Cell-Free Total Nucleic Acid-Based Genotyping of Aggressive Lymphoma: Comprehensive Analysis of Gene Fusions and Nucleotide Variants by Next-Generation Sequencing
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
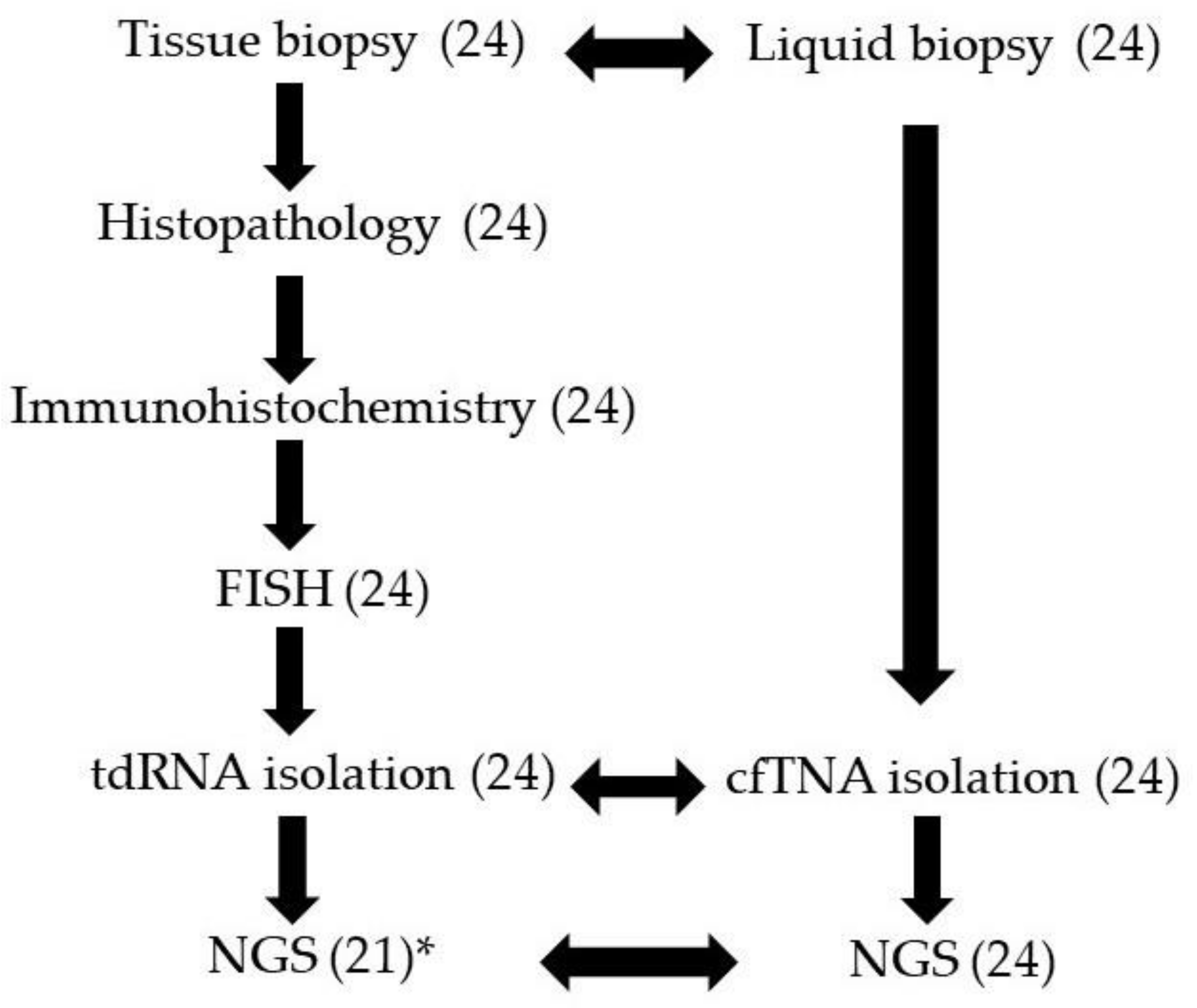
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cases and Samples
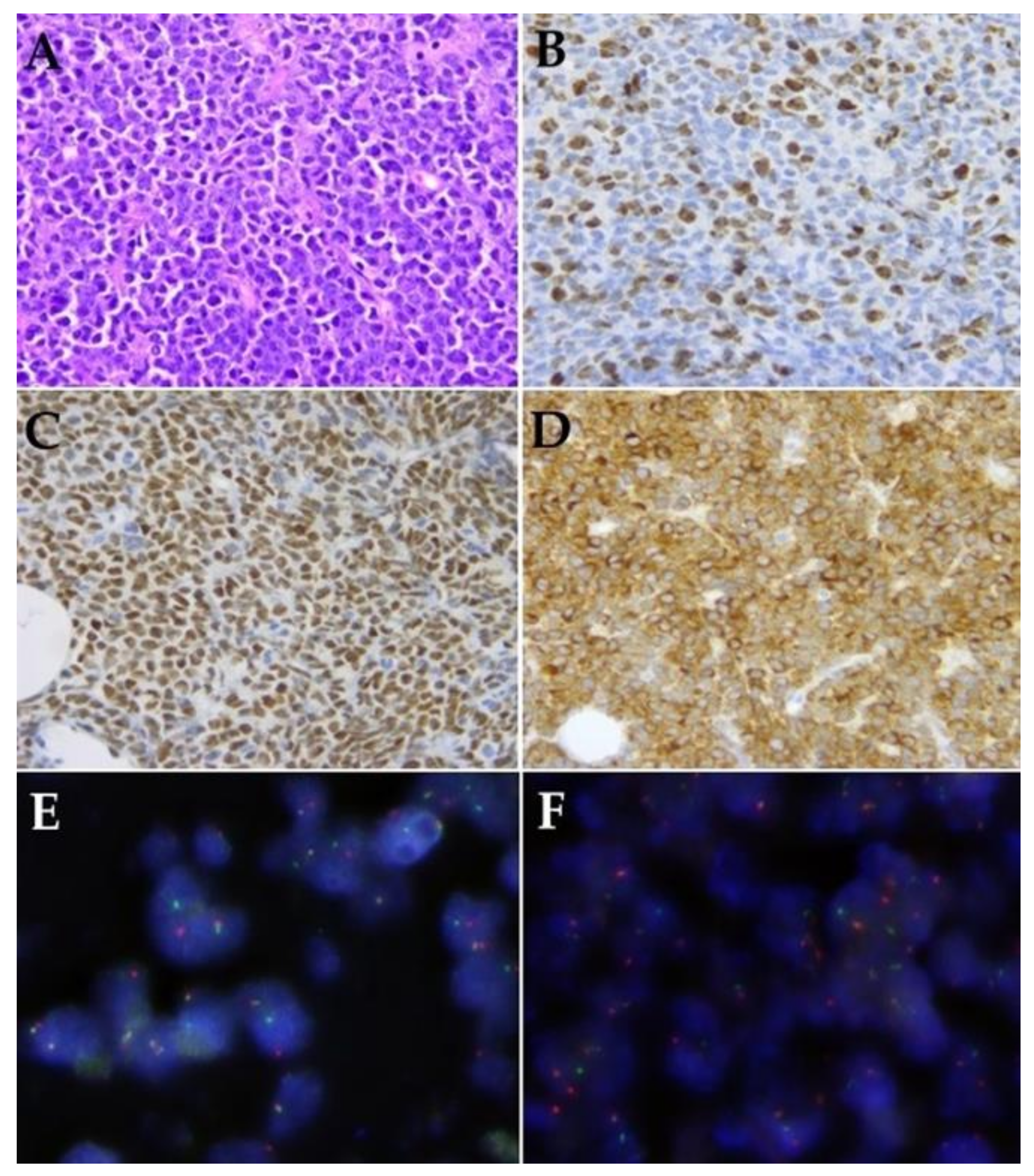
2.2. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
2.4. Tumor and Cell-Free Nucleic Acid Isolation
2.5. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Samples
3.2. Histological Features Including Immunohistochemistry and FISH
3.3. cfTNA Concentrations and Pre-Seq QC Assay
3.4. Gene Fusions Detected by NGS
3.5. NGS-Based Mutation Profiling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Méhes, G. Liquid Biopsy for Predictive Mutational Profiling of Solid Cancer: The Pathologist’s Perspective. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 297, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Bratman, S.V.; To, J.; Wynne, J.F.; Eclov, N.C.W.; Modlin, L.A.; Liu, C.L.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Merritt, R.E.; et al. An Ultrasensitive Method for Quantitating Circulating Tumor DNA with Broad Patient Coverage. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Diop, F.; Spaccarotella, E.; Monti, S.; Zanni, M.; Rasi, S.; Deambrogi, C.; Spina, V.; Bruscaggin, A.; Favini, C.; et al. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Genotyping on the Liquid Biopsy. Blood 2017, 129, 1947–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohers, E.; Viailly, P.-J.; Becker, S.; Marchand, V.; Ruminy, P.; Maingonnat, C.; Bertrand, P.; Etancelin, P.; Picquenot, J.-M.; Camus, V.; et al. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma by Cell-Free DNA High-Throughput Targeted Sequencing: Analysis of a Prospective Cohort. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfau-Larue, M.-H.; van der Gucht, A.; Dupuis, J.; Jais, J.-P.; Nel, I.; Beldi-Ferchiou, A.; Hamdane, S.; Benmaad, I.; Laboure, G.; Verret, B.; et al. Total Metabolic Tumor Volume, Circulating Tumor Cells, Cell-Free DNA: Distinct Prognostic Value in Follicular Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suehara, Y.; Sakata-Yanagimoto, M.; Hattori, K.; Nanmoku, T.; Itoh, T.; Kaji, D.; Yamamoto, G.; Abe, Y.; Narita, K.; Takeuchi, M.; et al. Liquid Biopsy for the Identification of Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Haematologica 2018, 103, e241–e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.