Allometric Scaling Approaches for Predicting Human Pharmacokinetic of a Locked Nucleic Acid Oligonucleotide Targeting Cancer-Associated miR-221
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.2. Allometric Scaling of Clearance Values
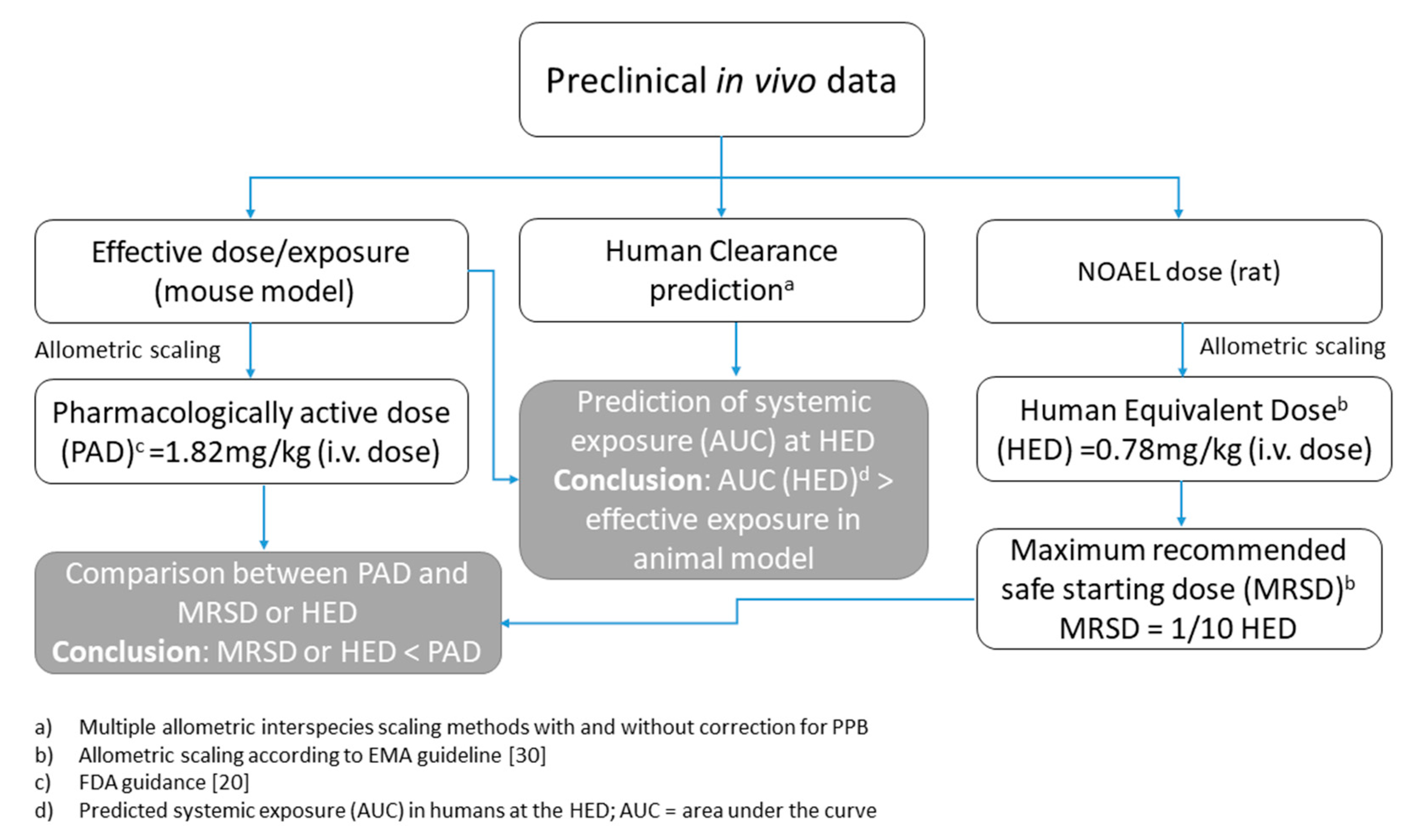
2.3. Calculation of Human Equivalent Dose (HED)
2.4. Allometric Scaling of PK Parameters
2.5. Two-Species Scaling
2.6. One-Species Scaling
2.7. Plasma Protein Binding and CLpu
- (i)
- specificity, linearity, range and lower limit of quantification (LOQ),
- (ii)
- within-batch precision and accuracy,
- (iii)
- matrix effect,
- (iv)
- stability in human, monkey, and rat plasma at 37 °C.
