Molecular Pathogenesis of Gene Regulation by the miR-150 Duplex: miR-150-3p Regulates TNS4 in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
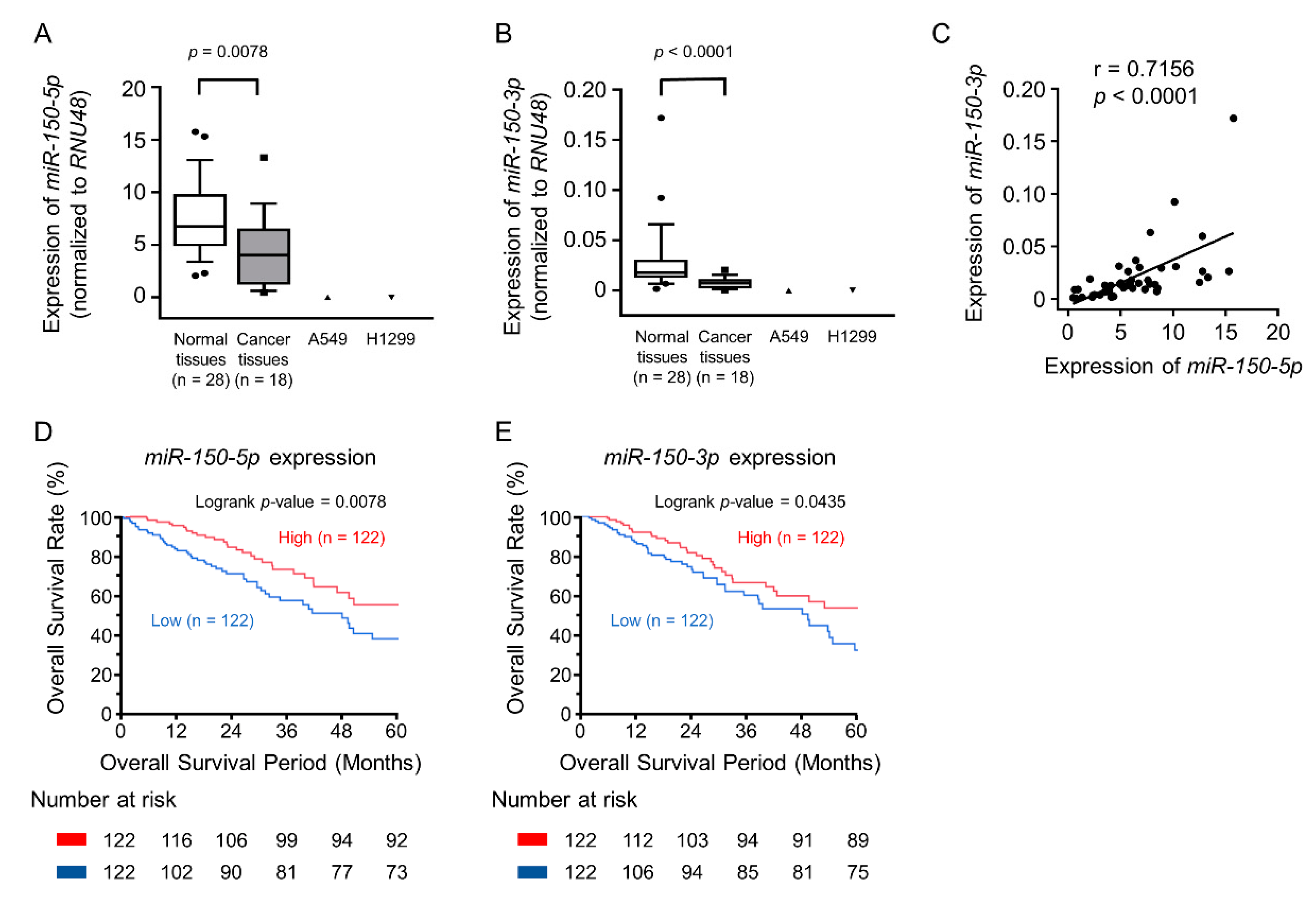
2.1. miR-150-5p and miR-150-3p were Downregulated in Lung Adenocarcinoma (LUAD) Specimens and Cell Lines
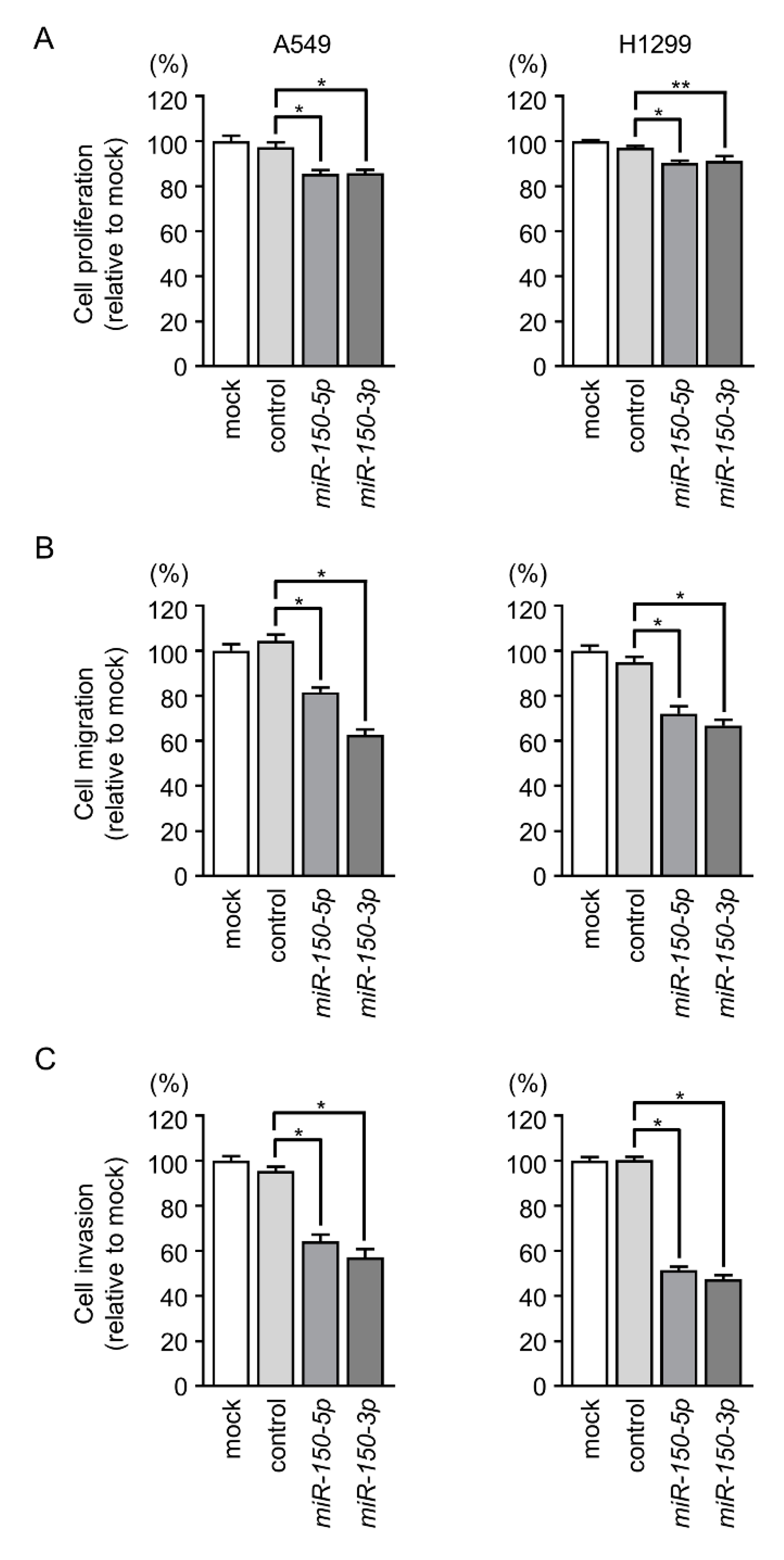
2.2. Overexpression of miR-150-5p and miR-150-3p Inhibits Cancer Cell Aggressiveness
2.3. Incorporation of miR-150-5p and miR-150-3p into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) in LUAD Cells
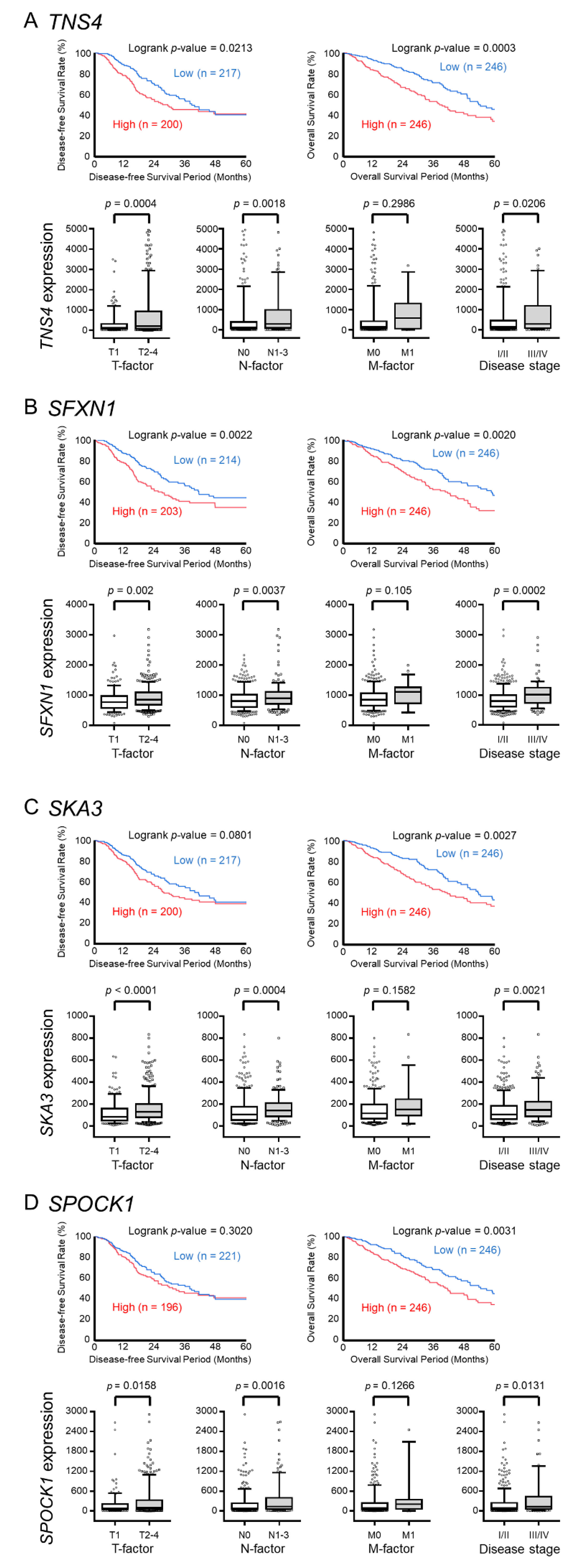
2.4. Candidate Target Genes of miR-150-5p and miR-150-3p Regulation in LUAD: Clinical Significance of TNS4, SFXN1, SKA3, and SPOCK1 Expression
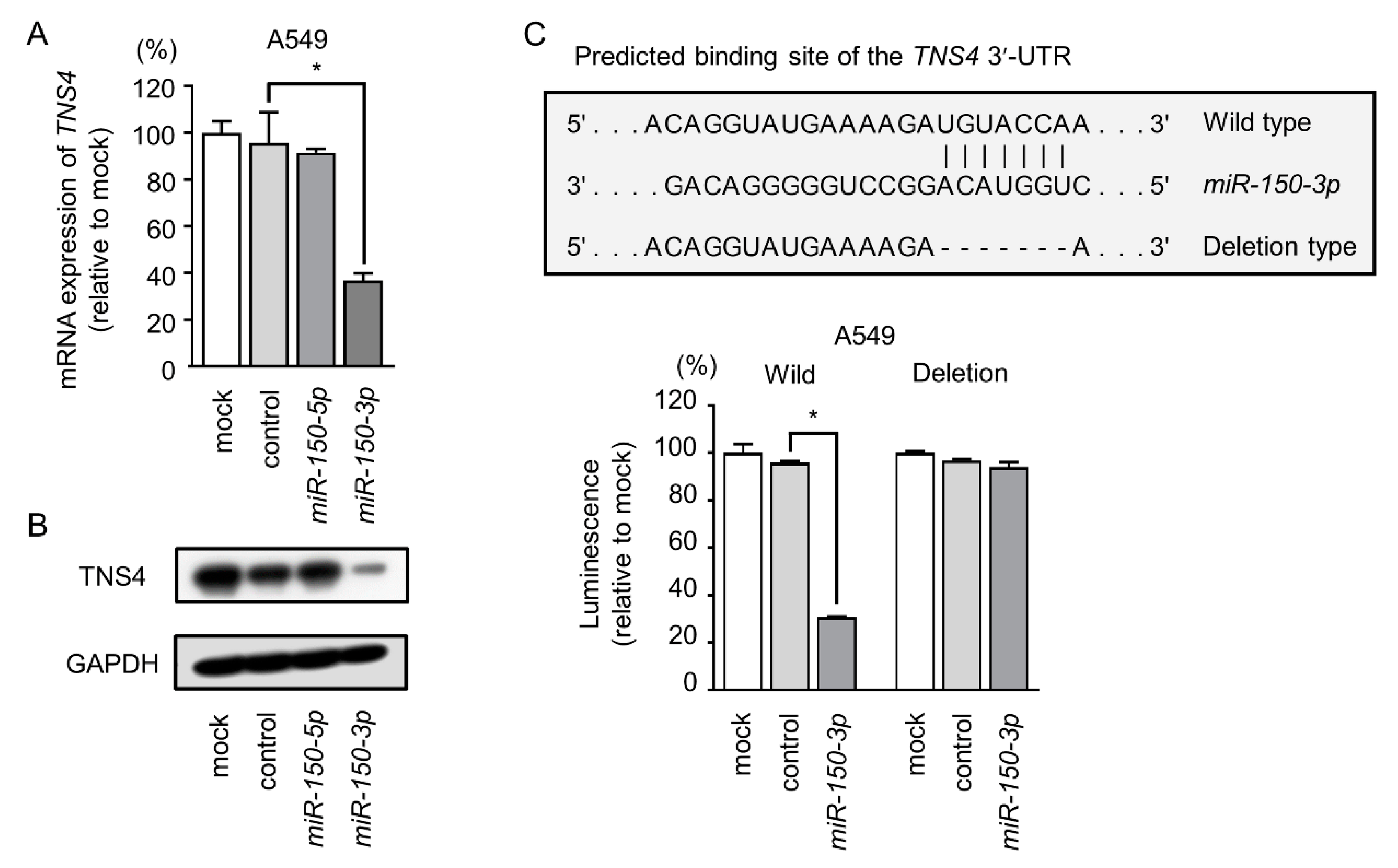
2.5. miR-150-3p Directly Regulated TNS4 in A549 Cells
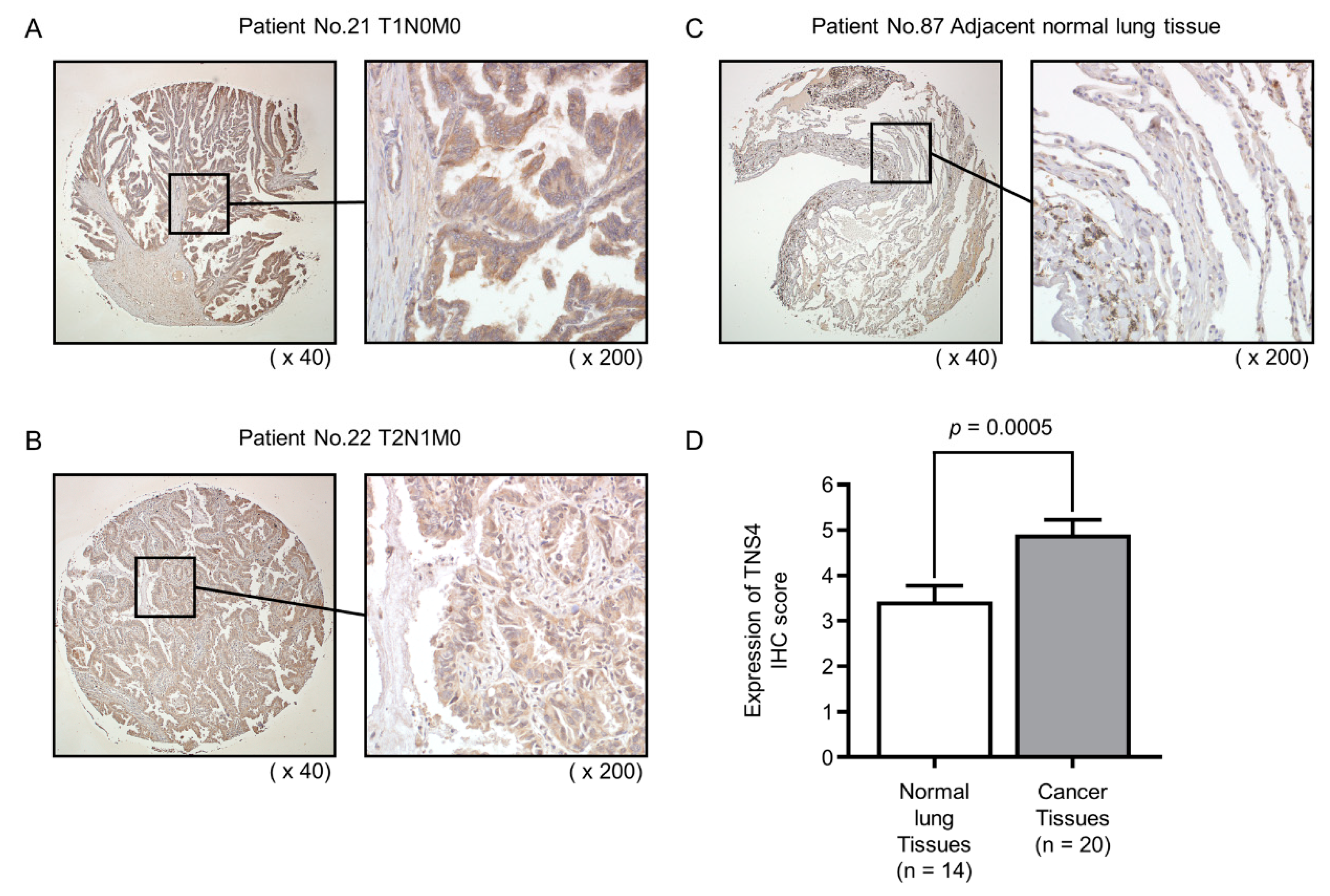
2.6. Expression of TNS4 Protein in Clinical LUAD Specimens
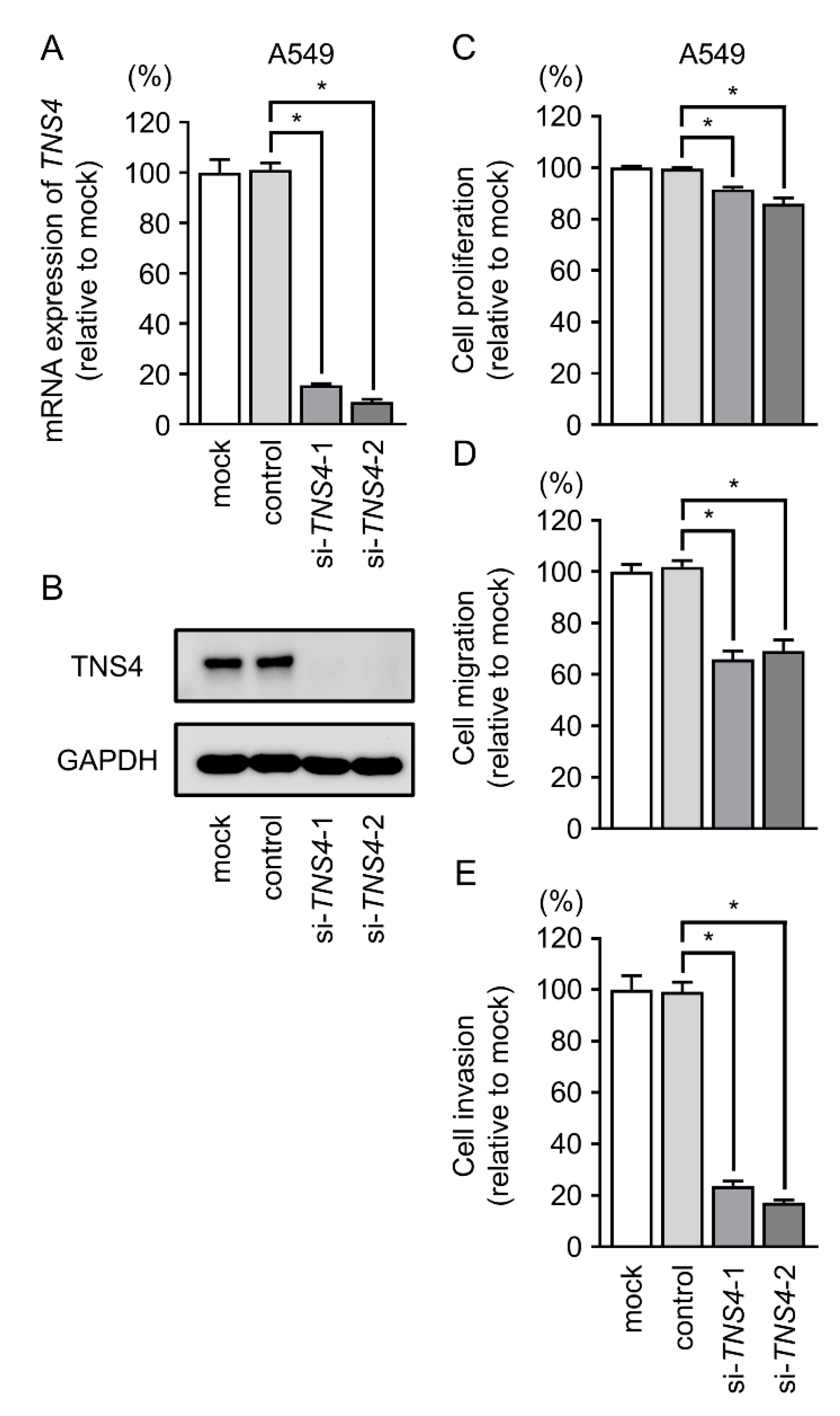
2.7. TNS4 Silencing Suppresses the Aggressiveness of LUAD Cells
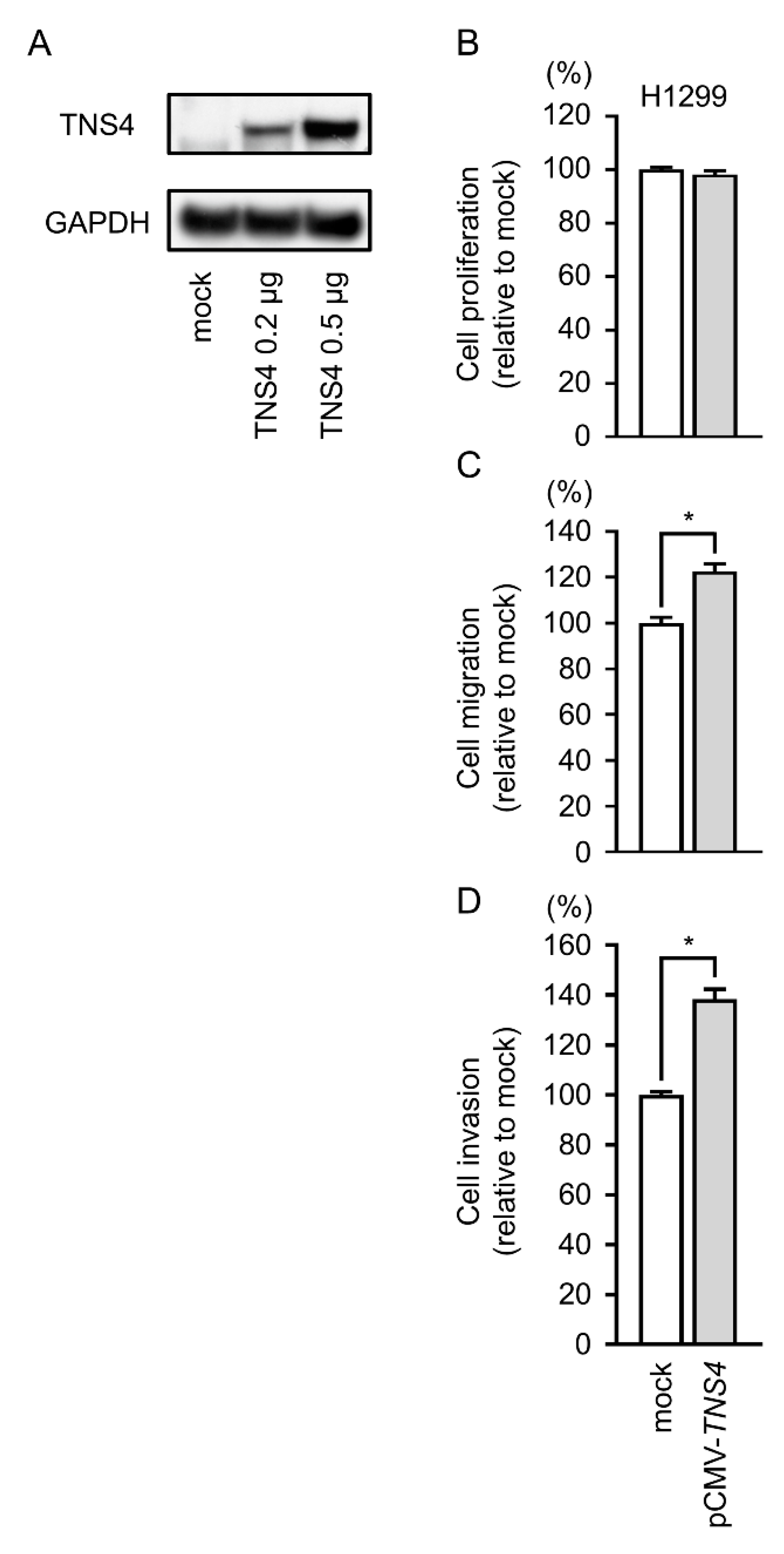
2.8. Gain-of-Function Studies by TNS4 Expression Vector
2.9. Downstream Genes Affected by the Silencing of TNS4 in LUAD Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human LUAD Specimens and Cell Lines
4.2. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.3. Transfection of miRNAs, siRNAs, and Plasmid Vectors into LUAD Cells
4.4. Incorporation of miR-150-5p or miR-150-3p into the RISC by Ago2 Immunoprecipitation
4.5. Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion Assays
4.6. Identification of Putative Target Genes Regulated by miR-150-5p and miR-150-3p in LUAD Cells
4.7. Plasmid Construction and Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.8. Clinical Database Analysis of LUAD
4.9. Western Blotting and Immunohistochemistry
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.Y.; Cramb, S.M.; Baade, P.D.; Youlden, D.R.; Nwogu, C.; Reid, M.E. The International Epidemiology of Lung Cancer: Latest Trends, Disparities, and Tumor Characteristics. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2016, 11, 1653–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Boshoff, C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 2018, 553, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyneman, L.E.; Herndon, J.E.; Goodman, P.C.; Patz, E.F., Jr. Stage distribution in patients with a small (< or = 3 cm) primary nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Implication for lung carcinoma screening. Cancer 2001, 92, 3051–3055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Tsui, H.C.; Yang, P.C. Tumor size matters differently in pulmonary adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2010, 67, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, Y.; Kurozumi, A.; Enokida, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Functional significance of aberrantly expressed microRNAs in prostate cancer. Int. J. Urol. Off. J. Jpn. Urol. Assoc. 2015, 22, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalanotto, C.; Cogoni, C.; Zardo, G. MicroRNA in Control of Gene Expression: An Overview of Nuclear Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshizuka, K.; Hanazawa, T.; Fukumoto, I.; Kikkawa, N.; Okamoto, Y.; Seki, N. The microRNA signatures: Aberrantly expressed microRNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 62, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Mataki, H.; Seki, N.; Kumamoto, T.; Kamikawaji, K.; Inoue, H. MicroRNAs in non-small cell lung cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 62, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyaeva, L.F.; Kushlinskiy, N.E. Regulatory mechanisms of microRNA expression. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramassone, A.; Pagotto, S.; Veronese, A.; Visone, R. Epigenetics and MicroRNAs in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumamoto, T.; Seki, N.; Mataki, H.; Mizuno, K.; Kamikawaji, K.; Samukawa, T.; Koshizuka, K.; Goto, Y.; Inoue, H. Regulation of TPD52 by antitumor microRNA-218 suppresses cancer cell migration and invasion in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mataki, H.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Nohata, N.; Kamikawaji, K.; Kumamoto, T.; Koshizuka, K.; Goto, Y.; Inoue, H. Dual-strand tumor-suppressor microRNA-145 (miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p) coordinately targeted MTDH in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 72084–72098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Mataki, H.; Arai, T.; Okato, A.; Kamikawaji, K.; Kumamoto, T.; Hiraki, T.; Hatanaka, K.; Inoue, H.; Seki, N. The microRNA expression signature of small cell lung cancer: Tumor suppressors of miR-27a-5p and miR-34b-3p and their targeted oncogenes. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 62, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misono, S.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Yamada, Y.; Uchida, A.; Arai, T.; Kumamoto, T.; Sanada, H.; Suetsugu, T.; Inoue, H. Dual strands of the miR-145 duplex (miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p) regulate oncogenes in lung adenocarcinoma pathogenesis. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 63, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetsugu, T.; Koshizuka, K.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Okato, A.; Arai, T.; Misono, S.; Uchida, A.; Kumamoto, T.; Inoue, H. Downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 14 by the antitumor miRNA, miR-150-5p, inhibits the aggressiveness of lung squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, A.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Misono, S.; Yamada, Y.; Kikkawa, N.; Sanada, H.; Kumamoto, T.; Suetsugu, T.; Inoue, H. Involvement of dual-strand of the miR-144 duplex and their targets in the pathogenesis of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matranga, C.; Tomari, Y.; Shin, C.; Bartel, D.P.; Zamore, P.D. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell 2005, 123, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshizuka, K.; Nohata, N.; Hanazawa, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Arai, T.; Okato, A.; Fukumoto, I.; Katada, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Seki, N. Deep sequencing-based microRNA expression signatures in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Dual strands of pre-miR-150 as antitumor miRNAs. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30288–30304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osako, Y.; Seki, N.; Koshizuka, K.; Okato, A.; Idichi, T.; Arai, T.; Omoto, I.; Sasaki, K.; Uchikado, Y.; Kita, Y.; et al. Regulation of SPOCK1 by dual strands of pre-miR-150 inhibit cancer cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 62, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshizuka, K.; Hanazawa, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Katada, K.; Okato, A.; Arai, T.; Idichi, T.; Osako, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Seki, N. Antitumor miR-150-5p and miR-150-3p inhibit cancer cell aggressiveness by targeting SPOCK1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. AurisNasusLarynx 2018, 45, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, Y.; Kurozumi, A.; Nohata, N.; Kojima, S.; Matsushita, R.; Yoshino, H.; Yamazaki, K.; Ishida, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Naya, Y.; et al. The microRNA signature of patients with sunitinib failure: Regulation of UHRF1 pathways by microRNA-101 in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59070–59086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, Y.; Kurozumi, A.; Arai, T.; Nohata, N.; Kojima, S.; Okato, A.; Kato, M.; Yamazaki, K.; Ishida, Y.; Naya, Y.; et al. Impact of novel miR-145-3p regulatory networks on survival in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemori, K.; Seki, N.; Idichi, T.; Kurahara, H.; Osako, Y.; Koshizuka, K.; Arai, T.; Okato, A.; Kita, Y.; Arigami, T.; et al. The microRNA expression signature of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by RNA sequencing: Anti-tumour functions of the microRNA-216 cluster. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 70097–70115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, H.; Kurozumi, S.; Kijima, Y.; Idichi, T.; Shinden, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Arai, T.; Maemura, K.; Fujii, T.; Horiguchi, J.; et al. Molecular pathogenesis of triple-negative breast cancer based on microRNA expression signatures: Antitumor miR-204-5p targets AP1S3. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 63, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonemori, M.; Seki, N.; Yoshino, H.; Matsushita, R.; Miyamoto, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Enokida, H. Dual tumor-suppressors miR-139-5p and miR-139-3p targeting matrix metalloprotease 11 in bladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshizuka, K.; Hanazawa, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Arai, T.; Okato, A.; Kurozumi, A.; Kato, M.; Katada, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Seki, N. Regulation of ITGA3 by the anti-tumor miR-199 family inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion in head and neck cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, S.; Yamada, Y.; Arai, T.; Okato, A.; Idichi, T.; Kato, M.; Koshizuka, K.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Dual strands of the miR-223 duplex (miR-223-5p and miR-223-3p) inhibit cancer cell aggressiveness: Targeted genes are involved in bladder cancer pathogenesis. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 63, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Arai, T.; Kojima, S.; Sugawara, S.; Kato, M.; Okato, A.; Yamazaki, K.; Naya, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Regulation of antitumor miR-144-5p targets oncogenes: Direct regulation of syndecan-3 and its clinical significance. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2919–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Arai, T.; Kojima, S.; Sugawara, S.; Kato, M.; Okato, A.; Yamazaki, K.; Naya, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Anti-tumor roles of both strands of the miR-455 duplex: Their targets SKA1 and SKA3 are involved in the pathogenesis of renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26638–26658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Koshizuka, K.; Hanazawa, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Okato, A.; Idichi, T.; Arai, T.; Sugawara, S.; Katada, K.; Okamoto, Y.; et al. Passenger strand of miR-145-3p acts as a tumor-suppressor by targeting MYO1B in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.H. C-terminal tensin-like (CTEN): A promising biomarker and target for cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 51, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, M.; Amit, I.; Citri, A.; Shay, T.; Carvalho, S.; Lavi, S.; Milanezi, F.; Lyass, L.; Amariglio, N.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; et al. A reciprocal tensin-3-cten switch mediates EGF-driven mammary cell migration. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Shih, Y.P.; Li, T.; Carraway, K.L., 3rd; Lo, S.H. CTEN prolongs signaling by EGFR through reducing its ligand-induced degradation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5266–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.C.; Chen, N.T.; Shih, Y.P.; Dong, Y.; Lo, S.H. Up-regulation of C-terminal tensin-like molecule promotes the tumorigenicity of colon cancer through beta-catenin. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4563–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albasri, A.; Al-Ghamdi, S.; Fadhil, W.; Aleskandarany, M.; Liao, Y.C.; Jackson, D.; Lobo, D.N.; Lo, S.H.; Kumari, R.; Durrant, L.; et al. Cten signals through integrin-linked kinase (ILK) and may promote metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2997–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghamdi, S.; Cachat, J.; Albasri, A.; Ahmed, M.; Jackson, D.; Zaitoun, A.; Guppy, N.; Otto, W.R.; Alison, M.R.; Kindle, K.B.; et al. C-terminal tensin-like gene functions as an oncogene and promotes cell motility in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2013, 42, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.K.; Chiu, Y.T.; Sze, K.M.; Ng, I.O. Tensin4 is up-regulated by EGF-induced ERK1/2 activity and promotes cell proliferation and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20964–20976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.T.; Reece, T.B.; Foley, L.S.; Sjoberg, A.; Meng, X.; Fullerton, D.A.; Weyant, M.J. C-terminal tensin-like protein mediates invasion of human lung cancer cells and is regulated by signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.X.; Zhu, T.; Zou, T.; Zhuo, W.; Chen, Y.X.; Huang, M.S.; Zheng, W.; Wang, C.J.; Li, X.; Mao, X.Y.; et al. Prognostic and predictive values of CDK1 and MAD2L1 in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 85235–85243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.; Harborth, J.; Schnabel, J.; Weber, K.; Hatzfeld, M. The mitotic-spindle-associated protein astrin is essential for progression through mitosis. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 4053–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Liu, D.; Zan, Y.; Yin, X. MicroRNA-1179 suppresses cell growth and invasion by targeting sperm-associated antigen 5-mediated Akt signaling in human non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanselmann, S.; Wolter, P.; Malkmus, J.; Gaubatz, S. The microtubule-associated protein PRC1 is a potential therapeutic target for lung cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 4985–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamikawaji, K.; Seki, N.; Watanabe, M.; Mataki, H.; Kumamoto, T.; Takagi, K.; Mizuno, K.; Inoue, H. Regulation of LOXL2 and SERPINH1 by antitumor microRNA-29a in lung cancer with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 61, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Kojima, S.; Yamada, Y.; Sugawara, S.; Kato, M.; Yamazaki, K.; Naya, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Pirin: A potential novel therapeutic target for castration-resistant prostate cancer regulated by miR-455-5p. Mol. Oncol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Sugawara, S.; Arai, T.; Kojima, S.; Kato, M.; Okato, A.; Yamazaki, K.; Naya, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Molecular pathogenesis of renal cell carcinoma: Impact of the anti-tumor miR-29 family on gene regulation. Int. J. Urol. Off. J. Jpn. Urol. Assoc. 2018, 25, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| A. Characteristics of the Lung Cancer Cases | ||
| Lung Cancer Patients | n | (%) |
| Total number | 18 | |
| Median age (range) | 73.5 (59–86) | |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 9 | 50.0 |
| Female | 9 | 50.0 |
| Pathological stage: | ||
| IA | 1 | 5.6 |
| IB | 4 | 22.2 |
| IIA | 8 | 44.4 |
| IIB | 1 | 5.6 |
| IIIA | 4 | 22.2 |
| IIIB | 0 | 0.0 |
| B. Characteristics of the Non-Cancerous Cases | ||
| Non-Cancerous Tissues | n | (%) |
| Total number | 28 | |
| Median age (range) | 71 (50–88) | |
| Gender: | ||
| Male | 25 | 89.3 |
| Female | 3 | 10.7 |
