Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer Pathology Image Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Current Challenges and Opportunities in Lung Cancer Pathology Image Analysis
2.1. Diagnosis: Tumor Detection and Classification
2.2. Tumor Microenvironment (TME) Characterization Based on Substructure Segmentation
2.3. Prognosis and Precision Medicine
2.4. Association and Integration with Patient Genomic and Genetic Profiles
3. Advantages of Deep Learning Methods
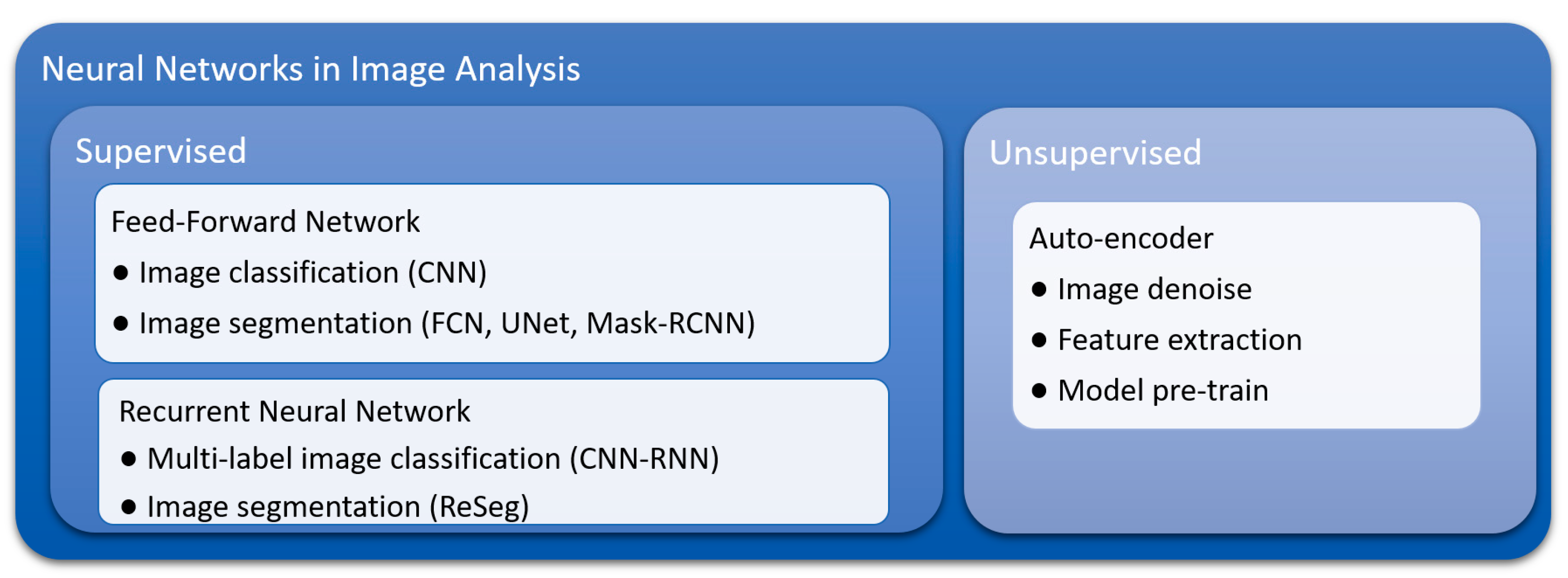
3.1. Inherent Characteristics and Advantages of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
3.2. Flexibility of Training and Model Construction Strategies of Deep Learning Methods
3.3. Suitability for Transfer Learning
4. Applications of Deep Learning in Lung Cancer Pathology Image Analysis
4.1. Lung Cancer Diagnosis
4.2. Lung Cancer Microenvironment Analysis
4.3. Lung Cancer Prognosis
5. Future Directions
5.1. Comprehensive Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis through Multi-Task Learning
5.2. Interpreting Deep Learning Models and Mining Knowledge from Trained Neural Networks
5.3. Integrating Knowledge Accumulated from Clinical and Biological Studies into Deep Learning Methods
5.4. Utilization and Integrating Multiple Methods of Medical Imaging
6. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dela Cruz, C.S.; Tanoue, L.T.; Matthay, R.A. Lung cancer: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2011, 32, 605–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, P.M.; Wu, C.C.; Carter, B.W.; Munden, R.F. The epidemiology of lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Bent, M.J. Interobserver variation of the histopathological diagnosis in clinical trials on glioma: A clinician’s perspective. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, L.A.; Kong, J.; Gutman, D.A.; Dunn, W.D.; Nalisnik, M.; Brat, D.J. Novel genotype-phenotype associations in human cancers enabled by advanced molecular platforms and computational analysis of whole slide images. Lab. Investig. A J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2015, 95, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alturkistani, H.A.; Tashkandi, F.M.; Mohammedsaleh, Z.M. Histological Stains: A Literature Review and Case Study. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2015, 8, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara-Lazaro, A.R.; Thamboo, T.P.; Teh, M.; Tan, P.H. Digital pathology: Exploring its applications in diagnostic surgical pathology practice. Pathology 2010, 42, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.D.; Dunstan, R.W. Whole-Slide Imaging and Automated Image Analysis: Considerations and Opportunities in the Practice of Pathology. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.H.; Sangoi, A.R.; Leung, S.; Marinelli, R.J.; Nielsen, T.O.; van de Vijver, M.J.; West, R.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Koller, D. Systematic analysis of breast cancer morphology uncovers stromal features associated with survival. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 108ra113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Failmezger, H.; Rueda, O.M.; Ali, H.R.; Graf, S.; Chin, S.F.; Schwarz, R.F.; Curtis, C.; Dunning, M.J.; Bardwell, H.; et al. Quantitative image analysis of cellular heterogeneity in breast tumors complements genomic profiling. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 157ra143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.J.; Hanby, A.; Millican-Slater, R.; Nijhawan, A.; Verghese, E.; Treanor, D. Digital pathology for the primary diagnosis of breast histopathological specimens: An innovative validation and concordance study on digital pathology validation and training. Histopathology 2018, 72, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, T.W.; Slaw, R.J.; McKenney, J.K.; Patil, D.T. Validation of whole slide imaging for frozen section diagnosis in surgical pathology. J. Pathol. Inform. 2015, 6, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snead, D.R.; Tsang, Y.W.; Meskiri, A.; Kimani, P.K.; Crossman, R.; Rajpoot, N.M.; Blessing, E.; Chen, K.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Matthews, P.; et al. Validation of digital pathology imaging for primary histopathological diagnosis. Histopathology 2016, 68, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, T.P.; Dilorio, R.; Havrilla, L.; O’Neill, D.G. Validation of a whole slide imaging system for primary diagnosis in surgical pathology: A community hospital experience. J. Pathol. Inform. 2014, 5, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordi, J.; Castillo, P.; Saco, A.; Del Pino, M.; Ordi, O.; Rodriguez-Carunchio, L.; Ramirez, J. Validation of whole slide imaging in the primary diagnosis of gynaecological pathology in a University Hospital. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 68, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Mukherjee, D.P. Mitosis Detection for Invasive Breast Cancer Grading in Histopathological Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. A Publ. IEEE Signal. Process. Soc. 2015, 24, 4041–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.; Hussain, M.; Aksam Iftikhar, M.; Jalil, A. Novel structural descriptors for automated colon cancer detection and grading. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2015, 121, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Sarkar, A.; Jain, A.K. Prostate cancer grading: Use of graph cut and spatial arrangement of nuclei. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 33, 2254–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliszewski, P.; Wagenlehner, F.; Gattenlohner, S.; Weidner, W. Fractal geometry in the objective grading of prostate carcinoma. Der Urol. Ausg. A 2014, 53, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atupelage, C.; Nagahashi, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Abe, T.; Hashiguchi, A.; Sakamoto, M. Computational grading of hepatocellular carcinoma using multifractal feature description. Comput. Med Imaging Graph. 2013, 37, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zang, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Liang, F.; Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Wistuba, I.I.; Gazdar, A.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, G. Comprehensive Computational Pathological Image Analysis Predicts Lung Cancer Prognosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.H.; Zhang, C.; Berry, G.J.; Altman, R.B.; Re, C.; Rubin, D.L.; Snyder, M. Predicting non-small cell lung cancer prognosis by fully automated microscopic pathology image features. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, e12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V.; et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, S.H.; Park, H.; Lee, G.; Lee, H.Y.; Sohn, I.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, K.S. Imaging phenotyping using radiomics to predict micropapillary pattern within lung adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Noguchi, M.; Nicholson, A.G.; Geisinger, K.R.; Yatabe, Y.; Beer, D.G.; Powell, C.A.; Riely, G.J.; Van Schil, P.E.; et al. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 244–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Lu, C.; Guo, J.; Chen, L.; Chu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Ge, D. Prognostic significance of the IASLC/ATS/ERS classification in Chinese patients-A single institution retrospective study of 292 lung adenocarcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, J.J.; Yeh, Y.C.; Jeng, W.J.; Wu, K.J.; Huang, B.S.; Wu, Y.C.; Chou, T.Y.; Hsu, W.H. Predictive value of the international association for the study of lung cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society classification of lung adenocarcinoma in tumor recurrence and patient survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, M.S.; Marguet, S.; Le Teuff, G.; Lantuejoul, S.; Shepherd, F.A.; Seymour, L.; Kratzke, R.; Graziano, S.L.; Popper, H.H.; Rosell, R.; et al. Subtype Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma Predicts Benefit From Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients Undergoing Complete Resection. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3439–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, Y.; Yano, T.; Asoh, H.; Yokoyama, H.; Yoshino, I.; Katsuda, Y. Prognostic factors obtained by a pathologic examination in completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer: An analysis in each pathologic stage. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1995, 110, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadota, K.; Nitadori, J.; Sima, C.S.; Ujiie, H.; Rizk, N.P.; Jones, D.R.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Travis, W.D. Tumor Spread through Air Spaces is an Important Pattern of Invasion and Impacts the Frequency and Location of Recurrences after Limited Resection for Small Stage I Lung Adenocarcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac, L.R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooden, M.J.; de Bock, G.H.; Leffers, N.; Daemen, T.; Nijman, H.W. The prognostic influence of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Silverman, J.F.; Santucci, T.S.; Macherey, R.S.; dAmato, T.A.; Tung, M.Y.; Weyant, R.J.; Landreneau, R.J. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in stage I non-small cell lung cancer correlates with neoangiogenesis and a poor prognosis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2001, 8, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremnes, R.M.; Donnem, T.; Al-Saad, S.; Al-Shibli, K.; Andersen, S.; Sirera, R.; Camps, C.; Marinez, I.; Busund, L.T. The role of tumor stroma in cancer progression and prognosis: Emphasis on carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, T.; Aokage, K.; Sugano, M.; Miyoshi, T.; Kojima, M.; Fujii, S.; Kuwata, T.; Ochiai, A.; Suzuki, K.; Tsuboi, M.; et al. The ratio of cancer cells to stroma within the invasive area is a histologic prognostic parameter of lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2018, 118, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltz, J.; Gupta, R.; Hou, L.; Kurc, T.; Singh, P.; Nguyen, V.; Samaras, D.; Shroyer, K.R.; Zhao, T.H.; Batiste, R.; et al. Spatial Organization and Molecular Correlation of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Using Deep Learning on Pathology Images. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 181–193.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.N.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Schreiber, R.D. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science 2015, 348, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ninomiya, H.; Hiramatsu, M.; Inamuraa, K.; Nomura, K.; Okui, M.; Miyoshi, T.; Okumura, S.; Satoh, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Nishio, M.; et al. Correlation between morphology and EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinomas Significance of the micropapillary pattern and the hobnail cell type. Lung Cancer 2009, 63, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, I.Y.S.; Chung, L.P.; Suen, W.S.; Wang, E.; Wong, M.C.M.; Ho, K.K.; Lam, W.K.; Chiu, S.W.; Girard, L.; Minna, J.D.; et al. Distinct epidermal growth factor receptor and KRAS mutation patterns in non-small cell lung cancer patients with different tobacco exposure and clinicopathologic features. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detecting Cancer Metastases on Gigapixel Pathology Images. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.02442 (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Deep Learning for Identifying Metastatic Breast Cancer. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.05718 (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Tabibu, S.; Vinod, P.K.; Jawahar, C.V. Pan-Renal Cell Carcinoma classification and survival prediction from histopathology images using deep learning. Sci. Rep. UK 2019, 9, e10509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvaniti, E.; Fricker, K.S.; Moret, M.; Rupp, N.; Hermanns, T.; Fankhauser, C.; Wey, N.; Wild, P.J.; Ruschoff, J.H.; Claassen, M. Automated Gleason grading of prostate cancer tissue microarrays via deep learning. Sci Rep. UK 2018, 8, e12054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmsbee, J.; Liu, X.L.; Brandwein-Weber, M.; Doyle, S. Active Deep Learning: Improved Training Efficiency of Convolutional Neural Networks for Tissue Classification in Oral Cavity Cancer. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 770–773. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.D.; Yang, D.H.; Rang, R.C.; Zhan, X.W.; Xiao, G.H. Pathology Image Analysis Using Segmentation Deep Learning Algorithms. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 1686–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shelhamer, E.; Long, J.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.M.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. IEEE Int. Conf. Comp. Vis. 2017, 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Mao, J.H.; Huang, Z.H.; Huang, C.; Xu, W. CNN-RNN: A Unified Framework for Multi-label Image Classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visin, F.; Romero, A.; Cho, K.; Matteucci, M.; Ciccone, M.; Kastner, K.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. ReSeg: A Recurrent Neural Network-based Model for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Xing, F.Y.; Kong, X.F.; Xie, Y.P.; Zhang, S.T.; Yang, L. Robust Cell Detection and Segmentation in Histopathological Images Using Sparse Reconstruction and Stacked Denoising Autoencoders. Adv. Comput Vis. Patt 2017, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Mo, X.; Wang, X.; Parwani, A.; Feng, Q.; Huang, K. Identification of topological features in renal tumor microenvironment associated with patient survival. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Ker, J.W.; Chen, Y.C. High-Performance SIFT Hardware Accelerator for Real-Time Image Feature Extraction. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Vid. Technol. 2012, 22, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessauer, M.P.; Hitchens, J.; Dua, S. GPU-enabled High Performance Feature Modeling for ATR Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2010 National Aerospace & Electronics Conference, Fairborn, OH, USA, 14–16 July 2010; pp. 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.L.; Chen, S.C.; Zhang, D.Q. Fast and robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithms incorporating local information for image segmentation. Pattern Recogn. 