Histone Deacetylase Expressions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Functional Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors on Liver Cancer Cells In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
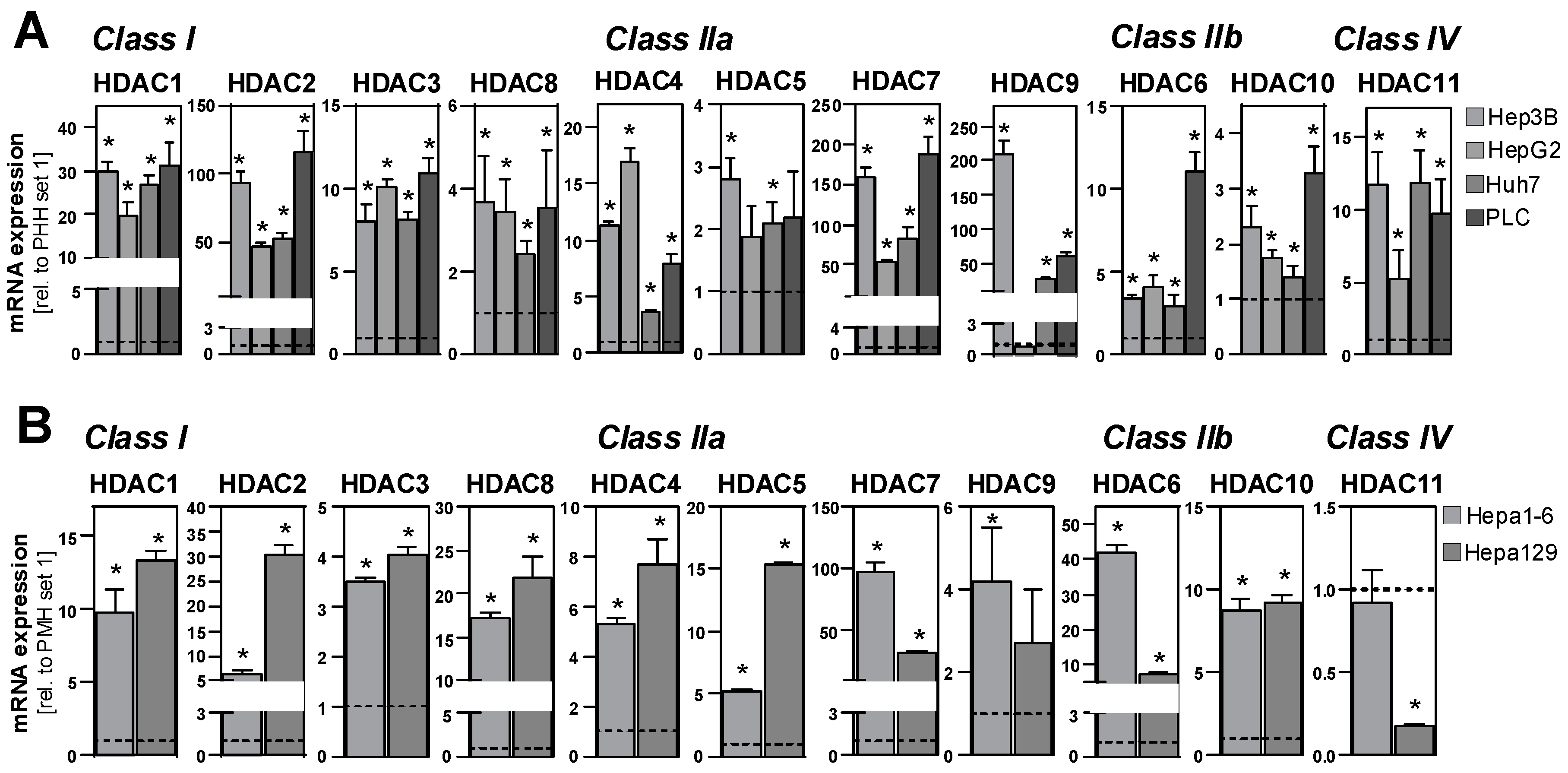
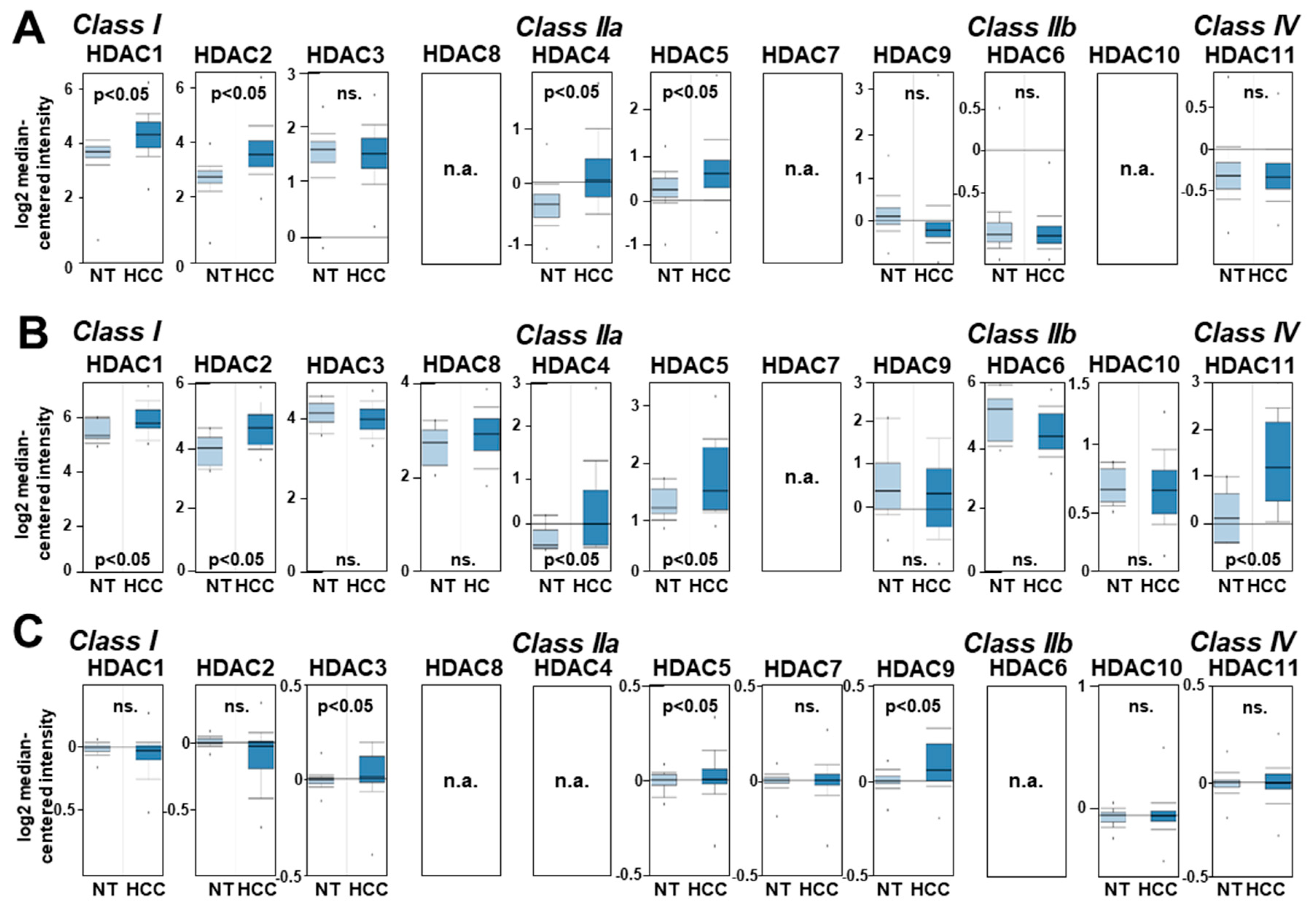
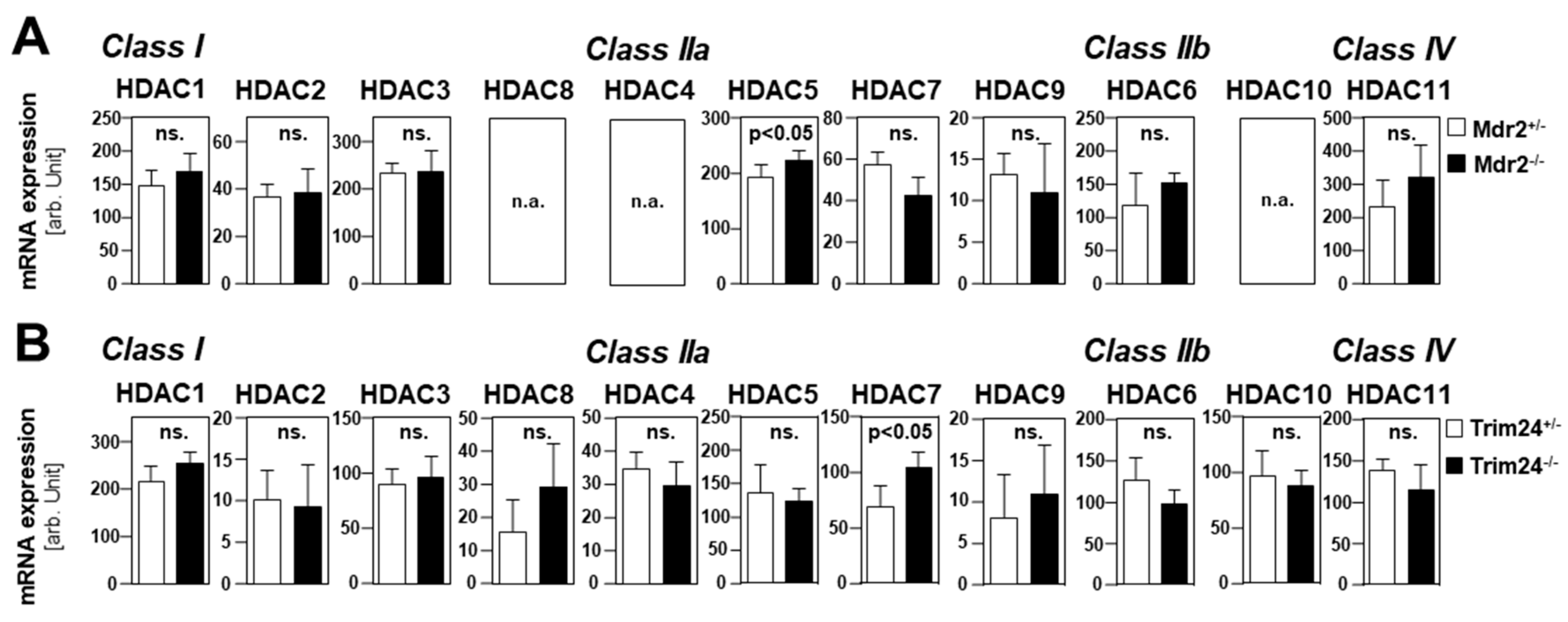
2.1. HDAC Expression in HCC Cells and Tissues
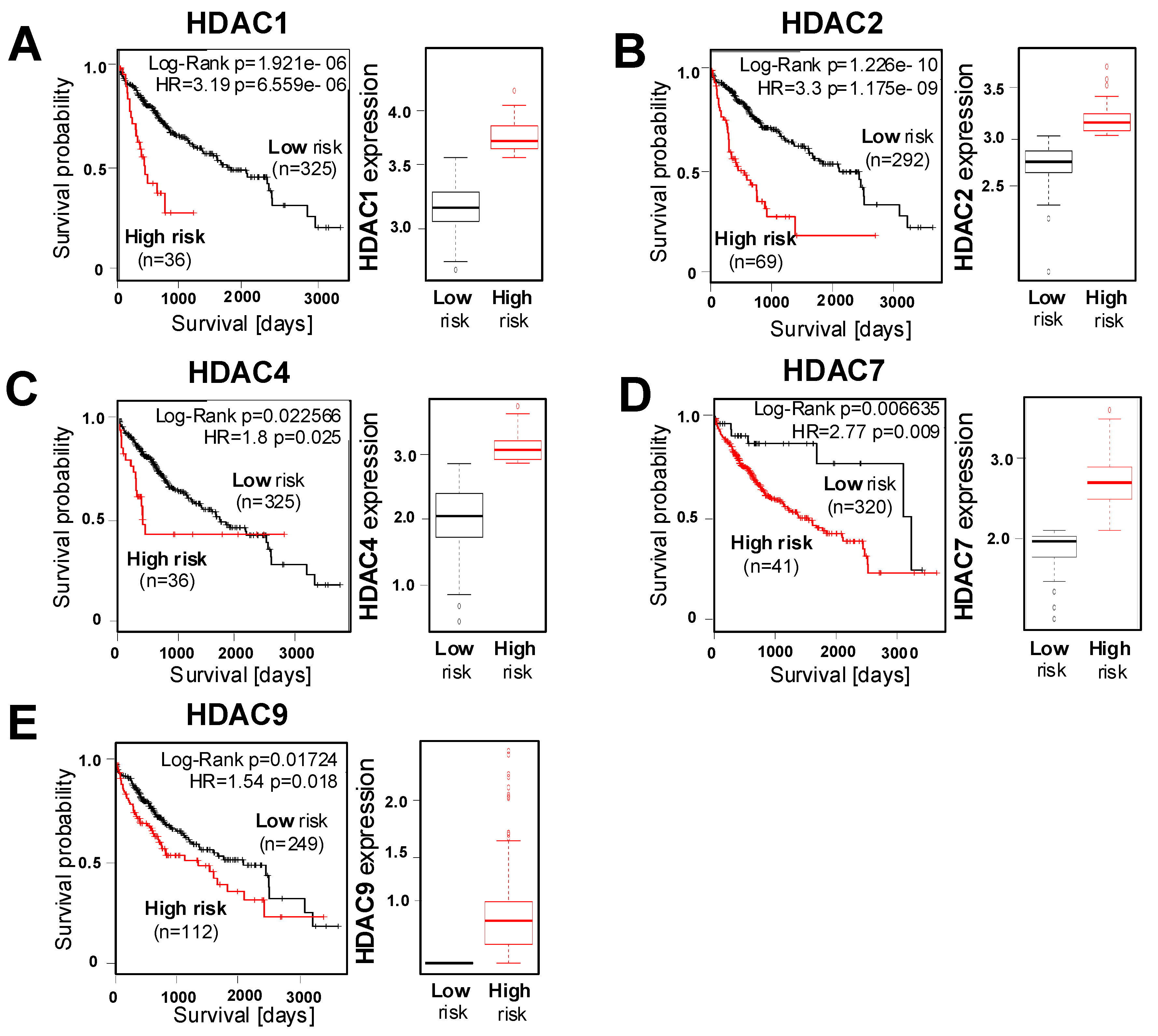
2.2. Correlation of HDAC Expression with Clinical Prognosis of HCC Patients
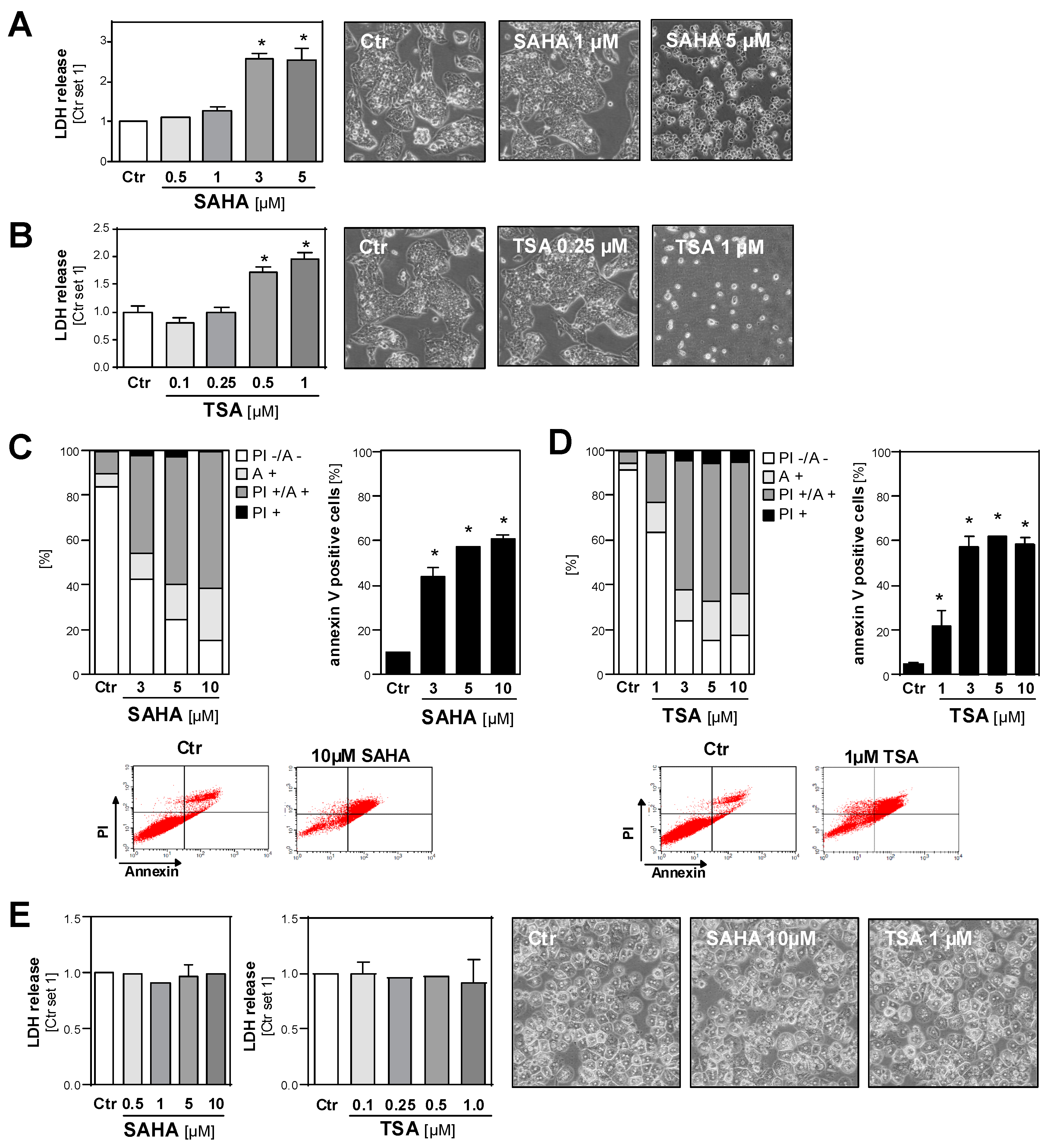
2.3. Effect of HDAC Inhibition on the Viability of HCC Cell Lines and Primary Hepatocytes
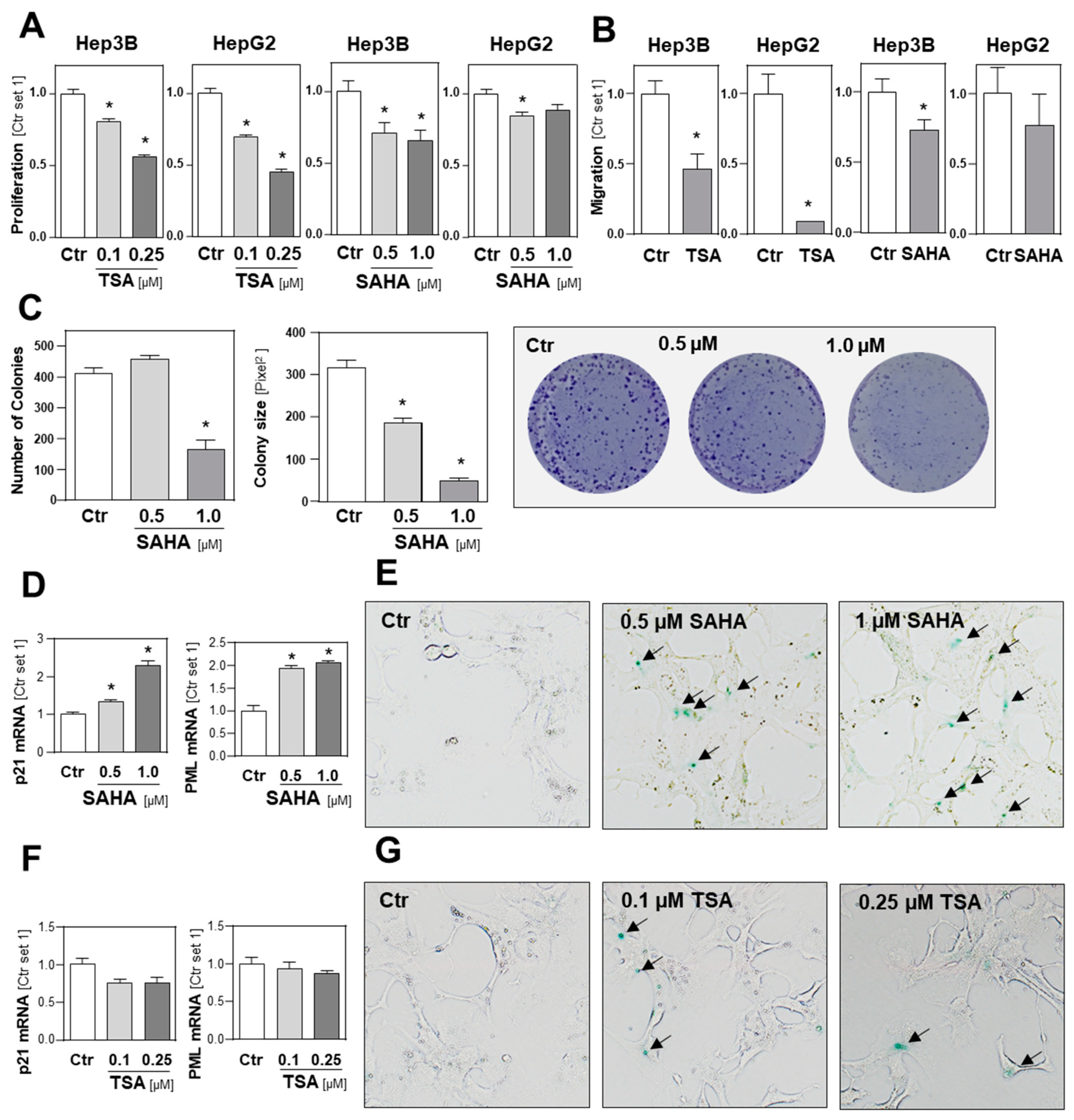
2.4. Functional Effects of HDAC Inhibition on HCC Cell Lines
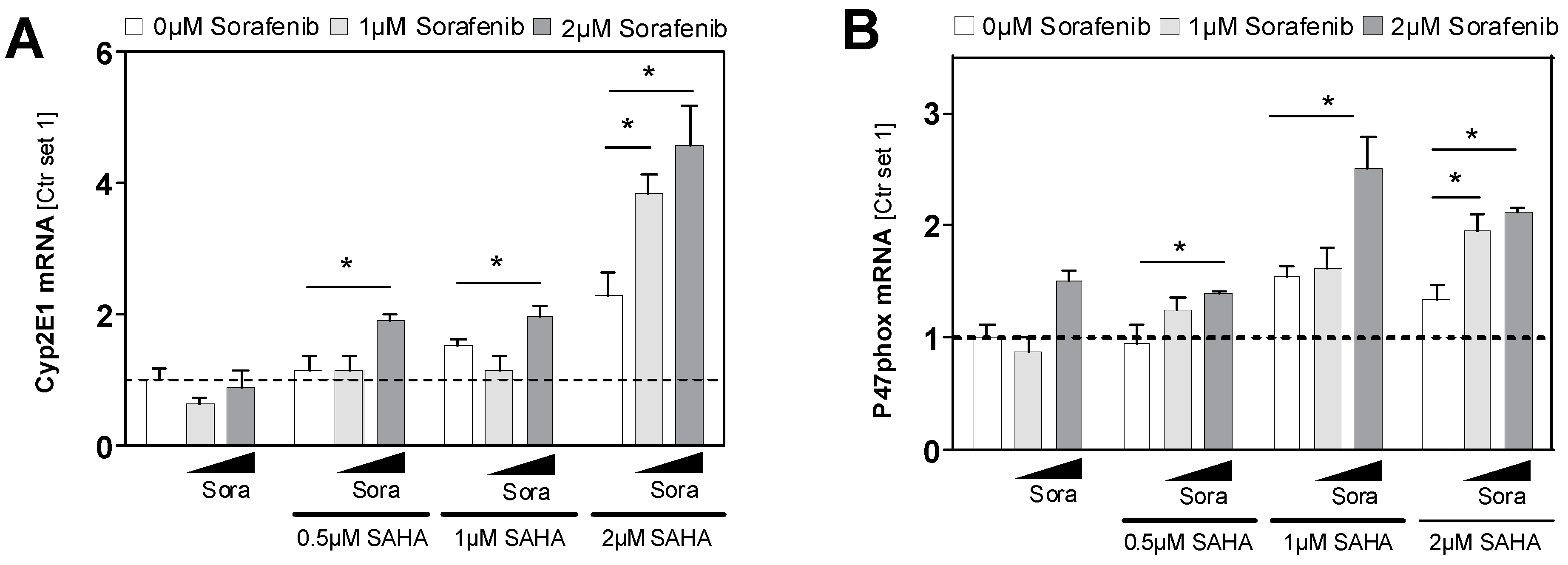
2.5. Effects of HDAC Inhibition on HCC Cell Lines in Combination with Sorafenib
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Cell Culture
4.2. Human Liver Tissues
4.3. In Silico Analysis
4.4. Analysis of mRNA Expression by Quantitative RT-PCR
4.5. Analysis of Cell Toxicity
4.6. Quantification of Apoptosis
