The Role of the Immune Metabolic Prognostic Index in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) in Radiological Progression during Treatment with Nivolumab
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
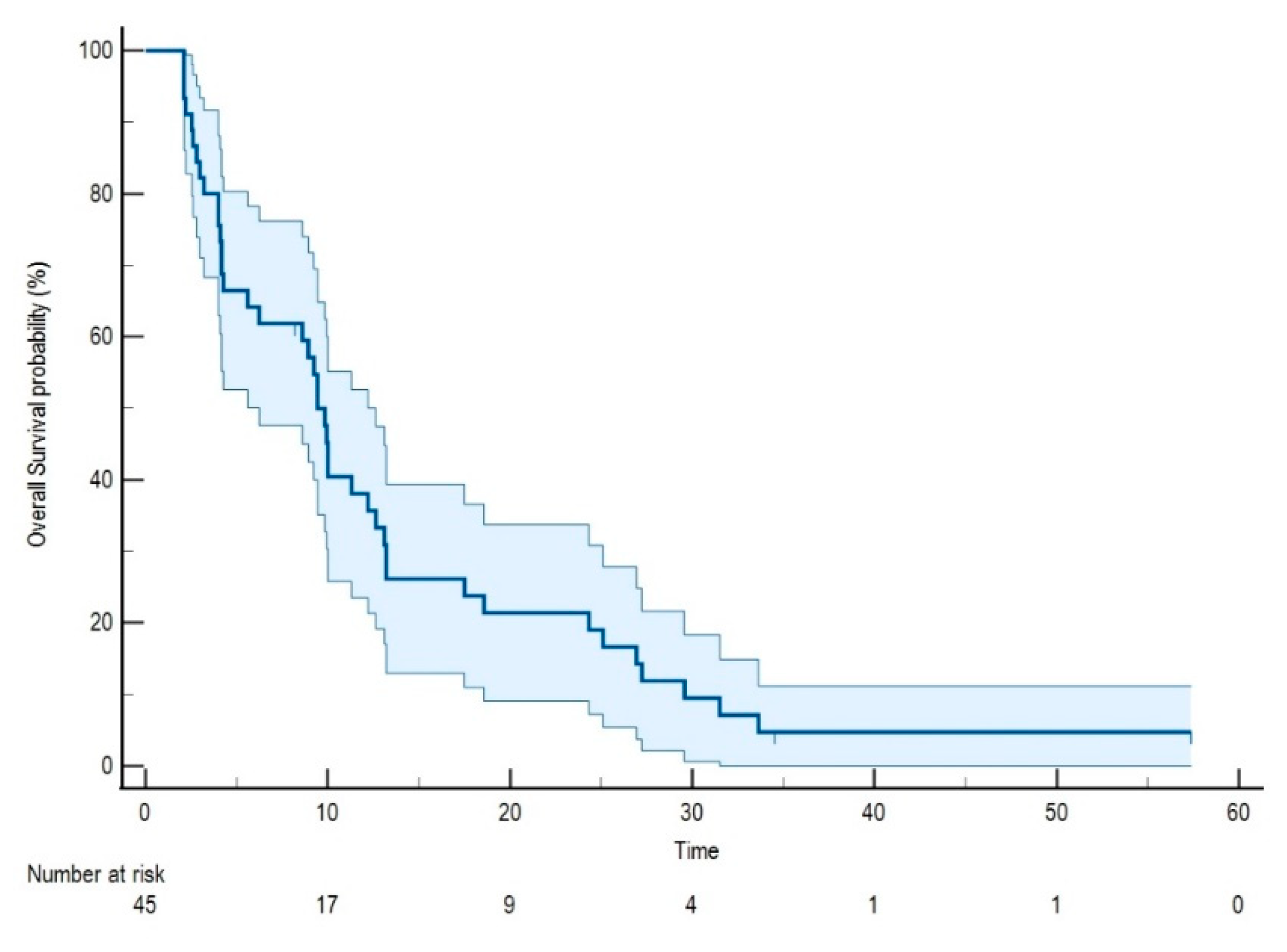
2.1. Patients’ and Treatment Characteristics
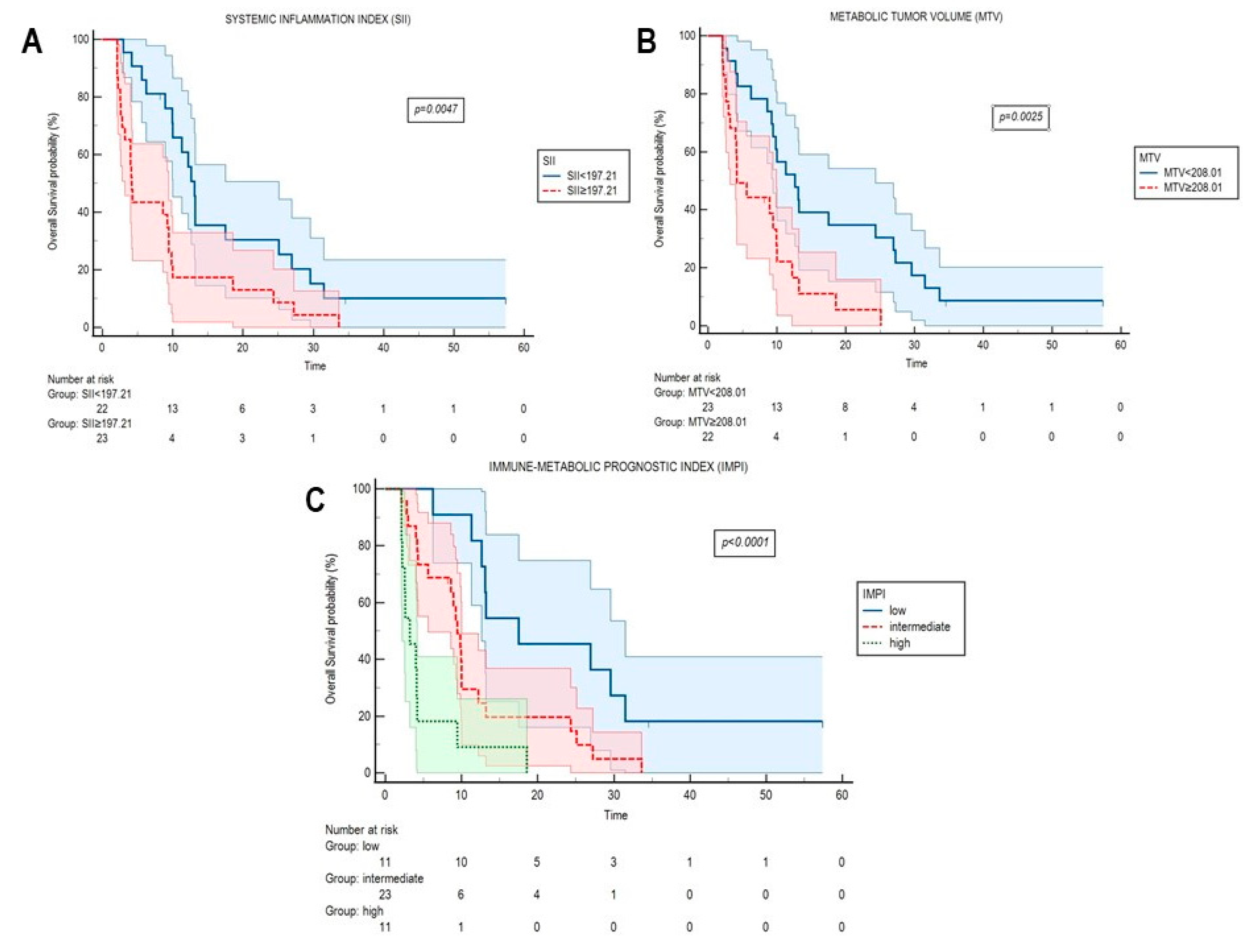
2.2. Systemic Inflammation Indexes and FDG-Derived Parameters at Radiological Progression
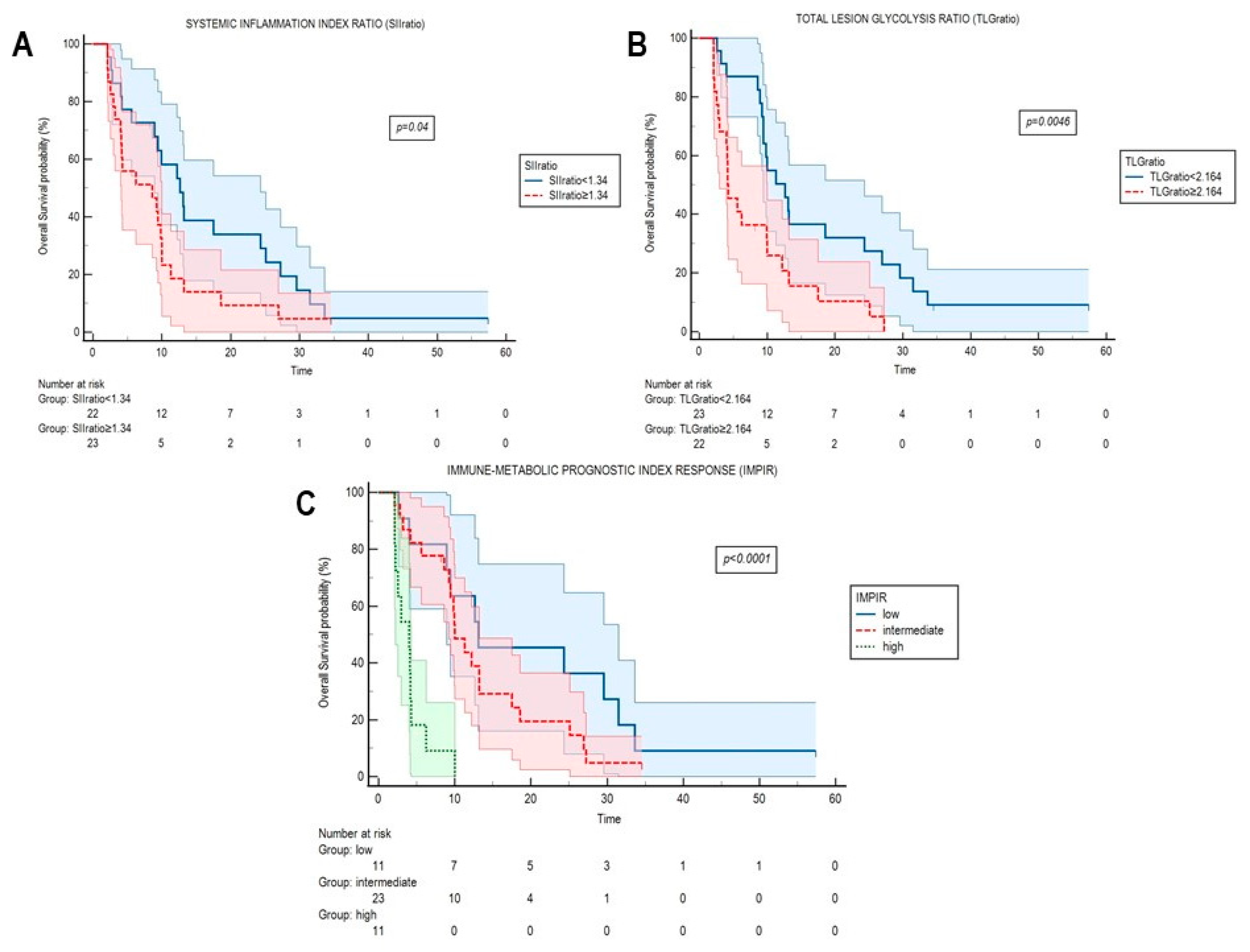
2.3. Systemic Inflammation Indexes and FDG-Derived Parameters in the Evaluation of Response
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Study Design
4.3. Systemic Inflammation Indexes
4.4. Images Acquisition and Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N. Eng. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Eng. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, F.; Genova, C.; Crinò, L.; Delmonte, A.; Turci, D.; Signorelli, D.; Passaro, A.; Soto Parra, H.; Catino, A.; Landi, L.; et al. Real-life results from the overall population and key subgroups within the Italian cohort of nivolumab expanded access program in non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 123, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crinò, L.; Bidoli, P.; Delmonte, A.; Grossi, F.; De Marinis, F.; Ardizzoni, A.; Vitiello, F.; Lo Russo, G.; Parra, H.S.; Cortesi, E.; et al. Italian Cohort of Nivolumab Expanded Access Program in Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results from a Real-World Population. Oncologist 2019, 24, e1165–e1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humbert, O.; Cadour, N.; Paquet, M.; Schiappa, R.; Poudenx, M.; Chardin, D.; Borchiellini, D.; Benisvy, D.; Ouvrier, M.J.; Zwarthoed, C.; et al. 18FDG PET/CT in the early assessment of non-small cell lung cancer response to immunotherapy: Frequency and clinical significance of atypical evolutive patterns. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, D.; Yoshioka, H.; Kataoka, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Hata, T.; Kim, Y.H.; Tomii, K.; Ishida, T.; Hirabayashi, M.; Hara, S.; et al. Pseudoprogression in Previously Treated Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Who Received Nivolumab Monotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazandjian, D.; Keegan, P.; Suzman, D.L.; Pazdur, R.; Blumenthal, G.M. Characterization of outcomes in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer treated with programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitors past RECIST version 1.1-defined disease progression in clinical trials. Semin. Oncol. 2017, 44, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S.I.; Hammer, M.; Bagley, S.J.; Aggarwal, C.; Bauml, J.M.; Thompson, J.C.; Nachiappan, A.C.; Simone, C.B.; Langer, C.J. Radiologic Pseudoprogression during Anti-PD-1 Therapy for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricciuti, B.; Genova, C.; Bassanelli, M.; De Giglio, A.; Brambilla, M.; Metro, G.; Baglivo, S.; Dal Bello, M.G.; Ceribelli, A.; Grossi, F.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Nivolumab in Patients With Advanced Non-small-cell Lung Cancer Treated Beyond Progression. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, 178–185.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, R.; Caramella, C.; Besse, B.; Champiat, S. Pseudoprogression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer upon Immunotherapy: Few Drops in the Ocean? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahl, R.L.; Jacene, H.; Kasamon, Y.; Lodge, M.A. From RECIST to PERCIST: Evolving Considerations for PET response criteria in solid tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 122S–150S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seymour, L.; Bogaerts, J.; Perrone, A.; Ford, R.; Schwartz, L.H.; Mandrekar, S.; Lin, N.U.; Litière, S.; Dancey, J.; Chen, A.; et al. iRECIST: Guidelines for response criteria for use in trials testing immunotherapeutics. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e143–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, B.W.; Bhosale, P.R.; Yang, W.T. Immunotherapy and the role of imaging. Cancer 2018, 124, 2906–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramanathan, A.; Saxena, A.; Morris, D.L. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the impact of pre-operative neutrophil lymphocyte ratio on long term outcomes after curative intent resection of solid tumours. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 23, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanizaki, J.; Haratani, K.; Hayashi, H.; Chiba, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Yonesaka, K.; Kudo, K.; Kaneda, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Peripheral Blood Biomarkers Associated with Clinical Outcome in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Nivolumab. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takenaka, Y.; Oya, R.; Kitamiura, T.; Ashida, N.; Shimizu, K.; Takemura, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Uno, A. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in head and neck cancer: A meta-analysis. Head Neck 2018, 40, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morbelli, S.; Alama, A.; Ferrarazzo, G.; Coco, S.; Genova, C.; Rijavec, E.; Bongioanni, F.; Biello, F.; Dal Bello, M.G.; Barletta, G.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Reflects Tumor Metabolism Rather Than Tumor Burden in Chemotherapy-Naive Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: 18F-FDG PET/CT Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1764–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alama, A.; Coco, S.; Genova, C.; Rossi, G.; Fontana, V.; Tagliamento, M.; Dal Bello, G.M.; Rosa, A.; Boccardo, S.; Rijavec, E.; et al. Prognostic Relevance of Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Cell-Free DNA Association in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Nivolumab. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ottonello, S.; Genova, C.; Cossu, I.; Fontana, V.; Rijavec, E.; Rossi, G.; Biello, F.; Dal Bello, M.G.; Tagliamento, M.; Alama, A.; et al. Association Between Response to Nivolumab Treatment and Peripheral Blood Lymphocyte Subsets in Patients With Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sacdalan, D.B.; Lucero, J.A.; Sacdalan, D.L. Prognostic utility of baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: A review and meta-analysis. Onco Target Ther. 2018, 11, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prelaj, A.; Rebuzzi, S.E.; Pizzutilo, P.; Bilancia, M.; Montrone, M.; Pesola, F.; Longo, V.; Del Bene, G.; Lapadula, V.; Cassano, F.; et al. EPSILoN: A Prognostic Score Using Clinical and Blood Biomarkers in Advanced Non-Small-cell Lung Cancer Treated with Immunotherapy. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 365–377.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castello, A.; Toschi, L.; Rossi, S.; Mazziotti, E.; Lopci, E. The immune-metabolic-prognostic index and clinical outcomes in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma under checkpoint inhibitors. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauckneht, M.; Piva, R.; Sambuceti, G.; Grossi, F.; Morbelli, S. Evaluation of response to immune checkpoint inhibitors: Is there a role for positron emission tomography? World J. Radiol. 2017, 9, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donegani, M.I.; Ferrarazzo, G.; Marra, S.; Miceli, A.; Raffa, S.; Bauckneht, M.; Morbelli, S. Positron Emission Tomography-Based Response to Target and Immunotherapies in Oncology. Medicina 2020, 56, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopci, E.; Toschi, L.; Grizzi, F.; Rahal, D.; Olivari, L.; Castino, G.F.; Marchetti, S.; Cortese, N.; Qehajaj, D.; Pistillo, D.; et al. Correlation of metabolic information on FDG-PET with tissue expression of immune markers in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who are candidates for upfront surgery. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aide, N.; Hicks, R.J.; Le Tourneau, C.; Lheureux, S.; Fanti, S.; Lopci, E. FDG PET/CT for assessing tumour response to immunotherapy: Report on the EANM symposium on immune modulation and recent review of the literature. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Hoos, A.; O’Day, S.; Weber, J.S.; Hamid, O.; Lebbé, C.; Maio, M.; Binder, M.; Bohnsack, O.; Nichol, G.; et al. Guidelines for the evaluation of immune therapy activity in solid tumors: Immune-related response criteria. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 7412–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, G.; Bauckneht, M.; Genova, C.; Rijavec, E.; Biello, F.; Mennella, S.; Dal Bello, M.G.; Cittadini, G.; Bruzzi, P.; Piva, R.; et al. Comparison Between 18F-FDG PET-Based and CT-Based Criteria in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Nivolumab. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaira, K.; Higuchi, T.; Naruse, I.; Arisaka, Y.; Tokue, A.; Altan, B.; Suda, S.; Mogi, A.; Shimizu, K.; Sunaga, N.; et al. Metabolic activity by 18F-FDG-PET/CT is predictive of early response after nivolumab in previously treated NSCLC. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, L.; Gemelli, M.; Gotuzzo, I.; Bauckneht, M.; Crivellaro, C.; Genova, C.; Cortinovis, D.; Zullo, L.; Ammoni, L.C.; Bernasconi, D.P.; et al. Metabolic Parameters as Biomarkers of Response to Immunotherapy and Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Real World Experience. Cancers 2021, 13, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachpekidis, C.; Anwar, H.; Winkler, J.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Larribere, L.; Haberkorn, U.; Hassel, J.C.; Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss, A. The role of interim 18F-FDG PET/CT in prediction of response to ipilimumab treatment in metastatic melanoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachpekidis, C.