| Entrez Gene | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Total Sites | A549 miR-150-5p Transfectant FC (log2) | GSE19188 FC (log2) | TCGA OncoLnc p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4751 | NEK2 | NIMA-related kinase 2 | 1 | −0.565 | 3.323 | <0.0001 |
| 64065 | PERP | PERP, TP53 apoptosis effector | 3 | −3.012 | 1.835 | <0.0001 |
| 5122 | PCSK1 | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 | 1 | −0.680 | 2.532 | 0.0006 |
| 84985 | FAM83A | Family with sequence similarity 83, member A | 1 | −0.717 | 3.188 | 0.0010 |
| 1033 | CDKN3 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 | 2 | −0.582 | 2.889 | 0.0011 |
| 6241 | RRM2 | Ribonucleotide reductase M2 | 3 | −2.433 | 3.000 | 0.0013 |
| 79801 | SHCBP1 | SHC SH2-domain binding protein 1 | 1 | −1.118 | 1.841 | 0.0015 |
| 29127 | RACGAP1 | Rac GTPase activating protein 1 | 2 | −0.545 | 1.677 | 0.0019 |
| 24137 | KIF4A | Kinesin family member 4A | 1 | −0.933 | 3.309 | 0.0030 |
| 6695 | SPOCK1 | Pparc/osteonectin, cwcv and kazal-like domains proteoglycan (testican) 1 | 1 | −0.764 | 1.696 | 0.0031 |
| 9837 | GINS1 | GINS complex subunit 1 (Psf1 homolog) | 2 | −0.749 | 2.991 | 0.0076 |
| 339761 | CYP27C1 | Cytochrome P450, family 27, subfamily C, polypeptide 1 | 4 | −2.360 | 1.706 | 0.0126 |
| 10331 | B3GNT3 | UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 3 | 2 | −0.939 | 1.608 | 0.0129 |
| 79962 | DNAJC22 | DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 22 | 5 | −0.908 | 2.031 | 0.0201 |
| 10635 | RAD51AP1 | RAD51-associated protein 1 | 1 | −0.611 | 2.470 | 0.0228 |
| 10797 | MTHFD2 | Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent) 2, methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase | 1 | −1.905 | 1.887 | 0.0236 |
| 9699 | RIMS2 | Regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis 2 | 2 | −0.697 | 1.976 | 0.0265 |
| 1058 | CENPA | Centromere protein A | 1 | −1.019 | 3.488 | 0.0365 |
| 23657 | SLC7A11 | Solute carrier family 7 (anionic amino acid transporter light chain, xc- system), member 11 | 3 | −1.093 | 2.014 | 0.0474 |
| 3755 | KCNG1 | Potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily G, member 1 | 5 | −1.069 | 1.887 | 0.0557 |
| 1825 | DSC3 | Desmocollin 3 | 1 | −1.247 | 2.488 | 0.0667 |
| 388228 | SBK1 | SH3 domain binding kinase 1 | 1 | −0.658 | 1.745 | 0.0939 |
| 8038 | ADAM12 | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 12 | 2 | −0.668 | 2.753 | 0.1097 |
| 84733 | CBX2 | Chromobox homolog 2 | 1 | −0.591 | 1.988 | 0.1116 |
| 130827 | TMEM182 | Transmembrane protein 182 | 1 | −0.690 | 1.568 | 0.1189 |
| 92312 | MEX3A | mex-3 RNA binding family member A | 3 | −0.584 | 1.986 | 0.1271 |
| 4323 | MMP14 | Matrix metallopeptidase 14 | 3 | −0.621 | 1.872 | 0.1296 |
| 4151 | MB | myoglobin | 3 | −1.119 | 1.614 | 0.1346 |
| 57167 | SALL4 | Sal-like 4 (Drosophila) | 1 | −0.582 | 2.836 | 0.2382 |
| 256714 | MAP7D2 | MAP7 domain containing 2 | 1 | −1.449 | 2.007 | 0.2798 |
| 6273 | S100A2 | S100 calcium binding protein A2 | 1 | −0.643 | 2.513 | 0.3132 |
| 200844 | C3orf67 | Chromosome 3 open reading frame 67 | 1 | −0.514 | 1.584 | 0.3482 |
| 1690 | COCH | Cochlin | 2 | −0.592 | 3.406 | 0.3696 |
| 10447 | FAM3C | Family with sequence similarity 3, member C | 1 | −1.570 | 1.536 | 0.3847 |
| 147920 | IGFL2 | IGF-like family member 2 | 1 | −0.719 | 2.569 | 0.4596 |
| 547 | KIF1A | Kinesin family member 1A | 4 | −0.733 | 2.518 | 0.6354 |
| 9066 | SYT7 | Synaptotagmin VII | 2 | −0.921 | 1.730 | 0.7141 |
| 55220 | KLHDC8A | Kelch domain containing 8A | 4 | −1.168 | 1.709 | 0.7484 |
| 440590 | ZYG11A | Zyg-11 family member A, cell cycle regulator | 2 | −1.619 | 1.826 | 0.7530 |
| 3141 | HLCS | Holocarboxylase synthetase | 1 | −0.897 | 1.791 | 0.8947 |
| 9547 | CXCL14 | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 14 | 2 | −0.750 | 1.800 | 0.9229 |
