Obesity and Breast Cancer: A Case of Inflamed Adipose Tissue
Abstract
1. The Statistics and Co-Morbidities of Obesity
2. Obesity and Breast Cancer
3. Mechanistic Link between Obesity and Breast Cancer
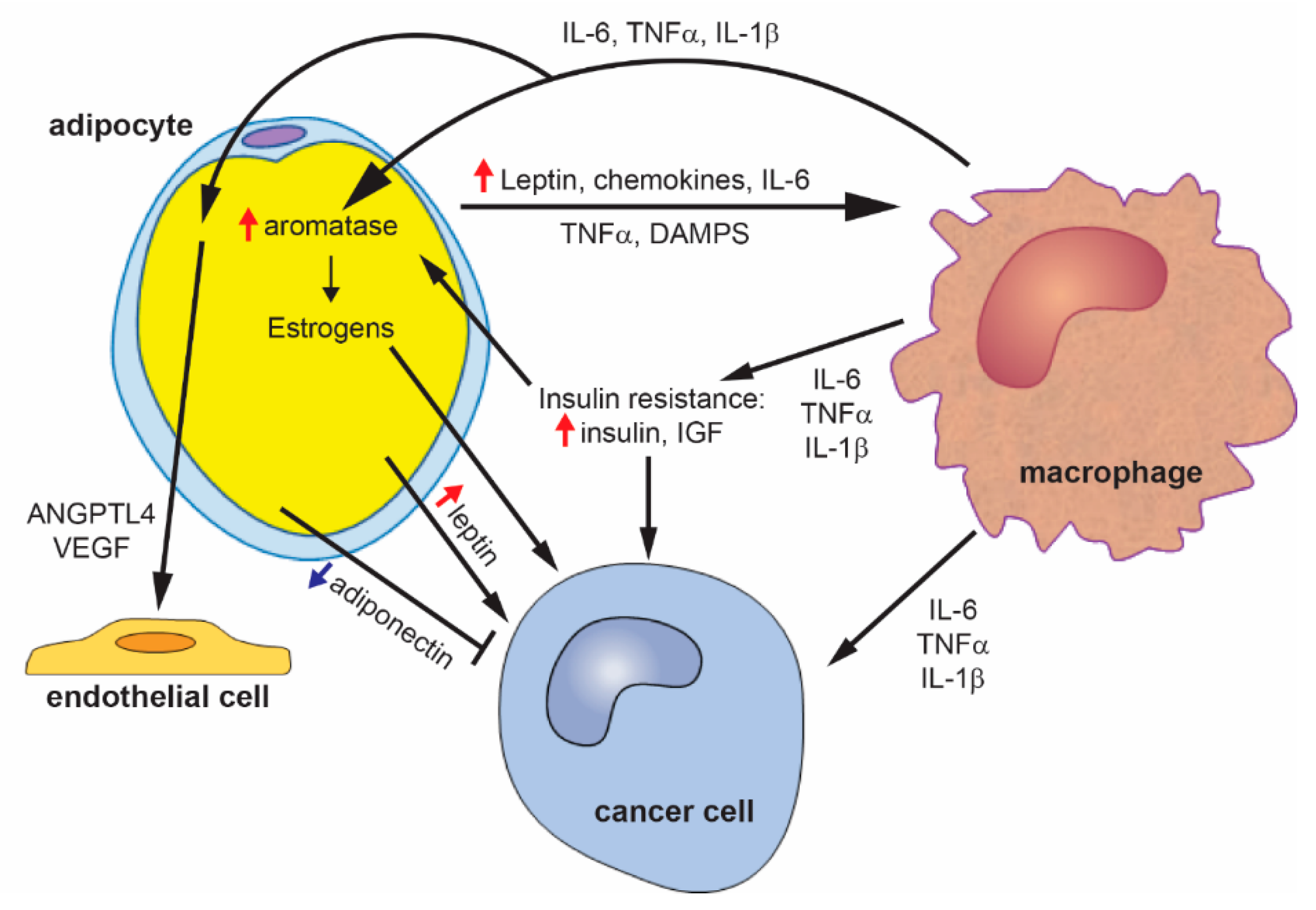
3.1. Adipocytes and Adipokines
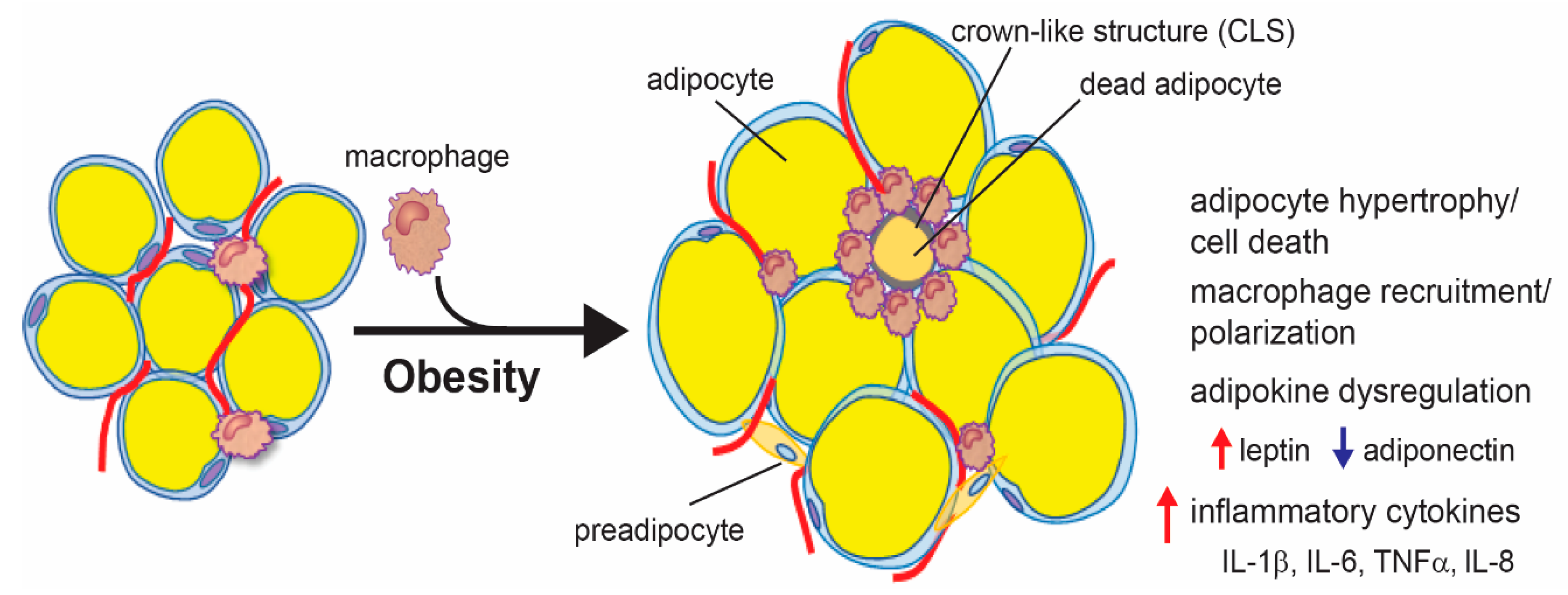
3.2. Adipose Tissue Inflammation
4. Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Breast Cancer in Non-Obese Women
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Sacks, G.; Hall, K.D.; McPherson, K.; Finegood, D.T.; Moodie, M.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. The global obesity pandemic: Shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet 2011, 378, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladabaum, U.; Mannalithara, A.; Myer, P.A.; Singh, G. Obesity, abdominal obesity, physical activity, and caloric intake in US adults: 1988 to 2010. Am. J. Med. 2014, 127, 717–727.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.W.; Popkin, B.M. Time use and physical activity: A shift away from movement across the globe. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 659–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrou, I.; Randeva, H.S.; Tsigos, C.; Kaltsas, G.; Weickert, M.O. Clinical Problems Caused by Obesity. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, R.; Sutterwala, F.S.; Zhang, W. Obesity and cancer: Inflammation bridges the two. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, G.; Lewington, S.; Sherliker, P.; Clarke, R.; Emberson, J.; Halsey, J.; Qizilbash, N.; Collins, R.; Peto, R.; Collaboration, P.S. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900,000 adults: Collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet 2009, 373, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apovian, C.M. Obesity: Definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am. J. Manag. Care 2016, 22, s176–s185. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NAFLD: A multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S47–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrini, E.; Sullivan, S.; Klein, S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Biochemical, metabolic, and clinical implications. Hepatology 2010, 51, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, A.; Fisher, R.A.; Ham, J.M.; Olzinski, A.T.; Shiffman, M.L.; Sanyal, A.J.; Luketic, V.A.; Sterling, R.K.; Olbrisch, M.E.; Posner, M.P. Selection and outcome of living donors for adult to adult right lobe transplantation. Transplantation 2000, 69, 2410–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilden, M.; Christoffersen, P.; Juhl, E.; Dalgaard, J.B. Liver histology in a ‘normal’ population—Examinations of 503 consecutive fatal traffic casualties. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1977, 12, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.G. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A study of 49 patients. Hum. Pathol. 1989, 20, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholam, P.M.; Kotler, D.P.; Flancbaum, L.J. Liver pathology in morbidly obese patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Obes. Surg. 2002, 12, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Ferrannini, E.; Groop, L.; Henry, R.R.; Herman, W.H.; Holst, J.J.; Hu, F.B.; Kahn, C.R.; Raz, I.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, T.W.; McPherson, M.; Gail Darlington, L. Obesity and cancer: Existing and new hypotheses for a causal connection. EBioMedicine 2018, 30, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thurmond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Pandeya, N.; Byrnes, G.; Renehan, P.A.G.; Stevens, G.A.; Ezzati, P.M.; Ferlay, J.; Miranda, J.J.; Romieu, I.; Dikshit, R.; et al. Global burden of cancer attributable to high body-mass index in 2012: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A. Overweight, obesity and risk of liver cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Useros, J.; Garcia-Foncillas, J. Obesity and colorectal cancer: Molecular features of adipose tissue. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.K.; Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Kahn, H.S.; Thun, M.J. Body mass index and colon cancer mortality in a large prospective study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 152, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, F. Ultrasonic visualization of an umbilical vein. Radiology 1976, 120, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.S.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Pou, K.M.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Liu, C.Y.; Vasan, R.S.; Murabito, J.M.; Meigs, J.B.; Cupples, L.A.; et al. Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments: Association with metabolic risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2007, 116, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, L.; He, T.; Hu, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, D.; Xu, S.; et al. Abdominal obesity and colorectal cancer risk: Systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, K.; Lindgren, T.H.; Koch, C.A.; Brodell, R.T. Obesity as a risk factor for malignant melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2016, 17, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, C.S.; White, E.; Lee, J.A. Case-control study of malignant melanoma in Washington State. II. Diet, alcohol, and obesity. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1994, 139, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, L.K.; Lowe, J.B.; Lynch, C.F.; Alavanja, M.C. Cutaneous melanoma and obesity in the Agricultural Health Study. Ann. Epidemiol. 2008, 18, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergentanis, T.N.; Antoniadis, A.G.; Gogas, H.J.; Antonopoulos, C.N.; Adami, H.O.; Ekbom, A.; Petridou, E.T. Obesity and risk of malignant melanoma: A meta-analysis of cohort and case-control studies. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, C.M.; Green, A.C.; Zens, M.S.; Stukel, T.A.; Bataille, V.; Berwick, M.; Elwood, J.M.; Gallagher, R.; Holly, E.A.; Kirkpatrick, C.; et al. Anthropometric factors and risk of melanoma in women: A pooled analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvi, P.; Chaube, B.; Singh, S.V.; Mohammad, N.; Vijayakumar, M.V.; Singh, S.; Chouhan, S.; Bhat, M.K. Elevated circulatory levels of leptin and resistin impair therapeutic efficacy of dacarbazine in melanoma under obese state. Cancer Metab. 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvi, P.; Chaube, B.; Singh, S.V.; Mohammad, N.; Pandey, V.; Vijayakumar, M.V.; Radhakrishnan, R.M.; Vanuopadath, M.; Nair, S.S.; Nair, B.G.; et al. Weight control interventions improve therapeutic efficacy of dacarbazine in melanoma by reversing obesity-induced drug resistance. Cancer Metab. 2016, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvi, P.; Chaube, B.; Pandey, V.; Vijayakumar, M.V.; Boreddy, P.R.; Mohammad, N.; Singh, S.V.; Bhat, M.K. Obesity induced rapid melanoma progression is reversed by orlistat treatment and dietary intervention: Role of adipokines. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, M.; Chen, J.; Ye, Y.; Tseng, H.Y.; Lai, F.; Tay, K.H.; Jin, L.; Guo, S.T.; Jiang, C.C.; Zhang, X.D. Adipocytes contribute to resistance of human melanoma cells to chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, A.; Monjazeb, A.M.; Decock, J. The Obesity Paradox in Cancer, Tumor Immunology, and Immunotherapy: Potential Therapeutic Implications in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Aguilar, E.G.; Luna, J.I.; Dunai, C.; Khuat, L.T.; Le, C.T.; Mirsoian, A.; Minnar, C.M.; Stoffel, K.M.; Sturgill, I.R.; et al. Paradoxical effects of obesity on T cell function during tumor progression and PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremmel, M.; Gerdtham, U.G.; Nilsson, P.M.; Saha, S. Economic burden of obesity: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, R.A.; Levine, R. The economic impact of obesity in the United States. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2010, 3, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, E.A.; Trogdon, J.G.; Cohen, J.W.; Dietz, W. Annual medical spending attributable to obesity: Payer-and service-specific estimates. Health Aff. 2009, 28, w822–w831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trogdon, J.G.; Finkelstein, E.A.; Hylands, T.; Dellea, P.S.; Kamal-Bahl, S.J. Indirect costs of obesity: A review of the current literature. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, A.R.; Bates, T. Obesity and breast cancer: A review of the literature. Breast 2004, 13, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andò, S.; Gelsomino, L.; Panza, S.; Giordano, C.; Bonofiglio, D.; Barone, I.; Catalano, S. Obesity, leptin and breast cancer: Epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Cancers 2019, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliassen, A.H.; Colditz, G.A.; Rosner, B.; Willett, W.C.; Hankinson, S.E. Adult weight change and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer. JAMA 2006, 296, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, F.; Ferrari, P.; Freisling, H.; Chajès, V.; Rinaldi, S.; de Batlle, J.; Dahm, C.C.; Overvad, K.; Baglietto, L.; Dartois, L.; et al. Healthy lifestyle and risk of breast cancer among postmenopausal women in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 2640–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbins, M.; Decorby, K.; Choi, B.C. The association between obesity and cancer risk: A meta-analysis of observational studies from 1985 to 2011. ISRN Prev. Med. 2013, 2013, 680536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munsell, M.F.; Sprague, B.L.; Berry, D.A.; Chisholm, G.; Trentham-Dietz, A. Body mass index and breast cancer risk according to postmenopausal estrogen-progestin use and hormone receptor status. Epidemiol. Rev. 2014, 36, 114–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keum, N.; Greenwood, D.C.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, R.; Aune, D.; Ju, W.; Hu, F.B.; Giovannucci, E.L. Adult weight gain and adiposity-related cancers: A dose-response meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhouser, M.L.; Aragaki, A.K.; Prentice, R.L.; Manson, J.E.; Chlebowski, R.; Carty, C.L.; Ochs-Balcom, H.M.; Thomson, C.A.; Caan, B.J.; Tinker, L.F.; et al. Overweight, obesity, and postmenopausal invasive breast cancer risk: A secondary analysis of the women’s health initiative randomized clinical trials. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Orsini, N.; Saji, S.; Key, T.J.; Wolk, A. Body weight and incidence of breast cancer defined by estrogen and progesterone receptor status—A meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierobon, M.; Frankenfeld, C.L. Obesity as a risk factor for triple-negative breast cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 137, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivers, K.F.; Lund, M.J.; Porter, P.L.; Liff, J.M.; Flagg, E.W.; Coates, R.J.; Eley, J.W. The epidemiology of triple-negative breast cancer, including race. Cancer Causes Control. 