Epigenetic Silencing of Ubiquitin Specific Protease 4 by Snail1 Contributes to Macrophage-Dependent Inflammation and Therapeutic Resistance in Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
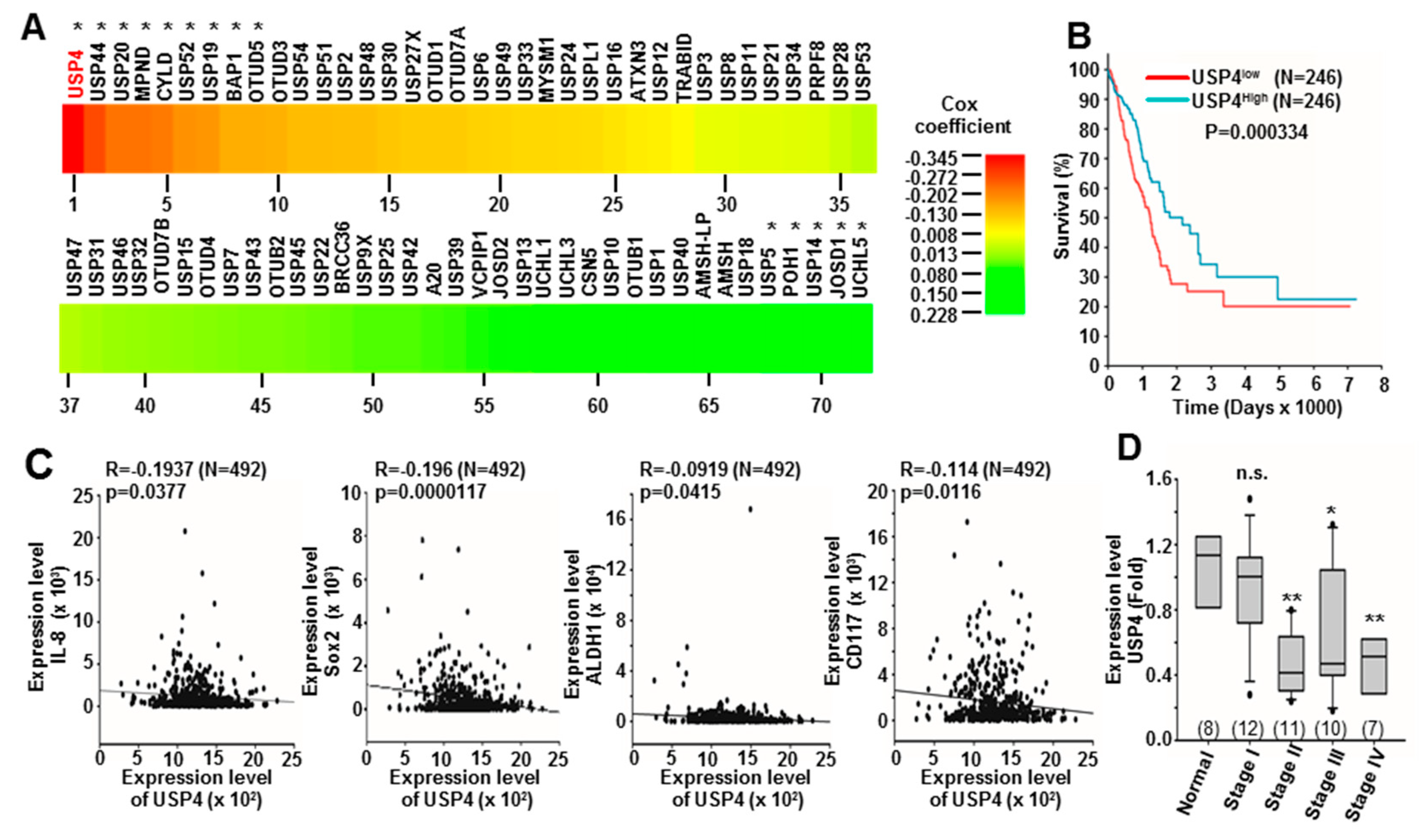
2.1. Downregulation of USP4 in Lung Cancer Is Associated with Poor Prognosis and High Expression of Stemness and Inflammation Markers
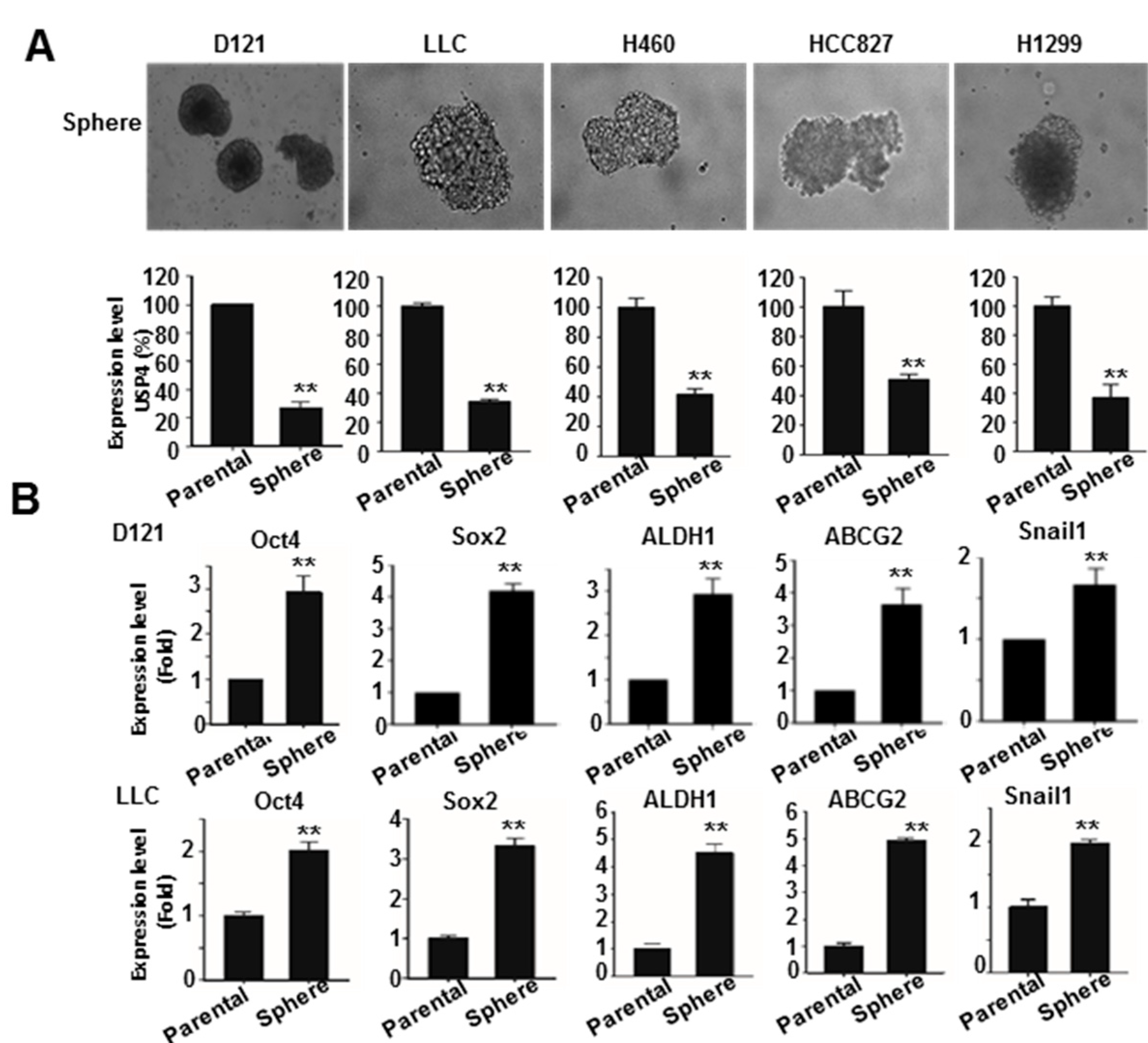
2.2. Downregulation of USP4 in Stemness-Enriched Cancer Cells
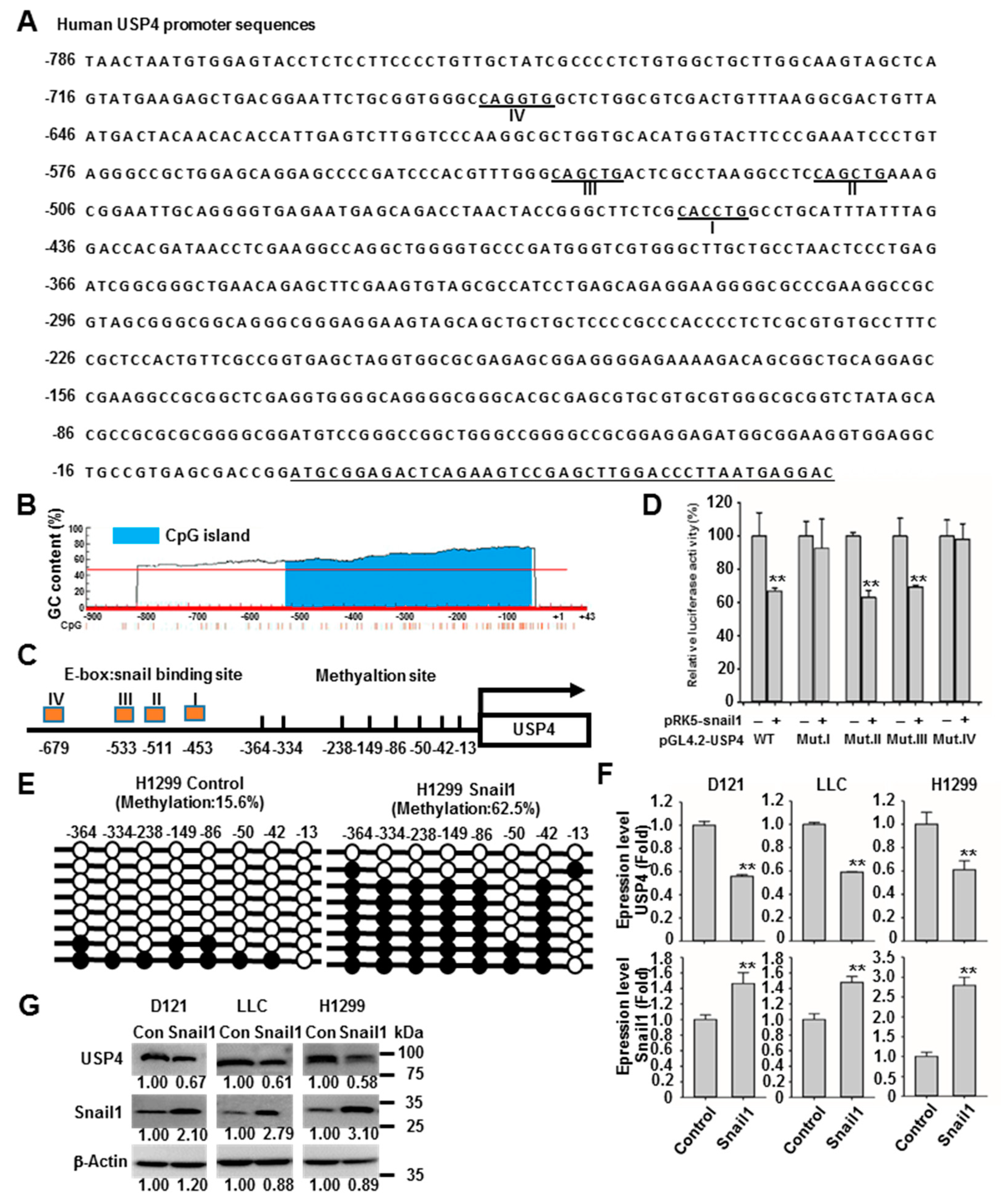
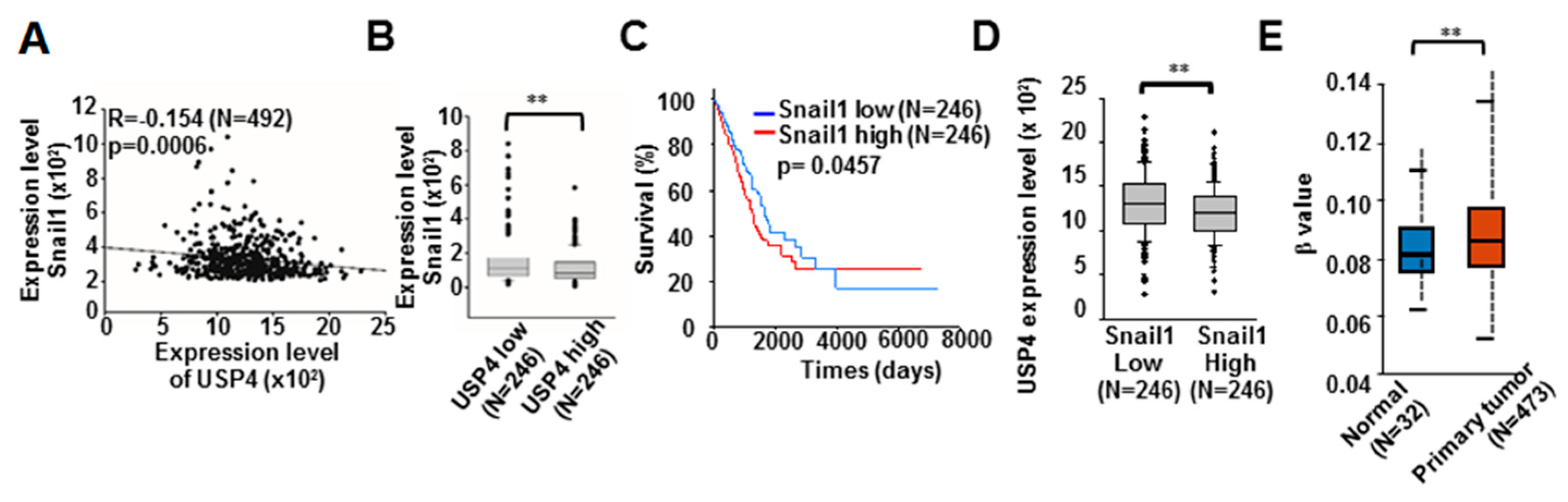
2.3. Snail1 Promotes DNA Methylation of the USP4 Promoter and Suppresses USP4 Expression
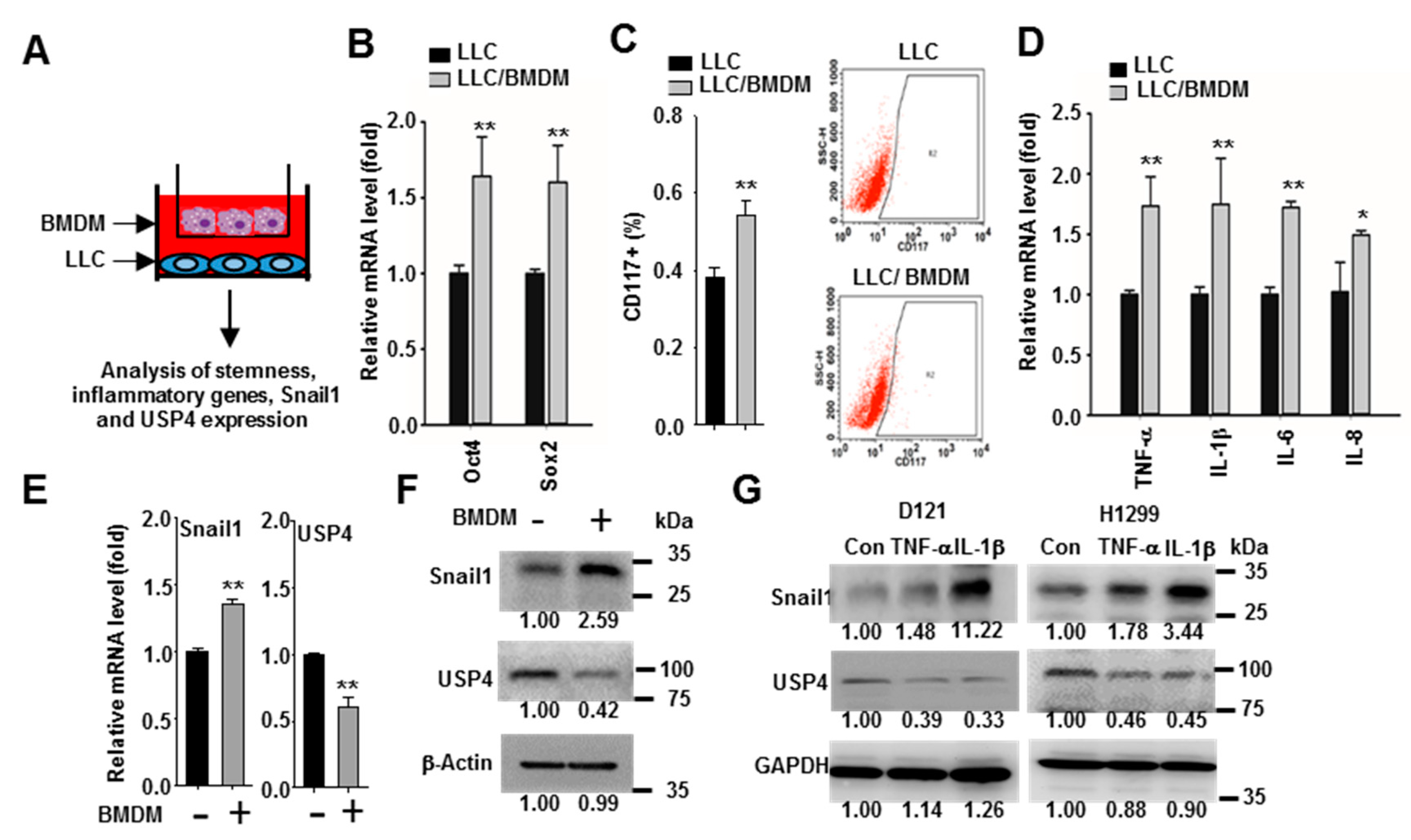
2.4. Macrophages Promote Snail1 Expression and USP4 Downregulation in Lung Cancer Cells
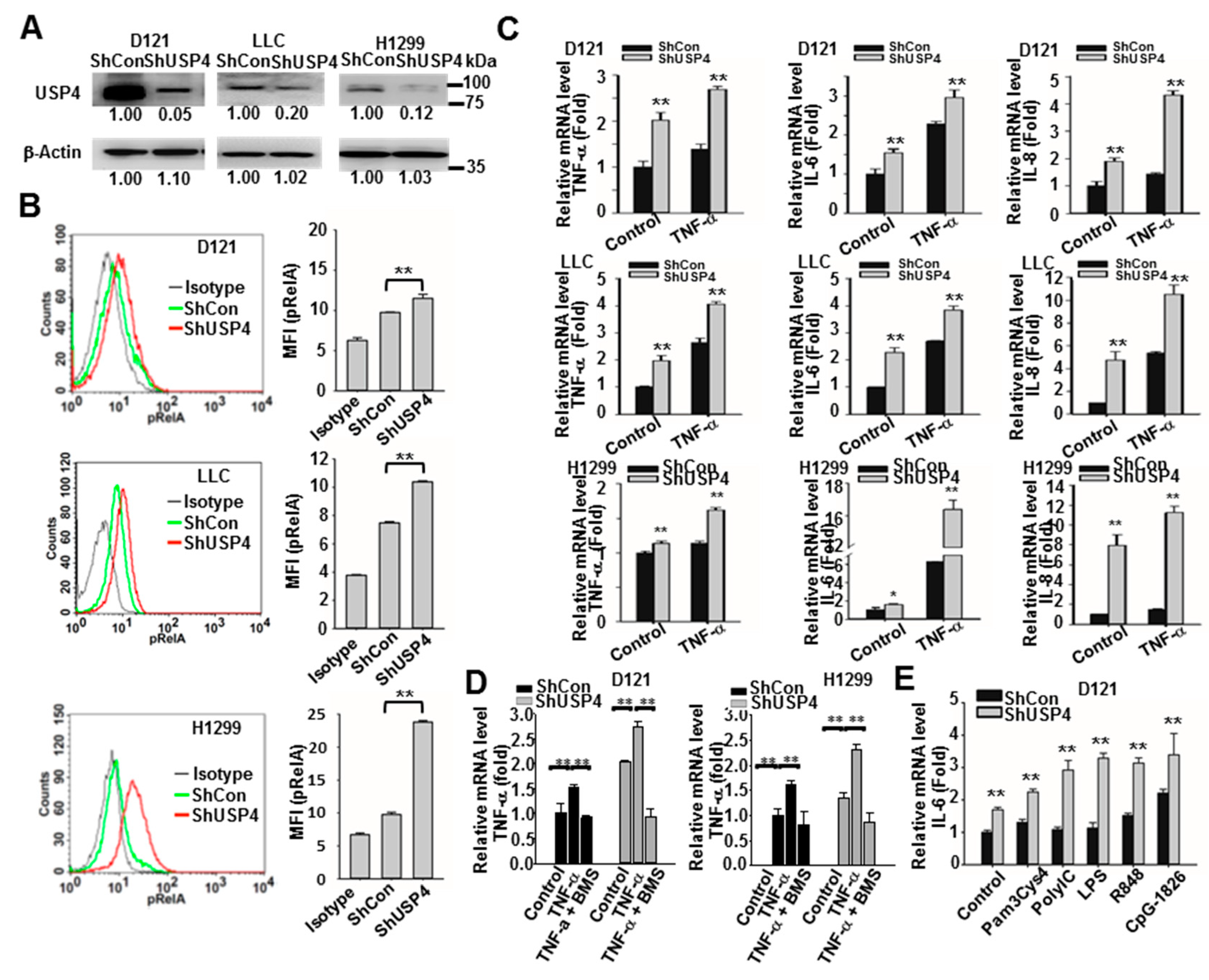
2.5. Downregulation of USP4 Increases Basal and Stimulus-Induced Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Factors by Cancer Cells
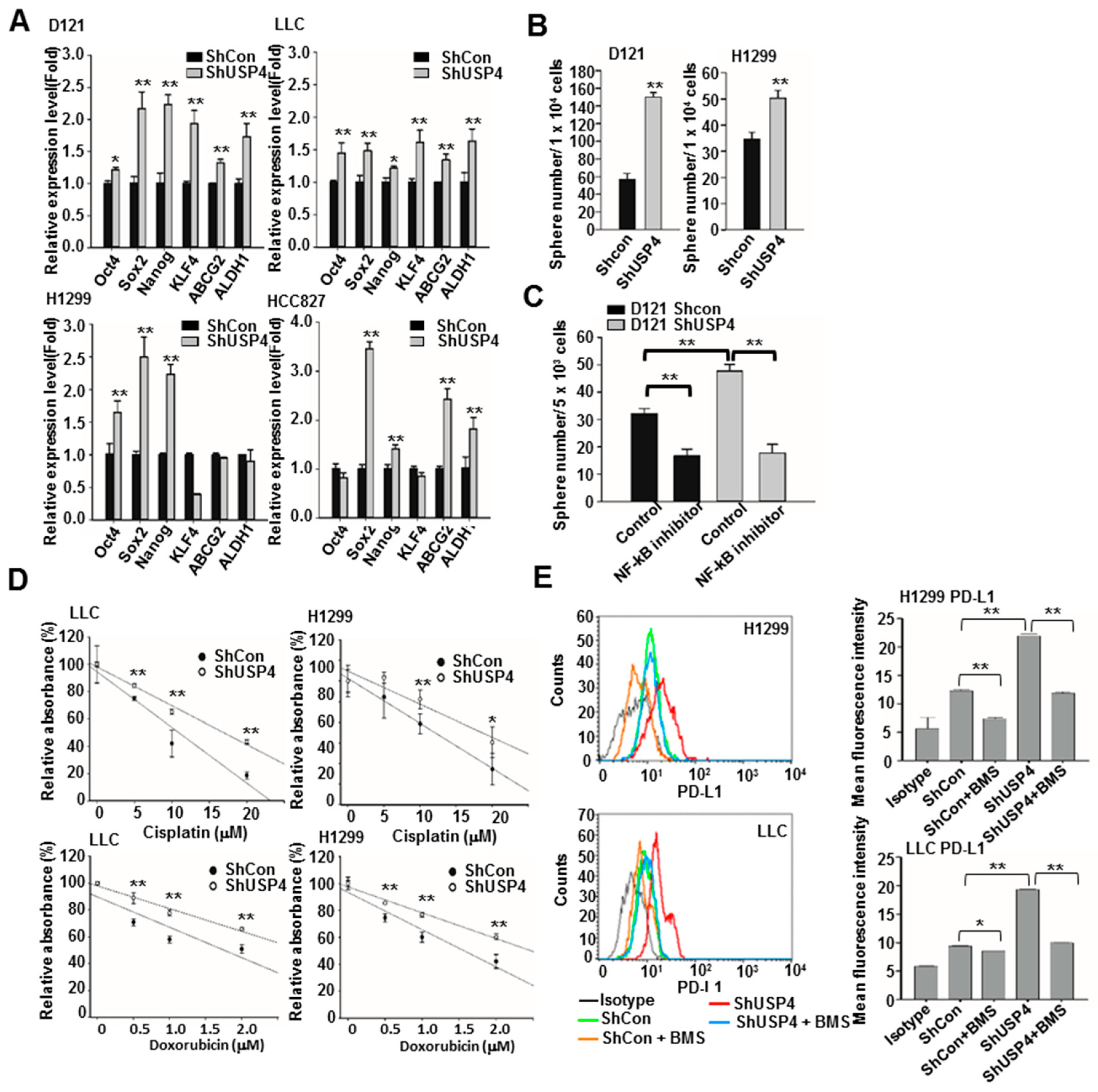
2.6. Downregulation of USP4 Promotes the Stemness and Therapeutic Resistance of Cancer Cells
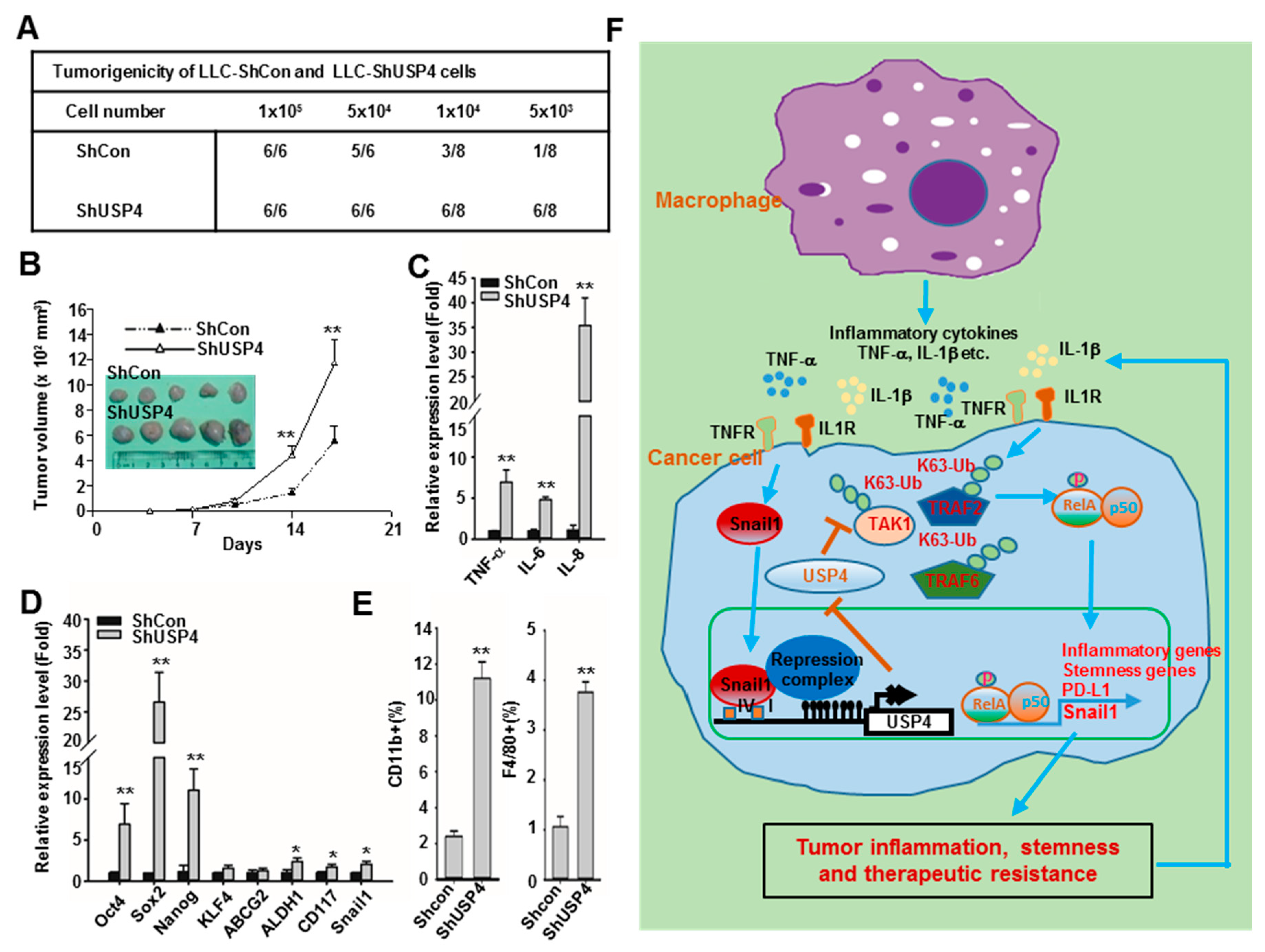
2.7. Downregulation of USP4 Promotes Tumorigenesis and Tumor Growth in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.3. Cell Culture and Macrophage Co-Culture Assays
4.4. Plasmid Construction
4.5. Generation of Lentiviruses and Stably Transfection
4.6. SDS-PAGE and Immunoblot Analysis
4.7. Flow Cytometry
4.8. Enrichment of Sphere-Forming Cancer Cells
4.9. Transfection and Luciferase Reporter Assays
4.10. RT-qPCR Analysis of Gene Expression
4.11. DNA Methylation Assay
4.12. Animal Experiments
4.13. Statistics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abb. | Full Name |
| USP4 | Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 4; |