-T.; Lu, L.; Xu, W.; Li, J.-Y. Circulating Tumor DNA: Clinical Roles in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, L.; Van der Linden, M.; De Vriendt, C.; Van den Broeck, B.; Muylle, K.; Deeren, D.; Dedeurwaerdere, F.; Verbeke, S.; Dendooven, A.; De Grove, K.; et al. Shallow-Depth Sequencing of Cell-Free DNA for Hodgkin and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (Differential) Diagnosis: A Standardized Approach with Underappreciated Potential. Haematologica 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, P.; Wlodarska, I.; Tousseyn, T.; Dehaspe, L.; Dierickx, D.; Verheecke, M.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Bechter, O.; Delforge, M.; Vandecaveye, V.; et al. Non-Invasive Detection of Genomic Imbalances in Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg Cells in Early and Advanced Stage Hodgkin’s Lymphoma by Sequencing of Circulating Cell-Free DNA: A Technical Proof-of-Principle Study. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e55–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Liebers, M.; Zhelyazkova, B.; Cao, Y.; Panditi, D.; Lynch, K.D.; Chen, J.; Robinson, H.E.; Shim, H.S.; Chmielecki, J.; et al. Anchored Multiplex PCR for Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussman, R.T.; Oran, A.R.; Paolillo, C.; Lieberman, D.; Morrissette, J.J.D.; Rosenbaum, J.N. Validation of a Next-Generation Sequencing Assay Targeting RNA for the Multiplexed Detection of Fusion Transcripts and Oncogenic Isoforms. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Vo, A.D.; Qin, F.; Li, H. Comparative Assessment of Methods for the Fusion Transcripts Detection from RNA-Seq Data. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltgesundheitsorganisation. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. In World Health Organization Classification of Tumours, 4th ed.; Swerdlow, S.H., Campo, E., Harris, N.L., Jaffe, E.S., Pileri, S.A., Stein, H., Thiele, J., Eds.