcriptional regulation by topotecan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.; Saha, P.; Das, T.; Dash, J. Target guided synthesis using DNA nano-templates for selectively assembling a G-quadruplex binding c-MYC inhibitor. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muench, D.; Rezzoug, F.; Thomas, S.D.; Xiao, J.; Islam, A.; Miller, D.M.; Sedoris, K.C. Quadruplex-forming oligonucleotide targeted to the VEGF promoter inhibits growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabharwal, N.C.; Chen, J.; Lee, J.H.J.; Gangemi, C.M.A.; D’urso, A.; Yatsunyk, L.A. Interactions between spermine-derivatized tentacle porphyrins and the human telomeric DNA G-Quadruplex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, N.M.; Labrunie, G.; Corry, B.; Tran, P.L.T.; Norret, M.; Djavaheri-Mergny, M.; Raston, C.L.; Mergny, J.L. Unraveling the relationship between structure and stabilization of triarylpyridines as G-quadruplex binding ligands. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 6154–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, J.; Xiong, X.; Cheng, M.; Hu, X.; Narva, S.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W. Design, synthesis of 4,5-diazafluorene derivatives and their anticancer activity via targeting telomeric DNA G-quadruplex. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 178, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J. Selective nuclei accumulation of ruthenium(II) complex enantiomers that target G-quadruplex DNA. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 150, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guliaev, A.B.; Leontis, N.B. Cationic 5,10,15,20-tetrakis (N-methylpyridinium-4-yl) porphyrin fully intercalates at 5′-CG-3′ steps of duplex DNA in solution. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 15425–15437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.A.; Kim, J.O.; Cho, T.S.; Song, R.; Kim, S.K. Binding of meso-tetrakis(N-methylpyridium-4-yl)porphyrin to triplex oligonucleotides: Evidence for the porphyrin stacking in the major groove. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 8106–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wu, G.; Wang, K.; Onel, B.; Sakai, S.; Shao, Y.; Yang, D. Molecular Recognition of the Hybrid-2 Human Telomeric G-Quadruplex by Epiberberine: Insights into Conversion of Telomeric G-Quadruplex Structures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10888–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, T.; Shibata, K.; Yoshida, M.; Takagi, M.; Tera, M.; Nagasawa, K.; Shin-Ya, K.; Takahashi, T. (S)-Stereoisomer of telomestatin as a potent G-quadruplex binder and telomerase inhibitor. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Iachettini, S.; Zizza, P.; Cingolani, C.; Porru, M.; Artuso, S.; Stevens, M.; Hummersone, M.; Biroccio, A.; Salvati, E.; et al. Identification of novel RHPS4-derivative ligands with improved toxicological profiles and telomere-targeting activities. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, R.; Müller, S.; Yeoman, J.A.; Trentesaux, C.; Riou, J.F.; Balasubramanian, S. A novel small molecule that alters shelterin integrity and triggers a DNA-damage response at telomeres. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15758–15759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, R.; Miller, K.M.; Forment, J.V.; Bradshaw, C.R.; Nikan, M.; Britton, S.; Oelschlaegel, T.; Xhemalce, B.; Balasubramanian, S.; Jackson, S.P. Small-molecule-induced DNA damage identifies alternative DNA structures in human genes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chambers, V.S.; Marsico, G.; Boutell, J.M.; Di Antonio, M.; Smith, G.P.; Balasubramanian, S. High-throughput sequencing of DNA G-quadruplex structures in the human genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.Y.; Duan, W.; Gleason-Guzman, M.; Hurley, L.H. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a series of fluoroquinoanthroxazines with contrasting dual mechanisms of action against topoisomerase II and G-quadruplexes. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drygin, D.; Siddiqui-Jain, A.; O’Brien, S.; Schwaebe, M.; Lin, A.; Bliesath, J.; Ho, C.B.; Proffitt, C.; Trent, K.; Whitten, J.P.; et al. Anticancer Activity of CX-3543: A Direct Inhibitor of rRNA Biogenesis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7653–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drygin, D.; Lin, A.; Bliesath, J.; Ho, C.B.; O’Brien, S.E.; Proffitt, C.; Omori, M.; Haddach, M.; Schwaebe, M.K.; Siddiqui-Jain, A.; et al. Targeting RNA polymerase I with an oral small molecule CX-5461 inhibits ribosomal RNA synthesis and solid tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1418–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackobel, A.J.; Zeberl, B.J.; Glover, D.M.; Fakhouri, A.M.; Knutson, B.A. DNA binding preferences of S. cerevisiae RNA polymerase I Core Factor reveal a preference for the GC-minor groove and a conserved binding mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 194408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muoio, D.; Berardinelli, F.; Leone, S.; Coluzzi, E.; di Masi, A.; Doria, F.; Freccero, M.; Sgura, A.; Folini, M.; Antoccia, A. Naphthalene diimide-derivatives G-quadruplex ligands induce cell proliferation inhibition, mild telomeric dysfunction and cell cycle perturbation in U251MG glioma cells. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 3769–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Răsădean, D.M.; Sheng, B.; Dash, J.; Pantoş, G.D. Amino-Acid-Derived Naphthalenediimides as Versatile G-Quadruplex Binders. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 8491–8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Recagni, M.; Tassinari, M.; Doria, F.; Cimino-reale, G.; Za, N.; Freccero, M.; Folini, M.; Richter, S.N. The Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in BRAF -Mutant Melanoma Cells Are Modulated by Naphthalene. Cells 2019, 8, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohnmacht, S.A.; Marchetti, C.; Gunaratnam, M.; Besser, R.J.; Haider, S.M.; Di Vita, G.; Lowe, H.L.; Mellinas-Gomez, M.; Diocou, S.; Robson, M.; et al. A G-quadruplex-binding compound showing anti-tumour activity in an in vivo model for pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchetti, C.; Zyner, K.G.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Robson, M.; Haider, S.M.; Morton, J.P.; Marsico, G.; Vo, T.; Laughlin-Toth, S.; Ahmed, A.A.; et al. Targeting Multiple Effector Pathways in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma with a G-Quadruplex-Binding Small Molecule. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2500–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Marchetti, C.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Neidle, S. A G-quadruplex-binding compound shows potent activity in human gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrado, J.; Brito, H.; Borralho, P.M.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Kim, N.S.; Leitão, C.; Pisco, S.; Gunaratnam, M.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Moreira, R.; et al. KRAS oncogene repression in colon cancer cell lines by G-quadruplex binding indolo[3,2-c]quinolines. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Funke, A.; Weisz, K. Thermodynamic signature of indoloquinolines interacting with G-quadruplexes: Impact of ligand side chain. Biochimie 2019, 157, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zhao, C.; Sun, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Metallo-supramolecular Complexes Enantioselectively Eradicate Cancer Stem Cells in Vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16201–16209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.J.; Turnidge, M.A.; Wai, D.H.; Patel, A.R.; Lee, D.W.; Gokhale, V.; Hurley, L.H.; Arceci, R.J.; Wetmore, C.; Azorsa, D.O. In vitro activity of a G-quadruplex-stabilizing small molecule that synergizes with Navitoclax to induce cytotoxicity in acute myeloid leukemia cells. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flusberg, D.A.; Rizvi, N.F.; Kutilek, V.; Andrews, C.; Saradjian, P.; Chamberlin, C.; Curran, P.; Swalm, B.; Kattar, S.; Smith, G.F.; et al. Identification of G-Quadruplex-Binding Inhibitors of Myc Expression through Affinity Selection–Mass Spectrometry. SLAS Discov. 2019, 24, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q.; Yang, C.; Xia, Y.; Guo, S.; Song, D.; Su, H. Preferential Binding of π-Ligand Porphyrin Targeting 5′-5′ Stacking Interface of Human Telomeric RNA G-Quadruplex Dimer. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 2143–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferino, A.; Nicoletto, G.; D’Este, F.; Zorzet, S.; Lago, S.; Richter, S.N.; Tikhomirov, A.; Shchekotikhin, A.; Xodo, L.E. Photodynamic Therapy for ras-Driven Cancers: Targeting G-Quadruplex RNA Structures with Bifunctional Alkyl-Modified Porphyrins. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 1245–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miglietta, G.; Cogoi, S.; Marinello, J.; Capranico, G.; Tikhomirov, A.S.; Shchekotikhin, A.; Xodo, L.E. RNA G-Quadruplexes in Kirsten Ras (KRAS) Oncogene as Targets for Small Molecules Inhibiting Translation. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 9448–9461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodoin, R.; Carrier, J.C.; Rivard, N.; Bisaillon, M.; Perreault, J.P. G-quadruplex located in the 5′UTR of the BAG-1 mRNA affects both its cap-dependent and cap-independent translation through global secondary structure maintenance. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10247–10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, J.; Santos, T.; Carrilho, R.; Sousa, F.; Salgado, G.F.; Queiroz, J.A.; Cruz, C. Ligand screening to pre-miRNA 149 G-quadruplex investigated by molecular dynamics. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 2276–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, K.; Largy, E.; Benzler, M.; Teulade-Fichou, M.P.; Hartig, J.S. Efficient Suppression of Gene Expression by Targeting 5′-UTR-Based RNA Quadruplexes with Bisquinolinium Compounds. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Harvey, S.E.; Cheng, C. A high-throughput screen identifies small molecule modulators of alternative splicing by targeting RNA G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3667–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, J.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wang, X.Q.; Lin, J.; Yao, P.F.; Huang, S.L.; Ou, T.M.; Tan, J.H.; Li, D.; Gu, L.Q.; et al. Discovery of small molecules for up-regulating the translation of antiamyloidogenic secretase, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 10 (ADAM10), by binding to the G-quadruplex-forming sequence in the 5′ untranslated region (UTR) of its mRNA. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3875–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, C.; Dacanay, J.G.; Gokhale, V.; Boddupally, P.V.L.; Behm-Ansmant, I.; Burley, G.A.; Branlant, C.; Hurley, L.H.; Dominguez, C.; Eperon, I.C. Specific G-quadruplex ligands modulate the alternative splicing of Bcl-X. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Yi, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, G. Hsa-miR-1587 G-quadruplex formation and dimerization induced by NH4+, molecular crowding environment and jatrorrhizine derivatives. Talanta 2018, 179, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirihana Arachchilage, G.; Kharel, P.; Reid, J.; Basu, S. Targeting of G-Quadruplex Harboring Pre-miRNA 92b by LNA Rescues PTEN Expression in NSCL Cancer Cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neckles, C.; Boer, R.E.; Aboreden, N.; Cross, A.M.; Walker, R.L.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, S.; Schneekloth, J.S.; Caplen, N.J. HNRNPH1-dependent splicing of a fusion oncogene reveals a targetable RNA G-quadruplex interaction. RNA 2019, 25, 1731–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Lu, H. Conjunction of potential G-quadruplex and adjacent cis-elements in the 5′ UTR of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-Alpha strongly inhibit protein expression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Kuang, G.T.