4.7. Clonogenic Assay
4.8. Analysis of Cell Proliferation
4.9. Analysis of Cell Migration
4.10. Analysis of Cellular Senescence
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Society, A.C. Cancer Facts and Figures 2014. Available online: http://www.cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstatistics/cancerfactsfigures2014/ (accessed on 7 August 2019).
- Bruix, J.; Llovet, J.M. Prognostic prediction and treatment strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2002, 35, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, M.G.; Slagter, A.E.; Nuttall, C.; Frizziero, M.; Pihlak, R.; Lamarca, A.; Tariq, N.; Valle, J.W.; Hubner, R.A.; Knox, J.J.; et al. Sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with advanced Child-Pugh B hepatocellular carcinoma—A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 105, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckschlager, T.; Plch, J.; Stiborova, M.; Hrabeta, J. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Anticancer Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anestopoulos, I.; Voulgaridou, G.P.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Franco, R.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I. Epigenetic therapy as a novel approach in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 145, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ler, S.Y.; Leung, C.H.; Khin, L.W.; Lu, G.D.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Hartman, M.; Iau, P.T.; Yap, C.T.; Hooi, S.C. HDAC1 and HDAC2 independently predict mortality in hepatocellular carcinoma by a competing risk regression model in a Southeast Asian population. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2238–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quint, K.; Agaimy, A.; Di Fazio, P.; Montalbano, R.; Steindorf, C.; Jung, R.; Hellerbrand, C.; Hartmann, A.; Sitter, H.; Neureiter, D.; et al. Clinical significance of histone deacetylases 1, 2, 3, and 7: HDAC2 is an independent predictor of survival in HCC. Virchows Arch. An Int. J. Pathol. 2011, 459, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Lou, B.