Regulators at Every Step—How microRNAs Drive Tumor Cell Invasiveness and Metastasis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
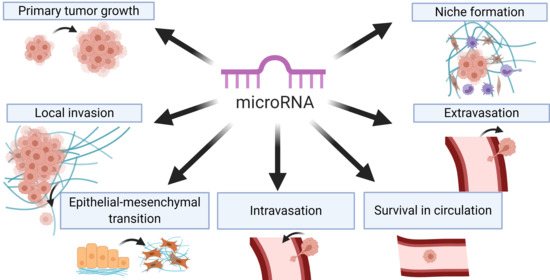
2. Tumor Cell Migration and Local Invasion
2.1. Step 1: Polarization of the Cytoskeleton and Formation of the Leading Protrusion
2.2. Step 2: Formation of Focalized Clusters by Recruitment and Adhesion of Cell Surface Receptors to ECM
2.2.1. Integrins
2.2.2. Podoplanin
2.2.3. CD44
2.2.4. Syndecan-1
2.2.5. Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK)
2.2.6. Production of ECM
2.2.7. Cadherins
2.2.8. JAM-A
2.3. Step 3: Local Proteolysis of ECM
2.4. Step 4: Cell Contraction by Actomyosin, Myosin II Activation by the Small GTPase Rho and Step 5: Rotation of the Adhesive Bonds on the Trailing Edge
3. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)
4. Angiogenesis
4.1. Regulation of Angiogenesis by miRNA
4.2. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A (VEGF-A)
4.3. Thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1)
4.4. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF)
4.5. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Alpha (HIF1a)
5. Chemokines and Growth Factors
6. Intravasation, Systemic Circulation, and Extravasation
6.1. Intravasation
6.2. Systemic Circulation
6.3. Extravasation
7. Metastatic Colonization
8. Tumor–Stroma Interactions
8.1. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs– Tumor Cells Interactions
8.2. Immune Cells–Tumor Cells Interactions
9. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Cancer
10. Challenges for the Use of miRNAs in Clinical Oncology
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedl, P.; Alexander, S. Cancer invasion and the microenvironment: Plasticity and reciprocity. Cell 2011, 147, 992–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.G.; Sanders, A.J.; Katoh, M.; Ungefroren, H.; Gieseler, F.; Prince, M.; Thompson, S.K.; Zollo, M.; Spano, D.; Dhawan, P.; et al. Tissue invasion and metastasis: Molecular, biological and clinical perspectives. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, S244–S275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, A.F.; Groom, A.C.; MacDonald, I.C. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doglioni, G.; Parik, S.; Fendt, S.-M. Interactions in the (Pre)metastatic Niche Support Metastasis Formation. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valastyan, S.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumor metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 2011, 147, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, L.F.R.; MacRae, I.J. Regulation of microRNA function in animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.-H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grzywa, T.M.; Klicka, K.; Rak, B.; Mehlich, D.; Garbicz, F.; Zieliński, G.; Maksymowicz, M.; Sajjad, E.; Włodarski, P.K. Lineage-dependent role of miR-410-3p as oncomiR in gonadotroph and corticotroph pituitary adenomas or tumor suppressor miR in somatotroph adenomas via MAPK, PTEN/AKT, and STAT3 signaling pathways. Endocrine 2019, 65, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dalmay, T.; Edwards, D.R. MicroRNAs and the hallmarks of cancer. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6170–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vincent, K.; Pichler, M.; Lee, G.-W.; Ling, H. MicroRNAs, genomic instability and cancer. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 14475–14491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shirjang, S.; Mansoori, B.; Asghari, S.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Mohammadi, A.; Gjerstorff, M.; Baradaran, B. MicroRNAs in cancer cell death pathways: Apoptosis and necroptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 139, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroza-Torres, A.; Romero-Córdoba, S.L.; Justo-Garrido, M.; Salido-Guadarrama, I.; Rodríguez-Bautista, R.; Montaño, S.; Muñiz-Mendoza, R.; Arriaga-Canon, C.; Fragoso-Ontiveros, V.; Álvarez-Gómez, R.M.; et al. MicroRNAs in Tumor Cell Metabolism: Roles and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Chu, X. New insights into the regulatory role of microRNA in tumor angiogenesis and clinical implications. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, M.; Xu, L.; Jiao, Y.; Luo, S.; Li, A.; Wu, K. The role of cancer-derived microRNAs in cancer immune escape. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayraktar, R.; Van Roosbroeck, K.; Calin, G.A. Cell-to-cell communication: MicroRNAs as hormones. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paladini, L.; Fabris, L.; Bottai, G.; Raschioni, C.; Calin, G.A.; Santarpia, L. Targeting microRNAs as key modulators of tumor immune response. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Syed, S.N.; Frank, A.-C.; Raue, R.; Brüne, B. MicroRNA-A Tumor Trojan Horse for Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cells 2019, 8, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Young, J.; Prabhala, H.; Pan, E.; Mestdagh, P.; Muth, D.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Reinhardt, F.; Onder, T.T.; Valastyan, S.; et al. miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 2007, 449, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Jin, T.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.B. MicroRNA-17-5p promotes chemotherapeutic drug resistance and tumour metastasis of colorectal cancer by repressing PTEN expression. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2974–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Shi, C.; Xia, Y.; Peng, J.; Liu, W.; Yang, Z.; et al. Elevated oncofoetal miR-17-5p expression regulates colorectal cancer progression by repressing its target gene P130. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Yin, S.; Hao, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Ma, M.; Chang, Q.; Xi, J.J. miR-19b promotes tumor growth and metastasis via targeting TP53. RNA 2014, 20, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asangani, I.A.; Rasheed, S.A.; Nikolova, D.A.; Leupold, J.H.; Colburn, N.H.; Post, S.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.-W.; Chang, Y.-L.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lin, J.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Pan, S.-H.; Wu, C.-T.; Chen, H.-Y.; Yang, S.-C.; Hong, T.-M.; et al. MicroRNA-135b promotes lung cancer metastasis by regulating multiple targets in the Hippo pathway and LZTS1. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, M.A.; Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Thompson, C.L.; Danielpour, D.; Schiemann, W.P. TGF-β upregulates miR-181a expression to promote breast cancer metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Penna, E.; Orso, F.; Cimino, D.; Tenaglia, E.; Lembo, A.; Quaglino, E.; Poliseno, L.; Haimovic, A.; Osella-Abate, S.; De Pittà, C.; et al. microRNA-214 contributes to melanoma tumour progression through suppression of TFAP2C. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1990–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, C.; Ashktorab, H.; Pang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sha, W.; Liu, Y.; Gu, X. MicroRNA-211 expression promotes colorectal cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo by targeting tumor suppressor CHD5. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Gong, T.; Li, M.; Sun, L.; Ji, G.; Shi, Y.; Han, Z.; et al. miRNA-223 promotes gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting tumor suppressor EPB41L3. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tivnan, A.; Tracey, L.; Buckley, P.G.; Alcock, L.C.; Davidoff, A.M.; Stallings, R.L. MicroRNA-34a is a potent tumor suppressor molecule in vivo in neuroblastoma. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Lv, Z.; He, G.; Zhao, W.; Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Bian, X.; Liao, W.; et al. MicroRNA-137, an HMGA1 target, suppresses colorectal cancer cell invasion and metastasis in mice by directly targeting FMNL2. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 624–635.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Chaudhuri, A.; Talmon, G.; Wisecarver, J.L.; Are, C.; Brattain, M.; Wang, J. MicroRNA-192 suppresses liver metastasis of colon cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5332–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.X.; Chang, Y.; Meng, F.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Xie, Q.H.; Tang, F.; Li, P.Y.; Song, Y.H.; Lin, J.S. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3357–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesanakurti, D.; Maddirela, D.R.; Chittivelu, S.; Rao, J.S.; Chetty, C. Suppression of tumor cell invasiveness and in vivo tumor growth by microRNA-874 in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 434, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Trang, P.; Wiggins, J.F.; Patrawala, L.; Cheng, A.; Ford, L.; Weidhaas, J.B.; Brown, D.; Bader, A.G.; Slack, F.J. The let-7 microRNA reduces tumor growth in mouse models of lung cancer. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhawan, A.; Scott, J.G.; Harris, A.L.; Buffa, F.M. Pan-cancer characterisation of microRNA across cancer hallmarks reveals microRNA-mediated downregulation of tumour suppressors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.C.; Yu, D.; Lee, Y.S.; Wentzel, E.A.; Arking, D.E.; West, K.M.; Dang, C.V.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A.; Mendell, J.T. Widespread microRNA repression by Myc contributes to tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merritt, W.M.; Lin, Y.G.; Han, L.Y.; Kamat, A.A.; Spannuth, W.A.; Schmandt, R.; Urbauer, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Cheng, J.F.; Nick, A.M.; et al. Dicer, Drosha, and outcomes in patients with ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martello, G.; Rosato, A.; Ferrari, F.; Manfrin, A.; Cordenonsi, M.; Dupont, S.; Enzo, E.; Guzzardo, V.; Rondina, M.; Spruce, T.; et al. A MicroRNA Targeting Dicer for Metastasis Control. Cell 2010, 141, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acunzo, M.; Romano, G.; Wernicke, D.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA and cancer—A brief overview. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2015, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theveneau, E.; Mayor, R. Cadherins in collective cell migration of mesenchymal cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedl, P.; Locker, J.; Sahai, E.; Segall, J.E. Classifying collective cancer cell invasion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, P.T.; Zech, T. Actin-Based Cell Protrusion in a 3D Matrix. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Liu, F.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, F. miR-133 is a key negative regulator of CDC42-PAK pathway in gastric cancer. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 2667–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Jin, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Song, X. MiR-186 Inhibited Migration of NSCLC via Targeting cdc42 and Effecting EMT Process. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, N.; Li, S.; Fang, J.H.; Chen, M.X.; Yang, J.; Jia, W.H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, S.M. MicroRNA-195 suppresses angiogenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the expression of VEGF, VAV2, and CDC42. Hepatology 2013, 58, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xu, W.; Wang, D.; Yan, J. miR-330 regulates the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells by targeting Cdc42. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 431, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lang, N.; Qiu, M.; Xu, F.; Li, Q.; Tang, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; et al. miR-137 targets Cdc42 expression, induces cell cycle G1 arrest and inhibits invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.C.; Lee, C.T.; Lee, J.C.; Liu, Y.W.; Chen, Y.J.; Tseng, J.T.; Kang, J.W.; Sheu, B.S.; Lin, B.W.; Hung, L.Y. Epigenetic silencing of miR-137 contributes to early colorectal carcinogenesis by impaired Aurora-A inhibition. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76852–76866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balaguer, F.; Link, A.; Lozano, J.J.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Nagasaka, T.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Epigenetic silencing of miR-137 is an early event in colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6609–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, S.; Paterson, H.F.; Marshall, C.J. Cdc42-MRCK and Rho-ROCK signalling cooperate in myosin phosphorylation and cell invasion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cai, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. MicroRNA-142-3p, a new regulator of RAC1, suppresses the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Pu, J.; Qi, T.; Qi, M.; Yang, C.; Li, S.; Huang, K.; Zheng, L.; Tong, Q. MicroRNA-145 inhibits the growth, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis of neuroblastoma cells through targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha. Oncogene 2014, 33, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.-Y.; Chung, K.-H.; Deo, M.; Thompson, R.C.; Turner, D.L. MicroRNA miR-124 regulates neurite outgrowth during neuronal differentiation. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 2618–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humphries, B.A.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C. MicroRNA Regulation of the Small Rho GTPase Regulators-Complexities and Opportunities in Targeting Cancer Metastasis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, A.; Yu, J.; Shi, F.; Zhou, X. MicroRNA-138 suppresses invasion and promotes apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 2009, 286, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rath, N.; Olson, M.F. Rho-associated kinases in tumorigenesis: Re-considering ROCK inhibition for cancer therapy. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, A.; Guan, Y. microRNA-124 inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulating ROCK1 in glioma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Guo, J.; Zheng, L.; Li, C.; Zheng, T.M.; Tanyi, J.L.; Liang, S.; Benedetto, C.; Mitidieri, M.; Katsaros, D.; et al. The heterochronic microRNA let-7 inhibits cell motility by regulating the genes in the actin cytoskeleton pathway in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwickert, A.; Weghake, E.; Brüggemann, K.; Engbers, A.; Brinkmann, B.F.; Kemper, B.; Seggewiß, J.; Stock, C.; Ebnet, K.; Kiesel, L.; et al. microRNA miR-142-3p Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Invasiveness by Synchronous Targeting of WASL, Integrin Alpha V, and Additional Cytoskeletal Elements. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Götte, M.; Mohr, C.; Koo, C.Y.; Stock, C.; Vaske, A.K.; Viola, M.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Peddibhotla, S.; Teng, Y.H.F.; Low, J.Y.; et al. miR-145-dependent targeting of Junctional Adhesion Molecule A and modulation of fascin expression are associated with reduced breast cancer cell motility and invasiveness. Oncogene 2010, 29, 6569–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, H.; Yin, S.; Dong, C. Downregulation of microRNA-138 enhances the proliferation, migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells through the upregulation of RhoC/p-ERK/MMP-2/MMP-9. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 2046–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Kolokythas, A.; Yu, J.; Wang, A.; Heidbreder, C.E.; Shi, F.; Zhou, X. Downregulation of the Rho GTPase signaling pathway is involved in the microRNA-138-mediated inhibition of cell migration and invasion in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Xiu, Y.L.; Sun, K.X.; Zong, Z.H.; Zhao, Y. RhoC is a major target of microRNA-93-5P in epithelial ovarian carcinoma tumorigenesis and progression. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.L.; Sun, K.X.; Zong, Z.H.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y. MicroRNA-372 inhibits endometrial carcinoma development by targeting the expression of the Ras homolog gene family member C (RhoC). Oncotarget 2016, 7, 6649–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, H.; Jin, Z.; Chen, S.; Sun, X.; Yu, J.; Guo, W. MiR-135b promotes proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells via targeting FOXO1. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2015, 400, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F.; Sharma, S.; Liu, Y.; Mo, Y.Y.; Wu, K.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Pochampally, R.; Martinez, L.A.; Lo, H.W.; Watabe, K. miR-509 suppresses brain metastasis of breast cancer cells by modulating RhoC and TNF-α. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4890–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ueno, K.; Hirata, H.; Majid, S.; Yamamura, S.; Shahryari, V.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Hinoda, Y.; Dahiya, R. Tumor suppressor microRNA-493 decreases cell motility and migration ability in human bladder cancer cells by downregulating RhoC and FZD4. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Shen, H.; Li, H.; Long, L.; Hui, L.; Xu, W. miR-137 inhibits the proliferation of lung cancer cells by targeting Cdc42 and Cdk6. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algaber, A.; Al-Haidari, A.; Madhi, R.; Rahman, M.; Syk, I.; Thorlacius, H. MicroRNA-340-5p inhibits colon cancer cell migration via targeting of RhoA. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Miao, R.; Xu, X.; Qu, X. CXCL12/CXCR4 promotes inflammation-driven colorectal cancer progression through activation of RhoA signaling by sponging miR-133a-3p. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, W.; Wu, B. MicroRNA-31 inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting RhoA in human gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Zhao, D.; Li, F.; Wang, H. MicroRNA-146a inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting RhoA in breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.G.; Li, J.S.; Liu, Y.F.; Xu, Q. MicroRNA-200b suppresses the invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating RhoA and circRNA_000839. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2017, 39, 1010428317719577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.C.; Lin, X.L.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, H.Y.; Shi, J.W.; Yang, S.; Zhao, W.T.; Xie, R.Y.; Wei, F.; et al. MicroRNA-122 triggers mesenchymal-epithelial transition and suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell motility and invasion by targeting RhoA. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fils-Aimé, N.; Dai, M.; Guo, J.; El-Mousawi, M.; Kahramangil, B.; Neel, J.C.; Lebrun, J.J. MicroRNA-584 and the protein phosphatase and actin regulator 1 (PHACTR1), a new signaling route through which transforming growth factor-β Mediates the migration and actin dynamics of breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11807–11823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sundararajan, V.; Gengenbacher, N.; Stemmler, M.P.; Kleemann, J.A.; Brabletz, T.; Brabletz, S. The ZEB1/miR-200c feedback loop regulates invasion via actin interacting proteins MYLK and TKS5. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27083–27096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, M.; Kim, S.; Patterson, N.; Rooney, K.; Searles, C.D. MiRNA-155 targets myosin light chain kinase and modulates actin cytoskeleton organization in endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014, 306, H1192–H1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cimino, D.; De Pittà, C.; Orso, F.; Zampini, M.; Casara, S.; Penna, E.; Quaglino, E.; Forni, M.; Damasco, C.; Pinatel, E.; et al. miR148b is a major coordinator of breast cancer progression in a relapse-associated microRNA signature by targeting ITGA5, ROCK1, PIK3CA, NRAS, and CSF1. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2013, 27, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maskey, N.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Song, H.; Wu, C.; Hua, K.; Song, J.; Fang, L. MicroRNA-340 inhibits invasion and metastasis by downregulating ROCK1 in breast cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2261–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Tang, H.; Lei, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.A. miR-335-5p inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer via ROCK1. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.D.; Zhou, Q.Q.; Dong, L.; Huang, Z.; Wu, F.; Deng, X. MiR-199a-5p Inhibits the Growth and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Targeting ROCK1. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533034618775509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Zuo, W. MicroRNA-145 inhibits growth and migration of breast cancer cells through targeting oncoprotein ROCK1. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2016, 37, 8189–8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, S.; Dar, A.A.; Saini, S.; Shahryari, V.; Arora, S.; Zaman, M.S.; Chang, I.; Yamamura, S.; Chiyomaru, T.; Fukuhara, S.; et al. MicroRNA-1280 inhibits invasion and metastasis by targeting ROCK1 in bladder cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, C.C.; Wong, C.M.; Tung, E.K.; Au, S.L.; Lee, J.M.; Poon, R.T.; Man, K.; Ng, I.O. The microRNA miR-139 suppresses metastasis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by down-regulating Rho-kinase 2. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Fan, M.; Ma, S.; Zhai, H. Myosin Heavy Chain-Associated RNA Transcripts Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression Through the miR-4529-5p/ROCK2 Axis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 3539–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Tang, G. miR-185-5p targets ROCK2 and inhibits cell migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 5087–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, X.; Wei, M. MicroRNA-144 suppresses osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by targeting ROCK1 and ROCK2. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10297–10308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kroiss, A.; Vincent, S.; Decaussin-Petrucci, M.; Meugnier, E.; Viallet, J.; Ruffion, A.; Chalmel, F.; Samarut, J.; Allioli, N. Androgen-regulated microRNA-135a decreases prostate cancer cell migration and invasion through downregulating ROCK1 and ROCK2. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2846–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X. MicroRNA-139-5p Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting RHO-Associated Coiled-Coil-Containing Protein Kinase 2 in Ovarian Cancer. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Liao, Y.J.; Cai, M.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, T.H.; Chen, S.P.; Bian, X.W.; Guan, X.Y.; Lin, M.C.; Zeng, Y.X.; et al. The putative tumour suppressor microRNA-124 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell aggressiveness by repressing ROCK2 and EZH2. Gut 2012, 61, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xiang, L.; Chen, M.; Xiang, C. MicroRNA‑130a inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasive ability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by downregulating Rho‑kinase 2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3077–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurmeister, S.; Baumann, M.; Balwierz, A.; Keklikoglou, I.; Ward, A.; Uhlmann, S.; Zhang, J.D.; Wiemann, S.; Sahin, Ö. MicroRNA-200c represses migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by targeting actin-regulatory proteins FHOD1 and PPM1F. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Jin, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J. Loss of PPM1F expression predicts tumour recurrence and is negatively regulated by miR-590-3p in gastric cancer. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Jin, M.; Hou, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J. CircSLC3A2 functions as an oncogenic factor in hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging miR-490-3p and regulating PPM1F expression. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, G.; Chao, Y.L.; Tang, B.; Li, B.S.; Xiao, Y.F.; Xie, R.; Wang, S.M.; Wu, Y.Y.; Dong, H.; Liu, X.D.; et al. miR-149 represses metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting actin-regulatory proteins PPM1F. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37808–37823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Downs-Kelly, E.; Das, M.; Izem, L.; Tubbs, R.; Plow, E.F. WAVE3, an actin remodeling protein, is regulated by the metastasis suppressor microRNA, miR-31, during the invasion-metastasis cascade. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 1331–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Bialkowska, K.; Plow, E.F. The miR200 family of microRNAs regulates WAVE3-dependent cancer cell invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 33019–33029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhan, M.N.; Yu, X.T.; Tang, J.; Zhou, C.X.; Wang, C.L.; Yin, Q.Q.; Gong, X.F.; He, M.; He, J.R.; Chen, G.Q.; et al. MicroRNA-494 inhibits breast cancer progression by directly targeting PAK1. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, K.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, X.; He, Q.; Duan, Y. microRNA-7 regulates cell growth, migration and invasion via direct targeting of PAK1 in thyroid cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, B.; Gao, Y.; Du, C.; Shi, Q.; Xu, S.; Wang, C.Q.; Wang, X.; He, D.; Guo, P. miR-145 inhibits invasion of bladder cancer cells by targeting PAK1. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J. MiR-98 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of non-small cell carcinoma lung cancer by targeting PAK1. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 20135–20145. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.J.; He, C.L.; Sun, T.; Duan, X.J.; Sun, Y.; Xiong, S.J. hsa-miR-485-5p reverses epithelial to mesenchymal transition and promotes cisplatin-induced cell death by targeting PAK1 in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.; Chang, K.; Fan, C.; Zhang, Y. MiR-26a/miR-26b represses tongue squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting PAK1. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, M.; Zauner, R.; Ablinger, M.; Piñón-Hofbauer, J.; Guttmann-Gruber, C.; Reisenberger, M.; Lettner, T.; Niklas, N.; Proell, J.; Sajinovic, M.; et al. A cancer stem cell-like phenotype is associated with miR-10b expression in aggressive squamous cell carcinomas. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.; Xiao, C.; Lu, H.; Yu, H.; Hong, H.; Guo, C.; Wu, Z. miR-200b regulates breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting radixin. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 2741–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hua, D.; Ding, D.; Han, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, N.; Foltz, G.; Lan, Q.; Huang, Q.; Lin, B. Human miR-31 targets radixin and inhibits migration and invasion of glioma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, L.; Stebbing, J.; Braga, V.M.; Frampton, A.E.; Jacob, J.; Buluwela, L.; Jiao, L.R.; Periyasamy, M.; Madsen, C.D.; Caley, M.P.; et al. miR-23b regulates cytoskeletal remodeling, motility and metastasis by directly targeting multiple transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 5400–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wu, X.; Guo, L.; Shi, J.; Li, J. MicroRNA-7-5p induces cell growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by targeting PAK2 in non-small cell lung cancer. FEBS Open Bio 2019, 9, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koo, K.H.; Kwon, H. MicroRNA miR-4779 suppresses tumor growth by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through direct targeting of PAK2 and CCND3. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, S.; Luo, C.; Abukiwan, A.; Wang, G.; He, J.; Huang, L.; Weber, C.E.; Lv, N.; Xiao, X.; Eichmüller, S.B.; et al. miR-137 inhibits proliferation of melanoma cells by targeting PAK2. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Ding, Y.; Yuan, H.; Shao, J.; Yan, Y.; Guo, R.; Luan, W.; Xu, M. Long non-coding RNA ZEB1-AS1 promotes colon adenocarcinoma malignant progression via miR-455-3p/PAK2 axis. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Xing, H.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y. MicroRNA-342 targets Cofilin 1 to suppress the growth, migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 687, 108385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockhorn, J.; Dalton, R.; Nwachukwu, C.; Huang, S.; Prat, A.; Yee, K.; Chang, Y.-F.; Huo, D.; Wen, Y.; Swanson, K.E.; et al. MicroRNA-30c inhibits human breast tumour chemotherapy resistance by regulating TWF1 and IL-11. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, Y.Q.; Zhu, Y.D.; Xie, G.Q.; Zhang, K.; Sheng, J.; Zhu, Z.F.; Ning, Z.Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Z.Q.; et al. Long non-coding SBF2-AS1 acting as a competing endogenous RNA to sponge microRNA-142-3p to participate in gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer via upregulating TWF1. Aging 2019, 11, 8860–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Pang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, H. MicroRNA-486-5p improves nonsmall-cell lung cancer chemotherapy sensitivity and inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting twinfilin actin binding protein 1. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 3745–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y. Profilin 1, negatively regulated by microRNA-19a-3p, serves as a tumor suppressor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.-M.; Yu, X.-N.; Liu, T.-T.; Zhu, H.-R.; Shi, X.; Bilegsaikhan, E.; Guo, H.-Y.; Song, G.-Q.; Weng, S.-Q.; Huang, X.-X.; et al. microRNA-19a-3p promotes tumor metastasis and chemoresistance through the PTEN/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Liu, M.; Song, X.; Li, X.R. Expression and regulatory function of miRNA-182 in triple-negative breast cancer cells through its targeting of profilin 1. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2013, 34, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, N.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, B. Knockdown of lncRNA HCP5 Suppresses the Progression of Colorectal Cancer by miR-299-3p/PFN1/AKT Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 4747–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, H.; Ma, X.; Zeng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yu, D.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, Y. HLA-F-AS1/miR-330-3p/PFN1 axis promotes colorectal cancer progression. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanuma, N.; Hoshino, I.; Akutsu, Y.; Murakami, K.; Isozaki, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Yusup, G.; Qin, W.; Toyozumi, T.; Takahashi, M.; et al. MicroRNA-133a regulates the mRNAs of two invadopodia-related proteins, FSCN1 and MMP14, in esophageal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiyomaru, T.; Enokida, H.; Tatarano, S.; Kawahara, K.; Uchida, Y.; Nishiyama, K.; Fujimura, L.; Kikkawa, N.; Seki, N.; Nakagawa, M. miR-145 and miR-133a function as tumour suppressors and directly regulate FSCN1 expression in bladder cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kano, M.; Seki, N.; Kikkawa, N.; Fujimura, L.; Hoshino, I.; Akutsu, Y.; Chiyomaru, T.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Matsubara, H. miR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b: Tumor-suppressive miRNAs target FSCN1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hong, W.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, G.; Wei, G.; Li, X. miR-539 inhibits FSCN1 expression and suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma migration and invasion. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2593–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.; Bhatnagar, H.; Lin, A.P.; Wang, L.; Aster, J.C.; Sill, H.; Aguiar, R.C.T. A microRNA-mediated regulatory loop modulates NOTCH and MYC oncogenic signals in B- and T-cell malignancies. Leukemia 2015, 29, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Xie, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, S.; Wang, J. MicroRNA‑663 suppresses the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by directly targeting FSCN1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 9707–9714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, H.; Yang, M. Down-regulation of miR-326 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes growth and metastasis by targeting FSCN1 in gastric cancer. Growth Factors 2015, 33, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, P.; Liu, W.; Zhou, H. miR-200b inhibits migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer cells via targeting FSCN1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, B.B.; Lu, M.; Zheng, M.J.; Chen, H.; Ding, J.Z.; Xu, A.M.; Xu, Y.H. miR-429 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting FSCN1 in gastric cancer cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.P.; Huang, H.Y.; Lai, Y.R.; Huang, J.X.; Chang, K.P.; Hsueh, C.; Chang, Y.S. Silencing of miRNA-148a by hypermethylation activates the integrin-mediated signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 7610–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, C.; Mojares, E.; Del Río Hernández, A. Role of Extracellular Matrix in Development and Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogusławska, J.; Rodzik, K.; Popławski, P.; Kędzierska, H.; Rybicka, B.; Sokół, E.; Tański, Z.; Piekiełko-Witkowska, A. TGF-β1 targets a microRNA network that regulates cellular adhesion and migration in renal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 412, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, H.; Ivaska, J. Every step of the way: Integrins in cancer progression and metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winograd-Katz, S.E.; Fässler, R.; Geiger, B.; Legate, K.R. The integrin adhesome: From genes and proteins to human disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, I.A.; Vermeulen, J.F.; Ercan, C.; Houthuijzen, J.M.; Saig, F.A.; Vlug, E.J.; van der Wall, E.; van Diest, P.J.; Vooijs, M.; Derksen, P.W.B. FER kinase promotes breast cancer metastasis by regulating α6- and β1-integrin-dependent cell adhesion and anoikis resistance. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5582–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peinado, H.; Zhang, H.; Matei, I.R.; Costa-Silva, B.; Hoshino, A.; Rodrigues, G.; Psaila, B.; Kaplan, R.N.; Bromberg, J.F.; Kang, Y.; et al. Pre-metastatic niches: Organ-specific homes for metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raab-Westphal, S.; Marshall, J.F.; Goodman, S.L. Integrins as Therapeutic Targets: Successes and Cancers. Cancers 2017, 9, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augoff, K.; Das, M.; Bialkowska, K.; McCue, B.; Plow, E.F.; Sossey-Alaoui, K. miR-31 is a broad regulator of β1-integrin expression and function in cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Hutchison, E.R.; Lee, E.K.; Kuwano, Y.; Kim, M.M.; Masuda, K.; Srikantan, S.; Subaran, S.S.; Marasa, B.S.; Mattson, M.P.; et al. miR-375 inhibits differentiation of neurites by lowering HuD levels. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 4197–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu da, Z.; Jickling, G.C.; Ander, B.P.; Hull, H.; Zhan, X.; Cox, C.; Shroff, N.; Dykstra-Aiello, C.; Stamova, B.; Sharp, F.R. Elevating microRNA-122 in blood improves outcomes after temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakaguchi, T.; Yoshino, H.; Yonemori, M.; Miyamoto, K.; Sugita, S.; Matsushita, R.; Itesako, T.; Tatarano, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Enokida, H. Regulation of ITGA3 by the dual-stranded microRNA-199 family as a potential prognostic marker in bladder cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzi, L.; Boshtam, M.; Shariati, L.; Kouhpayeh, S.; Gheibi, A.; Mirian, M.; Rahimmanesh, I.; Khanahmad, H.; Tabatabaiefar, M.A. The silencing effect of miR-30a on ITGA4 gene expression in vitro: An approach for gene therapy. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 456–464. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, S.-L.; Bian, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yan, B.; Jia, L.-T.; Zhao, J.; Gammoh, N.; Yang, A.-G.; et al. MicroRNA-26a promotes anoikis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting alpha5 integrin. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2277–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoni, E.; van der Horst, G.; van de Merbel, A.F.; Chen, L.; Rane, J.K.; Pelger, R.C.; Collins, A.T.; Visakorpi, T.; Snaar-Jagalska, B.E.; Maitland, N.J.; et al. miR-25 Modulates Invasiveness and Dissemination of Human Prostate Cancer Cells via Regulation of αv- and α6-Integrin Expression. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2326–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, T.; Nohata, N.; Hanazawa, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Yamamoto, N.; Yoshino, H.; Itesako, T.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Okamoto, Y.; et al. Tumour-suppressive microRNA-29s inhibit cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting laminin-integrin signalling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2636–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.P.; Hu, Y.P.; Wu, X.S.; Wu, Y.S.; Ye, Y.Y.; Li, H.F.; Liu, Y.C.; Jiang, L.; Liu, F.T.; Zhang, Y.J.; et al. miR-143-3p targeting of ITGA6 suppresses tumour growth and angiogenesis by downregulating PLGF expression via the PI3K/AKT pathway in gallbladder carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Kang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, D. Long Noncoding RNA CCAT1 Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Upregulate ITGA9 by Sponging MiR-296-3p in Melanoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 4699–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngalame, N.N.; Tokar, E.J.; Person, R.J.; Xu, Y.; Waalkes, M.P. Aberrant microRNA expression likely controls RAS oncogene activation during malignant transformation of human prostate epithelial and stem cells by arsenic. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2014, 138, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Long, H.; Ding, S.; Yin, H.; Lu, Q. MicroRNA-126 regulates DNA methylation in CD4+ T cells and contributes to systemic lupus erythematosus by targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, A.T.; Dittel, B.N. Taming of macrophage and microglial cell activation by microRNA-124. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, L.; Min, S.; Wu, X.; He, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. miR-223 suppresses differentiation of tumor-induced CD11b+ Gr1+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells from bone marrow cells. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2662–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrien-Elliott, M.M.; Sun, Y.; Neal, C.; Ireland, A.; Trissal, M.C.; Sullivan, R.P.; Wagner, J.A.; Leong, J.W.; Wong, P.; Mah-Som, A.Y.; et al. MicroRNA-142 Is Critical for the Homeostasis and Function of Type 1 Innate Lymphoid Cells. Immunity 2019, 51, 479–490.