2.8. Protein Binding
3. Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Ultrafiltration Procedure
3.2.1. LNA-i-miR-221 Protein Binding in Human, Rat, and Monkey
3.2.2. Non-Specific Binding of LNA-i-miR-221 to Amicon Plastic
3.3. Analytical Conditions
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Martino, M.T.; Rossi, M.; Caracciolo, D.; Gulla, A.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P. Mir-221/222 are promising targets for innovative anticancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo Cantafio, M.E.; Nielsen, B.S.; Mignogna, C.; Arbitrio, M.; Botta, C.; Frandsen, N.M.; Rolfo, C.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P.; Di Martino, M.T. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a 13-mer LNA-inhibitor-miR-221 in Mice and Non-human Primates. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Martino, M.T.; Gulla, A.; Cantafio, M.E.; Lionetti, M.; Leone, E.; Amodio, N.; Guzzi, P.H.; Foresta, U.; Conforti, F.; Cannataro, M.; et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity of miR-221/222 inhibitors in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Martino, M.T.; Gulla, A.; Gallo Cantafio, M.E.; Altomare, E.; Amodio, N.; Leone, E.; Morelli, E.; Lio, S.G.; Caracciolo, D.; Rossi, M.; et al. In vitro and in vivo activity of a novel locked nucleic acid (LNA)-inhibitor-miR-221 against multiple myeloma cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santolla, M.F.; Lappano, R.; Cirillo, F.; Rigiracciolo, D.C.; Sebastiani, A.; Abonante, S.; Tassone, P.; Tagliaferri, P.; Di Martino, M.T.; Maggiolini, M.; et al. miR-221 stimulates breast cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) through selective interference with the A20/c-Rel/CTGF signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2018, 37, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulla, A.; Di Martino, M.T.; Gallo Cantafio, M.E.; Morelli, E.; Amodio, N.; Botta, C.; Pitari, M.R.; Lio, S.G.; Britti, D.; Stamato, M.A.; et al. A 13 mer LNA-i-miR-221 Inhibitor Restores Drug Sensitivity in Melphalan-Refractory Multiple Myeloma Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.Z.; Grundy, J.S.; Geary, R.S. Clinical pharmacokinetics of second generation antisense oligonucleotides. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, S.; Vezzelli, A.; Turtoro, A.; Solazzo, L.; Greco, A.; Tassone, P.; Di Martino, M.T.; Breda, M. Development and validation of a bioanalytical method for quantification of LNA-i-miR-221, a 13-mer oligonucleotide, in rat plasma using LC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 150, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, R.S. Antisense oligonucleotide pharmacokinetics and metabolism. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Riviere, J.E. The application of allometric scaling principles to predict pharmacokinetic parameters across species. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.W.; Seol, I.C.; Son, C.G. Interpretation of Animal Dose and Human Equivalent Dose for Drug Development. J. Korean Orient. Med. 2010, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum, H. Interspecies scaling, allometry, physiological time, and the ground plan of pharmacokinetics. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1982, 10, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimbach, T.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; Hu, W.; He, H. Practical anticipation of human efficacious doses and pharmacokinetics using in vitro and preclinical in vivo data. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, M. Protein binding and drug clearance. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1984, 9, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, I. Interspecies Pharmacokinetic Scaling: Principles And Application of Allometric Scaling; Hardcover: Danvers, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Hussain, A.; Leal, M.; Mayersohn, M.; Fluhler, E. Interspecies prediction of human drug clearance based on scaling data from one or two animal species. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2007, 35, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.A.; Geary, R.S.; Levin, A.A. Plasma protein binding of an antisense oligonucleotide targeting human ICAM-1 (ISIS 2302). Oligonucleotides 2006, 16, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.Z.; Kim, T.W.; Hong, A.; Watanabe, T.A.; Gaus, H.J.; Geary, R.S. Cross-species pharmacokinetic comparison from mouse to man of a second-generation antisense oligonucleotide, ISIS 301012, targeting human apolipoprotein B-100. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2007, 35, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, I. Pharmacokinetic allometric scaling of oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2011, 21, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Guidance for Industry “Estimating the Maximum Safe Starting Dose in Initial Clinical Trials for Therapeutics in Adult Healthy Volunteers”; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Pharmacology and Toxicology: Rockville, MD, USA, 2005.