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, S.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Tan, J.H.; Huang, Z.S.; Ou, T.M. Discovery of Small Molecules for Repressing Cap-Independent Translation of Human Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (hVEGF) as Novel Antitumor Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 5306–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Sun, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, S.Q.; Wang, S.K.; Wang, X.N.; Kuang, G.T.; Su, X.X.; Tan, J.H.; Huang, Z.S.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Novel p-(Methylthio)styryl Substituted Quindoline Derivatives as Neuroblastoma RAS (NRAS) Repressors via Specific Stabilizing the RNA G-Quadruplex. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 6629–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuda, Y.; Sato, S.I.; Asano, L.; Morimura, Y.; Furuta, T.; Sugiyama, H.; Hagihara, M.; Uesugi, M. A Small Molecule That Represses Translation of G-Quadruplex-Containing mRNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9037–9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugaut, A.; Rodriguez, R.; Kumari, S.; Hsu, S.T.D.; Balasubramanian, S. Small molecule-mediated inhibition of translation by targeting a native RNA G-quadruplex. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 2771–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Zhou, J.; Gu, J.; Xu, M.; Xu, X.; Yuan, G. Probing the G-quadruplex from hsa-miR-3620-5p and inhibition of its interaction with the target sequence. Talanta 2016, 154, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Ekka, M.K.; Tawani, A.; Kumar, A.; Chakraborty, D.; Maiti, S. Restoration of miRNA-149 Expression by TmPyP4 Induced Unfolding of Quadruplex within Its Precursor. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Tan, W.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Xu, M.; Yuan, G. Up- and downregulation of mature miR-1587 function by modulating its G-quadruplex structure and using small molecules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faudale, M.; Cogoi, S.; Xodo, L.E. Photoactivated cationic alkyl-substituted porphyrin binding to g4-RNA in the 5′-UTR of KRAS oncogene represses translation. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 874–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawauchi, K.; Sugimoto, W.; Yasui, T.; Murata, K.; Itoh, K.; Takagi, K.; Tsuruoka, T.; Akamatsu, K.; Tateishi-Karimata, H.; Sugimoto, N.; et al. An anionic phthalocyanine decreases NRAS expression by breaking down its RNA G-quadruplex. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, A.; Iaccarino, N.; Abdelhamid, M.A.S.; Brancaccio, D.; Garzarella, E.U.; Di Porzio, A.; Novellino, E.; Waller, Z.A.E.; Pagano, B.; Amato, J.; et al. Common G-quadruplex binding agents found to interact with i-motif-forming DNA: Unexpected multi-target-directed compounds. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Cao, J.; Kuang, G.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Kang, S.; Ou, T.M.; et al. Syntheses and evaluation of new acridone derivatives for selective binding of oncogene c-: Myc promoter i-motifs in gene transcriptional regulation. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2036–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathi, S.; Sappati, S.; Das, K.; Hazra, P. Structural characteristics requisite for the ligand-based selective detection of i-motif DNA. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 5392–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Ghosh, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Bhowmik, S. Preferential targeting cancer-related i-motif DNAs by the plant flavonol fisetin for theranostics applications. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fu, H.; Qian, C.; Li, H.; Chen, D.D.Y. Characterization of interaction between Bcl-2 oncogene promoter I-Motif DNA and flavonoids using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and pressure-assisted capillary electrophoresis frontal analysis. Talanta 2020, 215, 120885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendrick, S.; Kang, H.J.; Alam, M.P.; Madathil, M.M.; Agrawal, P.; Gokhale, V.; Yang, D.; Hecht, S.M.; Hurley, L.H. The dynamic character of the BCL2 promoter i-motif provides a mechanism for modulation of gene expression by compounds that bind selectively to the alternative DNA hairpin structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4161–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, P.; Panda, D.; Müller, D.; Maity, A.; Schwalbe, H.; Dash, J. In situ formation of transcriptional modulators using non-canonical DNA i-motifs. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sedghi Masoud, S.; Yamaoki, Y.; Ma, Y.; Marchand, A.; Winnerdy, F.R.; Gabelica, V.; Phan, A.T.; Katahira, M.; Nagasawa, K. Analysis of Interactions between Telomeric i-Motif DNA and a Cyclic Tetraoxazole Compound. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 2268–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, C.E.; Van Ert, N.A.; Agrawal, P.; Chawla, R.; Yang, D.; Hurley, L.H. Insight into the Complexity of the i-Motif and G-Quadruplex DNA Structures Formed in the KRAS Promoter and Subsequent Drug-Induced Gene Repression. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8522–8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Wang, Y.; Wei, C. Interactions of phenanthroline compounds with i-motif DNA. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2014, 30, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Carboxyl-modified single-walled carbon nanotubes selectively induce human telomeric i-motif formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19658–19663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fedoroff, O.Y.; Rangan, A.; Chemeris, V.V.; Hurley, L.H. Cationic porphyrins promote the formation of i-motif DNA and bind peripherally by a nonintercalative mechanism. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 15083–15090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benabou, S.; Aviñó, A.; Lyonnais, S.; González, C.; Eritja, R.; De Juan, A.; Gargallo, R. i-motif structures in long cytosine-rich sequences found upstream of the promoter region of the SMARCA4 gene. Biochimie 2017, 140, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wright, E.P.; Day, H.A.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Kumar, J.; Boswell, L.J.E.; Huguin, C.; Stevenson, C.E.M.; Pors, K.; Waller, Z.A.E. Mitoxantrone and analogues bind and stabilize i-motif forming DNA sequences. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Qu, K.; Zhao, C.; Wu, L.; Ren, J.; Wang, J.; Qu, X. Insights into the biomedical effects of carboxylated single-wall carbon nanotubes on telomerase and telomeres. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
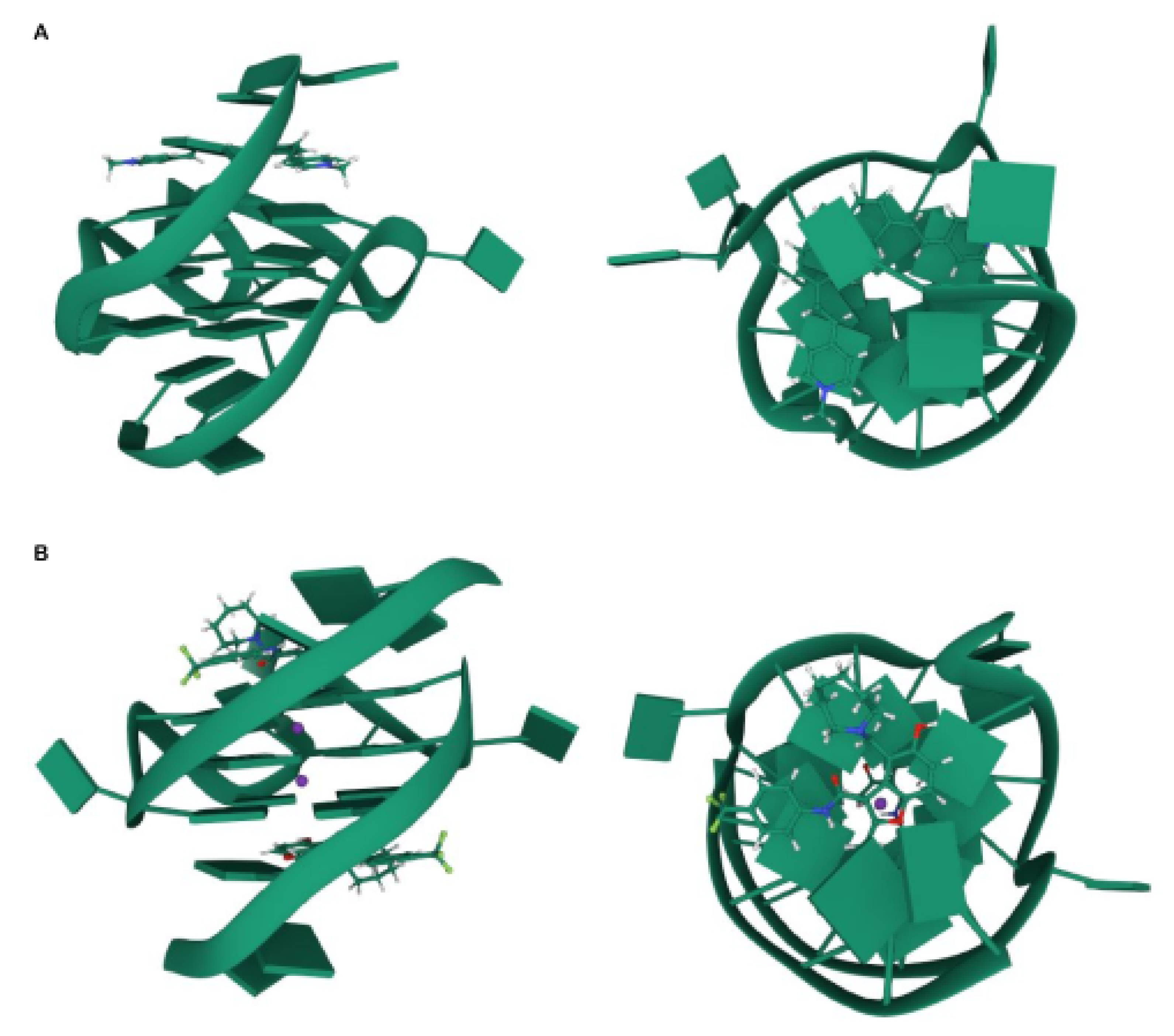



| Ligand | Target | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Adriamycin * | Tel [40] | Telomere dysfunction |
| APTO-253 * | c-KIT [41]; c-MYC [41]; Tel [41] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| Benzo[a]phenoxazines | c-KIT [42]; Tel [43] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| Benzofuran | c-MYC [44] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Berberine * | c-KIT [45]; k-RAS [46]; Tel [47] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| BRACO-19 * | Tel [48] | Telomere dysfunction |
| BTC-f | Tel [49] | Telomere dysfunction |