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Lv, F.F.; Chen, Y. Down-regulation of HDAC5 inhibits growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma by induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 11523–11532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.D.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Na, M.J.; Yang, G.; Eun, J.W.; Wang, H.J.; Cheong, J.Y.; Park, W.S.; Nam, S.W. HDAC6 Suppresses Let-7i-5p to Elicit TSP1/CD47-mediated Anti-tumorigenesis and Phagocytosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.L.; Liu, W.L.; Hsu, F.M.; Yang, P.S.; Yen, R.F.; Tzen, K.Y.; Cheng, A.L.; Chen, P.J.; Cheng, J.C. Targeting histone deacetylase 4/ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 9 impairs DNA repair for radiosensitization of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in mice. Hepatology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilimigras, D.I.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Moris, D.; Spartalis, E.; Pawlik, T.M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma: A therapeutic perspective. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 27, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottamal, M.; Zheng, S.; Huang, T.L.; Wang, G. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Clinical Studies as Templates for New Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 3898–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, F.A.; Lewis, M.C.; Fass, D.M.; Wagner, F.F.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Hennig, K.M.; Gale, J.; Zhao, W.-N.; Reis, S.; Barker, D.D.; et al. A Selective HDAC 1/2 Inhibitor Modulates Chromatin and Gene Expression in Brain and Alters Mouse Behavior in Two Mood-Related Tests. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Carr, T.; Dimtchev, A.; Zaer, N.; Dritschilo, A.; Jung, M. Attenuated DNA damage repair by trichostatin A through BRCA1 suppression. Radiat. Res. 2007, 168, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bioscience, B.P.S. HDAC/SIRT Screening and Profiling Services. Available online: http://bpsbioscience.com/screening-profiling-services/hdac-screening-profiling-services (accessed on 9 August 2019).
