Association of TIM-3 with BCLC Stage, Serum PD-L1 Detection, and Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
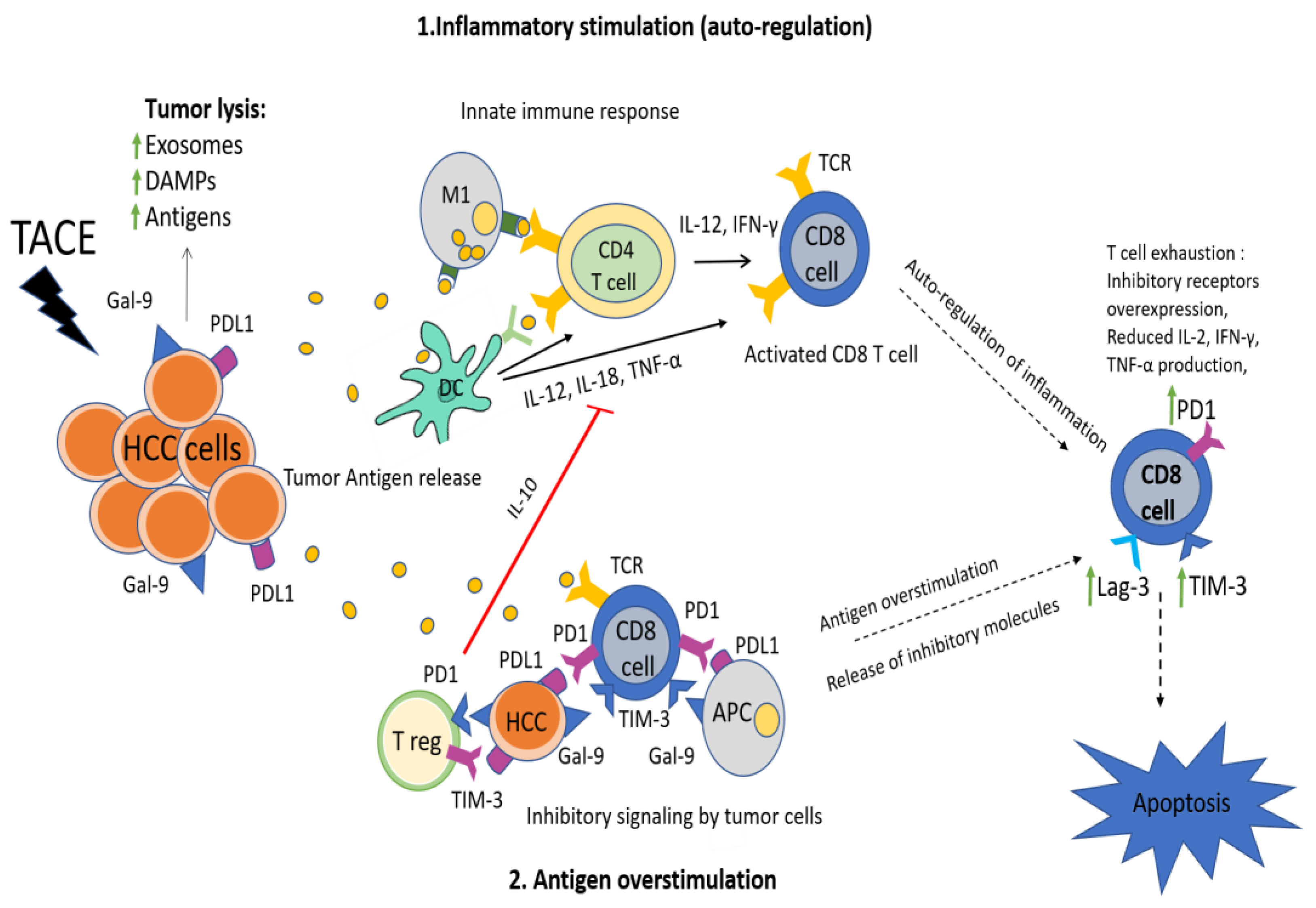
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
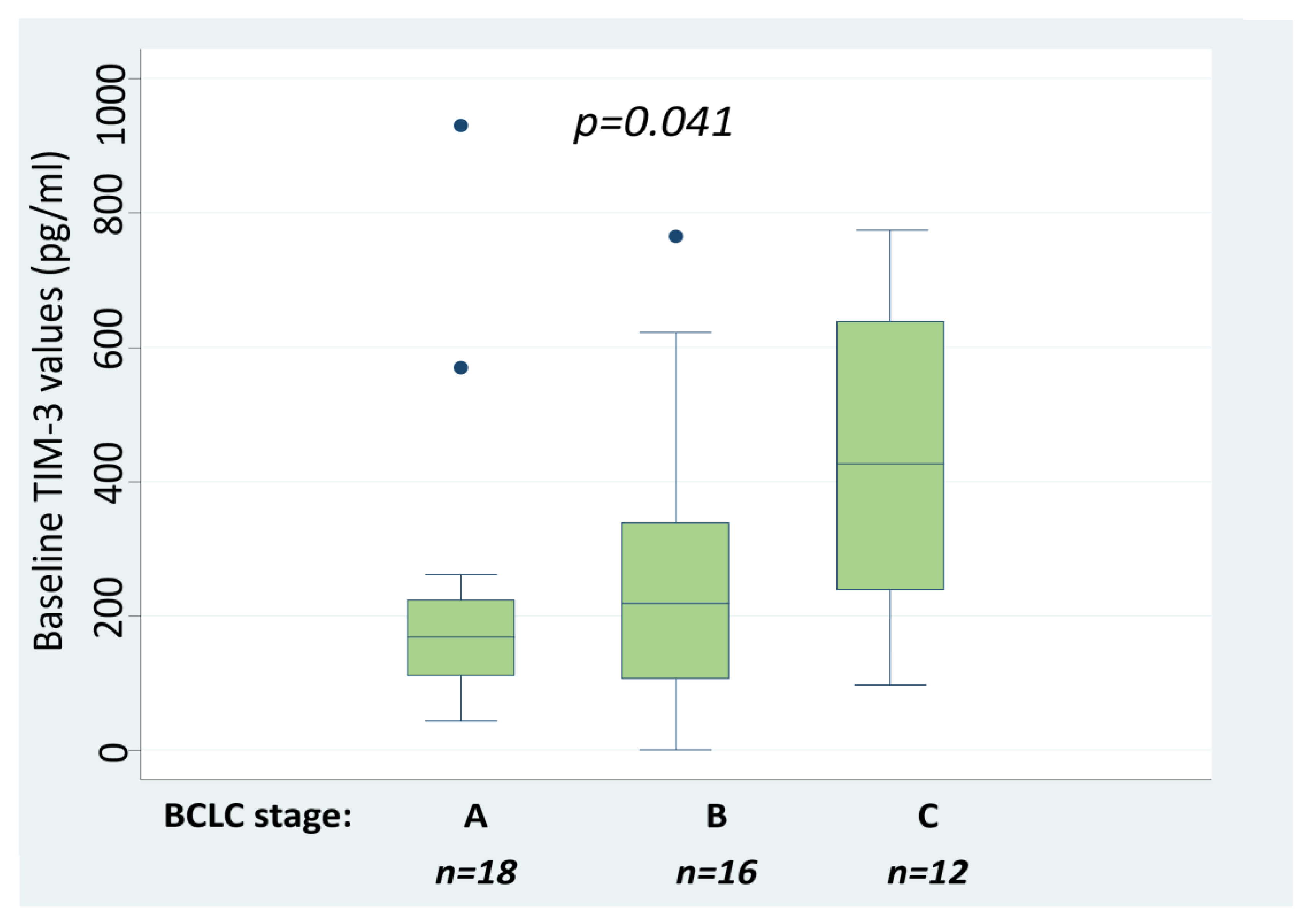
2.2. Serum TIM-3 Values Are Associated with HCC Stage
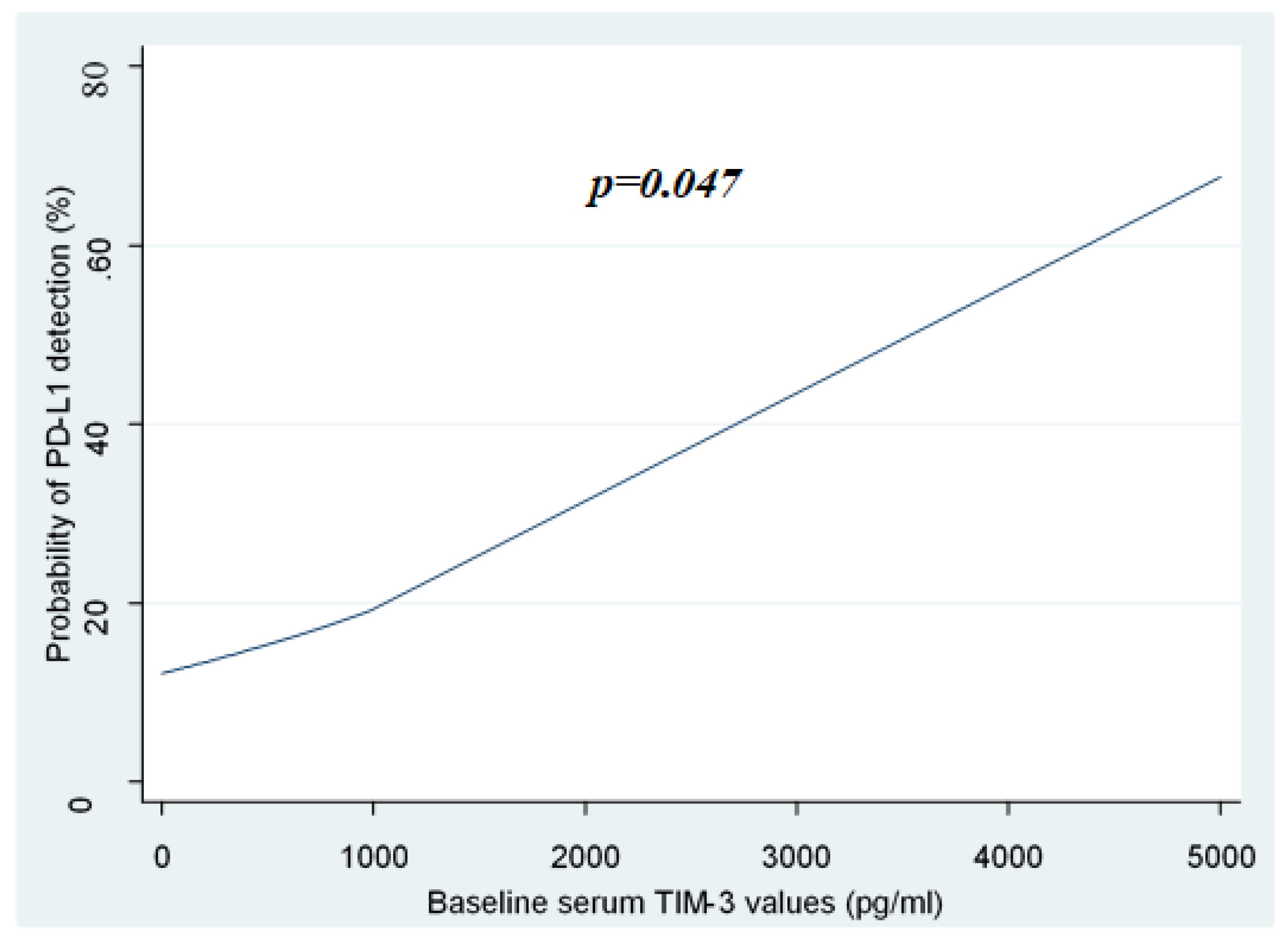
2.3. Association of sTIM-3 Levels with the Detection of sPD-L1
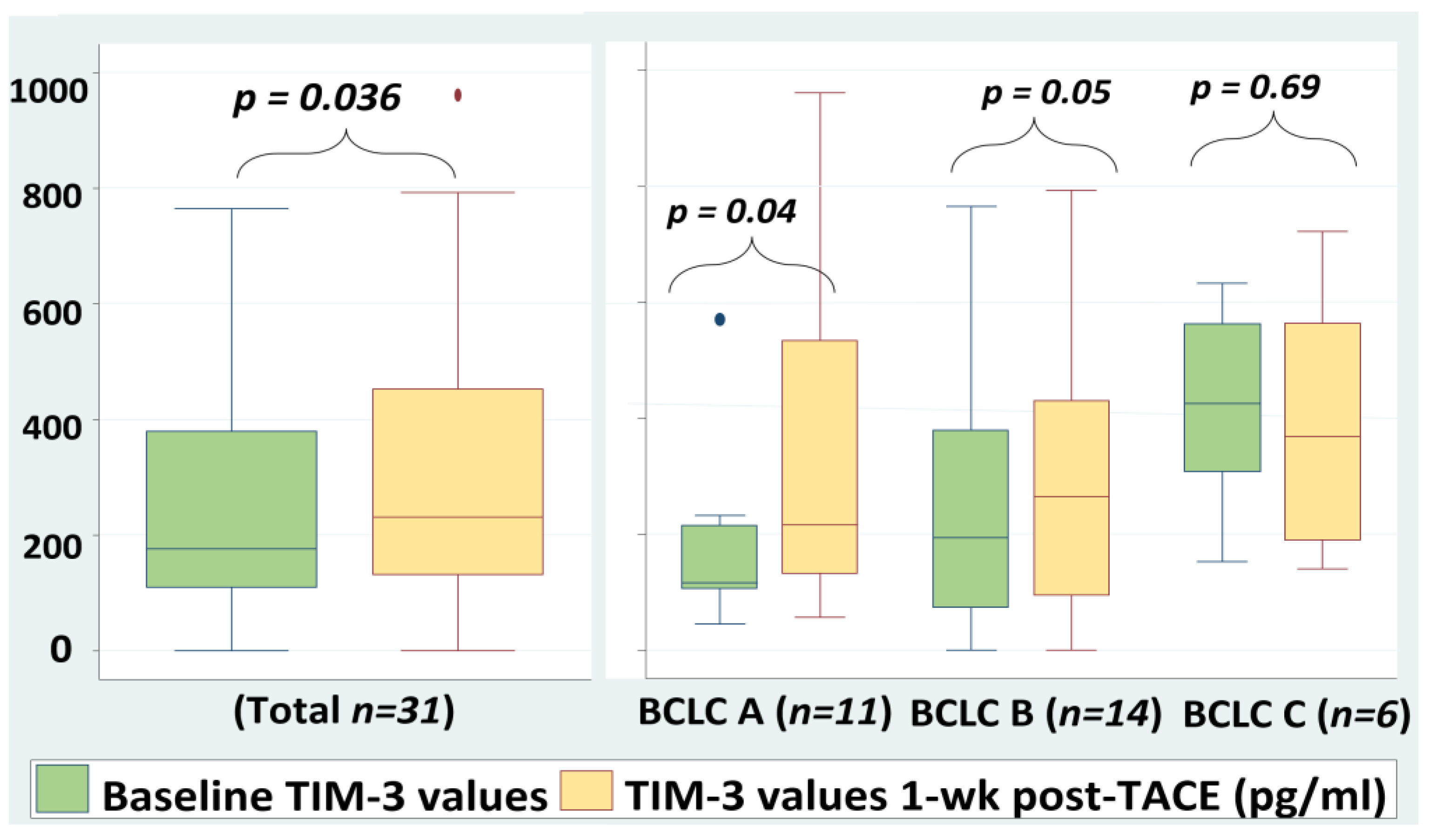
2.4. Serum TIM-3 Levels Are Increased Significantly 1-Week Post-TACE
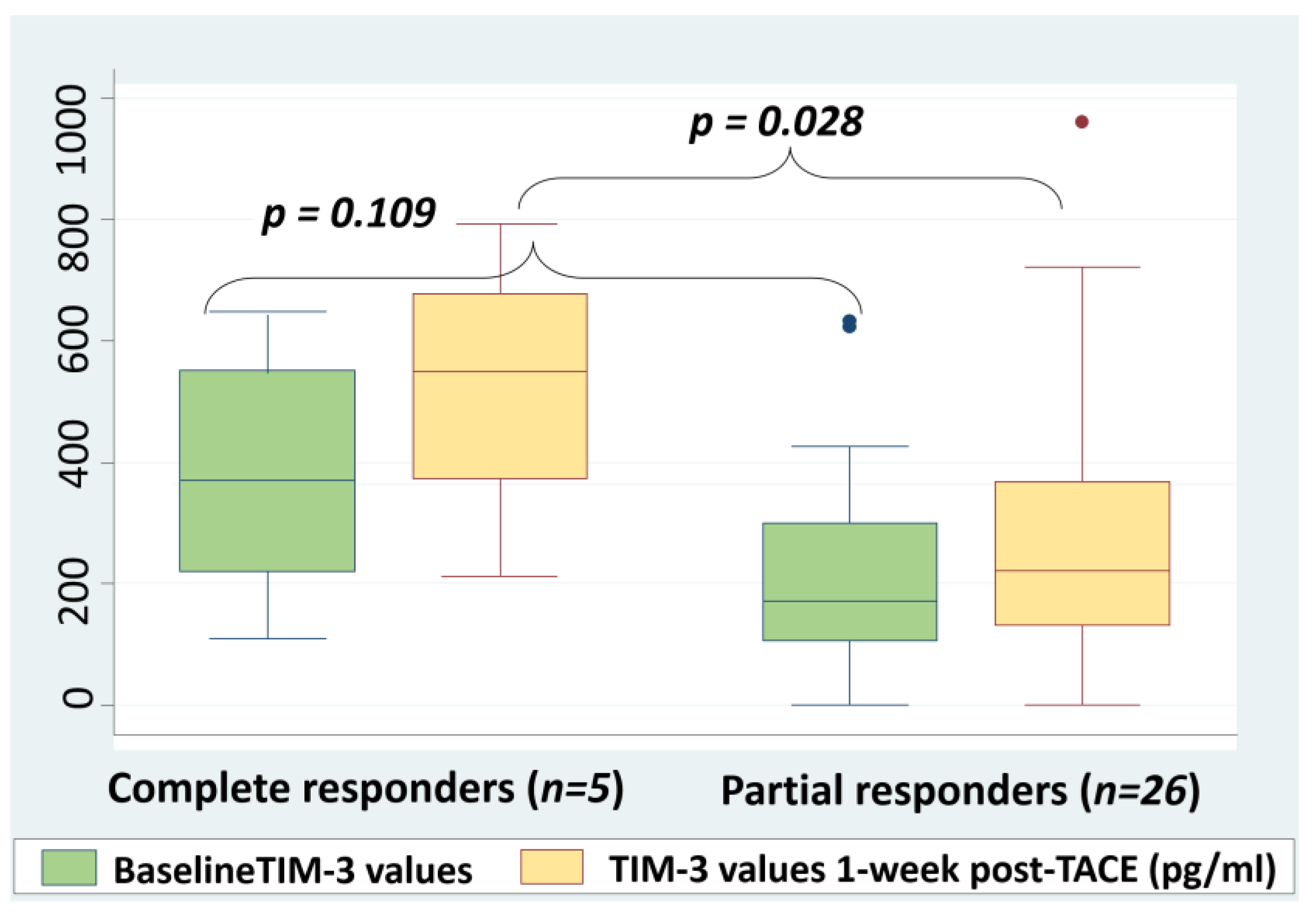
2.5. Correlation between Post-TACE sTIM-3 Levels and Response to Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Selection of Patients
4.2. Blood Sampling and Measurements
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Morizane, C.; Ueno, M.; Okusaka, T.; Ishii, H.; Furuse, J. Chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status and future perspectives. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 48, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M. Immuno-Oncology in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2017 Update. Oncology 2017, 93, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsegood, C.L.; Tirnitz-Parker, J.E.; Olynyk, J.K.; Yeoh, G.C. Immune checkpoint inhibition: Prospects for prevention and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2017, 6, e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M. Targeted and immune therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: Predictions for 2019 and beyond. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 789–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Jin, T.; Zhu, Y.; Dai, C. Immune checkpoint therapy in liver cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limagne, E.; Richard, C.; Thibaudin, M.; Fumet, J.D.; Truntzer, C.; Lagrange, A.; Favier, L.; Coudert, B.; Ghiringhelli, F. Tim-3/galectin-9 pathway and mMDSC control primary and secondary resistances to PD-1 blockade in lung cancer patients. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1564505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Prithviraj, P.; Anaka, M.; Bridle, K.R.; Crawford, D.H.G.; Dhungel, B.; Steel, J.C.; Jayachandran, A. Monitoring Immune Checkpoint Regulators as Predictive Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Hirsch, F.R. TIM-3, a promising target for cancer immunotherapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 7005–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Yang, M.; Turner, A.; Xu, C.; Ferris, R.L.; Huang, J.; Kane, L.P.; Lu, B. TIM-3 as a Target for Cancer Immunotherapy and Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, N.; Sang, J.; Fan, X.; Deng, H.; Zhang, X.; Han, Q.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Z. Highly elevated soluble Tim-3 levels correlate with increased hepatocellular carcinoma risk and poor survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; de Baere, T.; Soulen, M.C.; Rilling, W.S.; Geschwind, J.-F.H. Lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of efficacy and safety data. Hepatology 2016, 64, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaru, L.; Pereira, S.P.; Alisa, A.; Pathan, A.A.; Williams, R.; Davidson, B.; Burroughs, A.K.; Meyer, T.; Behboudi, S. Unmasking of alpha-fetoprotein-specific CD4(+) T cell responses in hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing embolization. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Jeong, H.; Bok, S.; Hong, B.J.; Choi, H.S.; Ahn, G.O. Radiation-induced immune responses: Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Blood Res. 2016, 51, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, V.; Gnoni, A.; Casadei Gardini, A.; Pisconti, S.; Licchetta, A.; Scartozzi, M.; Memeo, R.; Palmieri, V.O.; Aprile, G.; Santini, D.; et al. Immunotherapeutic approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33897–33910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardini, A.C.; Scarpi, E.; Faloppi, L.; Scartozzi, M.; Silvestris, N.; Santini, D.; de Stefano, G.; Marisi, G.; Negri, F.V.; Foschi, F.G.; et al. Immune inflammation indicators and implication for immune modulation strategies in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving sorafenib. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 67142–67149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C. Tim-3: An emerging target in the cancer immunotherapy landscape. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Zhu, C.; Kuchroo, V.K. Tim-3 and its role in regulating anti-tumor immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 276, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, N.; Kudo, M. Immune checkpoint blockade for the treatment of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z. Tim-3 