Lactate Activates the E2F Pathway to Promote Cell Motility by Up-Regulating Microtubule Modulating Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
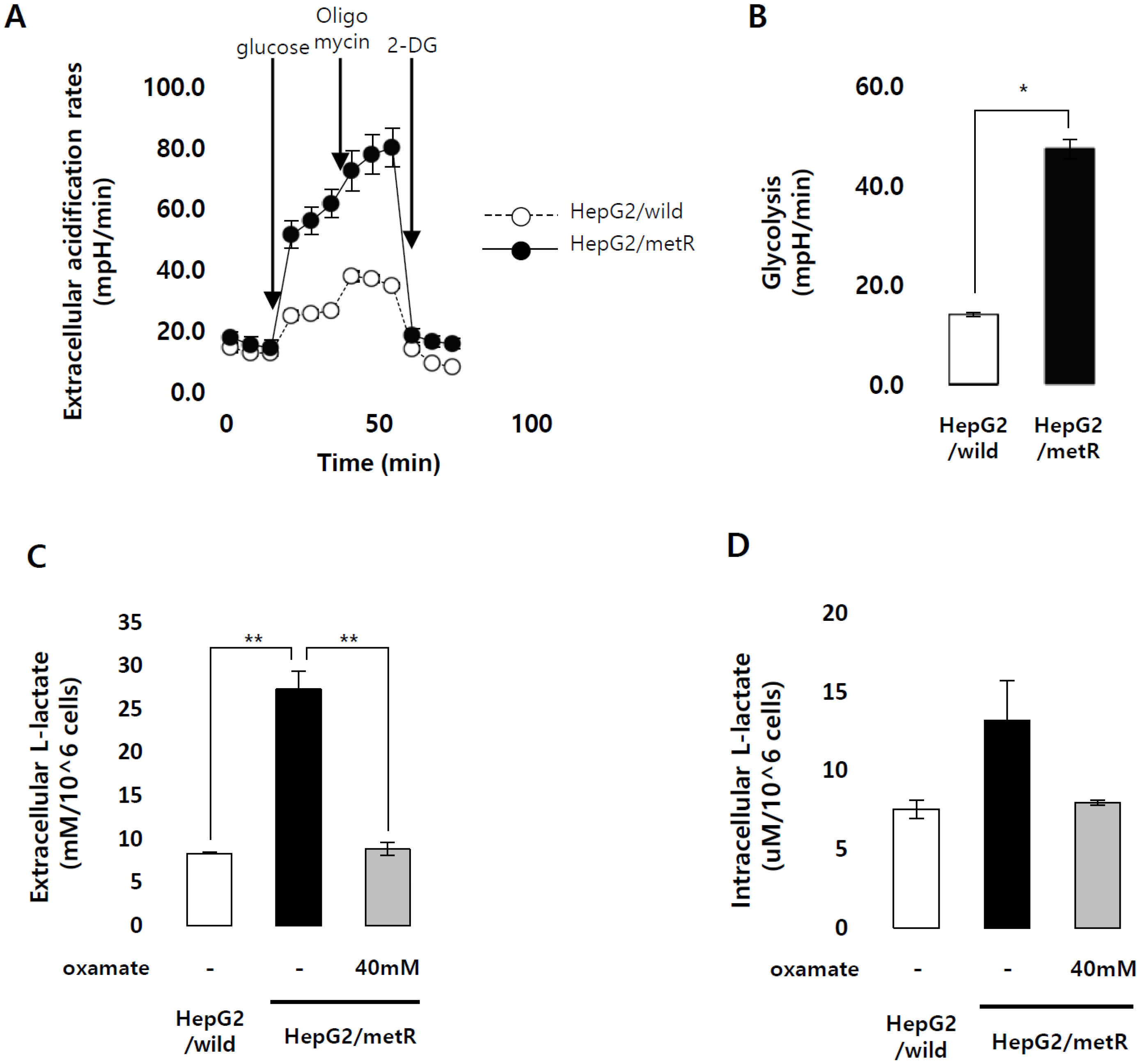
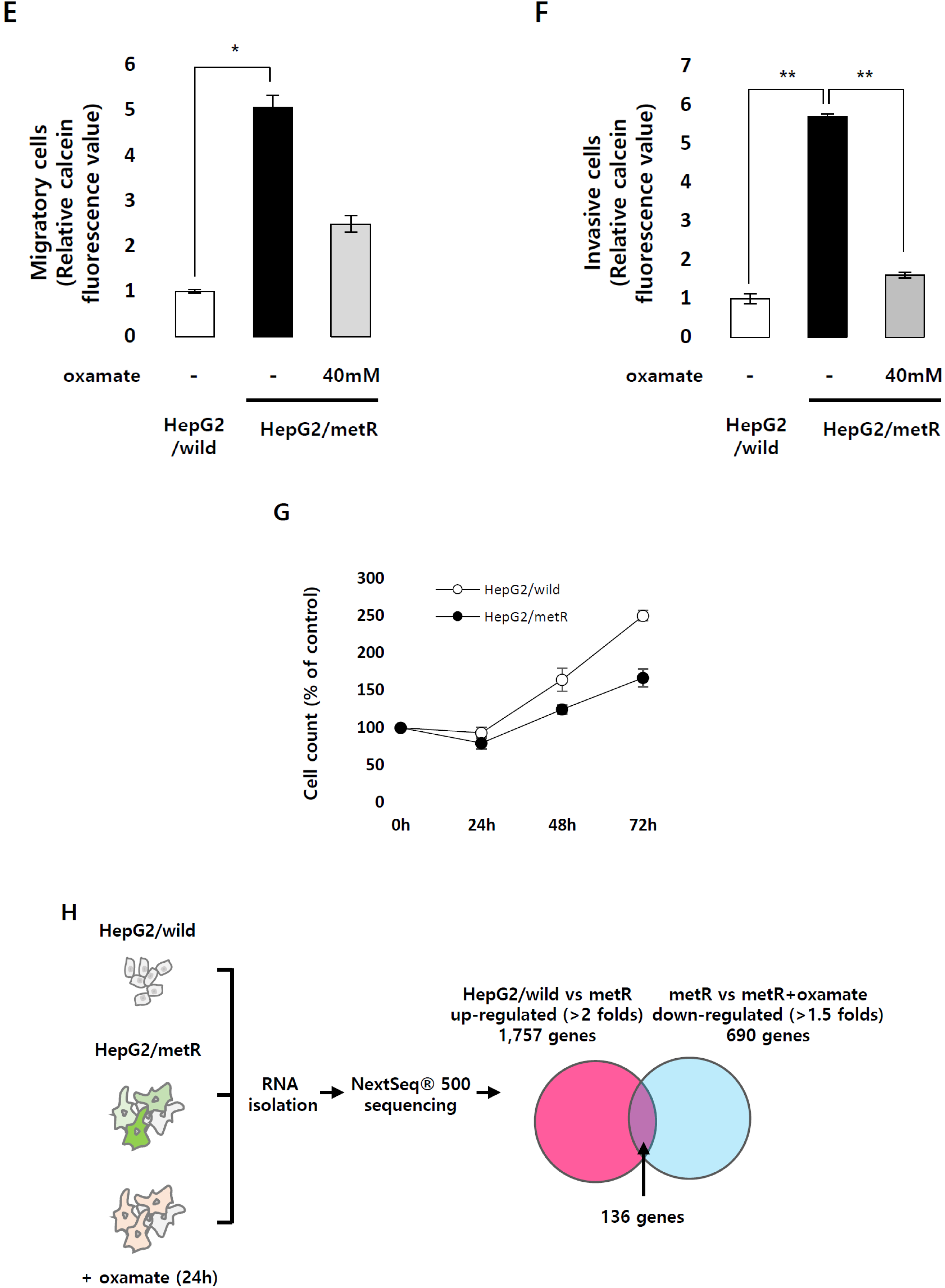
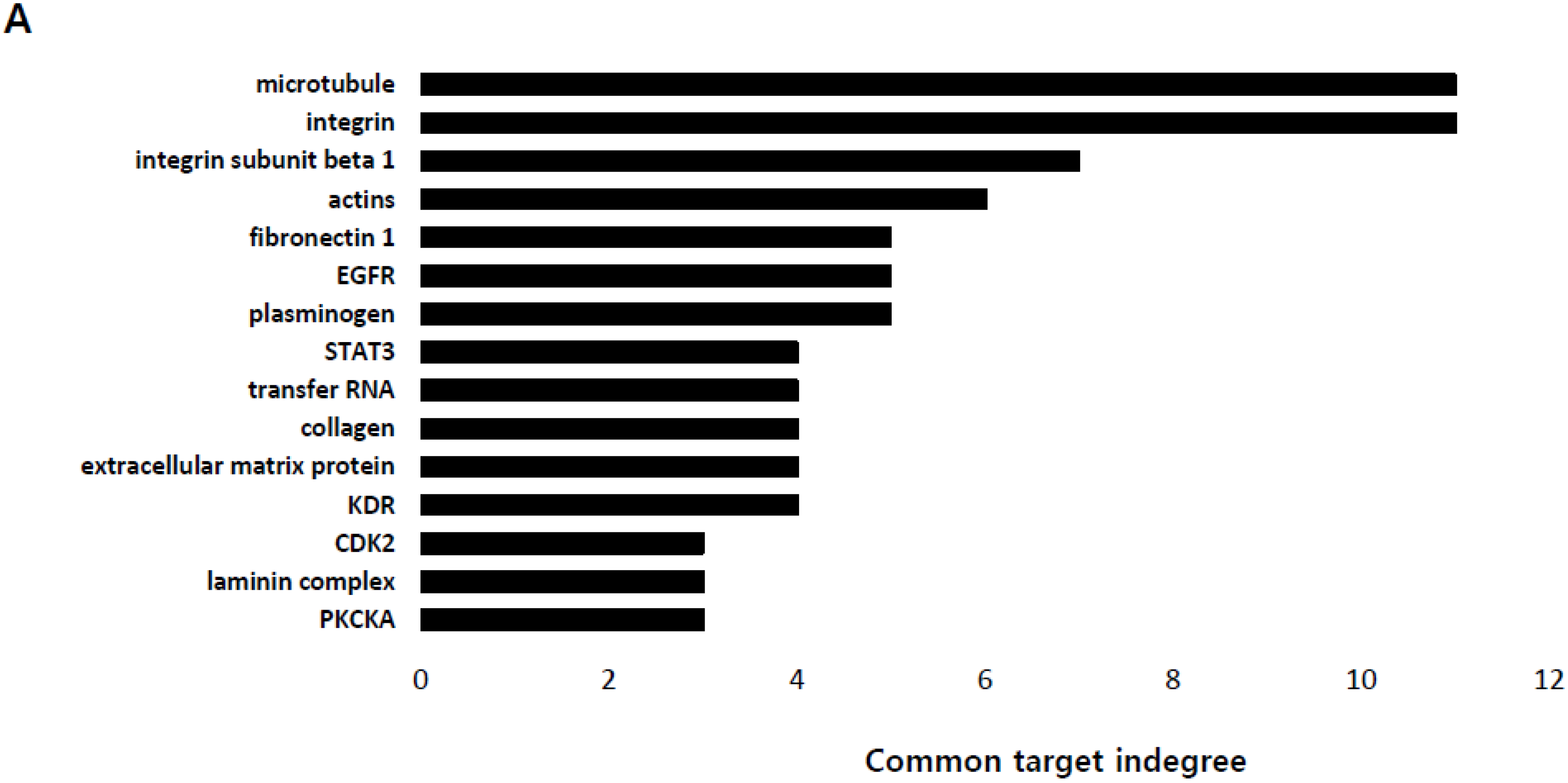
2.1. Identification of the Genes Associated with Lactate-Driven Cell Motility in a Metformin-Induced Glycolytic Cell Model
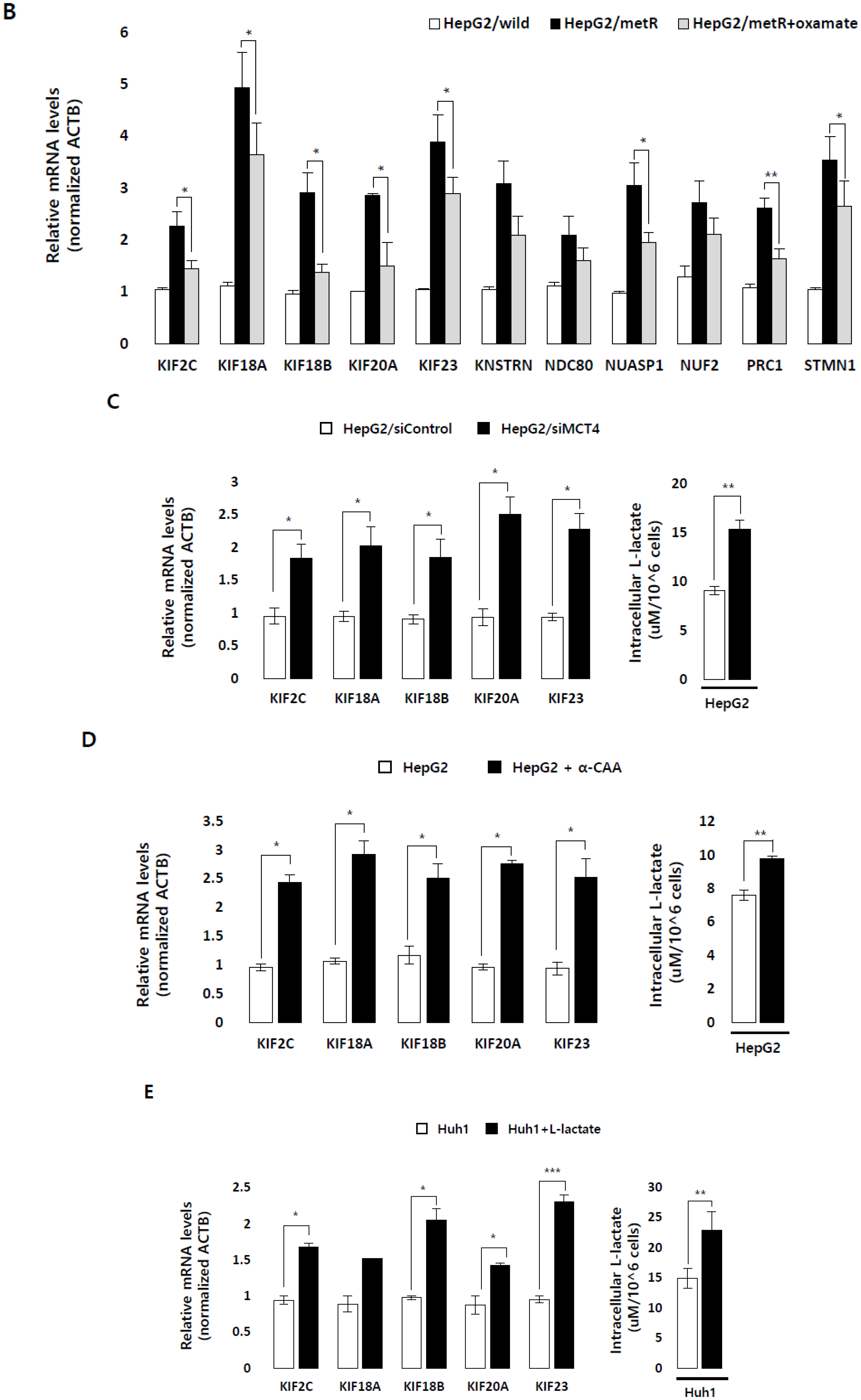
2.2. Lactate Up-Regulates the Expression of Genes Modulating Microtubules Including a Group of Kinesin Family Genes
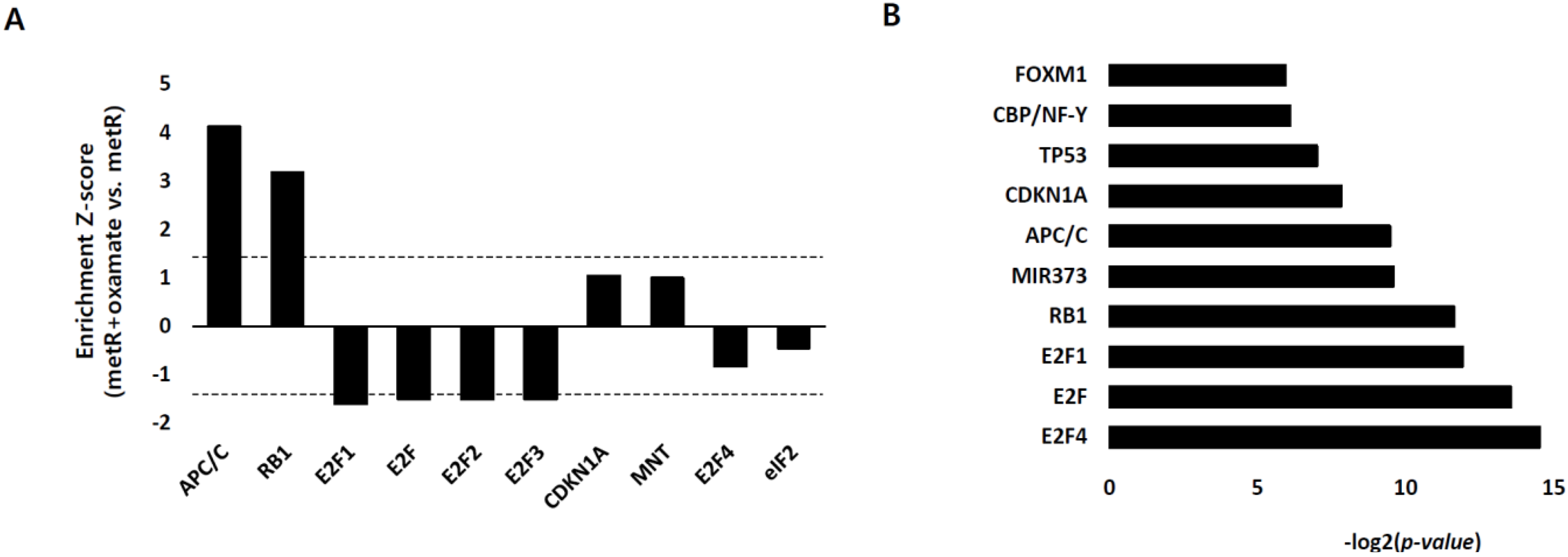
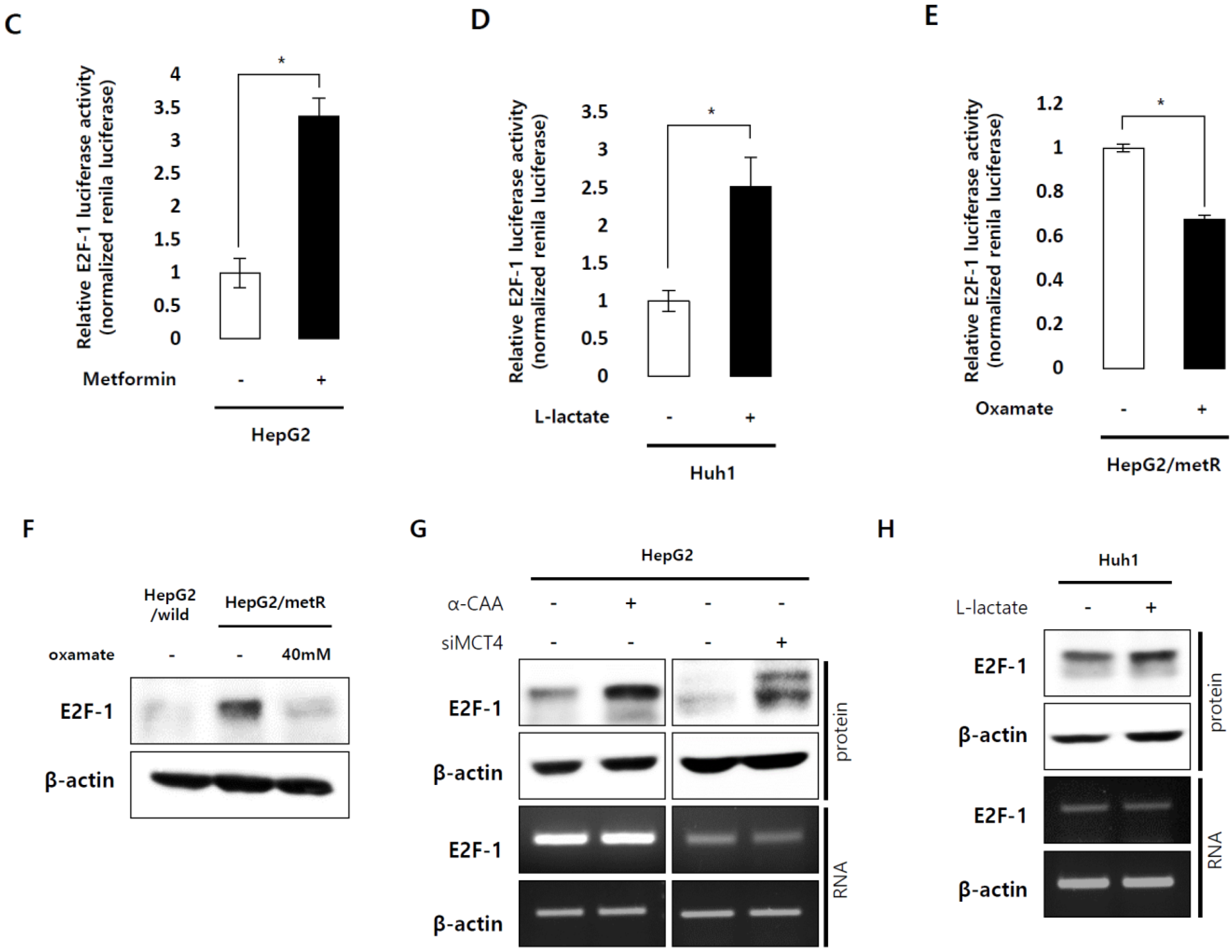
2.3. E2F1 Is a Pivotal Upstream Regulator of Lactate-Induced Gene Expression
2.4. E2F1 Regulates Microtubule Dynamics to Promote Lactate-Dependent Cell Motility
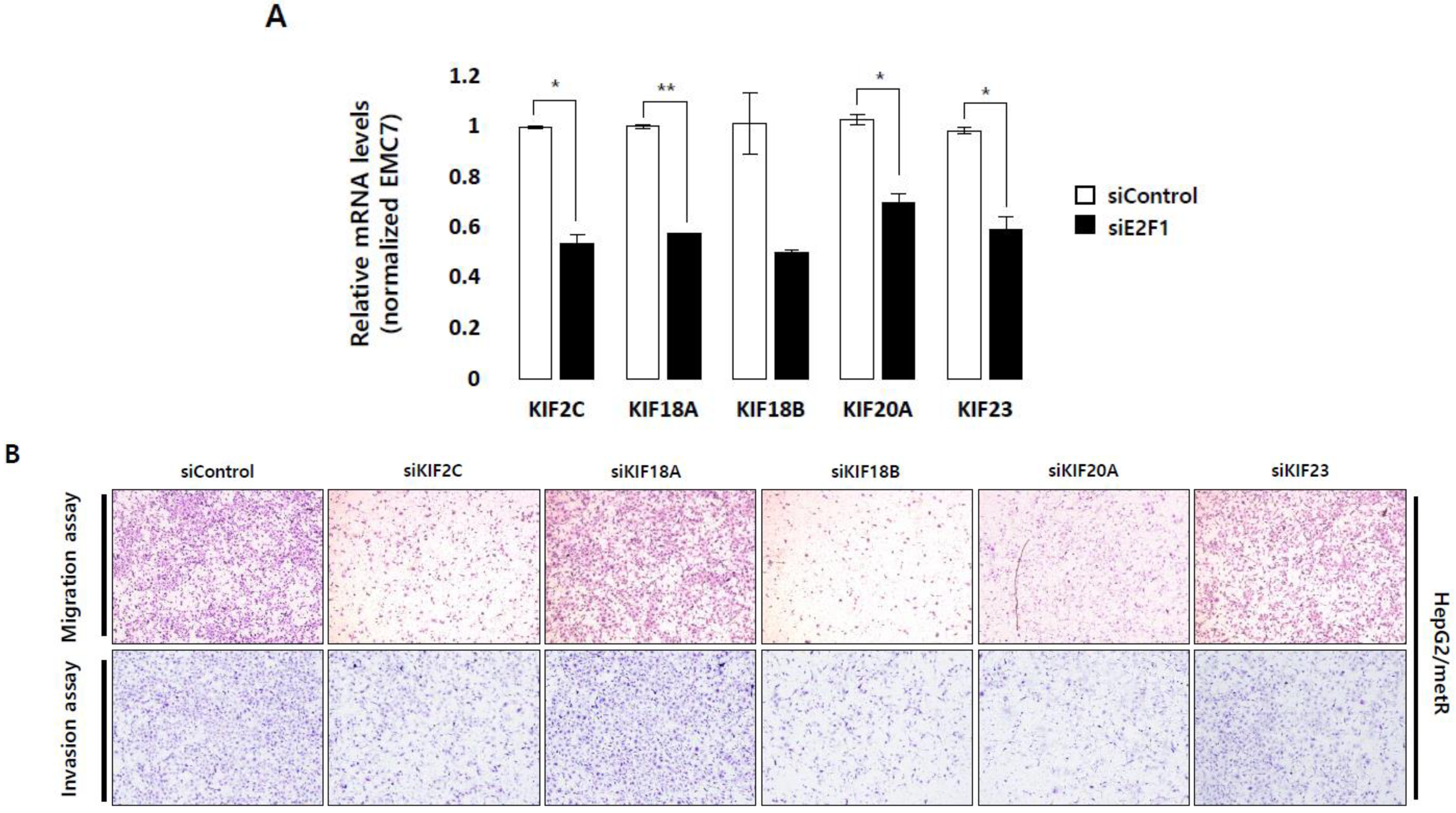
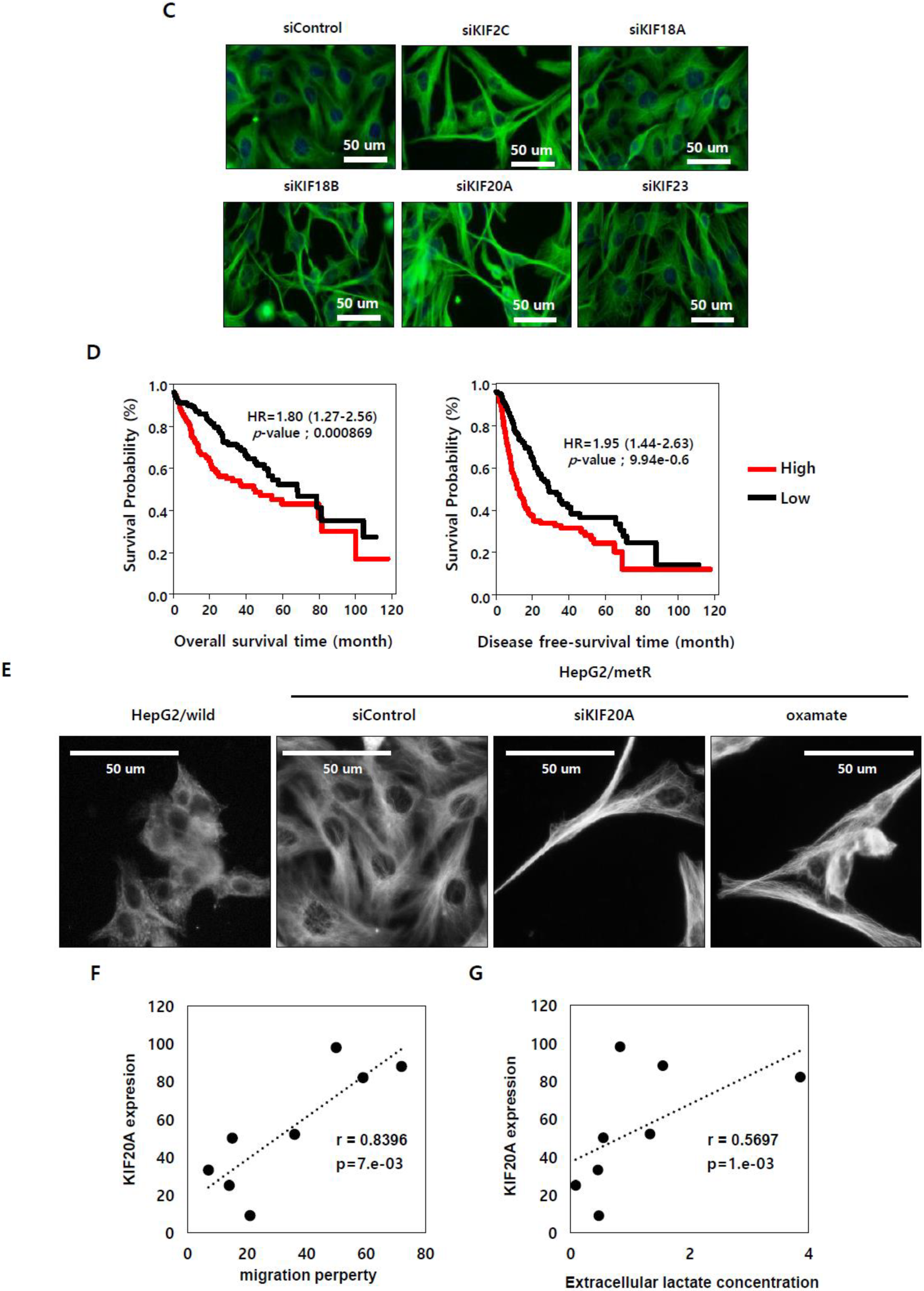
2.5. KIF Family Members Regulate Microtubule Dynamics and Cell Motility in an E2F1-Dependent Manner in the Lactate-Enriched Microenvironment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Reagent Treatment
4.3. Oxygen Consumption Rates and Extracellular Acidification Rates Measurement
4.4. Extra- and Intracellular Lactate Measurement
4.5. Invasion and Migration Assay
4.6. RNA-Sequencing for Expression Profiling
4.7. Transfection of Small-Interfering RNAs
4.8. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
4.9. Reporter Vector Constructs and Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Survival Analysis
4.12. Immunofluorescence