| BZT-Indolium | c-MYC [50] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Carbazole TO | BCL2 [51] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Cepharanthine | STAT3 [52] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| cIKP-PIP | c-MYC [53] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Co- and Pd-porphyrins * | k-RAS [54] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| CX-3543 * | Pan-binder [55] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| CX-5461 * | Pan-binder [55] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| C-3 | c-MYC [56] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| C8 | k-RAS [57] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| C-19 | k-RAS [58] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Diquinolinyl-pyridines | c-KIT [59]; c-MYC [60] Tel [59] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| Disubstituted amidoanthraquinones | Tel [61] | Telomere dysfunction |
| DIZ-3 | Tel [62] | Telomere dysfunction |
| DTE | Tel [63] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Epirubicin * | Tel [64] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Furopyridazinones | BCL2 [65] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| GQC-05 | c-MYC [66] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| GSA1129 | PDGFRb [67] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| dGTC365 | hTERT [68] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Indoloquinolines * | c-KIT [69]; c-MYC [70]; k-RAS [69]; Tel [69]; VEGF [71] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| Isoalloxazines | c-KIT [72] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| IZCZ-3 * | c-MYC [73] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| IZNP-1 | Tel [74] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Liensinine * | FGFR2 [75] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Mitoxantrone * | Tel [76]; WT1 [77] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| m-TMPipEOPP | Tel [78] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Naphthalene diimides * | BCL2 [79]; c-KIT [80]; MDM2 [81]; Ribosomal DNA [82]; Tel [83] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| Ni-M | Tel [84] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Ni-P | Tel [85] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Nitidine * | k-RAS [73] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Oxazole telomestatins | Tel [86,87] | Telomere dysfunction |
| PBP2 | BCL2 [88] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Phenanthrolines | c-KIT [89]; c-MYC [89]; Tel [90] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| Phen-DC3 | c-MYC [91]; Tel [92] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| PM2 | VEGF [93] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Porphyrin- photosensitizer | k-RAS [94] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Prolinamide- peptidomimetic | BCL2 [95]; c-MYC [95] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Pyridostatin * | Pan-binder [19] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| QN-1 | c-MYC [96] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Quercetin * | Tel [97] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Quinazolines | c-KIT [98]; c-MYC [99]; RET [100] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| RHPS4 * | Tel [101] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Ru-Schiff | Tel [102] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Se2SAP | VEGF [103] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Schizocommunins * | Tel [104] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Stiff-stilbenes | Tel [105] | Telomere dysfunction |
| S4-5 | c-MYC [106]; Tel [106] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| Telomestatin * | c-MYB [107]; Tel [108] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| TH3 | c-MYC [109] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| TMPyP4 * | BCL2 [110]; c-MYC [111]; k-RAS [112]; PDGFa [113]; Tel [114]; VEGF [115] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| Topotecan * | c-MYB [116] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Tz1 | c-MYC [117] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| VEGFq oligo | VEGF [118] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| (Zn)TCPPSpm4 | Tel [119] | Telomere dysfunction |
| 20A * | c-KIT [120], k-RAS [120], Tel [120] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