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Hakim-Meibodi, L.; Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss, A.; Hassel, J.C. 18F-FDG PET/CT longitudinal studies in patients with advanced metastatic melanoma for response evaluation of combination treatment with vemurafenib and ipilimumab. Mel. Res. 2019, 29, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Teng, R.; Schöder, H.; Humm, J.L.; Ni, A.; Michaud, L.; Nakajima, R.; Yamashita, R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Weber, W.A. 18F-FDG PET/CT for Monitoring of Ipilimumab Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.Y.; Lipson, E.J.; Im, H.J.; Rowe, S.P.; Gonzalez, E.M.; Blackford, A.; Chirindel, A.; Pardoll, D.M.; Topalian, S.L.; Wahl, R.L. Prediction of Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy Using Early-Time-Point 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guthrie, G.J.; Charles, K.A.; Roxburgh, C.S.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C.; Clarke, S.J. The systemic inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: Experience in patients with cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hemat. 2013, 88, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.J.; McNamara, M.G.; Šeruga, B.; Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Aneja, P.; Ocaña, A.; Leibowitz-Amit, R.; Sonpavde, G.; Knox, J.J.; Tran, B.; et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nat. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.J.; Wang, L.X.; Hong, Y.Q.; Lu, Z.H.; Tong, Q.; Fang, X.Z.; Tan, J. Lymphocyte to monocyte ratio is associated with response to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy and prognosis of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer patients. Tum. Biol. 2016, 37, 5285–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Lai, C.H.; Chang, H.C.; Chao, T.Y.; Tseng, C.C.; Fang, W.F.; Wang, C.C.; Chung, Y.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Su, M.C.; et al. Baseline and Trend of Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio as Prognostic Factors in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with First-Line Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Hong, L.; Sun, L.; Zhuang, H.; Sun, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X. Platelet-lymphocyte ratio is an independent prognostic factor in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Fut. Oncol. 2017, 13, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagley, S.J.; Kothari, S.; Aggarwal, C.; Bauml, J.M.; Alley, E.W.; Evans, T.L.; Kosteva, J.A.; Ciunci, C.A.; Gabriel, P.E.; Thompson, J.C.; et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a marker of outcomes in nivolumab-treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 106, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zer, A.; Sung, M.R.; Walia, P.; Khoja, L.; Maganti, M.; Labbe, C.; Shepherd, F.A.; Bradbury, P.A.; Feld, R.; Liu, G.; et al. Correlation of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Absolute Neutrophil Count With Outcomes With PD-1 Axis Inhibitors in Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung. Cancer 2018, 19, 426–434.