expression and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacekJilkova, Z.; Aspord, C.; Kurma, K.; Granon, A.; Sengel, C.; Sturm, N.; Marche, P.N.; Decaens, T. Immunologic Features of Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Before and During Sorafenib or Anti-programmed Death-1/Programmed Death-L1 Treatment. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, S.; Akbay, E.A.; Li, Y.Y.; Herter-Sprie, G.S.; Buczkowski, K.A.; Richards, W.G.; Gandhi, L.; Redig, A.J.; Rodig, S.J.; Asahina, H.; et al. Adaptive resistance to therapeutic PD-1 blockade is associated with upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelmeier, F.; Canli, Ö.; Tal, A.; Pleli, T.; Trojan, J.; Schmidt, M.; Kronenberger, B.; Zeuzema, S.; Piipera, A.; Greten, F.R.; et al. High levels of the soluble programmed death-ligand (sPD-L1) identify hepatocellular carcinoma patients with a poor prognosis. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 59, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.; Huang, T.; Wei, H.; Shen, L.; Zhu, D.; He, W.; Chen, O.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, R.; et al. The correlation and prognostic value of serum levels of soluble programmed death protein 1 (sPD-1) and soluble programmed death ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderaro, J.; Rousseau, B.; Amaddeo, G.; Mercey, M.; Charpy, C.; Costentin, C.; Luciani, A.; Zafrani, E.S.; Laurent, A.; Azoulay, D.; et al. Programmed death ligand 1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: Relationship With clinical and pathological features. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2038–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.T.; Anderson, A.C.; Tan, W.G.; West, E.E.; Ha, S.J.; Araki, K.; Freeman, G.J.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Ahmed, R. Cooperation of Tim-3 and PD-1 in CD8 T-cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14733–14738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourcade, J.; Sun, Z.; Benallaoua, M.; Guillaume, P.; Luescher, I.F.; Sander, C.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Kuchroo, V.; Zarour, H.M. Upregulation of Tim-3 and PD-1 expression is associated with tumor antigen-specific CD8 + T cell dysfunction in melanoma patients. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2175–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuishi, K.; Apetoh, L.; Sullivan, J.M.; Blazar, B.R.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Anderson, A.C. Targeting Tim-3 and PD-1 pathways to reverse T cell exhaustion and restore anti-tumor immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2187–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Jang, J.W.; Oh, B.S.; Kwon, J.H.; Chung, K.W.; Jung, H.S.; Jekarl, D.W.; Lee, S. Change in inflammatory cytokine profiles after transarterial chemotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cytokine 2013, 64, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C. Effect of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization on cellular immune function and regulatory T cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 6065–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Li, C.W.; Yuan, F.L. T cell immunoglobulin-3 as a new therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, W.D.; Anderson, D.E.; Kassam, N.; Koguchi, K.; Greenfield, E.A.; Kent, S.C.; Zheng, X.X.; Strom, T.B.; Hafler, D.; Kuchroo, V.K. TIM-3 is expressed on activated human CD4+ T cells and regulates Th1 and Th17 cytokines. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, Q.; Zhou, A.; Zeng, Y. Changes in Expression of Multiple Checkpoint Molecules and Infiltration of Tumor Immune Cells after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Gastric Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2754–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesnage, S.J.L.; Auguste, A.; Genestie, C.; Dunant, A.; Pain, E.; Drusch, F.; Gouy, S.; Morice, P.; Bentivegna, E.; Lhomme, C.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) increases immune infiltration and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, H.; Fouladdel, S.; Zhang, Z.; Soni, P.; Qin, A.; Zhao, L.; Azizi, E.; Lawrence, T.; Ramnath, N.; et al. PD-L1 Expression in Circulating Tumor Cells Increases during Radio(chemo)therapy and Indicates Poor Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsutani, S.; Shibutani, M.; Maeda, K.; Nagahara, H.; Fukuoka, T.; Nakao, S.; Hirakawa, K.; Ohira, M. Significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes before and after neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 966–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, V.; Lee, Y.H.; Pan, L.; Nasir, N.J.M.; Lim, C.J.; Chua, C.; Lai, L.; Hazirah, S.N.; Lim, T.K.H.; Goh, B.K.P.; et