- Frazier, K.S. Antisense oligonucleotide therapies: The promise and the challenges from a toxicologic pathologist’s perspective. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, R.S.; Leeds, J.M.; Henry, S.P.; Monteith, D.K.; Levin, A.A. Antisense oligonucleotide inhibitors for the treatment of cancer: 1. Pharmacokinetic properties of phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides. Anti-Cancer Drug Des. 1997, 12, 383–393. [Google Scholar]
- Leeds, J.M.; Henry, S.P.; Truong, L.; Zutshi, A.; Levin, A.A.; Kornbrust, D. Pharmacokinetics of a potential human cytomegalovirus therapeutic, a phosphorothioate oligonucleotide, after intravitreal injection in the rabbit. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 1997, 25, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.Z.; Zhang, H.; Geary, R.S.; Graham, M.; Masarjian, L.; Lemonidis, K.; Crooke, R.; Dean, N.M.; Levin, A.A. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of an antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotide targeting Fas mRNA in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 296, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geary, R.S.; Yu, R.Z.; Levin, A.A. Pharmacokinetics of phosphorothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2001, 2, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.; Tan, W.; Cai, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhang, R. In vivo pharmacokinetics of phosphorothioate oligonucleotides containing contiguous guanosines. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1997, 7, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.A.; Craig, S.J.; Bayley, D.; Christian, R.A.; Geary, R.; Nicklin, P.L. Pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and elimination of a 20-mer phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotide (CGP 69846A) after intravenous and subcutaneous administration. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997, 54, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossum, P.A.; Sasmor, H.; Dellinger, D.; Truong, L.; Cummins, L.; Owens, S.R.; Markham, P.M.; Shea, J.P.; Crooke, S. Disposition of the 14C-labeled phosphorothioate oligonucleotide ISIS 2105 after intravenous administration to rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993, 267, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar]
