MPT0G612, a Novel HDAC6 Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses IFN-γ-Induced Programmed Death-Ligand 1 in Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
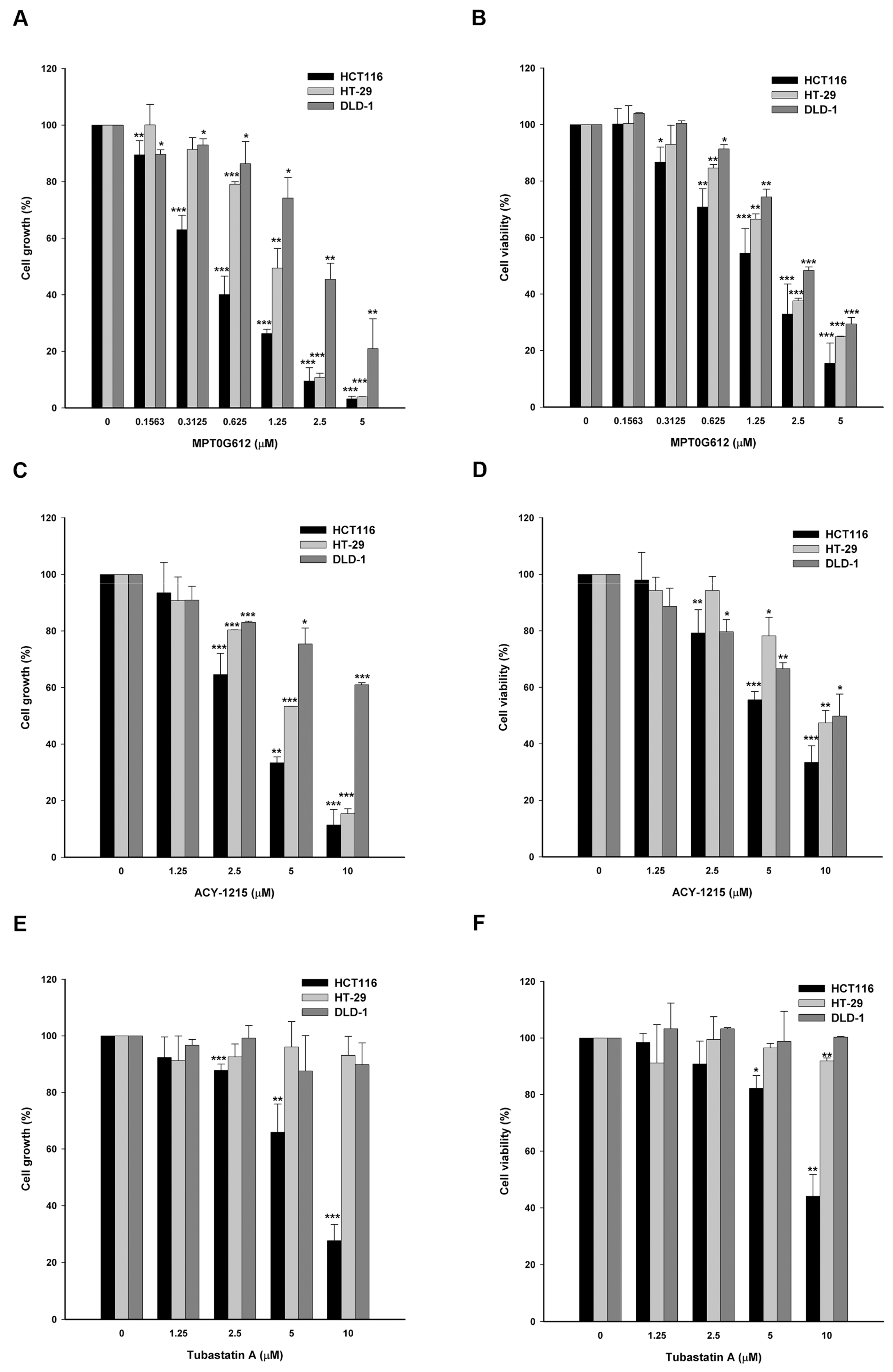
2.1. MPT0G612 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Viability in Colorectal Cancer Cells
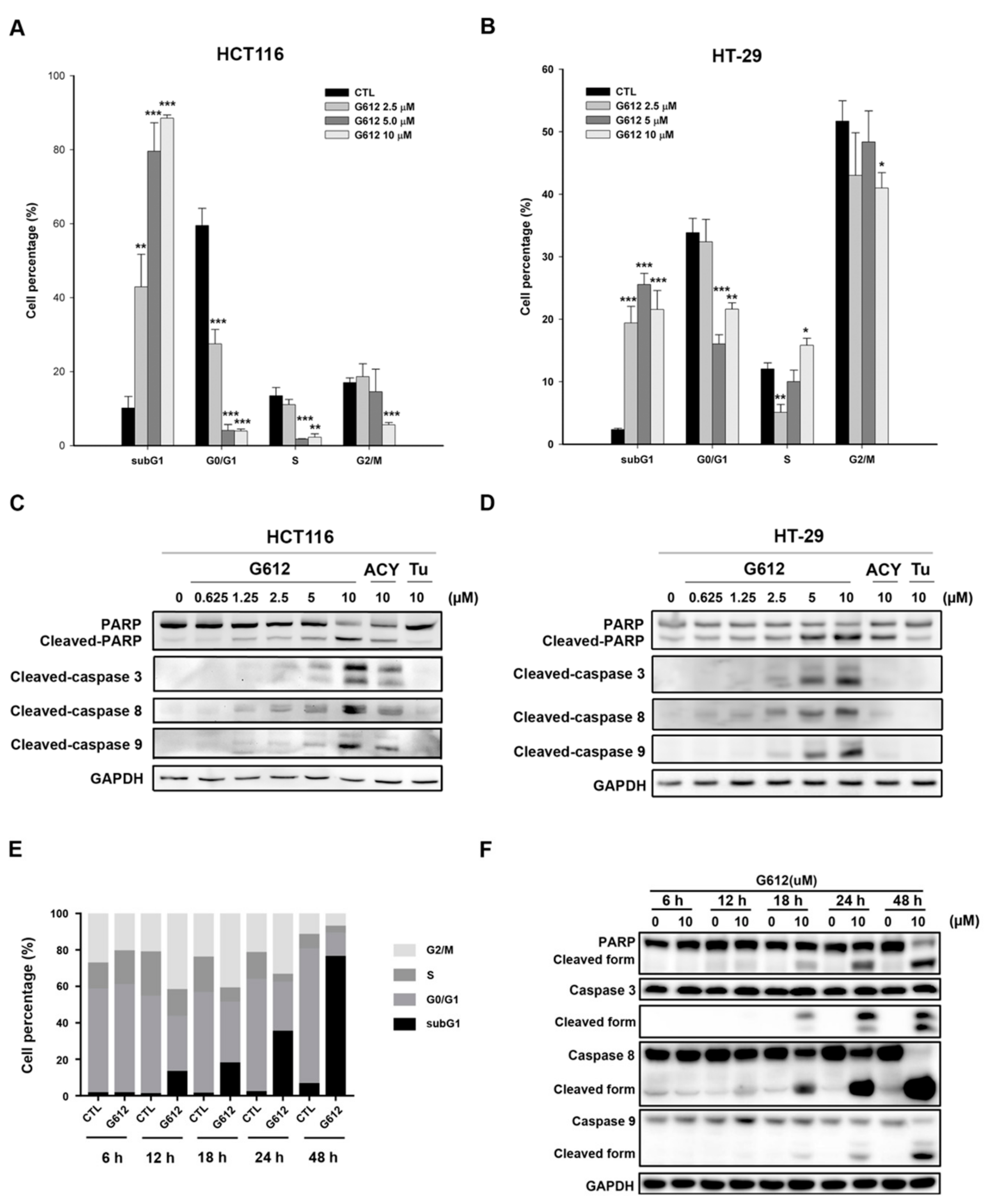
2.2. MPT0G612 Induces Cell Cycle Accumulation at subG1 Phase and Apoptosis in CRC Cells
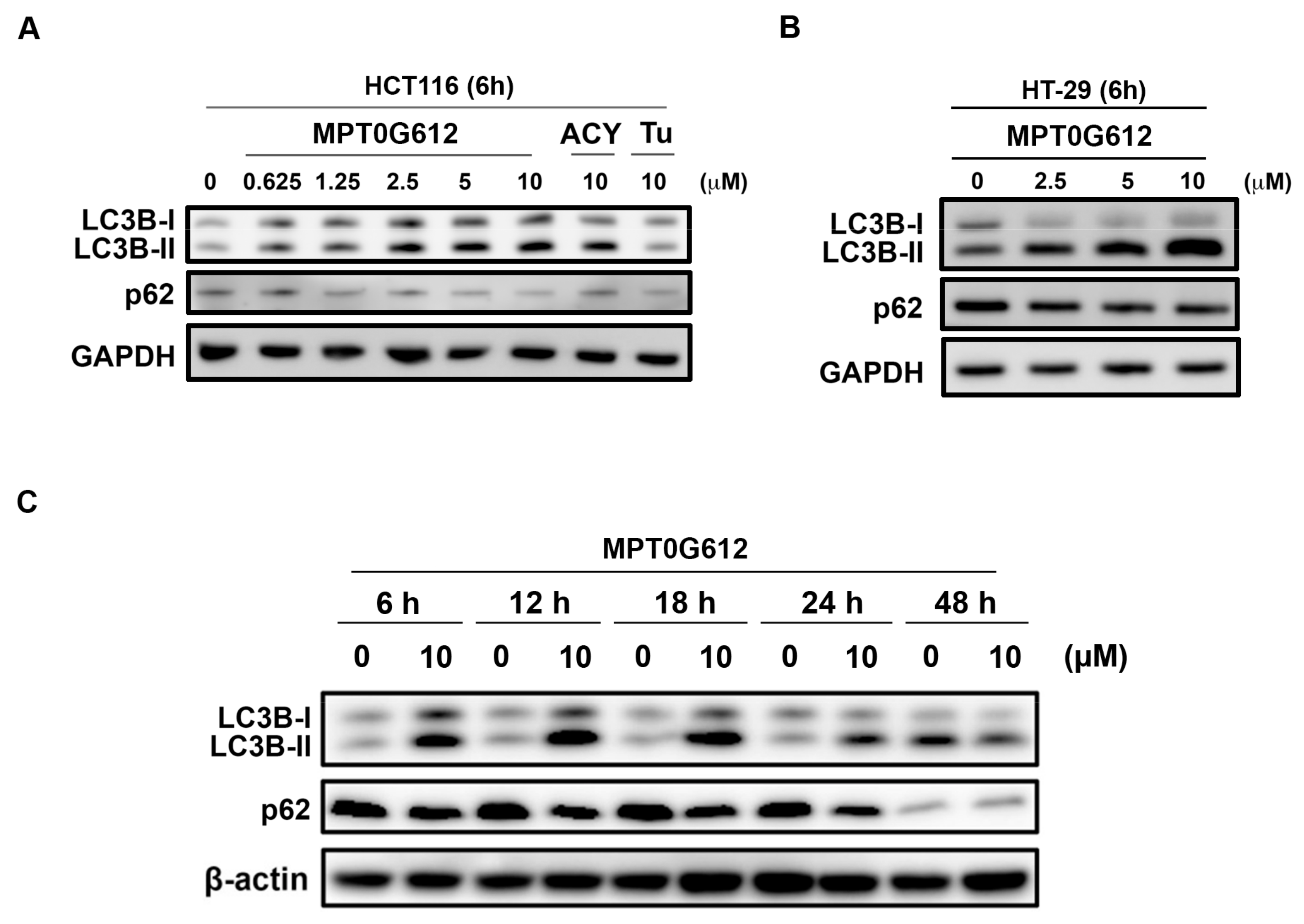
2.3. Effects of MPT0G612 on Autophagy in HCT116 Cells
2.4. Inhibition of Autophagy Enhances MPT0G612-Induced Cell Death
2.5. HDAC6 Is Crucial to MPT0G612-Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy in CRC Cells
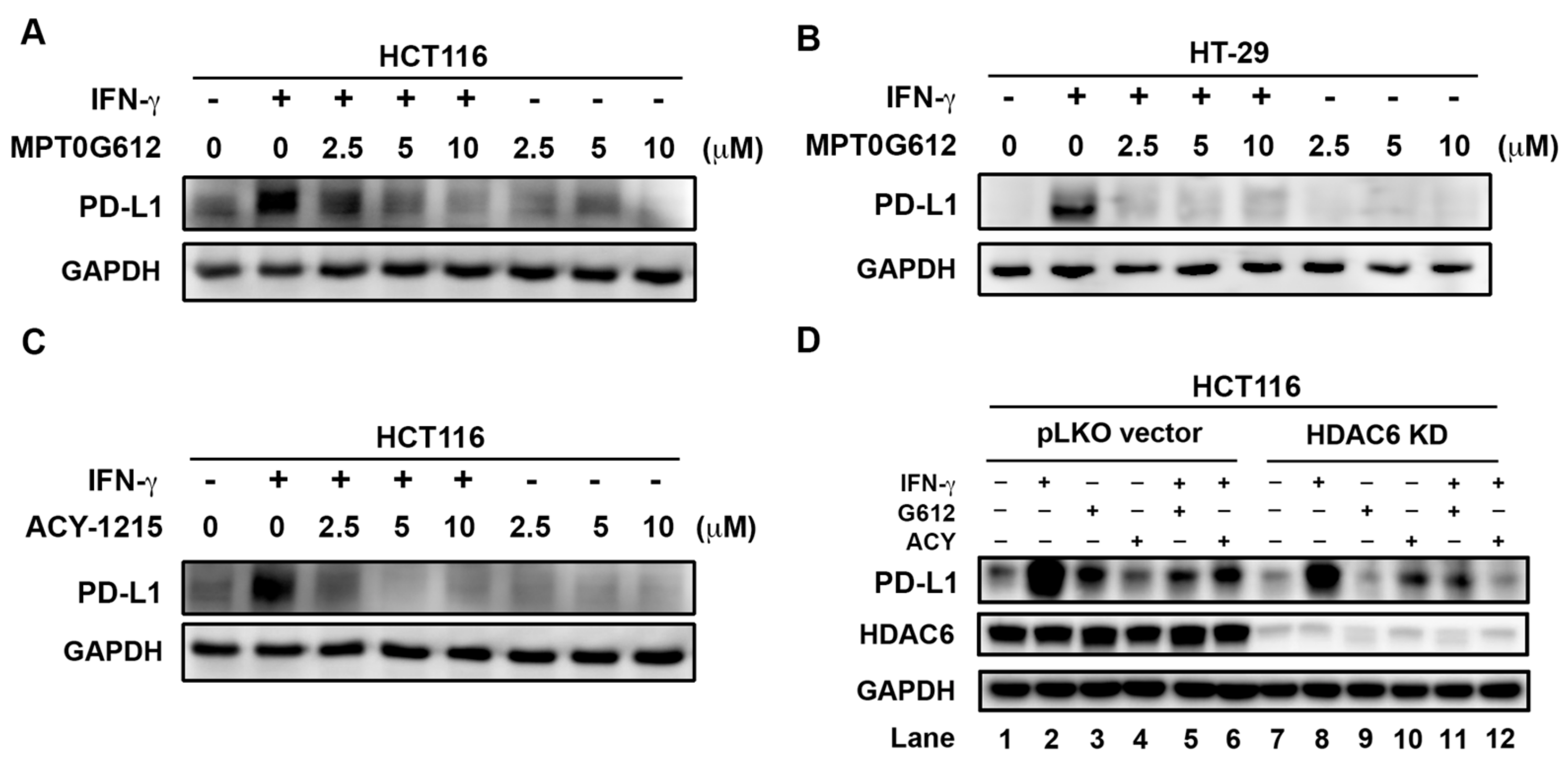
2.6. MPT0G612 Abrogates IFN-γ-Induced PD-L1 Expression in CRC Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. SRB (Sulforhodamine B) Assay
4.4. FACScan Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.5. Western Blot and Lentivirus Expression System
4.6. Statistics and Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelly, T.K.; De Carvalho, D.D.; Jones, P.A. Epigenetic modifications as therapeutic targets. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timp, W.; Feinberg, A.P. Cancer as a dysregulated epigenome allowing cellular growth advantage at the expense of the host. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, A.P.; Koldobskiy, M.A.; Gondor, A. Epigenetic modulators, modifiers and mediators in cancer aetiology and progression. Nat. Rev. Genet 2016, 17, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenberg, K.J.; Johnstone, R.W. Histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in cancer, neurological diseases and immune disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, P.; Rifkind, R.A.; Richon, V.M.; Breslow, R.; Miller, T.; Kelly, W.K. Histone deacetylases and cancer: Causes and therapies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, A.J.; Horwitz, S.M. Targeting histone deacetylases in T-cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 1306–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraweera, A.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Combination Therapy With Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi) for the Treatment of Cancer: Achieving the Full Therapeutic Potential of HDACi. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of histone acetylation: The histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a018713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.L.; Davis, C.A.; Potthoff, M.J.; Haberland, M.; Fielitz, J.; Qi, X.; Hill, J.A.; Richardson, J.A.; Olson, E.N. Histone deacetylases 1 and 2 redundantly regulate cardiac morphogenesis, growth, and contractility. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1790–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagger, G.; O’Carroll, D.; Rembold, M.; Khier, H.; Tischler, J.; Weitzer, G.; Schuettengruber, B.; Hauser, C.; Brunmeir, R.; Jenuwein, T.; et al. Essential function of histone deacetylase 1 in proliferation control and CDK inhibitor repression. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 2672–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraczek, J.; Vanhaecke, T.; Rogiers, V. Toxicological and metabolic considerations for histone deacetylase inhibitors. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Belani, C.P.; Ruel, C.; Frankel, P.; Gitlitz, B.; Koczywas, M.; Espinoza-Delgado, I.; Gandara, D. Phase II study of belinostat (PXD101), a histone deacetylase inhibitor, for second line therapy of advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, C.; Schnekenburger, M.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Histone deacetylase 6 in health and disease. Epigenomics 2015, 7, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalin, J.H.; Bergman, J.A. Development and therapeutic implications of selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 6297–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Gan, Y.H. Synergistic antitumor effects of the combined treatment with an HDAC6 inhibitor and a COX-2 inhibitor through activation of PTEN. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, A.J.; Bensinger, W.I.; Supko, J.G.; Voorhees, P.M.; Berdeja, J.G.; Richardson, P.G.; Libby, E.N.; Wallace, E.E.; Birrer, N.E.; Burke, J.N.; et al. Ricolinostat plus lenalidomide, and dexamethasone in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: A multicentre phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, D.T.; Raje, N.; Jagannath, S.; Richardson, P.; Hari, P.; Orlowski, R.; Supko, J.G.; Tamang, D.; Yang, M.; Jones, S.S.; et al. Ricolinostat, the First Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor, in Combination with Bortezomib and Dexamethasone for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3307–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longley, D.B.; Harkin, D.P.; Johnston, P.G. 5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Won, H.R.; Ryu, H.W.; Han, J.M.; Kwon, S.H. The HDAC6 inhibitor ACY1215 enhances the anticancer activity of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampakis, A.; Tampaki, E.C.; Nebiker, C.A.; Kouraklis, G. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and colorectal cancer: What is new? Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliszczak, M.; van Hechanova, E.; Li, Y.; Alsadah, H.; Parzych, K.; Auner, H.W.; Aboagye, E.O. The HDAC6 inhibitor C1A modulates autophagy substrates in diverse cancer cells and induces cell death. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, H.; Chu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, D.; Huo, J. Histone deacetylase 6 selective inhibitor ACY1215 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the chemotherapeutic effect of 5-fluorouracil in HCT116 cells. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepali, K.; Lee, H.Y.; Lai, M.J.; Ojha, R.; Wu, T.Y.; Wu, G.X.; Chen, M.C.; Liou, J.P. Ring-opened tetrahydro-gamma-carbolines display cytotoxicity and selectivity with histone deacetylase isoforms. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Lv, W.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Yuan, P.; Huang, S.; He, Z.; Hu, J. Ricolinostat (ACY-1215) suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via miR-30d/PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ERK pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Koga, H.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Tang, W.; Wong, E.; Gao, Y.S.; Pandey, U.B.; Kaushik, S.; Tresse, E.; Lu, J.; et al. HDAC6 controls autophagosome maturation essential for ubiquitin-selective quality-control autophagy. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenone, M.; Dancik, V.; Wagner, B.K.; Clemons, P.A. Target identification and mechanism of action in chemical biology and drug discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Huang, Y.; Liang, X.; Jiang, F.; He, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, G.; Zhao, H.; Yang, W.; Jiang, G.; et al. Metastatic prostate cancer-associated P62 inhibits autophagy flux and promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition by sustaining the level of HDAC6. Prostate 2018, 78, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laino, A.S.; Betts, B.C.; Veerapathran, A.; Dolgalev, I.; Sarnaik, A.; Quayle, S.N.; Jones, S.S.; Weber, J.S.; Woods, D.M. HDAC6 selective inhibition of melanoma patient T-cells augments anti-tumor characteristics. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienlaf, M.; Perez-Villarroel, P.; Knox, T.; Pabon, M.; Sahakian, E.; Powers, J.; Woan, K.V.; Lee, C.; Cheng, F.; Deng, S.; et al. Essential role of HDAC6 in the regulation of PD-L1 in melanoma. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 735–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Seto, E. HDACs and HDAC Inhibitors in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damaskos, C.; Garmpis, N.; Valsami, S.; Kontos, M.; Spartalis, E.; Kalampokas, T.; Kalampokas, E.; Athanasiou, A.; Moris, D.; Daskalopoulou, A.; et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: An Attractive Therapeutic Strategy Against Breast Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, B.S.; Johnson, J.R.; Cohen, M.H.; Justice, R.; Pazdur, R. FDA approval summary: Vorinostat for treatment of advanced primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncologist 2007, 12, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachmias, B.; Shaulov, A.; Lavie, D.; Goldschmidt, N.; Gural, A.; Saban, R.; Lebel, E.; Gatt, M.E. Romidepsin-Bendamustine Combination for Relapsed/Refractory T Cell Lymphoma. Acta Haematol. 2019, 141, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, M.; Kohrman, N.; Gore, S.D.; Kim, T.K.; Zeidan, A.M.; Prebet, T. Epigenetics in Cancer: A Hematological Perspective. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosenza, M.; Pozzi, S. The Therapeutic Strategy of HDAC6 Inhibitors in Lymphoproliferative Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brilli, L.L.; Swanhart, L.M.; de Caestecker, M.P.; Hukriede, N.A. HDAC inhibitors in kidney development and disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2013, 28, 1909–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnock-Jones, K.P. Panobinostat: First global approval. Drugs 2015, 75, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Gao, M.; Yang, G.; Tao, Y.; Kong, Y.; Yang, R.; Meng, X.; Ai, G.; Wei, R.; Wu, H.; et al. Synergistic Activity of Carfilzomib and Panobinostat in Multiple Myeloma Cells via Modulation of ROS Generation and ERK1/2. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 459052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana-Masangkay, G.I.; Sakamoto, K.M. The role of HDAC6 in cancer. J. BioMed Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 875824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.F. The development prospection of HDAC inhibitors as a potential therapeutic direction in Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2017, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoes-Pires, C.; Zwick, V.; Nurisso, A.; Schenker, E.; Carrupt, P.A.; Cuendet, M. HDAC6 as a target for neurodegenerative diseases: What makes it different from the other HDACs? Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noack, M.; Leyk, J.; Richter-Landsberg, C. HDAC6 inhibition results in tau acetylation and modulates tau phosphorylation and degradation in oligodendrocytes. Glia 2014, 62, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlomagno, Y.; Chung, D.C.; Yue, M.; Castanedes-Casey, M.; Madden, B.J.; Dunmore, J.; Tong, J.; DeTure, M.; Dickson, D.W.; Petrucelli, L.; et al. An acetylation-phosphorylation switch that regulates tau aggregation propensity and function. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15277–15286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, S.M.; Mizielinska, S.M.; Frenguelli, B.G.; Harvey, J.; Connolly, C.N. Mitochondrial dysfunction and dendritic beading during neuronal toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 26235–26244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, J.H.; Xie, L.; Song, S.; Xie, Y.; Allen, L.; Ajit, D.; Hong, J.S.; Chen, X.; Meeker, R.B.; Cohen, T.J. The Deacetylase HDAC6 Mediates Endogenous Neuritic Tau Pathology. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2169–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Lim, K.H.; Guo, X.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Gao, Y.; Barrientos, T.; Ordentlich, P.; Wang, X.F.; Counter, C.M.; Yao, T.P. The cytoplasmic deacetylase HDAC6 is required for efficient oncogenic tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7561–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarga, V.; Aymerich, I.; Tapia, O.; Mayor, F., Jr.; Penela, P. A novel GRK2/HDAC6 interaction modulates cell spreading and motility. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, T.; Uzawa, K.; Onda, T.; Shiiba, M.; Yokoe, H.; Shibahara, T.; Tanzawa, H. Aberrant expression of histone deacetylase 6 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2006, 29, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzaro, M.; Lin, Z.; Santillan, A.; Lee, M.K.; Wang, M.C.; Chan, K.C.; Bristow, R.E.; Mazitschek, R.; Bradner, J.; Roden, R.B. Ubiquitin proteasome system stress underlies synergistic killing of ovarian cancer cells by bortezomib and a novel HDAC6 inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7340–7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Yoshida, N.; Omoto, Y.; Oguchi, S.; Yamori, T.; Kiyama, R.; Hayashi, S. Development of cDNA microarray for expression profiling of estrogen-responsive genes. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 29, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgersen, M.L.; Engedal, N.; Boe, S.O.; Hokland, P.; Simonsen, A. Targeting autophagy potentiates the apoptotic effect of histone deacetylase inhibitors in t(8;21) AML cells. Blood 2013, 122, 2467–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyono, K.; Suzuki, H.I.; Matsuyama, H.; Morishita, Y.; Komuro, A.; Kano, M.R.; Sugimoto, K.; Miyazono, K. Autophagy is activated by TGF-beta and potentiates TGF-beta-mediated growth inhibition in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8844–8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seigneurin-Berny, D.; Verdel, A.; Curtet, S.; Lemercier, C.; Garin, J.; Rousseaux, S.; Khochbin, S. Identification of components of the murine histone deacetylase 6 complex: Link between acetylation and ubiquitination signaling pathways. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 8035–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbert, C.; Guardiola, A.; Shao, R.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Ito, A.; Nixon, A.; Yoshida, M.; Wang, X.F.; Yao, T.P. HDAC6 is a microtubule-associated deacetylase. Nature 2002, 417, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, Y.; Kovacs, J.J.; McLaurin, A.; Vance, J.M.; Ito, A.; Yao, T.P. The deacetylase HDAC6 regulates aggresome formation and cell viability in response to misfolded protein stress. Cell 2003, 115, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.S.; Hubbert, C.C.; Lu, J.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Yao, T.P. Histone deacetylase 6 regulates growth factor-induced actin remodeling and endocytosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 8637–8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoury, S.C.; Straughan, D.M.; Shukla, V. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy: Clinical Efficacy and Safety. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2015, 15, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril-Rodriguez, G.; Ribas, A. SnapShot: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.V. Developing combination strategies using PD-1 checkpoint inhibitors to treat cancer. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lin, J.; Yang, X.; Long, J.; Bai, Y.; Yang, X.; Mao, Y.; Sang, X.; Seery, S.; Zhao, H. Combination regimens with PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors for gastrointestinal malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, D.M.; Sodre, A.L.; Villagra, A.; Sarnaik, A.; Sotomayor, E.M.; Weber, J. HDAC Inhibition Upregulates PD-1 Ligands in Melanoma and Augments Immunotherapy with PD-1 Blockade. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terranova-Barberio, M.; Thomas, S.; Ali, N.; Pawlowska, N.; Park, J.; Krings, G.; Rosenblum, M.D.; Budillon, A.; Munster, P.N. HDAC inhibition potentiates immunotherapy in triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 114156–114172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, W.; Yan, C.; Watson, C.C.; Massengill, M.; Xie, M.; Massengill, C.; Noyes, D.R.; Martinez, G.V.; Afzal, R.; et al. HDAC Inhibitors Enhance T-Cell Chemokine Expression and Augment Response to PD-1 Immunotherapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4119–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhang, C.; Hassan, S.; Liu, X.; Song, F.; Chen, K.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J. Histone deacetylase 6 in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, D.M.; Woan, K.; Cheng, F.; Wang, H.; Perez-Villarroel, P.; Lee, C.; Lienlaf, M.; Atadja, P.; Seto, E.; Weber, J.; et al. The antimelanoma activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589) is mediated by direct tumor cytotoxicity and increased tumor immunogenicity. Melanoma Res. 2013, 23, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briere, D.; Sudhakar, N.; Woods, D.M.; Hallin, J.; Engstrom, L.D.; Aranda, R.; Chiang, H.; Sodre, A.L.; Olson, P.; Weber, J.S.; et al. The class I/IV HDAC inhibitor mocetinostat increases tumor antigen presentation, decreases immune suppressive cell types and augments checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, T.; Sahakian, E.; Banik, D.; Hadley, M.; Palmer, E.; Noonepalle, S.; Kim, J.; Powers, J.; Gracia-Hernandez, M.; Oliveira, V.; et al. Selective HDAC6 inhibitors improve anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy by decreasing the anti-inflammatory phenotype