Enzymatic Characterization of Wild-Type and Mutant Janus Kinase 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
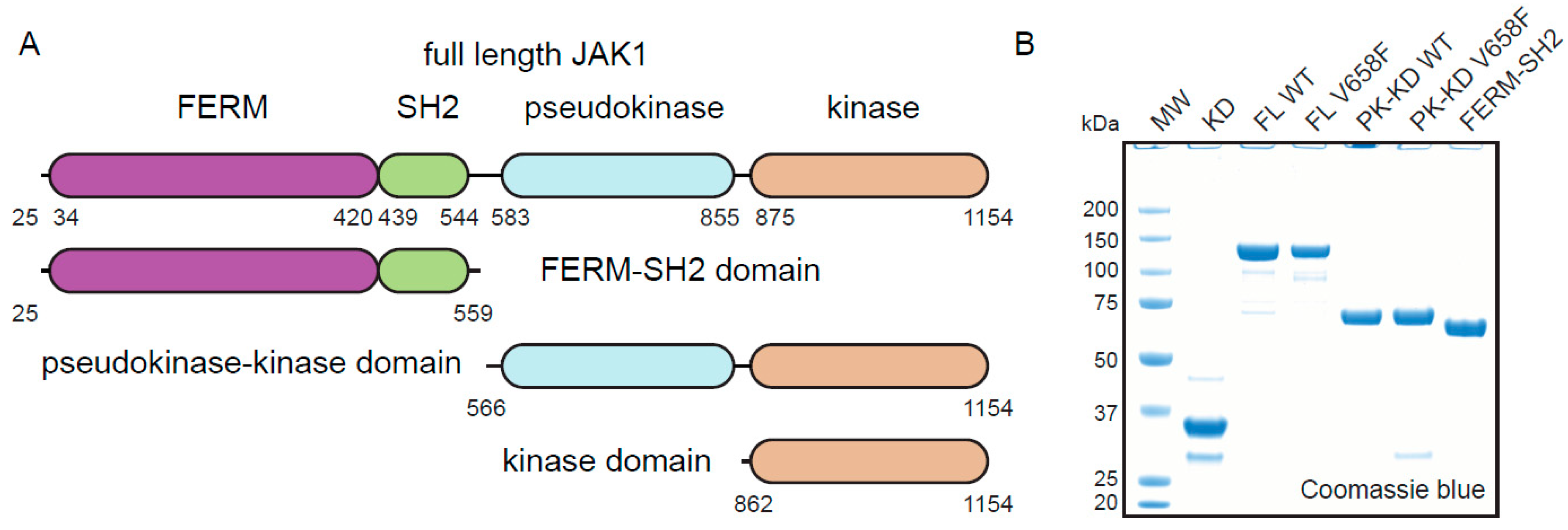
2.1. Expression and Purification of JAK1
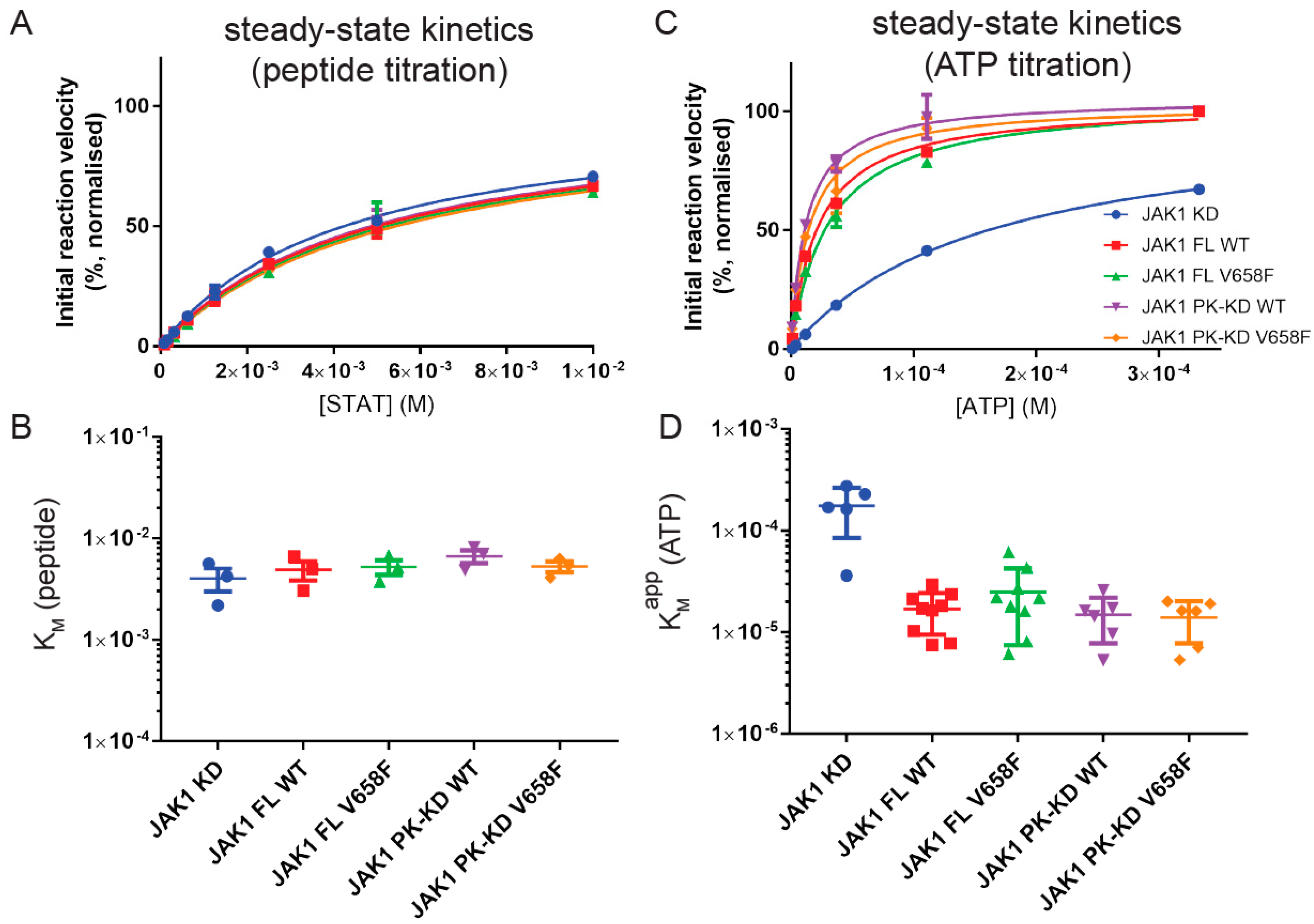
2.2. The Pseudokinase Domain Decreases the Turnover Rate of JAK1
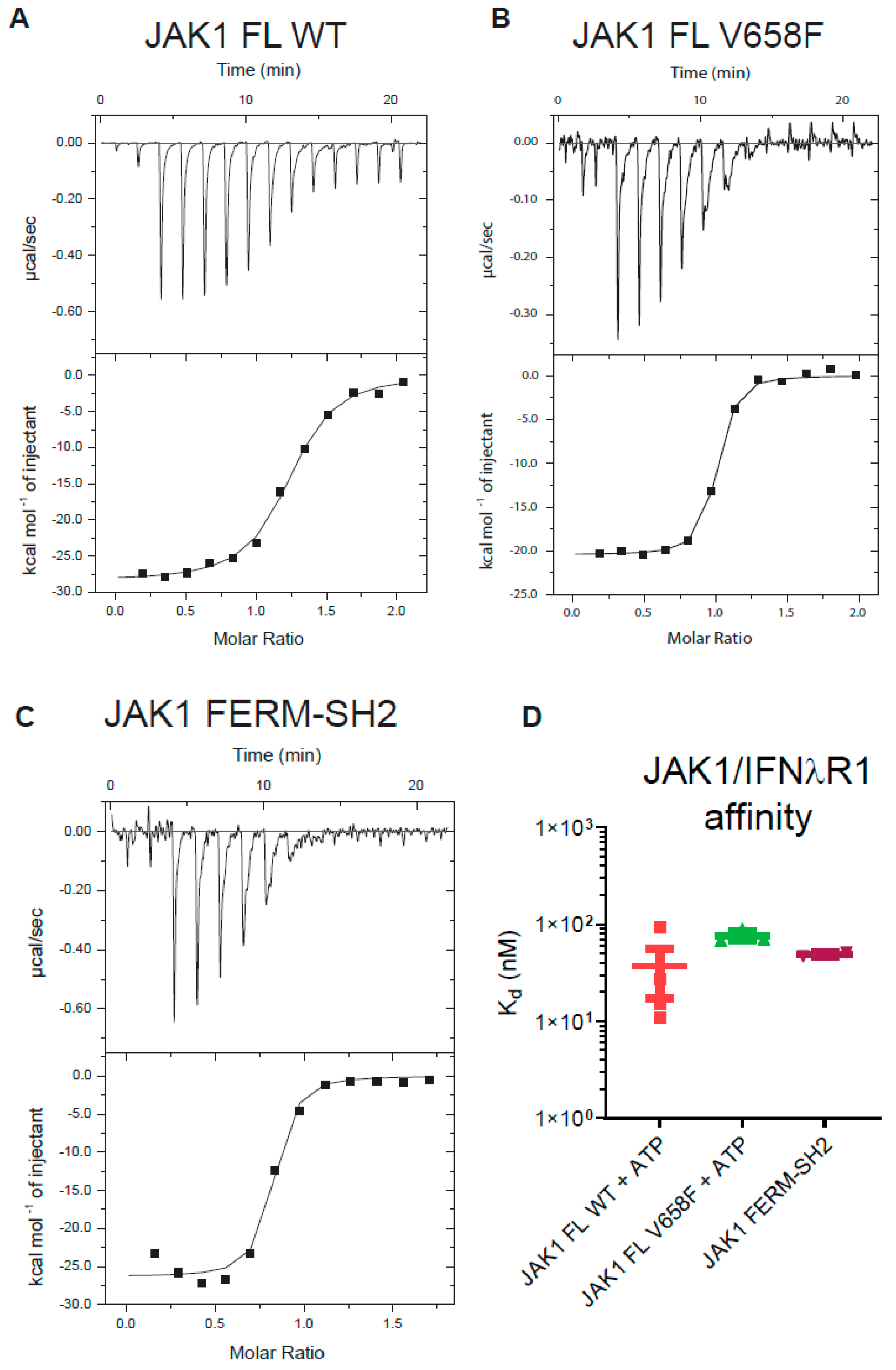
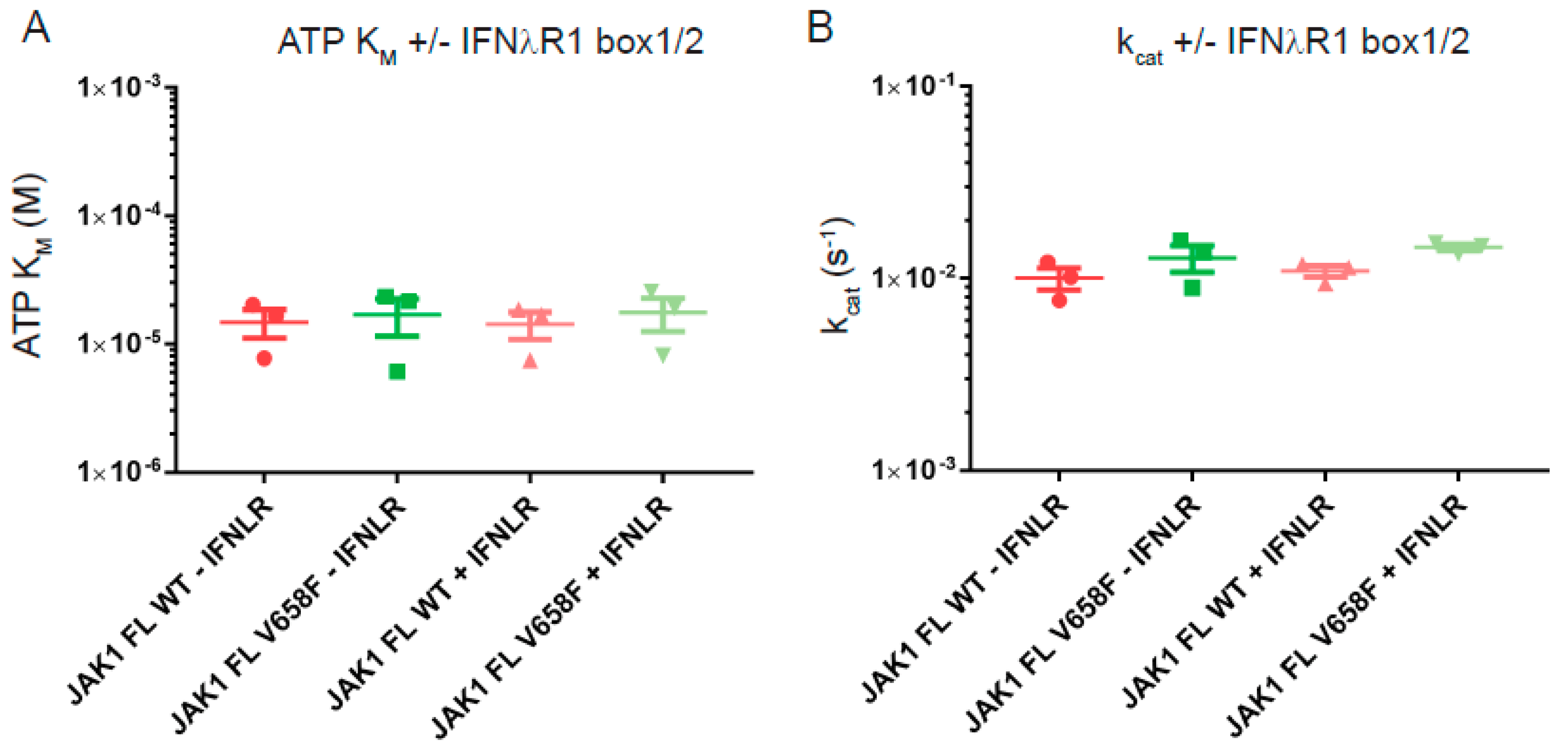
2.3. The V658F Mutation Has No Effect on ATP or Substrate Affinity
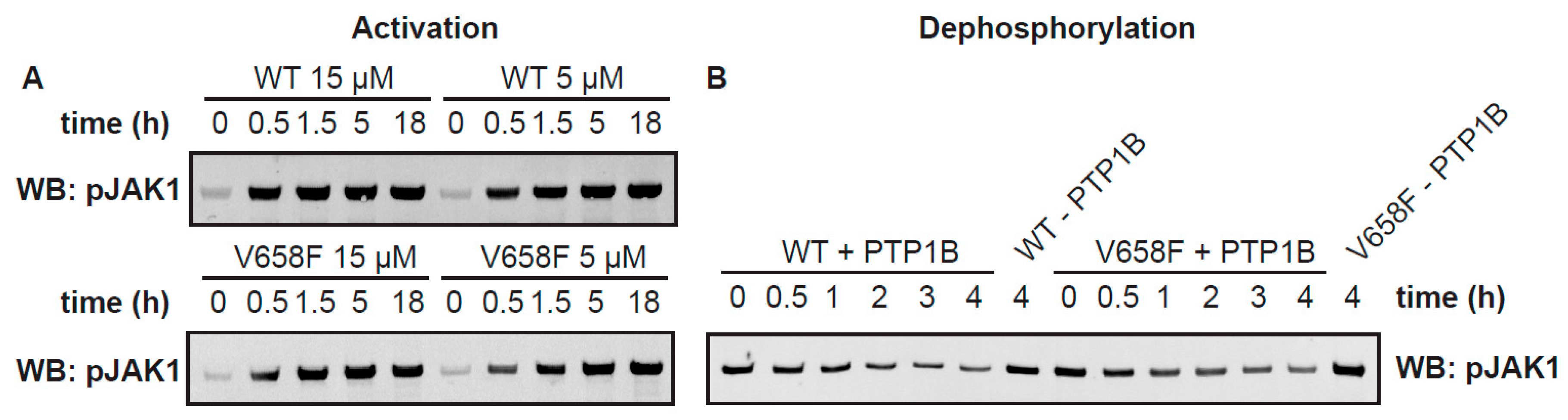
2.4. The V658F Mutation Has No Effect on Autophosphorylation or Dephosphorylation Rates In Vitro
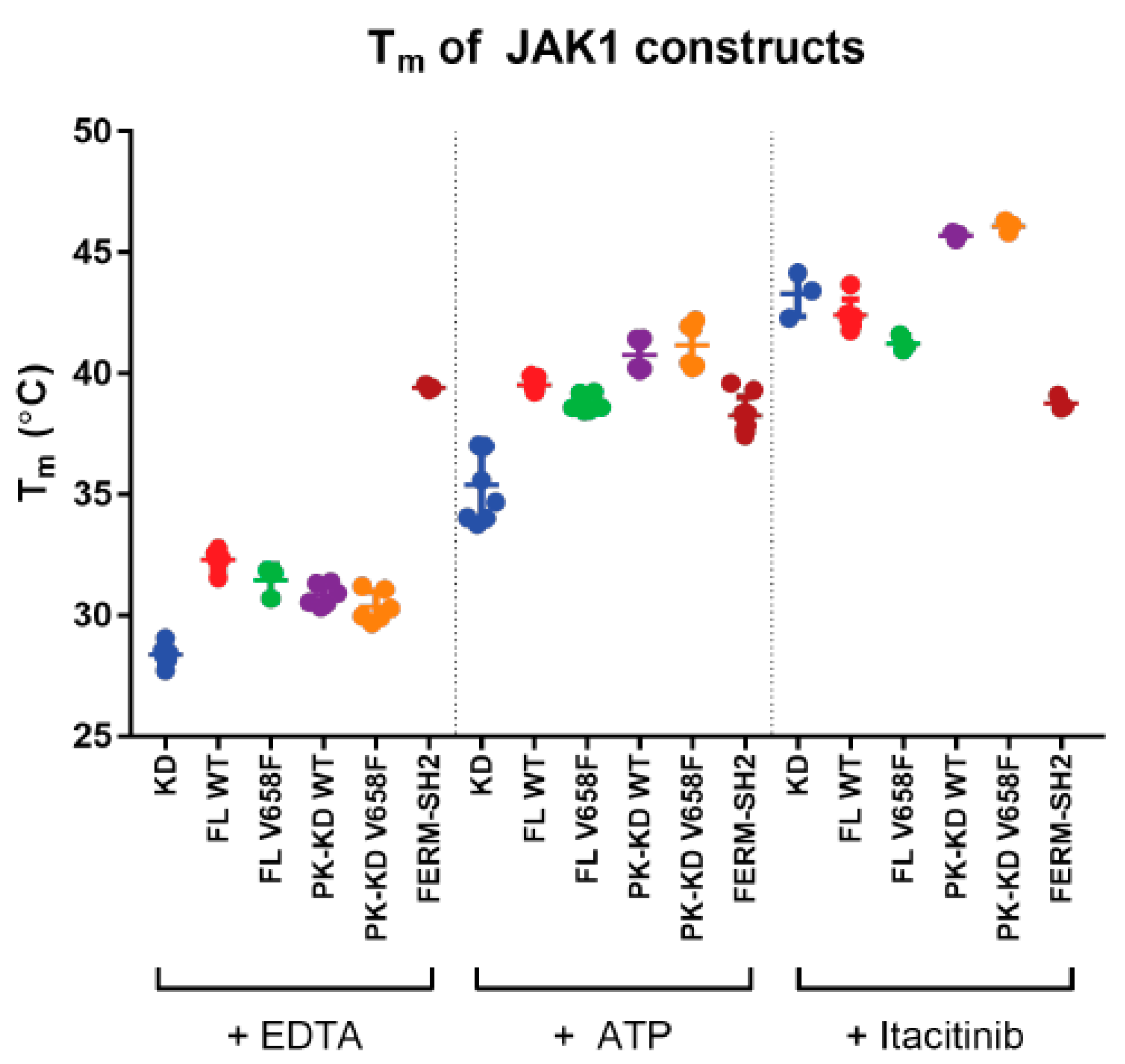
2.5. The V658F Mutation Does Not Affect the Thermal Stability of JAK1
2.6. Cytokine Receptor Box1/Box2 Binding Affinity Is Not Affected by Either the Pseudokinase and Kinase Domains or the V658F Mutation
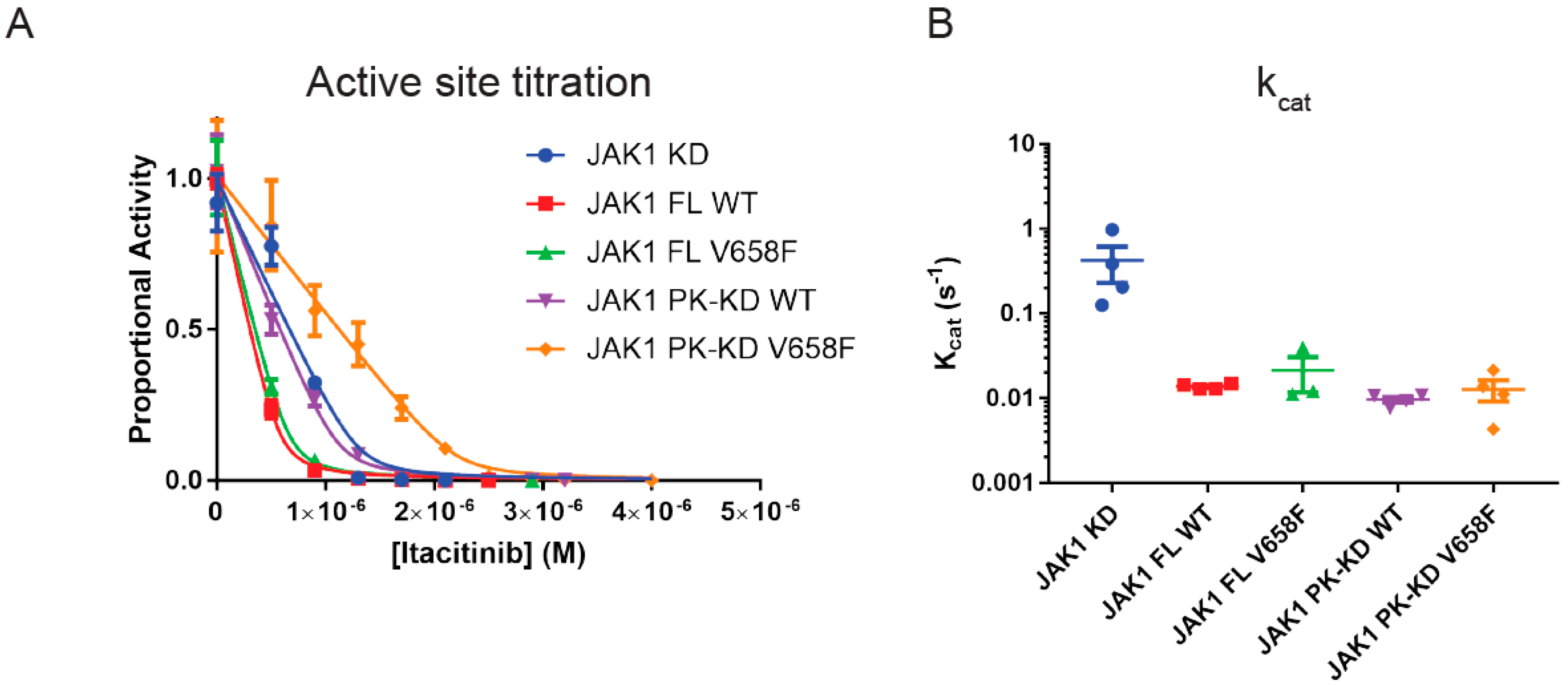
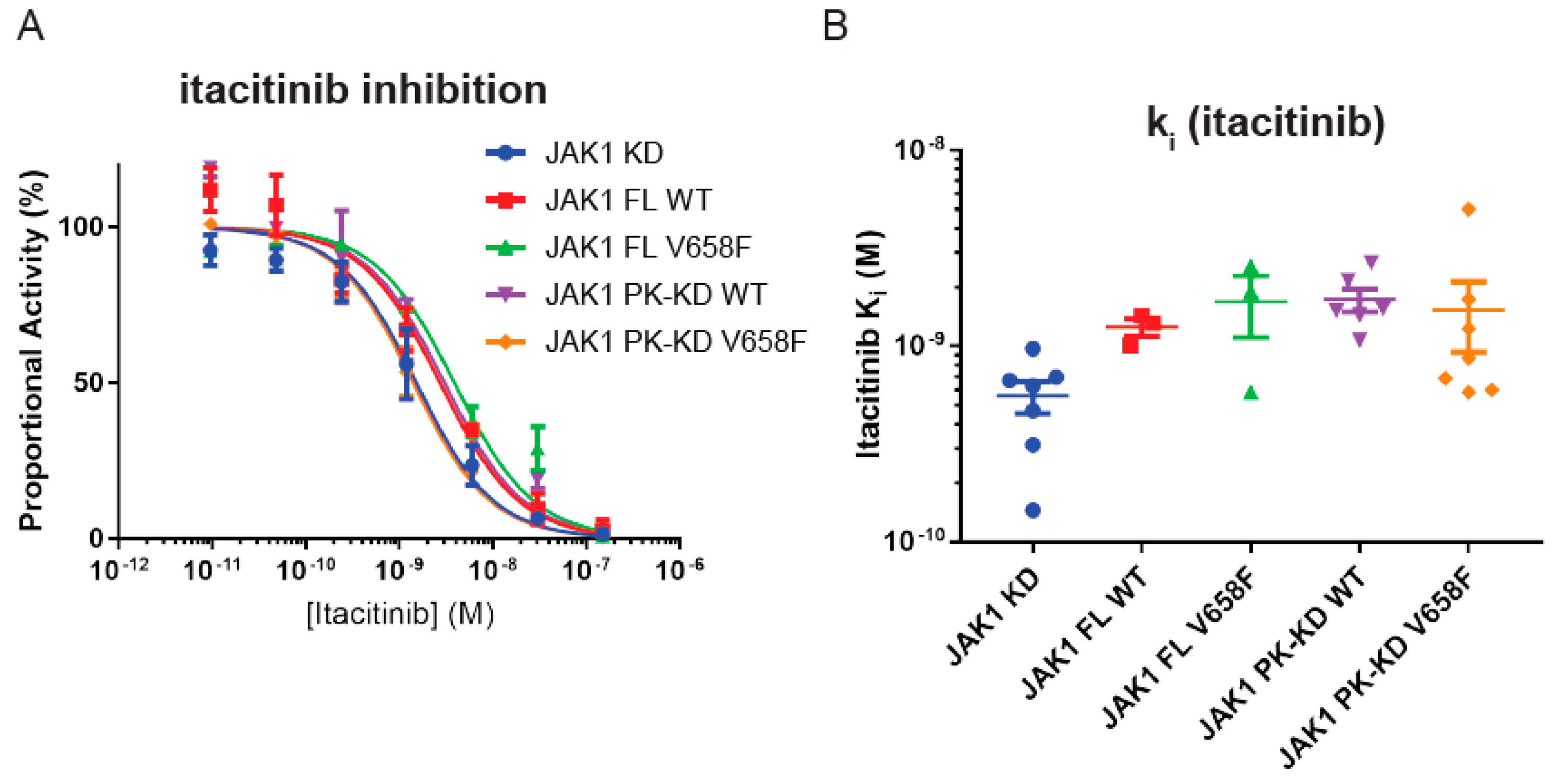
2.7. Wild-Type and Mutant JAK1 Are Equally Susceptible to Itacitinib Inhibition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cloning, Expression, and Purification of JAKs
4.2. Kinase Assay
4.3. Activation Assay
4.4. Deactivation Assay
4.5. Thermal Shift Assay
4.6. Data Fitting
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metcalf, D. The Hemopoietic Colony Stimulating Factors; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; p. 493. [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs, A.; Lindenmann, J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B-Biol. Sci. 1957, 147, 258–267. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Notarangelo, L.D.; Johnston, J.A.; Candotti, F. Advances in the understanding of cytokine signal transduction: The role of Jaks and STATs in immunoregulation and the pathogenesis of immunodeficiency. J. Clin. Immunol. 