- Armeanu, S.; Pathil, A.; Venturelli, S.; Mascagni, P.; Weiss, T.S.; Gottlicher, M.; Gregor, M.; Lauer, U.M.; Bitzer, M. Apoptosis on hepatoma cells but not on primary hepatocytes by histone deacetylase inhibitors valproate and ITF2357. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathil, A.; Armeanu, S.; Venturelli, S.; Mascagni, P.; Weiss, T.S.; Gregor, M.; Lauer, U.M.; Bitzer, M. HDAC inhibitor treatment of hepatoma cells induces both TRAIL-independent apoptosis and restoration of sensitivity to TRAIL. Hepatology 2006, 43, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Yang, X.; Xing, L.-H.; Kong, W.-Z. Effects of SAHA on proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and hepatitis B virus replication. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 5159–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Shimada, M.; Harimoto, N.; Rikimaru, T.; Shirabe, K.; Tanaka, S.; Sugimachi, K. Histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A induces cell-cycle arrest/apoptosis and hepatocyte differentiation in human hepatoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 103, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.R.; Yu, J.; Shanker, K.; Deshpande, N.; Varambally, R.; Ghosh, D.; Barrette, T.; Pandey, A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining platform. Neoplasia 2004, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, S.; Jia, H.L.; Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Ye, Q.H.; Lee, J.S.; Thorgeirsson, S.S.; Sun, Z.; Tang, Z.Y.; Qin, L.X.; et al. A unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10202–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurmbach, E.; Chen, Y.B.; Khitrov, G.; Zhang, W.; Roayaie, S.; Schwartz, M.; Fiel, I.; Thung, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Bruix, J.; et al. Genome-wide molecular profiles of HCV-induced dysplasia and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2007, 45, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, C.; Amaddeo, G.; Imbeaud, S.; Ladeiro, Y.; Pelletier, L.; Maad, I.B.; Calderaro, J.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Letexier, M.; Degos, F.; et al. Integrated analysis of somatic mutations and focal copy-number changes identifies key genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.J.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.M.; Li, J. Epigenetic modifications by histone deacetylases: Biological implications and therapeutic potential in liver fibrosis. Biochimie 2015, 116, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, M.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. The UCSC Xena platform for public and private cancer genomics data visualization and interpretation. bioRxiv 2019, 326470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, R.; Zhou, X.; Trim, N.; Millward-Sadler, H.; Krane, S.; Benyon, C.; Iredale, J. Mutation in collagen-1 that confers resistance to the action of collagenase results in failure of recovery from CCl4-induced liver fibrosis, persistence of activated hepatic stellate cells, and diminished hepatocyte regeneration. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenellenbogen, M.; Mizrahi, L.; Pappo, O.; Klopstock, N.; Olam, D.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Amariglio, N.; Rechavi, G.; Domany, E.; Galun, E.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of liver carcinogenesis in the mdr2-knockout mice. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Minter, L.C.; Stratton, S.A.; Yang, P.; Abbas, H.A.; Akdemir, Z.C.; Pant, V.; Post, S.; Gagea, M.; Lee, R.G.; et al. TRIM24 suppresses development of spontaneous hepatic lipid accumulation and hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Gamboa, R.; Gomez-Rueda, H.; Martinez-Ledesma, E.; Martinez-Torteya, A.; Chacolla-Huaringa, R.; Rodriguez-Barrientos, A.; Tamez-Pena, J.G.; Trevino, V. SurvExpress: An online biomarker validation tool and database for cancer gene expression data using survival analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, P.; Koch, A.; Fritz, V.; Hartmann, A.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Hellerbrand, C. Wild type Kirsten rat sarcoma is a novel microRNA-622-regulated therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma and contributes to sorafenib resistance. Gut 2018, 67, 1328–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Dominguez, N.; Ordonez, R.; Fernandez, A.; Mendez-Blanco, C.; Baulies, A.; Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Fernandez-Checa, J.C.; Mauriz, J.L.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J. Melatonin-induced increase in sensitivity of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib is associated with reactive oxygen species production and mitophagy. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Millonig, G.; Nair, J.; Patsenker, E.; Stickel, F.; Mueller, S.; Bartsch, H.; Seitz, H.K. Ethanol-induced cytochrome P4502E1 causes carcinogenic etheno-DNA lesions in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 50, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-G.; Yan, H.; Yao, P.; Zhang, W.; Zou, L.-J.; Song, F.-F.; Li, K.; Sun, X.-F. CYP2E1-dependent hepatotoxicity and oxidative damage after ethanol administration in human primary hepatocytes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 4530–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wen, Q.; Li, S.F.; Zhang, Y.F.; Gao, N.; Tian, X.; Fang, Y.; Gao, J.; Cui, M.Z.; He, X.P.; et al. Significant change of cytochrome P450s activities in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 50612–50623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Nie, Y.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.