| DUB | Deubiquitinase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| IL | Interleukin |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| TNFR | Tumor necrosis factor receptor |
| TRAF | TNFR-associated factor |
| MyD88 | Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 |
| IRAK | Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase |
| TAK | TGF-β-activated kinase |
| TRADD | Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated death domain protein |
| RIP | Receptor interacting protein |
| EMT | Epithelial−mesenchymal transition |
| CSC | Cancer stem-like cells |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| HEK | Human embryonic kidney |
| FCS | Fetal calf serum |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
References
- De Groot, P.M.; Wu, C.C.; Carter, B.W.; Munden, R.F. The epidemiology of lung cancer. Transl. Lung. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perwez-Hussain, S.; Harris, C.C. Inflammation and cancer: An ancient link with novel potentials. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quatromoni, J.G.; Eruslanov, E. Tumor-associated macrophages: Function, phenotype, and link to prognosis in human lung cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2012, 4, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Conway, E.M.; Pikor, L.A.; Kung, S.H.; Hamilton, M.J.; Lam, S.; Lam, W.L.; Bennewith, K.L. Macrophages, inflammation, and lung cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Mercurio, F.; Karin, M. NF-κB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.P.; Carmody, R.J. NF-κB and the transcriptional control of inflammation. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 335, 41–84. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.; Goto, Y.; Narita, N.; Hoon, D.S. Cancer cells expressing toll-like receptors and the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron. 2009, 2, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstrepen, L.; Bekaert, T.; Chau, T.