2009, 20, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona-Davis, L.; Rose, D.P.; Hazard, H.; Howard-McNatt, M.; Adkins, F.; Partin, J.; Hobbs, G. Triple-negative breast cancer and obesity in a rural Appalachian population. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2008, 17, 3319–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Buzdar, A.U.; Hursting, S.D. Inflammatory breast cancer and body mass index. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 3731–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schairer, C.; Li, Y.; Frawley, P.; Graubard, B.I.; Wellman, R.D.; Buist, D.S.; Kerlikowske, K.; Onega, T.L.; Anderson, W.F.; Miglioretti, D.L. Risk factors for inflammatory breast cancer and other invasive breast cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, R.L.; El-Zein, R.; Valero, V.; Lucci, A.; Bevers, T.B.; Fouad, T.; Liao, W.; Ueno, N.T.; Woodward, W.A.; Brewster, A.M. Epidemiological risk factors associated with inflammatory breast cancer subtypes. Cancer Causes Control. 2016, 27, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protani, M.; Coory, M.; Martin, J.H. Effect of obesity on survival of women with breast cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 123, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.S.; Vieira, A.R.; Aune, D.; Bandera, E.V.; Greenwood, D.C.; McTiernan, A.; Navarro Rosenblatt, D.; Thune, I.; Vieira, R.; Norat, T. Body mass index and survival in women with breast cancer-systematic literature review and meta-analysis of 82 follow-up studies. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewertz, M.; Jensen, M.B.; Gunnarsdóttir, K.; Højris, I.; Jakobsen, E.H.; Nielsen, D.; Stenbygaard, L.E.; Tange, U.B.; Cold, S. Effect of obesity on prognosis after early-stage breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P.J.; Ennis, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Trudeau, M.E.; Koo, J.; Taylor, S.K.; Hood, N. Insulin- and obesity-related variables in early-stage breast cancer: Correlations and time course of prognostic associations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechuta, S.; Chen, W.Y.; Cai, H.; Poole, E.M.; Kwan, M.L.; Flatt, S.W.; Patterson, R.E.; Pierce, J.P.; Caan, B.J.; Ou Shu, X. A pooled analysis of post-diagnosis lifestyle factors in association with late estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer prognosis. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewertz, M.; Gray, K.P.; Regan, M.M.; Ejlertsen, B.; Price, K.N.; Thürlimann, B.; Bonnefoi, H.; Forbes, J.F.; Paridaens, R.J.; Rabaglio, M.; et al. Obesity and risk of recurrence or death after adjuvant endocrine therapy with letrozole or tamoxifen in the breast international group 1-98 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3967–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestak, I.; Distler, W.; Forbes, J.F.; Dowsett, M.; Howell, A.; Cuzick, J. Effect of body mass index on recurrences in tamoxifen and anastrozole treated women: An exploratory analysis from the ATAC trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3411–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druesne-Pecollo, N.; Touvier, M.; Barrandon, E.; Chan, D.S.; Norat, T.; Zelek, L.; Hercberg, S.; Latino-Martel, P. Excess body weight and second primary cancer risk after breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 135, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majed, B.; Moreau, T.; Senouci, K.; Salmon, R.J.; Fourquet, A.; Asselain, B. Is obesity an independent prognosis factor in woman breast cancer? Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 111, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, J.G.; Carney, P.A.; Abraham, L.A.; Barlow, W.E.; Egger, J.R.; Fosse, J.S.; Cutter, G.R.; Hendrick, R.E.; D’Orsi, C.J.; Paliwal, P.; et al. The association between obesity and screening mammography accuracy. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, A.C.; Perrin, N.; Rosales, A.G.; Schneider, J.; Rix, M.M.; Glasgow, R.E. Patient barriers to mammography identified during a reminder program. J. Womens Health 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kruper, L.; Dieli-Conwright, C.M.; Mortimer, J.E. The impact of obesity on breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.P.; Cleveland, E.C.; Nelson, J.A.; Kovach, S.J.; Serletti, J.M.; Wu, L.C.; Kanchwala, S. Breast reconstruction in the morbidly obese patient: Assessment of 30-day complications using the 2005 to 2010 National Surgical Quality Improvement Program data sets. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.P.; Nelson, J.A.; Kovach, S.J.; Serletti, J.M.; Wu, L.C.; Kanchwala, S. Impact of obesity on outcomes in breast reconstruction: Analysis of 15,937 patients from the ACS-NSQIP datasets. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2013, 217, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, J.J.; Sorbero, M.E.; Lyman, G.H. Undertreatment of obese women receiving breast cancer chemotherapy. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colleoni, M.; Li, S.; Gelber, R.D.; Price, K.N.; Coates, A.S.; Castiglione-Gertsch, M.; Goldhirsch, A.; International Breast Cancer Study Group. Relation between chemotherapy dose, oestrogen receptor expression, and body-mass index. Lancet 2005, 366, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Mott, S.L.; Schroeder, M.C.; Phadke, S.; El Masri, J.; Thomas, A. Effect of body mass index- and actual weight-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy doses on pathologic complete response in operable breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2016, 16, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaysse, C.; Muller, C.; Fallone, F. Obesity: An heavyweight player in breast cancer’s chemoresistance. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 3207–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehuédé, C.; Li, X.; Dauvillier, S.; Vaysse, C.; Franchet, C.; Clement, E.; Esteve, D.; Longué, M.; Chaltiel, L.; Le Gonidec, S.; et al. Adipocytes promote breast cancer resistance to chemotherapy, a process amplified by obesity: Role of the major vault protein (MVP). Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabol, R.A.; Villela, V.A.; Denys, A.; Freeman, B.T.; Hartono, A.B.; Wise, R.M.; Harrison, M.A.A.; Sandler, M.B.; Hossain, F.; Miele, L.; et al. Obesity-altered adipose stem cells promote radiation resistance of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer through paracrine signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schech, A.; Yu, S.; Goloubeva, O.; McLenithan, J.; Sabnis, G. A nude mouse model of obesity to study the mechanisms of resistance to aromatase inhibitors. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y. Adipocyte and lipid metabolism in cancer drug resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3006–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, I.; Giordano, C.; Bonofiglio, D.; Andò, S.; Catalano, S. The weight of obesity in breast cancer progression and metastasis: Clinical and molecular perspectives. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 60, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.A.; Hennessy, B.T. Obesity correlation with metastases development and response to first-line metastatic chemotherapy in breast cancer. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2015, 9, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviani, A.; Neishaboury, M.; Mohammadzadeh, N.; Ansari-Damavandi, M.; Jamei, K. Effects of obesity on presentation of breast cancer, lymph node metastasis and patient survival: A retrospective review. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 2225–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Majed, B.; Senouci, K.; Asselain, B. Shortened survival and more metastasis recurrences among overweight breast cancer patients. Breast J. 2009, 15, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, S. Cancer-associated adipocytes: Key players in breast cancer progression. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incio, J.; Ligibel, J.A.; McManus, D.T.; Suboj, P.; Jung, K.; Kawaguchi, K.; Pinter, M.; Babykutty, S.; Chin, S.M.; Vardam, T.D.; et al. Obesity promotes resistance to anti-VEGF therapy in breast cancer by up-regulating IL-6 and potentially FGF-2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.T.; Phuong, T.N.T.; Tien, N.L.B.; Tran, D.K.; Nguyen, T.T.; Thanh, V.V.; Quang, T.L.; Minh, L.B.; Pham, V.H.; Ngoc, V.T.N.; et al. The effects of adipocytes on the regulation of breast cancer in the tumor microenvironment: An update. Cells 2019, 8, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ailhaud, G. Adipose tissue as a secretory organ: From adipogenesis to the metabolic syndrome. C. R. Biol. 2006, 329, 570–577, discussion 575–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, A.E.; Nelson, E.R. The contribution of cholesterol and its metabolites to the pathophysiology of breast cancer. Horm. Cancer 2016, 7, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunter, M.J.; Hoover, D.R.; Yu, H.; Wassertheil-Smoller, S.; Rohan, T.E.; Manson, J.E.; Li, J.; Ho, G.Y.; Xue, X.; Anderson, G.L.; et al. Insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I, and risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.W.; Lo, Y.H.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, P.J.; Yang, Y.F.; Wang, C.H.; Tan, C.H.; Hou, M.F.; et al. VLDL and LDL, but not HDL, promote breast cancer cell proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 388, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manabe, Y.; Toda, S.; Miyazaki, K.; Sugihara, H. Mature adipocytes, but not preadipocytes, promote the growth of breast carcinoma cells in collagen gel matrix culture through cancer-stromal cell interactions. J. Pathol. 2003, 201, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Jung, W.H.; Koo, J.S. Adipocytes can induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 153, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirat, B.; Bochet, L.; Dabek, M.; Daviaud, D.; Dauvillier, S.; Majed, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Meulle, A.; Salles, B.; Le Gonidec, S.; et al. Cancer-associated adipocytes exhibit an activated phenotype and contribute to breast cancer invasion. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, R.; Kluz, P.; Tan, Z.W.; Borcherding, N.; Bormann, N.; Vishwakarma, A.; Balcziak, L.; Zhu, P.; Davies, B.S.; Gourronc, F.; et al. Obesity-associated inflammation promotes angiogenesis and breast cancer via angiopoietin-like 4. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2351–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, J.; Ohtani, H.; Nakamura, K.; Shimokawa, I.; Kanematsu, T. Prognostic impact of marginal adipose tissue invasion in ductal carcinoma of the breast. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 130, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimijima, I.; Ohtake, T.; Sagara, H.; Watanabe, T.; Takenoshita, S. Scattered fat invasion: An indicator for poor prognosis in premenopausal, and for positive estrogen receptor in postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Oncology 2000, 59, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorincz, A.M.; Sukumar, S. Molecular links between obesity and breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2006, 13, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suba, Z. Circulatory estrogen level protects against breast cancer in obese women. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, T.J.; Appleby, P.N.; Reeves, G.K.; Roddam, A.; Dorgan, J.F.; Longcope, C.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Stephenson, H.E.; Falk, R.T.; Miller, R.; et al. Body mass index, serum sex hormones, and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Jiang, L.; Guo, W.; Shao, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. The association between leptin level and breast cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Deng, L.L.; Cui, J.Q.; Shi, L.; Yang, Y.C.; Luo, J.H.; Qin, D.; Wang, L. Association between serum leptin levels and breast cancer risk: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Pan, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Luo, X.; Chen, L. The association between obesity related adipokines and risk of breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75389–75399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delort, L.; Rossary, A.; Farges, M.C.; Vasson, M.P.; Caldefie-Chézet, F. Leptin, adipocytes and breast cancer: Focus on inflammation and anti-tumor immunity. Life Sci. 2015, 140, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Cao, C.; Fu, J.; Li, Q.; Li, D.H.; Chen, M.Y. Serum adiponectin in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Y.; Wang, M.; Ma, Z.B.; Yu, L.X.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, D.Z.; Wang, F.; Yu, Z.G. The role of adiponectin in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, E.; Benaitreau, D.; Dieudonne, M.N.; Leneveu, M.C.; Serazin, V.; Giudicelli, Y.; Pecquery, R. Adiponectin mediates an antiproliferative response in human MDA-MB 231 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 20, 971–977. [Google Scholar]
- Kijak, P.J.; Leadbetter, M.G.; Thomas, M.H.; Thompson, E.A. Confirmation of oxytetracycline, tetracycline and chlortetracycline residues in milk by particle beam liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Biol. Mass Spectrom. 1991, 20, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Qiu, J.; Gong, L.; Mao, H.; Jia, W.; Guo, J. The relationship between human serum resistin level and body fat content, plasma glucose as well as blood pressure. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2002, 82, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.H.; Yu, B.Y.; Youn, D.S. Relationship of serum adiponectin and resistin levels with breast cancer risk. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2007, 22, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assiri, A.M.; Kamel, H.F.; Hassanien, M.F. Resistin, visfatin, adiponectin, and leptin: Risk of breast cancer in pre- and postmenopausal Saudi females and their possible diagnostic and predictive implications as novel biomarkers. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 253519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Wu, C.C.; Lo, S.; Hou, M.F.; Yuan, S.S. Resistin expression in breast cancer tissue as a marker of prognosis and hormone therapy stratification. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 125, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalamaga, M.; Sotiropoulos, G.; Karmaniolas, K.; Pelekanos, N.; Papadavid, E.; Lekka, A. Serum resistin: A biomarker of breast cancer in postmenopausal women? Association with clinicopathological characteristics, tumor markers, inflammatory and metabolic parameters. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M.; Kocelak, P.; Nylec, M.; Chudek, J.; Zahorska-Markiewicz, B. Circulating visfatin level and visfatin/insulin ratio in obese women with metabolic syndrome. Arch. Med. Sci. 2012, 8, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Su, J.H.; Chang, H.L.; Hou, M.F.; Yuan, S.S. High visfatin expression in breast cancer tissue is associated with poor survival. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2011, 20, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulló, M.; Casas-Agustench, P.; Amigó-Correig, P.; Aranceta, J.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Inflammation, obesity and comorbidities: The role of diet. Public Health Nutr. 2007, 10, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser, N.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J.; Scheen, A.J.; Paquot, N. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Nakayama, T. Inflammation, a link between obesity and cardiovascular disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 535918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Karin, M. Obesity, inflammation, and liver cancer. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, H.; Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, G.; Reyes-Romero, M.A. Obesity and inflammation: Epidemiology, risk factors, and markers of inflammation. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 678159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Lund, P.K. Role of intestinal inflammation as an early event in obesity and insulin resistance. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnuolo, M.I.; Cicalese, M.P.; Caiazzo, M.A.; Franzese, A.; Squeglia, V.; Assante, L.R.; Valerio, G.; Merone, R.; Guarino, A. Relationship between severe obesity and gut inflammation in children: What’s next? Ital. J. Pediatr. 2010, 36, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jais, A.; Brüning, J.C. Hypothalamic inflammation in obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gukovsky, I.; Li, N.; Todoric, J.; Gukovskaya, A.; Karin, M. Inflammation, autophagy, and obesity: Common features in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1199–1209.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Skeletal muscle inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and inflammation: The linking mechanism and the complications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skurk, T.; Alberti-Huber, C.; Herder, C.; Hauner, H. Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaben, A.L.; Scherer, P.E. Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.K.; Das, S.K.; Mondal, A.K.; Hackney, O.G.; Chu, W.S.; Kern, P.A.; Rasouli, N.; Spencer, H.J.; Yao-Borengasser, A.; Elbein, S.C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress markers are associated with obesity in nondiabetic subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4532–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, G.; Duan, X.; Homko, C.; Molina, E.J.; Song, W.; Perez, O.; Cheung, P.; Merali, S. Increase in endoplasmic reticulum stress-related proteins and genes in adipose tissue of obese, insulin-resistant individuals. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2438–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Thematic review series: Adipocyte biology. Adipocyte stress: The endoplasmic reticulum and metabolic disease. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic adipose tissue inflammation linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trayhurn, P. Hypoxia and adipose tissue function and dysfunction in obesity. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.M.; Levings, M.K. Immune regulation in obesity-associated adipose inflammation. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, S.; Mitchell, G.; Barbatelli, G.; Murano, I.; Ceresi, E.; Faloia, E.; Wang, S.; Fortier, M.; Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iikuni, N.; Lam, Q.L.; Lu, L.; Matarese, G.; La Cava, A. Leptin and Inflammation. Curr. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 4, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Judd, R.L. Adiponectin regulation and function. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1031–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossus, L.; Jimenez-Corona, A.; Romieu, I.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Boutten, A.; Dupré, T.; Fagherazzi, G.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; Mesrine, S. C-reactive protein and postmenopausal breast cancer risk: Results from the E3N cohort study. Cancer Causes Control. 2014, 25, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, B.L.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Bernstein, L.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Wener, M.H.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Gilliland, F.D.; Sorensen, B.E.; McTiernan, A.; et al. Elevated biomarkers of inflammation are associated with reduced survival among breast cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3437–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Mattei, E.; Velazquez-Torres, G.; Phan, L.; Zhang, F.; Chou, P.C.; Shin, J.H.; Choi, H.H.; Chen, J.S.; Zhao, R.; Chen, J.; et al. Effects of obesity on transcriptomic changes and cancer hallmarks in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, P.G.; Hudis, C.A.; Giri, D.; Morrow, M.; Falcone, D.J.; Zhou, X.K.; Du, B.; Brogi, E.; Crawford, C.B.; Kopelovich, L.; et al. Inflammation and increased aromatase expression occur in the breast tissue of obese women with breast cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, C.; Brown, K.A. Obesity and breast cancer—Role of estrogens and the molecular underpinnings of aromatase regulation in breast adipose tissue. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2018, 466, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silswal, N.; Singh, A.K.; Aruna, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ehtesham, N.Z. Human resistin stimulates the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-12 in macrophages by NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 334, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, D.; Kant, S.; Pandey, S.; Ehtesham, N.Z. Resistin in metabolism, inflammation, and disease. FEBS J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, R.; Azevedo, I. Chronic inflammation in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Mediators Inflamm. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Hull, R.L.; Utzschneider, K.M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006, 444, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheus, M.; Peeters, P.H.; Rinaldi, S.; Dossus, L.; Biessy, C.; Olsen, A.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Jeppesen, M.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; et al. Serum C-peptide levels and breast cancer risk: Results from the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC). Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, T.J.; Appleby, P.N.; Reeves, G.K.; Roddam, A.W.; Breast Cancer Collaborative Group. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), IGF binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), and breast cancer risk: Pooled individual data analysis of 17 prospective studies. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Chiodini, P.; Capuano, A.; Bellastella, G.; Maiorino, M.I.; Rafaniello, C.; Giugliano, D. Metabolic syndrome and postmenopausal breast cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Menopause 2013, 20, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P.J.; Ennis, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Trudeau, M.E.; Koo, J.; Madarnas, Y.; Hartwick, W.; Hoffman, B.; Hood, N. Fasting insulin and outcome in early-stage breast cancer: Results of a prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, C.; Irwin, M.L.; Xiao, L.; Henderson, K.D.; Smith, A.W.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Bernstein, L.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; McTiernan, A. Associations of insulin resistance and adiponectin with mortality in women with breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C.A.; Slingerland, J.M. Cytokines, obesity, and cancer: New insights on mechanisms linking obesity to cancer risk and progression. Annu Rev. Med. 2013, 64, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knüpfer, H.; Preiss, R. Significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in breast cancer (review). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 102, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruceriu, D.; Baldasici, O.; Balacescu, O.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The dual role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in breast cancer: Molecular insights and therapeutic approaches. Cell Oncol. 2020, 43, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Yuan, R.Q.; Fuchs, A.; Yao, Y.; Joseph, A.; Schwall, R.; Schnitt, S.J.; Guida, A.; Hastings, H.M.; Andres, J.; et al. Expression of interleukin-1beta in human breast carcinoma. Cancer 1997, 80, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, R.; Phan, L.; Borcherding, N.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, F.; Janowski, A.M.; Xie, Q.; Markan, K.R.; Li, W.; Potthoff, M.J.; et al. Obesity-associated NLRC4 inflammasome activation drives breast cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, L.M.; McCready, J.; Keller, P.J.; Baker, D.D.; Naber, S.P.; Seewaldt, V.; Kuperwasser, C. Obesity promotes breast cancer by CCL2-mediated macrophage recruitment and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumura, D.; Incio, J.; Shankaraiah, R.C.; Jain, R.K. Obesity and cancer: An angiogenic and inflammatory link. Microcirculation 2016, 23, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarstedt, A.; Graham, T.E.; Kahn, B.B. Adipose tissue dysregulation and reduced insulin sensitivity in non-obese individuals with enlarged abdominal adipose cells. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2012, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, N.M.; Brown, K.A.; Zhou, X.K.; Gucalp, A.; Subbaramaiah, K.; Giri, D.D.; Zahid, H.; Bhardwaj, P.; Wendel, N.K.; Falcone, D.J.; et al. Metabolic Obesity, Adipose Inflammation and Elevated Breast Aromatase in Women with Normal Body Mass Index. Cancer Prev. Res. 2017, 10, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Chan, Z.; Magkos, F. Lean, but not healthy: The ‘metabolically obese, normal-weight’ phenotype. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murano, I.; Barbatelli, G.; Parisani, V.; Latini, C.; Muzzonigro, G.; Castellucci, M.; Cinti, S. Dead adipocytes, detected as crown-like structures, are prevalent in visceral fat depots of genetically obese mice. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigornia, S.J.; Farb, M.G.; Mott, M.M.; Hess, D.T.; Carmine, B.; Fiscale, A.; Joseph, L.; Apovian, C.M.; Gokce, N. Relation of depot-specific adipose inflammation to insulin resistance in human obesity. Nutr. Diabetes 2012, 2, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullooly, M.; Yang, H.P.; Falk, R.T.; Nyante, S.J.; Cora, R.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Radisky, D.C.; Visscher, D.W.; Hartmann, L.C.; Carter, J.M.; et al. Relationship between crown-like structures and sex-steroid hormones in breast adipose tissue and serum among postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, J.M.; Hoskin, T.L.; Pena, M.A.; Brahmbhatt, R.; Winham, S.J.; Frost, M.H.; Stallings-Mann, M.; Radisky, D.C.; Knutson, K.L.; Visscher, D.W.; et al. Macrophagic “crown-like structures” are associated with an increased risk of breast cancer in benign breast disease. Cancer Prev. Res. 2018, 11, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, N.M.; Zhou, X.K.; Gucalp, A.; Morris, P.G.; Howe, L.R.; Giri, D.D.; Morrow, M.; Wang, H.; Pollak, M.; Jones, L.W.; et al. Systemic correlates of white adipose tissue inflammation in early-stage breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2283–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Harvie, M.; Cutress, R.I.; Leitzmann, M.; Pischon, T.; Howell, S.; Howell, A. How to manage the obese patient with cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4284–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, N.S.; Wright, A.A. Impact of obesity on chemotherapy management and outcomes in women with gynecologic malignancies. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 138, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasznicki, J.; Sliwinska, A.; Drzewoski, J. Metformin in cancer prevention and therapy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monami, M.; Lamanna, C.; Balzi, D.; Marchionni, N.; Mannucci, E. Sulphonylureas and cancer: A case-control study. Acta Diabetol. 