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Varambally, S.; Maher, C.A.; Cao, Q.; Chockley, P.; Toubai, T.; Malter, C.; Nieves, E.; Tawara, I.; Wang, Y.; et al. Targeting of microRNA-142-3p in dendritic cells regulates endotoxin-induced mortality. Blood 2011, 117, 6172–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Yoshizato, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawada, N. Suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation by microRNA-29b. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, A.; Thomson, D.; Giles, K.; Maleki, S.; Mreich, E.; Wheeler, H.; Leedman, P.; Biggs, M.; Cook, R.; Little, N.; et al. miR-124a is frequently down-regulated in glioblastoma and is involved in migration and invasion. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Pfaff, S.L.; Gage, F.H. A functional study of miR-124 in the developing neural tube. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Luna, C.; Qiu, J.; Epstein, D.L.; Gonzalez, P. Targeting of integrin beta1 and kinesin 2alpha by microRNA 183. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5461–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuchiya, S.; Oku, M.; Imanaka, Y.; Kunimoto, R.; Okuno, Y.; Terasawa, K.; Sato, F.; Tsujimoto, G.; Shimizu, K. MicroRNA-338-3p and microRNA-451 contribute to the formation of basolateral polarity in epithelial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 3821–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, S.H.; Huang, W.C.; Chang, J.W.; Chang, K.J.; Kuo, W.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Lin, K.Y.; Uen, Y.H.; Hou, M.F.; Lin, C.M.; et al. MicroRNA-149 targets GIT1 to suppress integrin signaling and breast cancer metastasis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4496–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Miao, G.; Li, Y.; Isaji, T.; Gu, J.; Li, J.; Qi, R. MicroRNA- 130b suppresses migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through downregulation of integrin β1 [corrected]. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87938. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wu, C.; Zhang, P.; Tang, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G. miRNA-29c suppresses lung cancer cell adhesion to extracellular matrix and metastasis by targeting integrin β1 and matrix metalloproteinase2 (MMP2). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slezak, S.; Jin, P.; Caruccio, L.; Ren, J.; Bennett, M.; Zia, N.; Adams, S.; Wang, E.; Ascensao, J.; Schechter, G.; et al. Gene and microRNA analysis of neutrophils from patients with polycythemia vera and essential thrombocytosis: Down-regulation of micro RNA-1 and -133a. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Guo, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Zhang, H.; Peng, X.; Bosco, J.; Pretz, J.; Schlanger, R.; Wang, J.Y.; Mak, R.H.; et al. MicroRNA-mediated control of cell fate in megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitors. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, A.E.; Bradley, D.T.; Campbell, M.; Lechner, J.; Dash, D.P.; Simpson, D.A.; Willoughby, C.E. Mutation altering the miR-184 seed region causes familial keratoconus with cataract. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; He, R.; Luo, H.; Lu, C.; Ning, Z.; Wu, Y.; Han, C.; Tan, G.; Wang, Z. Integrin-β5, a miR-185-targeted gene, promotes hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis by regulating β-catenin stability. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, C.; Ma, G.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Huang, F.; Liu, K.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-17/20a impedes migration and invasion via TGF-β/ITGB6 pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Deng, Z.; Shatseva, T.; Yang, J.; Peng, C.; Du, W.W.; Yee, A.J.; Ang, L.C.; He, C.; Shan, S.W.; et al. MicroRNA miR-93 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting integrin-β8. Oncogene 2011, 30, 806–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martín-Villar, E.; Borda-d’Agua, B.; Carrasco-Ramirez, P.; Renart, J.; Parsons, M.; Quintanilla, M.; Jones, G.E. Podoplanin mediates ECM degradation by squamous carcinoma cells through control of invadopodia stability. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4531–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín-Villar, E.; Megías, D.; Castel, S.; Yurrita, M.M.; Vilaró, S.; Quintanilla, M. Podoplanin binds ERM proteins to activate RhoA and promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119 Pt 21, 4541–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cao, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Yan, M.; Wu, X.; Chen, W. Dysregulated miR-363 affects head and neck cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting podoplanin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A.; Nicoloso, M.S.; Shimizu, M.; Rossi, S.; Gopisetty, G.; Molina, J.R.; Carlotti, C., Jr.; Tirapelli, D.; Neder, L.; Brassesco, M.S.; et al. miR-29b and miR-125a regulate podoplanin and suppress invasion in glioblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2010, 49, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senbanjo, L.T.; Chellaiah, M.A. CD44: A Multifunctional Cell Surface Adhesion Receptor Is a Regulator of Progression and Metastasis of Cancer Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zöller, M. CD44: Can a cancer-initiating cell profit from an abundantly expressed molecule? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Karnad, A.; Freeman, J.W. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: Therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Kelnar, K.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Calhoun-Davis, T.; Li, H.; Patrawala, L.; Yan, H.; Jeter, C.; Honorio, S.; et al. The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Yao, W.; Xiao, W.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Lang, B. MicroRNA-34a functions as an anti-metastatic microRNA and suppresses angiogenesis in bladder cancer by directly targeting CD44. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, W.; Liu, T.; Wan, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H. MicroRNA-199a targets CD44 to suppress the tumorigenicity and multidrug resistance of ovarian cancer-initiating cells. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 2047–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bourguignon, L.Y.W. Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes c-Jun signaling and miRNA21 expression leading to Bcl-2 expression and chemoresistance in breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Tan, Z.; Hu, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, T.; Zheng, C.; Wang, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; et al. microRNA-21 promotes breast cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting LZTFL1. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourguignon, L.Y.; Wong, G.; Earle, C.; Krueger, K.; Spevak, C.C. Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes c-Src-mediated twist signaling, microRNA-10b expression, and RhoA/RhoC up-regulation, leading to Rho-kinase-associated cytoskeleton activation and breast tumor cell invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 36721–36735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szatmári, T.; Ötvös, R.; Hjerpe, A.; Dobra, K. Syndecan-1 in Cancer: Implications for Cell Signaling, Differentiation, and Prognostication. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 796052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Yip, G.W.; Stock, C.; Pan, J.-W.; Neubauer, C.; Poeter, M.; Pupjalis, D.; Koo, C.Y.; Kelsch, R.; Schüle, R.; et al. Targeting of syndecan-1 by microRNA miR-10b promotes breast cancer cell motility and invasiveness via a Rho-GTPase- and E-cadherin-dependent mechanism. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, E884–E896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Li, G.; Yuan, Y.; He, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Chen, T.; Wu, W.; Lobie, P.E.; et al. MicroRNA-7 inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer cells via targeting FAK expression. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.Y.; Zhan, Y.S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.X. MicroRNA‑7 suppresses human colon cancer invasion and proliferation by targeting the expression of focal adhesion kinase. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golubovskaya, V.M.; Sumbler, B.; Ho, B.; Yemma, M.; Cance, W.G. MiR-138 and MiR-135 directly target focal adhesion kinase, inhibit cell invasion, and increase sensitivity to chemotherapy in cancer cells. Anti-cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howe, E.N.; Cochrane, D.R.; Richer, J.K. Targets of miR-200c mediate suppression of cell motility and anoikis resistance. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, S.; den Boon, J.A.; Chen, I.H.; Newton, M.A.; Stanhope, S.A.; Cheng, Y.J.; Chen, C.J.; Hildesheim, A.; Sugden, B.; Ahlquist, P. MicroRNA 29c is down-regulated in nasopharyngeal carcinomas, up-regulating mRNAs encoding extracellular matrix proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5874–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Ghazwani, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, J.; Fan, J.; Gandhi, C.R.; Li, S. miR-122 regulates collagen production via targeting hepatic stellate cells and suppressing P4HA1 expression. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, C.C.-L.; Tse, A.P.-W.; Huang, Y.-P.; Zhu, Y.-T.; Chiu, D.K.-C.; Lai, R.K.-H.; Au, S.L.-K.; Kai, A.K.-L.; Lee, J.M.-F.; Wei, L.L.; et al. Lysyl oxidase-like 2 is critical to tumor microenvironment and metastatic niche formation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, N.S.; Colden, M.; Dar, A.A.; Saini, S.; Arora, P.; Shahryari, V.; Yamamura, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Kato, T.; Majid, S.; et al. MicroRNA-720 Regulates E-cadherin–αE-catenin Complex and Promotes Renal Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2840–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voss, G.; Haflidadóttir, B.S.; Järemo, H.; Persson, M.; Catela Ivkovic, T.; Wikström, P.; Ceder, Y. Regulation of cell–cell adhesion in prostate cancer cells by microRNA-96 through upregulation of E-Cadherin and EpCAM. Carcinogenesis 2019, 41, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, M.U.; Naik, T.U.; Suckow, A.T.; Duncan, M.K.; Naik, U.P. Attenuation of Junctional Adhesion Molecule-A Is a Contributing Factor for Breast Cancer Cell Invasion. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2194–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barash, U.; Cohen-Kaplan, V.; Dowek, I.; Sanderson, R.D.; Ilan, N.; Vlodavsky, I. Proteoglycans in health and disease: New concepts for heparanase function in tumor progression and metastasis. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 3890–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintero-Fabián, S.; Arreola, R.; Becerril-Villanueva, E.; Torres-Romero, J.C.; Arana-Argáez, V.; Lara-Riegos, J.; Ramírez-Camacho, M.A.; Alvarez-Sánchez, M.E. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Angiogenesis and Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cathcart, J.; Pulkoski-Gross, A.; Cao, J. Targeting matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: Bringing new life to old ideas. Genes Dis. 2015, 2, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob, A.; Prekeris, R. The regulation of MMP targeting to invadopodia during cancer metastasis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, S.; Luo, A.; Chen, H.; Ding, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-34 suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by directly targeting Fra-1. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4294–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wu, G.; Lv, L.; Ren, Y.F.; Zhang, X.J.; Xue, Y.F.; Li, G.; Lu, X.; Sun, Z.; Tang, K.F. MicroRNA-34a inhibits migration and invasion of colon cancer cells via targeting to Fra-1. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, R.; Ishikawa, C.; Rokkaku, T.; Janknecht, R.; Mori, N. Phosphorylated c-Jun and Fra-1 induce matrix metalloproteinase-1 and thereby regulate invasion activity of 143B osteosarcoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabriely, G.; Wurdinger, T.; Kesari, S.; Esau, C.C.; Burchard, J.; Linsley, P.S.; Krichevsky, A.M. MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 5369–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cal, S.; López-Otín, C. ADAMTS proteases and cancer. Matrix Biol. 2015, 44–46, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Lu, Y.; Han, X.; Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Mao, J.; Wang, B.; Shen, J.; Fan, S.; Wang, L.; et al. microRNA -140-5p inhibits colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting ADAMTS5 and IGFBP5. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Liu, L.; Zang, W.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Zhao, G. miR‑365 overexpression promotes cell proliferation and invasion by targeting ADAMTS-1 in breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Gou, Q.; Xie, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, H. ADAMTS6 suppresses tumor progression via the ERK signaling pathway and serves as a prognostic marker in human breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 61273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, A.; Shi, F.; Ye, H.; Zhou, X. MicroRNA-222 regulates cell invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1) and manganese superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2009, 6, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Zhang, L.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, B. MiR-361-5p inhibits glycolytic metabolism, proliferation and invasion of breast cancer by targeting FGFR1 and MMP-1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.; Wang, W. MicroRNA-539 suppresses osteosarcoma cell invasion and migration in vitro and targeting Matrix metallopeptidase-8. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 8075–8082. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Gao, F.; Liang, H.; Lv, Y.; Li, M.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J.; Dou, G.; Wang, Y. MicroRNA-188-5p regulates contribution of bone marrow-derived cells to choroidal neovascularization development by targeting MMP-2/13. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 175, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Zhang, L.; Meisgen, F.; Harada, M.; Heilborn, J.; Homey, B.; Grandér, D.; Ståhle, M.; Sonkoly, E.; Pivarcsi, A. MicroRNA-125b down-regulates matrix metallopeptidase 13 and inhibits cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29899–29908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Liu, X.; Chang, H. MicroRNA-143 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation by targeting MMP7. Minerva Med. 2017, 108, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Song, N.; Liu, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, S. Placental growth factor promotes metastases of ovarian cancer through MiR-543-regulated MMP7. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 37, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Liao, C.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Wu, M.H.; Chi, H.C.; Wu, S.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.H.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chung, I.H.; et al. Thyroid hormone receptor represses miR-17 expression to enhance tumor metastasis in human hepatoma cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4509–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Chopp, M.; Lu, Y.; Buller, B.; Jiang, F. MiR-15b and miR-152 reduce glioma cell invasion and angiogenesis via NRP-2 and MMP-3. Cancer Lett. 2013, 329, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, G.; Mi, Y.; Mei, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G. MicroRNA-192 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells and promotes apoptosis by targeting matrix metalloproteinase-11. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7265–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waresijiang, N.; Sun, J.; Abuduaini, R.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, H. The downregulation of miR‑125a‑5p functions as a tumor suppressor by directly targeting MMP‑11 in osteosarcoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 4859–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Pan, H.; Qu, P. microRNA‑145 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting matrix metallopeptidase-11 in renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, X.; Xia, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wu, N.; Liu, X.; Ding, Q.; Zha, X.; Sha, J.; Wang, S. Downregulation of miR-106b induced breast cancer cell invasion and motility in association with overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase 2. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steele, R.; Mott, J.L.; Ray, R.B. MBP-1 upregulates miR-29b that represses Mcl-1, collagens, and matrix-metalloproteinase-2 in prostate cancer cells. Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.J.; Li, L.J.; Huo, H.F.; Liu, X.Q.; Cui, H.W.; Jiang, D.M. MicroRNA-29b sensitizes osteosarcoma cells to doxorubicin by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) in osteosarcoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.; Wang, Y.; Qi, P.; Chen, Y.; Xu, P.; Yang, X.; Jin, X.; Tian, X. MicroRNA-183 functions as the tumor suppressor via inhibiting cellular invasion and metastasis by targeting MMP-9 in cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 141, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Zhang, W.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; You, G.; Wang, Y.; Kang, C.; You, Y.; Jiang, T. Identification of MMP-9 specific microRNA expression profile as potential targets of anti-invasion therapy in glioblastoma multiforme. Brain Res. 2011, 1411, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, M.; Li, S.; Qi, T.; Mei, H.; Huang, K.; Zheng, L.; Tong, Q. microRNA-9 targets matrix metalloproteinase 14 to inhibit invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis of neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, X.; Mei, H.; Zhao, X.; Pu, J.; Li, D.; Qu, H.; Jiao, W.; Zhao, J.; Huang, K.; Zheng, L.; et al. miRNA-337-3p suppresses neuroblastoma progression by repressing the transcription of matrix metalloproteinase 14. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22452–22466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, Q.F.; Cao, L.Y.; Yu, T.; Gong, L.; Wang, L.N.; Zhao, Y.L.; Xiao, B.; Zou, Q.M. MicroRNA-22 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in gastric cancer by directly targeting MMP14 and Snail. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, W.; Zhou, K.; Deng, M.; Lin, Q.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, J.; Song, Y. LINC00963 facilitates acute myeloid leukemia development by modulating miR-608/MMP-15. Aging 2020, 12, 18970–18981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.T.; Wu, C.; Wu, Z.W.; Li, Y.Y.; Yang, T.Q.; Chen, G.L.; Xie, X.S.; Huang, Y.L.; Du, Z.W.; et al. miR-132 can inhibit glioma cells invasion and migration by target MMP16 in vitro. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 3211–3218. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Shen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hu, T. MicroRNA-215 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung carcinoma cells through the downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-16 expression. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 3239–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; An, G.; Guan, Y.; Wei, T.; Peng, Z.; Liang, M.; Wang, Y. miR-328-3p mediates the anti-tumor effect in osteosarcoma via directly targeting MMP-16. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Astarci, E.; Erson-Bensan, A.E.; Banerjee, S. Matrix metalloprotease 16 expression is downregulated by microRNA-146a in spontaneously differentiating Caco-2 cells. Dev. Growth Differ. 2012, 54, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Qi, Y.; Ng, S.S.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Chen, S.; Ge, R.; Jiang, S.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; et al. microRNA-146b inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by targeting MMPs. Brain Res. 2009, 1269, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.K.; Meng, F.G.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Mao, G.P.; Huang, Z.Y.; Liao, W.M.; He, A.S. MicroRNA-193b-3p regulates matrix metalloproteinase 19 expression in interleukin-1β-induced human chondrocytes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 4775–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Wang, S.W.; Song, M.; Hu, Y.F.; Cao, X.N.; Ge, J.W. MicroRNA-16 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung carcinoma cells by down-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-19 expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5260–5269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; He, M.; Guo, J.; Cao, T. Upregulation of circular RNA circ-ERBB2 predicts unfavorable prognosis and facilitates the progression of gastric cancer via miR-503/CACUL1 and miR-637/MMP-19 signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 511, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, H.; Chu, H.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, G. Identification of miR-1293 potential target gene: TIMP-1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 384, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, M.; Mito, J.K.; Lee, C.-L.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Dodd, R.D.; Cason, D.; Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Van Mater, D.; et al. MicroRNA-182 drives metastasis of primary sarcomas by targeting multiple genes. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4305–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagai, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Uchida, F.; Terabe, T.; Ishibashi Kanno, N.; Kato, K.; Yamagata, K.; Sakai, S.; Kawashiri, S.; Sato, H.; et al. MicroRNA-205-5p suppresses the invasiveness of oral squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting TIMP‑2 expression. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y. MicroRNA-103 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma through targeting TIMP-3 and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, E75–E82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Zhu, Y.; Ai, F.; Li, Y.; Bai, B.; Yao, W.; Dong, L. MicroRNA-191 correlates with poor prognosis of colorectal carcinoma and plays multiple roles by targeting tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease 3. Neoplasma 2014, 61, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bo, P.; Julang, L. MicroRNA-21 up-regulates metalloprotease by down-regulating TIMP3 during cumulus cell-oocyte complex in vitro maturation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 477, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Hsu, S.H.; Majumder, S.; Kutay, H.; Huang, W.; Jacob, S.T.; Ghoshal, K. TGFbeta-mediated upregulation of hepatic miR-181b promotes hepatocarcinogenesis by targeting TIMP3. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, D.; Jiang, S.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Ao, L.; Zhang, Y. Upregulated long noncoding RNA Linc00261 in pre-eclampsia and its effect on trophoblast invasion and migration via regulating miR-558/TIMP4 signaling pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 13243–13253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.M.; Phillips, B.L.; Patel, R.S.; Cohen, D.M.; Jakymiw, A.; Kong, W.W.; Cheng, J.Q.; Chan, E.K. Keratinization-associated miR-7 and miR-21 regulate tumor suppressor reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (RECK) in oral cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29261–29272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Tang, B.; Zhu, E.D.; Li, B.S.; Zhuang, Y.; Yu, S.; Lu, D.S.; Zou, Q.M.; Xiao, B.; Mao, X.H. Increased miR-222 in H. pylori-associated gastric cancer correlated with tumor progression by promoting cancer cell proliferation and targeting RECK. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Gao, C.; Chen, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Xiao, S.; Lu, H. miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2008, 88, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Yoon, S.R.; Lim, J.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, H.G. Dysregulation of Rho GTPases in Human Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parri, M.; Chiarugi, P. Rac and Rho GTPases in cancer cell motility control. Cell Commun. Signal. 2010, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Si, M.L.; Wu, H.; Mo, Y.Y. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14328–14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Si, M.L.; Zhu, S.; Wu, H.; Lu, Z.; Wu, F.; Mo, Y.Y. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2799–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Wang, W.; Ding, W.; Zhang, L. MiR-9 is involved in TGF-β1-induced lung cancer cell invasion and adhesion by targeting SOX7. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.Z.; Li, X.A.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.F.; Wu, H.W.; Huang, G. MiR-9 promotes synovial sarcoma cell migration and invasion by directly targeting CDH1. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 112, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.A.; Neiman, J.M.; Reddi, A.; Han, G.; Birlea, S.; Mitra, D.; Dionne, L.; Fernandez, P.; Murao, K.; Bian, L.; et al. Epithelial stem cell mutations that promote squamous cell carcinoma metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4390–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, R.; Wang, D.; Lu, J. MicroRNA-10b inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion in cervical cancer cells via direct targeting of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 5009–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Chen, Z.Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.Q.; Zeng, F.; Cui, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, J.B.; Chen, H.Q. miR-10b suppresses cell invasion and metastasis through targeting HOXA3 regulated by FAK/YAP signaling pathway in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.J.; Li, W. MiR-10b suppresses the growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer cell by targeting FGF13. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 576–587. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, H.; Gore, J.; Deitz, S.; Korc, M. microRNA-10b enhances pancreatic cancer cell invasion by suppressing TIP30 expression and promoting EGF and TGF-β actions. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4664–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Cao, H.; Ren, H.; Fang, X. miR-10b promotes cell invasion through RhoC-AKT signaling pathway by targeting HOXD10 in gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, L.Q.; Yang, J.; Gong, Z.Q.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, C.Q.; Du, K.L. miR-10b promotes invasion by targeting KLF4 in osteosarcoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Fan, Y.; Xu, W.; Chen, J.; Xu, C.; Wei, X.; Fang, D.; Feng, Y. miR-10b Inhibits Apoptosis and Promotes Proliferation and Invasion of Endometrial Cancer Cells via Targeting HOXB3. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2016, 31, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, Z.N.; Cheng, X.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Dai, X.; Bao, G.M.; Zhou, L.B. MiR-29c suppresses cell invasion and migration by directly targeting CDK6 in gastric carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 7920–7928. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Hu, J.; Sun, W.; Li, S.; Deng, S.; Li, M. MiR-29c inhibits cell growth, invasion, and migration of pancreatic cancer by targeting ITGB1. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Tang, L.L.; Sun, Y.; Cui, R.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Huang, B.J.; He, Q.M.; Jiang, W.; Ma, J. MiR-29c suppresses invasion and metastasis by targeting TIAM1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2013, 329, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Cao, S.; Li, C.; Mengesha, A.; Kong, B.; Wei, M. Micro-RNA-21 regulates TGF-β-induced myofibroblast differentiation by targeting PDCD4 in tumor-stroma interaction. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Wu, H.; Wu, F.; Nie, D.; Sheng, S.; Mo, Y.-Y. MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, C.; Cheng, X.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.; Song, X.; Yu, D.; Cao, X.; Liu, Z. MiR-21 improves invasion and migration of drug-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cancer cell and transformation of EMT through targeting HBP1. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 2485–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chu, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, M. miR-21 promotes cell migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting KLF5. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, X.; Gao, J.; Sun, Q.W.; Wang, C.X.; Deng, W.; Mao, G.Y.; Li, H.Q.; Guo, S.S.; Cheng, J.; Wu, Y.N.; et al. MiR-34a inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma by directly targeting SATB2. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 4856–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X. miR-34a targets BCL-2 to suppress the migration and invasion of sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6566–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H. miR-34a inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of paediatric neuroblastoma cells via targeting HNF4α. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3072–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Xiong, Y.; Watari, H.; Hanley, S.J.; Konno, Y.; Ihira, K.; Yamada, T.; Kudo, M.; Yue, J.; Sakuragi, N. MiR-137 and miR-34a directly target Snail and inhibit EMT, invasion and sphere-forming ability of ovarian cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.F.; Wei, S.B.; Mitchelson, K.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Meng, Z.; Gan, Y.H.; Yu, G.Y. miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via targeting MMP9 and MMP14. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, X.; Wang, L.; Mo, L.; Yao, Y. MicroRNA-34a suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting Notch1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 4387–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.Y.; Lin, Y.M.; Chung, H.C.; Lang, Y.D.; Lin, C.J.; Huang, J.; Wang, W.C.; Lin, F.M.; Chen, Z.; Huang, H.D.; et al. miR-103/107 promote metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the metastasis suppressors DAPK and KLF4. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3631–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, B.; Lei, X.; Zhang, L.; Fu, J. miR-103 regulates triple negative breast cancer cells migration and invasion through targeting olfactomedin 4. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.L.; Yin, X.R.; Zhang, S.Q. miR-103 promotes the metastasis and EMT of hepatocellular carcinoma by directly inhibiting LATS2. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 2433–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.; Zhao, L. miR-103 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration in the simulation transition zone of RFA through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by targeting PTEN. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhu, K.; Cheng, M. miR-135a inhibits malignant proliferation and diffusion of non-small cell lung cancer cells by down-regulating ROCK1 protein. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20201276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zheng, X.; Ye, K.; Sun, Y.; Lu, Y.; Fan, Q.; Ge, H. miR-135a Inhibits the Invasion and Migration of Esophageal Cancer Stem Cells through the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway by Targeting Smo. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribollet, V.; Barenton, B.; Kroiss, A.; Vincent, S.; Zhang, L.; Forcet, C.; Cerutti, C.; Périan, S.; Allioli, N.; Samarut, J.; et al. miR-135a Inhibits the Invasion of Cancer Cells via Suppression of ERRα. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Gu, R.; Wu, H. MicroRNA-107 Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting Tropomyosin 1. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, N.; Tan, G.; You, W.; Chen, H.; Gong, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. MiR-145 inhibits human colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion via PAK4-dependent pathway. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Wei, D.; Yan, F. MicroRNA-145 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 11 and Rab GTPase family 27a in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, M.; Mo, Y.Y. MicroRNA-145 suppresses cell invasion and metastasis by directly targeting mucin 1. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. MicroRNA-145 Suppresses Osteosarcoma Metastasis via Targeting MMP16. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 37, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.B.; He, X.J.; Xia, Y.J.; Hu, W.J.; Luo, J.G.; Zhang, J.; Tao, H.Q. MicroRNA-145-5p inhibits gastric cancer invasiveness through targeting N-cadherin and ZEB2 to suppress epithelial-mesenchymal transition. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Pu, J.; Qi, T.; Qi, M.; Li, D.; Xiang, X.; Huang, K.; Tong, Q. miRNA-145 targets v-ets erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 1 to suppress the invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis of gastric cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minami, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Sugito, N.; Kuranaga, Y.; Inamoto, T.; Takahara, K.; Takai, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Kiyama, S.; Akao, Y.; et al. MiR-145 negatively regulates Warburg effect by silencing KLF4 and PTBP1 in bladder cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33064–33077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Che, X.; Yang, N.; Bai, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Pei, H. miR-135b-5p Promotes migration, invasion and EMT of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting NR3C2. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.D.; Xin, H.N.; Yang, Z.C.; Wang, W.J.; Dong, J.J.; Jin, L.Y.; Li, F.N. miR-135b promotes proliferation and metastasis by targeting APC in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 10819–10826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Luo, S.; Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, B.; Zhao, L.; Shan, Y.; Zhou, H. miR-182 and miR-135b Mediate the Tumorigenesis and Invasiveness of Colorectal Cancer Cells via Targeting ST6GALNAC2 and PI3K/AKT Pathway. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 3447–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, D.; Bao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhao, F.; Ding, J.; Liang, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; et al. MicroRNA-135b, a HSF1 target, promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating RECK and EVI5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2421–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.G.; Shi, Y.; Hong, D.F.; Song, M.; Huang, D.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhao, G. MiR-148b suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting WNT1/β-catenin pathway. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Ye, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Lai, Y.; Yi, Y. MicroRNA-148b suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by targeting metastasis-associated gene 2. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 2815–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Bo, L.; Lu, W.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Q. MicroRNA-148b targets Rho-associated protein kinase 1 to inhibit cell proliferation, migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, M.; Chen, D.; Xu, B.; Wang, R.; Chu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, L.; Lei, Z.; Nie, Y.; et al. miR-148b-3p inhibits gastric cancer metastasis by inhibiting the Dock6/Rac1/Cdc42 axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Ramirez, M.A.; Wu, D.; Pryce, G.; Simpson, J.E.; Reijerkerk, A.; King-Robson, J.; Kay, O.; de Vries, H.E.; Hirst, M.C.; Sharrack, B.; et al. MicroRNA-155 negatively affects blood-brain barrier function during neuroinflammation. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2014, 28, 2551–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, C. MiR-155 Promotes Uveal Melanoma Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Regulating NDFIP1 Expression. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 16, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Ji, W.; Zhao, X. MiR-155 promotes anaplastic thyroid cancer progression by directly targeting SOCS1. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Cui, T.; Guo, W.; Wang, D.; Mao, L. MiR-155-5p accelerates the metastasis of cervical cancer cell via targeting TP53INP1. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 3181–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Q.; Tao, X.; Huang, F.; Wu, T.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Kuang, Z.; Cheng, B. Overexpression of miR-155 promotes the proliferation and invasion of oral squamous carcinoma cells by regulating BCL6/cyclin D2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.T.; Byers, L.A.; Peng, D.H.; Roybal, J.D.; Diao, L.; Wang, J.; Tong, P.; Creighton, C.J.; Gibbons, D.L. The miR-200 family and the miR-183~96~182 cluster target Foxf2 to inhibit invasion and metastasis in lung cancers. Oncogene 2016, 35, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roybal, J.D.; Zang, Y.; Ahn, Y.H.; Yang, Y.; Gibbons, D.L.; Baird, B.N.; Alvarez, C.; Thilaganathan, N.; Liu, D.D.; Saintigny, P.; et al. miR-200 Inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell invasion and metastasis by targeting Flt1/VEGFR1. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.S.; Kurie, J.M.; Ahn, Y.H. BMP4 depletion by miR-200 inhibits tumorigenesis and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Shen, S.; Liu, X.; Tang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, M. MiR-429 inhibits cells growth and invasion and regulates EMT-related marker genes by targeting Onecut2 in colorectal carcinoma. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2014, 390, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Qiu, M.; Tan, G.; Liang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, J. miR-200c inhibits invasion, migration and proliferation of bladder cancer cells through down-regulation of BMI-1 and E2F3. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.S.; Luo, Q.Z.; Han, Y.; Li, X.B.; Cao, L.J.; Wu, L.X. microRNA-223 promotes the growth and invasion of glioblastoma cells by targeting tumor suppressor PAX6. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2263–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Liang, X.; Sun, M.; Wang, G.; De, W.; Wu, W. MicroRNA-223 functions as an oncogene in human gastric cancer by targeting FBXW7/hCdc4. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.H.; Ling, X.; Chen, C.; Tang, W.; Hu, D.M.; Yin, G.J. Role of miR-214-5p in the migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7214–7221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; Zhu, T.; Yin, R. miR-214-5p Targets ROCK1 and Suppresses Proliferation and Invasion of Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, H. MiR-214 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting CDC25B. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 1678–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.; Men, J.; Ma, R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ren, J. miR-214 down-regulates ARL2 and suppresses growth and invasion of cervical cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 484, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Xu, L.; Li, C.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, S.; Chen, H. miR-214 inhibits invasion and migration via downregulating GALNT7 in esophageal squamous cell cancer. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2016, 37, 14605–14614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Hu, Z. miR-214 down-regulates MKK3 and suppresses malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells. Gene 2020, 724, 144146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Du, J.; Jiang, R.; Li, L. MicroRNA-214 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung carcinoma cells by targeting JAK1. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, J.; Li, H.; Ma, T.; Bo, Y.; Bai, T.; Guo, H.; et al. miR-424-5p Promotes Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 10441–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, L. MiR-424-5p participates in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma invasion and metastasis via SMAD7 pathway mediated EMT. Diagn. Pathol. 2016, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Xiang, X.; Chen, K.; Liu, P.; Zhu, A. Targeting of NT5E by miR-30b and miR-340 attenuates proliferation, invasion and migration of gallbladder carcinoma. Biochimie 2018, 146, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Yu, L.; Li, F.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; He, X. MiR-340 suppresses the metastasis by targeting EphA3 in cervical cancer. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, Y. MicroRNA-340 inhibits the growth and invasion of angiosarcoma cells by targeting SIRT7. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L. microRNA-340 influences cell proliferation, apoptosis and invasion by targeting NF-κB1 in gastric cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 3812–3824. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Guo, W.; Jian, Q.; Xue, K.; Huang, M.; Chi, S.; Li, C.; Li, C. MicroRNA-340 inhibits squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by downregulating RhoA. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 92, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.; Ji, H.; Xiao, F.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Lu, J. MicroRNA-340 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting JAK1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R.A. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.-J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; et al. The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Generates Cells with Properties of Stem Cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahn, Y.-H.; Gibbons, D.L.; Chakravarti, D.; Creighton, C.J.; Rizvi, Z.H.; Adams, H.P.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Gregory, P.A.; Wright, J.A.; Goodall, G.J.; et al. ZEB1 drives prometastatic actin cytoskeletal remodeling by downregulating miR-34a expression. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3170–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.-M. MicroRNAs: Regulators of cancer metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Tang, F.; Li, X.; Yang, P. miR-10a controls glioma migration and invasion through regulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition via EphA8. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Chen, E.; Li, X.; Lv, B.; Vikis, H.G.; Liu, P. XRN2 promotes EMT and metastasis through regulating maturation of miR-10a. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3925–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, P.-W.; Ng, S.-W. The Functions of MicroRNA-200 Family in Ovarian Cancer: Beyond Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Behbahani, G.D.; Ghahhari, N.M.; Javidi, M.A.; Molan, A.F.; Feizi, N.; Babashah, S. MicroRNA-Mediated Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2017, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.I. MicroRNA Control of TGF-β Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, X.J.; Zhang, H.; Teng, Y.; Li, R.; Bai, F.; Elankumaran, S.; Xing, J. TGF-β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition proceeds through stepwise activation of multiple feedback loops. Science Signal. 2014, 7, ra91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.-S.; Park, J.-I. Wnt signaling in cancer: Therapeutic targeting of Wnt signaling beyond β-catenin and the destruction complex. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sedgwick, A.E.; D’Souza-Schorey, C. Wnt Signaling in Cell Motility and Invasion: Drawing Parallels between Development and Cancer. Cancers 2016, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhan, T.; Rindtorff, N.; Boutros, M. Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsani, Z.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S.; Kia, V.; Karimkhanloo, H.; Zarghami, N.; Paryan, M. WNT1 Gene from WNT Signaling Pathway Is a Direct Target of miR-122 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Dong, X.; Zhong, X.; Ye, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J. Inhibitions of epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells-like properties are involved in miR-148a-mediated anti-metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Xie, Y.; Yang, P.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L. HCV core protein-induced down-regulation of microRNA-152 promoted aberrant proliferation by regulating Wnt1 in HepG2 cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e81730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Pei, F.; Men, X.; Wang, K.; Ma, D. miR‑329 inhibits papillary thyroid cancer progression via direct targeting WNT1. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 3561–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wu, T.; Srinivas, S.; Yang, W.; Fan, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, S. Aflatoxin B1 negatively regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through activating miR-33a. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, F.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lv, Z.; Jiang, J. MiR-214 inhibits cell growth in hepatocellular carcinoma through suppression of β-catenin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 428, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ruan, B.; You, N.; Huang, Q.; Liu, W.; Dang, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhou, T.; Ji, R.; Cao, Y.; et al. Downregulation of miR-200a induces EMT phenotypes and CSC-like signatures through targeting the β-catenin pathway in hepatic oval cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liao, Z.; Cai, M.; Zhang, G. MicroRNA-320a downregulation mediates human liver cancer cell proliferation through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hua, H.W.; Jiang, F.; Huang, Q.; Liao, Z.; Ding, G. MicroRNA-153 promotes Wnt/β-catenin activation in hepatocellular carcinoma through suppression of WWOX. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3840–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, J.; Guan, H.; Fang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, J.; Wu, J.; Li, M. MicroRNA-374a activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling to promote breast cancer metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, T.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Lv, X.; Xu, T.; Hu, T.; Li, J. MiR-27a modulates the MDR1/P-glycoprotein expression by inhibiting FZD7/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Xiong, Y.; Xue, C.; Chen, G.; Yan, B.; Ye, Q. miR-202 suppresses cell proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating LRP6 post-transcriptionally. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, N.; Chen, W.-J.; Zhang, J.-W.; Xu, C.; Zeng, X.-C.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.-Y. Downregulation of miR-432 activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes human hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7866–7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Hua, L.; Yao, K.H.; Chen, J.T.; Hu, J.H. miR-107 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting Axin2. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5168–5174. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, S.; Ng, K.Y.; Tong, M.; Lau, E.Y.; Lee, T.K.; Chan, K.W.; Yuan, Y.F.; Cheung, T.T.; Cheung, S.T.; Wang, X.Q.; et al. Octamer 4/microRNA-1246 signaling axis drives Wnt/β-catenin activation in liver cancer stem cells. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2062–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, J.; Jenkins, R.H.; Bennagi, R.; Krupa, A.; Phillips, A.O.; Bowen, T.; Fraser, D.J. Post-transcriptional regulation of Transforming Growth Factor Beta-1 by microRNA-744. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turcatel, G.; Rubin, N.; El-Hashash, A.; Warburton, D. MIR-99a and MIR-99b modulate TGF-β induced epithelial to mesenchymal plasticity in normal murine mammary gland cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Deng, J.J.; Gowda, P.S.; Rao, M.K.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, C.L.; Huang, T.; Sun, L.Z. Androgen receptor and microRNA-21 axis downregulates transforming growth factor beta receptor II (TGFBR2) expression in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4097–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.E.; Zhang, C.; Maminishkis, A.; Dong, L.; Zhi, C.; Li, R.; Zhao, J.; Majerciak, V.; Gaur, A.B.; Chen, S.; et al. MicroRNA-204/211 alters epithelial physiology. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2010, 24, 1552–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flores-Pérez, A.; Marchat, L.A.; Rodríguez-Cuevas, S.; Bautista-Piña, V.; Hidalgo-Miranda, A.; Ocampo, E.A.; Martínez, M.S.; Palma-Flores, C.; Fonseca-Sánchez, M.A.; Astudillo-de la Vega, H.; et al. Dual targeting of ANGPT1 and TGFBR2 genes by miR-204 controls angiogenesis in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Yin, J.; Fu, W.; Mo, Y.; Pan, Y.; Dai, L.; Huang, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, J. MiRNA 17 family regulates cisplatin-resistant and metastasis by targeting TGFbetaR2 in NSCLC. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keklikoglou, I.; Koerner, C.; Schmidt, C.; Zhang, J.D.; Heckmann, D.; Shavinskaya, A.; Allgayer, H.; Gückel, B.; Fehm, T.; Schneeweiss, A.; et al. MicroRNA-520/373 family functions as a tumor suppressor in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer by targeting NF-κB and TGF-β signaling pathways. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4150–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpal, M.; Lee, E.S.; Hu, G.; Kang, Y. The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 14910–14914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kolokythas, A.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, X. MicroRNA-138 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Biochem. J. 2011, 440, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, N.M.; Khella, H.W.; Grigull, J.; Adzovic, S.; Youssef, Y.M.; Honey, R.J.; Stewart, R.; Pace, K.T.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Jewett, M.A.; et al. miRNA profiling in metastatic renal cell carcinoma reveals a tumour-suppressor effect for miR-215. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Shao, G. miR-154 inhibits migration and invasion of human non-small cell lung cancer by targeting ZEB2. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, J.; Li, Y.; Fang, N.; Liu, B.; Zu, L.; Chang, R.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q. MiR-132 suppresses the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells via targeting the EMT regulator ZEB2. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.J.; Hsu, C.C.; Chang, C.H.; Tsai, L.L.; Chang, Y.C.; Lu, S.W.; Yu, C.H.; Huang, H.S.; Wang, J.J.; Tsai, C.H.; et al. Let-7d functions as novel regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistant property in oral cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Han, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X. Down-regulation of miR-214 contributes to intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma metastasis by targeting Twist. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 2393–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nairismägi, M.L.; Vislovukh, A.; Meng, Q.; Kratassiouk, G.; Beldiman, C.; Petretich, M.; Groisman, R.; Füchtbauer, E.M.; Harel-Bellan, A.; Groisman, I. Translational control of TWIST1 expression in MCF-10A cell lines recapitulating breast cancer progression. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4960–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nairismägi, M.L.; Füchtbauer, A.; Labouriau, R.; Bramsen, J.B.; Füchtbauer, E.M. The proto-oncogene TWIST1 is regulated by microRNAs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, L.; Huang, G.; Zhu, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huo, J. Down-regulation of miR-138 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via directly targeting TWIST2. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Quan, Z. Long non-coding RNA CASC9 enhances breast cancer progression by promoting metastasis through the meditation of miR-215/TWIST2 signaling associated with TGF-β expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 515, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.T.; Ping, Y.H.; Wang, A.M.; Ke, C.C.; Fang, W.L.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, H.C.; Chi, C.W.; Yeh, T.S. The reciprocal regulation loop of Notch2 pathway and miR-23b in controlling gastric carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18012–18026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. MicroRNA-206 targets notch3, activates apoptosis, and inhibits tumor cell migration and focus formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 31921–31927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Ai, F.; Li, X.; Tian, L.; Wang, X.; Shen, S.; Liu, F. MicroRNA-34a suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis by regulating Notch signaling. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Li, L.; Cao, B.; Wang, B.; Ma, J.; Ding, F.; Wang, X.; Pang, D.; et al. MicroRNA-182 drives colonization and macroscopic metastasis via targeting its suppressor SNAI1 in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 4629–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, H.; Cheung, W.K.; Ng, S.S.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, S.; Sze, J.; Leung, G.K.; Lu, G.; Chan, D.T.; Bian, X.W.; et al. Loss of brain-enriched miR-124 microRNA enhances stem-like traits and invasiveness of glioma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9962–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Fu, L.; Fu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Dong, J.T. Epigenetic Silencing of miR-203 Upregulates SNAI2 and Contributes to the Invasiveness of Malignant Breast Cancer Cells. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarswamy, R.; Mudduluru, G.; Ceppi, P.; Muppala, S.; Kozlowski, M.; Niklinski, J.; Papotti, M.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNA-30a inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting Snai1 and is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Hu, Y. MicroRNA-124 suppresses Slug-mediated lung cancer metastasis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 3802–3811. [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga, E.; Yuasa, K.; Shimazaki, S.; Hijikata, T. MicroRNA-1 targets Slug and endows lung cancer A549 cells with epithelial and anti-tumorigenic properties. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Yu, J.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Yao, C.C.; Chao, J.I.; Chen, P.M.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Hsiung, C.N.; Chu, H.W.; Shen, C.Y.; et al. MicroRNA-30a increases tight junction protein expression to suppress the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by targeting Slug in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16462–16478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.X.; Zhang, Z.G.; Ding, Z.Y.; Liang, H.F.; Song, J.; Tan, X.L.; Wu, J.J.; Li, G.Z.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, B.X.; et al. MicroRNA-630 suppresses tumor metastasis through the TGF-β- miR-630-Slug signaling pathway and correlates inversely with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22674–22686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, M.; Ye, L.; Feng, X.; Shi, R.; Sun, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, T. MicroRNA-590-3p inhibits invasion and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer by targeting Slug. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 965–974. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.B.; Yao, Y.N.; Yu, J.J.; Chen, X.X.; Li, H.F. Extensive profiling of circular RNAs and the potential regulatory role of circRNA-000284 in cell proliferation and invasion of cervical cancer via sponging miR-506. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 592–604. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Xing, A.Y.; Zhou, G.Y.; Zhang, T.G.; Zhang, J.P.; Gao, C.; Li, H.; Shi, D.B. The molecular mechanism of microRNA-145 to suppress invasion-metastasis cascade in gastric cancer. Oncogene 2013, 32, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miao, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, S.; Zang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhan, R.; Gao, M.; Hu, M.; Li, J.; et al. miR-194 Suppresses Proliferation and Migration and Promotes Apoptosis of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting CDH2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 45, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockhorn, J.; Yee, K.; Chang, Y.F.; Prat, A.; Huo, D.; Nwachukwu, C.; Dalton, R.; Huang, S.; Swanson, K.E.; Perou, C.M.; et al. MicroRNA-30c targets cytoskeleton genes involved in breast cancer cell invasion. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 137, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.H.; Wang, Y.; Sims, M.; Cai, C.; Pfeffer, L.M. MicroRNA-1 suppresses glioblastoma in preclinical models by targeting fibronectin. Cancer Lett. 2019, 465, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Gao, B.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, W. MicroRNA-432 is downregulated in cervical cancer and directly targets FN1 to inhibit cell proliferation and invasion. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, G.; He, S.; Ni, J.; Xia, W. MicroRNA-139 targets fibronectin 1 to inhibit papillary thyroid carcinoma progression. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 7799–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Fan, D.; Jiang, H. MicroRNA-200c binding to FN1 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, S.; Kumar, A.; Gomez, C.R.; Akhtar, I.; Hancock, J.C.; Lage, J.M.; Pound, C.R.; Levenson, A.S. MTA1-activated Epi-microRNA-22 regulates E-cadherin and prostate cancer invasiveness. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, P.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.Y.; Yu, S.Y.; Xi, Q.S. MicroRNA-10b targets E-cadherin and modulates breast cancer metastasis. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2012, 18, Br299–Br308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Liang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zen, K.; Gu, H. Slug-upregulated miR-221 promotes breast cancer progression through suppressing E-cadherin expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.Y.; Li, X.F.; Li, P.Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Jin, X. MicroRNA-23b regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting E-cadherin. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, D.; Wang, Z.; Tan, F.; Tan, X.; Zhou, F.; Sun, J.; et al. MicroRNA-25 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.L.; Zhao, X.H.; Wang, J.W.; Li, B.Z.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Tan, F.W.; Ding, D.P.; Xu, X.H.; Zhou, F.; et al. microRNA-92a promotes lymph node metastasis of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via E-cadherin. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10725–10734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Jia, Y.; Chen, H. MicroRNA-103 regulates the progression in endometrial carcinoma through ZO-1. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 2058738419872621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Cui, S.; Fu, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. MicroRNA-146-5p promotes proliferation, migration and invasion in lung cancer cells by targeting claudin-12. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 2019, 25, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Pu, H. MicroRNA-421 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by targeting claudin-11. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Shi, Q.; Li, G.; Zheng, J.H.; Lin, J.; Qiu, W. MicroRNA-488 inhibits progression of colorectal cancer via inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by targeting claudin-2. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 316, C33–C47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Luo, J.; Gan, G.L.; Li, W. Overexpression of microRNA-98 inhibits cell proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis via claudin-1 in human colorectal carcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 6090–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Xiao, H.-X.; Tian, H.-P.; Liu, Z.-L.; Xia, S.-S.; Zhou, T. Upregulation of microRNA-155 promotes the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through the regulation of claudin-1 expression. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosano, S.; Corà, D.; Parab, S.; Zaffuto, S.; Isella, C.; Porporato, R.; Hoza, R.M.; Calogero, R.A.; Riganti, C.; Bussolino, F.; et al. A regulatory microRNA network controls endothelial cell phenotypic switch during sprouting angiogenesis. eLife 2020, 9, e48095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-F.; Liao, F.; Wu, H.; Dai, J. Glioma stem cells-derived exosomal miR-26a promotes angiogenesis of microvessel endothelial cells in glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Qin, T.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Mao, J. MicroRNA-140-5p inhibits invasion and angiogenesis through targeting VEGF-A in breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yue, X.; Wang, P.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, G.; Pang, Q.; Tao, R. MicroRNA-205 functions as a tumor suppressor in human glioblastoma cells by targeting VEGF-A. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, A.; Lu, J.; Wang, W.; Shi, C.; Han, B.; Yao, M. Role of miR-497 in VEGF-A-mediated cancer cell growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 70, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Li, B.; Yang, Z.; Fang, H.; Zhang, G.M.; Feng, Z.H.; Huang, B. Regulation of HIF-1alpha and VEGF by miR-20b tunes tumor cells to adapt to the alteration of oxygen concentration. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, J.; Lin, J.H.; Brenot, A.; Kim, J.W.; Provot, S.; Werb, Z. GATA3 suppresses metastasis and modulates the tumour microenvironment by regulating microRNA-29b expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, I.P.; Tsai, H.L.; Hou, M.F.; Chen, K.C.; Tsai, P.C.; Huang, S.W.; Chou, W.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Juo, S.H. MicroRNA-93 inhibits tumor growth and early relapse of human colorectal cancer by affecting genes involved in the cell cycle. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Peng, X.C.; Zheng, X.L.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y.W. MiR-126 restoration down-regulate VEGF and inhibit the growth of lung cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Lung Cancer 2009, 66, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Er, K.; Mao, C.; Yan, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cui, F.; Zhao, W.; Shi, H. miR-203 suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting VEGFA in cervical cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 32, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Ma, R.; Si, W.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Tu, X.; Wang, Q. MicroRNA-503 targets FGF2 and VEGFA and inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Lett. 2013, 333, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Liu, X.; Dong, J.; Li, J.; Huang, C.; Wu, R.; Lv, Y. Downregulation of miRNA-638 promotes angiogenesis and growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting VEGF. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 30702–30711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Wu, X.; Wu, D.; Wu, P.; Ni, C.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, F.; Xu, J.; Huang, J. miRNA-27b targets vascular endothelial growth factor C to inhibit tumor progression and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Pan, Y.; Liu, G.; Fu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, K.; Feng, Y. microRNA-128 plays a critical role in human non-small cell lung cancer tumourigenesis, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis by directly targeting vascular endothelial growth factor-C. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2336–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Zhang, J.; Pan, T.; Ai, S.; Tang, L.; Wang, F. miR‑378a enhances the sensitivity of liver cancer to sorafenib by targeting VEGFR, PDGFRβ and c‑Raf. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4581–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, Y.-M.; Li, L.-C.; Wang, L.-L.; Wu, X.-L. MicroRNA-338 Inhibits Growth, Invasion and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer by Targeting NRP1 Expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Zhai, B.; Zhu, H.; Li, W.; Jiang, W.; Lei, L.; Zhang, S.; Qiao, H.; Jiang, X.; Sun, X. The miR-141/neuropilin-1 axis is associated with the clinicopathology and contributes to the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Sul, K.; Krukovets, I.; Nestor, C.; Li, J.; Adognravi, O.S. Novel tissue-specific mechanism of regulation of angiogenesis and cancer growth in response to hyperglycemia. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2012, 1, e005967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amodeo, V.; Bazan, V.; Fanale, D.; Insalaco, L.; Caruso, S.; Cicero, G.; Bronte, G.; Rolfo, C.; Santini, D.; Russo, A. Effects of anti-miR-182 on TSP-1 expression in human colon cancer cells: There is a sense in antisense? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Q.; Wang, P.P.; Peng, R.; Zhou, H. MiR-19a enhances cell proliferation, migration, and invasiveness through enhancing lymphangiogenesis by targeting thrombospondin-1 in colorectal cancer. Biochem. Cell Biol. Biochim. Biol. Cell. 2019, 97, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Mei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Z. miR-5582-5p inhibits cell proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer through targeting FGF-10. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.Y.; Wang, Y.; An, Z.J.; Shi, C.G.; Zhu, G.A.; Wang, B.; Lu, M.Y.; Pan, C.K.; Chen, P. Downregulation of miR-497 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting HDGF in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 435, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, T.C.; Tien, Y.J.; Wen, C.J.; Yeh, T.S.; Yu, M.C.; Huang, C.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Yen, T.C.; Hsieh, S.Y. MicroRNA-214 downregulation contributes to tumor angiogenesis by inducing secretion of the hepatoma-derived growth factor in human hepatoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, R.; Cong, L.; Ni, G.; Chen, M.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, M. MicroRNA-195 inhibits the behavior of cervical cancer tumors by directly targeting HDGF. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Situ, J.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Z.; Li, K.; Mao, Y.; Huang, W. MicroRNA-939 Directly Targets HDGF to Inhibit the Aggressiveness of Prostate Cancer via Deactivation of the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 4257–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, W. MicroRNA-873 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of endometrial cancer cells by directly targeting hepatoma-derived growth factor. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.; Wang, G.; Ni, J.; Zhuang, J.; Zhuang, S.; Wang, G.; Ye, Y.; Xia, W. MicroRNA-511 Inhibits Cellular Proliferation and Invasion in Colorectal Cancer by Directly Targeting Hepatoma-Derived Growth Factor. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Jiang, D.; Liu, C.; Lai, Z. MicroRNA-139-5p inhibits cell viability, migration and invasion and suppresses tumor growth by targeting HDGF in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1806–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dodbele, S.; Park, T.; Glass, R.; Bhat, K.; Sulman, E.P.; Zhang, Y.; Abounader, R. MicroRNA-29a inhibits glioblastoma stem cells and tumor growth by regulating the PDGF pathway. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2019, 145, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, D.; Xie, H.; Tang, J.; Liu, R.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Su, J.; Zhou, X.; et al. miR-33a functions as a tumor suppressor in melanoma by targeting HIF-1α. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cha, S.T.; Chen, P.S.; Johansson, G.; Chu, C.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Jeng, Y.M.; Yu, S.L.; Chen, J.S.; Chang, K.J.; Jee, S.H.; et al. MicroRNA-519c suppresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression and tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2675–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cascio, S.; D’Andrea, A.; Ferla, R.; Surmacz, E.; Gulotta, E.; Amodeo, V.; Bazan, V.; Gebbia, N.; Russo, A. miR-20b modulates VEGF expression by targeting HIF-1 alpha and STAT3 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 224, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Umezu, T.; Tadokoro, H.; Azuma, K.; Yoshizawa, S.; Ohyashiki, K.; Ohyashiki, J.H. Exosomal miR-135b shed from hypoxic multiple myeloma cells enhances angiogenesis by targeting factor-inhibiting HIF-1. Blood 2014, 124, 3748–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Sun, W. microRNA-222-Mediated VHL Downregulation Facilitates Retinoblastoma Chemoresistance by Increasing HIF1α Expression. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, G. Downregulation of miR-21 inhibits the malignant phenotype of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting VHL. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 7215–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, W.; He, L.; Richards, E.J.; Challa, S.; Xu, C.X.; Permuth-Wey, J.; Lancaster, J.M.; Coppola, D.; Sellers, T.A.; Djeu, J.Y.; et al. Upregulation of miRNA-155 promotes tumour angiogenesis by targeting VHL and is associated with poor prognosis and triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, J.; Zhi, X.; Xie, K.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z. miR-874 functions as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting angiogenesis through STAT3/VEGF-A pathway in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, W. MicroRNA-1299 is a negative regulator of STAT3 in colon cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, D.; Shang, Y.; Hu, T. MicroRNA-411 Inhibits Cervical Cancer Progression by Directly Targeting STAT3. Oncol. Res. 2019, 27, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Cui, H.; Xu, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Kang, L.; Han, B.; Meng, J.; Yan, Z.; Yan, X.; et al. MiR-125a suppresses tumor growth, invasion and metastasis in cervical cancer by targeting STAT3. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25266–25280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Q.; Dong, H.; Huang, J. MicroRNA-544 down-regulates both Bcl6 and Stat3 to inhibit tumor growth of human triple negative breast cancer. Biol. Chem. 2016, 397, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Choi, D.W.; Kim, C.S.; Yu, S.K.; Kim, H.J.; Go, D.S.; Lee, S.A.; Moon, S.M.; Kim, S.G.; Chun, H.S.; et al. MicroRNA-203 Induces Apoptosis by Targeting Bmi-1 in YD-38 Oral Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3477–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Sun, B.L.; Tian, S.X.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Shi, P.P. MicroRNA-132 reverses cisplatin resistance and metastasis in ovarian cancer by the targeted regulation on Bmi-1. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 3635–3644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Yan, D.; He, J.; Liu, D. MicroRNA-183 inhibits gastric cancer proliferation and invasion via directly targeting Bmi-1. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 2345–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, M.; Liang, Z.; Chen, L.; Tan, G.; Liu, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, H.; Liu, J. MicroRNA-200c suppresses cell growth and metastasis by targeting Bmi-1 and E2F3 in renal cancer cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Tao, J.; Lu, Q. MicroRNA-218 inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting BMI-1. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 8015–8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, L.; He, H.; Huang, W.; Zhang, R.; Li, P.; Meng, Y.; Jiang, X. Up-regulation of microRNA-16 in Glioblastoma Inhibits the Function of Endothelial Cells and Tumor Angiogenesis by Targeting Bmi-1. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Du, M.; Zhang, W.; Bai, H.; Yin, L.; Chen, W.; He, X.; Chen, Q. MicroRNA-432 Suppresses Invasion and Migration via E2F3 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 11271–11280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, H.F.; Qin, C.F. MicroRNA-217 functions as a prognosis predictor and inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and invasion via targeting E2F3. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 4050–4057. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. MicroRNA-449a inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by directly repressing E2F3 in gastric cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 35, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Wang, C.; Guo, W.; Tang, Q.; Wang, M. MiR-194-5p inhibits cell migration and invasion in bladder cancer by targeting E2F3. J. BUON 2018, 23, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhou, J.; Chang, L.; Sui, H.; Han, Y.; Piao, D.; Sha, R.; Bai, Y. MiR-590-5p inhibits colorectal cancer angiogenesis and metastasis by regulating nuclear factor 90/vascular endothelial growth factor A axis. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melincovici, C.S.; Boşca, A.B.; Şuşman, S.; Mărginean, M.; Mihu, C.; Istrate, M.; Moldovan, I.M.; Roman, A.L.; Mihu, C.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)—Key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. Rev. Roum. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Pengcheng, S.; Ziqi, W.; Luyao, Y.; Xiangwei, Z.; Liang, L.; Yuwei, L.; Lechen, L.; Wanhai, X. MicroRNA-497 suppresses renal cell carcinoma by targeting VEGFR-2 in ACHN cells. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20170270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamijo, H.; Miyagaki, T.; Takahashi-Shishido, N.; Nakajima, R.; Oka, T.; Suga, H.; Sugaya, M.; Sato, S. Thrombospondin-1 promotes tumor progression in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma via CD47. Leukemia 2020, 34, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, A.; He, S.; Tian, B.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z. MicroRNA-221 Mediates the Effects of PDGF-BB on Migration, Proliferation, and the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaelin, W.G., Jr. The VHL Tumor Suppressor Gene: Insights into Oxygen Sensing and Cancer. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2017, 128, 298–307. [Google Scholar]