of macrophages and down-regulation of immunosuppressive proteins in tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Lim, S.O.; Xia, W.; Lee, H.H.; Chan, L.C.; Kuo, C.W.; Khoo, K.H.; Chang, S.S.; Cha, J.H.; Kim, T.; et al. Glycosylation and stabilization of programmed death ligand-1 suppresses T-cell activity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Qin, Q.; Shu, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Continuous targeted kinase inhibitors treatment induces upregulation of PD-L1 in resistant NSCLC. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Hsieh, T.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Liu, Y.R.; Liou, J.P.; Yen, Y. Targeting Autophagy by MPT0L145, a Highly Potent PIK3C3 Inhibitor, Provides Synergistic Interaction to Targeted or Chemotherapeutic Agents in Cancer Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Changou, C.A.; Hsieh, T.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Chu, C.Y.; Hsu, K.C.; Wang, H.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Lo, Y.N.; Liu, Y.R.; et al. Dual Inhibition of PIK3C3 and FGFR as a New Therapeutic Approach to Treat Bladder Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Liao, Y.-H.; Liou, J.-P.; Chen, C.-H. MPT0G612, a Novel HDAC6 Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses IFN-γ-Induced Programmed Death-Ligand 1 in Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101617
Chen M-C, Lin Y-C, Liao Y-H, Liou J-P, Chen C-H. MPT0G612, a Novel HDAC6 Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses IFN-γ-Induced Programmed Death-Ligand 1 in Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. Cancers. 2019; 11(10):1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101617
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Mei-Chuan, Yu-Chen Lin, Yu-Hsuan Liao, Jing-Ping Liou, and Chun-Han Chen. 2019. "MPT0G612, a Novel HDAC6 Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses IFN-γ-Induced Programmed Death-Ligand 1 in Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells" Cancers 11, no. 10: 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101617
APA StyleChen, M.-C., Lin, Y.-C., Liao, Y.-H., Liou, J.-P., & Chen, C.-H. (2019). MPT0G612, a Novel HDAC6 Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses IFN-γ-Induced Programmed Death-Ligand 1 in Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. Cancers, 11(10), 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101617