al. Immune activation underlies a sustained clinical response to Yttrium-90 radioembolisation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2019, 68, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, C.G.; Turcotte, J.G. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl. Clin. Surg. 1964, 1, 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) Assessment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | |
|---|---|
| Age (median, range) | 76, (30–88) years |
| Sex n, (%) | |
| Male | 38, (71.7%) |
| Female | 15, (28.3%) |
| BCLC stage n, (%) | |
| 0 | 3, (5.7%) |
| A | 18, (34%) |
| B | 17, (32.1%) |
| C | 12, (22.6%) |
| D | 3, (5.7%) |
| Liver disease n, (%) | |
| HCV infection | 28, (52.8%) |
| HBV infection | 17, (32.1%) |
| NASH | 4, (7.5%) |
| Alcoholic liver disease | 2, (3.8%) |
| Other | 2, (3.8%) |
| Child–Pugh score n, (%) | |
| A | 33, (62.3%) |
| B | 19, (35.8%) |
| C | 1, (1.9%) |
| Tumor size n, (%) | |
| >5 cm | 40, (75.4%) |
| ≤5 cm | 13, (24.5%) |
| Number of lesions n, (%) | |
| Single | 16, (30.2%) |
| Multiple | 37, (69.8%) |
| Patients submitted to TACE | 33, (62.3%) |
| BCLC A | 12, (36.4%) |
| BCLC B | 15, (45.5%) |
| BCLC C | 6, (18.1%) |
| BCLC Stages (Median sTIM-3 Values, Q25–Q75 Values) | BCLC A (171 pg/mL, 113–232 pg/mL) | BCLC B (218 pg/mL, 108–339 pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| BCLC B (218 pg/mL, 108–339 pg/mL) | p = 0.364 | |
| BCLC C (425 pg/mL, 266–633 pg/mL) | p = 0.009 | p = 0.019 |
| Patients with Detectable sPD-L1 | Child–Pugh Score | BCLC Stage | Response to TACE | sTIM-3 Levels (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | A | C | N/A | 266 |