1997, 17, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marg, A.; Shan, Y.; Meyer, T.; Meissner, T.; Brandenburg, M.; Vinkemeier, U. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling by nucleoporins Nup153 and Nup214 and CRM1-dependent nuclear export control the subcellular distribution of latent Stat1. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 165, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihle, J.N. Janus kinases in cytokine signalling. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1996, 351, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Neubauer, H.; Cumano, A.; Müller, M.; Wu, H.; Huffstadt, U.; Pfeffer, K. Jak2 deficiency defines an essential developmental checkpoint in definitive hematopoiesis. Cell 1998, 93, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parganas, E.; Wang, D.; Stravopodis, D.; Topham, D.J.; Marine, J.C.; Teglund, S.; Vanin, E.F.; Bodner, S.; Colamonici, O.R.; Van Deursen, J.M.; et al. Jak2 is essential for signaling through a variety of cytokine receptors. Cell 1998, 93, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodig, S.J.; Meraz, M.A.; White, J.M.; Lampe, P.A.; Riley, J.K.; Arthur, C.D.; King, K.L.; Sheehan, K.C.; Yin, L.; Pennica, D.; et al. Disruption of the Jak1 gene demonstrates obligatory and nonredundant roles of the Jaks in cytokine-induced biologic responses. Cell 1998, 93, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Saijo, K.; Takahashi, T.; Osawa, M.; Areas, H.; Hirayama, N.; Miyake, K.; Nakauchi, H.; Shirasawa, T.; Saito, T. Developmental defects of lymphoid cells in Jak3 kinase-deficient mice. Immunity 1995, 3, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomis, D.C.; Gurniak, C.B.; Tivol, E.; Sharpe, A.H.; Berg, L.J. Defects in B lymphocyte maturation and T lymphocyte activation in mice lacking Jak3. Science 1995, 270, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaghiosoff, M.; Neubauer, H.; Lassnig, C.; Kovarik, P.; Schindler, H.; Pircher, H.; McCoy, B.; Bogdan, C.; Decker, T.; Brem, G.; et al. Partial impairment of cytokine responses in Tyk2-deficient mice. Immunity 2000, 13, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallweber, H.J.; Tam, C.; Franke, Y.; Starovasnik, M.A.; Lupardus, P.J. Structural basis of recognition of interferon-alpha receptor by tyrosine kinase 2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Narazaki, M.; Hibi, M.; Yawata, H.; Yasukawa, K.; Hamaguchi, M.; Taga, T.; Kishimoto, T. Critical cytoplasmic region of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130 is conserved in the cytokine receptor family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 11349–11353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, E.A.; Aguet, M.; Schreiber, R.D. The IFN gamma receptor: A paradigm for cytokine receptor signaling. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 563–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauber, D.J.; Debler, E.W.; Horton, P.A.; Smith, K.A.; Wilson, I.A. Crystal structure of the IL-2 signaling complex: Paradigm for a heterotrimeric cytokine receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2788–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, S.N.; Huang, L.J.S.; Nam, H.S.; Lodish, H.F. The erythropoietin receptor cytosolic juxtamembrane domain contains an essential, precisely oriented, hydrophobic motif. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharinen, P.; Takaluoma, K.; Silvennoinen, O. Regulation of the Jak2 tyrosine kinase by its pseudokinase domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 3387–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, E.J.; Scott, L.M.; Campbell, P.J.; East, C.; Fourouclas, N.; Swanton, S.; Vassiliou, G.S.; Bench, A.J.; Boyd, E.M.; Curtin, N. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet 2005, 365, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.; Ugo, V.; Le Couédic, J.P.; Staerk, J.; Delhommeau, F.; Lacout, C.; Garçon, L.; Raslova, H.; Berger, R.; Bennaceur-Griscelli, A. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature 2005, 434, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralovics, R.; Passamonti, F.; Buser, A.S.; Teo, S.S.; Tiedt, R.; Passweg, J.R.; Tichelli, A.; Cazzola, M.; Skoda, R.C. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.L.; Wadleigh, M.; Cools, J.; Ebert, B.L.; Wernig, G.; Huntly, B.J.; Boggon, T.J.; Wlodarska, I.; Clark, J.J.; Moore, S. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Aviles, L.; Besses, C.; Álvarez-Larrán, A.; Cervantes, F.; Hernández-Boluda, J.C.; Bellosillo, B. JAK2 exon 12 mutations in polycythemia vera or idiopathic erythrocytosis. Haematologica 2007, 92, 1717–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, L.M.; Beer, P.A.; Bench, A.J.; Erber, W.N.; Green, A.R. Prevalance of JAK2 V617F and exon 12 mutations in polycythaemia vera. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 139, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercovich, D.; Ganmore, I.; Scott, L.M.; Wainreb, G.; Birger, Y.; Elimelech, A.; Shochat, C.; Cazzaniga, G.; Biondi, A.; Basso, G. Mutations of JAK2 in acute lymphoblastic leukaemias associated with Down’s syndrome. Lancet 2008, 372, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, L.; Castro, D.G.; Yeung, J.; Procter, J.; Horsley, S.W.; Eguchi-Ishimae, M.; Bateman, C.M.; Anderson, K.; Chaplin, T.; Young, B.D.; et al. Specific JAK2 mutation (JAK2R683) and multiple gene deletions in Down syndrome acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2009, 113, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Zhang, J.; Harvey, R.C.; Collins-Underwood, J.R.; Schulman, B.A.; Phillips, L.A.; Tasian, S.K.; Loh, M.L.; Su, X.; Liu, W.; et al. JAK mutations in high-risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9414–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Huang, L.J.S.; Lodish, H.F. Dimerization by a cytokine receptor is necessary for constitutive activation of JAK2V617F. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 5258–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Levine, R.; Tong, W.; Wernig, G.; Pikman, Y.; Zarnegar, S.; Gilliland, D.G.; Lodish, H. Expression of a homodimeric type I cytokine receptor is required for JAK2V617F-mediated transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18962–18967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flex, E.; Petrangeli, V.; Stella, L.; Chiaretti, S.; Hornakova, T.; Knoops, L.; Ariola, C.; Fodale, V.; Clappier, E.; Paoloni, F.; et al. Somatically acquired JAK1 mutations in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, S.N.; Girardot, M.; Pecquet, C. Mining for JAK-STAT mutations in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerk, J.; Kallin, A.; Demoulin, J.B.; Vainchenker, W.; Constantinescu, S.N. JAK1 and Tyk2 activation by the homologous polycythemia vera JAK2 V617F mutation: Cross-talk with IGF1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 41893–41899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucet, I.S.; Fantino, E.; Styles, M.; Bamert, R.; Patel, O.; Broughton, S.E.; Walter, M.; Burns, C.J.; Treutlein, H.; Wilks, A.F.; et al. The structural basis of Janus kinase 2 inhibition by a potent and specific pan-Janus kinase inhibitor. Blood 2006, 107, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandaranayake, R.M.; Ungureanu, D.; Shan, Y.; Shaw, D.E.; Silvennoinen, O.; Hubbard, S.R. Crystal structures of the JAK2 pseudokinase domain and the pathogenic mutant V617F. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, J.F. Kinetics of the reversible inhibition of enzyme-catalysed reactions by tight-binding inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Enzymol. 1969, 185, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvorogov, D.; Thomas, D.; Liau, N.P.; Dottore, M.; Barry, E.F.; Lathi, M.; Kan, W.L.; Hercus, T.R.; Stomski, F.; Hughes, T.P.; et al. Accumulation of JAK activation loop phosphorylation is linked to type I JAK inhibitor withdrawal syndrome in myelofibrosis. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, T.J.; Forero-Torres, A.; Sher, T.; Diefenbach, C.S.; Johnston, P.; Talpaz, M.; Pulini, J.; Zhou, L.; Scherle, P.; Chen, X.; et al. Phase 1 study of the PI3Kdelta inhibitor INCB040093 ± JAK1 inhibitor itacitinib in relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupardus, P.J.; Ultsch, M.; Wallweber, H.; Kohli, P.B.; Johnson, A.R.; Eigenbrot, C. Structure of the pseudokinase-kinase domains from protein kinase TYK2 reveals a mechanism for Janus kinase (JAK) autoinhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8025–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharinen, P.; Silvennoinen, O. The pseudokinase domain is required for suppression of basal activity of Jak2 and Jak3 tyrosine kinases and for cytokine-inducible activation of signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 47954–47963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andraos, R.; Qian, Z.; Bonenfant, D.; Rubert, J.; Vangrevelinghe, E.; Scheufler, C.; Marque, F.; Régnier, C.H.; De Pover, A.; Ryckelynck, H.; et al. Modulation of activation-loop phosphorylation by JAK inhibitors is binding mode dependent. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucet, I.S.; Murphy, J.M. Characterization of Ligand Binding to Pseudokinases Using a Thermal Shift Assay. In Kinase Signaling Networks; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1636, pp. 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrao, R.; Wallweber, H.J.; Ho, H.; Tam, C.; Franke, Y.; Quinn, J.; Lupardus, P.J. The Structural Basis for Class. II Cytokine Receptor Recognition by JAK1. Structure 2016, 24, 897–905. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.A. Kinetic and catalytic mechanisms of protein kinases. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2271–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClendon, C.L.; Kornev, A.P.; Gilson, M.K.; Taylor, S.S. Dynamic architecture of a protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4623–E4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrao, R.D.; Wallweber, H.J.; Lupardus, P.J. Receptor-mediated dimerization of JAK2 FERM domains is required for JAK2 activation. Elife 2018, 7, e38089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernig, G.; Gonneville, J.R.; Crowley, B.J.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Reddy, M.M.; Hudon, H.E.; Walz, C.; Reiter, A.; Podar, K.; Royer, Y.; et al. The Jak2V617F oncogene associated with myeloproliferative diseases requires a functional FERM domain for transformation and for expression of the Myc and Pim proto-oncogenes. Blood 2008, 111, 3751–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorantla, S.P.; Dechow, T.N.; Grundler, R.; Illert, A.L.; zum Büschenfelde, C.M.; Kremer, M.; Peschel, C.; Duyster, J. Oncogenic JAK2V617F requires an intact SH2-like domain for constitutive activation and induction of a myeloproliferative disease in mice. Blood 2010, 116, 4600–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Narazaki, M.; Taga, T. Leptin