| 4,5-diazafluorenes | Tel [121] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Λ-Ru | Tel [122] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Ligand | Target | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Alkyl porphyrins * | k-RAS [147]; n-RAS [147] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| Anthrafurandione | k-RAS [148] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| Bisquinoliniums | BAG1 [149]; pre-miRNA149 [150]; TRF2 [151] | Inhibition of oncogene translation and alteration of miRNA biogenesis |
| Carboxypyridostatin | BAG1 [149] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| Cephaeline | Pan-binder [152] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| C-12459 | hTERT [31] | Telomere dysfunction |
| C-14 | ADAM10 [153] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| Emetine * | Pan-binder [152] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| GQC-05 | BCLX [154] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| Jatrorrhizines | miRNA-1587 [155] | Alteration of miRNA targeting |
| LNA | pre-miRNA-92b [156] | Alteration of miRNA biogenesis |
| Pyridostatin * | EWSR1 [157]; HNF4a [158] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| Quinazolines * | VEGF [159] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| Quindolines | n-RAS [160] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| RGB-1 | n-RAS [161] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| RR82 and RR110 | n-RAS [162] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| Sanguinarine * | miRNA-3620-5p [163] | Alteration of miRNA targeting |
| TMPyP4 * | miRNA-149 [164]; miRNA-1587 [165]; TERRA [146] | Alteration of miRNA targeting and telomere dysfunction |
| TMPyP4-C14 | k-RAS [166] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| ZnAPC | n-RAS [167] | Inhibition of oncogene translation |
| Ligand | Target | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Berberine * | Tel [168] | Telomere dysfunction |
| BRACO-19 * | Tel [168] | Telomere dysfunction |
| B19 | c-MYC [169] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| C343 | Pan-binder [170] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Fisetin | VEGF [171] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Flavonoids | BCL2 [172] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| IMC-48 * | BCL2 [173] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| iM nanoparticles | BCL2 [174]; c-MYC [174] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| L2H2-4OTD | Tel [175] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Mitoxantrone * | Tel [168] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Nitidine * | k-RAS [176] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| NSC309874 | PDGFRb [67] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| PBP1 | BCL2 [88] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription |
| Phenanthrolines | Tel [177] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Phen-DC3 | Tel [168] | Telomere dysfunction |
| Pyridostatin * | Tel [168] | Telomere dysfunction |
| RHPS4 * | Tel [168] | Telomere dysfunction |
| SWNTs * | Tel [178] | Telomere dysfunction |
| TMPyP4 * | Tel [179]; SMARCA4 [180] | Inhibition of oncogene transcription and telomere dysfunction |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez-Martin, V.; Soriano, M.; Garcia-Salcedo, J.A. Quadruplex Ligands in Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133156
Sanchez-Martin V, Soriano M, Garcia-Salcedo JA. Quadruplex Ligands in Cancer Therapy. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133156
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez-Martin, Victoria, Miguel Soriano, and Jose Antonio Garcia-Salcedo. 2021. "Quadruplex Ligands in Cancer Therapy" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133156
APA StyleSanchez-Martin, V., Soriano, M., & Garcia-Salcedo, J. A. (2021). Quadruplex Ligands in Cancer Therapy. Cancers, 13(13), 3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133156