| Patient 2 | B | C | N/A | 317 |
| Patient 3 | A | A | N/A | 166 |
| Patient 4 | A | C | N/A | 186 |
| Patient 5 | B | C | N/A | 4.893 |
| Patient 6 | B | C | CR | 562 |
| Patient 7 | B | C | PR | 633 |
| Patient 8 | A | C | PR | 153 |
| Patient 9 | B | C | PR | 1.896 |
| Association of sTIM-3 values with the probability of sPD-L1 detection (univariate logistic regression): | p = 0.047. | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tampaki, M.; Ionas, E.; Hadziyannis, E.; Deutsch, M.; Malagari, K.; Koskinas, J. Association of TIM-3 with BCLC Stage, Serum PD-L1 Detection, and Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010212
Tampaki M, Ionas E, Hadziyannis E, Deutsch M, Malagari K, Koskinas J. Association of TIM-3 with BCLC Stage, Serum PD-L1 Detection, and Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2020; 12(1):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010212
Chicago/Turabian StyleTampaki, Maria, Evangelos Ionas, Emilia Hadziyannis, Melanie Deutsch, Katerina Malagari, and John Koskinas. 2020. "Association of TIM-3 with BCLC Stage, Serum PD-L1 Detection, and Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 12, no. 1: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010212
APA StyleTampaki, M., Ionas, E., Hadziyannis, E., Deutsch, M., Malagari, K., & Koskinas, J. (2020). Association of TIM-3 with BCLC Stage, Serum PD-L1 Detection, and Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 12(1), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010212