2009, 46, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacke, F. Cenicriviroc for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 27, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Sun, Q. Macrophage recruitment in obese adipose tissue. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, M.; Laskou, F.; Stapleton, P.P.; Hadavi, S.; Dasgupta, B. Tocilizumab (Actemra). Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 1972–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogan, P.A.; Hofer, M.; Kuemmerle-Deschner, J.B.; Kone-Paut, I.; Roesler, J.; Kallinich, T.; Horneff, G.; Calvo Penades, I.; Sevilla-Perez, B.; Goffin, L.; et al. Rapid and sustained long-term efficacy and safety of canakinumab in patients with cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome ages five years and younger. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenauer, B.; Judd, M.; Wells, G.; Burls, A.; Cranney, A.; Hochberg, M.; Tugwell, P. Infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teras, L.R.; Patel, A.V.; Wang, M.; Yaun, S.S.; Anderson, K.; Brathwaite, R.; Caan, B.J.; Chen, Y.; Connor, A.E.; Eliassen, A.H.; et al. Sustained weight loss and risk of breast cancer in women ≥50 years: A pooled analysis of prospective data. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigelson, H.S.; Caan, B.; Weinmann, S.; Leonard, A.C.; Powers, J.D.; Yenumula, P.R.; Arterburn, D.E.; Koebnick, C.; Altaye, M.; Schauer, D.P. Bariatric surgery is associated with reduced risk of breast cancer in both premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Ann. Surg. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, D.P.; Feigelson, H.S.; Koebnick, C.; Caan, B.; Weinmann, S.; Leonard, A.C.; Powers, J.D.; Yenumula, P.R.; Arterburn, D.E. Bariatric surgery and the risk of cancer in a large multisite cohort. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Quattrocchi, A.; Degrassi, F.; Catalano, F.; Basile, G.; Agodi, A. The effects of diet and dietary interventions on the quality of life among breast cancer survivors: A cross-sectional analysis and a systematic review of experimental studies. Cancers 2020, 12, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Campbell, K.L.; Hayes, S.C. Weight management and its role in breast cancer rehabilitation. Cancer 2012, 118, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.P.; Morais, C.C.; Cominetti, C. Normal-weight obesity syndrome: Diagnosis, prevalence, and clinical implications. Nutr. Rev. 2016, 74, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conus, F.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Péronnet, F. Characteristics of metabolically obese normal-weight (MONW) subjects. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 32, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study Type | Cohort | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer Risk | |||
| Prospective | 87,143 postmenopausal women | RR 1.45 (95% CI 1.27–1.66) of ER + BC in women who gained 25 kg or more since age 18 | [36] |
| Prospective | 242,918 postmenopausal women | HR 1.23 (95% CI 1.15–1.35) for ER + BC in women with a BMI > 29 | [37] |
| Meta-analysis | 57 studies from 1985–2011 | RR 1.25 (95% CI 1.07–1.46) for postmenopausal breast cancer in obese women | [38] |
| Meta-analysis | 89 studies from 1980–2012 | RR 1.39 (95% CI 1.14–1.70) for ER + BC in obese postmenopausal women No association between BMI and ER- BC | [39] |
| Prospective | 67,142 postmenopausal women | HR 1.86 (95% CI 1.60–2.17) ER + BC in women with BMI > 35.0 No association with ER- BC | [41] |
| Meta-analysis | 31 studies from 1970–2007 | 33% increase risk of ER + BC for every 5 point increase in BMI in postmenopausal women 20% decrease risk of ER + BC in obese premenopausal women | [42] |
| Meta-analysis | 11 studies through 2012 | OR 1.43 (95% CI 1.23–1.65) for TNBC in obese premenopausal women | [43] |
| Prospective | 620 patients | Increase risk of all subtypes of inflammatory breast cancer in women with BMI > 25 | [46] |
| Outcomes | |||
| Meta-analysis | 43 studies from 1965–2005 | HR 1.33 for overall (95% CI 1.21–1.47) and BC-specific survival (95% CI 1.19–1.50) | [49] |
| Meta-analysis | 82 studies through 2013 | RR 1.41 (95% CI 1.29–1.53) for overall mortality for obese women RR higher in premenopausal women (RR 1.75) then postmenopausal women (RR 1.34) | [50] |
| Prospective | 18,967 women with early stage BC | HR 1.46 for developing distant metastasis after 10 years in obese women | [51] |
| Meta-analysis | 26 studies through 2012 | RR 1.37 (95% CI 1.20–1.57) of contralateral BC in obese women | [56] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolb, R.; Zhang, W. Obesity and Breast Cancer: A Case of Inflamed Adipose Tissue. Cancers 2020, 12, 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061686
Kolb R, Zhang W. Obesity and Breast Cancer: A Case of Inflamed Adipose Tissue. Cancers. 2020; 12(6):1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061686
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolb, Ryan, and Weizhou Zhang. 2020. "Obesity and Breast Cancer: A Case of Inflamed Adipose Tissue" Cancers 12, no. 6: 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061686
APA StyleKolb, R., & Zhang, W. (2020). Obesity and Breast Cancer: A Case of Inflamed Adipose Tissue. Cancers, 12(6), 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061686