2007, 40, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsubaie, N.; Trahearn, N.; Raza, S.E.A.; Snead, D.; Rajpoot, N.M. Stain Deconvolution Using Statistical Analysis of Multi-Resolution Stain Colour Representation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556 (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Pham, B.; Gaonkar, B.; Whitehead, W.; Moran, S.; Dai, Q.; Macyszyn, L.; Edgerton, V.R. Cell Counting and Segmentation of Immunohistochemical Images in the Spinal Cord: Comparing Deep Learning and Traditional Approaches. Conf Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2018, 2018, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobadersany, P.; Yousefi, S.; Amgad, M.; Gutman, D.A.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Vega, J.E.V.; Brat, D.J.; Cooper, L.A.D. Predicting cancer outcomes from histology and genomics using convolutional networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2970–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundermeyer, M.; Schluter, R.; Ney, H. LSTM Neural Networks for Language Modeling. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association 2012 (Interspeech 2012), Portland, OR, USA, 9–13 September 2012; Volume 1–3, pp. 194–197. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Xie, Y.P.; Xing, F.Y.; McGough, M.; Yang, L. MDNet: A Semantically and Visually Interpretable Medical Image Diagnosis Network. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2017), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3549–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q.A. A Survey on Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Ma, S.; Minna, J.; Xie, Y. Adaptive prediction model in prospective molecular signature-based clinical studies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, K.; Czerwinska, P.; Wiznerowicz, M. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp. Oncol. (Pozn.) 2015, 19, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.C.; Roth, H.R.; Gao, M.C.; Lu, L.; Xu, Z.Y.; Nogues, I.; Yao, J.H.; Mollura, D.; Summers, R.M. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Computer-Aided Detection: CNN Architectures, Dataset Characteristics and Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.D.; Chen, A.; Yang, L.; Cai, L.; Xie, Y.; Fujimoto, J.; Gazdar, A.; Xiao, G.H. Comprehensive analysis of lung cancer pathology images to discover tumor shape and boundary features that predict survival outcome. Sci Rep. UK 2018, 8, e10393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Lung Carcinoma Using Deep Learning-a Pilot Study. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.05471 (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Pan-Cancer Classifications of Tumor Histological Images Using Deep Learning. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/715656v1.abstract (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Yu, K.-H.; Wang, F.; Berry, G.J.; Re, C.; Altman, R.B.; Snyder, M.; Kohane, I.S.J.b. Classifying Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology Types and Transcriptomic Subtypes using Convolutional Neural Networks. bioRxiv 2019. bioRxiv:530360. [Google Scholar]