| Entrez Gene | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Total Sites | A549 miR-150-3p Transfectant FC (log2) | GSE19188 FC (log2) | TCGA OncoLnc p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 84951 | TNS4 | Tensin 4 | 1 | −1.318 | 2.560 | 0.0003 |
| 94081 | SFXN1 | Sideroflexin 1 | 1 | −1.307 | 1.404 | 0.0020 |
| 221150 | SKA3 | Spindle and kinetochore-associated complex subunit 3 | 1 | −1.006 | 2.015 | 0.0027 |
| 6695 | SPOCK1 | Sparc/osteonectin, cwcv and kazal-like domains proteoglycan (testican) 1 | 3 | −2.040 | 1.696 | 0.0031 |
| 89874 | SLC25A21 | Solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial oxoadipate carrier), member 21 | 2 | −2.557 | 1.358 | 0.0149 |
| 94032 | CAMK2N2 | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor 2 | 1 | −1.303 | 1.538 | 0.0208 |
| 5738 | PTGFRN | Prostaglandin F2 receptor inhibitor | 2 | −1.750 | 1.237 | 0.0291 |
| 23105 | FSTL4 | Follistatin-like 4 | 1 | −1.602 | 1.485 | 0.0589 |
| 130574 | LYPD6 | LY6/PLAUR domain containing 6 | 1 | −1.004 | 1.917 | 0.0591 |
| 150223 | YDJC | YdjC homolog (bacterial) | 1 | −1.592 | 1.088 | 0.0699 |
| 3174 | HNF4G | Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4, gamma | 1 | −1.827 | 1.709 | 0.0717 |
| 6857 | SYT1 | Synaptotagmin I | 1 | −2.264 | 2.058 | 0.0735 |
| 5522 | PPP2R2C | Protein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit B, gamma | 2 | −1.004 | 2.491 | 0.1067 |
| 8038 | ADAM12 | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 12 | 2 | −1.555 | 2.753 | 0.1097 |
| 84216 | TMEM117 | Transmembrane protein 117 | 1 | −3.167 | 1.049 | 0.1894 |
| 55753 | OGDHL | Oxoglutarate dehydrogenase-like | 1 | −1.896 | 1.776 | 0.3167 |
| 79944 | L2HGDH | L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase | 1 | −1.921 | 1.730 | 0.3221 |
| 79776 | ZFHX4 | Zinc finger homeobox 4 | 1 | −2.113 | 1.248 | 0.3578 |
| 4647 | MYO7A | Myosin VIIA | 1 | −1.193 | 1.047 | 0.4080 |
| 23321 | TRIM2 | Tripartite motif containing 2 | 2 | −1.550 | 1.755 | 0.4560 |
| 401474 | SAMD12 | Sterile alpha motif domain containing 12 | 1 | −1.950 | 1.027 | 0.4853 |
| 145282 | MIPOL1 | Mirror-image polydactyly 1 | 1 | −1.401 | 1.108 | 0.5861 |
| 8821 | INPP4B | Inositol polyphosphate-4-phosphatase, type II, 105kDa | 3 | −1.412 | 1.414 | 0.6077 |
| 80310 | PDGFD | Platelet-derived growth factor D | 1 | −1.555 | 1.142 | 0.6859 |
| 9802 | DAZAP2 | DAZ-associated protein 2 | 2 | −1.439 | 1.144 | 0.8241 |
| 85439 | STON2 | Stonin 2 | 1 | −1.371 | 1.079 | 0.9773 |
| Entrez Gene | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | GSE19188 FC (log2) | A549 si-TNS4-2 Transfectant FC (log2) | TCGA OncoLnc p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 114904 | C1QTNF6 | C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 6 | 2.046 | −1.159 | <0.0001 |
| 983 | CDK1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 | 2.400 | −1.119 | 0.0003 |
| 10615 | SPAG5 | Sperm-associated antigen 5 | 2.196 | −1.598 | 0.0003 |
| 84951 | TNS4 | Tensin 4 | 2.560 | −2.690 | 0.0003 |
| 4288 | MKI67 | Marker of proliferation Ki-67 | 2.835 | −1.475 | 0.0004 |
| 8208 | CHAF1B | Chromatin assembly factor 1, subunit B (p60) | 1.723 | −1.112 | 0.0005 |
| 9824 | ARHGAP11A | Rho GTPase activating protein 11A | 1.638 | −1.263 | 0.0007 |
| 9055 | PRC1 | Protein regulator of cytokinesis 1 | 2.540 | −1.120 | 0.0007 |
| 171177 | RHOV | Ras homolog family member V | 2.330 | −1.890 | 0.0008 |
| 1033 | CDKN3 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 | 2.889 | −1.594 | 0.0011 |
| 6241 | RRM2 | Ribonucleotide reductase M2 | 3.000 | −1.356 | 0.0013 |
| 57405 | SPC25 | SPC25, NDC80 kinetochore complex component | 2.417 | −1.456 | 0.0014 |
| 5318 | PKP2 | Plakophilin 2 | 1.584 | −1.108 | 0.0016 |
| 701 | BUB1B | BUB1 mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine kinase B | 2.669 | −1.278 | 0.0017 |