4.13. Tail-Vein Injection Model
4.14. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, P.; Weaver, V.M.; Werb, Z. The extracellular matrix: A dynamic niche in cancer progression. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Ozawa, S.; Miyamoto, C.; Maehata, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Maeda, T.; Baba, Y. Acidic extracellular microenvironment and cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Garcia, S.; Moreno-Altamirano, M.M.; Prado-Garcia, H.; Sanchez-Garcia, F.J. Lactate Contribution to the Tumor Microenvironment: Mechanisms, Effects on Immune Cells and Therapeutic Relevance. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San-Millan, I.; Brooks, G.A. Reexamining cancer metabolism: Lactate production for carcinogenesis could be the purpose and explanation of the Warburg Effect. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, L.; Supuran, C.T.; Alfarouk, K.O. The Warburg Effect and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, A.; Serganova, I.; Khanin, R.; Karabeber, H.; Ni, X.; Thakur, S.; Zakian, K.L.; Blasberg, R.; Koutcher, J.A. Relationships between LDH-A, lactate, and metastases in 4T1 breast tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5158–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhup, S.; Dadhich, R.K.; Porporato, P.E.; Sonveaux, P. Multiple biological activities of lactic acid in cancer: Influences on tumor growth, angiogenesis and metastasis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckert, S.; Farrahi, F.; Aslam, R.S.; Scheuenstuhl, H.; Konigsrainer, A.; Hussain, M.Z.; Hunt, T.K. Lactate stimulates endothelial cell migration. Wound Repair Regen. 