- Šarić, M.; Russo, M.; Stella, M.; Sikora, M. CNN-based Method for Lung Cancer Detection in Whole Slide Histopathology Images. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech), Split, Croatia, 18–21 June 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Coudray, N.; Ocampo, P.S.; Sakellaropoulos, T.; Narula, N.; Snuderl, M.; Fenyo, D.; Moreira, A.L.; Razavian, N.; Tsirigos, A. Classification and mutation prediction from non-small cell lung cancer histopathology images using deep learning. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.W.; Tafe, L.J.; Linnik, Y.A.; Vaickus, L.J.; Tomita, N.; Hassanpour, S. Pathologist-level classification of histologic patterns on resected lung adenocarcinoma slides with deep neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, e3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, L.; Osinski, B.L.; Ho, I.Y.; Tan, T.L.; Willis, C.; Weiss, H.; Beaubier, N.; Mahon, B.M.; Taxter, T.J.; Yip, S.S.F. Multi-Field-of-View Deep Learning Model Predicts Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Status from Whole-Slide Hematoxylin and Eosin Images. J. Pathol. Inf. 2019, 10, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilaloglu, S.; Wu, J.; Fierro, E.; Sanchez, R.D.; Ocampo, P.S.; Razavian, N.; Coudray, N.; Tsirigos, A. Efficient pan-cancer whole-slide image classification and outlier detection using convolutional neural networks. bioRxiv 2019. bioRxiv:633123. [Google Scholar]
- Gertych, A.; Swiderska-Chadaj, Z.; Ma, Z.X.; Ing, N.; Markiewicz, T.; Cierniak, S.; Salemi, H.; Guzman, S.; Walts, A.E.; Knudsen, B.S. Convolutional neural networks can accurately distinguish four histologic growth patterns of lung adenocarcinoma in digital slides. Sci Rep. UK 2019, 9, e1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Yang, L.; Yi, F.; Luo, X.; Yang, Y.; Gazdar, A.; Fujimoto, J.; Wistuba, I.I.; Yao, B. ConvPath: A Software Tool for Lung Adenocarcinoma Digital Pathological Image Analysis Aided by Convolutional Neural Network. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.10240. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, F.L.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.D.; Guo, L.; Huang, C.L.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, G.H. Microvessel prediction in H&E Stained Pathology Images using fully convolutional neural networks. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Computational Staining of Pathology Images to Study Tumor Microenvironment in Lung Cancer. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3391381 (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Abousamra, S.; Hou, L.; Gupta, R.; Chen, C.; Samaras, D.; Kurc, T.; Batiste, R.; Zhao, T.; Kenneth, S.; Saltz, J. Learning from Thresholds: Fully Automated Classification of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes for Multiple Cancer Types. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.03960. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.X.; Janowczyk, A.; Zhou, Y.; Thawani, R.; Fu, P.F.; Schalper, K.; Velcheti, V.; Madabhushi, A. Prediction of recurrence in early stage non-small cell lung cancer using computer extracted nuclear features from digital H&E images. Sci Rep. UK 2017, 7, e13543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Wu, P.; Huang, Q.; Yi, J.; Riedlinger, G.M.; De, S.; Metaxas, D.N. Weakly Supervised Deep Nuclei Segmentation using Points Annotation in Histopathology Images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning (MIDL 2019), London, UK, 8–10 July 2019; pp. 390–400. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, H.; Halig, L.V.; Zhang, H.Z.; Wang, D.S.; Chen, Z.G.; Fei, B.W. Detection of Cancer Metastasis Using a Novel Macroscopic Hyperspectral Method. Proc. SPIE 2012, 8317, e831711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucheron, L.E.; Bi, Z.Q.; Harvey, N.R.; Manjunath, B.S.; Rimm, D.L. Utility of multispectral imaging for nuclear classification of routine clinical histopathology imagery. BMC Cell Biol. 2007, 8 (Suppl. 