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horne, Z.D.; Jack, R.; Gray, Z.T.; Siegfried, J.M.; Wilson, D.O.; Yousem, S.A.; Nason, K.S.; Landreneau, R.J.; Luketich, J.D.; Schuchert, M.J. Increased levels of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are associated with improved recurrence-free survival in stage 1A non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 171, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiriu, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagano, T.; Hazama, D.; Sekiya, R.; Katsurada, M.; Katsurada, N.; Tachihara, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishimura, Y. Pseudo-Progression and the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Case-Control Study. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 10559–10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.H.; Zhai, E.T.; Yuan, Y.J.; Wu, K.M.; Xu, J.B.; Peng, J.J.; Chen, C.Q.; He, Y.L.; Cai, S.R. Systemic immune-inflammation index for predicting prognosis of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6261–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Zheng, J.; Cai, J.; Zeng, K.; Yao, J.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) is Useful to Predict Survival Outcomes in Patients After Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Hangzhou Criteria. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Cheng, Y. A novel systemic immune-inflammation index predicts survival and quality of life of patients after curative resection for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.M.; Qiu, S.J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhu, J.; Xin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Cheng, Y. Systemic immune-inflammation index, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio can predict clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezquita, L.; Auclin, E.; Ferrara, R.; Charrier, M.; Remon, J.; Planchard, D.; Ponce, S.; Ares, L.P.; Leroy, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; et al. Association of the Lung Immune Prognostic Index With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Outcomes in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Oh, D.Y.; Park, H.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Han, S.W.; Im, S.A.; Kim, T.Y.; Bang, Y.J. More Accurate Prediction of Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients’ Survival with Prognostic Model Using Both Host Immunity and Tumor Metabolic Activity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyürek, B.A.; Özmen, Ö.; Özdemirel, T.Ş.; Erdoğan, Y.; Kaplan, B.; Kaplan, T. Relation between neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and primary tumor metabolic activity in patients with malign pleural mesothelioma. Clin. Resp. J. 2018, 12, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSorley, S.T.; Khor, B.Y.; Tsang, K.; Colville, D.; Han, S.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C. The relationship between 18 F-FDG-PETCT-derived markers of tumour metabolism and systemic inflammation in patients with recurrent disease following surgery for colorectal cancer. Col. Dis. 2018, 20, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujii, T.; Yanai, K.; Tokuda, S.; Nakazawa, Y.; Kurozumi, S.; Obayashi, S.; Yajima, R.; Hirakata, T.; Shirabe, K. Relationship Between FDG Uptake and Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer. Anticanc. Res. 2018, 38, 4927–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirili, C.; Guney, I.B.; Paydas, S.; Seydaoglu, G.; Kapukaya, T.K.; Ogul, A.; Gokcay, S.; Buyuksimsek, M.; Yetisir, A.E.; Karaalioglu, B.; et al. Prognostic