-J.Y. Histone modification-mediated CYP2E1 gene expression and apoptosis of HepG2 cells. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 235, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Ruiz, I.; Solis-Munoz, P.; Fernandez-Moreira, D.; Munoz-Yague, T.; Solis-Herruzo, J.A. In vitro treatment of HepG2 cells with saturated fatty acids reproduces mitochondrial dysfunction found in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dis. Models Mech. 2015, 8, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, S.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, Q.R.; Huo, Y.; et al. HDAC3 deficiency promotes liver cancer through a defect in H3K9ac/H3K9me3 transition. Cancer Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, L.; Tao, S.; Dai, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Clinical significance of HDAC9 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2019, 65, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Liu, H.D.; Huang, Q.; Liang, H.X.; Ding, Z.H.; Liao, Z.J.; Huang, G. HDAC6 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting P53 transcriptional activity. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Zeng, Z.; Yi, F.; Wu, J. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 11 promotes human liver cancer cell apoptosis. Am. J. Trans. Res. 2019, 11, 983–990. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, N.; Seto, E. Regulation of histone deacetylase activities. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 93, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikimaru, T.; Taketomi, A.; Yamashita, Y.; Shirabe, K.; Hamatsu, T.; Shimada, M.; Maehara, Y. Clinical significance of histone deacetylase 1 expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 2007, 72, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Shen, P.; Xie, R. Expression of HDAC4 in Stage B Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Influence on Survival. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2019, 49, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghayad, S.E.; Rammal, G.; Sarkis, O.; Basma, H.; Ghamloush, F.; Fahs, A.; Karam, M.; Harajli, M.; Rabeh, W.; Mouawad, J.E.; et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid (SAHA) as a therapeutic agent in rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaletsch, A.; Pinkerneil, M.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Jaguva Vasudevan, A.A.; Wang, C.; Hansen, F.K.; Wiek, C.; Hanenberg, H.; Gertzen, C.; Gohlke, H.; et al. Effects of novel HDAC inhibitors on urothelial carcinoma cells. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishna, G.; Rastogi, A.; Trehanpati, N.; Sen, B.; Khosla, R.; Sarin, S.K. From cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma: New molecular insights on inflammation and cellular senescence. Liver Cancer 2013, 2, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, W.Y.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Lim, H.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Okusaka, T.; Ikeda, M.; Hidaka, H.; Yeon, J.E.; Mizukoshi, E.; Morimoto, M.; et al. Phase I/II study of first-line combination therapy with sorafenib plus resminostat, an oral HDAC inhibitor, versus sorafenib monotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in east Asian patients. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitzer, M.; Horger, M.; Giannini, E.G.; Ganten, T.M.; Worns, M.A.; Siveke, J.T.; Dollinger, M.M.; Gerken, G.; Scheulen, M.E.; Wege, H.; et al. Resminostat plus sorafenib as second-line therapy of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma - The SHELTER study. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Li, A.J.; Ma, S.L.; Cui, L.J.; Wu, B.; Yin, L.; Wu, M.C. Inhibition of autophagy signi fi cantly enhances combination therapy with sorafenib and HDAC inhibitors for human hepatoma cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 4953–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Dai, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Wu, J.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhou, L.; Wu, J.; et al. The HDAC Inhibitor Quisinostat (JNJ-26481585) Supresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma alone and Synergistically in Combination with Sorafenib by G0/G1 phase arrest and Apoptosis induction. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1845–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmayer, A.; Toffanin, S.; Cabellos, L.; Alsinet, C.; Hoshida, Y.; Villanueva, A.; Minguez, B.; Tsai, H.-W.; Ward, S.C.; Thung, S.; et al. Combination therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Additive preclinical efficacy of the HDAC inhibitor panobinostat with sorafenib. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukupova, J.; Bertran, E.; Penuelas-Haro, I.; Urdiroz-Urricelqui, U.; Borgman, M.; Kohlhof, H.; Fabregat, I. Resminostat induces changes in epithelial plasticity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and sensitizes them to sorafenib-induced apoptosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 110367–110379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, T.; Maegdefrau, U.; Hartmann, A.; Agaimy, A.; Marienhagen, J.; Weiss, T.S.; Stoeltzing, O.; Warnecke, C.; Schölmerich, J.; Oefner, P.J.; et al. GLUT1 Expression Is Increased in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Promotes Tumorigenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.L.; Schelcher, C.; Demmel, M.; Hauner, M.; Thasler, W.E. Isolation of Human Hepatocytes by a Two-step Collagenase Perfusion Procedure. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 50615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosserhoff, A.K.; Moser, M.; Scholmerich, J.; Buettner, R.; Hellerbrand, C. Specific expression and regulation of the new melanoma inhibitory activity-related gene MIA2 in hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 15225–15231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thasler, W.E.; Weiss, T.S.; Schillhorn, K.; Stoll, P.T.; Irrgang, B.; Jauch, K.W. Charitable State-Controlled Foundation Human Tissue and Cell Research: Ethic and Legal Aspects in the Supply of Surgically Removed Human Tissue for Research in the Academic and Commercial Sector in Germany. Cell Tissue Bank. 2003, 4, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellerbrand, C.; Mühlbauer, M.; Wallner, S.; Schuierer, M.; Behrmann, I.; Bataille, F.; Weiss, T.; Schölmerich, J.; Bosserhoff, A.-K. Promoter-hypermethylation is causing functional relevant downregulation of methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2005, 27, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, C.; Weiss, T.S.; Heilmann, J.; Hellerbrand, C. Xanthohumol, a prenylated chalcone derived from hops, inhibits proliferation, migration and interleukin-8 expression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 36, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HDAC Class | Class I | Class IIa | Class IIb | Class IV | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDAC | 1 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 6 | 10 | 11 |
| Col I | r = 0.33 p = 0.04 | r = 0.26 p = 0.07 | r = 0.13 p = 0.75 | r = 0.21 p = 0.14 | r = 0.37 p = 0.01 | r = 0.22 p = 0.41 | r = 0.63 p < 0.01 | r = 0.55 p = 0.01 | r = 0.35 p = 0.03 | r = −0.08 p = 0.08 | r = 0.45 p < 0.01 |
| HDAC Class | Class I | Class IIa | Class IIb | Class IV | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDAC | 1 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 6 | 10 | 11 | |
| Class I | 1 | 0.41 | 0.60 | 0.29 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.62 | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.79 | |
| 2 | 0.07 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.63 | 0.94 | −0.12 | 0.93 | 0.80 | |||
| 3 | −0.14 | 0.15 | 0.07 | −0.17 | −0.11 | 0.59 | 0.28 | 0.32 | ||||
| 8 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.69 | 0.96 | −0.18 | 0.86 | 0.74 | |||||
| Class IIa | 4 | 0.97 | 0.72 | 0.95 | 0.01 | 0.96 | 0.90 | |||||
| 5 | 0.62 | 0.96 | −0.14 | 0.92 | 0.80 | |||||||
| 7 | 0.76 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 0.76 | ||||||||
| 9 | −0.12 | 0.89 | 0.81 | |||||||||
| Class IIb | 6 | 0.12 | 0.20 | |||||||||
| 10 | 0.87 | |||||||||||
| Class IV | 11 | |||||||||||
| Gene | Forward (5’-3’) | Reverse (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| human primer | ||
| Cyp2E1 | CCCTGCAACGTCATAGCC | TTTCCACGAGCAGGCAGT |
| HDAC1 | ACTACGACGGGGATGTTGGA | CAGCATTGGCTTTGTGAGGG |
| HDAC2 | GCTCTCAACTGGCGGTTCAG | AGCCCAATTAACAGCCATATCAG |
| HDAC3 | GGCCTATTTCTACGACCCCG | TGGTATGGCTTGAAGACGATCA |
| HDAC8 | TGTGACTCCCTGGCCAAGAT | AGATGCTTCATCTCTCATCTGCT |
| HDAC4 | CCACCTCACTCCCTACCTGA | CCCAGGCCTGTGACGAG |
| HDAC5 | GCACCATCGCTGAGAATGGC | GGGAGGCAGTGAGGTGTGAG |
| HDAC7 | AGCAGCTTTTTGCCTCCTGTT | TCTTGCGCAGAGGGAAGTG |
| HDAC9 | AGGCTCTCCTGCAGCATTTATT | AAGGGAACTCCACCAGCTACAA |
| HDAC6 | CTGGCGGAGTGGAAGAACC | GGGGAACGGCTCCCTTTTTA |
| HDAC10 | TGGCCTTTGAGTTTGACCCTG | GGCTGAGTCAAATCCTGCCG |
| HDAC11 | CCCCTTGGTCATGGGATTT | CATCCACACCAGTGCCTATAGC |
| KRAS | AACAGGCTCAGGACTTAGCAA | TCATCAACACCCTGTCTTGTCT |
| p21 | CGAGGCACCGAGGCACTCAGAGG | CCTGCCTCCTCCCAACTCATCCC |
| PML | CAGCAGTGAGTCCAGTGACC | GACACGGCCTTGGAGTAGAT |
| murine primers | ||
| HDAC1 | ACTACGACGGGGATGTTGGA | CAGCATTGGCTTTGTGAGGG |
| HDAC2 | AGGTGAAGGAGGTCGTAGGAA | TCTGACTTGGCTCCTTTGGG |
| HDAC3 | ATGCCTTCAACGTGGGTGAT | CAGAAGCCAGAGGCCTCAAA |
| HDAC8 | GCAATGAGCCCCACCGAATC | TCCACAAACCGCTTGCATCA |
| HDAC4 | GGGGAGCAGCATCATGGTTCA | GGTCCCAGCTGCGTAAACT |
| HDAC5 | GGTCGTAAAGCCACACTGGA | TGTCACTGTCCACCCCAATG |
| HDAC7 | TAGCCAGCAGTGTGGTCAAG | GGGCAGGCTGTAGGGAATAC |
| HDAC6 | CACCGCATTCAGAGGGTTCT | CCTTAAGGTGGGGCCAGAAG |
| HDAC10 | CTCCACGCACTGTCTAAGCA | GTGAAAGGTGTCCGGGTGAA |
| HDAC11 | CTGGCCCATCGTGTACTCAC | GTTGAGATAGCGCCTCGTGT |
| 18S | AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG | CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freese, K.; Seitz, T.; Dietrich, P.; Lee, S.M.L.; Thasler, W.E.; Bosserhoff, A.; Hellerbrand, C. Histone Deacetylase Expressions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Functional Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors on Liver Cancer Cells In Vitro. Cancers 2019, 11, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101587
Freese K, Seitz T, Dietrich P, Lee SML, Thasler WE, Bosserhoff A, Hellerbrand C. Histone Deacetylase Expressions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Functional Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors on Liver Cancer Cells In Vitro. Cancers. 2019; 11(10):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101587
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreese, Kim, Tatjana Seitz, Peter Dietrich, Serene M.L. Lee, Wolfgang E. Thasler, Anja Bosserhoff, and Claus Hellerbrand. 2019. "Histone Deacetylase Expressions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Functional Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors on Liver Cancer Cells In Vitro" Cancers 11, no. 10: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101587
APA StyleFreese, K., Seitz, T., Dietrich, P., Lee, S. M. L., Thasler, W. E., Bosserhoff, A., & Hellerbrand, C. (2019). Histone Deacetylase Expressions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Functional Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors on Liver Cancer Cells In Vitro. Cancers, 11(10), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101587





