Molecular Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Mechanisms and Targeted Therapies
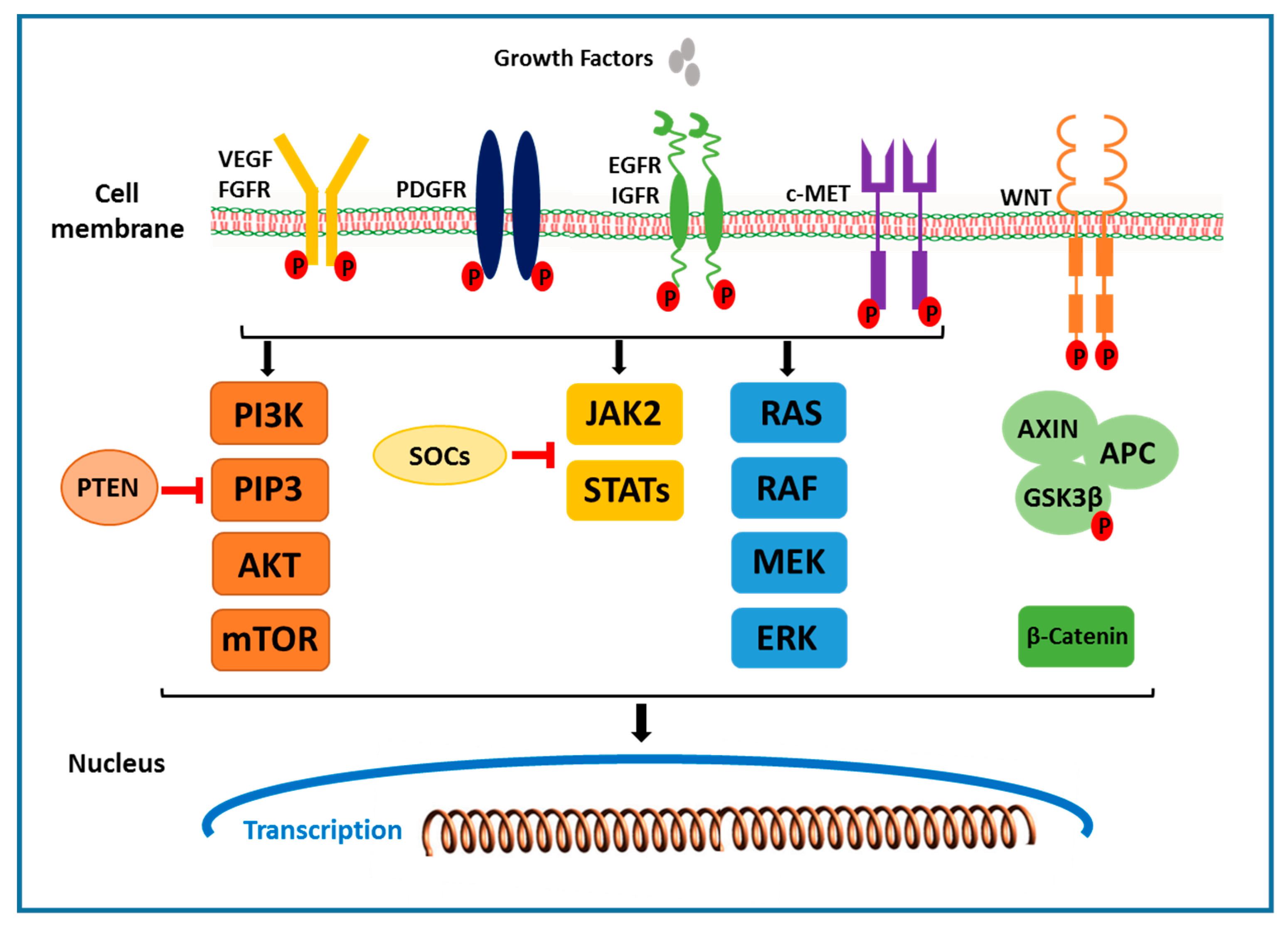
2.1. The Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Pathways
2.1.1. VEGF Receptor
2.1.2. EGFR and HGF/c-MET Signals
2.2. RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway
2.3. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
2.4. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
2.5. JAK/STAT Pathway
2.6. Hippo Signaling Pathway
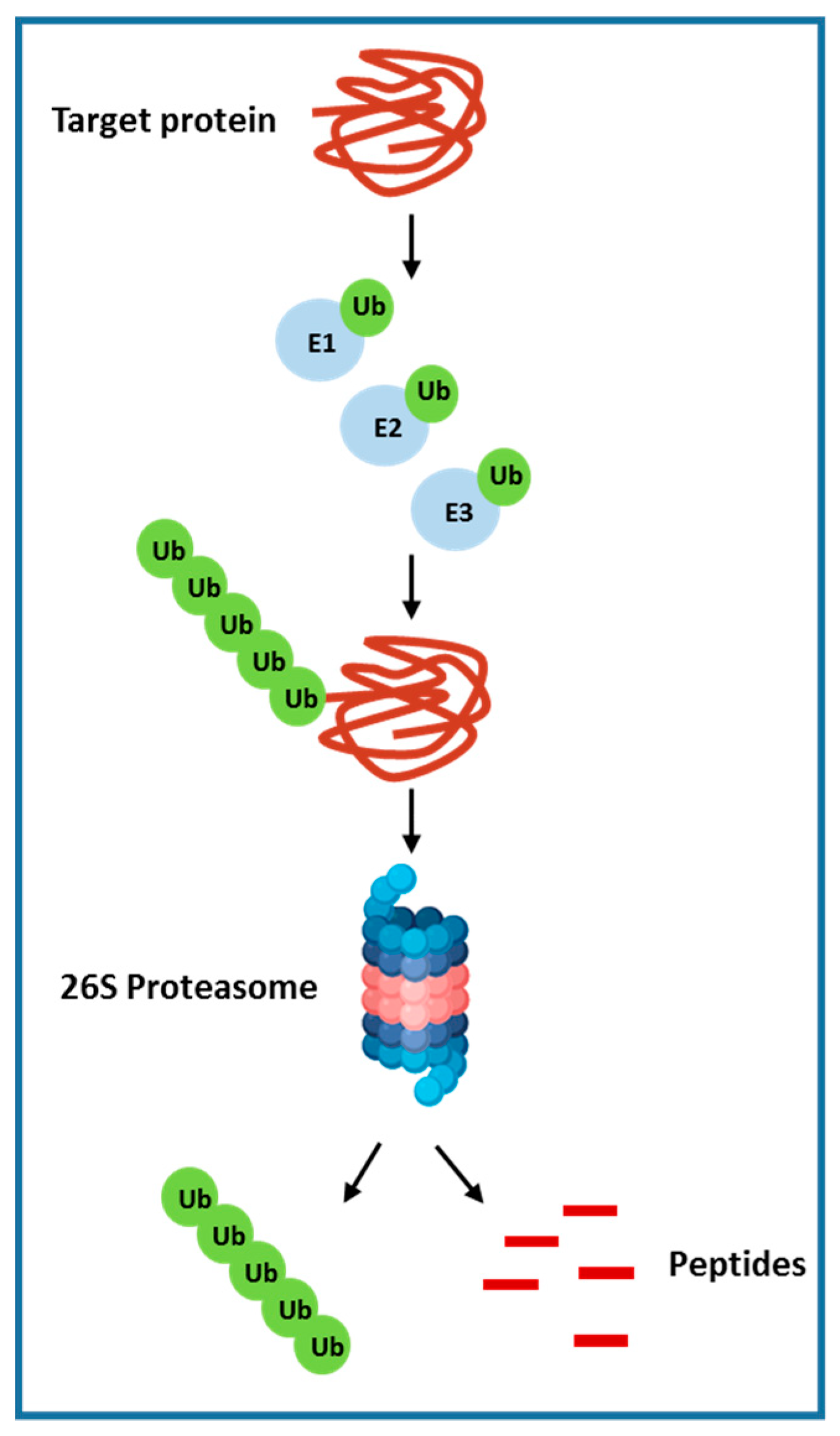
2.7. Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway
2.8. Hedgehog Signaling Pathway
2.9. Liver Cancer Stem Cells
2.10. Immune Suppression or Immune escape Mechanisms in HCC
3. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 136, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of HCC: Consider the population. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordenstedt, H.; White, D.L.; El-Serag, H.B. The changing pattern of epidemiology in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, S206–S214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Roberts, L.R. Hepatocellular carcinoma: A global view. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, H. Hepatocellular carcinoma development in cirrhosis. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 21, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.B.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Opportunities for Targeted Therapies in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8093–8108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinati, F.; Sergio, A.; Baldan, A.; Giacomin, A.; Di Nolfo, M.A.; Del Poggio, P.; Benvegnu, L.; Rapaccini, G.; Zoli, M.; Borzio, F. Early and very early hepatocellular carcinoma: When and how much do staging and choice of treatment really matter? A multi-center study. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma—Authors’ reply. Lancet 2012, 380, 470–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitroulis, D.; Damaskos, C.; Valsami, S.; Davakis, S.; Garmpis, N.; Spartalis, E.; Athanasiou, A.; Moris, D.; Sakellariou, S.; Kykalos, S. From diagnosis to treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: An epidemic problem for both developed and developing world. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 5282–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jiang, L.; Guan, X.-Y. The genetic and epigenetic alterations in human hepatocellular carcinoma: A recent update. Protein Cell 2014, 5, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y. Therapeutic approaches targeting tumor vasculature in gastrointestinal cancers. Front. Biosci. 2011, 3, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chuma, M.; Terashita, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Terashita, K. New molecularly targeted therapies against advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: From molecular pathogenesis to clinical trials and future directions. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45, E1–E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Seo, D.; Choi, K.-J.; Andersen, J.B.; Won, M.-A.; Kitade, M.; Gómez-Quiroz, L.E.; Judge, A.D.; Marquardt, J.U.; Raggi, C. Antitumor effects in hepatocarcinoma of isoform-selective inhibition of HDAC2. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4752–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimri, M.; Bilogan, C.; Pierce, L.X.; Naegele, G.; Vasanji, A.; Gibson, I.; McClendon, A.; Tae, K.; Sakaguchi, T.F. Three-dimensional structural analysis reveals a Cdk5-mediated kinase cascade regulating hepatic biliary network branching in zebrafish. Development 2017, 144, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elattar, S.; Dimri, M.; Satyanarayana, A. The tumor secretory factor ZAG promotes white adipose tissue browning and energy wasting. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4727–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Adnane, J.; Trail, P.A.; Levy, J.; Henderson, A.; Xue, D.; Bortolon, E.; Ichetovkin, M.; Chen, C.; McNabola, A. Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006) inhibits tumor growth and vascularization and induces tumor apoptosis and hypoxia in RCC xenograft models. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 59, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Carter, C.; Tang, L.; Wilkie, D.; McNabola, A.; Rong, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Vincent, P.; McHugh, M. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7099–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.R.; Gores, G.J. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Molecular Pathways and New Therapeutic Targets. Semin. Liver Dis. 2005, 25, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Steelman, L.; Lee, J.; Shelton, J.; Navolanic, P.; Blalock, W.L.; Franklin, R.; McCubrey, J. Signal transduction mediated by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway from cytokine receptors to transcription factors: Potential targeting for therapeutic intervention. Nature Publishing Group: 2003. Leukemia 2003, 17, 1263–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, G. Targeting the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semela, D.; Dufour, J.-F. Angiogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 864–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, J.; Shirabe, K.; Sugimachi, K.; Maehara, Y. Review of angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 45, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamura, T.; Saito, S.; Morita, K.; Kitamura, T.; Morimoto, M.; Kiba, T.; Numata, K.; Tanaka, K.; Sekihara, H. Detection of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma biopsy specimens. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 15, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, I.O.; Poon, R.T.; Lee, J.M.; Fan, S.T.; Ng, M.; Tso, W.K. Microvessel density, vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors Flt-1 and Flk-1/KDR in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 116, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, D.K.; Naora, H.; Yamanoi, A.; Ono, T.; Kohno, H.; Otani, H.; Nagasue, N. Requisite role of VEGF receptors in angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A comparison with angiopoietin/Tie pathway. Anticancer. Res. 2002, 22, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Poon, R.; Ho, J.; Tong, C.; Lau, C.; Ng, I.; Fan, S.T. Prognostic significance of serum vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. BJS 2004, 91, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Yano, H.; Iemura, A.; Ogasawara, S.; Haramaki, M.; Kojiro, M. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1998, 28, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Arbuthnot, P.; Kew, M.; Feitelson, M.A. Hepatitis B x antigen up-regulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 in hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2007, 45, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexia, C.; Fallot, G.; Lasfer, M.; Schweizer-Groyer, G.; Groyer, A. An evaluation of the role of insulin-like growth factors (IGF) and of type-I IGF receptor signalling in hepatocarcinogenesis and in the resistance of hepatocarcinoma cells against drug-induced apoptosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariani, E.; Lasserre, C.; Seurin, D.; Hamelin, B.; Kemeny, F.; Franco, D.; Czech, M.P.; Ullrich, A.; Brechot, C. Differential expression of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA in human primary liver cancers, benign liver tumors, and liver cirrhosis. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 6844–6849. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schirmacher, P.; Held, W.; Yang, D.; Chisari, F.; Rustum, Y.; Rogler, C. Reactivation of insulin-like growth factor II during hepatocarcinogenesis in transgenic mice suggests a role in malignant growth. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 2549–2556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lund, P.; Schubert, D.; Niketeghad, F.; Schirmacher, P. Autocrine inhibition of chemotherapy response in human liver tumor cells by insulin-like growth factor-II. Cancer Lett. 2004, 206, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. Emerging Multipotent Aspects of Hepatocyte Growth Factor. J. Biochem. 1996, 119, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, T.; Fujimoto, J.; Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Okamoto, E. Expression of hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor c-met proto-oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1997, 25, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strumberg, D.; Richly, H.; Hilger, R.A.; Schleucher, N.; Korfee, S.; Tewes, M.; Faghih, M.; Brendel, E.; Voliotis, D.; Haase, C.G. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of the Novel Raf kinase and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor BAY 43-9006 in patients with advanced refractory solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 23, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höpfner, M.; Sutter, A.P.; Huether, A.; Schuppan, D.; Zeitz, M.; Scherübl, H. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor by gefitinib for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.K.; Man, K.; Ho, J.W.; Wang, X.H.; Poon, R.T.; Sun, C.K.; Ng, K.T.; Ng, I.O.; Xu, R.; Fan, S.T. Significance of the Rac signaling pathway in HCC cell motility: Implications for a new therapeutic target. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, S.; Marais, R.; Zhu, A. The role of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4989–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.-F.; De Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Forner, A. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Kang, Y.-K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.-J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Luo, R.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Yang, T.-S. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-J.; Baik, I.H.; Ye, S.-K.; Lee, Y.-H. Molecular targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Present status and future directions. Boil. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, P.A.; Mahoney, M.R.; Allmer, C.; Thomas, J.; Pitot, H.C.; Kim, G.; Donehower, R.C.; Fitch, T.; Picus, J.; Erlichman, C. Phase II study of Erlotinib (OSI-774) in patients with advanced hepatocellular cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 6657–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissler, E.K.; Schnitzbauer, A.A.; Zülke, C.; Lamby, P.E.; Proneth, A.; Duvoux, C.; Burra, P.; Jauch, K.-W.; Rentsch, M.; Ganten, T.M. Sirolimus use in liver transplant recipients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized, multicenter, open-label phase 3 trial. Transplantation 2016, 100, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.J.; Qin, S.; Park, J.-W.; Poon, R.; Raoul, J.-L.; Philip, P.A.; Hsu, C.-H.; Hu, T.-H.; Heo, J.; Xu, J. Brivanib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with unresectable, advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Results from the randomized phase III BRISK-FL study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3517–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Decaens, T.; Raoul, J.-L.; Boucher, E.; Kudo, M.; Chang, C.; Kang, Y.-K.; Assenat, E.; Lim, H.-Y.; Boige, V. Brivanib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who were intolerant to sorafenib or for whom sorafenib failed: Results from the randomized phase III BRISK-PS study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3509–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Kang, Y.-K.; Lin, D.-Y.; Park, J.-W.; Kudo, M.; Qin, S.; Chung, H.-C.; Song, X.; Xu, J.; Poggi, G. Sunitinib versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular cancer: Results of a randomized phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 4067–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, H.C.; Chen, P.J.; Carr, B.I.; Knox, J.J.; Gill, S.; Ansell, P.; McKeegan, E.M.; Dowell, B.; Pedersen, M.; Qin, Q. Phase 2 trial of linifanib (ABT-869) in patients with unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2012, 119, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.B.; Cohen, E.I.; Ocean, A.; Lehrer, D.; Goldenberg, A.; Knox, J.J.; Chen, H.; Clark-Garvey, S.; Weinberg, A.; Mandeli, J. Phase II trial evaluating the clinical and biologic effects of bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2992–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, S. NCCTG phase II trial (N044J) of AZD2171 for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)-interim review of toxicity. In Proceedings of the 4th Gastrointestinal Cancer Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 19–21 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, A.; Rimassa, L.; Borbath, I.; Daniele, B.; Salvagni, S.; Van Laethem, J.L.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; Trojan, J.; Kolligs, F.T.; Weiss, A. Tivantinib for second-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, I.; Baron, A.; Roberts, S.; Junker, U.; Palacay-Ramona, M.; Masson, E.; Kay, A.; Wiedenmann, B.; Laurent, D.; Cebon, J. Influence of hepatic dysfunction on safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics (PK) of PTK787/ZK 222584 in patients (Pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.; Gansukh, B.; Chou, J.; Shia, J.; Capanu, M.; Kalin, M.; Chen, H.; Zojwalla, N.; Katz, S.; Reidy, D. Phase II study of cixutumumab (IMC-A12, NSC742460; C) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29 (Suppl. 15), 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Doria, C.; Liu, Y. Targeted Therapies in the Treatment of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2013, 7, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, S.; Fartoux, L.; Bouattour, M.; Bumsel, F.; Dreyer, C.; Raymond, E.; Rosmorduc, O. A phase I study of AVE1642, a human monoclonal antibody–blocking insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), given as a single agent and in combination with sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29 (Suppl. 4), 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, G. Mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma and challenges and opportunities for molecular targeted therapy. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1964–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.D.; Bharathkumar, H.; Bulusu, K.C.; Pandey, V.; Rangappa, S.; Fuchs, J.E.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Dai, X.; Li, F.; Deivasigamani, A. Development of a novel azaspirane that targets the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 34296–34307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, X.; Sun, X.; Sun, K.; Sui, H.; Qin, J.; Li, Q. Inhibitory effect of bufalin combined with Hedgehog signaling pathway inhibitors on proliferation and invasion and metastasis of liver cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, K.-S.; Jeng, C.-J.; Jeng, W.-J.; Sheen, I.-S.; Chang, C.-F.; Hsiau, H.-I.; Hung, Z.-H.; Yu, M.-C.; Chang, F.-Y. Sonic hedgehog pathway inhibitor mitigates mouse hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. 2015, 210, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollob, J.A.; Wilhelm, S.; Carter, C.; Kelley, S.L. Role of Raf kinase in cancer: Therapeutic potential of targeting the Raf/MEK/ERK signal transduction pathway. Semin. Oncol. 2006, 33, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galuppo, R.; Ramaiah, D.; Ponte, O.M.; Gedaly, R. Molecular therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma: What can we target? Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaschek-Wiener, J.; Wacheck, V.; Kloog, Y.; Jansen, B. Ras inhibition leads to transcriptional activation of p53 and down-regulation of Mdm2: Two mechanisms that cooperatively increase p53 function in colon cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2004, 16, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, H.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Chow, P.K.-H.; Tan, P.H.; Soo, K.C.; Tran, E. Over-expression of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK in hepatocellular carcinoma: Its role in tumor progression and apoptosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2003, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Horimoto, M.; Wada, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Kasahara, A.; Ueki, T.; Hirano, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Fujimoto, J. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases/extracellular signal-regulated kinases in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1998, 27, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.Y.; Zheng, H.; Tan, Y.; Cheng, R.X. Effect of phosphorylation of MAPK and Stat3 and expression of c-fos and c-jun proteins on hepatocarcinogenesis and their clinical significance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 7, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galuppo, R.; Maynard, E.; Shah, M.; Daily, M.F.; Chen, C.; Spear, B.T.; Gedaly, R. Synergistic inhibition of HCC and liver cancer stem cell proliferation by targeting RAS/RAF/MAPK and WNT/β-catenin pathways. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 1709–1713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huether, A.; Höpfner, M.; Sutter, A.P.; Baradari, V.; Schuppan, D.; Scherübl, H. Signaling pathways involved in the inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor by erlotinib in hepatocellular cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5160–5167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Avila, M.A.; Berasain, C.; Sangro, B.; Prieto, J. New therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2006, 25, 3866–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; Abrams, S.L.; Wong, E.W.; Chang, F.; Lehmann, B.; Terrian, D.M.; Milella, M.; Tafuri, A. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2006, 1773, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Lui, V.W.; Yeo, W. Erratum: Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2011, 7, 1149–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, J.; Cao, H.; Pilo, M.G.; Cigliano, A.; Shao, Z.; Xu, M.; Ribback, S.; Dombrowski, F.; Calvisi, D.F. Loss of Pten synergizes with c-Met to promote hepatocellular carcinoma development via mTORC2 pathway. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, e417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Kataoka, E.; Sasaki, T.; Hamada, K.; Sasaki, J.; Mizuno, K.; Hasegawa, G.; Kishimoto, H.; Iizuka, M. Hepatocyte-specific Pten deficiency results in steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinomas. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyault, S.; Rickman, D.S.; De Reyniès, A.; Balabaud, C.; Rebouissou, S.; Jeannot, E.; Hérault, A.; Saric, J.; Belghiti, J.; Franco, D. Transcriptome classification of HCC is related to gene alterations and to new therapeutic targets. Hepatology 2007, 45, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, A.; Chiang, D.Y.; Newell, P.; Peix, J.; Thung, S.; Alsinet, C.; Tovar, V.; Roayaie, S.; Minguez, B.; Sole, M. Pivotal role of mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1972–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, F.; Kannangai, R.; Adegbola, O.; Wang, J.; Su, G.; Torbenson, M. mTOR and P70 S6 kinase expression in primary liver neoplasms. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8421–8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dynlacht, B.D. Live or let die: E2F1 and PI3K pathways intersect to make life or death decisions. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ladu, S.; Calvisi, D.F.; Conner, E.A.; Farina, M.; Factor, V.M.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. E2F1 inhibits c-Myc-driven apoptosis via PIK3CA/Akt/mTOR and COX-2 in a mouse model of human liver cancer. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-L.; Ning, G.; Chen, L.-B.; Lian, Y.-F.; Gu, Y.-R.; Wang, J.-L.; Chen, D.-M.; Wei, H.; Huang, Y.-H. Promising diagnostic and prognostic value of E2Fs in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 1725–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieghart, W.; Fuereder, T.; Schmid, K.; Cejka, D.; Werzowa, J.; Wrba, F.; Wang, X.; Gruber, D.; Rasoul-Rockenschaub, S.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M. Mammalian target of rapamycin pathway activity in hepatocellular carcinomas of patients undergoing liver transplantation. Transplantation 2007, 83, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semela, D.; Piguet, A.-C.; Kolev, M.; Schmitter, K.; Hlushchuk, R.; Djonov, V.; Stoupis, C.; Dufour, J.-F. Vascular remodeling and antitumoral effects of mTOR inhibition in a rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Kudo, M.; Assenat, E.; Cattan, S.; Kang, Y.-K.; Lim, H.Y.; Poon, R.T.; Blanc, J.-F.; Vogel, A.; Chen, C.-L. Effect of everolimus on survival in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma after failure of sorafenib: The EVOLVE-1 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014, 312, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabinski, N.; Ewald, F.; Hofmann, B.T.; Staufer, K.; Schumacher, U.; Nashan, B.; Jücker, M. Combined targeting of AKT and mTOR synergistically inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, U.; Thompson, M.D.; Cui, S.; Liu, B.; Cieply, B.; Monga, S.P. Wnt/β-catenin signaling mediates oval cell response in rodents. Hepatology 2008, 47, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langeswaran, K.; Gowthamkumar, S.; Vijayaprakash, S.; Revathy, R.; Balasubramanian, M. Influence of limonin on Wnt signalling molecule in HepG2 cell lines. J. Nat. Sci. Boil. Med. 2013, 4, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renumathy, D.; Salome, B.; Roberts, L.R. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma and impact of therapeutic advances. F1000Research 2016, 5, 879. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, R.H.; Van Es, J.H.; Clevers, H. Caught up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2003, 1653, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.M.; Fan, S.T.; Ng, I.O. β-Catenin mutation and overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance. Cancer 2001, 92, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.A.; Chiariello, C.S.; Capilla, E.; Miller, F.; Bahou, W.F. Development of hepatocellular carcinoma in Iqgap2-deficient mice is IQGAP1 dependent. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2008, 28, 1489–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, K.H.; Nguyen, C.; Ma, H.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, K.W.; Eguchi, M.; Moon, R.T.; Teo, J.-L.; Oh, S.W.; Kim, H.Y. A small molecule inhibitor of β-catenin/cyclic AMP response element-binding protein transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12682–12687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; He, B.; Xu, Z.; Uematsu, K.; Mazieres, J.; Fujii, N.; Mikami, I.; Reguart, N.; McIntosh, J.K.; Kashani-Sabet, M. An anti-Wnt-2 monoclonal antibody induces apoptosis in malignant melanoma cells and inhibits tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5385–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, E.; Keller, J.; Wormhoudt, T.; Giardiello, F.M.; Offerhaus, G.; Van Der Neut, R.; Pals, S. Sulindac targets nuclear β-catenin accumulation and Wnt signalling in adenomas of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis and in human colorectal cancer cell lines. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dihlmann, S.; Klein, S.; Von Knebel Doeberitz, M. Reduction of β-catenin/T-cell transcription factor signaling by aspirin and indomethacin is caused by an increased stabilization of phosphorylated β-catenin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2003, 2, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aittomäki, S.; Pesu, M. Therapeutic Targeting of the JAK/STAT Pathway. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 114, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, J.S.; Rosler, K.M.; Harrison, D. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1281–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wormald, S.; Hilton, D. Inhibitors of Cytokine Signal Transduction. J. Boil. Chem. 2003, 279, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, D.L.; Hilton, D. SOCS Proteins: Negative Regulators of Cytokine Signaling. Stem Cells 2001, 19, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, F.; Khoshmirsafa, M.; Aazami, H.; Mohsenzadegan, M.; Sedighi, G.; Bahar, M. The role of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and its regulators in the fate of T helper cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2017, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Snowden, J.; Zeidler, M.; Danson, S. The role of JAK/STAT signalling in the pathogenesis, prognosis and treatment of solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.; Zheng, H.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Barber, T.D.; Gong, Z.; Gao, H.; Hao, K.; Willard, M.D.; Xu, J. Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, E.; Kumada, T.; Takai, S.; Ishisaki, A.; Noda, T.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Yoshimi, N.; Kato, K.; Toyoda, H.; Kaneoka, Y. Attenuated phosphorylation of heat shock protein 27 correlates with tumor progression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 337, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvisi, D.F.; Ladu, S.; Gorden, A.; Farina, M.; Conner, E.A.; Lee, J.S.; Factor, V.M.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Ubiquitous activation of Ras and Jak/Stat pathways in human HCC. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.; Zatloukal, K.; Scheuch, H.; Stepniak, E.; Wagner, E.F. Proliferation of human HCC cells and chemically induced mouse liver cancers requires JNK1-dependent p21 downregulation. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3943–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boopathy, G.T.K.; Hong, W. Role of Hippo Pathway-YAP/TAZ Signaling in Angiogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Boil. 2019, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calses, P.C.; Crawford, J.J.; Lill, J.R.; Dey, A. Hippo Pathway in Cancer: Aberrant Regulation and Therapeutic Opportunities. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Zhu, H.-R.; Liu, T.-T.; Shen, X.-Z.; Zhu, J.-M. The Hippo pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma: Non-coding RNAs in action. Cancer Lett. 2017, 400, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Wei, X.; Li, W.; Udan, R.S.; Yang, Q.; Kim, J.; Xie, J.; Ikenoue, T.; Yu, J.; Li, L. Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genome Res. 2007, 21, 2747–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam-Himlin, D.M.; Daniels, J.A.; Gayyed, M.F.; Dong, J.; Maitra, A.; Pan, D.; Montgomery, E.A.; Anders, R.A. The hippo pathway in human upper gastrointestinal dysplasia and carcinoma: A novel oncogenic pathway. Int. J. Pancreatol. 2007, 37, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, A.A.; Gayyed, M.F.; Klein, A.P.; Dong, J.; Maitra, A.; Pan, D.; Montgomery, E.A.; Anders, R.A. Expression of Yes-associated protein in common solid tumors. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, C.; Huang, W.; Tu, S.; Wan, F. Effect of Mst1 overexpression on the growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells and the sensitivity to cisplatin in vitro. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodowska, K.; Al-Moujahed, A.; Marmalidou, A.; zu Horste, M.M.; Cichy, J.; Miller, J.W.; Gragoudas, E.; Vavvas, D.G. The clinically used photosensitizer Verteporfin (VP) inhibits YAP-TEAD and human retinoblastoma cell growth in vitro without light activation. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 124, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Xie, M.; Scott, A.W.; Jin, J.; Ma, L.; Dong, X.; Skinner, H.D.; Johnson, R.L.; Ding, S.; Ajani, J.A. A novel YAP1 inhibitor targets CSC-enriched radiation-resistant cells and exerts strong antitumor activity in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 17, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bum-Erdene, K.; Zhou, D.; Gonzalez-Gutierrez, G.; Ghozayel, M.K.; Si, Y.; Xu, D.; Shannon, H.E.; Bailey, B.J.; Corson, T.W.; Pollok, K.E. Small-Molecule Covalent Modification of Conserved Cysteine Leads to Allosteric Inhibition of the TEAD⋅Yap Protein-Protein Interaction. Cell Chem. Boil. 2019, 26, 378–389.