significance of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and correlation with PET-CT metabolic parameters in small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 24, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.; Yoh, T.; Morino, K.; Fuji, H.; Taura, K.; Fukumitsu, K.; Ishii, T.; Nakamoto, Y.; Kaido, T.; Uemoto, S. The Relationship Between 18F-FDG Uptake on PET/CT and Markers of Systemic Inflammatory Response in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Anticanc. Res. 2019, 39, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Jin, F.; Jing, W.; Li, M.; Chen, D.; Zou, B.; Jiang, G.; Fu, L.; Zhu, H.; Kong, L.; et al. Incorporation of the SUVmax Measured From FDG PET and Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio Improves Prediction of Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Locally Advanced Non-small-cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Di Costanzo, G.G.; Tortora, R.; Pelle, G.; Saltarelli, A.; Marino Marsilia, G.; Cianni, R.; Schillaci, O.; Bagni, O. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and its correlation with fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose metabolic parameters in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma submitted to 90Y-radioembolization. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2020, 41, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Tokuda, S.; Nakazawa, Y.; Kurozumi, S.; Obayashi, S.; Yajima, R.; Shirabe, K. Relationship Between FDG Uptake and the Platelet/lymphocyte Ratio in Patients With Breast Invasive Ductal Cancer. In Vivo 2020, 34, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauckneht, M.; Rebuzzi, S.E.; Signori, A.; Donegani, M.I.; Murianni, V.; Miceli, A.; Borea, R.; Raffa, S.; Damassi, A.; Ponzano, M.; et al. The Prognostic Role of Baseline Metabolic Tumor Burden and Systemic Inflammation Biomarkers in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Patients Treated with Radium-223: A Proof of Concept Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seban, R.D.; Mezquita, L.; Berenbaum, A.; Dercle, L.; Botticella, A.; Le Pechoux, C.; Caramella, C.; Deutsch, E.; Grimaldi, S.; Adam, J.; et al. Baseline metabolic tumor burden on FDG PET/CT scans predicts outcome in advanced NSCLC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seban, R.D.; Assié, J.B.; Giroux-Leprieur, E.; Massiani, M.A.; Soussan, M.; Bonardel, G.; Chouaid, C.; Playe, M.; Goldfarb, L.; Duchemann, B.; et al. Association of the Metabolic Score Using Baseline FDG-PET/CT and dNLR with Immunotherapy Outcomes in Advanced NSCLC Patients Treated with First-Line Pembrolizumab. Cancers 2020, 12, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzi, F.; Castello, A.; Lopci, E. Is it time to change our vision of tumor metabolism prior to immunotherapy? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castello, A.; Rossi, S.; Toschi, L.; Lopci, E. Comparison of Metabolic and Morphological Response Criteria for Early Prediction of Response and Survival in NSCLC Patients Treated With Anti-PD-1/PD-L. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castello, A.; Rossi, S.; Mazziotti, E.; Toschi, L.; Lopci, E. Hyperprogressive Disease in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Checkpoint Inhibitors: The Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamatsu, H.; Mori, K.; Naito, T.; Imai, H.; Ono, A.; Shukuya, T.; Taira, T.; Kenmotsu, H.; Murakami, H.; Endo, M.; et al. Progression-free survival at 2 years is a reliable surrogate marker for the 5-year survival rate in patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, A.; Franchina, T.; Ricciardi, G.; Battaglia, A.; Scimone, A.; Berenato, R.; Giordano, A.; Adamo, V. Baseline neutrophilia, derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (dNLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and outcome in non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with Nivolumab or Docetaxel. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6337–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katayama, Y.; Yamada, T.; Chihara, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Tanimura, K.; Okura, N.; Hirose, K.; Uda, S.; Shiotsu, S.; Hirai, S.; et al. Significance of inflammatory indexes in atezolizumab monotherapy outcomes in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, T.; Kang, K.H.; Gawdi, R.; Bajor, D.; Machtay, M.; Jindal, C.; Efird, J.T. Using the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) as a Mid-Treatment Marker for Survival among Patients with Stage-III Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boellaard, R.; Delgado-Bolton, R.; Oyen, W.J.; Giammarile, F.; Tatsch, K.; Eschner, W.; Verzijlbergen, F.J.; Barrington, S.F.; Pike, L.C.; Weber, W.A.; et al. European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). FDG PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging: Version 2. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 328–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, V.; Mees, G.; Maes, A.; D’Asseler, Y.; Borms, M.; Cocquyt, V.; Van De Wiele, C. Reproducibility of FDG PET based metabolic tumor volume measurements and of their FDG distribution within. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 59, 462–468. [Google Scholar]
| Age | 70.6 (Range 50.3–81.5) | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 16/45 (35.5%) |
| Male | 29/45 (64.5%) | |
| ECOG PS | 0 | 18/45 (40%) |
| 1 | 25/45 (55.5%) | |
| 2 | 2/45 (4.5%) | |
| Steroid use | Yes No Unknown | 13/45 (29%) 21/45 (47%) 11/45 (24%) |
| Presence of brain metastases | Yes No | 5/45 (11%) 40/45 (89%) |
| Smoking status | Never smoker | 5/45 (11%) |
| Former smoker | 29/45 (65%) | |
| Smoker | 11/45 (24%) | |
| Histology | Squamous | 11/45 (24%) |
| Non-squamous | 34/45 (76%) | |
| Prior surgery | Yes | 17/45 (38%) |
| No | 28/45 (62%) | |
| Prior lines of therapy | 1 | 18/45 (40%) |
| 2 | 16/45 (36%) | |
| ≥3 | 11/45 (24%) | |
| Number administered cycles of ICI before PD | 6.6 (range 4–33) |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Clinical characteristics | ||||
| ECOG Performance Status | 0.149 | |||
| 0–1 | 1.00 (ref) | - | ||
| 2 | 1.858 (0.80–4.31) | - | ||
| Presence of brain metastases | 0.823 | |||
| No | 1.00 (ref) | - | ||
| Yes | 1.104 (0.46–2.63) | - | ||
| Steroids use | 0.484 | |||
| No | 1.00 (ref) | - | ||
| Yes | 1.335 (0.59–2.99) | - | ||
| Inflammatory biomarkers | ||||
| NLR (1-unit) | 1.089 (1.02–1.16) | 0.013 | ||
| d-NLR (1-unit) | 1.206 (1.04–1.39) | 0.013 | ||
| LMR (1-unit) | 1.031 (0.89–1.19) | 0.684 | ||
| PLR (100-unit) | 1.000 (0.99–1.002) | 0.771 | ||
| SII (100-unit) | 1.002 (1.001–1.004) | <0.0001 | 1.002 (1.001–1.002) | <0.0001 |