- London, UK European Medicines Agency. Available online: http://www.emea.europa.eu/ (accessed on 19 July 2007).
- EMA; Commitee for Medical Products for Human Use (CHMP). Guideline on Strategies to Identify and Mitigate Risks for First-In Human Clinical Trials with Investigational Medical Products; EMEA; CHMP: London, UK, 19 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
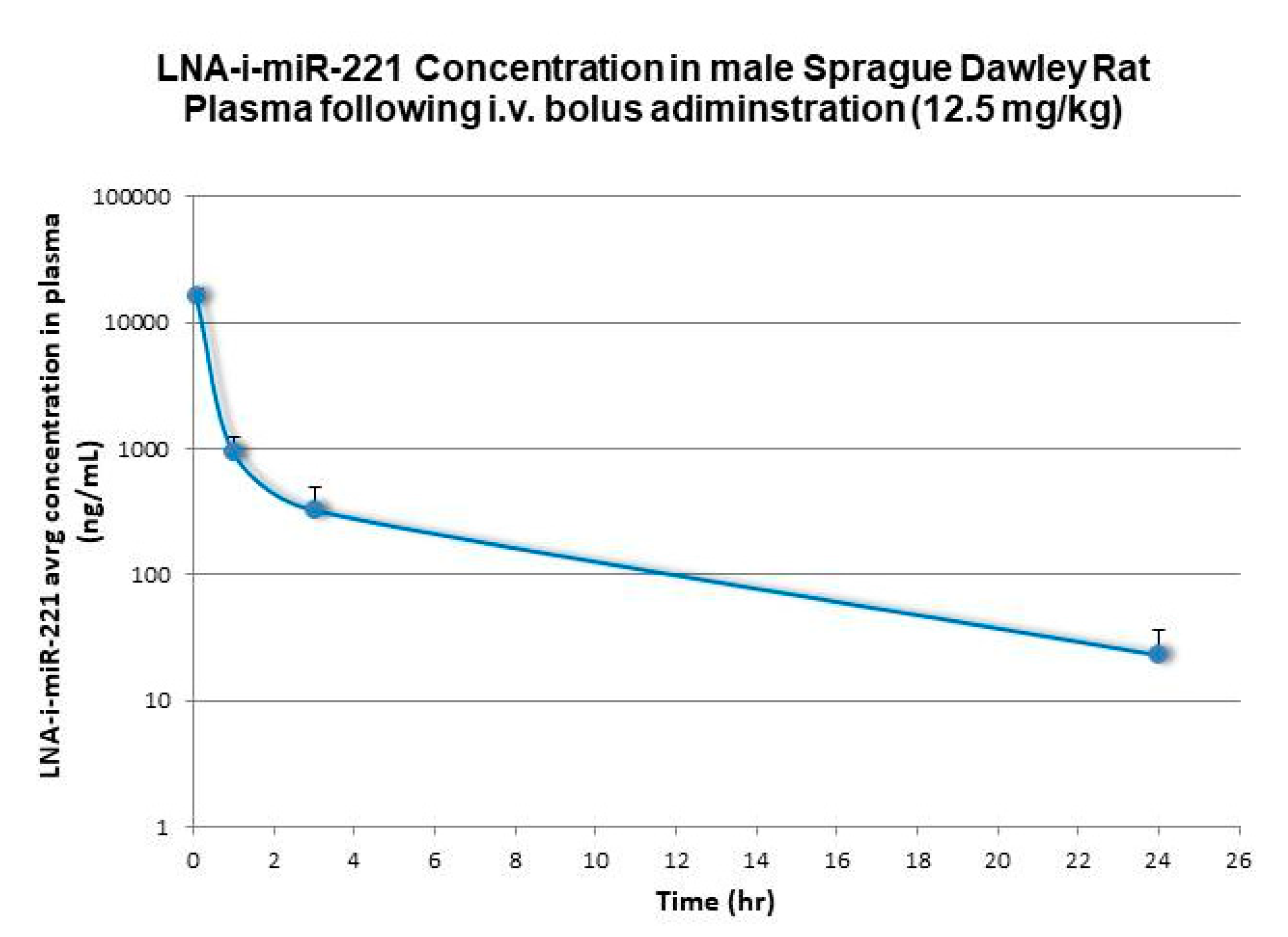
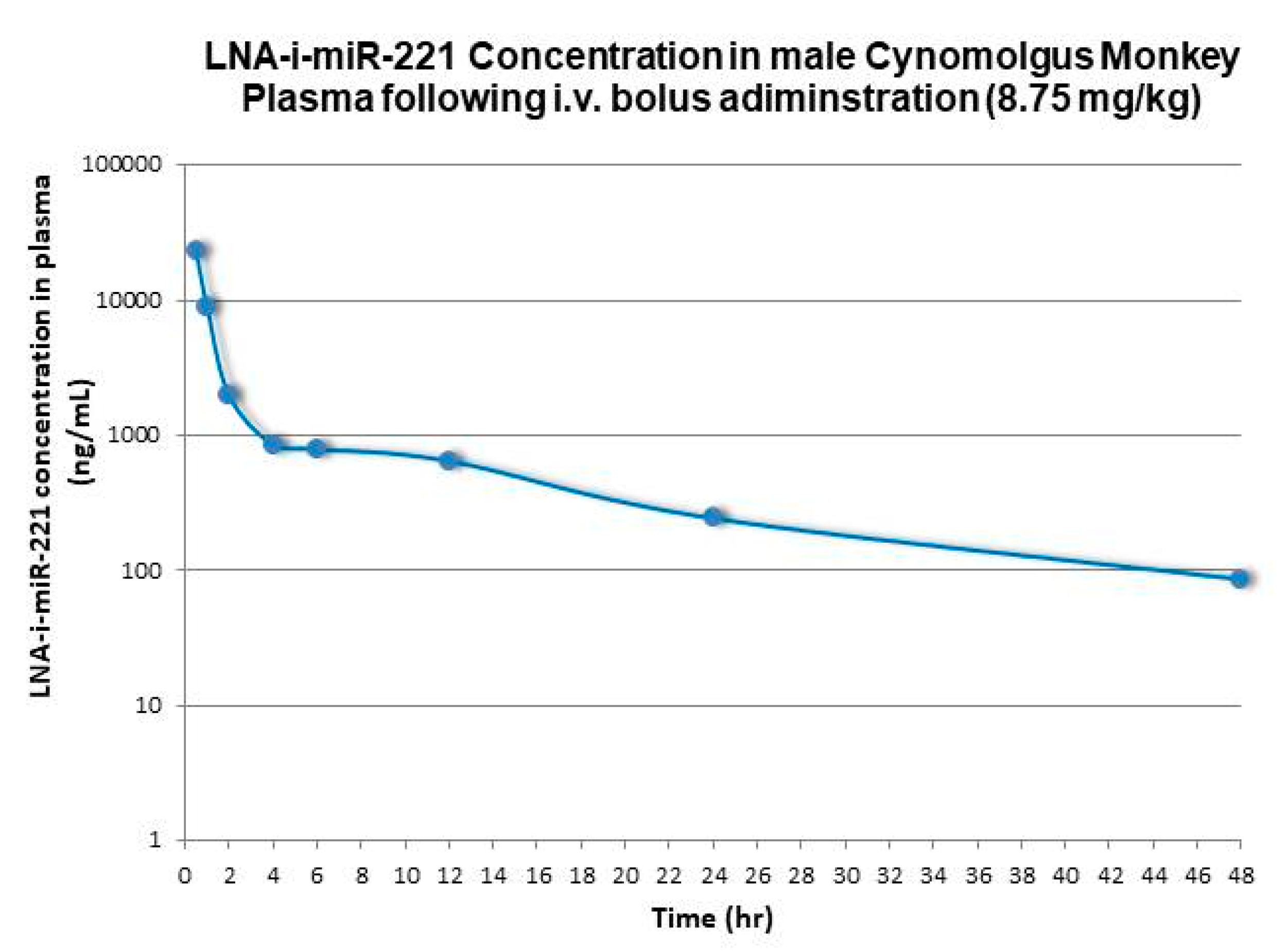

| Species | Dose (i.v. Bolus) | C0/Dose | AUC 1 | AUC/Dose | CL | Terminal Half-Life | Vd Terminal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/kg | ng/mL/mg | (h·ng/mL) | (h·ng/mL)/mg | mL/min/kg | h | mL/Kg | |
| Rat | 12.5 | 4462 | 27192 | 2160 | 7.9 | 3.9 | 2626 |
| Mouse 2 | 25 | 82 | 3226 | 129 | 129 | 1.5 | 16443 |
| Monkey | 8.75 | 7017 | 49300 | 5634 | 3.0 | 12.8 | 3286 |
| Species | Average Body Weights (kg) Used for Allometric Scaling |
|---|---|
| Mouse | 0.025 |
| Rat | 0.25 |
| Monkey (Cynomolgus) | 3.75 |
| Human | 70 |
| b | −0.362198 |
| a | 0.6789 |
| CLhuman (mL/min/kg) | 1.02 |
| CLhuman (mL/min) | 71.7 |
| b | 0.65 |
| arat–monkey | 0.6789 |
| CLhuman (mL/min/kg) | 1.1 |
| CLhuman (mL/min) | 76 |
| Species Used for Scaling | Human CLp (mL/min/kg) | Human CLp (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|
| Single Species Allometry | ||
| rat | 1.9 | 135 |
| monkey | 1.4 | 100 |
| Total Plasma Clearance | AUC/Dose | AUC for 0.78 ‡ mg/kg i.v. Dose | AUC for 1.82 ‡ mg/kg i.v. Dose | AUC for 5.0 ‡ mg/kg i.v. Dose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allometric Method Used for Prediction | mL/min/kg | h·ng/mL·(mg Dose)−1 | h·ng/mL | h·ng/mL | h·ng/mL |
| Direct scaling two-species (r, mk) (Equation (1a)) | 1.0 | 16,264 | 12,686 | 29,600 | 81,318 |
| Tang et al. method two-species (r, mk) (Equation (3)) | 1.1 | 15,443 | 12,046 | 28,106 | 77,215 |
| One-species (r) allometric scaling (Equation (4)) | 1.9 | 8643 | 6741 | 15,730 | 43,214 |