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2017; ISBN 978-92-832-4494-3. [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 Revision of the World Health Organization Classification of Lymphoid Neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the Molecular Classification of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma by Immunohistochemistry Using a Tissue Microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargis, A.S.; Kalman, L.; Berry, M.W.; Bick, D.P.; Dimmock, D.P.; Hambuch, T.; Lu, F.; Lyon, E.; Voelkerding, K.V.; Zehnbauer, B.A.; et al. Assuring the Quality of Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Laboratory Practice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, L.J.; Arcila, M.E.; Corless, C.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Lubin, I.M.; Pfeifer, J.; Temple-Smolkin, R.L.; Voelkerding, K.V.; Nikiforova, M.N. Guidelines for Validation of Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Oncology Panels: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology and College of American Pathologists. J. Mol. Diagn. JMD 2017, 19, 341–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamanova, L.; Coffey, A.J.; Scott, C.E.; Kozarewa, I.; Turner, E.H.; Kumar, A.; Howard, E.; Shendure, J.; Turner, D.J. Target-Enrichment Strategies for next-Generation Sequencing. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.J.; Chen, R.; Lam, H.Y.K.; Karczewski, K.J.; Chen, R.; Euskirchen, G.; Butte, A.J.; Snyder, M. Performance Comparison of Exome DNA Sequencing Technologies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Abbott, T.E.; Larson, D.; Chen, K. BreakDancer: Identification of Genomic Structural Variation from Paired-End Read Mapping. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 45, 15.6.1–15.6.1.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, J.; Hsu, A.; Boyle, S.E.; Macintyre, G.; Cmero, M.; Tothill, R.W.; Johnstone, R.W.; Shackleton, M.; Papenfuss, A.T. Socrates: Identification of Genomic Rearrangements in Tumour Genomes by Re-Aligning Soft Clipped Reads. Bioinform. Oxf. Engl. 2014, 30, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawroński, A.R.; Lin, Y.-Y.; McConeghy, B.; LeBihan, S.; Asghari, H.; Koçkan, C.; Orabi, B.; Adra, N.; Pili, R.; Collins, C.C.; et al. Structural Variation and Fusion Detection Using Targeted Sequencing Data from Circulating Cell Free DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, F.; Shen, J. Bioinformatic Validation Identifies Candidate Key Genes in Diffuse Large-B Cell Lymphoma. Pers. Med. 2019, 16, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eich, M.-L.; Athar, M.; Ferguson, J.E.; Varambally, S. EZH2-Targeted Therapies in Cancer: Hype or a Reality. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 5449–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloudi, H.; Bohers, É.; Guillonneau, F.; Taly, A.; Gibouin, V.C.; Viailly, P.-J.; Jego, G.; Grumolato, L.; Jardin, F.; Sola, B. XPO1E571K Mutation Modifies Exportin 1 Localisation and Interactome in B-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto-Soares, M.A.; de Oliveira, R.D.; Cortopassi, G.M.; Machado-Neto, J.A.; Palma, L.C.; Figueiredo-Pontes, L.L. de Clinical and Molecular Profile of a Brazilian Cohort of Patients with Classical BCR-ABL1-Negative Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2020, 42, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Case | Sex | Age (Year) | Localization | Histological Diagnosis | Tumor Ratio (%) | COO | IHC (%) | FISH (%) | Gene Fusions Detected by NGS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ki-67 | MYC | BCL2 | MYC | BCL2 | BCL6 | ||||||||
| 1 | F | 50 | lymph node | DLBCL | 30 | GCB | 70 | 10 | 80 | negative | 54 | 25 | BCL2/IGH, BCL6/IGH |
| 2 | M | 87 | lymph node | DLBCL | 50 | non-GCB | 90 | 40 | 50 | negative | negative | negative | negative |
| 3 | M | 58 | lymph node | DLBCL | 70 | non-GCB | 70 | 20 | 10 | negative | negative | negative | MYC, B2M/TNFR |
| 4 | M | 62 | lymph node | DLBCL | 60 | GCB | 65 | 5 | 5 | negative | negative | negative | negative |
| 5 | F | 37 | lymph node | DLBCL | 90 | non-GCB | 40 | 20 | 15 | negative | negative | negative | negative |
| 6 | M | 73 | skin | cutaneous DLBCL (leg type) | 80 | non-GCB | 80 | 0 | 70 | negative | negative | negative | negative |
| 7 | M | 83 | colon | DLBCL | 60 | non-GCB | 50 | 5 | 100 | negative | negative | negative | negative |
| 8 | F | 68 | liver | DLBCL | 50 | non-GCB | 80 | 30 | 100 | negative | negative | negative | MYC |
| 9 | F | 67 | liver | DLBCL | 80 | non-GCB | 70 | 20 | 95 | negative | negative | 40 | BCL6/IGH, CCND3/CCND1 |
| 10 | F | 58 | parotis | DLBCL | 60 | non-GCB | 30 | 0 | 40 | negative | negative | negative | negative |
| 11 | F | 58 | lung | DLBCL | 70 | non-GCB | 75 | 25 | 50 | negative | negative | negative | MYC |
| 12 | M | 45 | lung | DLBCL | 60 | non-GCB | 30 | 40 | 0 | negative | negative | negative | DLEU1/DLEU2, CCND3/CCND1 |
| 13 | M | 47 | lung | DLBCL | 70 | non-GCB | 30 | 10 | 10 | negative | negative | 10 | BCL6/IGH |