| 4085 | MAD2L1 | MAD2 mitotic arrest deficient-like 1 (yeast) | 2.768 | −1.726 | 0.0018 |
| 81624 | DIAPH3 | Diaphanous-related formin 3 | 1.926 | −1.016 | 0.0022 |
| 3832 | KIF11 | Kinesin family member 11 | 2.479 | −1.007 | 0.0022 |
| 79019 | CENPM | Centromere protein M | 2.391 | −1.057 | 0.0023 |
| 55635 | DEPDC1 | DEP domain containing 1 | 3.443 | −1.282 | 0.0024 |
| 147841 | SPC24 | SPC24, NDC80 kinetochore complex component | 2.179 | −1.490 | 0.0031 |
| 195828 | ZNF367 | Zinc finger protein 367 | 1.583 | −1.454 | 0.0033 |
| 1063 | CENPF | Centromere protein F, 350/400kDa | 2.985 | −1.129 | 0.0048 |
| 83540 | NUF2 | NUF2, NDC80 kinetochore complex component | 3.442 | −1.069 | 0.0048 |
| 29089 | UBE2T | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T | 3.317 | −1.092 | 0.0051 |
| 7348 | UPK1B | Uroplakin 1B | 1.603 | −1.179 | 0.0059 |
| 11130 | ZWINT | ZW10 interacting kinetochore protein | 2.184 | −1.188 | 0.0064 |
| 11169 | WDHD1 | WD repeat and HMG-box DNA binding protein 1 | 2.094 | −1.151 | 0.0065 |
| 55215 | FANCI | Fanconi anemia, complementation group I | 2.298 | −1.563 | 0.0073 |
| 4176 | MCM7 | Minichromosome maintenance complex component 7 | 1.555 | −1.164 | 0.0076 |
| 10403 | NDC80 | NDC80 kinetochore complex component | 2.493 | −1.053 | 0.0076 |
| 699 | BUB1 | BUB1 mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine kinase | 3.206 | −1.180 | 0.0081 |
| 79075 | DSCC1 | DNA replication and sister chromatid cohesion 1 | 1.704 | −1.187 | 0.0088 |
| 51514 | DTL | Denticleless E3 ubiquitin protein ligase homolog (Drosophila) | 2.098 | −1.187 | 0.0091 |
| 8914 | TIMELESS | Timeless circadian clock | 1.650 | −1.447 | 0.0093 |
| 79733 | E2F8 | E2F transcription factor 8 | 2.879 | −2.313 | 0.0114 |
| 4605 | MYBL2 | v-Myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog-like 2 | 3.003 | −1.063 | 0.0122 |
| 5427 | POLE2 | Polymerase (DNA directed), epsilon 2, accessory subunit | 1.600 | −1.074 | 0.0122 |
| 10331 | B3GNT3 | UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 3 | 1.608 | −1.005 | 0.0129 |
| 7083 | TK1 | Thymidine kinase 1, soluble | 2.086 | −1.399 | 0.0131 |
| 6790 | AURKA | Aurora kinase A | 2.542 | −1.018 | 0.0132 |
| 79623 | GALNT14 | Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 14 | 2.572 | −1.075 | 0.0140 |
| 64151 | NCAPG | Non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G | 2.833 | −2.675 | 0.0147 |
| 8318 | CDC45 | Cell division cycle 45 | 3.829 | −1.605 | 0.0159 |
| 55165 | CEP55 | Centrosomal protein 55kDa | 2.875 | −1.077 | 0.0203 |
| 54478 | FAM64A | Family with sequence similarity 64, member A | 2.713 | −1.697 | 0.0219 |
| 79172 | CENPO | Centromere protein O | 1.620 | −1.048 | 0.0248 |
| 2491 | CENPI | Centromere protein I | 2.088 | −1.685 | 0.0258 |
| 1356 | CP | Ceruloplasmin (ferroxidase) | 1.604 | −2.134 | 0.0300 |
| 2244 | FGB | Fibrinogen beta chain | 1.887 | −3.066 | 0.0305 |
| 29128 | UHRF1 | Ubiquitin-like with PHD and ring finger domains 1 | 2.576 | −1.442 | 0.0312 |
| 1058 | CENPA | Centromere protein A | 3.488 | −1.338 | 0.0365 |
| 2877 | GPX2 | Glutathione peroxidase 2 (gastrointestinal) | 3.579 | −1.038 | 0.0446 |
| 5888 | RAD51 | RAD51 recombinase | 2.085 | −1.344 | 0.0478 |
| 8438 | RAD54L | RAD54-like (S. cerevisiae) | 2.920 | −1.013 | 0.0509 |
| 1789 | DNMT3B | DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 3 beta | 1.606 | −1.029 | 0.0607 |
| 5984 | RFC4 | Replication factor C (activator 1) 4, 37kDa | 2.004 | −1.166 | 0.0938 |
| 91057 | CCDC34 | Coiled-coil domain containing 34 | 1.995 | −1.985 | 0.1035 |
| 202915 | TMEM184A | Transmembrane protein 184A | 1.940 | −1.983 | 0.1067 |
| 8038 | ADAM12 | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 12 | 2.753 | −1.464 | 0.1097 |
| 51557 | LGSN | Lengsin, lens protein with glutamine synthetase domain | 1.721 | −1.008 | 0.1253 |