-L.; Tavernier, J.; Chariot, A.; Beyaert, R. TLR-4, IL-1R and TNF-R signaling to NF-κB: Variations on a common theme. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2964–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P. The TLR and IL-1 signalling network at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Park, H.H. Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-mediated cellular signaling pathways. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajant, H.; Scheurich, P. TNFR1-induced activation of the classical NF-κB pathway. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.H.; Hong, J.T. Roles of NF-κB in cancer and inflammatory diseases and their therapeutic approaches. Cells 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puar, Y.R.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Fan, L.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G.; Tergaonkar, V. Evidence for the involvement of the master transcription factor NF-κB in cancer initiation and progression. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, N.M.; Kang, Y. Context-dependent EMT programs in cancer metastasis. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Hu, H.; Ling, H. Signalling mechanism (s) of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells in tumour therapeutic resistance. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 483, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Farhood, B.; Mortezaee, K. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) in cancer progression and therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8381–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccalli, C.; Rasul, K.I.; Elawad, M.; Ferrone, S. The role of cancer stem cells in the modulation of anti-tumor immune responses. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 53, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, D.W.; Huang, L.R.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, C.Y.F.; Chuang, T.H. Interplay between inflammation and stemness in cancer cells: The role of toll-like receptor signaling. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 436810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, S.; Achilleos, C.; Panayiotou, T.; Strati, K. Inflammation shapes stem cells and stemness during infection and beyond. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuri, A.; O’Hagan, H. Interplay between inflammation and epigenetic changes in cancer. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2016, 144, 69–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, D.; Jha, S. An epi (c) genetic war: Pathogens, cancer and human genome. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018, 1869, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufhold, S.; Bonavida, B. Central role of Snail1 in the regulation of EMT and resistance in cancer: A target for therapeutic intervention. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baulida, J.; Díaz, V.M.; García de Herreros, A. Snail1: A transcriptional factor controlled at multiple levels. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulida, J. Snail1 controls cooperative cell plasticity during metastasis. Oncoscience 2015, 2, 898. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, C.; P Zhou, B. Epigenetic regulation of EMT: The Snail story. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Gomez, S.J.; Maziveyi, M.; Alahari, S.K. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through epigenetic and post-translational modifications. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, D.; Vucic, D.; Dikic, I. Ubiquitination in disease pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1242–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Kang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Tang, X.; Yan, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Mao, F. Ubiquitination regulation of inflammatory responses through NF-κB pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mevissen, T.E.; Komander, D. Mechanisms of deubiquitinase specificity and regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 159–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leznicki, P.; Kulathu, Y. Mechanisms of regulation and diversification of deubiquitylating enzyme function. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Mao, R.; Tan, X.; Xu, G.; Zhang, H.; Lu, X.; Fu, S.; Yang, J. USP4 targets TAK1 to downregulate TNF α-induced NF-κ B activation. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Li, H.; Luo, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, P. Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 (USP4) targets TRAF2 and TRAF6 for deubiquitination and inhibits TNFα-induced cancer cell migration. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhang, X.; van Dam, H.; ten Dijke, P.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L. Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 mitigates Toll-like/interleukin-1 receptor signaling and regulates innate immune activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11002–11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy, P.; Linder, S. Molecular pathways: Translational potential of deubiquitinases as drug targets. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3908–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heideker, J.; Wertz, I.E. DUBs, the regulation of cell identity and disease. Biochem. J. 2014, 465, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya, J. OncoLnc: Linking TCGA survival data to mRNAs, miRNAs, and lncRNAs. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2016, 2, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Bashel, B.; Balasubramanya, S.A.H.; Creighton, C.J.; Ponce-Rodriguez, I.; Chakravarthi, B.V.; Varambally, S. UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, T.M.; Sokolov, A.; Gentles, A.J.; Burzykowski, T.; Poisson, L.; Weinstein, J.N.; Kamińska, B.; Huelsken, J.; Omberg, L.; Gevaert, O. Machine learning identifies stemness features associated with oncogenic dedifferentiation. Cell 2018, 173, 338–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. Macrophages and NF-κB in cancer. NF-kB Health Dis. 2010, 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Capece, D.; Fischietti, M.; Verzella, D.; Gaggiano, A.; Cicciarelli, G.; Tessitore, A.; Zazzeroni, F.; Alesse, E. The inflammatory microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: A pivotal role for tumor-associated macrophages. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 187204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Transcription factor NF-κB: A sensor for smoke and stress signals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1056, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. NF-κB signaling pathway, inflammation and colorectal cancer. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 6, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, C.; Mackensen, A. Contribution of the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway to T-cell exhaustion: An update on implications for chronic infections and tumor evasion. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 56, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Xiong, F.; Ge, J.; Xiang, B.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; et al. Role of the tumor microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M.; Jiang, Q.; Jin, R. USP4 expression independently predicts favorable survival in lung adenocarcinoma. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Cai, Z. Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 inhibits breast cancer cell growth through the upregulation of PDCD4. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yan, B.; Ma, Y.; Weng, J.; Yang, S.; Zhao, N.; Wang, X.; Sun, X. Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via cyclophilin A stabilization and deubiquitination. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ma, J.; Pei, T.; Zhao, T.; Guo, S.; Yi, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, G.; Jian, Z.; et al. Up-regulated deubiquitinase USP 4 plays an oncogenic role in melanoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 2944–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, C.; Lu, X.X.; Guo, P.D.; Shen, T.; Zhang, S.; He, X.S.; Gan, W.J.; Li, X.M.; Wang, J.R.; Zhao, Y.Y.; et al. Ubiquitin-specific protease 4-mediated deubiquitination and stabilization of PRL-3 is required for potentiating colorectal oncogenesis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Pu, J.; Fan, R.; Zhu, W.; Ding, X.; Shen, X.; Zhang, T. Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 improves the prognosis of the patients in esophageal cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 20, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Qiu, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhang, L.; Zou, J. USP4 deficiency exacerbates hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion injury via TAK1 signalling. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigdar, S.; Li, Y.; Bhattacharya, S.; O’Connor, M.; Pu, C.; Lin, J.; Wang, T.; Xiang, D.; Kong, L.; Wei, M.Q.; et al. Inflammation and cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkenbaugh, A.L.; Baldwin, A.S. The NF-κB pathway and cancer stem cells. Cells 2016, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Gao, Z.; Lao, X.M.; Lin, W.M.; Chen, D.P.; Mu, M.; Huang, C.X.