- Puchert, M.; Obst, J.; Koch, C.; Zieger, K.; Engele, J. CXCL11 promotes tumor progression by the biased use of the chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CXCR7. Cytokine 2020, 125, 154809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Matsui, S.; Touma, M.; Wu, Q.; Sugimoto, K. MicroRNA-342 inhibits tumor growth via targeting chemokine CXCL12 involved in macrophages recruitment/activation. Genes Cells 2018, 23, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhao, S.; Sun, B.; Cheng, L.; Tang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, W.; et al. CXCR4-mediated osteosarcoma growth and pulmonary metastasis is suppressed by MicroRNA-613. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2412–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Li, D.; Yang, C.; Ji, J.S. MicroRNA-34a Inhibition of the TLR Signaling Pathway Via CXCL10 Suppresses Breast Cancer Cell Invasion and Migration. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1286–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.J.; Shin, J.Y.; Lee, K.D.; Bae, Y.K.; Sung, K.W.; Nam, S.J.; Chun, K.H. MicroRNA let-7a suppresses breast cancer cell migration and invasion through downregulation of C-C chemokine receptor type 7. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizeq, B.; Malki, M.I. The Role of CCL21/CCR7 Chemokine Axis in Breast Cancer Progression. Cancers 2020, 12, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Du, R.; Tang, Z.; Kuang, Y. MiRNALet-7a mediates prostate cancer PC-3 cell invasion, migration by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through CCR7/MAPK pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 3725–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Feng, D.; Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Luo, F.; Zhou, L.; Liu, F. MicroRNA-144 mediates chronic inflammation and tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer progression via regulating C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 11. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, X.; Liu, Y.; Kao, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Yu, M.; Wei, J.; Yang, Z.; et al. miR-144 suppresses cell proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer by targeting NRAS. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 3871–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedmi, M.; Sas-Chen, A.; Yarden, Y. MicroRNAs and Growth Factors: An Alliance Propelling Tumor Progression. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 1578–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masliah-Planchon, J.; Garinet, S.; Pasmant, E. RAS-MAPK pathway epigenetic activation in cancer: miRNAs in action. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38892–38907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roncarati, R.; Lupini, L.; Shankaraiah, R.C.; Negrini, M. The Importance of microRNAs in RAS Oncogenic Activation in Human Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, F.; Ferns, G.A.; Talebian, S.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Avan, A.; Shahidsales, S. Role of regulatory miRNAs of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of breast cancer. Gene 2020, 737, 144459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Z. MicroRNA Control of p53. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Meng, G.; Lv, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, J. The relationship between microRNAs and the STAT3-related signaling pathway in cancer. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317719869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, W.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y. MicroRNA-196a/-196b regulate the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through modulating the JAK/STAT pathway via targeting SOCS2. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, R.; Gregory, P.A.; Fernandes, R.C.; Denis, I.; Wang, Q.; Townley, S.L.; Zhao, S.G.; Hanson, A.R.; Pickering, M.A.; Armstrong, H.K.; et al. MicroRNA-194 Promotes Prostate Cancer Metastasis by Inhibiting SOCS2. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Follain, G.; Herrmann, D.; Harlepp, S.; Hyenne, V.; Osmani, N.; Warren, S.C.; Timpson, P.; Goetz, J.G. Fluids and their mechanics in tumour transit: Shaping metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, M.; Na’ara, S.; Gil, Z. Mechanisms of cancer dissemination along nerves. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaman, S.; Detmar, M. Mechanisms of lymphatic metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Fong, M.Y.; Min, Y.; Somlo, G.; Liu, L.; Palomares, M.R.; Yu, Y.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.F.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Cancer-Secreted miR-105 Destroys Vascular Endothelial Barriers to Promote Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Yao, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Xue, Y. MiR-181a regulates blood-tumor barrier permeability by targeting Krüppel-like factor 6. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 1826–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohme, M.; Riethdorf, S.; Pantel, K. Circulating and disseminated tumour cells—Mechanisms of immune surveillance and escape. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Chen, C.; Zhao, X.; Xu, M.; Sun, Q.; Deng, R.; et al. MiRNA-296-3p-ICAM-1 axis promotes metastasis of prostate cancer by possible enhancing survival of natural killer cell-resistant circulating tumour cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, M. Role of platelets and platelet receptors in cancer metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, R.; Kohanbash, G.; Sasaki, K.; Fujita, M.; Zhu, X.; Kastenhuber, E.R.; McDonald, H.A.; Potter, D.M.; Hamilton, R.L.; Lotze, M.T.; et al. Dicer-regulated microRNAs 222 and 339 promote resistance of cancer cells to cytotoxic T-lymphocytes by down-regulation of ICAM-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10746–10751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paoli, P.; Giannoni, E.; Chiarugi, P. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 3481–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mak, C.S.L.; Yung, M.M.H.; Hui, L.M.N.; Leung, L.L.; Liang, R.; Chen, K.; Liu, S.S.; Qin, Y.; Leung, T.H.Y.; Lee, K.-F.; et al. MicroRNA-141 enhances anoikis resistance in metastatic progression of ovarian cancer through targeting KLF12/Sp1/survivin axis. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tominaga, N.; Kosaka, N.; Ono, M.; Katsuda, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tamura, K.; Lötvall, J.; Nakagama, H.; Ochiya, T. Brain metastatic cancer cells release microRNA-181c-containing extracellular vesicles capable of destructing blood-brain barrier. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Lan, X.; Song, F.; Sun, J.; Zhou, K.; Liu, X.; Ren, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Cancer-derived exosomal miR-25-3p promotes pre-metastatic niche formation by inducing vascular permeability and angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Penna, E.; Orso, F.; Cimino, D.; Vercellino, I.; Grassi, E.; Quaglino, E.; Turco, E.; Taverna, D. miR-214 Coordinates Melanoma Progression by Upregulating ALCAM through TFAP2 and miR-148b Downmodulation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4098–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, L.; Huot, J.; Simard, M.J. p38 activation induces production of miR-146a and miR-31 to repress E-selectin expression and inhibit transendothelial migration of colon cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomsen, K.G.; Terp, M.G.; Lund, R.R.; Søkilde, R.; Elias, D.; Bak, M.; Litman, T.; Beck, H.C.; Lyng, M.B.; Ditzel, H.J. miR-155, identified as anti-metastatic by global miRNA profiling of a metastasis model, inhibits cancer cell extravasation and colonization in vivo and causes significant signaling alterations. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29224–29239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, D.; Pereira, E.R.; Padera, T.P. Growth and Immune Evasion of Lymph Node Metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, M.; Assen, F.P.; Leithner, A.; Abe, J.; Schachner, H.; Asfour, G.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Stein, J.V.; Uhrin, P.; Sixt, M.; et al. Lymph node blood vessels provide exit routes for metastatic tumor cell dissemination in mice. Science 2018, 359, 1408–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peinado, H.; Alečković, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; García-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chin, A.R.; Wang, S.E. Cancer Tills the Premetastatic Field: Mechanistic Basis and Clinical Implications. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3725–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langley, R.R.; Fidler, I.J. The seed and soil hypothesis revisited--the role of tumor-stroma interactions in metastasis to different organs. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Groot, A.E.; Roy, S.; Brown, J.S.; Pienta, K.J.; Amend, S.R. Revisiting Seed and Soil: Examining the Primary Tumor and Cancer Cell Foraging in Metastasis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grange, C.; Tapparo, M.; Collino, F.; Vitillo, L.; Damasco, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; Tetta, C.; Bussolati, B.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles released from human renal cancer stem cells stimulate angiogenesis and formation of lung premetastatic niche. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5346–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sánchez, C.A.; Andahur, E.I.; Valenzuela, R.; Castellón, E.A.; Fullá, J.A.; Ramos, C.G.; Triviño, J.C. Exosomes from bulk and stem cells from human prostate cancer have a differential microRNA content that contributes cooperatively over local and pre-metastatic niche. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3993–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, M.Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, L.; Alontaga, A.Y.; Chandra, M.; Ashby, J.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.F.; Li, S.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, S.L.; Yang, Y.; Allen, C.L.; Maguire, O.; Minderman, H.; Sen, A.; Ciesielski, M.J.; Collins, K.A.; Bush, P.J.; Singh, P.; et al. Metabolic reprogramming of stromal fibroblasts by melanoma exosome microRNA favours a pre-metastatic microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostenfeld, M.S.; Jeppesen, D.K.; Laurberg, J.R.; Boysen, A.T.; Bramsen, J.B.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Hendrix, A.; Lamy, P.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Rasmussen, M.H.; et al. Cellular disposal of miR23b by RAB27-dependent exosome release is linked to acquisition of metastatic properties. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5758–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takano, Y.; Masuda, T.; Iinuma, H.; Yamaguchi, R.; Sato, K.; Tobo, T.; Hirata, H.; Kuroda, Y.; Nambara, S.; Hayashi, N.; et al. Circulating exosomal microRNA-203 is associated with metastasis possibly via inducing tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 78598–78613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Attieh, Y.; Clark, A.G.; Grass, C.; Richon, S.; Pocard, M.; Mariani, P.; Elkhatib, N.; Betz, T.; Gurchenkov, B.; Vignjevic, D.M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts lead tumor invasion through integrin-β3-dependent fibronectin assembly. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 3509–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyazaki, K.; Oyanagi, J.; Hoshino, D.; Togo, S.; Kumagai, H.; Miyagi, Y. Cancer cell migration on elongate protrusions of fibroblasts in collagen matrix. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitra, A.K.; Zillhardt, M.; Hua, Y.; Tiwari, P.; Murmann, A.E.; Peter, M.E.; Lengyel, E. MicroRNAs reprogram normal fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts in ovarian cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Ning, Z.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Shao, C.; Shu, Y.; Shen, H. Exosomal miRNAs and miRNA dysregulation in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Hou, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Tang, S.; Du, Y.E.; Yang, L.; Yu, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, M.; et al. Stromal miR-200s contribute to breast cancer cell invasion through CAF activation and ECM remodeling. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, A.; Jana, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Wastall, L.M.; Mandal, G.; Nargis, N.; Roy, H.; Hughes, T.A.; Bhattacharyya, A. MicroRNA-222 reprogrammed cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaverina, N.; Borovjagin, A.V.; Kadagidze, Z.; Baryshnikov, A.; Baryshnikova, M.; Malin, D.; Ghosh, D.; Shah, N.; Welch, D.R.; Gabikian, P.; et al. Astrocytes promote progression of breast cancer metastases to the brain via a KISS1-mediated autophagy. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1905–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Yao, J.; Lowery, F.J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, W.C.; Li, P.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. Microenvironment-induced PTEN loss by exosomal microRNA primes brain metastasis outgrowth. Nature 2015, 527, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ell, B.; Mercatali, L.; Ibrahim, T.; Campbell, N.; Schwarzenbach, H.; Pantel, K.; Amadori, D.; Kang, Y. Tumor-induced osteoclast miRNA changes as regulators and biomarkers of osteolytic bone metastasis. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Cao, M.; Palomares, M.; Wu, X.; Li, A.; Yan, W.; Fong, M.Y.; Chan, W.C.; Wang, S.E. Metastatic breast cancer cells overexpress and secrete miR-218 to regulate type I collagen deposition by osteoblasts. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, H.A.; El-Serafi, A.T.; Hersi, F.; Arafa, E.-S.A.; Zaher, D.M.; Madkour, M.; Arab, H.H.; Tolba, M.F. Immunomodulatory MicroRNAs in cancer: Targeting immune checkpoints and the tumor microenvironment. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 3540–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, S.; Tao, Z.; Hai, B.; Liang, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, T.; Song, W.; Chen, Y.; OuYang, J.; Chen, J.; et al. miR-424(322) reverses chemoresistance via T-cell immune response activation by blocking the PD-L1 immune checkpoint. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Chen, L.; Chen, G.; Hu, C.; Jiang, S.; Sevilla, J.; Wan, Y.; Sampson, J.H.; Zhu, B.; Li, Q.J. Targeting miR-23a in CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes prevents tumor-dependent immunosuppression. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5352–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cheung, I.Y.; Guo, H.F.; Cheung, N.K. MicroRNA miR-29 modulates expression of immunoinhibitory molecule B7-H3: Potential implications for immune based therapy of human solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6275–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsukerman, P.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Gur, C.; Glasner, A.; Nachmani, D.; Bauman, Y.; Yamin, R.; Vitenshtein, A.; Stanietsky, N.; Bar-Mag, T.; et al. MiR-10b downregulates the stress-induced cell surface molecule MICB, a critical ligand for cancer cell recognition by natural killer cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5463–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daveri, E.; Vergani, E.; Shahaj, E.; Bergamaschi, L.; La Magra, S.; Dosi, M.; Castelli, C.; Rodolfo, M.; Rivoltini, L.; Vallacchi, V.; et al. microRNAs Shape Myeloid Cell-Mediated Resistance to Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Breyne, K.; Ughetto, S.; Laurent, L.C.; Breakefield, X.O. RNA delivery by extracellular vesicles in mammalian cells and its applications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooks, T.; Pateras, I.S.; Jenkins, L.M.; Patel, K.M.; Robles, A.I.; Morris, J.; Forshew, T.; Appella, E.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Harris, C.C. Mutant p53 cancers reprogram macrophages to tumor supporting macrophages via exosomal miR-1246. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Tai, S.K.; Yang, M.H. Snail-overexpressing Cancer Cells Promote M2-Like Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages by Delivering MiR-21-Abundant Exosomes. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, X.; Wu, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, X.; Jiang, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Epithelial ovarian cancer-secreted exosomal miR-222-3p induces polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 43076–43087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Chen, J.; Su, F.; Yu, B.; Su, F.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.D.; Song, E. Microvesicles secreted by macrophages shuttle invasion-potentiating microRNAs into breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zonari, E.; Pucci, F.; Saini, M.; Mazzieri, R.; Politi, L.S.; Gentner, B.; Naldini, L. A role for miR-155 in enabling tumor-infiltrating innate immune cells to mount effective antitumor responses in mice. Blood 2013, 122, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Lai, L.; Chen, Q.; Song, Y.; Xu, S.; Ma, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Cao, X.; et al. MicroRNA-494 is required for the accumulation and functions of tumor-expanded myeloid-derived suppressor cells via targeting of PTEN. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5500–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzywa, T.M.; Sosnowska, A.; Matryba, P.; Rydzynska, Z.; Jasinski, M.; Nowis, D.; Golab, J. Myeloid Cell-Derived Arginase in Cancer Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, Q.J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Markowitz, G.J.; Ning, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Y.; et al. TGF-β-miR-34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Diao, W.; Wang, D.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zen, K. MicroRNA-155 and MicroRNA-21 Promote the Expansion of Functional Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Jin, H. MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Cancer: Opportunities and Challenges. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 125094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in body fluids—the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipów, S.; Łaczmański, Ł. Blood Circulating miRNAs as Cancer Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment Response. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Wang, H.; Yao, X.; Zhang, D.; Xie, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhang, X. Circulating MicroRNAs in Cancer: Potential and Challenge. Front. Gen. 2019, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouyssou, J.M.; Manier, S.; Huynh, D.; Issa, S.; Roccaro, A.M.; Ghobrial, I.M. Regulation of microRNAs in cancer metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1845, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jinling, W.; Sijing, S.; Jie, Z.; Guinian, W. Prognostic value of circulating microRNA-21 for breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.Y.; Tao, F.; Wang, W.; Ji, K.W. Prognostic value of microRNA-21 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hur, K.; Toiyama, Y.; Schetter, A.J.; Okugawa, Y.; Harris, C.C.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Identification of a metastasis-specific MicroRNA signature in human colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, dju492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzywa, T.M.; Klicka, K.; Paskal, W.; Dudkiewicz, J.; Wejman, J.; Pyzlak, M.; Włodarski, P.K. miR-410-3p is induced by vemurafenib via ER stress and contributes to resistance to BRAF inhibitor in melanoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, K.; Toiyama, Y.; Okugawa, Y.; Ide, S.; Imaoka, H.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Circulating microRNA-203 predicts prognosis and metastasis in human colorectal cancer. Gut 2017, 66, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Huang, D.; Ma, K.; Deng, X.; Shao, Z. MiR-19a as a prognostic indicator for cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20182370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Yao, D.; Chen, J.; Ding, N. Circulating miRNA-20a and miRNA-203 for screening lymph node metastasis in early stage cervical cancer. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2013, 17, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, A.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Du, L.; Wang, C. Development of a preoperative prediction nomogram for lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer based on a novel serum miRNA signature and CT scans. EBioMedicine 2018, 37, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.G.; Gu, J. Serum microRNA-29a is a promising novel marker for early detection of colorectal liver metastasis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2012, 36, e61–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, H.; Fabbri, M.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 847–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forterre, A.; Komuro, H.; Aminova, S.; Harada, M. A Comprehensive Review of Cancer MicroRNA Therapeutic Delivery Strategies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setten, R.L.; Rossi, J.J.; Han, S.P. The current state and future directions of RNAi-based therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 421–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.S.; Brenner, A.J.; Sachdev, J.; Borad, M.; Kang, Y.-K.; Stoudemire, J.; Smith, S.; Bader, A.G.; Kim, S.; Hong, D.S. Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest. New Drugs 2017, 35, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Brenner, A.J.; Park, K.; Lee, J.L.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zandwijk, N.; Pavlakis, N.; Kao, S.C.; Linton, A.; Boyer, M.J.; Clarke, S.; Huynh, Y.; Chrzanowska, A.; Fulham, M.J.; Bailey, D.L.; et al. Safety and activity of microRNA-loaded minicells in patients with recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma: A first-in-man, phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Pel, M.E.; Kirschner, M.B.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Mugridge, N.; Weiss, J.; Williams, M.; Wright, C.; Edelman, J.J.; Vallely, M.P.; et al. Restoring expression of miR-16: A novel approach to therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2013, 24, 3128–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, A.G.; Beatty, X.; Lynch, J.M.; Hermreck, M.; Tetzlaff, M.; Duvic, M.; Jackson, A.L. Cobomarsen, an oligonucleotide inhibitor of miR-155, co-ordinately regulates multiple survival pathways to reduce cellular proliferation and survival in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 183, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Narang, A.S.; Mahato, R.I. Subcellular Fate and Off-Target Effects of siRNA, shRNA, and miRNA. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 2996–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoszewski, R.; Sikorski, A.F. Editorial focus: Understanding off-target effects as the key to successful RNAi therapy. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.A.; Betel, D.; Miller, M.L.; Sander, C.; Leslie, C.S.; Marks, D.S. Transfection of small RNAs globally perturbs gene regulation by endogenous microRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.S.; Kasinski, A.L. Animal Models to Study MicroRNA Function. Adv. Cancer Res. 2017, 135, 53–118. [Google Scholar]