1), e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, S.; Botta, F.; Raimondi, S.; Origgi, D.; Fanciullo, C.; Morganti, A.G.; Bellomi, M. Radiomics: The facts and the challenges of image analysis. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes, M.D.; Schuch, A.; Hochhegger, B.; Gross, J.L.; Chojniak, R.; Marchiori, E. Functional magnetic resonance imaging in oncology: State of the art. Radiol. Bras. 2014, 47, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croteau, E.; Renaud, J.M.; Richard, M.A.; Ruddy, T.D.; Benard, F.; deKemp, R.A. PET Metabolic Biomarkers for Cancer. Biomark. Cancer 2016, 8, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, J.P.; Tofts, P.S.; Miles, K.A.; Parkes, L.M.; Thompson, G.; Jackson, A. Dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging techniques: CT and MRI. Br. J. Radiol. 2011, 84, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, B.J.; Korfiatis, P.; Akkus, Z.; Kline, T.L. Machine Learning for Medical Imaging(1). Radiographics 2017, 37, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ye, J.C.; Mueller, K.; Fessler, J.A. Image Reconstruction Is a New Frontier of Machine Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Integrating Deep and Radiomics Features in Cancer Bioimaging. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/568170v1.abstract (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Aeffner, F.; Zarella, M.D.; Buchbinder, N.; Bui, M.M.; Goodman, M.R.; Hartman, D.J.; Lujan, G.M.; Molani, M.A.; Parwani, A.V.; Lillard, K.; et al. Introduction to Digital Image Analysis in Whole-slide Imaging: A White Paper from the Digital Pathology Association. J. Pathol. Inf. 2019, 10, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltz, J.; Almeida, J.; Gao, Y.; Sharma, A.; Bremer, E.; DiPrima, T.; Saltz, M.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Kurc, T. Towards Generation, Management, and Exploration of Combined Radiomics and Pathomics Datasets for Cancer Research. AMIA Jt. Summits Transl. Sci. Proc. 2017, 2017, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haghighi, B.; Choi, S.; Choi, J.; Hoffman, E.A.; Comellas, A.P.; Newell, J.D.; Barr, R.G.; Bleecker, E.; Cooper, C.B.; Couper, D.; et al. Imaging-based clusters in current smokers of the COPD cohort associate with clinical characteristics: The SubPopulations and Intermediate Outcome Measures in COPD Study (SPIROMICS). Resp. Res. 2018, 19, e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighi, B.; Choi, S.; Choi, J.; Hoffman, E.A.; Comellas, A.P.; Newell, J.D.; Lee, C.H.; Barr, R.G.; Bleecker, E.; Cooper, C.B.; et al. Imaging-based clusters in former smokers of the COPD cohort associate with clinical characteristics: The SubPopulations and intermediate outcome measures in COPD study (SPIROMICS). Resp. Res. 2019, 20, e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gang, P.; Zhen, W.; Zeng, W.; Gordienko, Y.; Kochura, Y.; Alienin, O.; Rokovyi, O.; Stirenko, S. Dimensionality Reduction in Deep Learning for Chest X-Ray Analysis of Lung Cancer. In Proceedings of the 2018 Tenth International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Xiamen, China, 29–31 March 2018; pp. 878–883. [Google Scholar]