| 14 | M | 72 | kidney | DLBCL | 60 | non-GCB | 90 | 60 | 60 | 88 | negative | negative | MYC, NSL1/BATF3, P2RY8/ASMTL |
| 15 | F | 31 | CNS | DLBCL | 50 | non-GCB | 70 | 15 | 10 | 5 | negative | negative | MYC |
| 16 | F | 64 | CNS | DLBCL | 80 | non-GCB | 80 | 30 | 70 | negative | negative | negative | negative |
| 17 | F | 51 | CNS | DLBCL | 80 | non-GCB | 90 | 20 | 80 | negative | negative | negative | negative |
| 18 | M | 47 | lymph node | double hit DLBCL, high-grade | 90 | GCB | 50 | 80 | 100 | 64 | 70 | negative | MYC, BCL2/IGH |
| 19 | F | 47 | lymph node | double hit DLBCL, high-grade | 80 | GCB | 90 | 80 | 90 | 74 | 80 | negative | MYC, BCL2/IGH |
| 20 | M | 53 | upper lip | Burkitt | 70 | - | 90 | 90 | 5 | 70 | negative | negative | MYC |
| 21 | F | 85 | lymph node | follicular, grade 3A | 50 | - | 25 | 0 | 30 | negative | negative | negative | negative |
| 22 | M | 42 | lymph node | follicular, grade 3A | 60 | - | 10 | 0 | 100 | negative | 80 | negative | BCL2/IGH |
| 23 | M | 50 | parotis | follicular, grade 3A | 70 | - | 15 | 5 | 100 | negative | negative | negative | negative |
| 24 | M | 37 | lymph node | PTCL, high-grade | 60 | - | 80 | 5 | 0 | negative | negative | negative | CCND3/CCND1 |
| Case | Histological Diagnosis | Tumor Ratio (%) | Gene | Nucleotide Variant | Amino Acid Change | Tissue Biopsy VAF (%) | Liquid Biopsy VAF (%) | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DLBCL | 30 | CD79B | c.573_575del | p.Glu192del | 11.6 | 0 | pathogenic |
| STAT6 | c.1256A > G | p.Asp419Gly | 29.8 | 0 | pathogenic | |||
| 2 | DLBCL | 50 | RANBP1 | c.254A > G | p.His85Arg | insufficient for NGS | 36 | uncertain |
| 3 | DLBCL | 70 | CCND3 | c.65G > A | p.Arg22His | 8 | 0 | uncertain |
| 4 | DLBCL | 60 | PAICS | c.422C > G | p.Ser141Cys | 52 | 51 | SNP |
| TNFRSF13B | c.215G > A | p.Arg72His | 42 | 54 | likely benign | |||
| 5 | DLBCL | 90 | ETV6 | c.838A > G | p.Asn280Asp | 23 | 0 | uncertain |
| RAB29 | c.-130-4G > A | splice region | 44 | 49 | uncertain | |||
| STAT6 | c.1256A > G | p.Asp419Gly | 49 | 35 | pathogenic | |||
| 6 | cutaneous DLBCL (leg type) | 80 | MYD88 | c.794T > C | p.Leu265Pro | 36.9 | 2.3 | pathogenic |
| 7 | DLBCL | 60 | CDKN2A | c.442G > A | p.Ala148Thr | 56 | 50 | benign |
| CYB5R2 | c.488T > G | p.Leu163Trp | 42 | 46.4 | SNP | |||
| PAICS | c.422C > G | p.Ser141Cys | 47.9 | 49.5 | SNP | |||