| 4151 | MB | Myoglobin | 1.614 | −2.307 | 0.1346 |
| 201299 | RDM1 | RAD52 motif containing 1 | 1.503 | −1.596 | 0.1583 |
| 5080 | PAX6 | Paired box 6 | 1.602 | −1.692 | 0.1649 |
| 114907 | FBXO32 | F-box protein 32 | 1.990 | −1.044 | 0.1654 |
| 286151 | FBXO43 | F-box protein 43 | 1.569 | −1.906 | 0.1729 |
| 10293 | TRAIP | TRAF interacting protein | 2.362 | −1.114 | 0.1742 |
| 83990 | BRIP1 | BRCA1 interacting protein C-terminal helicase 1 | 2.051 | −1.439 | 0.1829 |
| 349136 | WDR86 | WD repeat domain 86 | 1.653 | −1.306 | 0.1904 |
| 1870 | E2F2 | E2F transcription factor 2 | 1.704 | −1.075 | 0.1993 |
| 3007 | HIST1H1D | Histone cluster 1, H1d | 1.568 | −1.265 | 0.2918 |
| 6676 | SPAG4 | Sperm-associated antigen 4 | 1.552 | −1.003 | 0.3275 |
| 200844 | C3orf67 | Chromosome 3 open reading frame 67 | 1.584 | −1.436 | 0.3482 |
| 57016 | AKR1B10 | Aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B10 (aldose reductase) | 3.628 | −2.490 | 0.3591 |
| 1719 | DHFR | Dihydrofolate reductase | 1.538 | −1.033 | 0.4901 |
| 8581 | LY6D | Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus D | 2.171 | −1.384 | 0.5123 |
| 6518 | SLC2A5 | Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose/fructose transporter), member 5 | 1.986 | −1.018 | 0.5410 |
| 10535 | RNASEH2A | Ribonuclease H2, subunit A | 1.751 | −1.020 | 0.5517 |
| 10018 | BCL2L11 | BCL2-like 11 (apoptosis facilitator) | 1.592 | −1.310 | 0.5755 |
| 25837 | RAB26 | RAB26, member RAS oncogene family | 2.112 | −1.420 | 0.5804 |
| 57834 | CYP4F11 | Cytochrome P450, family 4, subfamily F, polypeptide 11 | 1.795 | −1.032 | 0.6899 |
| 100133941 | CD24 | CD24 molecule | 2.092 | −1.777 | 0.7765 |
| 56521 | DNAJC12 | DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 12 | 2.208 | −1.687 | 0.7922 |
| 3141 | HLCS | Holocarboxylase synthetase | 1.791 | −1.020 | 0.8947 |
| 222962 | SLC29A4 | Solute carrier family 29 (equilibrative nucleoside transporter), member 4 | 1.617 | −1.100 | 0.9072 |
| 1645 | AKR1C1 | Aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C1 | 2.257 | –1.546 | 0.9583 |
| 152404 | IGSF11 | Immunoglobulin superfamily, member 11 | 1.590 | –1.572 | 0.9790 |
| 85285 | KRTAP4-1 | Keratin-associated protein 4-1 | 2.215 | –1.029 | no data |
| 25859 | PART1 | Prostate androgen-regulated transcript 1 (non-protein coding) | 1.915 | –1.383 | no data |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Misono, S.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Yamada, Y.; Uchida, A.; Sanada, H.; Moriya, S.; Kikkawa, N.; Kumamoto, T.; Suetsugu, T.; et al. Molecular Pathogenesis of Gene Regulation by the miR-150 Duplex: miR-150-3p Regulates TNS4 in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050601
Misono S, Seki N, Mizuno K, Yamada Y, Uchida A, Sanada H, Moriya S, Kikkawa N, Kumamoto T, Suetsugu T, et al. Molecular Pathogenesis of Gene Regulation by the miR-150 Duplex: miR-150-3p Regulates TNS4 in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2019; 11(5):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050601
Chicago/Turabian StyleMisono, Shunsuke, Naohiko Seki, Keiko Mizuno, Yasutaka Yamada, Akifumi Uchida, Hiroki Sanada, Shogo Moriya, Naoko Kikkawa, Tomohiro Kumamoto, Takayuki Suetsugu, and et al. 2019. "Molecular Pathogenesis of Gene Regulation by the miR-150 Duplex: miR-150-3p Regulates TNS4 in Lung Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 11, no. 5: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050601
APA StyleMisono, S., Seki, N., Mizuno, K., Yamada, Y., Uchida, A., Sanada, H., Moriya, S., Kikkawa, N., Kumamoto, T., Suetsugu, T., & Inoue, H. (2019). Molecular Pathogenesis of Gene Regulation by the miR-150 Duplex: miR-150-3p Regulates TNS4 in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 11(5), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050601