- Luyapan, J.; Ji, X.M.; Zhu, D.K.; MacKenzie, T.A.; Amos, C.I.; Gui, J. An Efficient Survival Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction Method for Detecting Gene-Gene Interactions of Lung Cancer Onset. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Mardid, Spain, 3–6 December 2018; pp. 2779–2781. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi, B.; Jahani, N.; LaRiviere, M.J.; Cohen, E.; Hsieh, M.-K.; Luna, J.M.; Chitalia, R.D.; Thompson, J.C.; Carpenter, E.L.; Katz, S.I. Correlative hierarchical clustering-based low-rank dimensionality reduction of radiomics-driven phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2019: Imaging Informatics for Healthcare, Research, and Applications, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–18 February 2019; p. 1095416. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighi, B.; Ellingwood, N.; Yin, Y.B.; Hoffman, E.A.; Lin, C.L. A GPU-based symmetric non-rigid image registration method in human lung. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
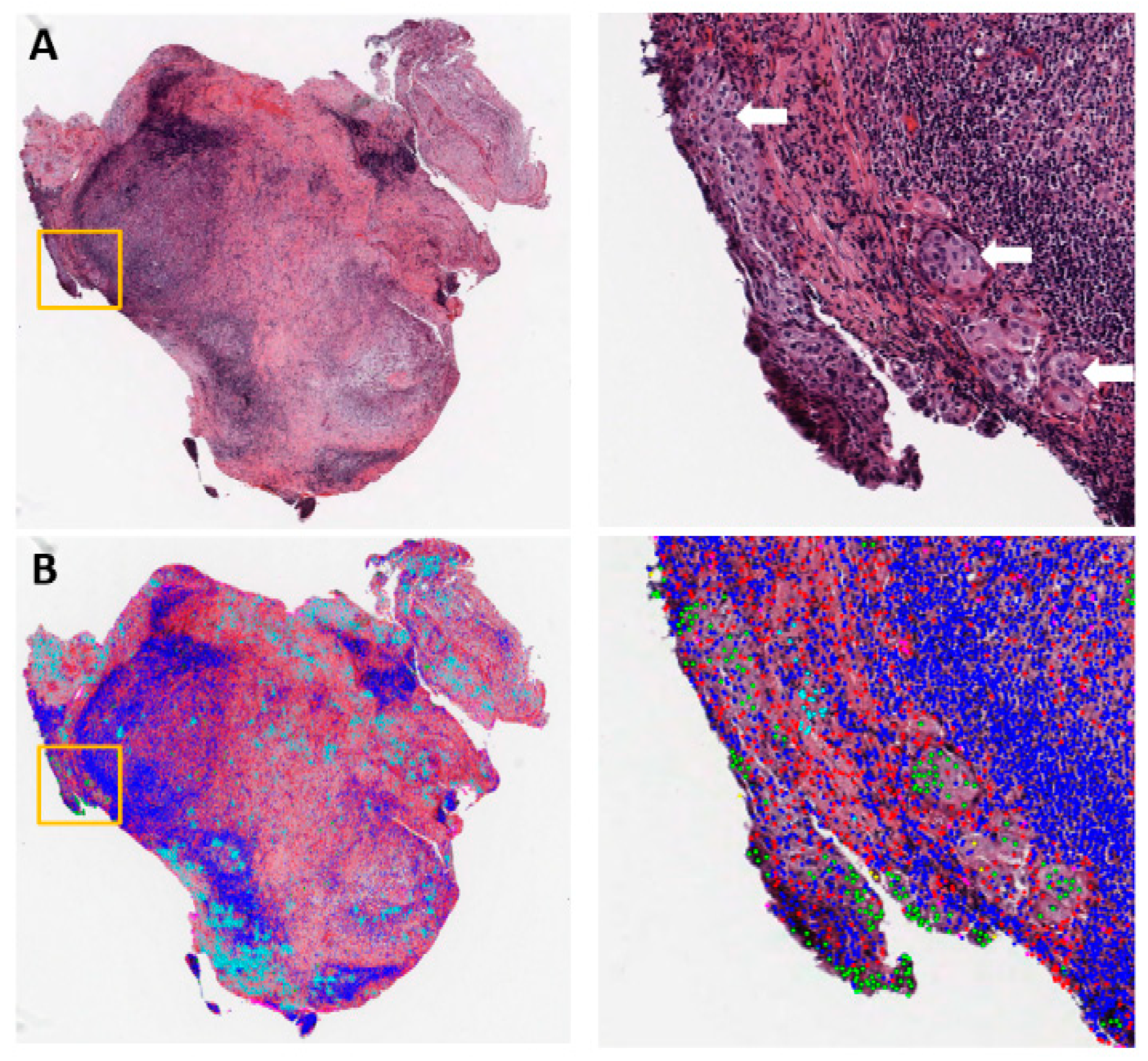
| Topic | Lung Cancer Subtype | Task | Model | Prognostic Value Reported? | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung cancer detection | ADC | Maglinant vs. non-malignant classification | CNN | Yes | 2018 | [69] |
| NSCLC and SCLC | CNN | No | 2018 | [70] | ||
| ADC and SCC | CNN | No | 2019 | [71] | ||
| ADC | CNN | No | 2019 | [72] | ||
| SCC | CNN | No | 2019 | [72] | ||
| Not specified | CNN | No | 2019 | [73] | ||
| Lung cancer classification | ADC and SCC | ADC vs. SCC vs. non-malignant classification | CNN | No | 2018 | [74] |
| ADC and SCC | Mutation status prediction | CNN | No | 2018 | [74] | |
| ADC | Histological subtype classification | CNN | No | 2019 | [75] | |
| NSCLC | PD-L1 status prediction | FCN | No | 2019 | [76] | |
| ADC and SCC | ADC vs. SCC classification | CNN | No | 2019 | [71] | |
| ADC and SCC | ADC vs. SCC classification | CNN | No | 2019 | [72] | |
| ADC and SCC | Transcriptome subtype classification | CNN | No | 2019 | [72] | |
| ADC and SCC | ADC vs. SCC vs. non-malignant classification | CNN | No | 2019 | [77] | |
| ADC | Hisotological subtype classification | CNN | No | 2019 | [78] | |
| Micro-environment analysis | ADC and SCC | TIL positive vs. negative classification | CNN | Yes | 2018 | [39] |
| ADC and SCC | Necrosis positive vs. negative classification | CNN | Yes | 2018 | [39] | |
| ADC | Tumor vs. stromal cell vs. lymphcyte classification | CNN | Yes | 2018 | [79] | |
| ADC | Microvessel segmentation | FCN | Yes | 2018 | [80] | |
| ADC | Computation staining of 6 different nuclei types | Mask-RCNN | Yes | 2019 | [81] | |
| ADC and SCC | TIL positive vs. negative classification | CNN | No | 2019 | [82] | |
| Other | Early-stage NSCLC | Nucleus boundary segmentation | CNN | Yes | 2017 | [83] |
| Not specified | Nucleus segmentation | Unet + CRF | No | 2019 | [84] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Yang, D.M.; Rong, R.; Zhan, X.; Fujimoto, J.; Liu, H.; Minna, J.; Wistuba, I.I.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, G. Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer Pathology Image Analysis. Cancers 2019, 11, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111673
Wang S, Yang DM, Rong R, Zhan X, Fujimoto J, Liu H, Minna J, Wistuba II, Xie Y, Xiao G. Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer Pathology Image Analysis. Cancers. 2019; 11(11):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111673
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shidan, Donghan M. Yang, Ruichen Rong, Xiaowei Zhan, Junya Fujimoto, Hongyu Liu, John Minna, Ignacio Ivan Wistuba, Yang Xie, and Guanghua Xiao. 2019. "Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer Pathology Image Analysis" Cancers 11, no. 11: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111673
APA StyleWang, S., Yang, D. M., Rong, R., Zhan, X., Fujimoto, J., Liu, H., Minna, J., Wistuba, I. I., Xie, Y., & Xiao, G. (2019). Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer Pathology Image Analysis. Cancers, 11(11), 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111673