| One-species (mk) allometric scaling (Equation (4)) | 1.4 | 11,711 | 9135 | 21,315 | 58,557 |
| Geometric mean | Geometric mean | Geometric mean | Geometric mean | Geometric mean | |
| 1.3 | 12,627 | 9849 | 22,981 | 63,135 |
| Total Plasma Clearance | AUC/Dose | AUC for 0.78 ‡ mg/kg i.v. Dose | AUC for 1.82 ‡ mg/kg i.v. Dose | AUC for 5.0 ‡ mg/kg i.v. Dose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allometric Method Used for Prediction | mL/min/kg | h·ng/mL·(mg Dose)−1 | h·ng/mL | h·ng/mL | h·ng/mL |
| Direct scaling two-species (r, mk) (Equation (1a)) | 1.0 | 16,386 | 12781 | 29,823 | 81,931 |
| Tang et al. method two-species (r, mk) (Equation (3)) | 1.15 | 14,462 | 11280 | 26,320 | 72,309 |
| One-species (r) allometric scaling (Equation (4)) | 2.2 | 7749 | 6044 | 14,103 | 38,743 |
| One-species (mk) allometric scaling (Equation (4)) | 1.5 | 11,106 | 8662 | 20,212 | 55,528 |
| Geometric mean | Geometric mean | Geometric mean | Geometric mean | Geometric mean | |
| 1.4 | 11950 | 9321 | 21,749 | 59,750 |
| Species | LNA-i-miR-221 Concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 µM | 10 µM | Mean PPB | Mean fu | |
| Human | 98.6 ± 0.32 | 98.5 ± 0.09 | 98.55 | 0.0145 |
| Monkey | 98.2 ± 0.39 | 99.05 ± 0.39 | 98.63 | 0.0138 |
| Rat | 98.5 ± 0.17 | 98.9 ± 0.17 | 98.70 | 0.0130 |
| Species | Sex | Supplier | Anticoagulant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rat a (Sprague–Dawley) | Male Pool of 25 animals | Citoxlab | K2EDTA |
| Monkey b (Cynomolgus) | Male Pool of 10 animals | Citoxlab | K2EDTA |
| Human c | Male Pool of 10 donors | Biopredic (PLA152A050) | K2EDTA |
| Sex | λ | t1/2 | C0 | AUC0–∞ | AUC0–∞/Dose | AUC Extrapolated | Vz | Cl | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/h | h | ng/mL | h·ng/mL | % | mL/kg | mL/min/kg | |||
| F | 0.174 | 3.99 | 43,094 | 23,980 | 1918 | 0.869 | 3000 | 8.7 | |
| 0.187 | 3.70 | 47,033 | 24,961 | 1997 | 0.603 | 2672 | 8.3 | ||
| 0.187 | 3.70 | 64,272 | 31,455 | 2516 | 0.561 | 2120 | 6.6 | ||
| mean | 0.183 | 3.80 | 51,467 | 26,799 | 2144 | 0.678 | 2597 | 7.9 | |
| SD | 0.008 | 0.168 | 11,264 | 4062 | 325 | 0.167 | 445 | 1.1 | |