2006, 14, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, F.; Leukel, P.; Doerfelt, A.; Beier, C.P.; Dettmer, K.; Oefner, P.J.; Kastenberger, M.; Kreutz, M.; Nickl-Jockschat, T.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Lactate promotes glioma migration by TGF-beta2-dependent regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Neuro Oncol. 2009, 11, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonuccelli, G.; Tsirigos, A.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Pavlides, S.; Pestell, R.G.; Chiavarina, B.; Frank, P.G.; Flomenberg, N.; Howell, A.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; et al. Ketones and lactate “fuel” tumor growth and metastasis: Evidence that epithelial cancer cells use oxidative mitochondrial metabolism. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3506–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walenta, S.; Schroeder, T.; Mueller-Klieser, W. Lactate in solid malignant tumors: Potential basis of a metabolic classification in clinical oncology. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zijl, F.; Krupitza, G.; Mikulits, W. Initial steps of metastasis: Cell invasion and endothelial transmigration. Mutat. Res. 2011, 728, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, A.; Straube, A. Kinesins in cell migration. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, A.; Dang, K.; Buslig, F.; Baird, M.A.; Davidson, M.W.; Waterman, C.M.; Myers, K.A. Rac1 and Aurora A regulate MCAK to polarize microtubule growth in migrating endothelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 206, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, E.J.; Nader, G.P.; Ramalingam, N.; Bartolini, F.; Gundersen, G.G. Kif4 interacts with EB1 and stabilizes microtubules downstream of Rho-mDia in migrating fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Boehlke, C.; Kotsis, F.; Buchholz, B.; Powelske, C.; Eckardt, K.U.; Walz, G.; Nitschke, R.; Kuehn, E.W. Kif3a guides microtubular dynamics, migration and lumen formation of MDCK cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Li, X.; Ye, F.; Lu, C.; Huang, H.; Wang, F.; Cao, X.; Zhong, C. High KIF2A expression promotes proliferation, migration and predicts poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 497, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Yan, C.; Li, J.; Yan, M.; Liu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Q. KIF14 promotes tumor progression and metastasis and is an independent predictor of poor prognosis in human gastric cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesi, G.N.; Jin, L.; Li, D.; Magliocca, K.R.; Kang, Y.; Chen, Z.G.; Shin, D.M.; Khuri, F.R.; Kang, S. RSK2 signals through stathmin to promote microtubule dynamics and tumor metastasis. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5412–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Noritake, J.; Kaibuchi, K. Regulation of microtubules in cell migration. Trends Cell Biol. 2005, 15, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Muller, G.A. Cell cycle transcription control: DREAM/MuvB and RB-E2F complexes. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 52, 638–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alla, V.; Engelmann, D.; Niemetz, A.; Pahnke, J.; Schmidt, A.; Kunz, M.; Emmrich, S.; Steder, M.; Koczan, D.; Putzer, B.M. E2F1 in melanoma progression and metastasis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollern, D.P.; Honeysett, J.; Cardiff, R.D.; Andrechek, E.R. The E2F transcription factors regulate tumor development and metastasis in a mouse model of metastatic breast cancer. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 34, 3229–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuo, Y.; An, N.; Zhang, M. Feature genes in metastatic breast cancer identified by MetaDE and SVM classifier methods. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBerardinis, R.J. Is cancer a disease of abnormal cellular metabolism? New angles on an old idea. Genet. Med. 2008, 10, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschhaeuser, F.; Sattler, U.G.; Mueller-Klieser, W. Lactate: A metabolic key player in cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6921–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetze, K.; Walenta, S.; Ksiazkiewicz, M.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Mueller-Klieser, W. Lactate enhances motility of tumor cells and inhibits monocyte migration and cytokine release. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, R. Hyaluronidases in cancer biology. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2008, 18, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walenta, S.; Mueller-Klieser, W.F. Lactate: Mirror and motor of tumor malignancy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 14, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fife, C.M.; McCarroll, J.A.; Kavallaris, M. Movers and shakers: Cell cytoskeleton in cancer metastasis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 5507–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Rebowe, R.E.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; DePaolo, J.S.; Guo, J.; Qian, C.; Liu, W. KIF3a promotes proliferation and invasion via Wnt signaling in advanced prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimbo, T.; Kawasaki, Y.; Koyama, R.; Sato, R.; Takada, S.; Haraguchi, K.; Akiyama, T. Identification of a link between the tumour suppressor APC and the kinesin superfamily. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.H.; Nakajima, Y.; Geyer, M.; Wary, K.K.; Ushio-Fukai, M.; Komarova, Y.; Malik, A.B. KIF13B regulates angiogenesis through Golgi to plasma membrane trafficking of VEGFR2. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 4518–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Liao, M.; Liao, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Fan, J.; Liao, W. The role of kinesin KIF18A in the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, J.; Fukushima, S.; Jinnin, M.; Honda, N.; Makino, K.; Sakai, K.; Masuguchi, S.; Inoue, Y.; Ihn, H. Kinesin family member 20A is a novel melanoma-associated antigen. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2012, 92, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangel, D.; Erkan, M.; Buchholz, M.; Gress, T.; Michalski, C.; Raulefs, S.; Friess, H.; Kleeff, J. Kif20a inhibition reduces migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 197, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasnereau, I.; Boissan, M.; Margall-Ducos, G.; Couchy, G.; Wendum, D.; Bourgain-Guglielmetti, F.; Desdouets, C.; Lacombe, M.L.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Sobczak-Thepot, J. KIF20A mRNA and its product MKlp2 are increased during hepatocyte proliferation and hepatocarcinogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.Y.; Chang, F.H.; Tsai, J.H.; Chang, Y. Epstein-Barr virus Rta promotes invasion of bystander tumor cells through paracrine of matrix metalloproteinase 9. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2160–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, K.; Yuwanita, I.; Hollern, D.P.; Andrechek, E.R. Prediction and genetic demonstration of a role for activator E2Fs in Myc-induced tumors. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1924–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Bieda, M.; Jin, V.X.; Rabinovich, A.; Oberley, M.J.; Green, R.; Farnham, P.J. A comprehensive ChIP-chip analysis of E2F1, E2F4, and E2F6 in normal and tumor cells reveals interchangeable roles of E2F family members. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1550–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, Y.-d.; Cho, J.H.; Park, S.; Kang, M.; Park, S.-j.; Choi, D.H.; Jeong, M.; Park, K.C.; Yeom, Y.I.; Lee, D.C. Lactate Activates the E2F Pathway to Promote Cell Motility by Up-Regulating Microtubule Modulating Genes. Cancers 2019, 11, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030274
Jung Y-d, Cho JH, Park S, Kang M, Park S-j, Choi DH, Jeong M, Park KC, Yeom YI, Lee DC. Lactate Activates the E2F Pathway to Promote Cell Motility by Up-Regulating Microtubule Modulating Genes. Cancers. 2019; 11(3):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030274
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Yi-deun, Jung Hee Cho, Seulki Park, Minho Kang, Seung-jin Park, Dong Hee Choi, Moonkyung Jeong, Kyung Chan Park, Young Il Yeom, and Dong Chul Lee. 2019. "Lactate Activates the E2F Pathway to Promote Cell Motility by Up-Regulating Microtubule Modulating Genes" Cancers 11, no. 3: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030274
APA StyleJung, Y.-d., Cho, J. H., Park, S., Kang, M., Park, S.-j., Choi, D. H., Jeong, M., Park, K. C., Yeom, Y. I., & Lee, D. C. (2019). Lactate Activates the E2F Pathway to Promote Cell Motility by Up-Regulating Microtubule Modulating Genes. Cancers, 11(3), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030274