- Segal, M.; Biscans, A.; Gilles, M.E.; Anastasiadou, E.; De Luca, R.; Lim, J.; Khvorova, A.; Slack, F.J. Hydrophobically Modified let-7b miRNA Enhances Biodistribution to NSCLC and Downregulates HMGA2 In Vivo. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox, K.A.; Behlke, M.A. Chemical modification and design of anti-miRNA oligonucleotides. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z. Recent progress in microRNA-based delivery systems for the treatment of human disease. ExRNA 2019, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segal, M.; Slack, F.J. Challenges identifying efficacious miRNA therapeutics for cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, A.; Panda, J.J.; Singh, A.K.; Yadav, N.; Bihari, C.; Biswas, S.; Sarin, S.K.; Chauhan, V.S. Targeted delivery of microRNA-199a-3p using self-assembled dipeptide nanoparticles efficiently reduces hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1392–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gemeinhart, R.A. Progress in microRNA delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Huang, L. Nanoparticles modified with tumor-targeting scFv deliver siRNA and miRNA for cancer therapy. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2010, 18, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilles, M.E.; Hao, L.; Huang, L.; Rupaimoole, R.; Lopez-Casas, P.P.; Pulver, E.; Jeong, J.C.; Muthuswamy, S.K.; Hidalgo, M.; Bhatia, S.N.; et al. Personalized RNA Medicine for Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1734–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayraktar, R.; Bertilaccio, M.T.S.; Calin, G.A. The Interaction Between Two Worlds: MicroRNAs and Toll-Like Receptors. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, M.; Paone, A.; Calore, F.; Galli, R.; Croce, C.M. A new role for microRNAs, as ligands of Toll-like receptors. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
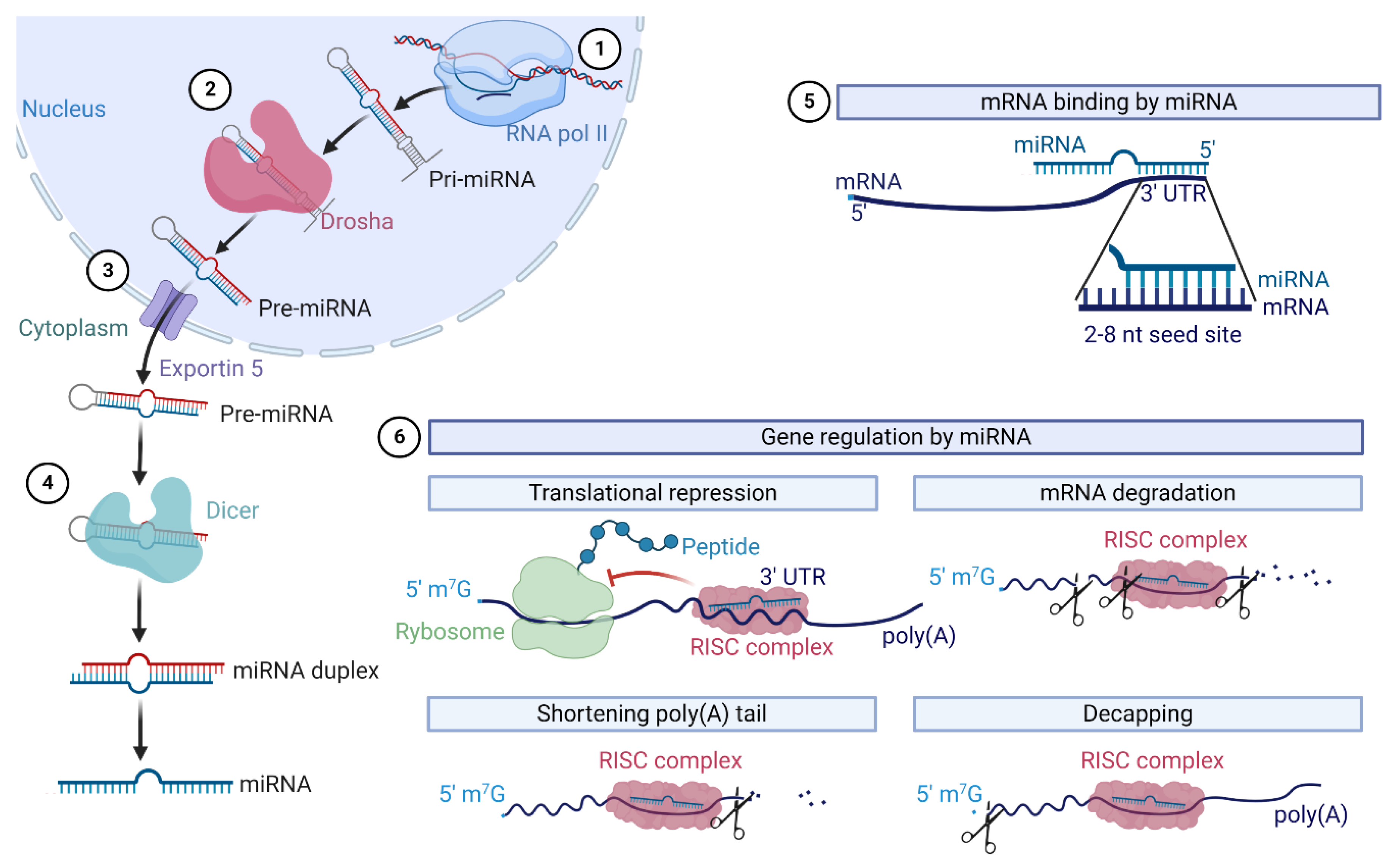
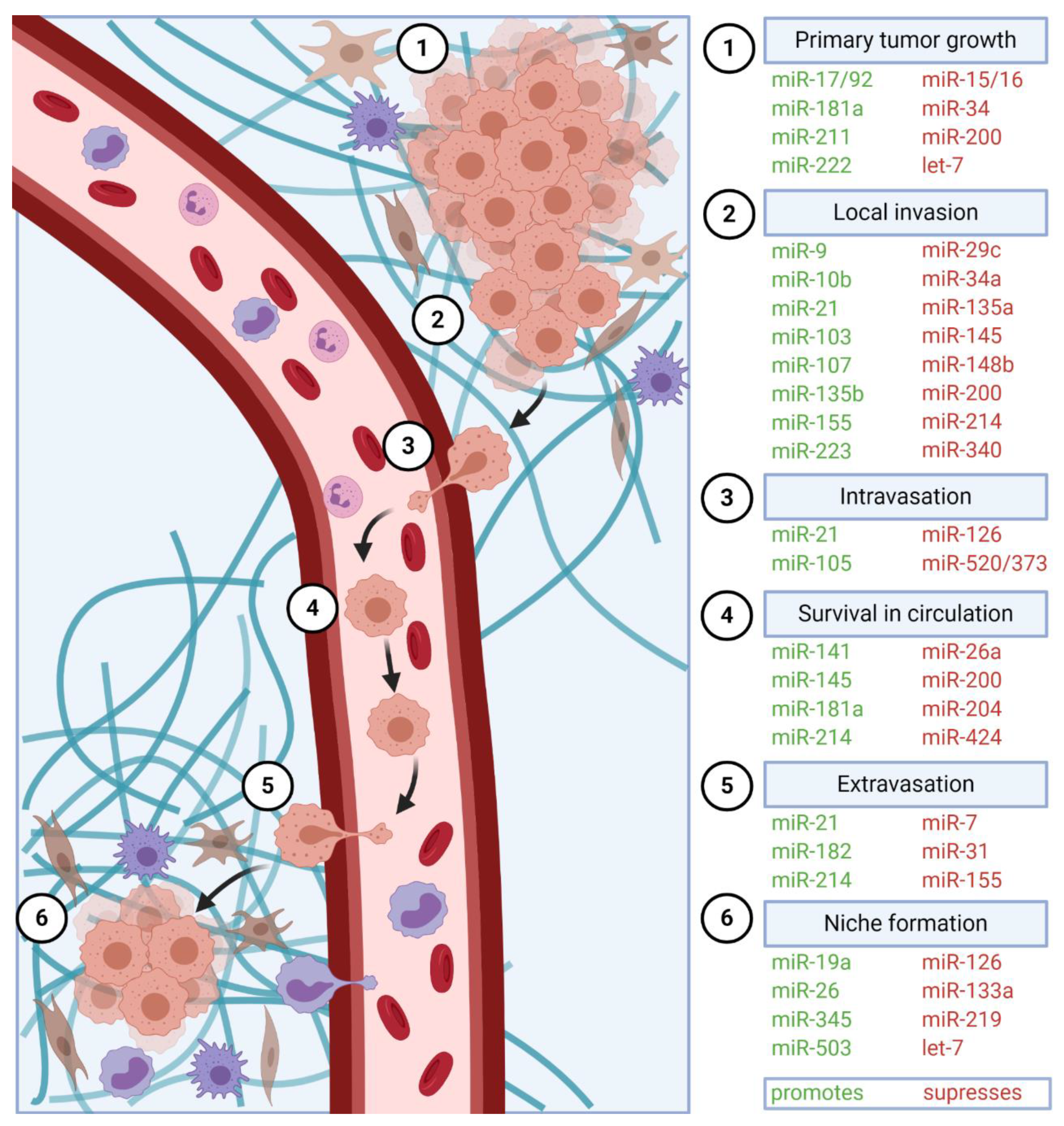
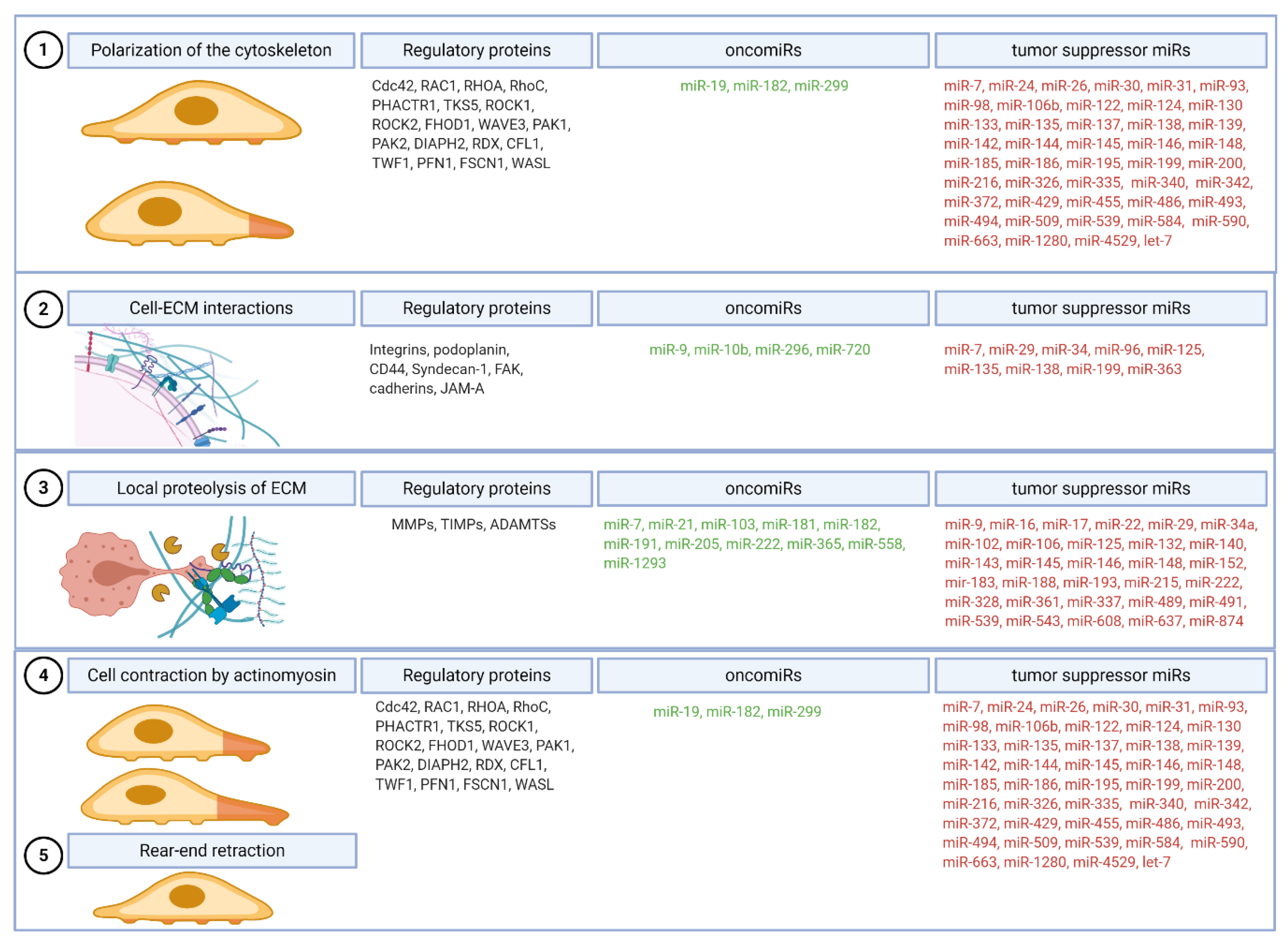

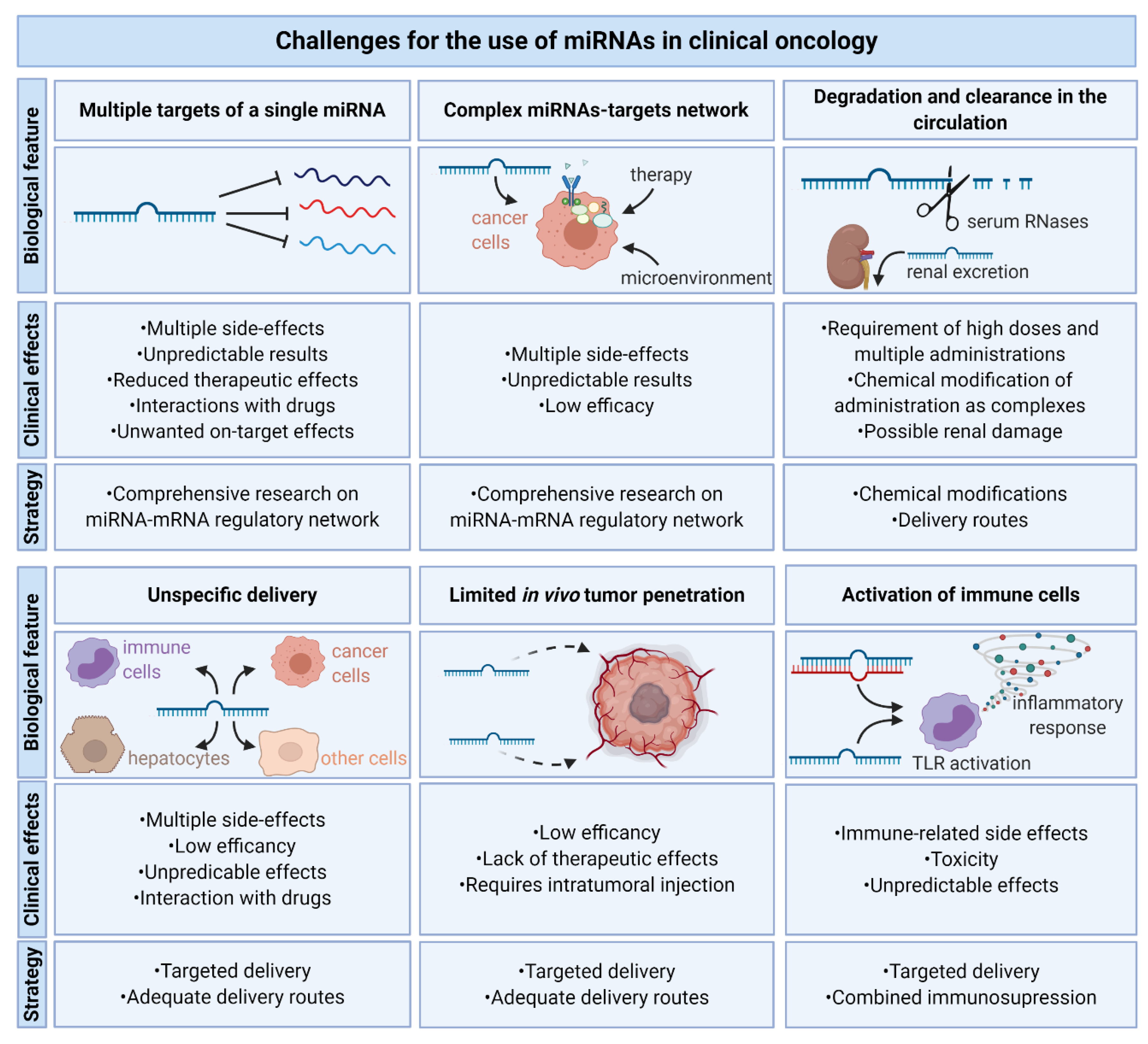
| miRNA | Cancer Type | Target | Role in Vitro | Role in Vivo | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OncomiRs | miR-9 | Breast cancer | CDH1 | ↑ cell migration and invasiveness | ↑ tumor invasion and metastasis ↑ angiogenesis | [24] |
| miR-10b | Breast cancer | HOXD10 | ↑ cell migration and invasiveness | ↑ tumor invasion and metastasis | [25] | |
| miR-17-5p | Colorectal cancer | PTEN, P130 | ↑ cell migration and invasiveness | ↑ tumor growth | [26,27] | |
| miR-19b | Breast cancer | TP53 | ↑ cell migration and invasiveness, cell cycle progression | ↑ tumor growth and metastasis | [28] | |
| miR-21 | Colorectal cancer | Pdcd4 | ↑ cell invasiveness | ↑ intravasation and metastasis | [29] | |
| miR-135b | Lung cancer | LZTS1, Hippo pathway | ↑ cell migration and invasiveness | ↑ tumor growth and metastasis | [30] | |
| miR-181a | Breast cancer | Bim | ↑ cell migration and invasiveness ↓ anoikis | ↑ tumor growth and metastasis | [31] | |
| miR-214 | Melanoma | TFAP2C, ITGA3 | ↑ cell migration and invasiveness | ↑ extravasation and metastasis | [32] | |
| miR-211 | Colorectal cancer | CHD5 | ↑ cells proliferation and migration | ↑ tumor growth | [33] | |
| miR-223 | Gastric cancer | EPB41L3 | ↑ cells motility and invasiveness | ↑ metastasis | [34] | |
| Tumor suppressor miRs | miR-34a | Neuroblastoma | MAP3K9 | ↑ induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis | ↓ tumor growth | [35] |
| miR-137 | Colorectal cancer | FMNL2 | ↓ cells proliferation and invasion | ↓ metastasis | [36] | |
| miR-192 | Colon cancer | Bcl-2, ZEB2 | ↑ apoptosis | ↓ metastasis | [37] | |
| miR-375 | Liver cancer | AEG-1 | ↓ cell growth and invasiveness | ↓ tumor growth | [38] | |
| miR-874 | Non-small cell lung cancer | MMP-2, uPA | ↓ cells invasiveness | ↓ tumor growth | [39] | |
| let-7 | Lung cancer | KRAS | ↓ cell proliferation | ↓ tumor growth | [40] | |
| Target | Role | miRNA | Role | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RhoC | Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and regulates cell shape and motility. | miR-93, miR-106b, miR-138, miR-372, miR-493, miR-509 | Decreases migration and invasiveness, reorganization of the stress fibers. | [67,68,69,70,71,72,73] |
| CDC42 | Transduces signals to the actin cytoskeleton, promotes the formation of filopodia. | miR-133, miR-137, miR-186, miR-195, miR-330 | Decreases cell migration and invasiveness. | [49,50,51,52,53,74] |
| RAC1 | Regulates reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, promotes the formation of lamellipodia. | miR-142-3p, miR-145 | Decreases cell migration and invasiveness. | [57,58] |
| RHOA | Regulates cell adhesion and migration, provides contractile force by the formation of stress fibers. | miR-31, miR-122, miR-133a-3p, miR-146a, miR-200b, miR-340-5p | Decreases cell migration. | [75,76,77,78,79,80] |
| PHACTR1 | Binds actin and regulates the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. | miR-584 | Decreases expression leads to the induction of migration. | [81] |
| TKS5 | Regulates actin cytoskeleton and invadopodia formation. | miR-200c | Decreases invasiveness. | [82] |
| MYLK | Regulates the phosphorylation of myosin light chains. | miR-155, miR-200c |
Decreases invasiveness and ability to form invadopodia. | [82,83] |
| ROCK1 | Regulates actinomyosin cytoskeleton. | miR-124, miR-145, miR-148b, miR-199a, miR-335, miR-340, miR-584, miR-1280 | Decreases cells migration and invasiveness. | [63,84,85,86,87,88,89] |
| ROCK2 | Regulates actinomyosin cytoskeleton. | miR-124, miR-130a, miR-135a, miR-138, miR-139, miR-144, miR-185, miR-4529-5p | Decreases cells migration and invasiveness. | [90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97] |
| FHOD1 | Regulates actin cytoskeleton. | miR-200c | Decreases migration and invasiveness. | [98] |
| PPM1F | Regulates actin cytoskeleton. | miR-149, miR-200c, miR-490, miR-590 | Decreases migration and invasiveness. | [98,99,100,101] |
| WAVE3 | Regulates actin cytoskeleton. | miR-31, miR-200 | Decreases invasiveness. | [102,103] |
| PAK1 | Regulates cell motility and cytoskeletal remodeling. | Let-7, miR-7, miR-26a, miR-26b, miR-98, miR-145, miR-485, miR-494, | Decreases migration and invasiveness. | [64,103,104,105,106,107,108,109] |
| DIAPH2 | Regulates microtubule attachment to kinetochores. | Let-7, miR-10b | Decreases migration and invasiveness. | [64,110] |
| RDX | Regulates of membrane domains through interaction with the cytoskeleton and transmembrane proteins. | Let-7, miR-31, mir-200b, miR-409 | Decreases migration and invasiveness. | [64,111,112] |
| PAK2 | Regulates of cell motility and cytoskeletal remodeling. | miR-7, miR-23b, miR-137, miR-216a, miR-455, miR-4779, | Decreases migration and invasiveness, cytoskelet remodeling. | [113,114,115,116,117] |
| CFL1 | Binds actin and regulates cell proliferation and migration. | miR-342 | Decreases invasion and migration. | [118] |
| TWF1 | Binds actin and promotes EMT. | miR-30c, miR-142, miR-486 | Decreases stress fibers F-actin formation. | [119,120,121] |
| PFN1 | Binds actin and inhibits cells proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT. | miR-19a-3p, miR-182, miR-299-3p, miR-330-3p, | Increases migration and invasiveness. | [122,123,124,125,126] |
| FSCN1 | Stabilizes actin filaments in invadopodia. | miR-24, miR-133a, miR-133b, miR-145, miR-200b, miR-326, miR-429, miR-539, miR-663 | Decreases invasiveness. | [127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135] |
| WASL | Regulates actin polymerization. | miR-142-3p, miR-148a | Decreases invasiveness, reduced number of membrane protrusions. | [65,136] |
| Integrin | Protein Name | Synonyms [146] | miRNA | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITGA1 | α1 | CD49a | miR-375 | [145] |
| ITGA2 | α2 | CD49b, α2 subunit of very late antigen 2 (VLA-2) | miR-31 | [144] |
| ITGA2B | αIIb | GTA, CD41, GP2B, HPA3, CD41b, GPIIb | miR-122 | [147] |
| ITGA3 | α3 | CD49c, α3 subunit of VLA-3 | miR-199 family | [148] |
| ITGA4 | α4 | CD49d, α4 subunit of VLA-4 | miR-30a | [149] |
| ITGA5 | α5 | CD49e, fibronectin receptor alpha | miR-25-3p, miR-26a, miR-31, miR-92, miR-142-3p, miR-148b, miR-149 | [65,84,138,144,150] |
| ITGA6 | α6 | CD49f, ITGA6B | miR-25, miR-29s, miR-143-3p | [151,152,153] |
| ITGA7 | α7 | nd | ||
| ITGA8 | α8 | nd | ||
| ITGA9 | α9 | miR-296-3p | [154] | |
| ITGA10 | α10 | miR-34a | [155] | |
| ITGA11 | α11 | miR-148a | [136] | |
| ITGAD | αD | nd | ||
| ITGAE | αE | CD103, human mucosal lymphocyte antigen 1α | nd | |
| ITGAL | αL | CD11a (p180), lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) α subunit | miR-126 | [156] |
| ITGAM | αM | Mac-1, CD11b, complement receptor 3 (CR3) subunit | miR-124 miR-223 | [157,158] |
| ITGAV | αV | CD51, MSK8, vitronectin receptor α (VNRα) | miR-25, miR-31, miR-92, miR-142-3p | [65,144,151,159] |
| ITGAX | αX | CD11c, CR4 subunit | miR-142 | [160] |
| ITGB1 | β1 | Fibronectin receptor β, CD29, MDF2, MSK12 | miR-29b, miR-29c miR-31, miR-124 miR-130b, miR-149 miR-183, miR-338-3p, miR-451 | [144,161,162,163,164,165,166,167] |
| ITGB2 | β2 | Leukocyte cell adhesion molecule, CD18, CR3 subunit, CR4 subunit | miR-1, miR-133a | [168] |
| ITGB3 | β3 | CD61; GP3A; GPIIIa, platelet glycoprotein IIIa | miR-31, mir-150 | [144,169] |
| ITGB4 | β4 | CD104 | miR-29a, miR-184 | [170] |
| ITGB5 | β5 | miR-185 | [171] | |
| ITGB6 | β6 | miR-17/20a | [172] | |
| ITGB7 | β7 | nd | ||
| ITGB8 | β8 | let-7, miR-93 miR-145, miR-148a | [64,136,173] |
| MMP | Role | Role in Cancer | miRNA | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collagenases | ||||
| MMP-1 | Degradation of collagen types I, II, III, V, IX and fibrillary collagen | Initial invasion, metastasis | miR-222, miR-361-5p | [212,213] |
| MMP-8 | Degradation of collagen types I, II, III, V, IX and fibrillary collagen | Inhibits invasion and metastasis | miR-539, miR-2682-3p | [214] |
| MMP-13 | Degradation of collagens types I, II, III, V, IX and fibrillary collagen | Tumor growth, invasion | miR-125b,miR-148a, miR-188-5p | [215,216] |
| Matrilysins | ||||
| MMP-7 | Proteolysis of fibronectin, collagen type IV, laminin, elastin, entactin, osteopontin, and cartilage proteoglycan aggregates | Invasive potential, proliferation, anti-apoptotic | miR-143, miR-489, miR-543 | [217,218] |
| MMP-26 | Degradation of collagen type IV, fibronectin, fibrinogen, casein, vitronectin, and others | Activates MMP-9 | nd | |
| Metalloelastase | ||||
| MMP-12 | Degradation of elastin | Protective inhibition of tumor growth | nd | |
| Stromelysins | ||||
| MMP-3 | Degradation of collagen types II, III, IV, IX, and X, proteoglycans, fibronectin, laminin, and elastin | Invasion, metastasis, EMT, angiogenesis | miR-17, miR-152 | [219,220] |
| MMP-10 | Degradation of proteoglycans and fibronectin | Invasion, migration, tumor growth | nd | |
| MMP-11 | Degradation of alpha-1 antitrypsin | Early tumor invasion | miR-125a-5p, miR-145, miR-192 | [221,222,223] |
| Gelatinases | ||||
| MMP-2 | Degradation of type IV collagen | Degradation of ECM | miR-29b, miR-29c, miR-106b, miR-874 | [39,203,224,225] |
| MMP-9 | Degradation of type IV collagen | Degradation of ECM | miR-29b, miR-183, miR-491-5p | [226,227,228] |
| Enamelysin | ||||
| MMP-20 | Tooth-specific MMP | nd | ||
| Membrane-Type | ||||
| MMP-14 | Degradation of fibronectin, collagen, and gelatin | Activation of other MMPs | miR-9, miR-22, miR-337-3p | [229,230,231] |
| MMP-15 | EMT, angiogenesis | miR-608 | [232] | |
| MMP-16 | Invasion, metastasis | miR-132, miR-146a, miR-146b, miR-215, miR-328-3p | [233,234,235,236,237] | |
| MMP-17 | Angiogenesis, metastasis | nd | ||
| MMP-24 | Migration, metastasis | nd | ||
| MMP-25 | Tumor growth | nd | ||
| Others | ||||
| MMP-19 | Tumor growth, adhesion, metastasis | miR-16, miR-193b-3p, miR-637 | [238,239,240] | |
| Inhibitors of metalloproteinase | ||||
| TIMP1 | Inhibition of MMP-14 -16, -19, -24 and ADAM10 | Inhibition of cancer growth and metastasis | miR-182, miR-1293 | [241,242] |
| TIMP2 | Inhibition of all MMPs and ADAM12 | Inhibition of cancer growth and metastasis | miR-205-5p | [243] |
| TIMP3 | Inhibition of all MMPs and ADAM10, 12, 17, 28 and 33; ADAMTS-1, -4, and -5, ADAMTS-2 | Inhibition of tumor growth, angiogenesis, and invasion | miR-21, miR-103, miR-181b, miR-191 | [244,245,246,247] |
| TIMP4 | Inhibition of most MMPs and ADAM17d, -28, and -33 | Inhibition of angiogenesis, and invasion, promotion of apoptosis | miR-558 | [248] |
| RECK | Inhibition of MMP-9 | Inhibition of metastasis | miR-7, miR-21, miR-222 | [207,249,250,251] |
| miRNAs Promoting Invasiveness | miRNAs Suppressing Invasiveness | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA | Targets | Ref. | miRNA | Targets | Ref. |
| miR-9 | SOX7, CDH1, α-catenin | [24,256,257,258] | miR-10b | IGF-1R, HOXA-3, FGF13 | [259,260,261] |
| miR-10b | TP53, PAX6, NOTCH1, HOXD10, TIP30, KLF4, HOXB3 | [259,262,263,264,265] | miR-29c | CDK6, ITGB1, TIAM1, Collagens, Laminin γ1 | [193,266,267,268] |
| miR-21 | PDCD4, maspin, HBP1, LZTFL1, KLF5 | [185,269,270,271,272] | miR-34a | SATB2, BCL-2, HNF4α, Snail, MMP9, MMP14, Notch1 | [273,274,275,276,277,278] |
| miR-103 | DAPK, KLF4, OLFM4, LATS2, PTEN | [279,280,281,282] | miR-135a | ROCK1, Smo, ERRα | [283,284,285] |
| miR-107 | TPM1, DAPK, KLF4 | [279,286] | miR-145 | PAK4, ROCK1, MMP11, Rab27a, MUC1, MMP16, N-cadherin, ZEB2, Ets1, KLF4 | [88,287,288,289,290,291,292,293] |
| miR-135b | NR3C2, LZTS1, APC, FOXO1, ST6GALNAC2, RECK, EVI5 | [30,71,294,295,296,297] | miR-148b | WNT1, MTA2, ROCK1, Dock6 | [298,299,300,301] |
| miR-155 | DOCK-1, SDCBP, ANXA-2, CLDN-1, NDFIP1, SOCS1, TP53INP1, BCL6 | [302,303,304,305,306] | miR-200 | Foxf2, Flt1, BMP4, Onecut2, LIMK1, BMI-1, E2F3 | [307,308,309,310,311] |
| miR-223 | PAX6, hFBXW7, EPB41L3 | [34,312,313] | miR-214 | JAG1, ROCK1, CDC25B, ARL2, GALNT7, MKK3, JAK1 | [314,315,316,317,318,319,320] |
| miR-424 | CADM1, SMAD7 | [321,322] | miR-340 | NT5E, EphA3, SIRT7, NF-κB1, RhoA, ROCK1, JAK1 | [85,323,324,325,326,327,328] |
| Target | miRNAs | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| TGF-β1 | miR-99a, miR-99b, miR-744 | [359,360] |
| TGFBR2 | miR-17 family, miR-21, miR-204, miR-211, miR-373, miR-520 | [361,362,363,364,365] |
| ZEB1 | miR-200 family, miR-205 | [366,367] |
| ZEB2 | miR-132, miR-138, miR-154, miR-200 family, miR-205, miR-215 | [367,368,369,370,371] |
| Twist1 | let-7d, miR-33a, miR-145a-5p, miR-151-5p, miR-214, miR-580 | [372,373,374,375] |
| Twist2 | miR-138, miR-215 | [376,377] |
| Notch | miR-23b, miR-30a, miR-34a, miR-206 | [131,378,379,380] |
| Snail1 | miR-22, miR-34a, miR-137, miR-182 | [231,276,381] |
| Snail2 | miR-30a, miR-124, miR-203, miR-204, miR-211 | [362,382,383,384] |
| EZH2 | miR-138 | [368] |
| Slug | miR-1, miR-30a, miR-124, miR-506, miR-630, miR-590-3p | [385,386,387,388,389,390] |
| N-cadherin | miR-145, miR-194 | [391,392] |
| Vimentin | miR-30c | [393] |
| Fibronectin | miR-1, miR-139, miR-200c, miR-432 | [394,395,396,397] |
| E-Cadherin | miR-10b, miR-22, miR-23b, miR-25, miR-92a, miR-221, miR-720, | [196,398,399,400,401,402,403] |
| ZO-1 | miR-103 | [404] |
| Claudins | miR-98 (claudin-1), miR-146-5p (claudin-12), miR-421 (claudin-11), miR-488 (claudin-2), miR-155 (claudin-1) | [405,406,407,408,409] |
| Target | miRNA | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| VEGF | miR-20b, miR-27b, miR-29b, miR-93, miR-126, miR-128, miR-140-5p, miR-195, miR-203, miR-205, miR-497, miR-503, miR-638, | [51,245,413,414,415,416,417,418,419,420,421,422,423,424] |
| VEGFR | miR-378a, miR-497 | [425] |
| NRP1 | miR-141, miR-338 | [426,427] |
| TSP-1 | miR-19a, miR-182, miR-467 | [428,429,430] |
| FGF | miR-503, miR-5582-5p | [421,431] |
| HDGF | miR-139, miR-195, miR-214, miR-497, miR-511, miR-873, miR-939 | [432,433,434,435,436,437,438] |
| Angiogenin | miR-204 | [363] |
| PDGF | miR-29a | [439] |
| HIF1a | miR-20b, miR-33a, miR-107, miR-135b, miR-519c | [440,441,442,443] |
| HIF2a | miR-145 | [58] |
| VHL | miR-21, miR-155, miR-222 | [444,445,446] |
| STAT3 | miR-125a, miR-411, miR-544, miR-874, miR-1299 | [447,448,449,450,451] |
| Bmi-1 | miR-16, miR-132, miR-183, miR-200c, miR-203, miR-218 | [452,453,454,455,456,457] |
| E2F3 | miR-194-5p, miR-200c, miR-217, miR-432, miR-449a | [311,458,459,460,461] |
| NF90 | miR-590-5p | [462] |
| miRNA | Cancer | Type of Tissue | Mirna Level | Lymph Node Metastasis | Distant Metastasis | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-203 | Colorectal | Serum | High | OR 2.9; 95%CI 1.4–6.1; p = 0.0035 | OR 5.3; 95%CI 2.4–11.5; p < 0.0001 | [549] |
| miR-885-5p | Colorectal | Serum | High | OR 3.0; 95%CI 1.3–7.2; p = 0.0116 | OR 3.1; 95%CI 1.0–10.0; p = 0.0456 | [547] |
| miR-19a | Various carcinomas | Serum and tissue | High | OR 0.564; 95%CI 0.346–0.921 | nd | [550] |
| miR-20a | Cervical | Serum | High | OR 1.552; 95%CI 1.137–2.118 | nd | [551] |
| miR-21 | Breast | Serum and tissue | High | OR 2.36; 95%CI 1.04–4.78; p = 0.03 | nd | [545] |
| miR-21 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Serum and tissue | High | OR 1.45; 95%CI 1.02–2.06; p = 0.038 | [546] | |
| miR-122-5p | Colorectal | Serum | High | OR 1.621; 95%CI 1.255–2.092; p = 0.0002 | nd | [552] |
| miR-146b-5p | Colorectal | Serum | High | OR 2.096; 95%CI 1.594–2.756; p < 0.0001 | nd | [552] |
| miR-186-5 | Colorectal | Serum | High | OR 2.910; 95%CI 1.810–4.678; p < 0.0001 | nd | [552] |
| miR-193a-5p | Colorectal | Serum | High | OR 0.656; 95%CI 0.577–0.774; p < 0.0001 | nd | [552] |
| let-7i | Colorectal | Tissue | Low | nd | OR 5.5; 95%CI 1.1–26.8; p = 0.0334 | [547] |
| miR-10b | Colorectal | Tissue | High | nd | OR 4.9; 95%CI 1.2–19.7; p = 0.0248 | [547] |
| miR-29a | Colorectal | Serum | High | nd | OR 3.500; 95%CI 1.274–9.617; p < 0.05 | [553] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grzywa, T.M.; Klicka, K.; Włodarski, P.K. Regulators at Every Step—How microRNAs Drive Tumor Cell Invasiveness and Metastasis. Cancers 2020, 12, 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123709
Grzywa TM, Klicka K, Włodarski PK. Regulators at Every Step—How microRNAs Drive Tumor Cell Invasiveness and Metastasis. Cancers. 2020; 12(12):3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123709
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrzywa, Tomasz M., Klaudia Klicka, and Paweł K. Włodarski. 2020. "Regulators at Every Step—How microRNAs Drive Tumor Cell Invasiveness and Metastasis" Cancers 12, no. 12: 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123709
APA StyleGrzywa, T. M., Klicka, K., & Włodarski, P. K. (2020). Regulators at Every Step—How microRNAs Drive Tumor Cell Invasiveness and Metastasis. Cancers, 12(12), 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123709