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, S.P. Hepatocellular carcinoma and the ubiquitin–proteasome system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2008, 1782, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, A.M.; Seth, A.K. The ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation pathway in cancer: Therapeutic implications. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 2217–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, C.-C.H.; Weissman, A.M. Regulating the p53 system through ubiquitination. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2096–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Hakimi, M.-A.; Chen, X.; Kumaraswamy, E.; Cooch, N.S.; Godwin, A.K.; Shiekhattar, R. Regulation of BRCC, a holoenzyme complex containing BRCA1 and BRCA2, by a signalosome-like subunit and its role in DNA repair. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chang, C.; Gehling, D.J.; Hemmati-Brivanlou, A.; Derynck, R. Regulation of Smad degradation and activity by Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nybakken, K.; Perrimon, N. Hedgehog signal transduction: Recent findings. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002, 12, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, C.M.; Viscardi, G.; Papaccio, F.; Esposito, G.; Martini, G.; Ciardiello, D.; Martinelli, E.; Ciardiello, F.; Morgillo, F. Implication of the Hedgehog pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4330–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, C.; Lu, L.; Magliato, S.; Wu, T. Hedgehog signaling pathway regulates autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 2013, 58, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.M.; Karhadkar, S.S.; Maitra, A.; De Oca, R.M.; Gerstenblith, M.R.; Briggs, K.; Parker, A.R.; Shimada, Y.; Eshleman, J.R.; Watkins, D.N. Widespread requirement for Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract tumours. Nature 2003, 425, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzumanyan, A.; Sambandam, V.; Clayton, M.M.; Choi, S.S.; Xie, G.; Diehl, A.M.; Yu, D.-Y.; Feitelson, M.A. Hedgehog signaling blockade delays hepatocarcinogenesis induced by hepatitis B virus X protein. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5912–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicklick, J.K.; Li, Y.-X.; Jayaraman, A.; Kannangai, R.; Qi, Y.; Vivekanandan, P.; Ludlow, J.W.; Owzar, K.; Chen, W.; Torbenson, M.S. Dysregulation of the Hedgehog pathway in human hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2005, 27, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; He, J.; Zhang, X.; Bian, Y.; Yang, L.; Xie, G.; Zhang, K.; Tang, W.; Stelter, A.A.; Wang, Q. Activation of the hedgehog pathway in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Yoon, J.W.; Xiao, X.; Dean, N.M.; Monia, B.P.; Marcusson, E.G. Selective down-regulation of glioma-associated oncogene 2 inhibits the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3583–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, N.; Wang, X.W. Novel therapeutic strategies for targeting liver cancer stem cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, H.; Tao, K.; Li, R.; Song, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, F.; Dou, K. Expression and clinical significance of the stem cell marker CD133 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2008, 62, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, C.; Kim, B.H.; Yi, E.H.; Choi, K.J.; Kim, E.K.; Jeong, J.M.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, J.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Jeong, W.I. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-mediated CD133 up-regulation contributes to promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1160–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormandy, L.A.; Hillemann, T.; Wedemeyer, H.; Manns, M.P.; Greten, T.F.; Korangy, F. Increased populations of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2457–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.-Q.; Li, W.-M.; Lu, Z.-Q.; Yao, Y.-M. Roles of Tregs in development of hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7971–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Ye, Q.-H.; Jia, H.-L.; He, P.; Zanetti, K.A.; Kammula, U.S.; Chen, Y.; Qin, L.-X.; Tang, Z.-Y. Prediction of venous metastases, recurrence, and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma based on a unique immune response signature of the liver microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, E.; Okumoto, K.; Adachi, T.; Takeda, T.; Ito, J.-I.; Sugahara, K.; Watanabe, H.; Saito, K.; Saito, T.; Togashi, H. Possible contribution of circulating interleukin-10 (IL-10) to anti-tumor immunity and prognosis in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2003, 27, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Kryczek, I.; Chen, L.; Zou, W.; Welling, T.H. Kupffer cell suppression of CD8+ T cells in human hepatocellular carcinoma is mediated by B7-H1/programmed death-1 interactions. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8067–8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Shi, M.; Zeng, Z.; Qi, R.Z.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yang, Y.P.; Tien, P.; Wang, F.S. PD-1 and PD-L1 upregulation promotes CD8+ T-cell apoptosis and postoperative recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 128, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Melero, I.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Welling, T.H.; Yau, T.C.; Yeo, W.; Chopra, A.; Grosso, J.; Lang, L.; Anderson, J. Phase I/II safety and antitumor activity of nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): CA209-040. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33 (Suppl. 18), LBA101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, M.; Joshi, J.; Shrivastava, N.; Ghosh, S.; Chakraborti, R.; Indracanti, P.K. Prilocaine hydrochloride protects zebrafish from lethal effects of ionizing radiation: Role of hematopoietic cell expansion. Tokai J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2015, 40, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dimri, M.; Joshi, J.; Chakrabarti, R.; Sehgal, N.; Sureshbabu, A.; Prem Kumar, I. Todralazine protects zebrafish from lethal effects of ionizing radiation: Role of hematopoietic cell expansion. Zebrafish 2015, 12, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J.; Dimri, M.; Ghosh, S.; Shrivastava, N.; Chakraborti, R.; Sehgal, N.; Ray, J.; Kumar, I.P. Ligand and Structure Based Models for the Identification of Beta 2 Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists. Curr. Comput. Drug Des. 2015, 11, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, M.; Humphries, A.; Laknaur, A.; Elattar, S.; Lee, T.J.; Sharma, A.; Kolhe, R.; Ande, S. Nqo1 ablation inhibits activation of the PI 3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways and blocks metabolic adaptation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 71, 549–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ng, H.L.H.; Lu, A.; Lin, C.; Zhou, L.; Lin, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H. Drug delivery system targeting advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Current and future. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Boil. Med. 2016, 12, 853–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Targets | Therapeutic Agents | Phase | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| VEGFR, Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK, PDGFR, c-KIT, RET | Sorafenib | 3 | [40,41] |
| VEGFR | Ramucirumab | 3 | [42] |
| VEGFR, PDGFR, FGFR, RET, SCFR | Lenvatinib | 3 | [42] |
| VEGFR, PDGFR, BRAFFGFR, KIT, RET | Regorafenib | 3 | |
| EGFR/ErbB1/Her1 | Erlotinib | 3 | [43] |
| PI3K/Akt/mTOR | Everolimus | 3 | |
| PI3K/Akt/mTOR | Sirolimus | 3 | [44] |
| c-MET | Cabozantinib | 3 | |
| VEGFR2, FGFR1 | Brivanib | 3 | [45,46] |
| VEGFR, PDGFR, c-KIT, RET | Sunitinib | 3 | [47] |
| VEGFR, PDGFR | Linifanib | 2 | [48] |
| VEGFR, FGFR, PDGFR, c-KIT | E-7080 | 2 | |
| VEGFR2, FGFR, PDGFR | TSU-68 | 2 | |
| VEGFR2, MET, RET | XL-184 | 2 | |
| VEGF | Bevacizumab | 2 | [49] |
| VEGFR, PDGFR, c-KIT | Cediranib | 2 | [50] |
| EGFR | Cetuximab | 2 | [42] |
| c-MET | Tivanitib | 2 | [51] |
| VEGFR, PDGFR, FGFR | BIBF-1120 | 2 | [42] |
| VEGFR, EGFR | Vatalanib (PTK787) | 2 | [52] |
| IGF/IGFR | IMC-A12 | 2 | [53] |
| IGF/IGFR | AVE1642 | 1 | [54,55] |
| VEGFR, PDGFR, FGFR-1Raf, RET, c-KIT | BAY73-4506 | 1 | [42] |
| IGF/IGFR | BIIB922 | ||
| MEK inhibitor | CI-1040 | [19] | |
| MEK inhibitor | PD 0325901 | [19] | |
| PI3K/Akt/mTOR | AZD8055 | [56] | |
| Wnt-β-catenin | PFK118-310 | [56] | |
| Wnt-β-catenin | PFK115-584 | ||
| Wnt-β-catenin | CGP049090 | ||
| 26 S Proteasome | Bortezomib | [19] | |
| STAT3 | CIMO | [57] | |
| Gli1 and Gli3 | Bufalin | [58] | |
| Smo | GDC-0449 | [59] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimri, M.; Satyanarayana, A. Molecular Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020491
Dimri M, Satyanarayana A. Molecular Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2020; 12(2):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020491
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimri, Manali, and Ande Satyanarayana. 2020. "Molecular Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 12, no. 2: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020491
APA StyleDimri, M., & Satyanarayana, A. (2020). Molecular Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 12(2), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020491