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, B.; et al. The local immune landscape determines tumor PD-L1 heterogeneity and sensitivity to therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3347–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, C.-Y.; Yeh, D.-W.; Lu, C.-H.; Liu, Y.-L.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Ruan, J.-W.; Kao, C.-Y.; Huang, L.-R.; Chuang, T.-H. Epigenetic Silencing of Ubiquitin Specific Protease 4 by Snail1 Contributes to Macrophage-Dependent Inflammation and Therapeutic Resistance in Lung Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010148
Lai C-Y, Yeh D-W, Lu C-H, Liu Y-L, Chuang Y-C, Ruan J-W, Kao C-Y, Huang L-R, Chuang T-H. Epigenetic Silencing of Ubiquitin Specific Protease 4 by Snail1 Contributes to Macrophage-Dependent Inflammation and Therapeutic Resistance in Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2020; 12(1):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010148
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Chao-Yang, Da-Wei Yeh, Chih-Hao Lu, Yi-Ling Liu, Yu-Chen Chuang, Jhen-Wei Ruan, Cheng-Yuan Kao, Li-Rung Huang, and Tsung-Hsien Chuang. 2020. "Epigenetic Silencing of Ubiquitin Specific Protease 4 by Snail1 Contributes to Macrophage-Dependent Inflammation and Therapeutic Resistance in Lung Cancer" Cancers 12, no. 1: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010148
APA StyleLai, C.-Y., Yeh, D.-W., Lu, C.-H., Liu, Y.-L., Chuang, Y.-C., Ruan, J.-W., Kao, C.-Y., Huang, L.-R., & Chuang, T.-H. (2020). Epigenetic Silencing of Ubiquitin Specific Protease 4 by Snail1 Contributes to Macrophage-Dependent Inflammation and Therapeutic Resistance in Lung Cancer. Cancers, 12(1), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010148