| CV% | 4 | 4 | 22 | 15 | 15 | 25 | 17 | 0.2 | |
| M | 0.178 | 3.90 | 49,251 | 24,364 | 1949 | 0.724 | 2890 | 8.6 | |
| 0.184 | 3.76 | 86,432 | 34,091 | 2727 | 0.490 | 1990 | 6.1 | ||
| 0.175 | 3.95 | 44,593 | 23,120 | 1850 | 0.792 | 3083 | 9.0 | ||
| mean | 0.179 | 3.87 | 60,092 | 27,192 | 2175 | 0.669 | 2654 | 7.9 | |
| SD | 0.005 | 0.099 | 22,930 | 6008 | 481 | 0.158 | 583 | 1.6 | |
| CV% | 3 | 3 | 38 | 22 | 22 | 24 | 22 | 0.3 | |
| M + F | mean | 0.181 | 3.83 | 55,779 | 26,995 | 2160 | 0.673 | 2626 | 7.9 |
| SD | 0.006 | 0.131 | 16,834 | 4592 | 367 | 0.145 | 465 | 1.2 | |
| CV% | 3 | 3 | 30 | 17 | 17 | 22 | 18 | 0.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Martino, M.T.; Arbitrio, M.; Fonsi, M.; Erratico, C.A.; Scionti, F.; Caracciolo, D.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P. Allometric Scaling Approaches for Predicting Human Pharmacokinetic of a Locked Nucleic Acid Oligonucleotide Targeting Cancer-Associated miR-221. Cancers 2020, 12, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010027
Di Martino MT, Arbitrio M, Fonsi M, Erratico CA, Scionti F, Caracciolo D, Tagliaferri P, Tassone P. Allometric Scaling Approaches for Predicting Human Pharmacokinetic of a Locked Nucleic Acid Oligonucleotide Targeting Cancer-Associated miR-221. Cancers. 2020; 12(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Martino, Maria Teresa, Mariamena Arbitrio, Massimiliano Fonsi, Claudio Alberto Erratico, Francesca Scionti, Daniele Caracciolo, Pierosandro Tagliaferri, and Pierfrancesco Tassone. 2020. "Allometric Scaling Approaches for Predicting Human Pharmacokinetic of a Locked Nucleic Acid Oligonucleotide Targeting Cancer-Associated miR-221" Cancers 12, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010027
APA StyleDi Martino, M. T., Arbitrio, M., Fonsi, M., Erratico, C. A., Scionti, F., Caracciolo, D., Tagliaferri, P., & Tassone, P. (2020). Allometric Scaling Approaches for Predicting Human Pharmacokinetic of a Locked Nucleic Acid Oligonucleotide Targeting Cancer-Associated miR-221. Cancers, 12(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010027