receptor (OB-R) oligomerizes with itself but not with its closely related cytokine signal transducer gp130. FEBS Lett. 1997, 403, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.J.; Dai, W.; O’Mara, M.L.; Abankwa, D.; Chhabra, Y.; Pelekanos, R.A.; Gardon, O.; Tunny, K.A.; Blucher, K.M.; Morton, C.J.; et al. Mechanism of activation of protein kinase JAK2 by the growth hormone receptor. Science 2014, 344, 1249783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainchenker, W.; Leroy, E.; Gilles, L.; Marty, C.; Plo, I.; Constantinescu, S.N. JAK inhibitors for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms and other disorders. F1000Research 2018, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liau, N.P.D.; Laktyushin, A.; Morris, R.; Sandow, J.J.; Nicola, N.A.; Kershaw, N.J.; Babon, J.J. Enzymatic Characterization of Wild-Type and Mutant Janus Kinase 1. Cancers 2019, 11, 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111701
Liau NPD, Laktyushin A, Morris R, Sandow JJ, Nicola NA, Kershaw NJ, Babon JJ. Enzymatic Characterization of Wild-Type and Mutant Janus Kinase 1. Cancers. 2019; 11(11):1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111701
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiau, Nicholas P. D., Artem Laktyushin, Rhiannon Morris, Jarrod J. Sandow, Nicos A. Nicola, Nadia J. Kershaw, and Jeffrey J. Babon. 2019. "Enzymatic Characterization of Wild-Type and Mutant Janus Kinase 1" Cancers 11, no. 11: 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111701
APA StyleLiau, N. P. D., Laktyushin, A., Morris, R., Sandow, J. J., Nicola, N. A., Kershaw, N. J., & Babon, J. J. (2019). Enzymatic Characterization of Wild-Type and Mutant Janus Kinase 1. Cancers, 11(11), 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111701