| FDG-PET parameters | ||||
| SUVmax (1-unit) | 1.032 (0.98–1.07) | 0.161 | ||
| MTV (1-unit) | 1.001 (1.001–1.002) | <0.0001 | 1.001 (1.001–1.002) | <0.0001 |
| TLG (1-unit) | 1.001 (1.001–1.002) | <0.0001 | ||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| CT-based response criteria | ||||
| irRC classes | 0.005 | 0.027 | ||
| PR | 1.00 (ref) | - | 1.00 (ref) | - |
| SD | 4.826 (0.55–42.01) | - | 3.746 (0.42–33.04) | - |
| PD (uPD + cPD) | 10.573 (1.28–87.22) | - | 7.742 (0.91–65.49) | - |
| iRECIST classes | 0.024 | |||
| iPR | 1.00 (ref) | - | ||
| iSD | 5.088 (0.31–86.38) | - | ||
| iPD (iuPD + icPD) | 7.887 (1.03–60.55) | - | ||
| Inflammatory biomarkers | ||||
| NLRratio | 1.080 (0.96–1.20) | 0.164 | ||
| dNLRratio | 1.083 (0.97–1.21) | 0.140 | ||
| LMRratio | 1.057 (0.97–1.14) | 0.164 | ||
| PLRratio | 0.873 (0.48–1.56) | 0.648 | ||
| SIIratio | 1.186 (1.03–1.36) | 0.019 | 1.162 (0.98–1.37) | 0.041 |
| FDG-PET parameters | ||||
| PERCIST classes | 0.352 | |||
| PMR | 1.00 (ref) | - | ||
| SMD | 2.232 (0.52–9.46) | - | ||
| PMD | 1.482 (0.31–7.01) | - | ||
| SUVmax-ratio | 3.285 (1.25–8.62) | 0.016 | ||
| MTVratio | 1.217 (1.08–1.36) | <0.001 | ||
| TLGratio | 1.209 (1.21–1.34) | <0.001 | 1.171 (1.04–1.31) | 0.007 |
| Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| IMPI | 0.0004 | |
| Low risk | 1.00 (ref) | - |
| Intermediate risk | 2.271 (0.99–5.19) | - |
| High risk | 7.036 (2.55–19.40) | - |
| IMPIR | 0.003 | |
| Low risk | 1.00 (ref) | - |
| Intermediate risk | 1.204 (0.52–2.78) | - |
| High risk | 6.259 (2.16–18.14) | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bauckneht, M.; Genova, C.; Rossi, G.; Rijavec, E.; Dal Bello, M.G.; Ferrarazzo, G.; Tagliamento, M.; Donegani, M.I.; Biello, F.; Chiola, S.; et al. The Role of the Immune Metabolic Prognostic Index in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) in Radiological Progression during Treatment with Nivolumab. Cancers 2021, 13, 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133117
Bauckneht M, Genova C, Rossi G, Rijavec E, Dal Bello MG, Ferrarazzo G, Tagliamento M, Donegani MI, Biello F, Chiola S, et al. The Role of the Immune Metabolic Prognostic Index in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) in Radiological Progression during Treatment with Nivolumab. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133117
Chicago/Turabian StyleBauckneht, Matteo, Carlo Genova, Giovanni Rossi, Erika Rijavec, Maria Giovanna Dal Bello, Giulia Ferrarazzo, Marco Tagliamento, Maria Isabella Donegani, Federica Biello, Silvia Chiola, and et al. 2021. "The Role of the Immune Metabolic Prognostic Index in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) in Radiological Progression during Treatment with Nivolumab" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133117
APA StyleBauckneht, M., Genova, C., Rossi, G., Rijavec, E., Dal Bello, M. G., Ferrarazzo, G., Tagliamento, M., Donegani, M. I., Biello, F., Chiola, S., Zullo, L., Raffa, S., Lanfranchi, F., Cittadini, G., Marini, C., Lopci, E., Sambuceti, G., Grossi, F., & Morbelli, S. (2021). The Role of the Immune Metabolic Prognostic Index in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) in Radiological Progression during Treatment with Nivolumab. Cancers, 13(13), 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133117