| 8 | DLBCL | 50 | CYB5R2 | c.488T > G | p.Leu163Trp | insufficient for NGS | 25.2 | SNP |
| NOTCH2 | c.7198C > T | p.Arg2400Ter | 27.6 | pathogenic | ||||
| PIM1 | c.322T > C | p.Cys108Arg | 16 | uncertain | ||||
| 9 | DLBCL | 80 | CD79B | c.489G > A | p.Met163Ile | 48 | 2.2 | uncertain |
| ETV6 | c.26G > C | p.Ser9Thr | 81.2 | 20 | uncertain | |||
| PAICS | c.422C > G | p.Ser141Cys | 39.4 | 48.4 | SNP | |||
| PIM1 | c.302C > A | p.Ala101Asp | 28.2 | 6.6 | uncertain | |||
| 10 | DLBCL | 60 | CCND3 | c.71A > G | p.Glu24Gly | 7.14 | 3 | uncertain |
| RANBP1 | c.254A > G | p.His85Arg | 2 | 36 | uncertain | |||
| 11 | DLBCL | 70 | EIF4A1 | c.6del | p.Ala3ArgfsTer35 | insufficient for NGS | 96 | uncertain |
| NFKB2 | c.1947G > T | p.Leu649Phe | 6.9 | uncertain | ||||
| PAICS | c.1076T > C | p.Val359Ala | 9.9 | SNP | ||||
| STAT6 | c.1249A > T | p.Asn417Tyr | 28.5 | pathogenic | ||||
| 12 | DLBCL | 60 | EZH2 | c.1921T > A | p.Tyr641Asn | 46 | 19 | pathogenic |
| TCF3 | c.1291_1293delinsAGT | p.Gly431Ser | 46 | 50 | SNP | |||
| 13 | DLBCL | 70 | NFKB2 | c.1947G > T | p.Leu649Phe | 0 | 5.3 | uncertain |
| 14 | DLBCL | 60 | TCF3 | c.1291_1293delinsAGT | p.Gly431Ser | 64 | 53 | SNP |
| 15 | DLBCL | 50 | CCND3 | c.531_532delinsTG | p.Ser178Ala | 83.3 | 52.1 | uncertain |
| JAK2 | c.1177C > G | p.Leu393Val | 74.5 | 75 | SNP | |||
| PLCG2 | c.2011A > G | p.Ile671Val | 33.4 | 35.4 | benign | |||
| RANBP1 | c.254A > G | p.His85Arg | 17.3 | 19.2 | uncertain | |||
| STAT6 | c.1249A > T | p.Asn417Tyr | 34.6 | 32.5 | pathogenic | |||
| 16 | DLBCL | 80 | LMO2 | c.35C > T | p.Pro12Leu | 52 | 48 | uncertain |
| MYD88 | c.794T > C | p.Leu265Pro | 38 | 2 | pathogenic | |||
| PIM1 | c.816G > C | p.Glu272Asp | 44 | 0 | pathogenic | |||
| XPO1 | c.1711G > A | p.Glu571Lys | 40 | 0 | pathogenic | |||
| 17 | DLBCL | 80 | CCDC50 | c.363A > T | p.Leu121Phe | 64 | 51.5 | benign |
| MYD88 | c.794T > C | p.Leu265Pro | 51.6 | 2 | pathogenic | |||
| PIM1 | c.850C > T | p.Leu284Phe | 88.8 | 2.2 | pathogenic | |||
| PTPN1 | c.899G > A | p.Arg300Gln | 49.1 | 0 | uncertain | |||
| 18 | double-hit DLBCL, high-grade | 90 | BCL2 | c.-287 + 8C > G | splice region | 87.3 | 9.3 | uncertain |
| BCR | c.1461_1461 + 1insA | p.Ser488LysfsTer2 | 59.5 | 0 | uncertain | |||
| KMT2A | c.11321 + 2del | splice region | 63.8 | 0 | uncertain | |||
| RAB29 | c.-130-4G > A | splice region | 24.8 | 0 | uncertain | |||
| 19 | double-hit DLBCL, high-grade | 80 | EIF4A1 | c.115C > T | p.Leu39Phe | 10.7 | 0 | uncertain |
| EZH2 | c.1922A > T | p.Tyr641Phe | 56.9 | 32.5 | pathogenic | |||
| TCF3 | c.1291_1293delinsAGT | p.Gly431Ser | 37 | 52.3 | SNP | |||
| 20 | Burkitt | 70 | CCDC50 | c.363A > T | p.Leu121Phe | 36 | 65 | benign |
| CYB5R2 | c.488T > G | p.Leu163Trp | 0 | 6 | SNP | |||
| 21 | follicular, grade 3A | 50 | CYB5R2 | c.488T > G | p.Leu163Trp | 19.8 | 37 | SNP |
| STAT6 | c.1256A > G | p.Asp419Gly | 24.2 | 5.2 | pathogenic | |||
| 22 | follicular, grade 3A | 60 | BCL2 | c.-289C > T | splice region | 84 | 8 | pathogenic |
| CYB5R2 | c.488T > G | p.Leu163Trp | 21 | 40 | SNP | |||
| EZH2 | c.1922A > T | p.Tyr641Phe | 45 | 10 | pathogenic | |||
| MYD88 | c.664 + 2T > A | splice region | 19 | 12 | uncertain | |||
| 23 | follicular, grade 3A | 70 | PAICS | c.422C > G | p.Ser141Cys | 23 | 50 | SNP |
| RANBP1 | c.254A > G | p.His85Arg | 0 | 29 | uncertain | |||
| STAT6 | c.1263T > G | p.Asn421Lys | 34 | 0 | uncertain | |||
| 24 | PTCL, high-grade | 60 | negative | negative | negative | negative | negative | negative |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mokánszki, A.; Bicskó, R.; Gergely, L.; Méhes, G. Cell-Free Total Nucleic Acid-Based Genotyping of Aggressive Lymphoma: Comprehensive Analysis of Gene Fusions and Nucleotide Variants by Next-Generation Sequencing. Cancers 2021, 13, 3032. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123032
Mokánszki A, Bicskó R, Gergely L, Méhes G. Cell-Free Total Nucleic Acid-Based Genotyping of Aggressive Lymphoma: Comprehensive Analysis of Gene Fusions and Nucleotide Variants by Next-Generation Sequencing. Cancers. 2021; 13(12):3032. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123032
Chicago/Turabian StyleMokánszki, Attila, Réka Bicskó, Lajos Gergely, and Gábor Méhes. 2021. "Cell-Free Total Nucleic Acid-Based Genotyping of Aggressive Lymphoma: Comprehensive Analysis of Gene Fusions and Nucleotide Variants by Next-Generation Sequencing" Cancers 13, no. 12: 3032. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123032
APA StyleMokánszki, A., Bicskó, R., Gergely, L., & Méhes, G. (2021). Cell-Free Total Nucleic Acid-Based Genotyping of Aggressive Lymphoma: Comprehensive Analysis of Gene Fusions and Nucleotide Variants by Next-Generation Sequencing. Cancers, 13(12), 3032. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123032






